Anatomy 102 mid term study
1/1338
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
1339 Terms
What term refers to the contraction of a heart chamber?
Systole
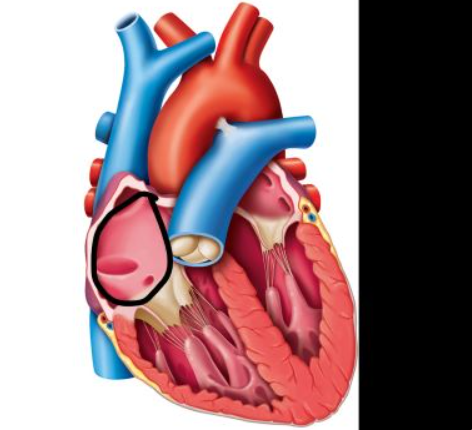
right atrium
The cardiovascular system pumps blood through two separate circuits.
The______circuit sends_____blood to the lungs.
The______circuit sends_______blood and nutrients to the body.
pulmonary; oxygen-poor
systemic; oxygen-rich
Which vein is the longest vein in the body?
great saphenous vein
The pulmonary trunk divides into what two vessels?
Left and right pulmonary arteries
Which cavity is the heart found in?
Thoracic cavity
Where would oxygen-poor blood be found?
Pulmonary arteries and systemic veins
In the cardiovascular system, what vessels are the site of nutrient, gas, and waste exchange?
Capillaries
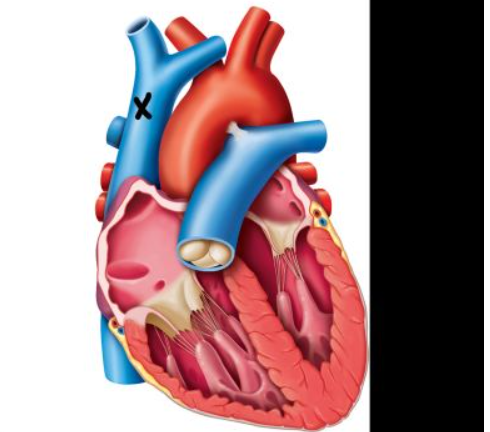
Right ventricle
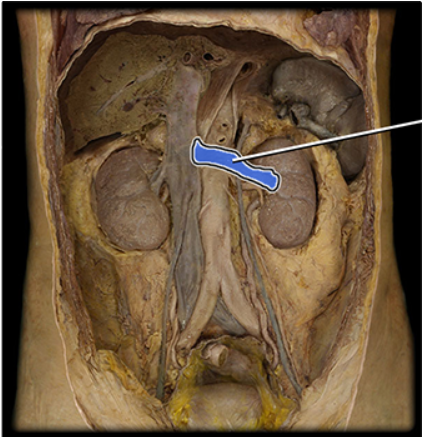
Left renal vein
Which valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle?
Tricuspid valve
Aortic valve
Pulmonary valve
Mitral valve/Bicuspid valve
Mitral valve/Bicuspid valve
Which ECG wave is correctly described?
QRS complex: depolarization of atria
P wave: depolarization of atria
QRS complex: repolarization of ventricles
T wave: depolarization of ventricles
P wave: depolarization of atria
The left ventricle pushes blood into what vessel(s)?
Pulmonary veins
Aorta
Pulmonary trunk
Venae cavae
Aorta
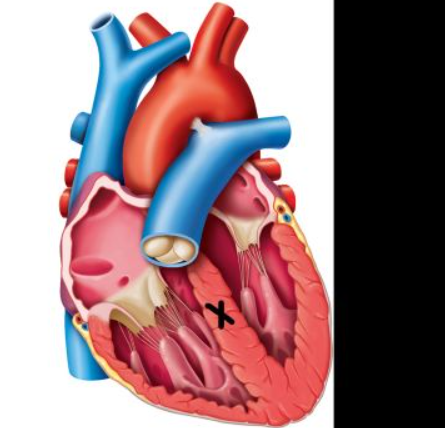
tricuspid valve
interventricular septum
pulmonary trunk
bicuspid (mitral) valve
interventricular septum
Name the tough outermost layer of the sac that surrounds the heart.
