BioChem Unit 2 Practice Questions
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Which of the following base pairs are found in DNA double helix?
a. A-A, G-G, C-C, T-T
b. G-A, A-G, C-T, C-T
c. G-C, C-G, A-T, T-A
c. G-C, C-G, A-T, T-A
What are nucleosomes composed of?
a. DNA and histones and 1 copy of H1, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4.
b. DNA and histones H1, and two copies of each H2A, H2B, H3, and H4.
c. DNA only.
d. DNA and histone H1.
b. DNA and histones H1, and two copies of each H2A, H2B, H3, and H4.
What are the correct dimensions of the DNA double helix?
a. 10 bp per turn, 35 A per turn, 20 A wide.
b. 34 bp per turn, 10 A per turn, 20 A wide.
c. 10 bp per turn, 10 A per turn, 34 A wide.
a. 10 bp per turn, 35 A per turn, 20 A wide.
Which of the following is an example of a transition mutation?
a. G-C
b. C-A
c. A-G
c. A-G
Which is an example of a transversion mutation?
a. A-T
b. T-C
c. A-G
a. A-T
Which of the following bases changes is a result of deamination?
a. C-T
b. C-U
c. U-C
b. C-U
Thymine dimers result from which kind of environment mutagen?
a. deaminating agents.
b. alkylating agents.
c. ultraviolet radiation.
c. ultraviolet radiation.
What does RecA protein do?
a. recognizes mismatches in DNA during mismatch repair.
b. binds single-stranded DNA during double strand break repair.
c. binds single-strand DNA during DNA replication.
b. binds single-stranded DNA during double strand break repair.
What is the role of p-factor in transcription?
a. recognize promoter sequence.
b. assist in transcription elongation.
c. trigger transcription termination.
c. trigger transcription termination.
Place the 3 main types of RNA in their order of abundance, from most to least.
rRNA < tRNA < mRNA
What makes RNA adopt the A-form and DNA adopt the B-form?
a. ribose has C2’ endo sugar pucker and deoxyribose has C3’ endo sugar pucker.
b. ribose has C3’ endo sugar pucker and deoxyribose has C2’ endo sugar pucker.
c. RNA is more hydrophobic than DNA.
b. ribose has C3’ endo sugar pucker and deoxyribose has C2’ endo sugar pucker.
What effect would mutations that prevent lactose binding to the lac repressor have on production of B-galactosidase?
a. B-galactosidase would not be expressed at all.
b. B-galactosidase would be expressed all the time.
c. B-galactosidase would be expressed only when lactose is available.
a. B-galactosidase would not be expressed at all.
What’s the effect of the two tandem Trp codons in the TrpL sequence?
a. the ribosome stalls at the Trp codons when tryptophan levels are low.
b. the ribosome reads through the Trp codons when tryptophan levels are low.
c. The ribosome stalls at the Trp codons when tryptophan levels are high.
a. the ribosome stalls at the Trp codons when tryptophan levels are low.
What is the function of polyadenylation of mRNA?
a. prevent degradation by nucleases.
b. aid in guiding ribosomes to the mRNA.
c. tether the mRNA to the RNA Pol II CTD
a. prevent degradation by nucleases.
Which kind of splicing involves the participation of proteins?
a. group 1
b. spliceosomal
c. both group 1 and spliceosomal
b. spliceosomal
What kind of chemical reaction occurs during splicing?
a. hydrolysis
b. transamination
c. transesterification
c. transesterification
Which types of splicing does not involve a lariat intermediate?
a. group 1
b. spliceosomal
c. both group 1 and spliceosomal
a. group 1
Which codons are read as signaling translation termination?
a. AAU, AGU, GAU
b. UAA, UAG, UGA
c. UAA, CAA, GAA
b. UAA, UAG, UGA
Human mitochondrial tRNA has the anticodon 5’-UCA-3’. What are the first two nucleotides in the Trp codon?
a. 5’-CA-3’
b. 5’-UG-3’
c. 5’-GU-3’
b. 5’-UG-3’
How many different mRNA sequences can code for the following polypeptide? Met-Gly-Phe-Trp-Glu-Arg
96
What statement best describes our current understanding of the role of ribosomal proteins?
a. they catalyze the reactions of protein synthesis.
b. they catalyze some steps of protein synthesis, but not others.
c. they aid assembly, stabilize ribosome structure, and speed up protein synthesis.
c. they aid assembly, stabilize ribosome structure, and speed up protein synthesis.
What is the function of the Shine-Dalgarno interactions?
a. position the ribosome on the mRNA near the start codon.
b. prevent formation of the 70S initiation complex.
c. form RNA polymerase closed complex.
a. position the ribosome on the mRNA near the start codon.
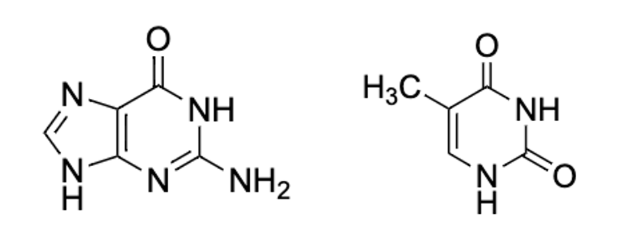
Identify the two bases (from left to right).
a. G-T
b. G-U
c. G-C
a. G-T
tRNAs move through the ribosomal RNA binding sites in what order? (except the first tRNA in protein synthesis)
a. P-A-E
b. A-P-E
b. E-P-A
b. A-P-E
DNA polymerases proofread using the _________ enzymatic activity.
