Phosphorus Cycle, Carbon cycle 2018, Nitrogen Cycle 2018, Water Cycle 2018 Diagram | Quizlet
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What is phosphorus needed for?
DNA and RNA and lipids
Where is it not found?
Air
Where does it cycle through?
Soil and oceans
What happened when water runs over rocks containing phosphorus?
It erodes
Inorganic phosphate
Taken up by roots of plants and incorporated into tissues
Heterotrophs
Eat plants and drink water
Extraction and decomposition
Releases phosphorus into soil
Where can it be stored?
In rock sediment
How do humans accelerate the cycle?
Use fertilizer, flush waste, clear cutting
Phosphate ions are absorbed by plant roots and used to build two organic molecules like?
ATP and DNA
Low phosphorus levels in freshwater lakes limits the overgrown of what?
Algae
An excessive increase in phosphorus, or other nutrients is called?
Euthrophication
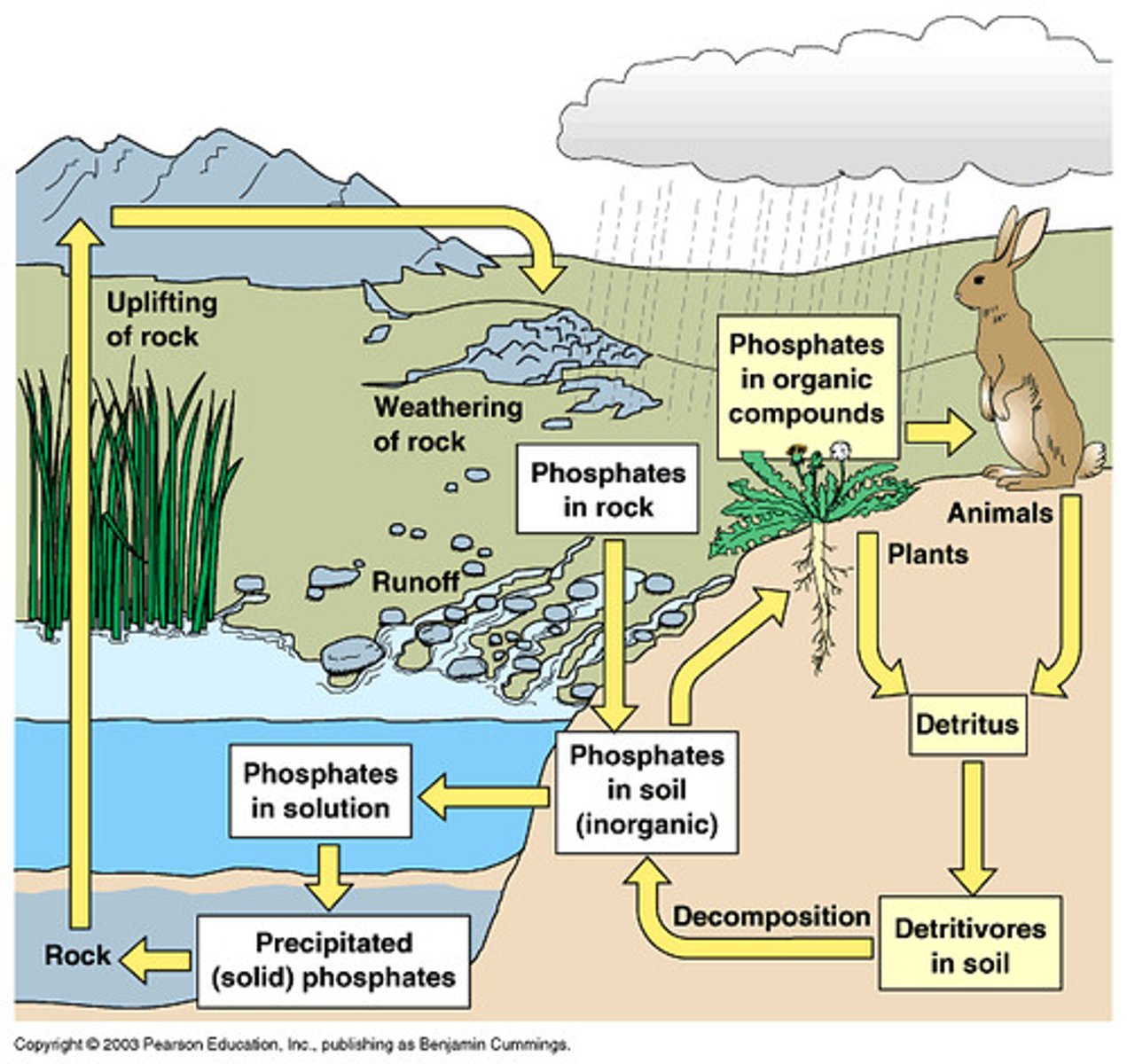
Phosphorus Cycle
The movement of phosphorus atoms from rocks through the biosphere and hydrosphere and back to rocks.
Photosynthesis, cellular respiration
_____ and cellular respiration are the 2 main biotic processes of the carbon cycle.
cellular respiration
What is process 4?
