openstax biology 2e: chapter 5
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
plasma membrane
the__________ __________ separates the living cell from its surroundings
selective permeability
the plasma membrane exhibits __________ ___________ allowing some substances to cross it more easily than others.
fluid mosaic model
the ______ _______ _______states that the membrane is a mosaic of protein molecules bobbing in fluid bilayer of phospholipids
- including phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates
integral proteins
_________ __________ penetrate the hydrophobic interior of the lipid bilayer
peripheral proteins
__________ __________are loosely bound to the surface of the membrane (may serve as enzymes)
carbohydrates
______________ on the external side of the plasma membrane vary among species, individuals, and even cell types in an individual.
carbohydrates
___________ on the external side of the plasma membrane allow cells to recognize each other.
membrane fluidity
__________ __________ refers to the viscosity of the lipid bilayer of a cell membrane. Viscosity of the membrane can affect the rotation and diffusion of proteins and other bio-molecules within the membrane, there by affecting the functions of these molecules.
lipids, proteins
most of the _____ and some ______ in a membrane can shift about laterally.
amphiphilic
molecule possessing a polar or charged area and a nonpolar or uncharged area capable of interacting with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic environments (phospholipid bilayer)
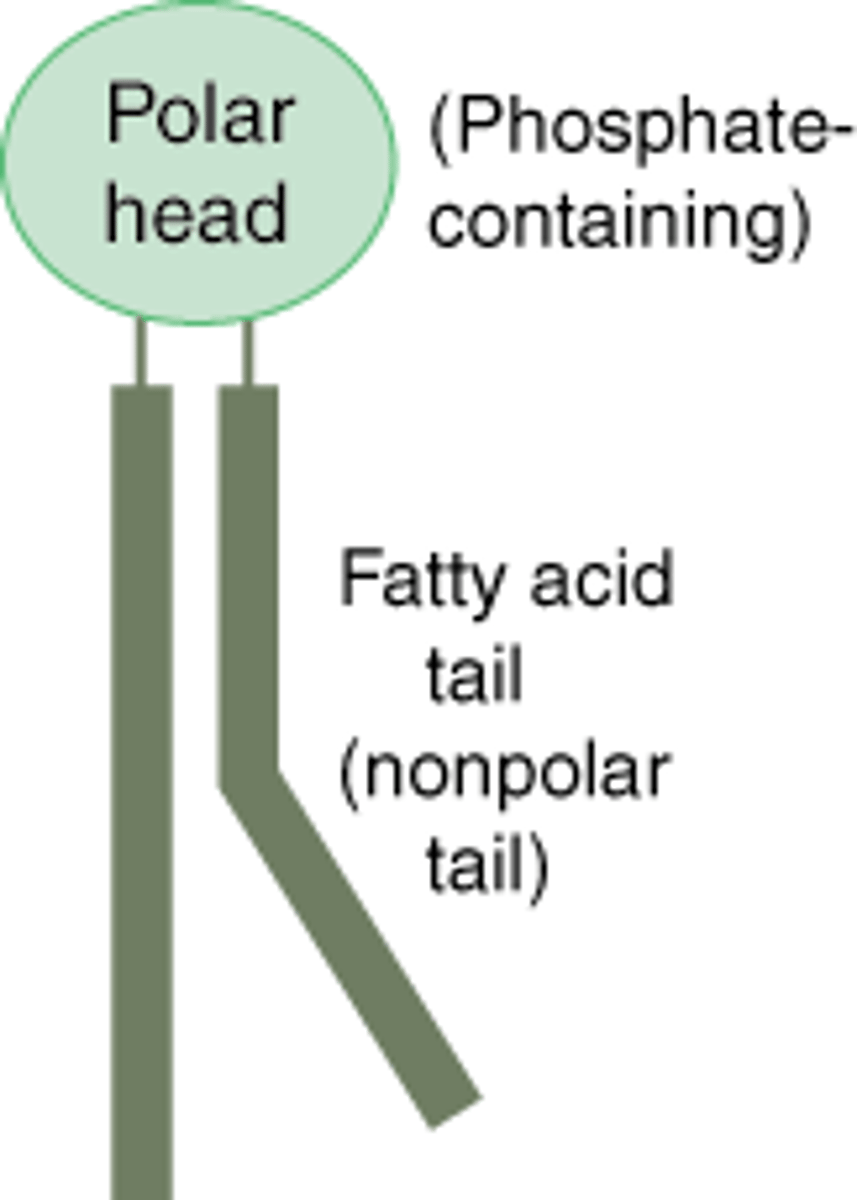
rapid, slowly
the lateral movement of phospholipids is _____; proteins move more _____.
