Botany | Algae | Dr. Sara Browning | PBA Fall 2024
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
With flagellated zoospores
Reproductions: Asexual
zoospores
flagellated spores
Most with alternation of generations- both isomorphic and heteromorphic; others haploid or diploid
Reproduction: Sexual
isomorphic
Referring to alternating generations in plants and certain algae in which the sporophytes and gametophytes look alike, although they differ in chromosome number.
heteromorphic
Referring to a condition in the life cycle of plants and certain algae in which the sporophyte and gametophyte generations differ in morphology.
Phytoplankton
Unicellular Algae
___________- very important producers globally
Blooms
Unicellular Algae
Population explosions or "____" common
Dead zones
Unicellular Algae
Some blooms may be toxic or cause "_____ _____" due to eutrophication
Dead zones
In a body of water, an area with extremely low oxygen concentration and very little life
Eutrophication
A process by which nutrients, particularly phosphorus and nitrogen, become highly concentrated in a body of water, leading to increased growth of organisms such as algae or cyanobacteria.
Coccolithophores
microscopic algae with calcium carbonate shells, form the base of many marine food webs
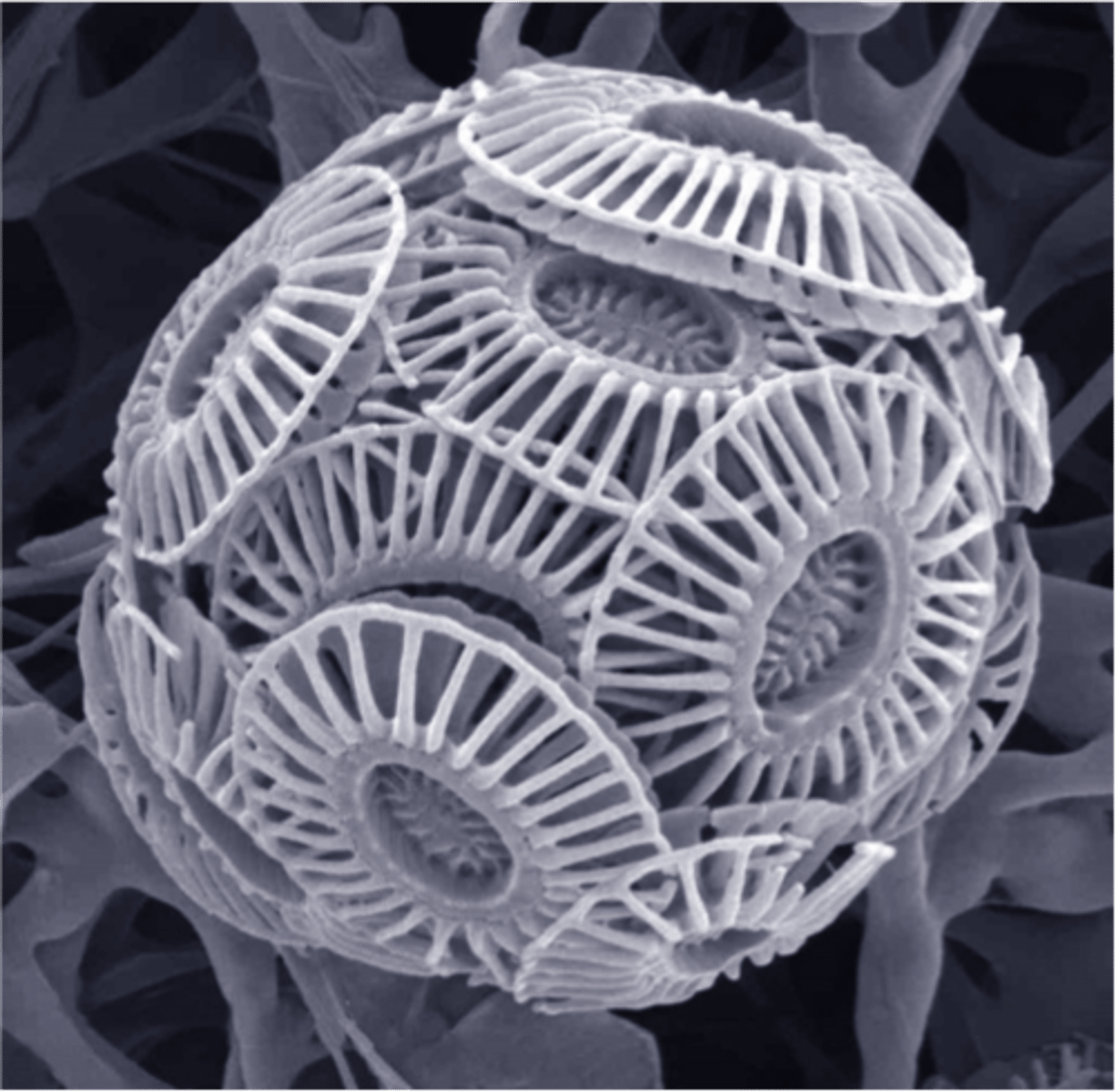
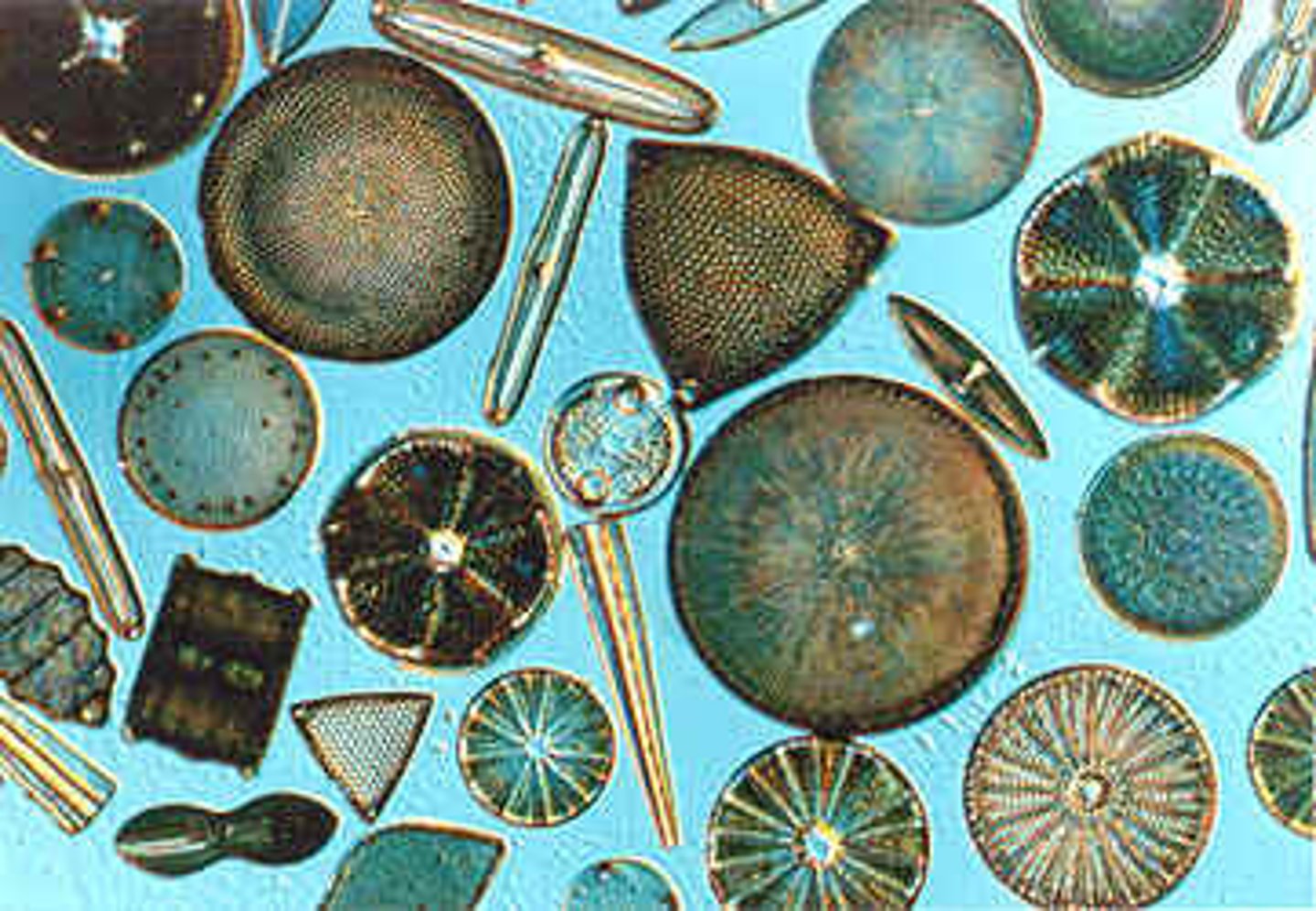
Diatoms
A unicellular photosynthetic alga with a unique glassy cell wall containing silica

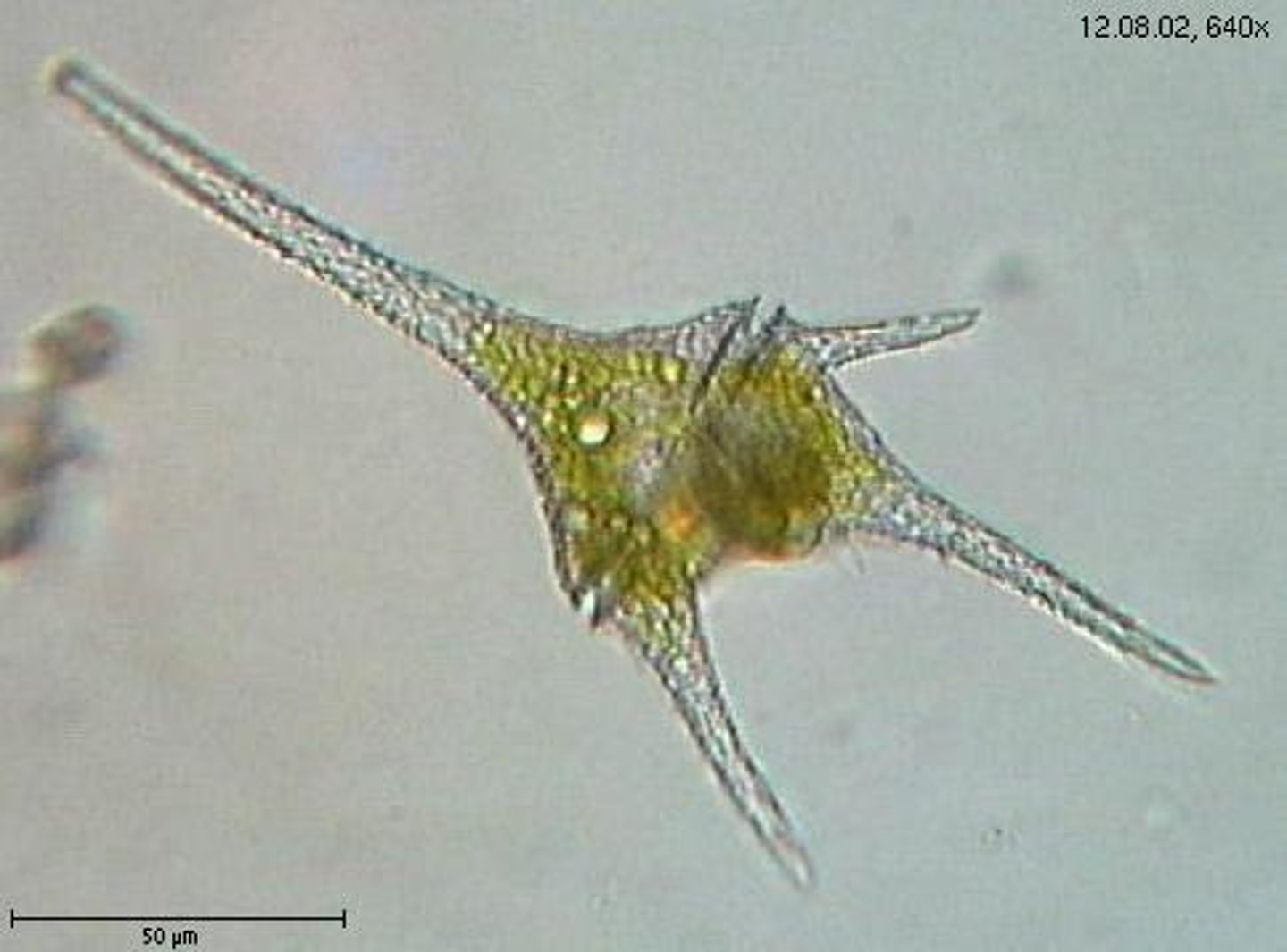
Dinoflagellates
plant-like protist that causes red tide

Bacillariophyceae
Diatoms- Class ___________
(old Phylum Chrysophyta)
* Stramenopile supergroup
Silicious (SiO2)
Diatom Characteristics
Cell wall:
Fucoxanthin, Chl c
Diatom Characteristics
Color:
Motile by secretion
Diatom Characteristics
Mobility:
Salt Water (SW), Fresh Water (FW), terrestrial
Diatom Characteristics
Environment:
Very abundant phytoplankton at all surface of the world's oceans
Diatom Ecology
Undefined
Dinoflagellates
