Biology Test 2 Vocab
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/51
Last updated 11:57 AM on 11/3/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
1
New cards
Character
Detectable inheritable feature
e.g. flower colour
e.g. flower colour
2
New cards
Trait
Character determined by an allele
e.g. purple or white flower
e.g. purple or white flower
3
New cards
Dominant trait
Trait that only requires one copy the gene to express itself (capital letters)
e.g. brown eyes
e.g. brown eyes
4
New cards
Recessive trait
Trait that requires both copies of the gene to express itself (lower case letters)
e.g. blue eyes
e.g. blue eyes
5
New cards
True breeding
Fertilization that produces offsprings with the same traits
6
New cards
Allele
Alternate form of a gene. Responsible for variations in the inherited characters
7
New cards
Locus
Location of a gene
8
New cards
Phenotype
Physical expression of a gene
9
New cards
Genotype
Organism's genetic makeup
10
New cards
Homozygous
Having two identical alleles of a gene (BB or bb)
11
New cards
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a gene
12
New cards
Punnett square
Table showing all possible combinations of alleles.
13
New cards
Test crossing
Test done to determine if an organism expressing the dominant phenotype is homozygous or heterozygous
14
New cards
Monohybrid cross
Cross of heterozygous F1s with their parents differering in only one gene
15
New cards
Dihybrid cross
Cross of heterozygous F1s with their parents differing in two genes
16
New cards
Incomplete dominance
Heterozygotes show an intermediate phenotype
e.g. red pink white flower
e.g. red pink white flower
17
New cards
Codominance
Heterozygotes express both alleles
e.g. AB blood type
e.g. AB blood type
18
New cards
Multiple alleles
More than two possible alleles for a gene
e.g. Iᴬ, Iᴮ, i blood genotypes
e.g. Iᴬ, Iᴮ, i blood genotypes
19
New cards
Pleiotropy
A single gene has multiple phenotypic effects
e.g. sickle cell anemia
e.g. sickle cell anemia
20
New cards
Epistasis
Gene at one locus alters the phenotypic expression of a gene at another locus
e.g. black brown blond dog
e.g. black brown blond dog
21
New cards
Polygenic inheritance
Two or more genes leads to a single phenotypic character
e.g. skin color
e.g. skin color
22
New cards
Autosomal recessive disorder
Phenotype that is expressed by two recessive alleles found on an autosome
23
New cards
Autosomal dominant disorder
Phenotype that is expressed by only one disease allele on an autosome
24
New cards
X-linked trait
Phenotype that is expressed by recessive alleles in the X chromosome
25
New cards
Lyon hypothesis
X-Inactivation occurs randomly in embryonic cells
26
New cards
Pedigree
Diagram showing the occurrence of a genetic trait in several generations of a family.
27
New cards
Fimbriae
Appendage to attach to host and gain entrance
28
New cards
Sex pili
Structure for bacterial conjugation
29
New cards
Photoautotroph
Organism that uses light as a source of energy to synthesize organic substances.
30
New cards
Chemoautotroph
Organism that produces energy by oxidation of inorganic compounds
31
New cards
Chemoheterotroph
Organism that consumes organic molecules for energy and ATP
32
New cards
Saprophytic
Organism that absorb nutrients from dead organisms
33
New cards
Symbiosis
Interaction between smaller symbiont and larger host
34
New cards
Obligate aerobe
Bacteria that require oxygen to grow
35
New cards
Facultative anaerobe
Bacteria that grows with or without oxygen (is capable of fermentation)
36
New cards
Obligate anaerobe
Organism that cannot grow in the presence of oxygen
37
New cards
Colonial
Collection of unicellular organisms living together
38
New cards
Charophyte
Group of green algae most closely related to land plants
39
New cards
Volvox
Colonial chlorophyta algae exhibiting division of labour between cells
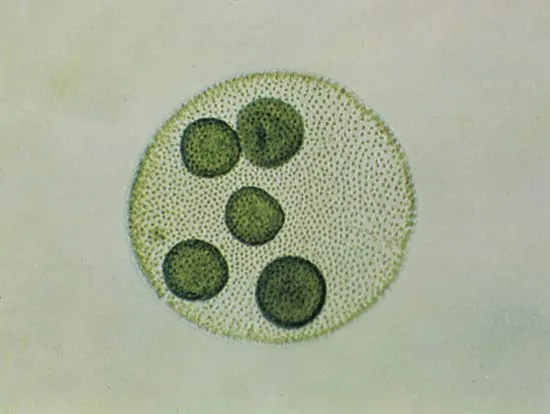
40
New cards
Chlamydomonas
Unicellular chlorophyta algae with two flagella
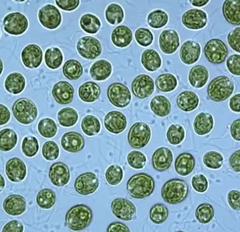
41
New cards
Phragmoplast
A group of microtubules
42
New cards
Rhizoid
Primitive roots of the moss
43
New cards
Stomata
Pores for gas exchange
44
New cards
Waxy cuticle
Very waxy (lipid) material which prevents leaves from drying out in the sun
45
New cards
Desiccation
Drying out of a living organism
46
New cards
Vascular system
Composed of the xylem and the phloem
47
New cards
Xylem
Nonliving vascular tissue that carries water and dissolved minerals up using passive transport
48
New cards
Phloem
Living vascular tissue that carries sugar and organic substances up and down using active transport
49
New cards
Lignin
Complexe polysaccharide which enables plants to have support and grow tall
50
New cards
H2O fertilization
The sperm needs water to meet the female gamete
51
New cards
Pollen
Male sperm in plants
52
New cards
Seed
Fertilized egg (zygote) in a protective coat which provides nutrition and protection