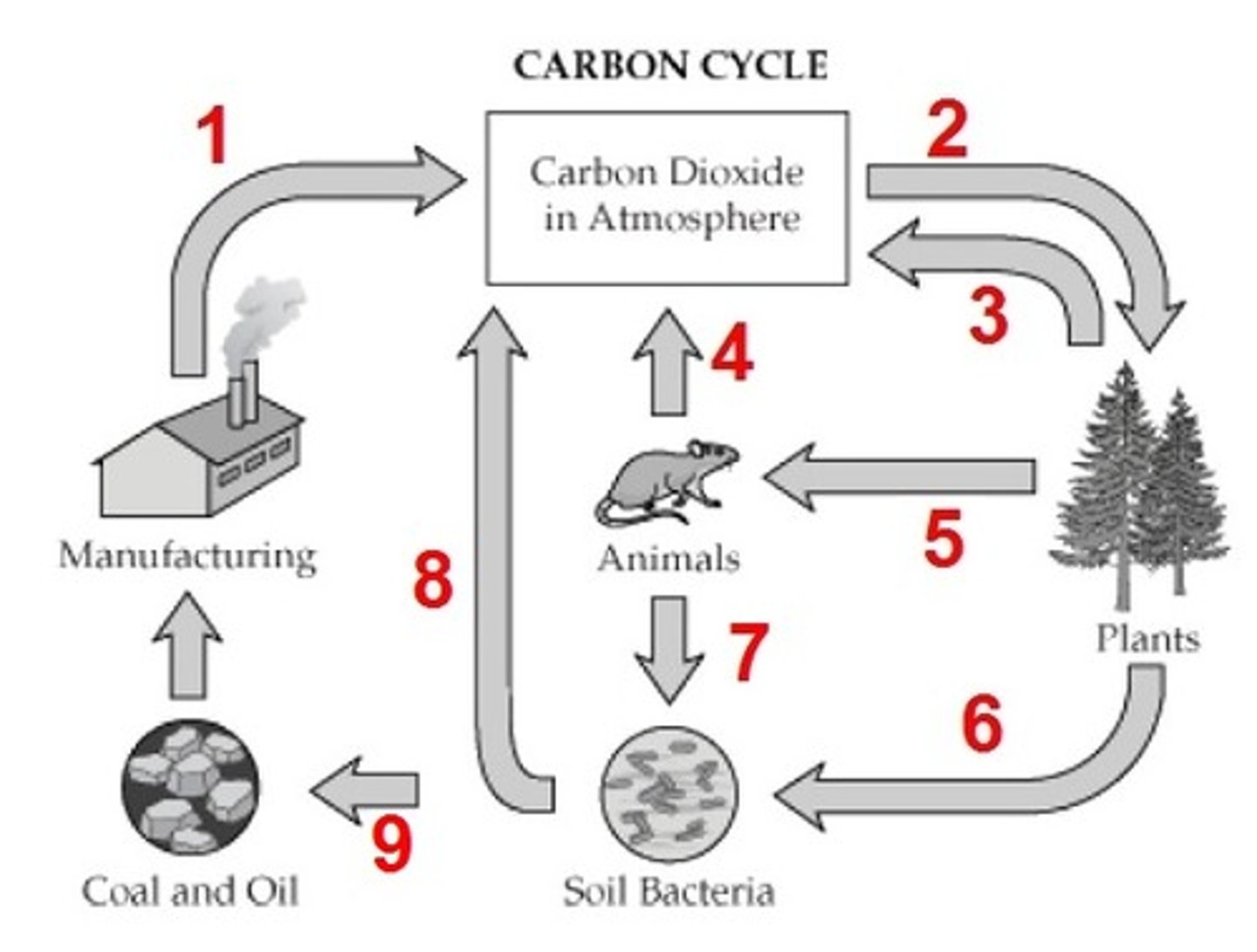
Combustion
What process adds carbon to the atmosphere (in the form of CO2)?
CO2
Carbon (in the form of _____) is removed from the atmosphere by producers that do photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis
____ removes CO2 from the atmosphere. This is only done by autotrophs.
photosynthesis
What is process 2?
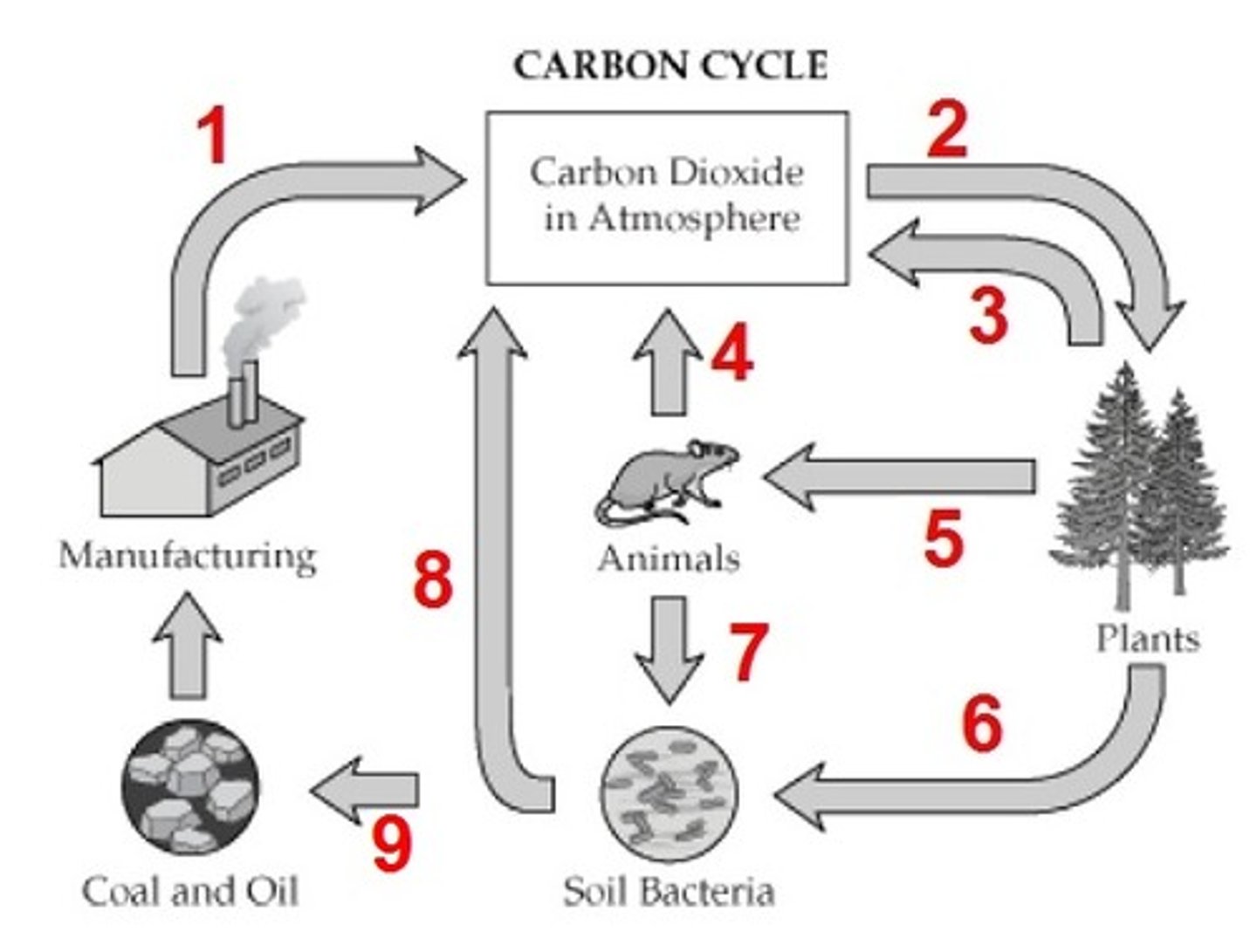
Consumption
What is process 5?