a. 5' → 3' polymerase
b. 3' → 5' polymerase
c. 3' → 5' exonuclease
c. 3' → 5' exonuclease
What is the role of RNA Polymerase σ (sigma) subunit in bacterial transcription?
a. recognize promoter sequences
b. proofread during transcription
c. unwind double helical DNA
a. recognize promoter sequences
What is the function of DNA gyrase during E. coli DNA replication?
a. synthesis of DNA strands
b. unwinding of double stranded DNA
c. relief of supercoiling
c. relief of supercoiling
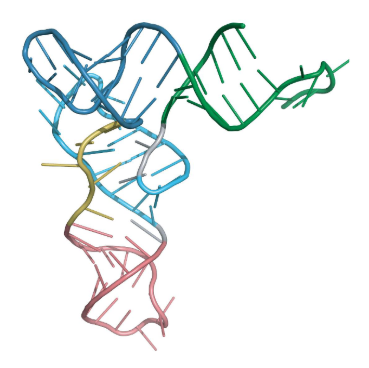
What is the structure below?
a. a ribosomal protein molecule
b. a tRNA molecule
c. an mRNA molecule
b. a tRNA molecule
Which statement is correct about translation based on what we learned?
a. Ribosome assembly does not require ribosomal proteins
b. tRNA selection involves initial selection and proofreading
c. Protein synthesis is fundamentally complex and releases energy
b. tRNA selection involves initial selection and proofreading
Which is false about DNA mutation and repair based on what we learned?
a. DNA repair mechanisms include homologous recombination
b. DNA mutations always lead to impaired protein function
c. Environmental mutagens is related to cancer
b. DNA mutations always lead to impaired protein function
Which of the following gives the steps of transcription initiation in their proper order?
a. promoter binding > open complex > closed complex > promoter escape
b. promoter escape > promoter binding > open complex > closed complex
c. promoter binding > closed complex > open complex > promoter escape
c. promoter binding > closed complex > open complex > promoter escape
Below are some steps in bacterial protein synthesis. In which step GTP hydrolysis does not happen?
a. translocation
b. peptide bond formation
c. termination
b. peptide bond formation
Which statement is correct based on what we learned?
a. Group I intron splicing only involves one transesterification reaction.
b. In Eukaryotic genes, the percentage of introns is much higher than exons.
c. Group I introns require snRNPs; spliceosomal introns self-splice.
b. In Eukaryotic genes, the percentage of introns is much higher than exons.
Which is correct about Okazaki fragments in E. coli DNA replication?
a. they are synthesized on the leading strand
b. they are the RNA primers synthesized by DnaG primase
c. they are synthesized by the DNA Polymerase III
c. they are synthesized by the DNA Polymerase III
The precursors (reactants) for DNA replication are _________.
a. dNMPs
b. NMPs
c. dNTPs
c. dNTPs
Which feature(s) of mRNA processing is(are) found in Eukaryotes?
i. 5' cap addition
ii. 3' polyadenylation
iii. removal of exons by splicing
iv. removal of introns by splicing
i, ii, iv
The "DNA mismatch repair" is used to repair which kind of DNA lesion for E. coli?
a. DNA replication errors
b. DNA double strand breaks
c. base deamination
a. DNA replication errors
When glucose is absent, cAMP will be _______ and the lac operon expression is ________ in E. coli.
a. very low; repressed
b. very low; stimulated
c. high; stimulated
c. high; stimulated
What is the function of the β-sliding clamp in DNA replication?
a. relieve supercoiling
b. unwind the DNA double helix
c. increase DNA polymerase processivity
c. increase DNA polymerase processivity
The protein factor EF-Tu performs what function during protein synthesis?
a. formation of the 30S initiation complex
b. proofreading
c. delivery of aminoacyl-tRNA to the ribosome
c. delivery of aminoacyl-tRNA to the ribosome
Which is correct about RNA?
a. mRNA has the lowest percentage (by mass) among the three RNA types.
b. The base-pairing within an RNA strictly follows Watson-Crick base pairing rule.
c. Each RNA synthesis (transcription) uses both DNA strands as template.
a. mRNA has the lowest percentage (by mass) among the three RNA types.
What posttranscriptional modifications are used for tRNAs in Eukaryotes based on what we learned?
i. trimming of the 5' and 3' ends
ii. 5' cap and 3' polyadenylation
iii. chemical modification of bases
iv. removal of introns
i, iii, iv
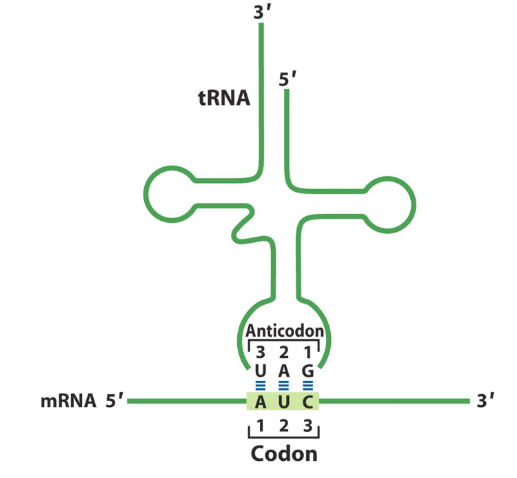
For the anticodon: 5'-GAC-3', what are the first two nucleotides in the codon (5' to 3')?
a. 5'-AG-3'
b. 5'-UC-3'
c. 5'-GU-3'
c. 5'-GU-3'