(old Phylum Pyrrophyta)
* Alveolata supergroup
Biflagellates
Dinoflagellate Characteristics
-
Naked (no cell wall) or Armored (cellulose plates)
Dinoflagellate Characteristics
Cell wall:
Peridinin (Carotenoid); Chl c
Dinoflagellate Characteristics
Color:
Very abundant phytoplankton at the surface of the world's oceans
Dinoflagellate Ecology
1) Red Tide
2) Shellfish Poisoning
3) Bioluminescence
4) Zooxanthellae
Four Special Features of Dinoflagellates
1)
2)
3)
4)
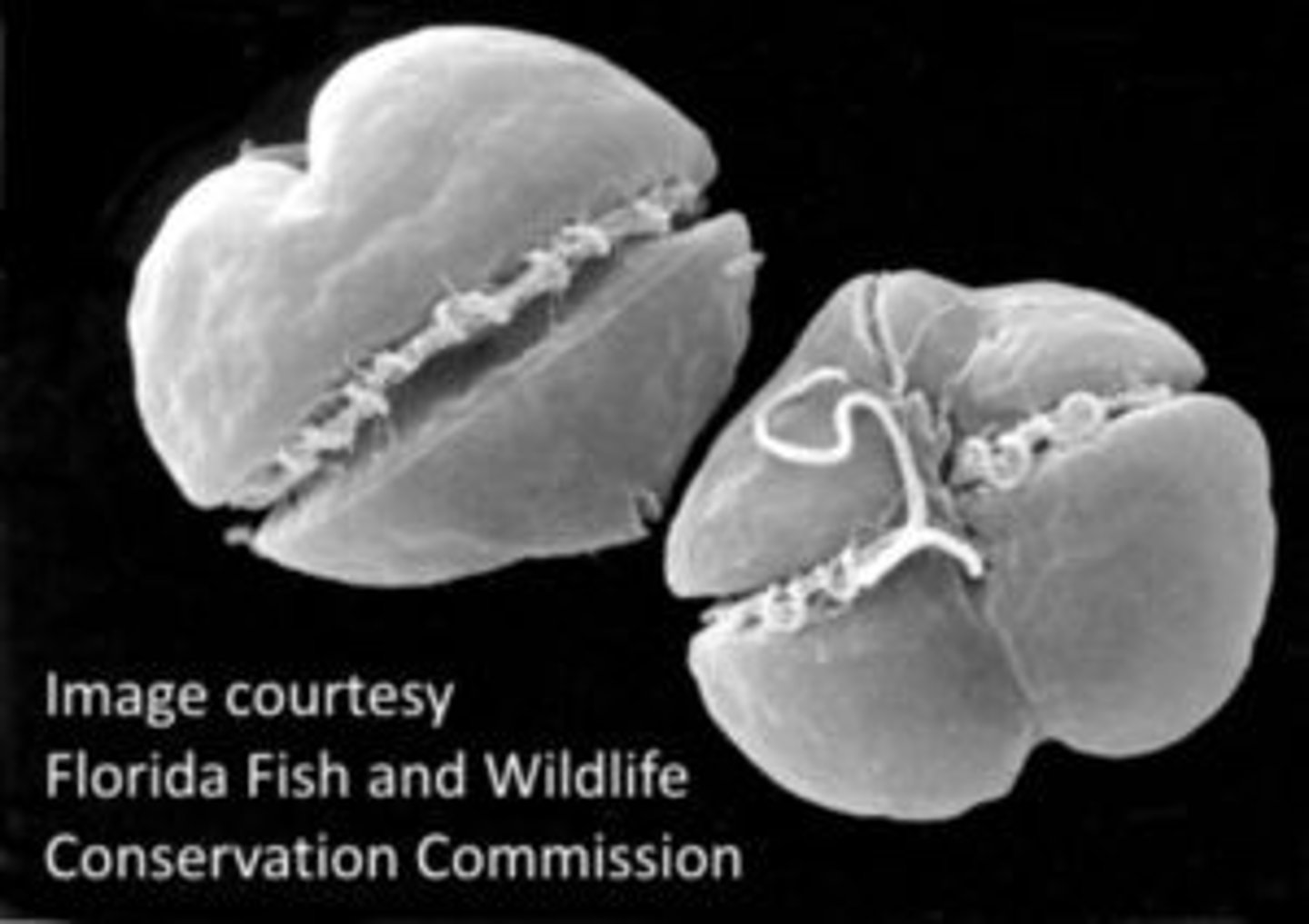
Red Tide
An algal bloom that occurs in salt water
Karenia brevis
dinoflagellate that causes red tide
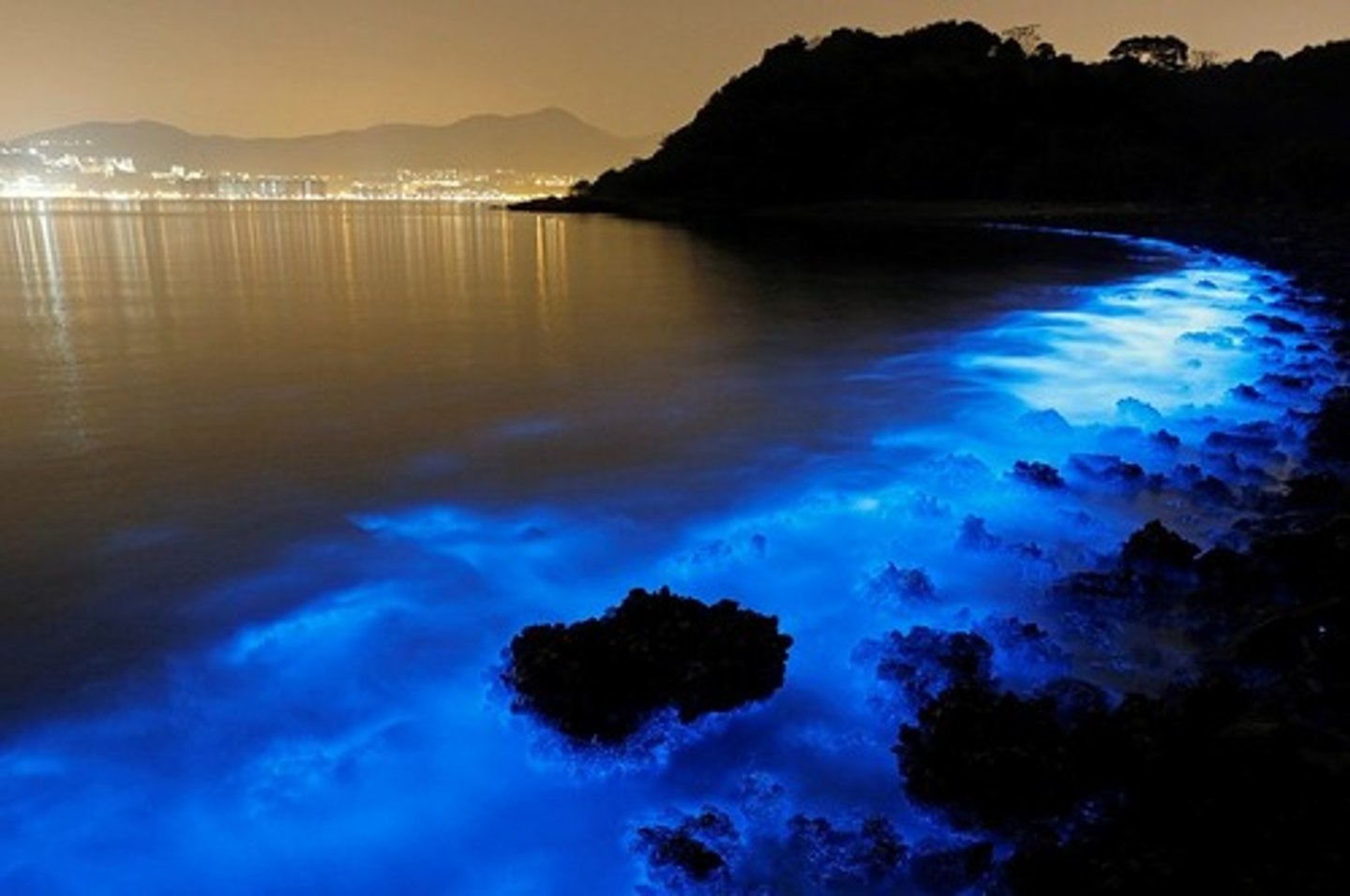
Bioluminescence
the production of light by means of a chemical reaction in an organism
Noctiluca
microscopic marine animals that make the ocean glow during the night

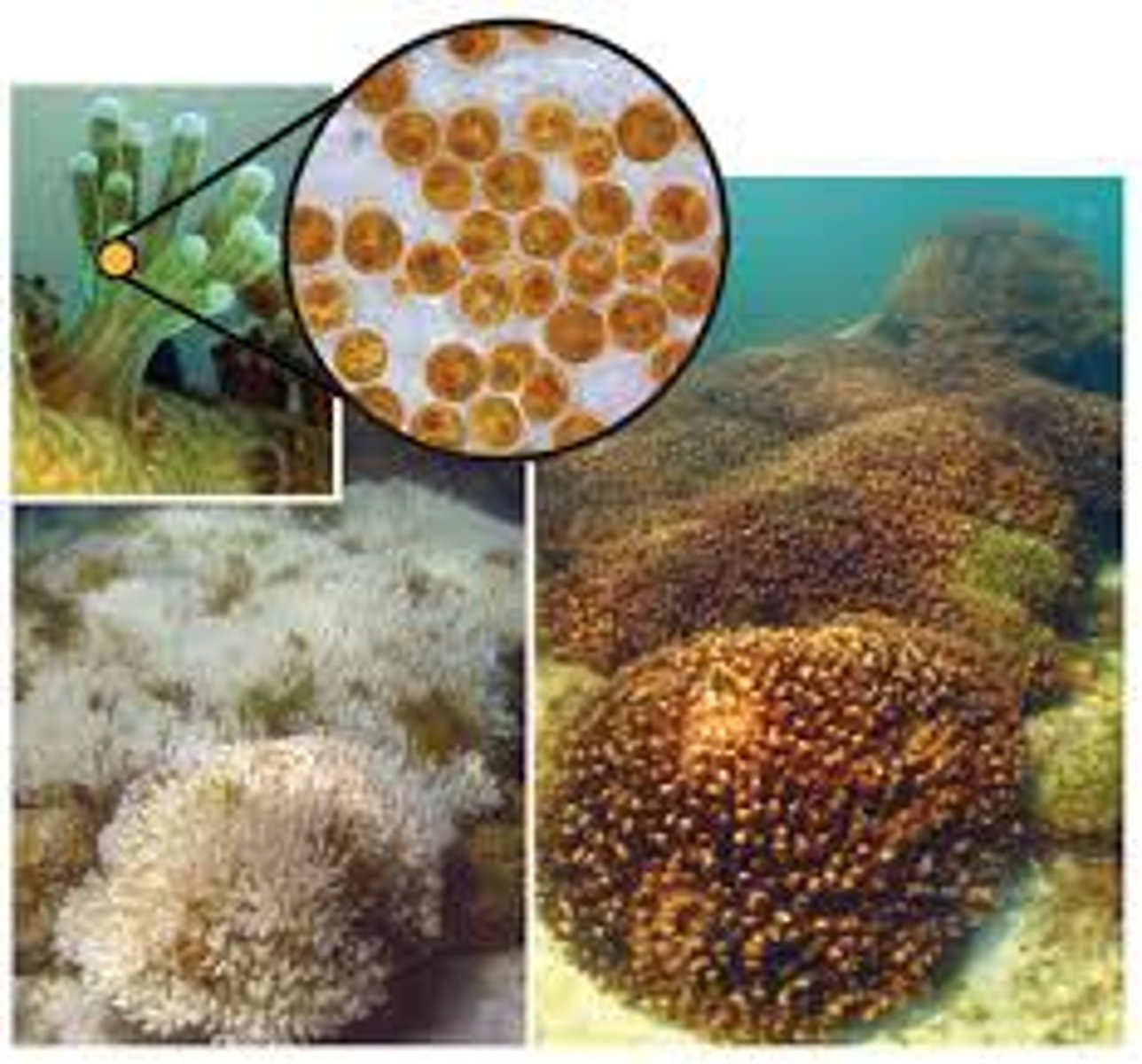
Zooxanthellae
a yellowish-brown symbiotic dinoflagellate present in large numbers in the cytoplasm of many marine invertebrates.