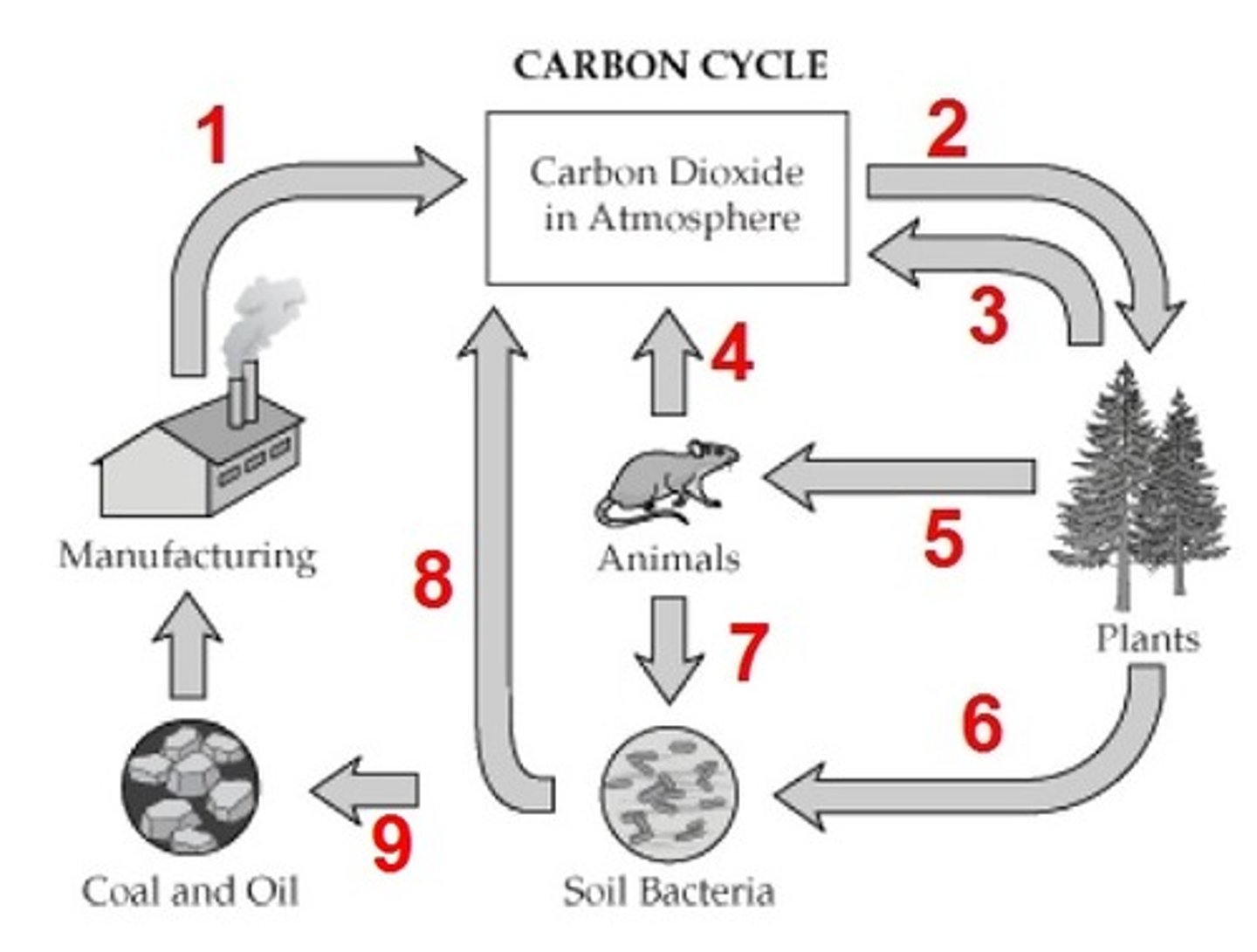
decomposition
What is process 7?