regulate
A cell must _______ transport of substances across cellular boundaries.
selectively permeable
Plasma membranes are _________ ________, regulating the cell's molecular traffic
passive transport
_________ _________ is diffusion of a substance across a membrane with no energy investment.
hydrophobic (nonpolar)
_______ _________molecules, such as hydrocarbons can dissolve in the lipid bilayer of the membrane across it easily.
basic structure of plasma membrane:
- it is boundary, separates living cells from their nonliving surroundings
- contains a phospholipid bilayer
- amphipathic, contains both hydrophobic and hydrophilic components
- fluid mosaic
where is cholesterol found in the cell membrane?
attached between phospholipids and between the two phospholipid layers
where is integral proteins found in the cell membrane?
embedded within the phospholipid layer(s); may or may not penetrate through both layers
where are peripheral proteins found in the cell membrane?
on the phospholipid bilayer's inner or outer surface; not embedded within the phospholipids
concentration gradient
difference in the concentration of a substance from one location to another
facilitated transport
a process by which material moves down a concentration gradient (from high to low concentration) using integral membrane proteins
plasmolysis
a phenomenon in walled cells in which the cytoplasm shrivels and the plasma membrane pulls away from the cell wall; occurs when the cell loses water to a hypertonic environment
polar
______ molecules, such as sugars, do not cross the membrane easily.
aquaporin
_________ channel used exclusively to facilitate the movement of water through the bilayer.
diffusion
process of passive transport;_______ is the tendency for molecules to spread out evenly into the available space. (from higher concentration to lower)
more, less
substances diffuse down their concentration gradient, from it is ________ concentrated to where it is _______ concentrated. No work must be down to move substances down the concentration gradient.
facilitated transport (diffusion)
in______ _____ _____transport proteins speed the passive movement of molecules across the plasma membrane.
channel proteins
_____ ______ provide corridors that allow a specific molecule or ion to cross the membrane.
carrier proteins
_______ _______ undergo a subtle change in shape that translocate the solute binding site across the membrane. the shape change may be triggered by binding and release of the transported molecule. (no net energy input required)
osmosis
the diffusion of free water across a selectively permeable membrane.
lower, higher
Water diffuses across a membrane from the region of ______ solute concentration to the region of ______solute concentration until the solute concentration is equal on both sides.
tonicity
_______ is the ability of a surrounding solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water.
isotonic solution
concentration is the same as inside the cell; no net water movement across the plasma membrane.
hypertonic solution
solute concentration is greater than that inside the cell; cell loses water.
hypotonic solution
solute concentration is less than that inside the cell; cell gains water.
osmoregulation
is the control of solute concentrations and water balance.
cell wall
help maintain water balance
hypotonic, turgid
a plant cell in a _______ solution swells until wall opposes uptake; the cell is now _____(very firm)
isotonic, flaccid
if a plant cell and its surrounding are ________, there is no net movement of water into the cell; the cell becomes _______(limp), and the plant may wilt.
hypertonic, plasmolysis
in a _______ environment, plant cells lose water; eventually, the membrane pulls away from the wall, a usually lethal effect called ________.
facilitated transport, direction
____ _____ speeds transport of a solute by providing efficient passage through the membrane but does not alter the ______ of transport.
transport proteins
Some _____ ______, however, can move solute against their concentration gradients. Lower to higher.
active transport
_____ _______ uses energy to move solutes against their gradients. (ATP)
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
- is considered by biologists to be the energy currency of life
electrochemical gradient
is the combined gradient of concentration and electrical charge that affects an ion.