Seaweeds and Pondweeds
Multicellular Algae
-
-
Seaweed blade
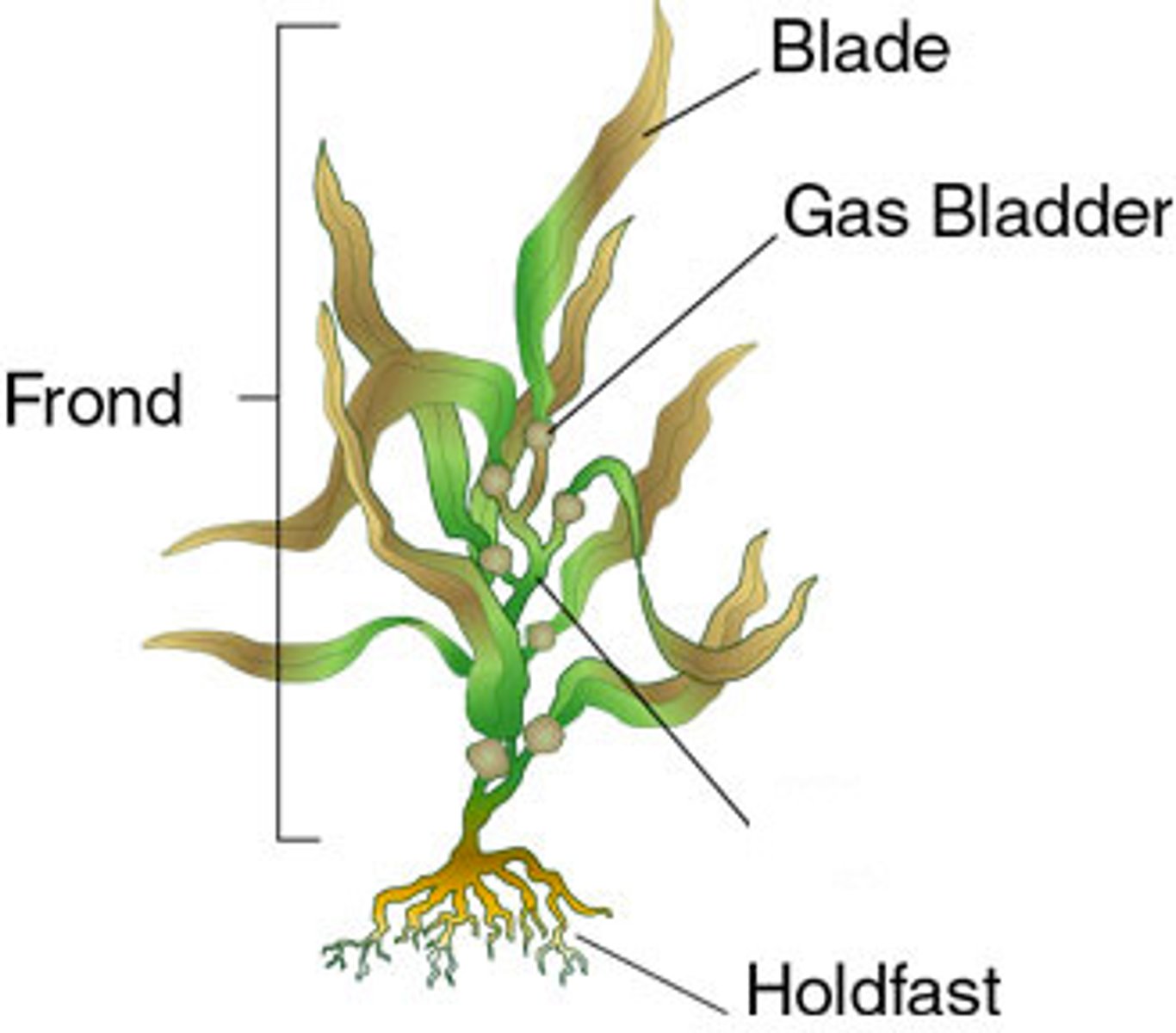
Seaweed Stipe
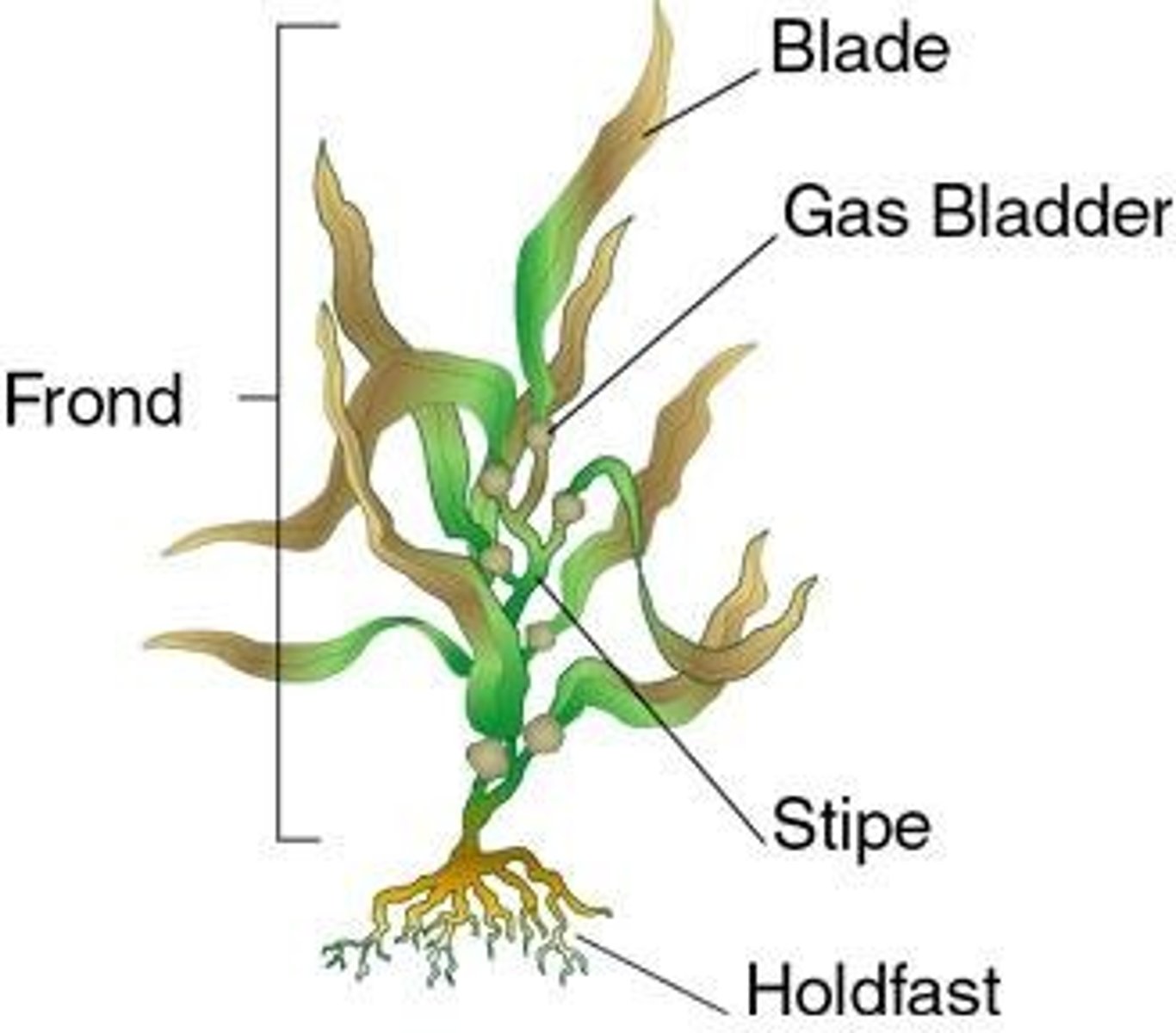
Seaweed holdfast
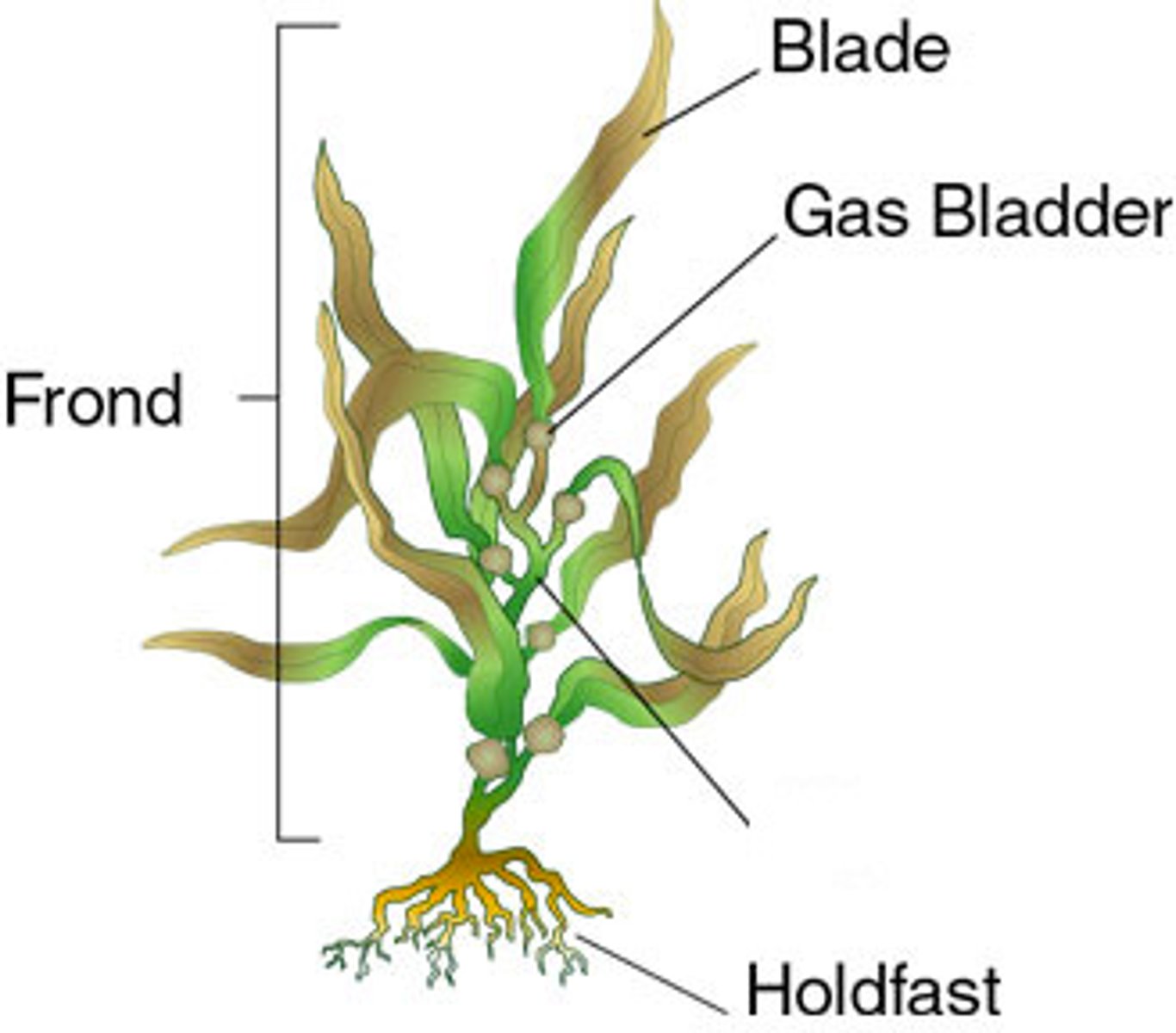
Phaeophyceae
Brown Algae
Class __________
* Stramenopile supergroup
Marine seaweeds
Brown Algae Characteristics
Environment:
Fucoxanthin; Chl c
Brown Algae Characteristics
Color:
Common in cold and temperate Salt water
Kelp "Forest"
Brown Algae Ecology
Sargassum
- Sargassum or Gulfweed scientific name

