Chapter 8 - Transport in plants
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
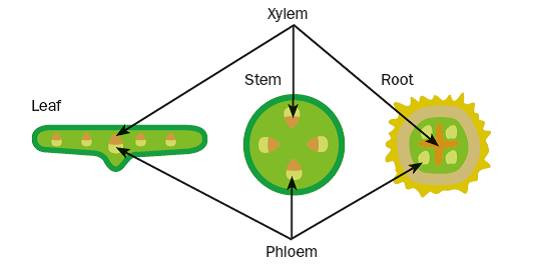
xylem
transport of water and mineral ions, and support
thick walls with lignin
no cell contents
cells joined end to end with no cross walls to form a long continuous tube'
vascular tissue
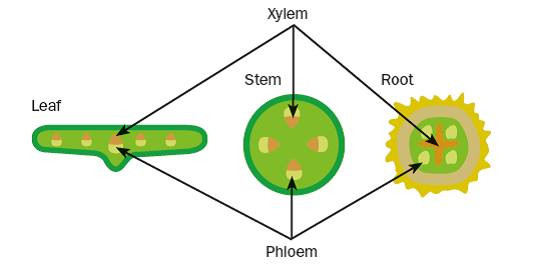
phloem
transport of sucrose and amino acids
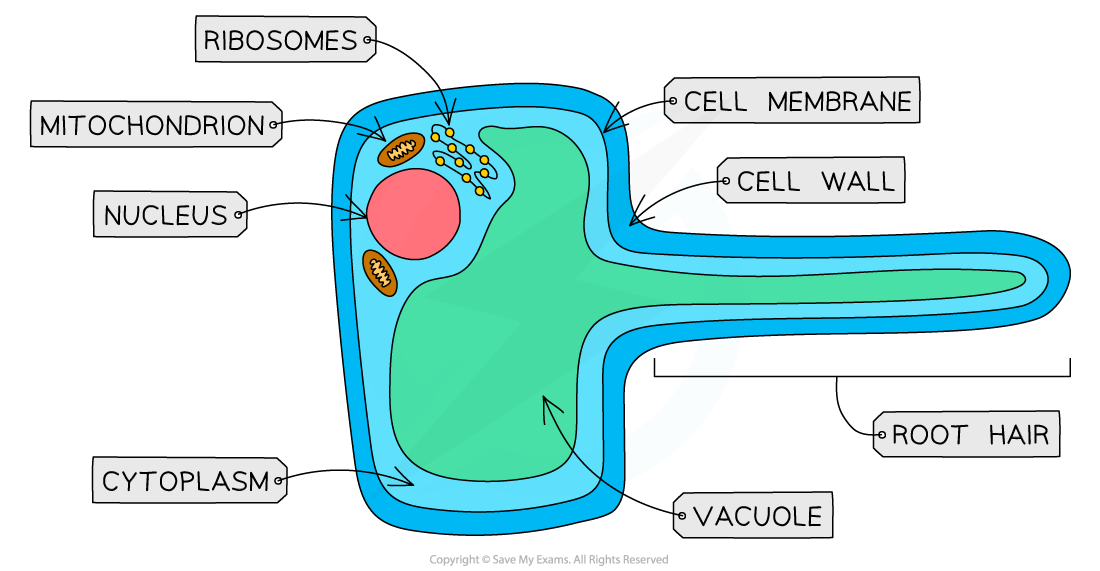
what are the characteristics of root hair cell?