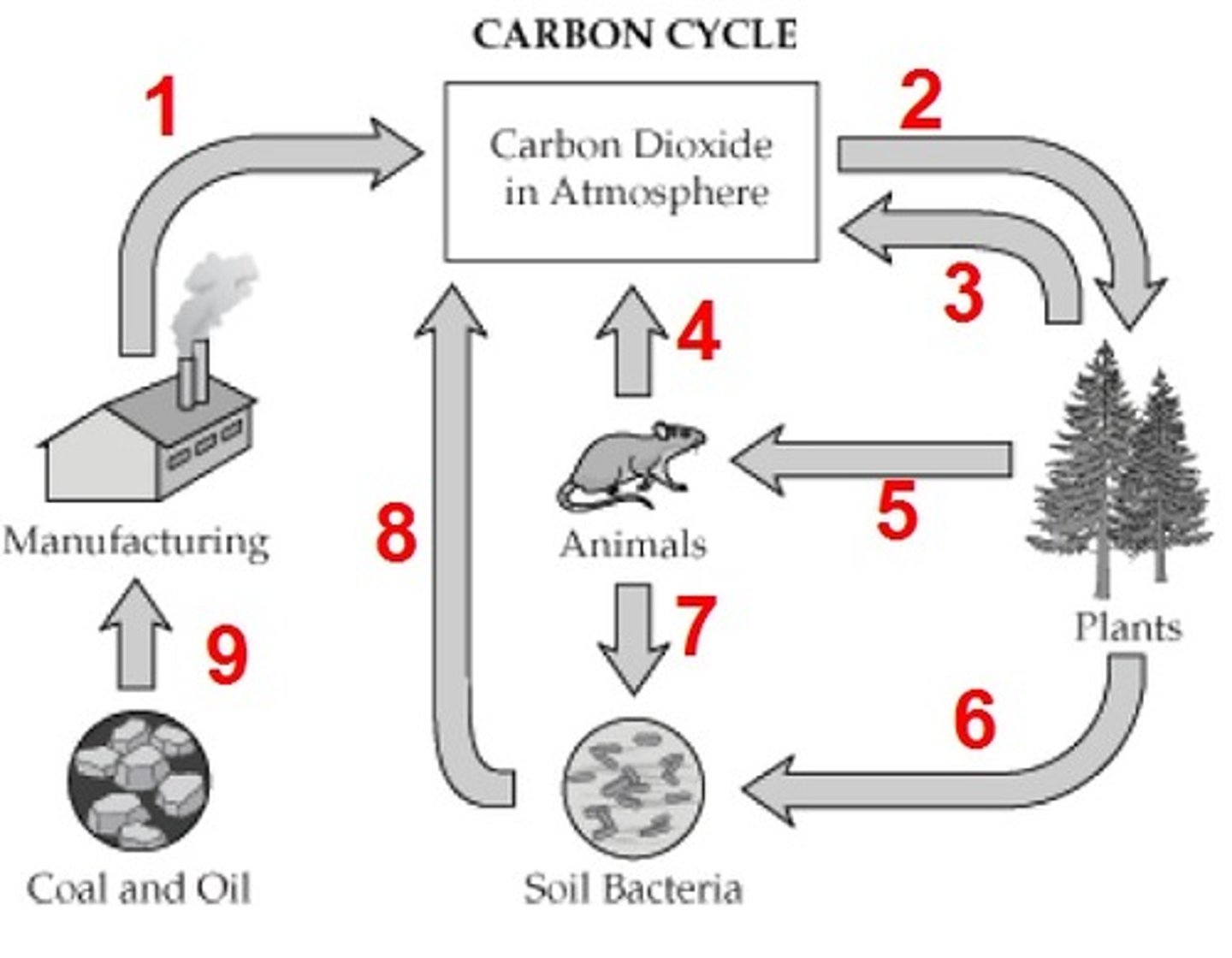
combustion (burning of fossil fuels)
What is process 1?
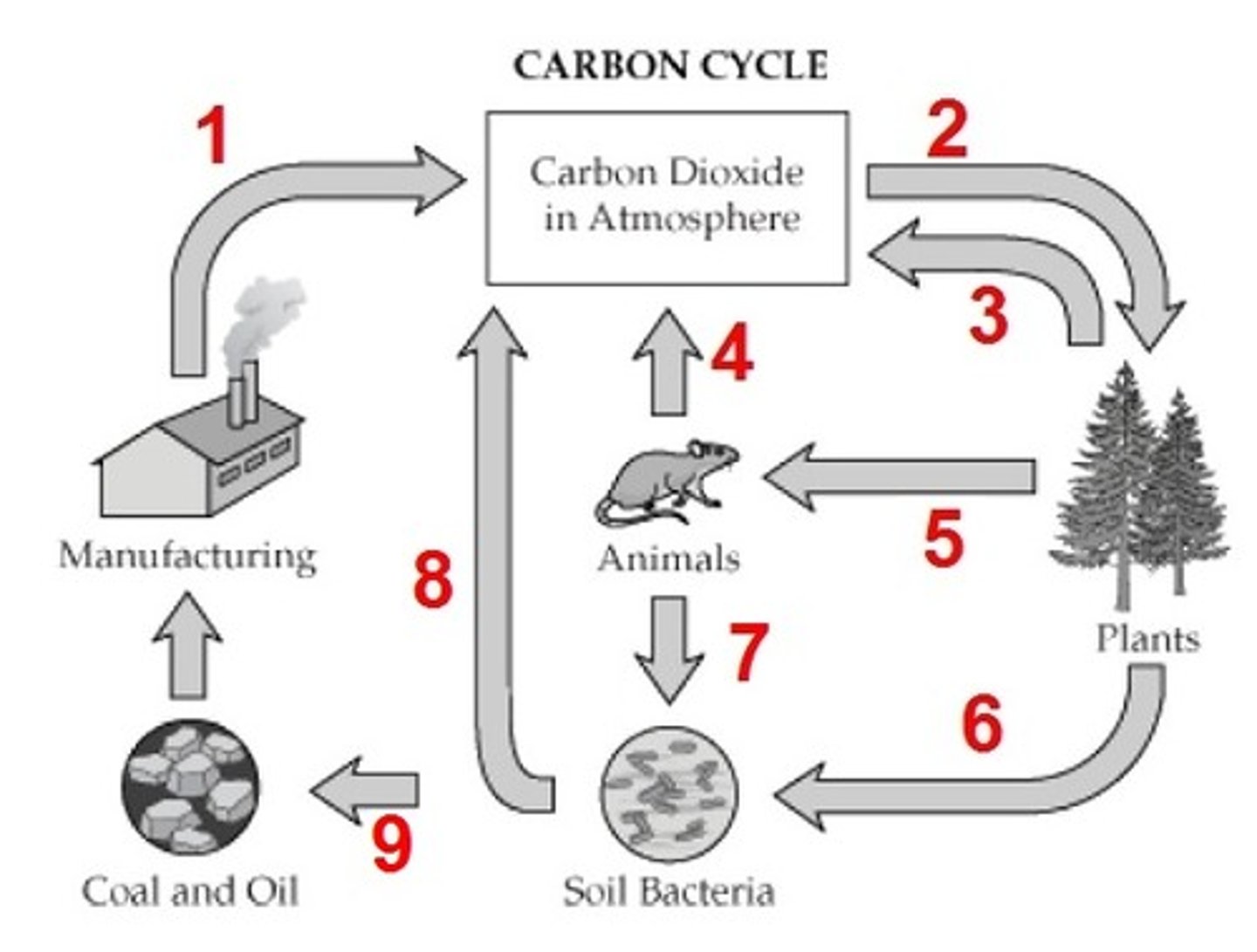
decomposition
What is process 6?