Tubinaria

Rhodophyta
Red Algae
Phylum ________
* Plants and algal relatives supergroup
Marine Seaweeds
Red Algae Characteristics
Environment:
Phycobilins- Phycoerythrin and phycocyanin; Chl d
Red Algae Characteristics
Color:
Common in tropical and warm Salt Water
Deepest seaweed ~ 970 ft
Many are calcareous and coralline
Red Algae Ecology
Calcareous
containing calcium carbonate
Coralline
resemble corals
Undefined
Green Algae
(old Phylum Chlorophyta)
* Plants and algal relatives supergroup
Unicellular, colonial, filamentous, coenocytic, flat sheets of cells, parenchyma-like tissue
Green Algae Characteristics
Diverse body plans:
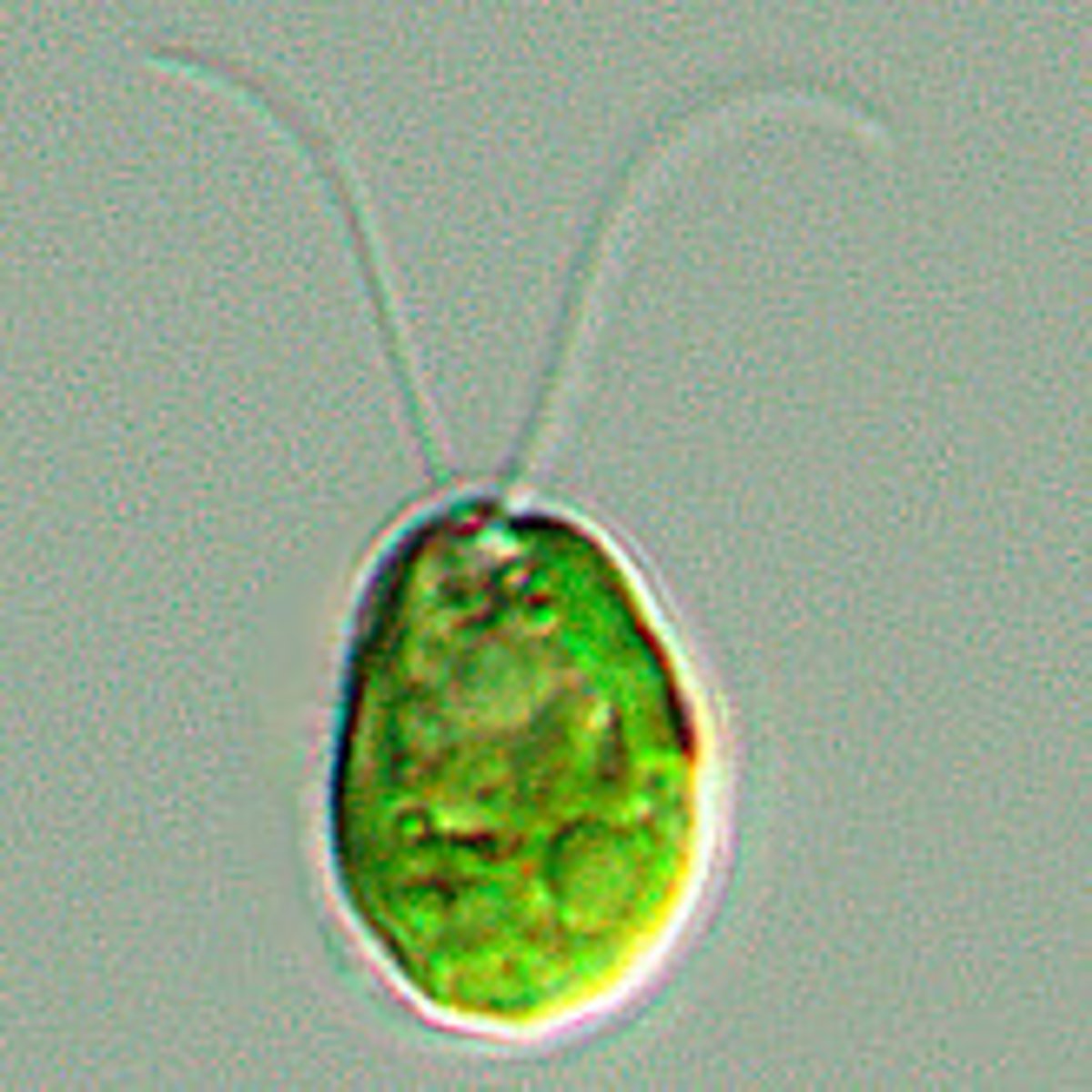
Unicellular green algae
Chlamydomonas
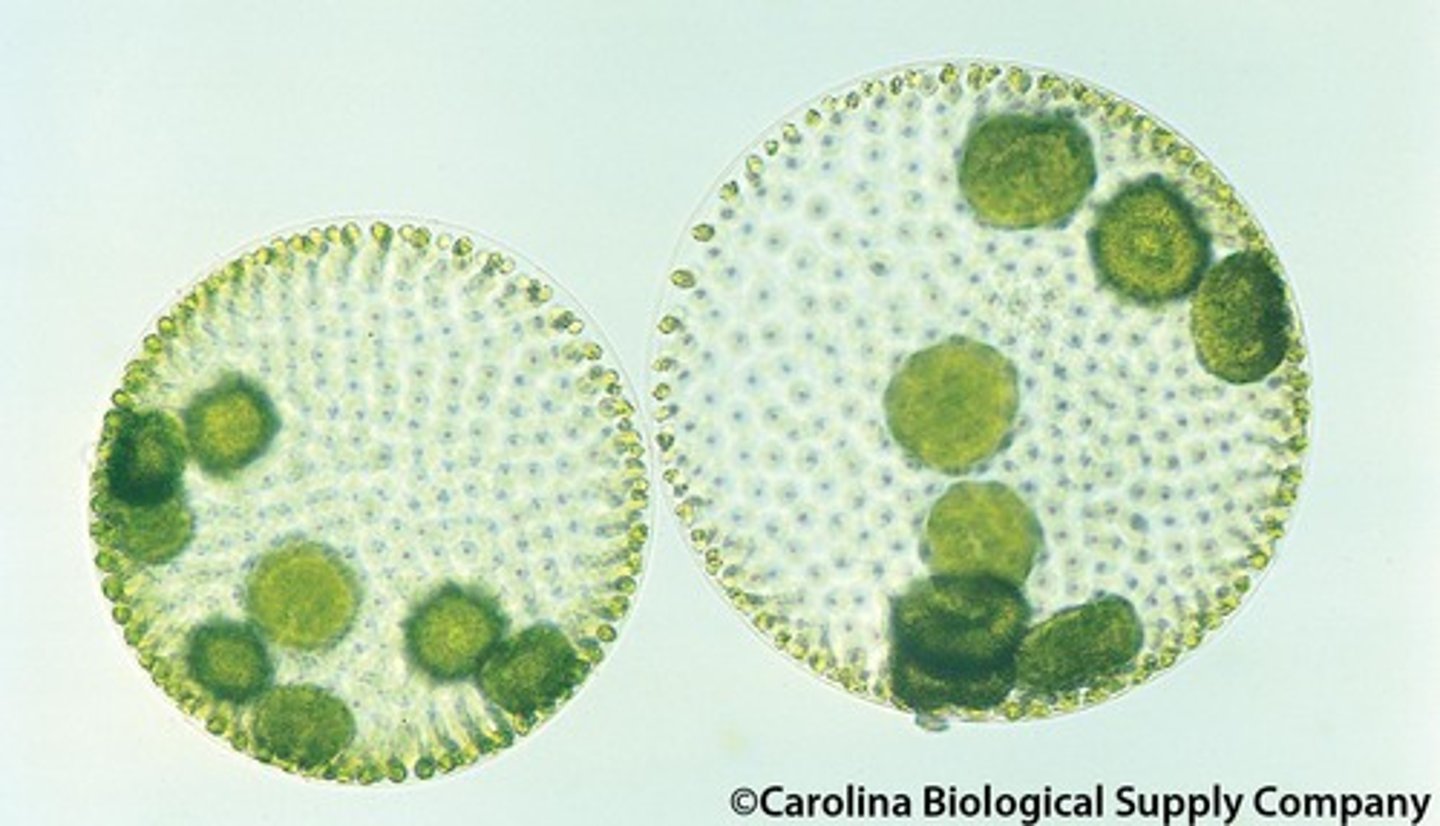
Colonial green algae
volvox and spirogyra
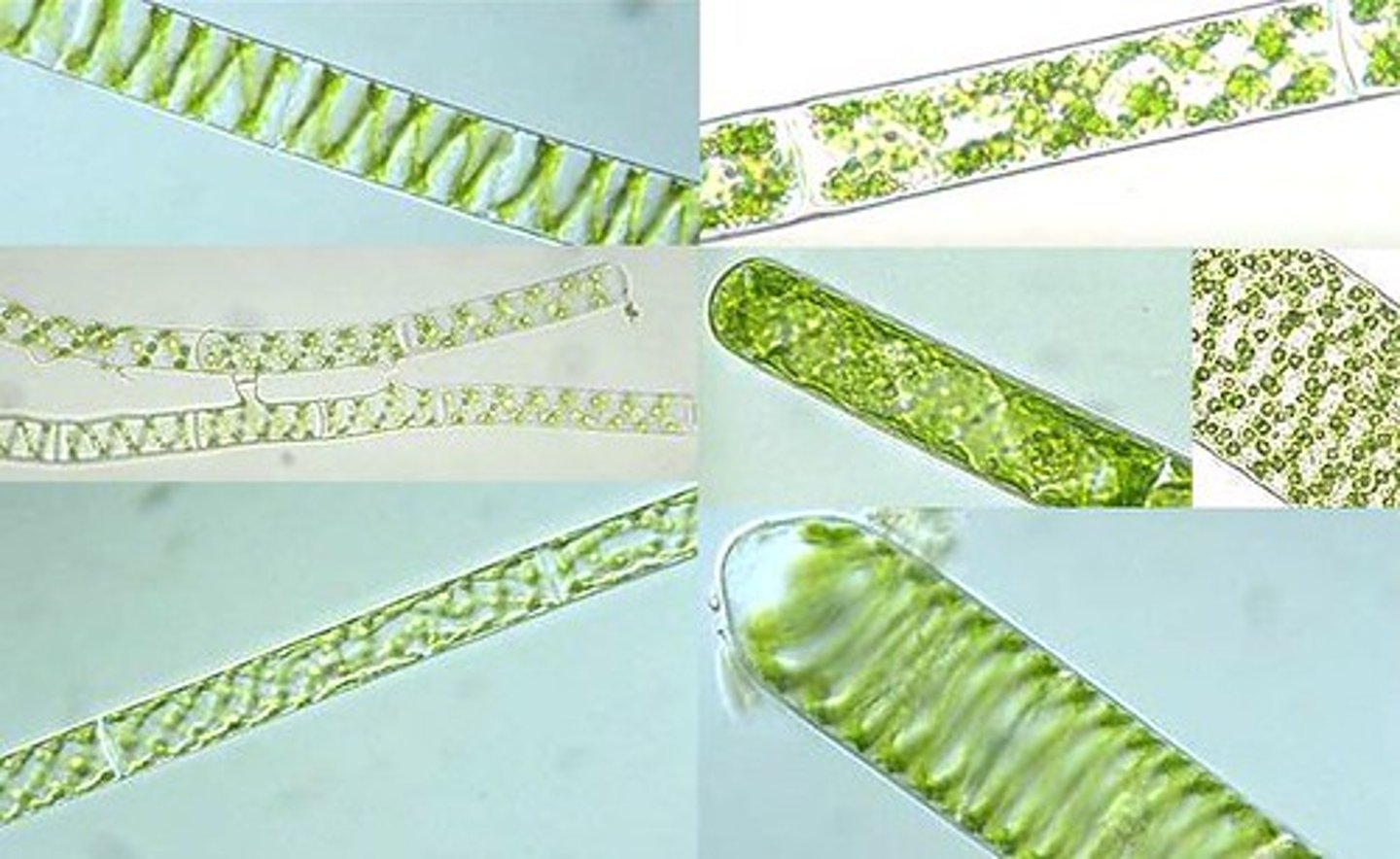
Filamentous green algae
spirogyra and cladophora
Coenocytic green algae
Cell grows and the nucleus divides, but the cell does not divide, resulting in a large, multinucleated cell
