Edexcel A-level Economics Theme 4
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
Globalisation
The process in which national economies have become increasingly integrated and interdependant
Trade liberalisation
Trading blocs
Growth of MNCs
Technological advances
Greater mobility of labour and capital
Causes of globalisation (5)
Advantages of globalisation (5)
Lower prices
Benefits of trade
Greater employment
Large economies of scale
Free movement of labour and captial
Disadvantages of globalisation (6)
Growing inequality
Higher structural unemployment
Environmental costs
Trade imbalances
Risk of external shocks
Less cultural diversity
Absolute advantage
When a country can produce a product using fewer factors of production than another nation
Comparative advantage
A country should specialise in the goods and services it can produce at the lowest opportunity cost, and then trade with another country
Specialisation
When a worker, firm, region or country produces a narrow range of goods and services
Advantages of specialisation (5)
Larger range of goods and services
Greater output
Greater quality
Benefits of trade
Reduces problem of scarcity
Disadvantages of specialisation (5)
Finite resources
Over-reliance on weather
Changing tastes/fashions
Interdependence
De-industrialisation
Terms of trade equation
(Weighted average of export prices) x (Weighted average of import prices) x100
Terms of trade
Indicates the quantity of exports that must be sold to purchase a given level of imports
Factors influencing the terms of trade (short run)
Change in demand/supply of exports/imports
Inflation rates
Exchange rate movements
Factors influencing the terms of trade (long run)
Incomes
Productivity
Technology
Trading bloc
A group of countries that join together and agree to increase trade between themselves
Free trade area
No trade barriers
Can trade with other countries
Customs union
No trade barriers
Common external barrier
Common market
No trade barriers
Common external barrier
Free movement of labour and capital
Monetary union
No trade barriers
Common external barrier
Free movement of labour and capital
Common currency and central bank
World Trade Organisation (WTO)
International organisation that regulates world trade
WTO's ideal world trade (5)
Non-discriminatory
Free from barriers/protectionism
Predictable
Promotes fair competition
Beneficial for developing countries
Role of WTO (7)
Set and enforce rules of international trade
Resolve trade disputes
Provide a forum for negotiating trade liberalisation
To monitor further trade liberalisation
Increase transparency of decision making process
Help developing countries benefit
Cooperate with other major economic instituions
How WTO conflicts with trading blocs (5)
Distort world trade
Averse effects on non-member states
Inefficient allocation of resources
Increased protectionism
WTO loses power as trading blocs become more powerful
Tariff
Tax on imports
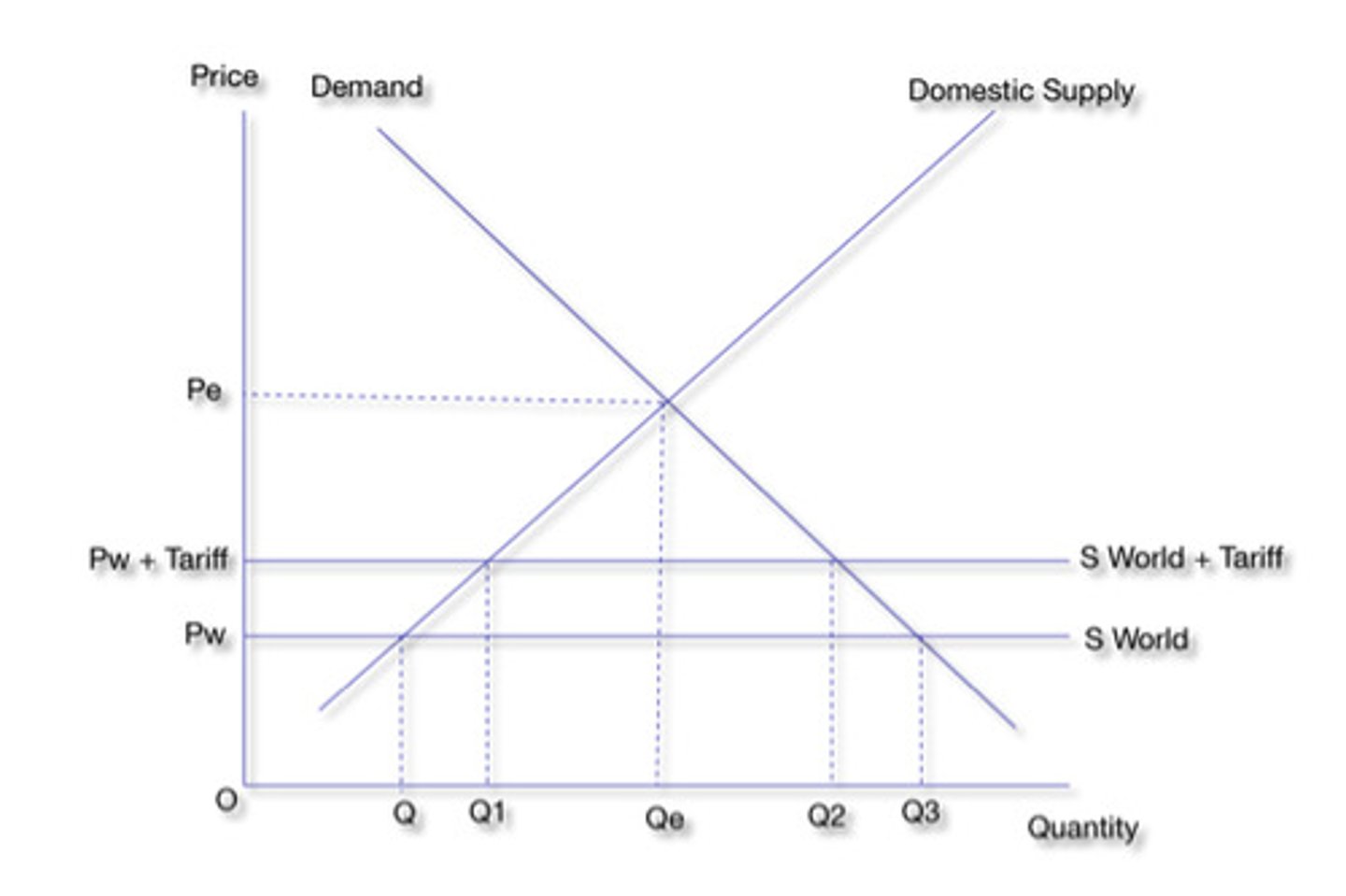
Tariff revenue =
(Sw+t-Sw) x (Q4-Q3)
Quota
Quantity limit on amount of imports

Trade subsidy
Subsidy given to domestic suppliers
Aim of trade subsidy
To reduce costs of production → passed onto consumer as lower prices → makes firm more competitive
Non-tariff barriers
Voluntary export restraint (countries limit exports to each other
Intellectual property laws (patents, copyright etc)
Technical barriers (health and safety etc)
Financial protectionism (govt. tells banks to prioritise local firms when allocating loans)
Hidden protectionism (discrimination against foreign workers)
Exchange controls (limit of capital flows between countries)
Currency intervention (competitive devaluation)
Balance of Payments
Measures the inflows and outflows of money into and out of a country
Components of the current account
Trade in goods (trade balance)
Trade in services (trade balance)
Income e.g. remittances (income balance)
Transfers - govt. fees e.g. aid, EU payments (income balance)