Visceral pericardium
Endocardium
Epicardium
Fibrous pericardium
Fibrous pericardium
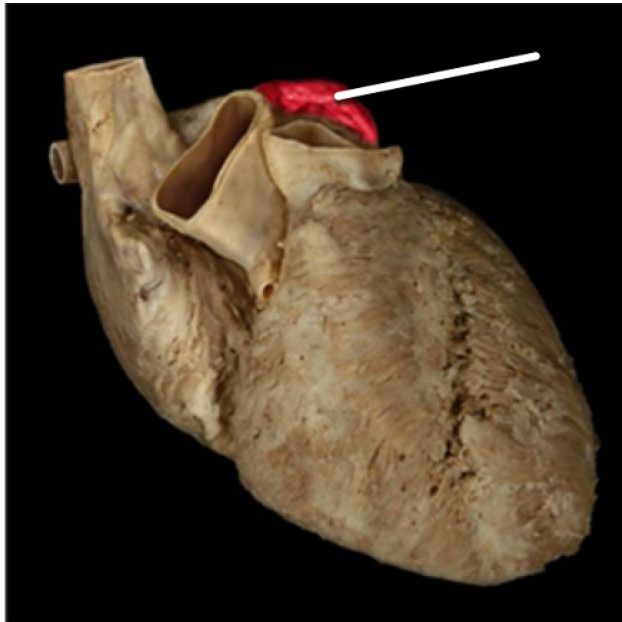
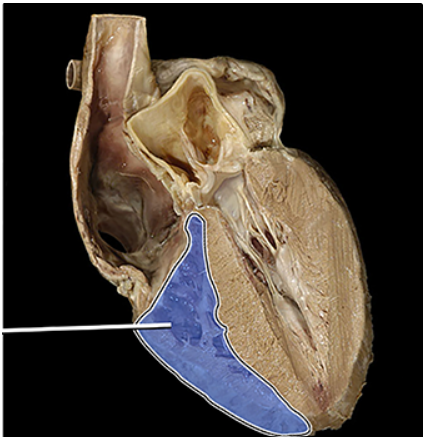
right auricle
right ventricle
superior vena cava
left auricle
left auricle
What is the deepest layer in the wall of the heart?
Epicardium
Myocardium
Pericardium
Endocardium
Endocardium
Valves help to ensure one-way blood flow in the
arteries and veins
capillaries
heart and arteries
heart and veins
heart and veins
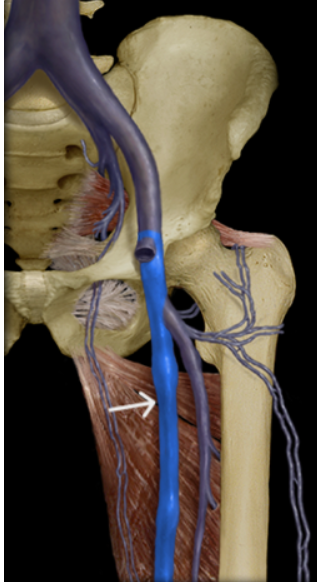
fibular vein
anterior tibial vein
popliteal vein
femoral vein
femoral vein
Where is the popliteal artery located?
In the abdominal cavity
Behind the knee
In the groin
Deep to the scapula
Behind the knee
Which of the following helps return blood to the heart?
Contracting skeletal muscles
Valves in the arteries
End systolic volume
Positive pressure in thoracic cavity
Contracting skeletal muscles
What chambers of the heart will contain oxygen-poor blood?
Right atrium and left atrium
Left atrium and right ventricle
Left atrium and left ventricle
Right atrium and right ventricle
Right atrium and right ventricle
What is the correct sequence of components of the cardiac conduction system?
AV node → SA node → Purkinje fibers→ AV bundle
SA node → AV node → AV bundle → Purkinje fibers
AV node → AV bundle → Purkinje fibers → SA node
SA node → Purkinje fibers → AV node → AV bundle
SA node → AV node → AV bundle → Purkinje fibers
A man collapses to the ground. A bystander feels the man's neck to check for a pulse. Which arterial pulse is the bystander trying to feel?
carotid arterial pulse
temporal arterial pulse
brachial arterial pulse
facial arterial pulse
carotid arterial pulse
Blood vessels called __________ carry blood toward the heart, and __________ carry blood away from the heart.
veins; arteries
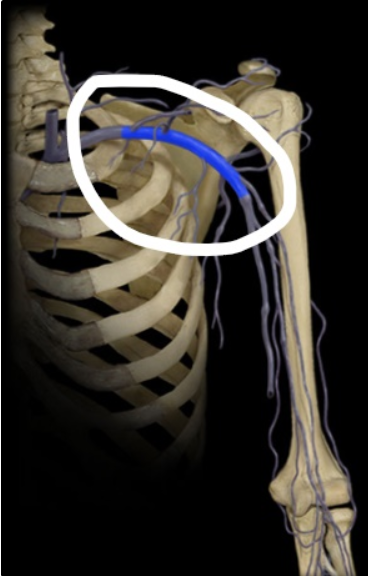
Axillary Vein
Blood flowing from the vena cavae to the pulmonary trunk passes through what series of structures?