large surface area - increase uptake of water & mineral ions
thin cell wall - easier transfer of water & nutrients by osmosis & active transport
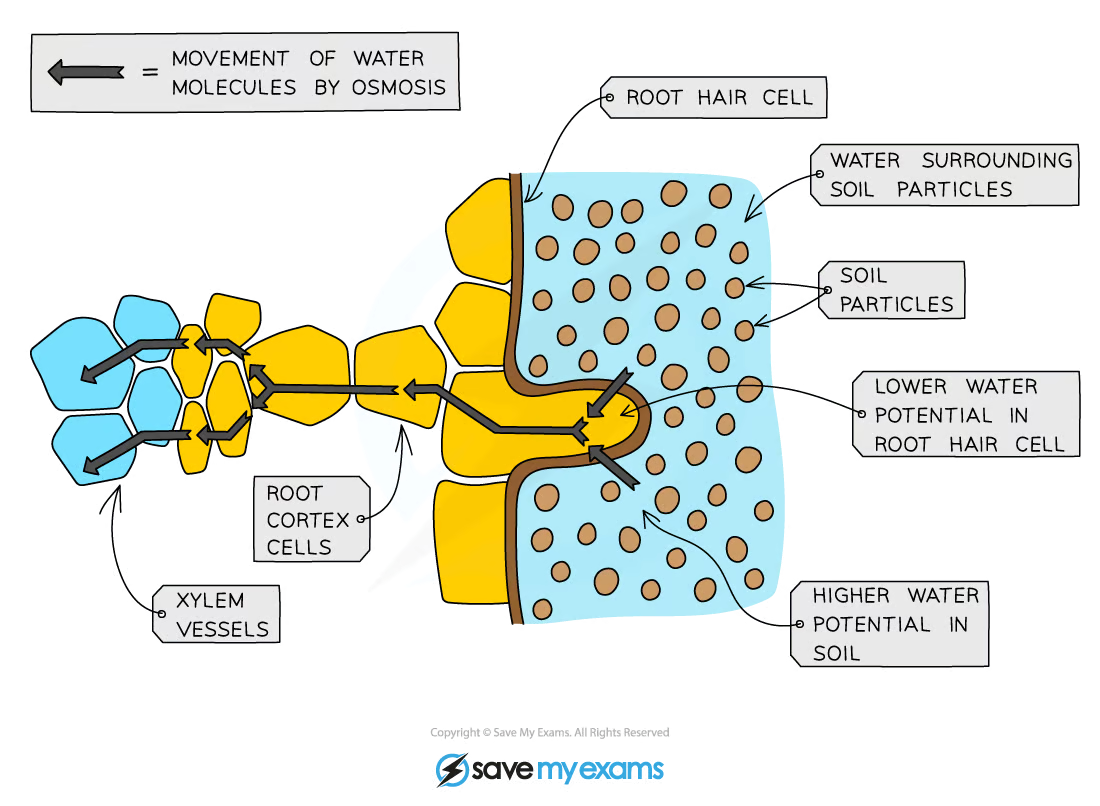
pathway of water through root → stem → leaf
root hair cell
root cortex cells
xylem - moves up in a column
leaf mesophyll cells
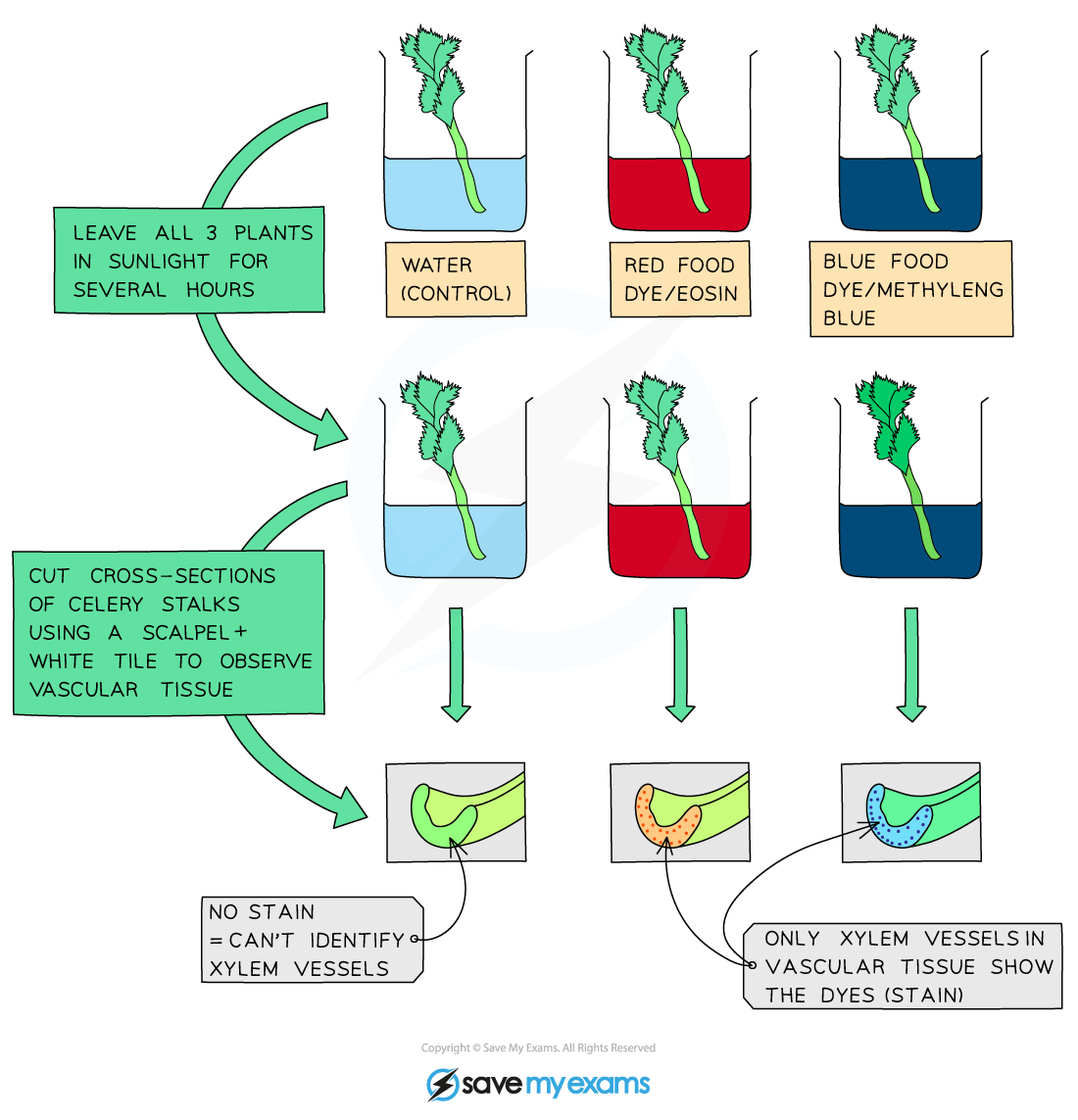
Investigation: water movement in plants
place plant in beaker of water with colouring added
after few hours leaves of plant turns same colour as water - shows water taken up by plant
if cross section of plant cut, only certain areas of stalk stained (xylem)
transpiration
loss of water vapour from leaves
explain how transpiration works
water evaporates from surfaces of mesophyll cells into air spaces
diffuses out of leaves through stomata as water vapour
Explain how water vapour loss is related to
large internal surface area from interconnecting air spaces between mesophyll cells
size and num of stomata
translocation
movement of sucrose & amino acids in phloem from source to sink
source
parts of plants that release sucrose or amino acids
sinks
parts of plants that use or store sucrose or amino acids
explain why some parts of a plant may act as a source and a sink at different times [6]
leaf typically functions as a source when it is mature, producing sugars through photosynthesis.
sugars transported to different parts of the plant - act as sinks (roots/ fruits)
same leaf can become a sink during growth phase/during repair damage
requires energy & nutrients for its development - receives from other parts of the plant acting as sources.