Causes of current account surplus (6)
Exporting more than importing
Recession
Competitive exports (deflation/disinflation/high quality exports)
High level of natural resources
Exports worth more than imports
High levels of exports
Causes of current account deficit (6)
Importing more than exporting
Sustained economic growth
Uncompetitive exports (inflation/poor quality products)
Low level of natural resources
Exports worth less than imports
Low levels of exports
Components of financial account (3)
FDI
Portfolio investment
Reserves
Capital account
Minor payments/transfers
Floating exchange rate
Currency value set by market
No govt. intervention
No target for exchange rate
Speculation causes change in floating exchange rate
e.g. British Pound
Advantages of a floating exchange rate (4)
Reduces need to hold large foreign currency reserves
Freedom to set interest rates
Automatic correction
Less risk
Disadvantages of floating exchange rate (2)
Can be volatile - reduces FDI
A lower, more competitive exchange rate does not guarantee a current account surplus
Fixed exchange rate
Govt. fixes currency value to another currency
Central bank must hold sufficient currency reserves
e.g. Chinese Yuan
Advantages of a fixed exchange rate
Stability attracts FDI
Stability controls inflation
Leads to lower borrowing costs
Less speculation
Disadvantages of a fixed exchange rate
Cannot use interest rates in macro policies (monetary policy)
Developing countries may not have sufficient foreign currency reserves to fix
Devaluation of exchange rate leads to cost-push inflation
Managed exchange rate
Currency value set by market forces
Central bank occasionally intervenes
Currency is a key target of monetary policy
e.g. Japanese Yen
Competitive devaluation intentions
Make exports cheaper and imports more expensive
Increases growth
Increases inflation
Improved current account
Revaluation
When the value of the currency is adjusted
Appreciation
When the value of the currency increases
Devaluation
When the value of the currency is lowered in a fixed exchange rate system
Depreciation
When the value of the currency falls
Factors influencing exchange rates
Inflation
Speculation
Other currencies
Govt. finances
Balance of payments
International competitiveness
Government intervention in the currency markets - interest rates (hot money)
An increase in interest rates is more attractive for foreign investors
This increases demand for currency, appreciating the value of the currency
Government intervention in the currency markets - quantitative easing
Increases supply of money and depreciates currency
Government intervention in the currency markets - foreign currency transactions
Buying and selling foreign currency to manipulate domestic currency
International competitiveness
The ability of a nation to compete successfully overseas and to sustain improvements in living standards and output
Components of international competitiveness
Price competitiveness
Non-price competitiveness
Ability to attract FDI
Unit labour costs =
Total labour cost / output
Relative export prices
Ratio of one country's export prices relative to another country
Factors that influence international competitiveness (8)
Unit labour costs
Labour flexibility
Labour skills
Tax regimes
Innovation
Infrastructure
Regulation
Economic stabilility
Absolute poverty
Cannot access the most basic, life sustaining goods and services
Relative poverty
Incomes below a given average in society
Equity
Fair distribution of income
Equality
Equal distribution of income
Causes of poverty (10)
Unemployment - structural and cyclical
Poor education/skills
Poor health/healthcare
Born into poverty
Tax cuts for the rich
Subsistence agriculture
Natural disasters
Corruption
Wars and conflicts
Regressive taxes
Income
A flow measured over a given period of time
Wealth
A stock; assets with a market value that can generate income
What are the 2 measurements of inequality?