Right ventricle, tricuspid valve, right atrium, pulmonary valve
Right ventricle, pulmonary valve, right atrium, tricuspid valve
Right atrium, pulmonary valve, right ventricle, tricuspid valve
Right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, pulmonary valve
Right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, pulmonary valve
Blood entering the right atrium comes from what structure(s)?
Pulmonary veins
Pulmonary trunk
Right ventricle
Venae cavae and coronary sinus
Venae cavae and coronary sinus
The visceral pericardium lines the pericardial cavity, whereas the parietal pericardium covers the surface of the heart.
True or False
False
Why is the cardiovascular system vital to survival?
It ensures that the lungs fully inflate.
It delivers carbon dioxide to tissues and removes excess oxygen.
It supplies oxygen and nutrients to cells.
It delivers waste molecules to vital organs.
It supplies oxygen and nutrients to cells.
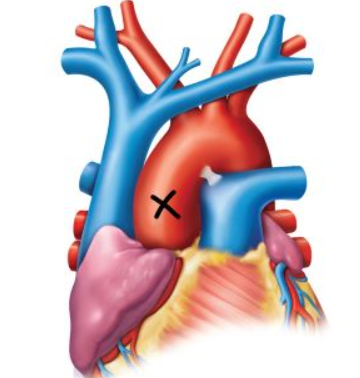
Aorta
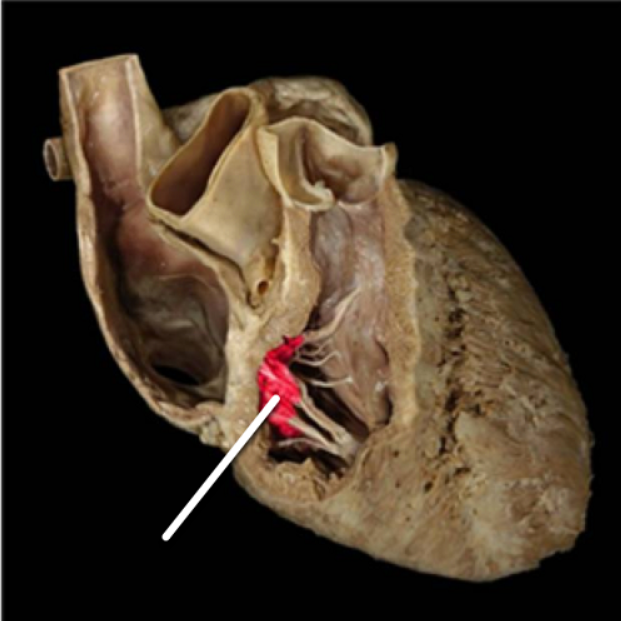
right atrioventricular valve/tricuspid valve
left atrioventricular valve/mitral valve/bicuspid valve
aortic valve
semilunar valve
pulmonary valve
right atrioventricular valve/tricuspid valve
What valve is located between the right atrium and right ventricle?
Pulmonary valve
Aortic valve
Tricuspid valve/Right atrioventricular valve
Bicuspid valve/Mitral valve/Left atrioventricular valve
Tricuspid valve
When taking a pulse at the wrist, which artery is being palpated?
Ulnar artery
Radial artery
Palmar arch
Brachial artery
Radial artery
What is the effect of vasoconstriction?
Heart rate decreases
Viscosity increases
Peripheral resistance decreases
Blood pressure increases
Blood pressure increases
Which of the following is a large vein that drains directly into the right atrium?
coronary sinus
cephalic vein
superior mesenteric vein
hepatic portal vein
coronary sinus
Arteries are strong, elastic vessels that carry blood to the heart.
True or False
False
What causes the first heart sound? When does this occur?
