Applied physio lecture 25 and 26 (exam 3)
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts and vocabulary related to the cardiovascular system, including its components, functions, and processes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Hemoglobin
A protein in red blood cells that binds to oxygen. Gives blood red color. Four polypeptide globin chains each with one herm group that binds to and O2. Hemoglobin binds 4O2
Platelets
Cell fragments of megakaryocytes that stabilize formation of fibrin clot. coated with glycoproteins
Colloid osmotic pressure
Pressure exerted by plasma proteins that draws fluid into capillaries.
Systole
The contraction phase of the heart cycle. ejecting blood
Diastole
The relaxation phase of the heart cycle. filling with blood
Ventricles
Lower chambers of the heart that pump blood out to the body and lungs.
Atria
Upper chambers of the heart that collect blood.
SA Node
The pacemaker of the heart that initiates action potentials independent of nerves. Spontaneous action potentials due to voltage gated channels. Ca channels open and enters the cell causes depolarization
AV Node
The node that delays electrical signal to allow for complete ventricular filling.
Bundle of His
A collection of heart muscle cells that conduct impulses from the AV node to the ventricles.
Aortic Valve
The valve that opens to allow blood to flow from the left ventricle into the aorta.
Mitral Valve
The valve between the left atrium and left ventricle.
Ejection Fraction
The percentage of blood pumped out of the ventricles with each heartbeat.
stroke volume/EDV
End-Diastolic Volume (EDV)
The volume of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole.
End-Systolic Volume (ESV)
The volume of blood left in the ventricles after contraction.
Intercalated Discs
neighboring cardiomyocytes electrically coupled through intercalated disks.
ECG (Electrocardiogram)
A recording of the electrical activity of the heart from the body surface. Conducts electrical signals between cells
Plasma
92% water, electrolytes, proteins, nutrients (glucose, cholesterol, triglycerides) and gases (take in O2 and remove CO2)
Erythrocytes (Red blood cells)
Biconcave disk shape allows to deform through capillaries, no nucleus, carries oxygen with the help of hemoglobin
Leukocytes (white blood cells)
Large and nucleated, released in blood in response to injection/injury in tissue
First heart sound “lub”
closure of AV valves
Second heart sound “dub”
closure of aortic and pulmonary valves
Stroke Volume
EDV - ESV
End diastolic pressure (EDP)
4-7 mmHg
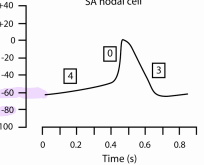
SA Nodal cell action potential
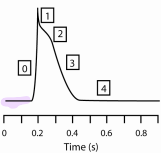
Atrial cell Action potential
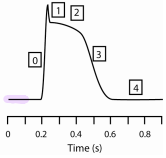
Ventricular cell action potential
Sympathetic effect on SA node
increase slope of pacemaker potential and increases action potential rate, epinephrine/adrenaline increases conductance of ion channels
Parasympathetic effect on SA node
decreases heart rate, decrease slope of pacemaker potential, acetylcholine decrease conductance of ion channels