FBLA Economic Systems
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Traditional Economy
Decisions about production and distribution are based on customs, history, and long-standing beliefs
Command Economy
The govt controls all economic activity, making decisions about what to produce, how much to produce, and at what price
Market Economy
Economic decisions are made by individuals and businesses based on the forces of supply and demand, with minimal govt interference
Mixed Economy
A hybrid system that combines elements of both market and command economies. IT allows for private ownership and free markets while also including govt regulation, social programs, and public services
What is Capitalism?
Businesses are privately owned with minimal govt ownership or interference
Who controls Capitalist markets?
Complete freedom of trade; no or little govt control
Work incentives of Capitalism
Strong incentive to work and innovate because profits are retained by owners
Management of Capitalist Enterprises
Each enterprise is managed by owners or professional managers with little govt intervention.
Examples of Capitalist Countries
US, Japan, Chile
The 4 main types of economic systems are:
Traditional, command, market, and mixed
What is communism?
Govt owns all or most enterprises
Control of markets in communism
Complete govt control of markets
Work incentives in communism
No incentive to work hard or produce quality products
Management of Enterprise in communism
Centralized management by the govt bureaucracy; little or no flexibility in decision making at the factory level
Examples of communist countries
North Korea, China, Vietnam, Laos
What is socialism
Basic industries such as railroads and utilities are owned by the govt; very high taxation as govt redistributes income from successful private businesses to entrepreneurs.
Control of Markets in socialism
Some markets are controlled, and some are free; significant central govt planning; state enterprises are managed by bureaucrats; these enterprises are rarely profitable
Worker incentives in socialism
Private sector incentives are the same as capitalism, and public sector incentives are the same as in a planned economy (AKA command economy)
Management of enterprises in Socialism
Significant govt planning and regulation; bureaucrats run govt enterprises
Control of markets in a mixed economy
some markets, such as nuclear energy and the post office, are controlled or highly regulated
Socialist countries
Finland, India, Israel
Work incentives in mixed economies
Private sector incentives are the same as capitalism; limited incentives in the public sector
Management of enterprise in mixed economies
private sector management similar to capitalism; public sector similar to socialism
Mixed economy countries
UK, France, Sweden, Canada
Laissez-faire
type of economic system in which transactions between private individuals are free from any form of economic interventionism
Feudalism
economic system where land was the primary source of wealth, granting large estates in exchange for military service and loyalty
Mercantilism
eocnomic system (16th-18th century) focused on a nation accumulating wealth, primarily gold and silver, by maintaining favorable balance of trade
Market capitalism
private individuals and companies owns the means of production, and the market, driven by supply and demand, determines prices and the allocation of resources withh minmal govt intervention
Keynesian Economies
Theory advocating for govt intervention through fiscal and monetary policies to manage economic downturns by boosting aggregate demand
Stagflation
Economic conditions characterized by high inflation, stagnant economic growth, and high unemployment all happening at the same time
Market socialism
economic system that combines social ownership of the means of production with a market economy. Instead of relying on govt planning, it uses market forces like supply and demand to allocate sources and guide production
State capitalism
Economic system where the state, not private individuals, controls or heavily influenced the means of production to generate profits for further economic activity and for political goals
planned socialism
economic system where the state or a collective body owns the means of production and the govt makes central decisions about production, distribution, and prices, rather than relying on market forces.
Path dependency
concept where historical choices and events constrain or channel future development, making it difficult to change course
Negative externalities
Costs imposed on third parties whoa re not involved in an economic transaction
Ecological footprint
Measure of human demand on Earth’s ecosystems, quantifying the biologically productive land and water area needed to produce the resources consumed and absorbed the waste generated
Green growth
concept of fostering economic growth while minimizing environmental damage, aiming to make development environmentally sustainable
steady-state economy
an economic model that focuses on stability rather than perpetual growth, maintaining a constant population and level of physical wealth
Degrowth
an economic theory and movement that advocates for shrinking the economy to reduce consumption and prioritize human and ecological well being over endless growth
Central question that distinguishes capitalism from socialism
Who should own the means of production?
Means of production
the inputs used in production
private ownership
occurs when somebody has a legal right to possess something as private property; owner has control over the income generated from that as well as the right to prevent others from using it or to charge people to access it
Social ownership
means of production may be owned and managed by public institutions, by workers, or through other cooperative or collective ownership arrangements
State ownership
means of production belongs to the state
The 3 main types economic systems can be further classified based on the dominant ownership type, which are:
Market Capitalism, Market Socialism, Mixed Economies, State Capitalism, and Planned Socialism
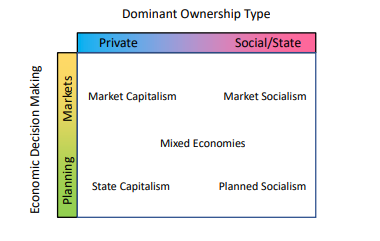
Key Characteristics of Capitalism
Dominance of private ownership in means of production
Emphasis on capital accumulation
Predominance of wage labor
Emphasis on decentralized decision-making; big on self interest
Individuality and freedom
Markets are the primary means of economic coordination
Negative effects of capitalism
Competition to reduce costs leads to the exploitation of workers and bad working conditions
lowering environmental standards
spending excessively
Capitalism summarized
A capitalist system focused on profit-making often neglects these negative externalities. As decision-making is decentralized, there is nothing that requires individuals to consider how their decisions might affect social outcomes. Hence, high inequality and environmental degradation is often a characteristic of capitalist societies.
Key features of Socialism
Means of production is owned publicly
High levels of central decision-making
A great role of egalitarnian values in guiding social decisions
Importance on colectivist goals such as equality of opportunity
Govt has bigger role
Negatie characteristics of Socialism
Too idealistic, especially hard to implement on a national basis
Large size and conflicting goals means it requires a lot of planning
Prevalence of censorship and undemocratic insittutitons
Socialist countries with overwhelming govt control of their society are label as
Communist
Communist vs Socailist
The main difference is the high Utopian nature of communism; private property is entirely abolished, and all property is owned communally