Closure of the atrioventricular valves at the beginning of ventricular diastole
Closure of the atrioventricular valves soon after the beginning of ventricular systole
Closure of the semilunar valves at the beginning of ventricular diastole
Closure of the semilunar valves soon after the beginning of ventricular systole
Closure of the atrioventricular valves soon after the beginning of ventricular systole
The ventricular walls and the atrial walls each form a functional syncytium. What does this term mean?
A hollow structure lined by endothelium
A mass of cells functioning as a unit
Tissue with a high rate of blood flow
A structure that contains blood
A mass of cells functioning as a unit
Blood pressure is stated as a fraction, with _____ pressure over ______ pressure.
systolic, diastolic
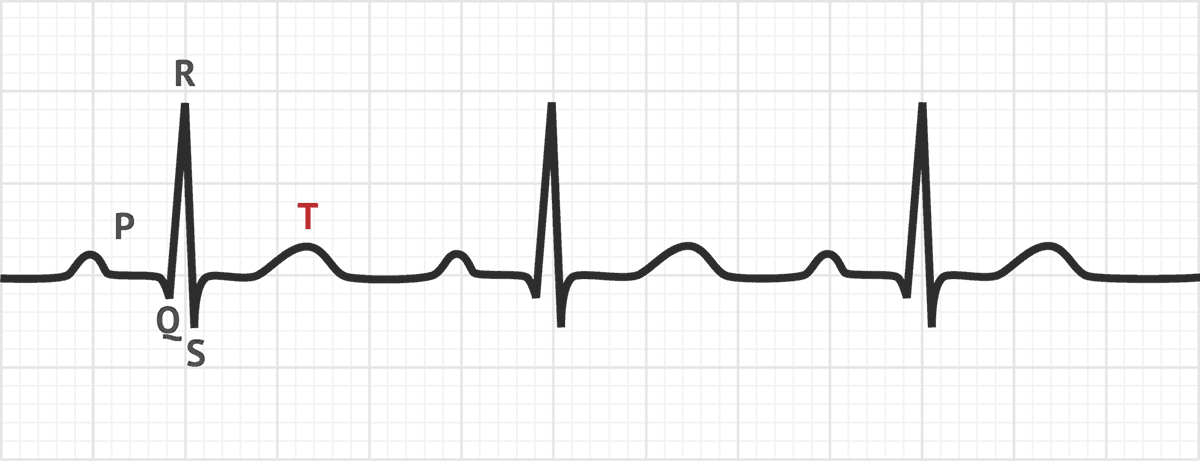
The T wave on an ECG represents ventricular repolarization.
True or False
True
Choose which statement is correct.
The left auricle is proximal to the left ventricle.
The left auricle is inferior to the left ventricle.
The left auricle is distal to the left ventricle.
The left auricle is superior to the left ventricle.
The left auricle is superior to the left ventricle.
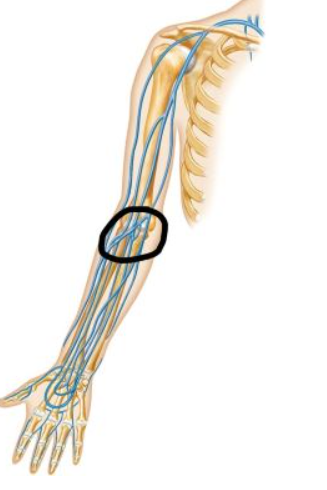
Median cubital vein
Sounds from the closing of which valve are best heard at the fifth intercostal space just to the left of the sternum?