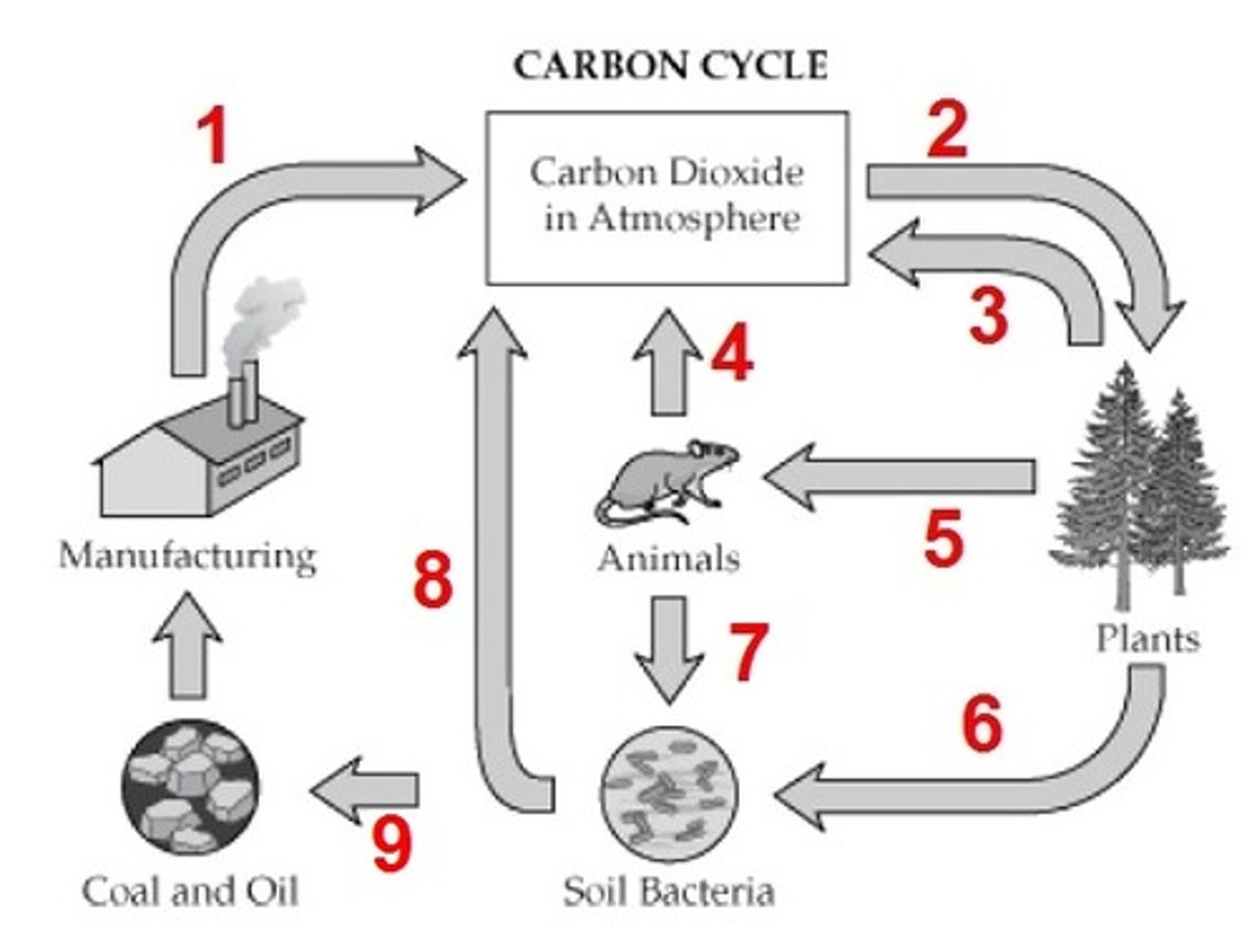
fossil fuels
formed by process 9
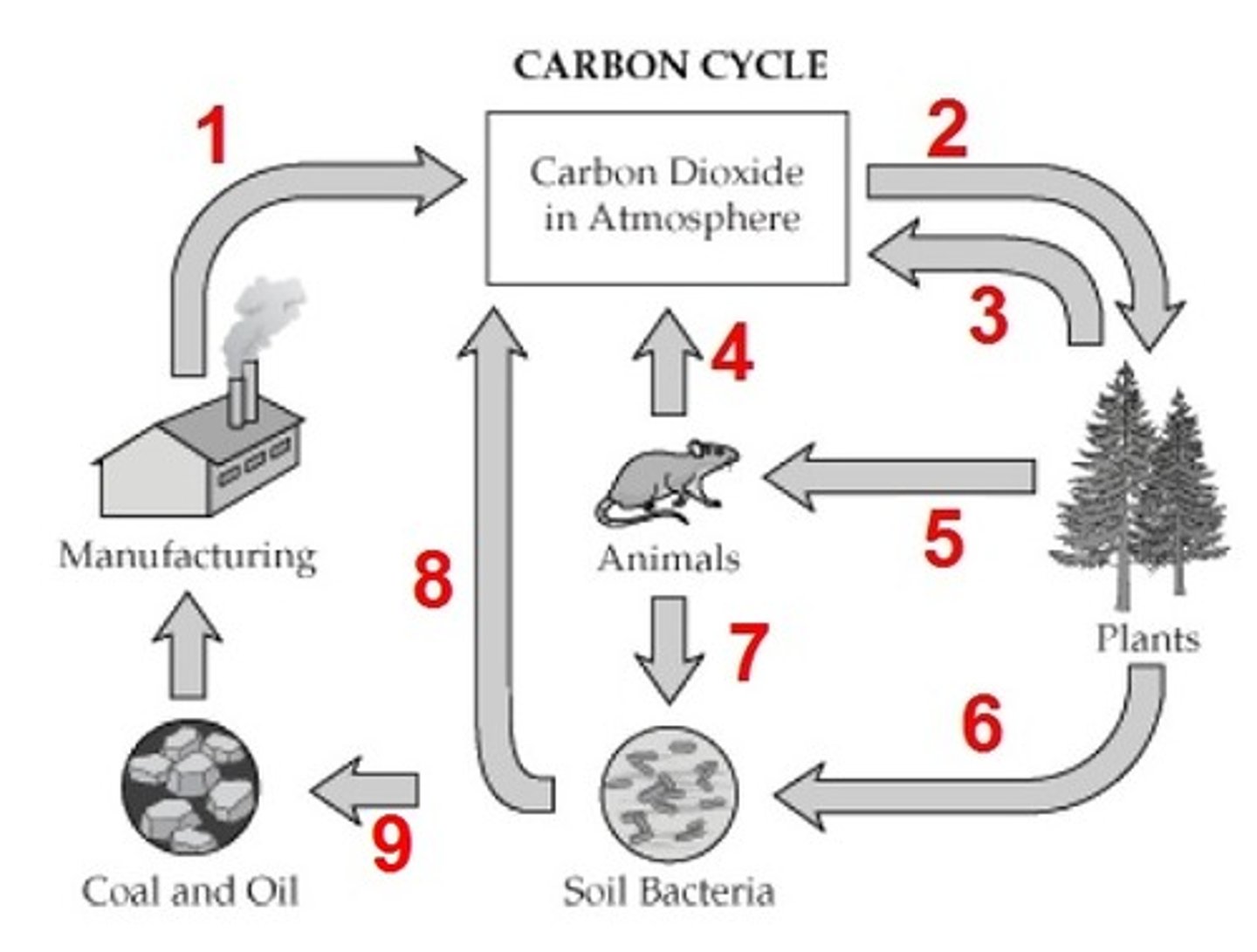
O2
molecular formula for oxygen gas
CO2
molecular formula for carbon dioxide
CO2
gas made by cellular respiration
O2
gas made by photosynthesis
greenhouse gases
gases in the atmosphere that trap heat (eg. water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane..)
Abiotic
Non-living
Biotic
Living
Exchange
Carbon released from the ocean into the air or from the air to the ocean.
Sedimentation
Carbon dioxide dissolved in ocean combines with calcium ions in water to form calcium carbonate.
extraction
Taking up the carbon that is buried within in the Earth
Nitrogen
An important element needed by living things.
Nitrogen is needed to build proteins.
Nitrogen is a key component in DNA (body's genetic program for life)
Nitrogen Cycle
The cycling of nitrogen between organisms, soil, water, and the atmosphere (Earth's spheres)
Nitrogen gas (N2)
78% of the atmosphere is made of nitrogen gas.
Plants and animals cannot get the nitrogen they need in this form.
Nitrogen Fixation
Process of converting nitrogen gas into nitrogen compounds, which are a usable form of nitrogen that plants can use.
Certain types of Bacteria and also Lightning can turn nitrogen gas into nitrogen compounds.
Lightning
converts nitrogen gas from the air into a usable form of nitrogen plants can use.
Denitrification