ATP
since active transport moves substances against their concentration gradients it requires energy, usually in the form of ______.
three types of transporters in active transport:
uniporter, symporter, antiporter
uniporter
a carrier protein that transports a single molecule across the plasma membrane.
symporter
transporter that carries two different ions or small molecules, both in the same direction
antiporter
transporter that carries two ions or small molecules in different directions
lipid bilayer, transport proteins
Small solutes and water enter or leave the cell trough the ______ _______ or by means of _______ ______.
vesicles
Large molecules, such as polysaccharides and proteins cross the membrane in bulk by means of ______.
endocytosis
the cell takes in molecules and particulate matter by forming new vesicles from the plasma membrane.
phagocytosis
large particles are taken into the cell. The cell membrane surrounds the particle and engulfs it.
pinocytosis-
the cell membrane invaginates, surrounds a small volume of fluid and pinches off.
exocytosis
active transport in which vesicles migrate to the membrane, fuse with it, and release their contents.
amphipathic
a molecule that contains both a hydrophobic and hydrophilic region
integral proteins
proteins that penetrate the hydrophobic interior of the lipid bilayer; most are transmembrane, which span the membrane with ends that protrude out either side
glycolipids
carbohydrates covalently bonded to lipids
glycoproteins
carbohydrates covalently bonded to proteins
polar
A molecule which utilizes polar covalent bonds, leaving areas with partial charges
nonpolar
A molecule which utilizes nonpolar covalent bonds, leaving a neutral charge over the entire molecule
hydrophobic
a molecule that is 'water-fearing' due to its nonpolar covalent bonds, which are repelled from the polarity of water
hydrophilic
a molecule that is 'water-loving' due to its polar covalent bonds, which are attracted to the polarity of water
transport proteins
a transmembrane protein that helps a certain substance or class of closely related substances to cross the membrane; carrier and channel proteins are types of transport proteins
passive transport
The diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane
osmosis
the diffusion of free water across a selectively permeable membrane, whether artificial or cellular
isotonic
no net movement of water across the plasma membrane
hypertonic
a solution that has more solute particles than the inside of the cell; water will move out of the cell, causing it to shrivel (crenate)
hypotonic
a solution that has less solute particles than the inside of the cell; water will move into the cell, possibly causing it to burst (lyse)
turgid
very firm; the healthy state of most plant cells
facilitated diffusion
diffusion across the plasma membrane with the aid of transport proteins
sodium-potassium pump
a type of carrier protein that exchanges sodium for potassium across the plasma membrane, moving both against their concentration gradients and thus requiring energy
cotransport
the coupling of the downhill' diffusion of one substance to the 'uphill' transport of another against its own concentration gradient
pinocytosis
A type of endocytosis that transports fluid into cells
receptor mediated endocytosis
a type of endocytosis in the is activated by a ligand binding to a cell surface receptor.
primary active transport
a type of active transport in which the energy is supplied from the hydrolysis of ATP
secondary active transport
a type of active transport in which the energy is supplied from the movement of another molecule with its concentration gradient (does not directly require ATP)
caveolin
protein that coats the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane and participates in the process of liquid update by potocytosis
paracrine signaling
secreted molecules diffuse locally and trigger a response in neighboring cells
endocrine signaling
specialized cells release hormone molecules into vessels of the circulatory system, by which they travel to target cells in other parts of the body
Types of cell signaling
autocrine, across a gap junction, paracrine, endocrine
autocrine signaling
secreted molecules diffuse locally and trigger a response in the cells that secrete them (itself)
gap junctions (communicating junctions)
provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent cells