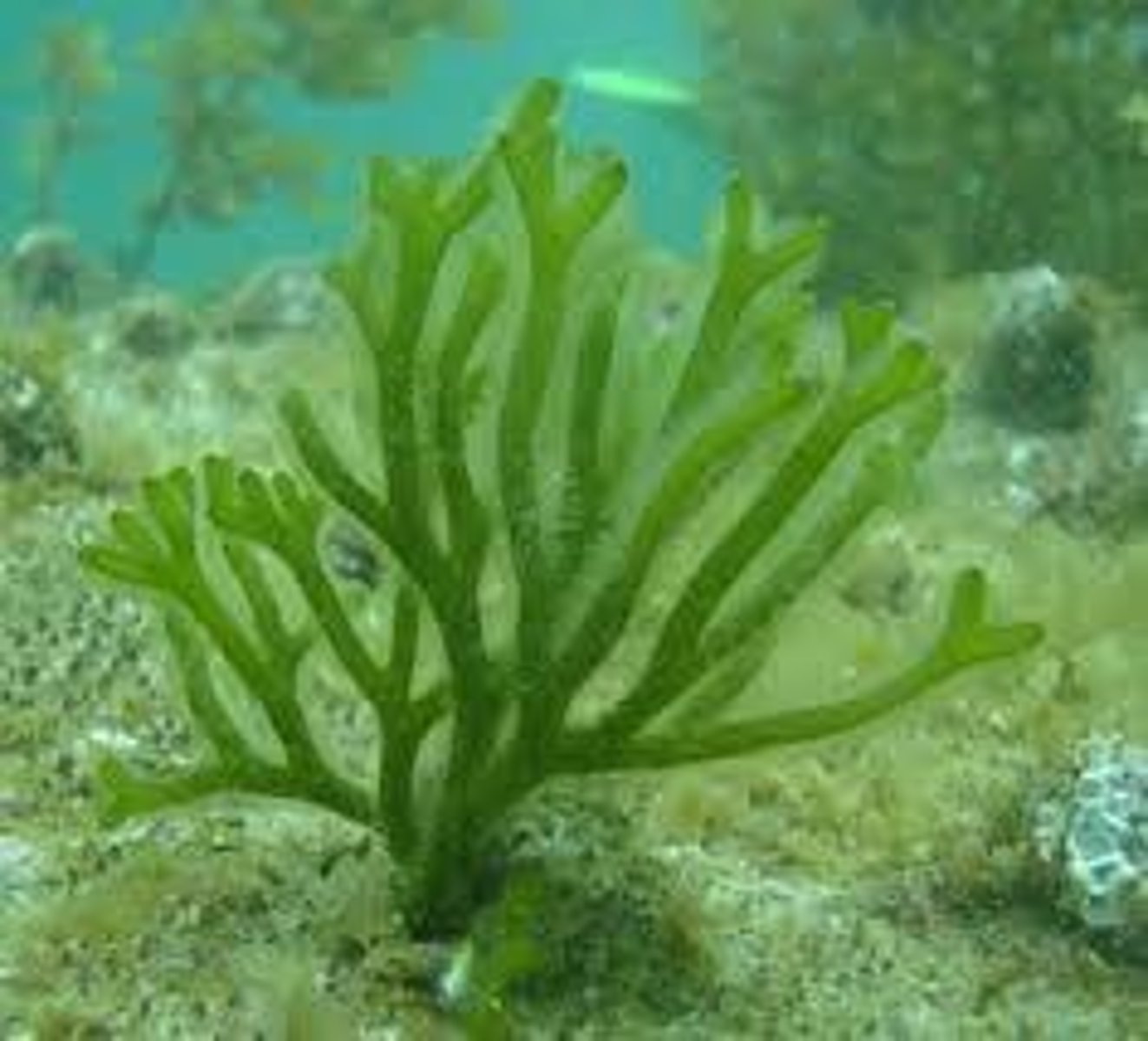

Flat sheets of cells green algae
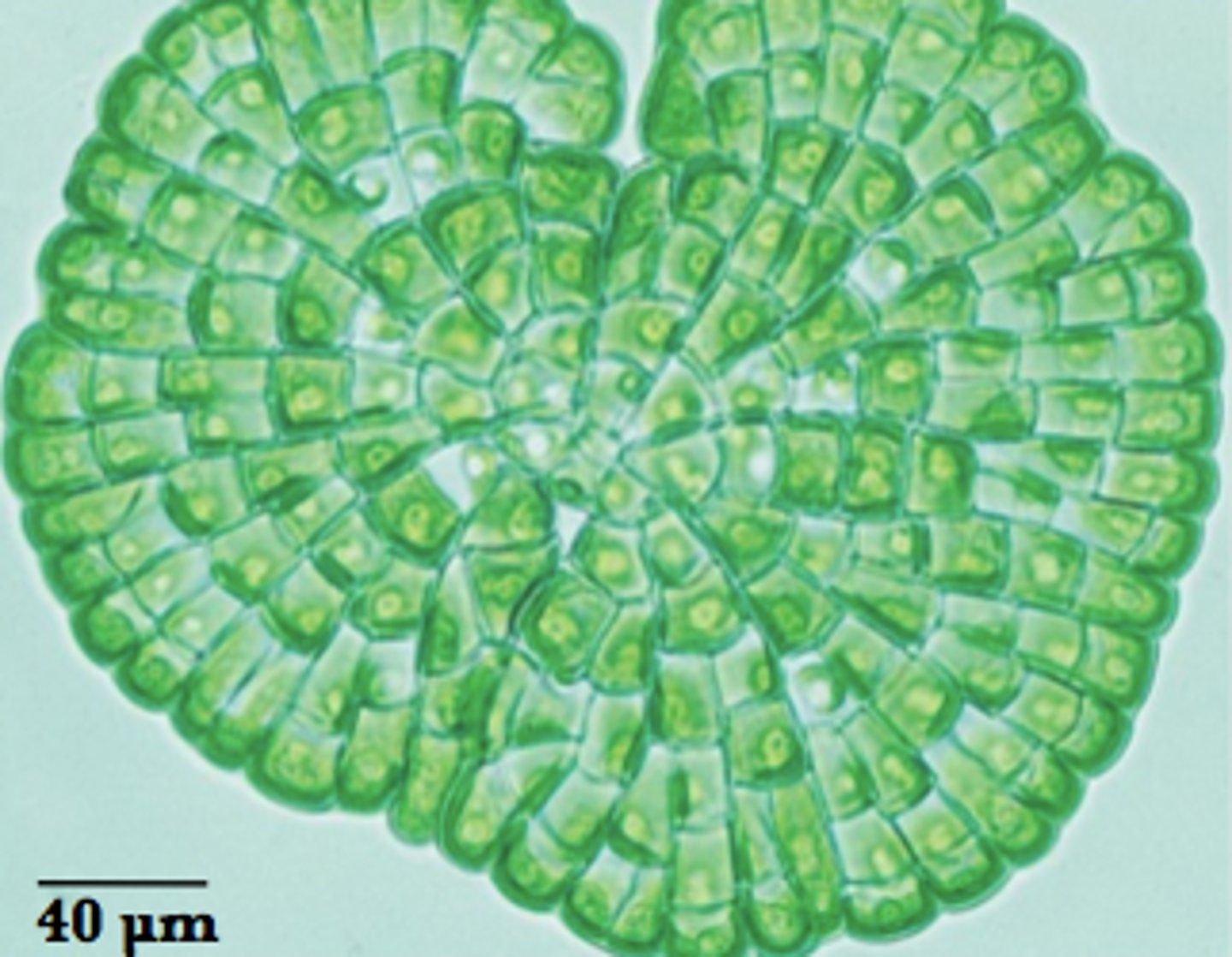
Parenchyma-like tissue green algae
Chl b; beta carotene
Green Algae Characteristics
Color:
Store starch
Green Algae Characteristics
Storage:
Plant-like chloroplasts
Green Algae Characteristics
Chloroplasts:
Plant
Green Algae Characteristics
One group probably sister group to ______ Kingdom
Common in FW
Common in shallow, tropical SW
Calcareous species common
Green Algae Ecology