shows plant's ability to adapt resource allocation based on developmental stage & environmental conditions
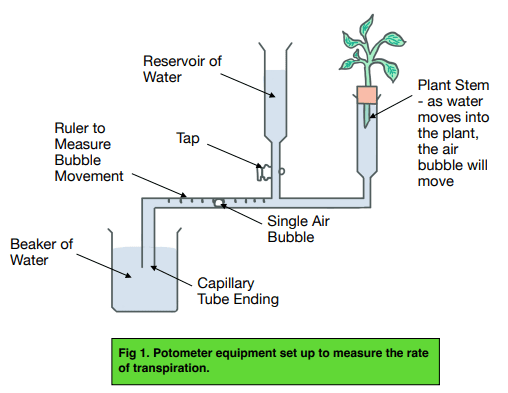
investigate Effect of Temperature & Wind Speed on Transpiration Rate
Set up the potometer in water & leave the tap for the reservoir of water open - prevent air bubbles entering equipment.
cut the stem of the plant at a slant under water - prevent air from entering the xylem & slant increase surface area where water is absorbed.
Lift potometer out of the water but leave the opening end of capillary tube submerged in the water - the water that will supply the plant.
Double check that the entire equipment is airtight and watertight. You don’t want any air bubbles or extra water interfering with your experiment.
Give time for the plant to adapt to new setting & pat dry its leaves.
Close tap for the reservoir of water.
Remove the capillary tube end from the water until one air bubble enters and then immediately place the capillary tube end back in the water.
Measure and record the starting position of the air bubble and start the stopwatch.
Time how long it takes the bubble to move a certain distance and calculate the rate of transpiration
effect of temp, wind speed, humidity on transpiration
as temp increase, transpiration increase
wind speed increase, transpiration increase
humidity increase, transpiration decrease
explain effect of high humidity on stomata
stomata will take longer to close
reduced water vapour concentration
guard cells lose less water and remain turgid, keeping stomata open longer.

cohesion
attraction between water and water

adhesion
attraction between water and xylem