Process of converting nitrogen compounds into nitrogen gas, which is then released into the atmosphere.
Denitrifying bacteria carry out the process of denitrification.
Decomposition
A chemical reaction that breaks down compounds into simpler products.
When plants and animals decompose, nitrogen compounds are returned to the soil.

Bacteria
Microscopic living organisms that play an important role in the nitrogen cycle.
Nitrogen fixing bacteria change nitrogen gas to nitrogen compounds plants can use.
Denitrifying bacteria change nitrogen compounds to nitrogen gas to release back into the atmosphere.
Animals
Animals, including humans, get the nitrogen they need by eating plants or other animals that contain nitrogen.
When organisms die, their bodies decompose bringing the nitrogen into soil on land or into ocean water.
Animals also release nitrogen through their animal waste.
Plants
Plants take in the nitrogen they need through their roots. The nitrogen has to be "fixed" in a usable form.
Some plants (legumes) contain nitrogen fixing bacteria that live on their roots. The bacteria change nitrogen gas into nitrogen compounds the plants can use.
Soil
Nitrogen Compounds are found in the soil.
Nitrogen fixing bacteria change nitrogen gas to nitrogen compounds in the soil.
Denitrifying bacteria change nitrogen compounds in the soil to nitrogen gas.
Decomposers break down dead plants and animals and return the nitrogen to the soil.