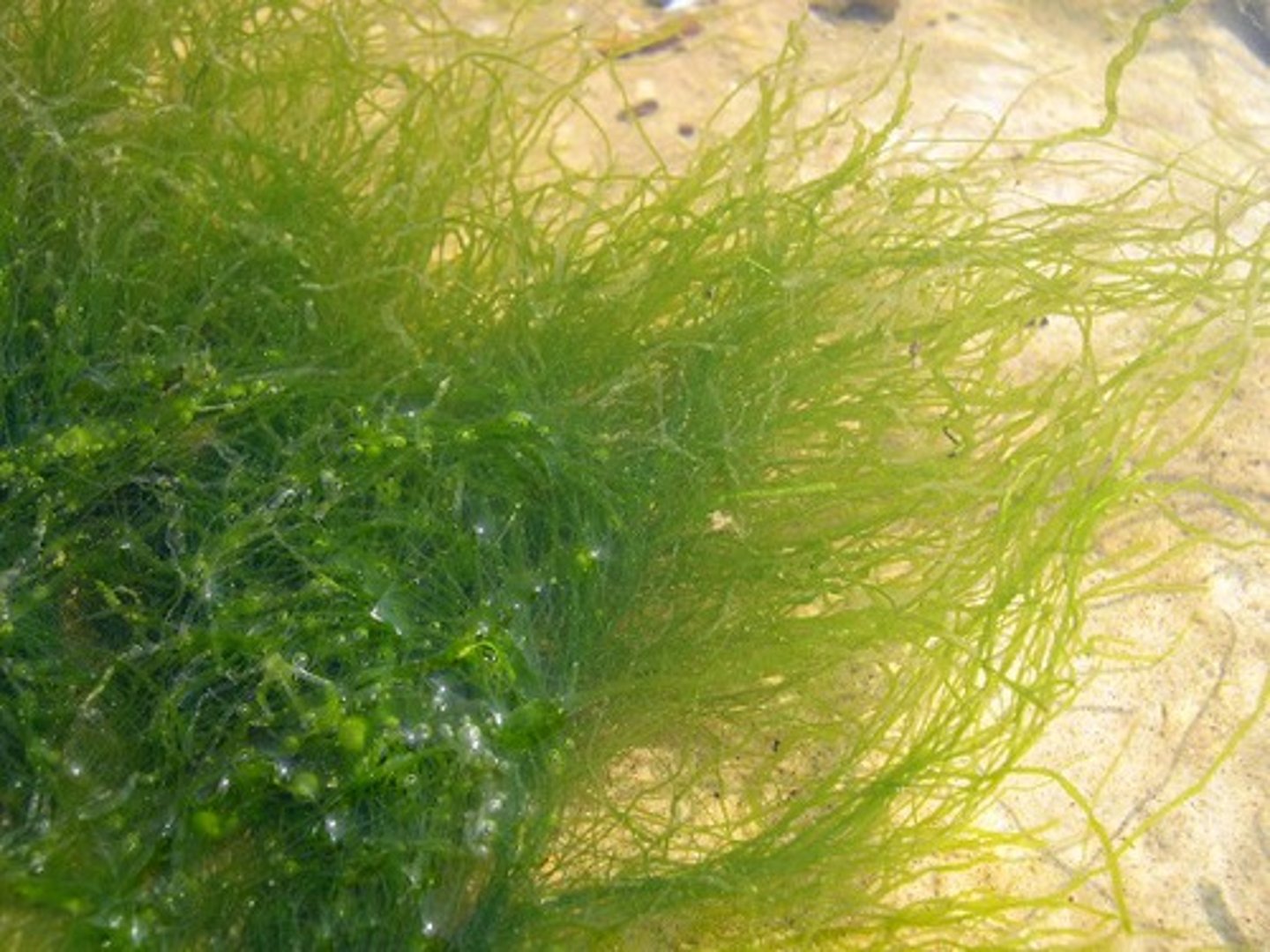
Mermaids hair

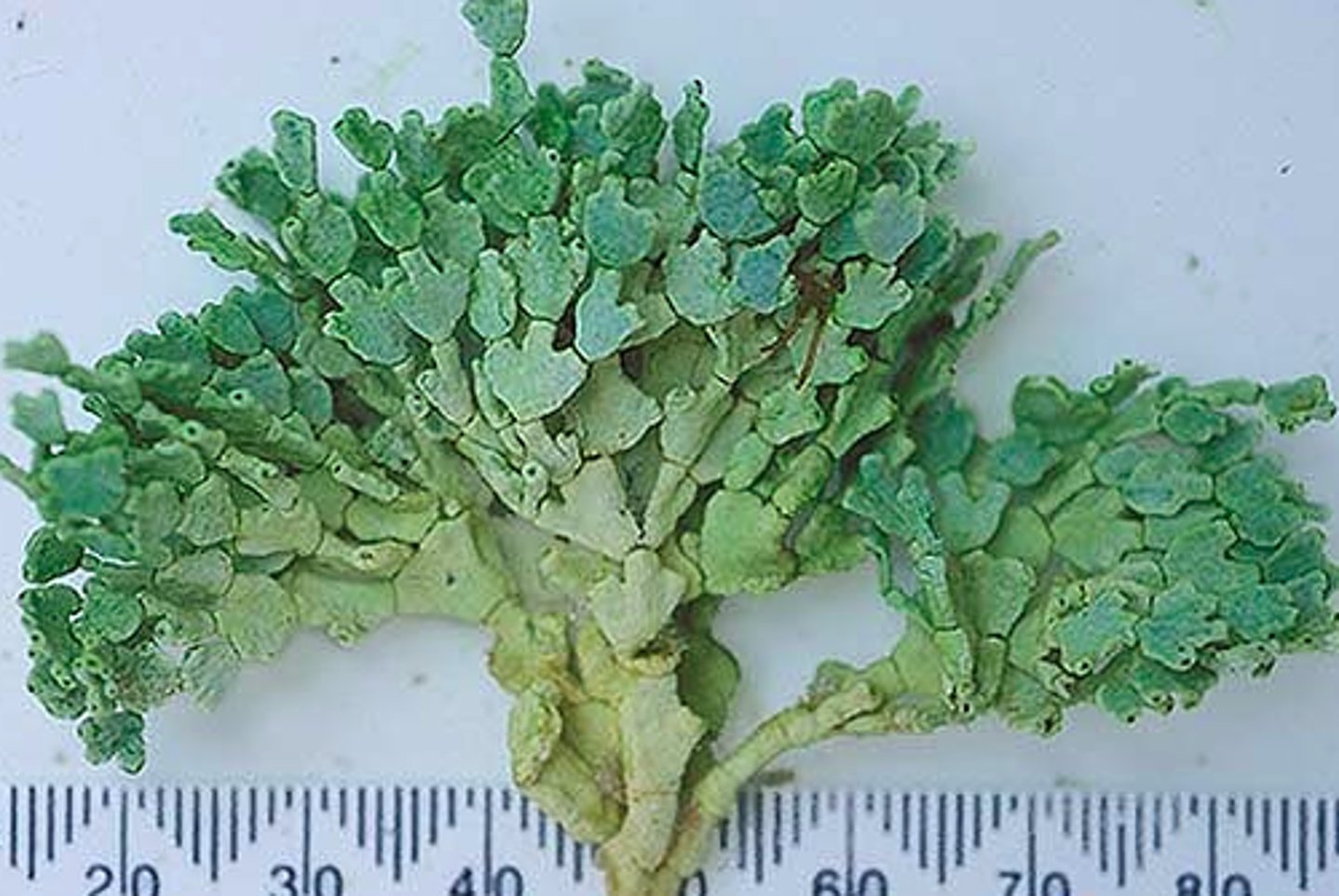
Caulerpa
Caulerpa scientific name
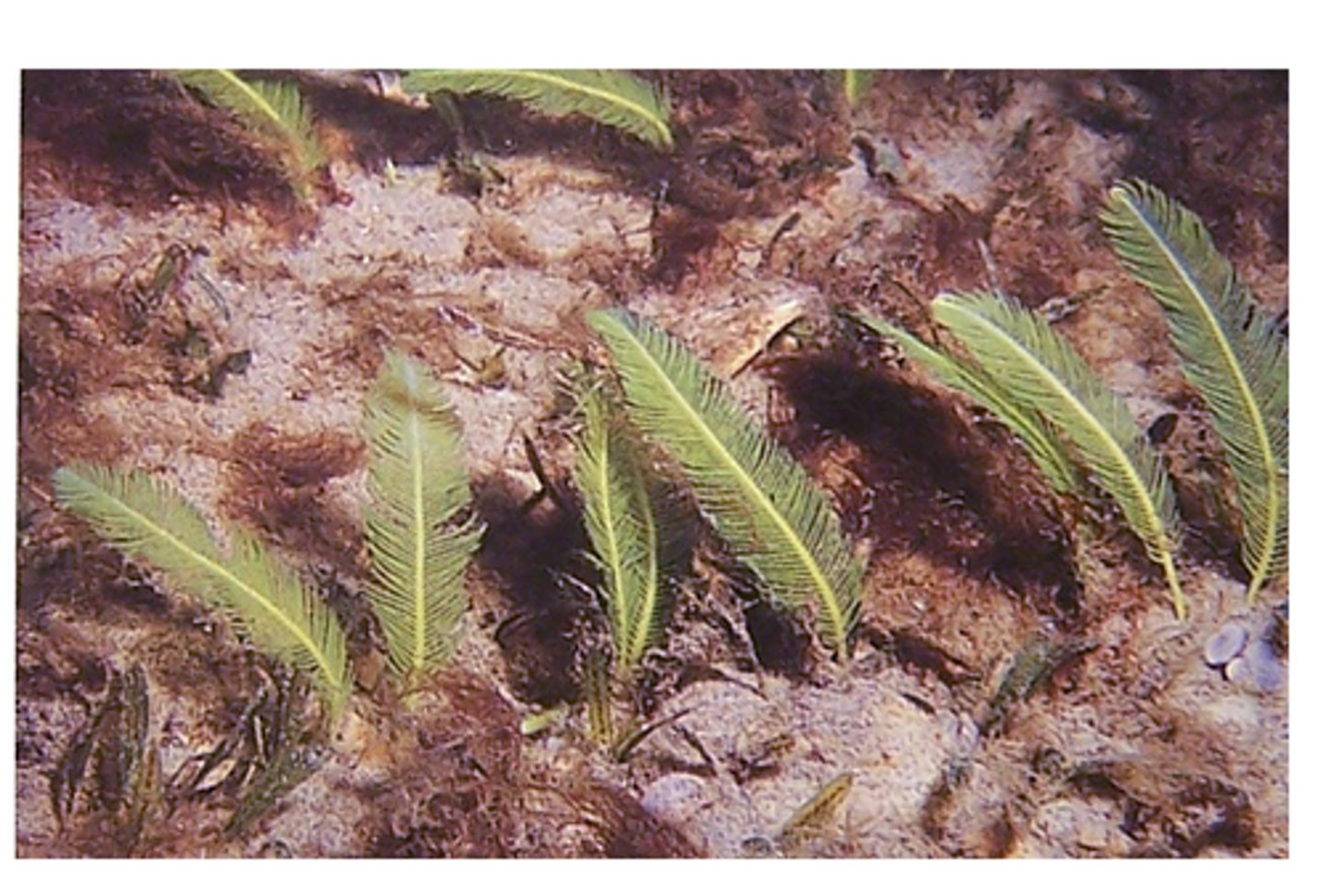

Halimeda
Halimeda scientific name

Nori (red); Wakame (kelp); Kombu (kelp)
Commercial Importance
Food:
Thickeners and stabilizers from kelp and other brown algae
Commercial Importance
Alginates:
Growth medium for microorganisms from red algae
Commercial Importance
Agars:
Emulsifiers from red algae
Commercial Importance
Carrageenans