mitral
aortic
tricuspid
pulmonary
tricuspid

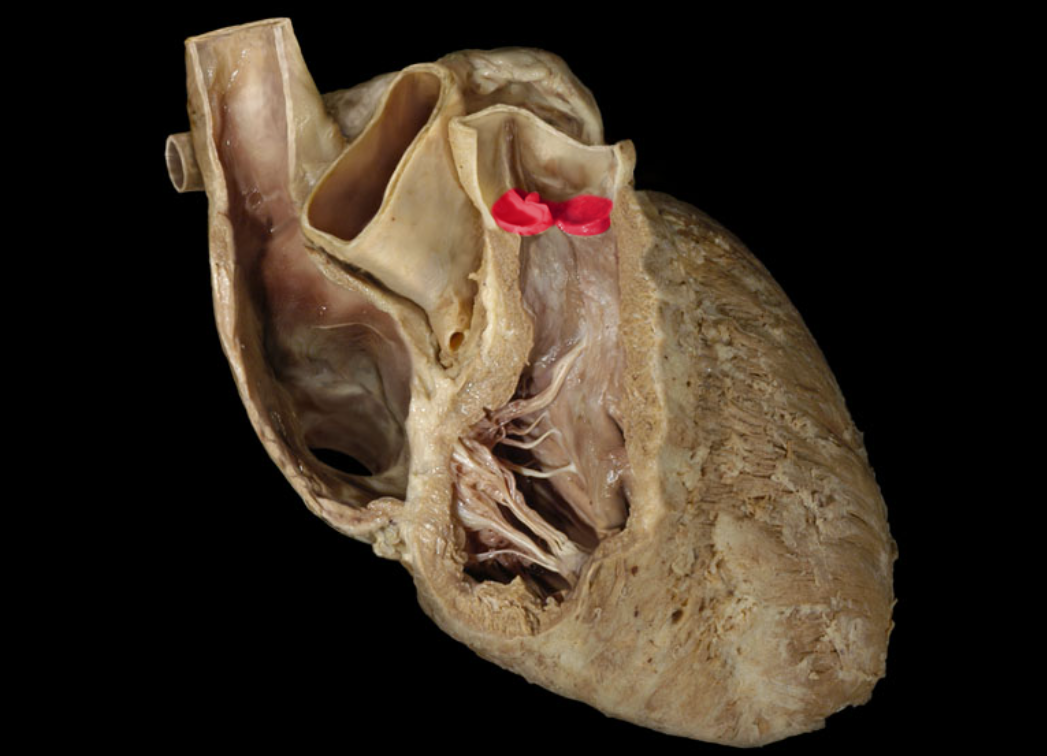
Aortic valve
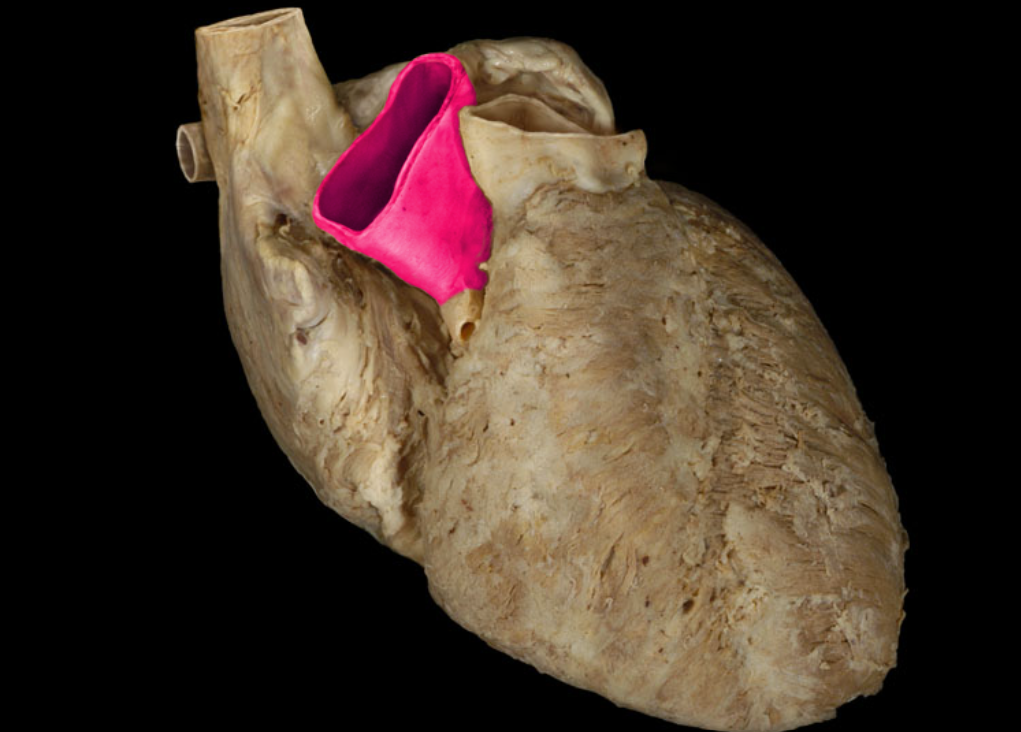