Water Cycle
the process of recycling water
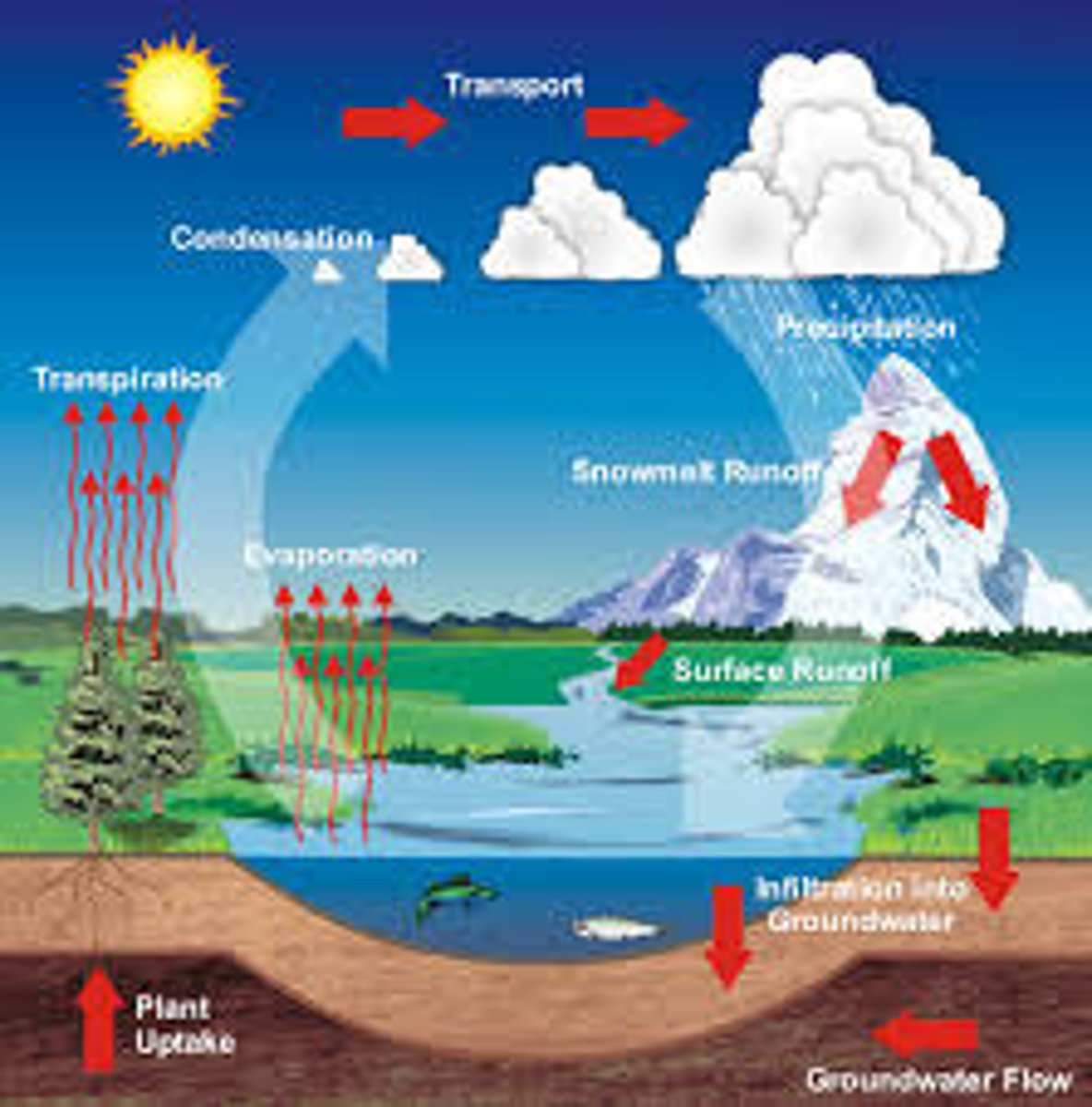
Evaporation
liquid water changes to gas

Condensation
gas changes to liquid

Precipitation
water falling from the sky

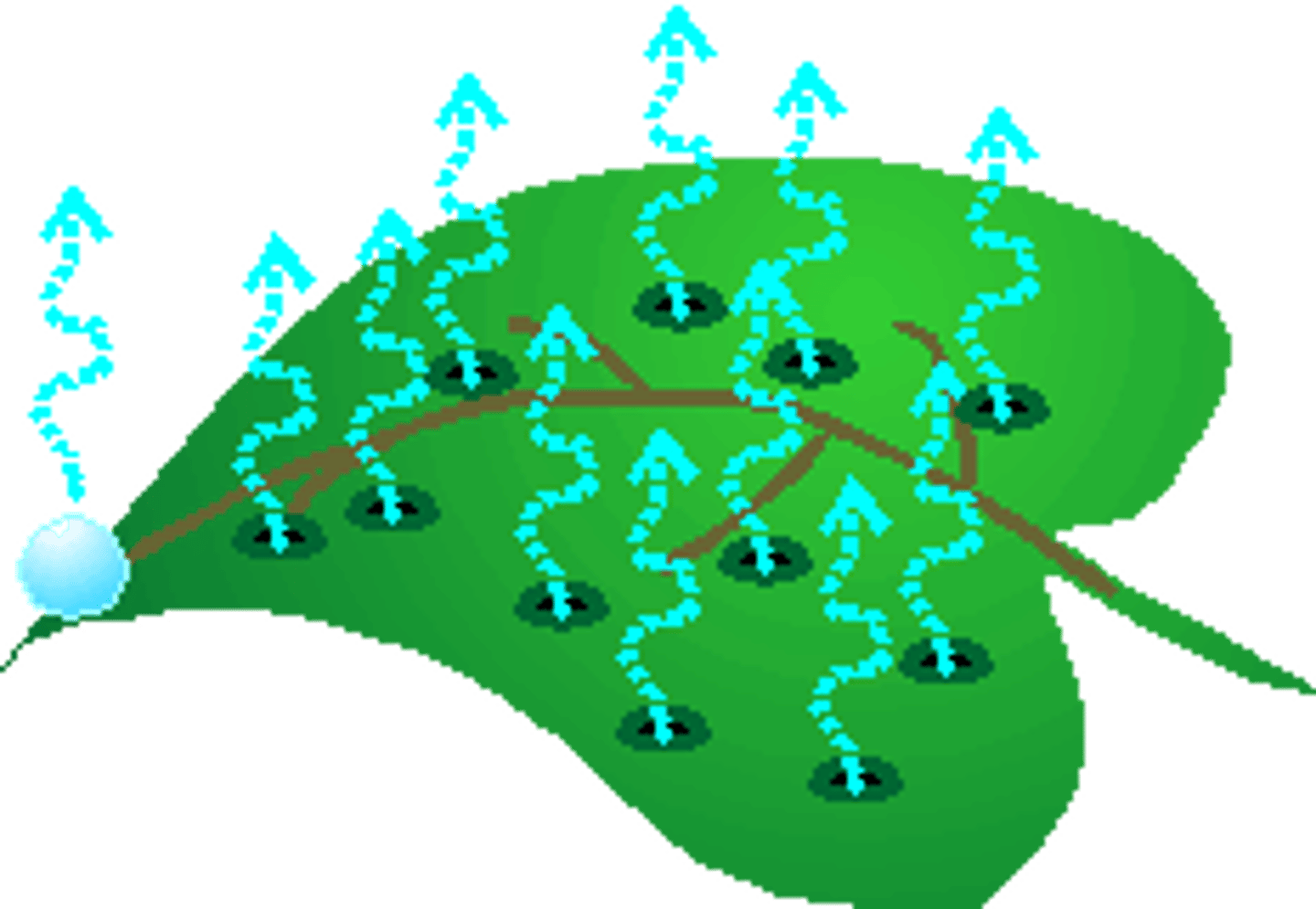
Transpiration
water from plants evaporating
Run off
water that flows along the ground returning to rivers, ponds, lakes, and oceans.