Lorenz curve - visual indicator
Gini coefficient - mathematical indicator
Causes of inequality
Wages - underemployment and discrimination
Regressive payments and taxes
Unemployment
Inequality between countries
What 3 areas does the Human Development Index (HDI) measure and how?
Education - adult literacy, school enrolment
Health - life expectancy
Living standards - GDP/capita, PPP
How is each measure in the HDI weighted?
Equally
Advantages of the HDI
Broad measure
Focuses on development outcomes
Allows progress to be measured over time
Disadvantages of the HDI
Distribution of income/inequality not measured
No weighted averages
No measures of freedom and choice
Other factors not measured (e.g. crime, corruption, negative externalities, poverty)
Other indicators of development
Gender-related Development Index (GDI)
Human Poverty Index (HPI)
Factors influencing growth and development (11)
Primary product dependency
Harrod-Domar Model
Foreign currency gap
Capital flight
Demographic factors
Debt
Access to credit and banking
Infrastructure
Education/skills
Property rights
Non-economic factors
Primary product dependency
Developing countries rely on primary products/raw materials
Volatile prices makes long-term planning difficult
Fall in prices leads to fall in export incomes, funding for infrastructure and education falls
Not sustainable as resources are finite
Harrod-Domar Model
Investment, saving and technological change are required for economic growth
(Developing countries do not have this)
Harrod-Domar Model: rate of growth =
Savings ratio / capital output ratio
Foreign currency gap
Current account deficit > value of capital inflows
Capital flight
When money leaves the economy through outward investment
Triggered by economic threat (e.g. hyperinflation)
Demographic factors
High birth rate links with poverty and environmental damage
Debt
Links with poverty and inequality
Access to credit and banking
Difficult to save in a country with a poor banking system
Infrastructure
Poor infrastructure discourages FDI due to high production costs
Education/skills
Important for developing human capital
Ensures that the economy can be productive and produce high quality goods and services
Property rights
No property rights mean that entrepreneurs cannot protect their ideas
No incentive to innovate
Non-economic factors (3)
War
Corruption
External shocks
Market-orientated strategies for growth and development (7)
Trade liberalisation
Promotion of FDI
Removal of subsidies
Floating exchange rate systems
Microfinance schemes
Privatisation
Trade liberalisation
Free trade increases world GDP
Promotion of FDI
Creates employment
Encourages innovation
Promotes long-term, sustainable growth
Provides developing countries with funds to invest and develop
Removal of subsidies
Subsidies distort the free market
Leads to inefficient allocation of resources
However, certain goods will be under-provided (e.g. farming)
Floating exchange rate systems
Determined by the market mechanism
Microfinance schemes
Distribution of small loans to individual entrepreneurs to stimulate growth
Reduces dependency on primary products
Reduces inequality
Privatisation
Govt. sells a firm to a private company
Increases efficiency
Increases quality
Increases allocative effieciency
Increases govt. revenue
Interventionist strategies for growth and development (6)
Development of human capital
Protectionism
Managed exchange rates
Infrastructure development
Joint ventures with global companies
Buffer stock schemes
Development of human capital
Improves productivity
Helps countries move up supply chain
Advantages of protectionism
Reduces trade deficit
Protects infant industries
Disadvantages of protectionism
Distorts the market → loss of allocative efficiency
Higher prices
Less choice
No competition → no incentive to increase efficiency
Tariffs are regressive
Risk of retaliation
Infrastructure development
Lower supply costs
Increases mobility of labour
Attracts FDI
Increases employment
Joint ventures with global companies
Partnership between 2 global firms
Increases technological knowledge
Foreign markets
Advantages of buffer stock schemes
Reduces price volatility
Incomes of farmers remain stable
Disadvantages of buffer stock schemes
Historically unsuccessful
Govt. may not have financial resources to buy up stock
Storage is difficult and expensive
Other strategies for growth and development (3)
Fairtrade
Aid
Debt relief
Advantages of fairtrade schemes
Ensures farmers recieve fair price for goods
Helps farmers plan for long-term due to stable income
Encourages sustainability, environmental protection and stops child labour
Disadvantages of fairtrade:
Distorts market
Non-fairtrade