Ascending aorta
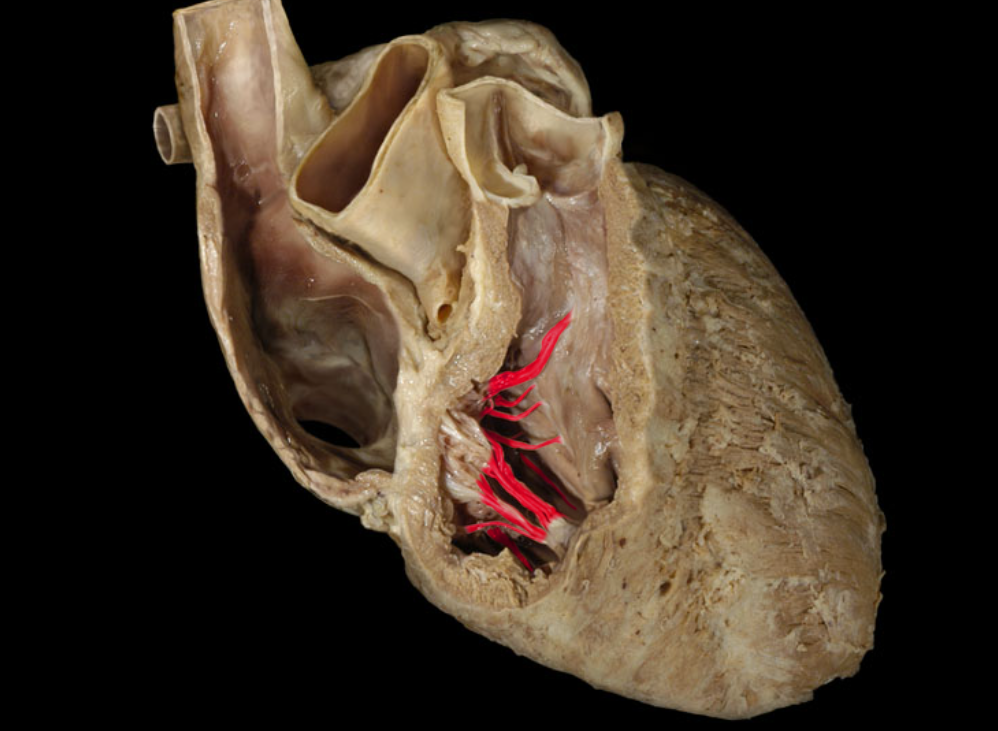
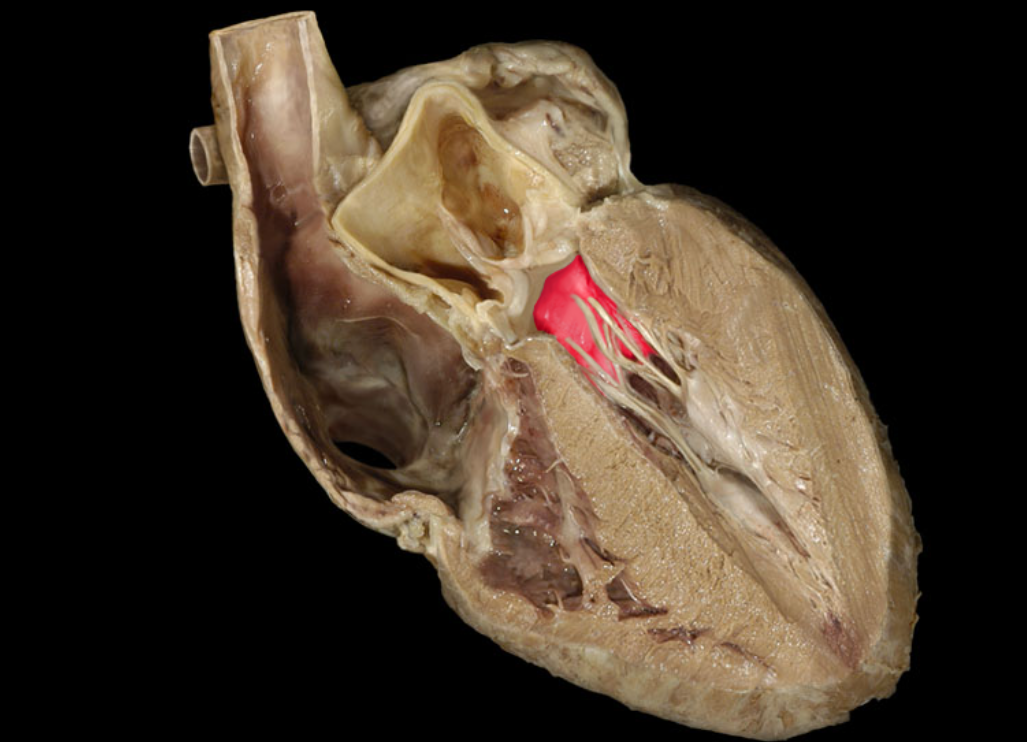