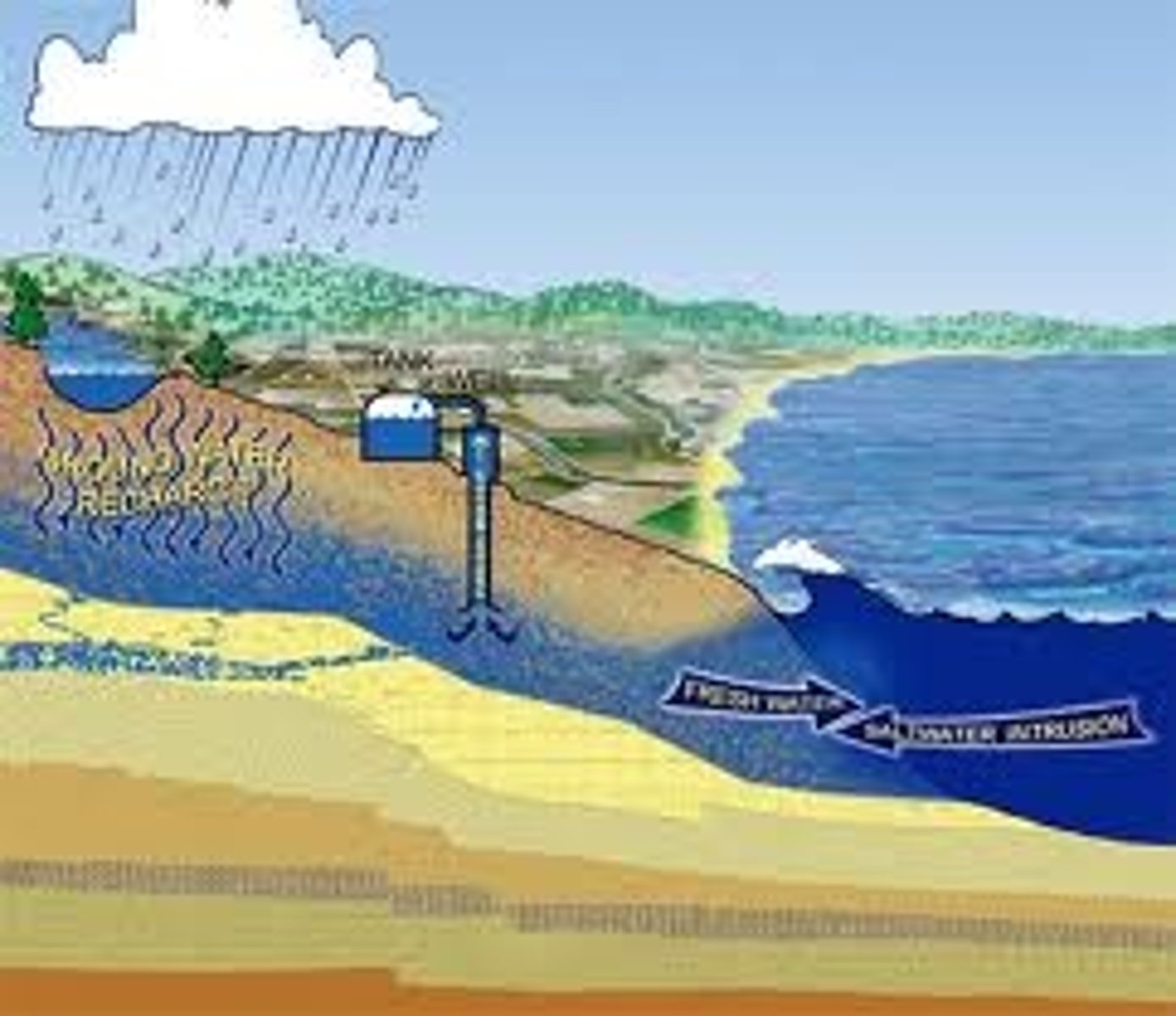
Ground Water
the water that gets absorbed and collect by the ground
Collection
places where water collects and then gets evaporated. Includes lakes, ponds, seas, and oceans.

Water Vapor
the gaseous form of water
Radiation
a type of heat energy from the sun that is responsible for heating and evaporating water from bodies of water

Water Droplet
a droplet of water

Snow
a type of solid precipitation

Rain
a type of liquid precipitation