Chordae tendineae
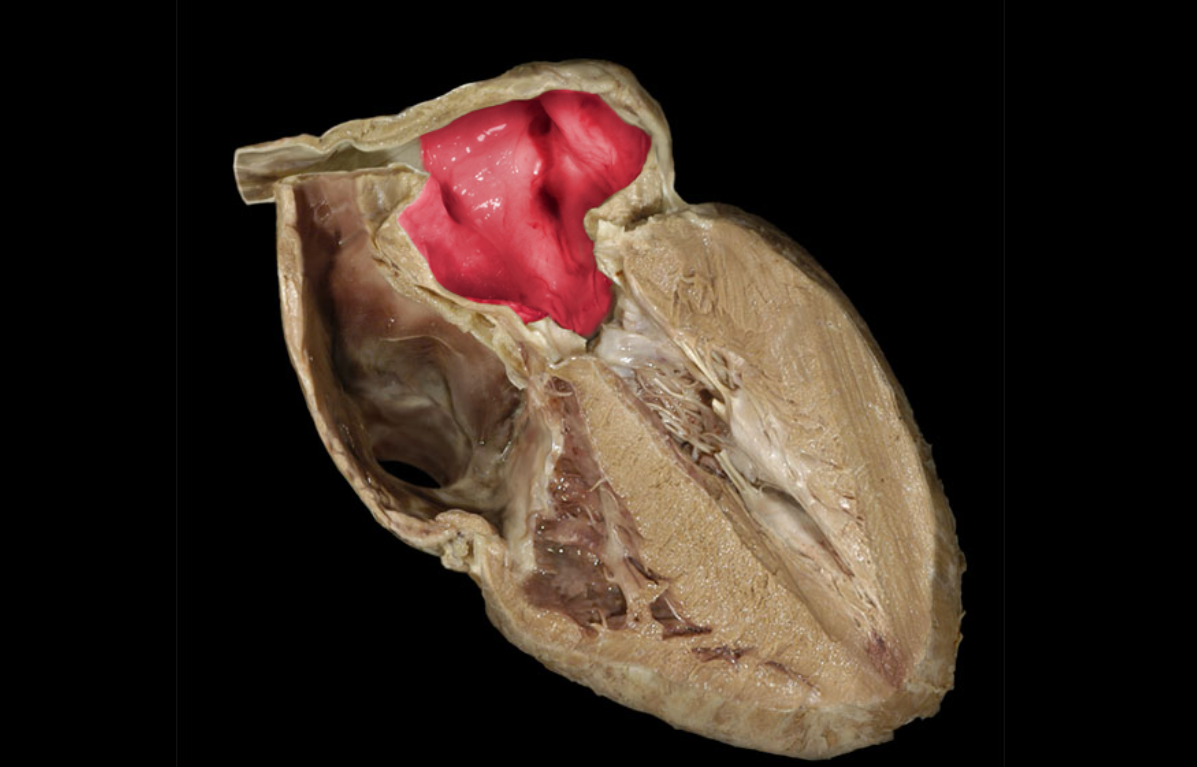
Left atrioventricular valve/mitral valve
Left atrium
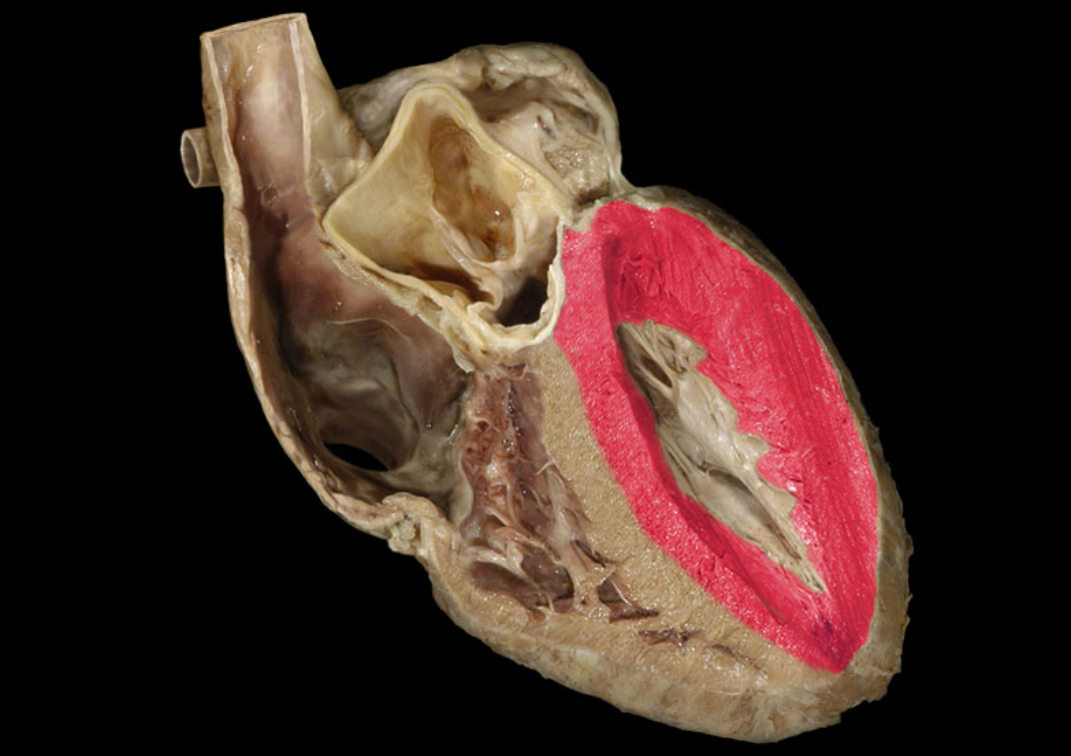
Myocardium of left ventricle
Myocardium of right ventricle
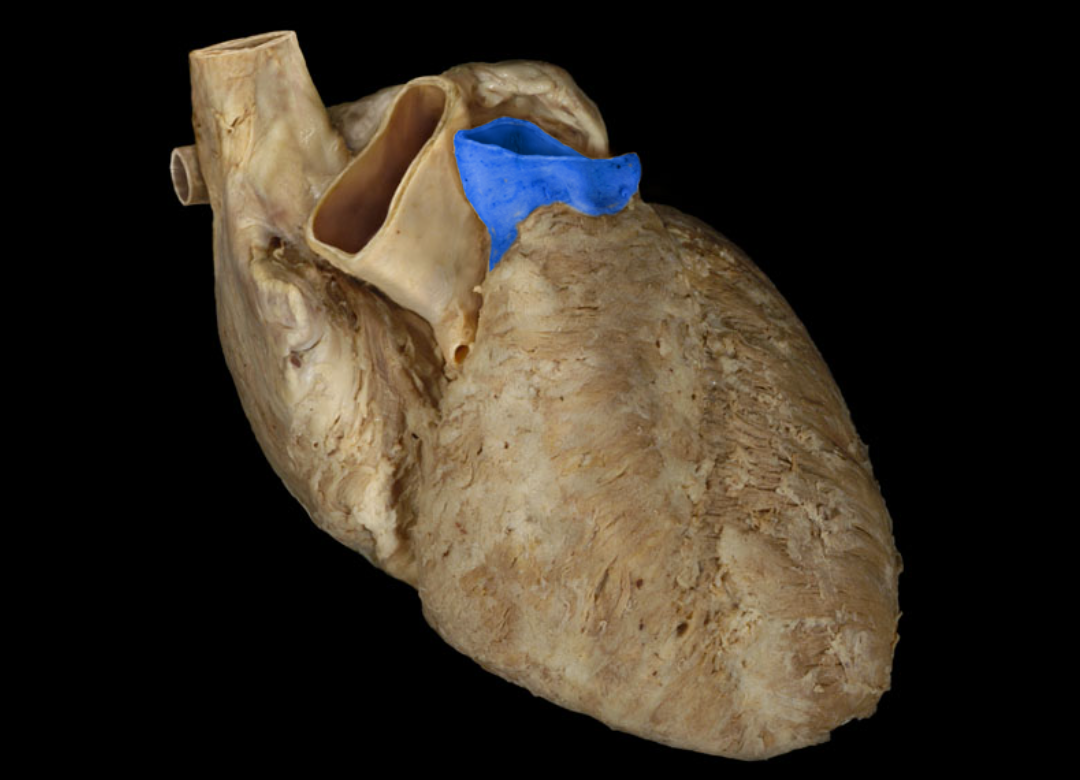
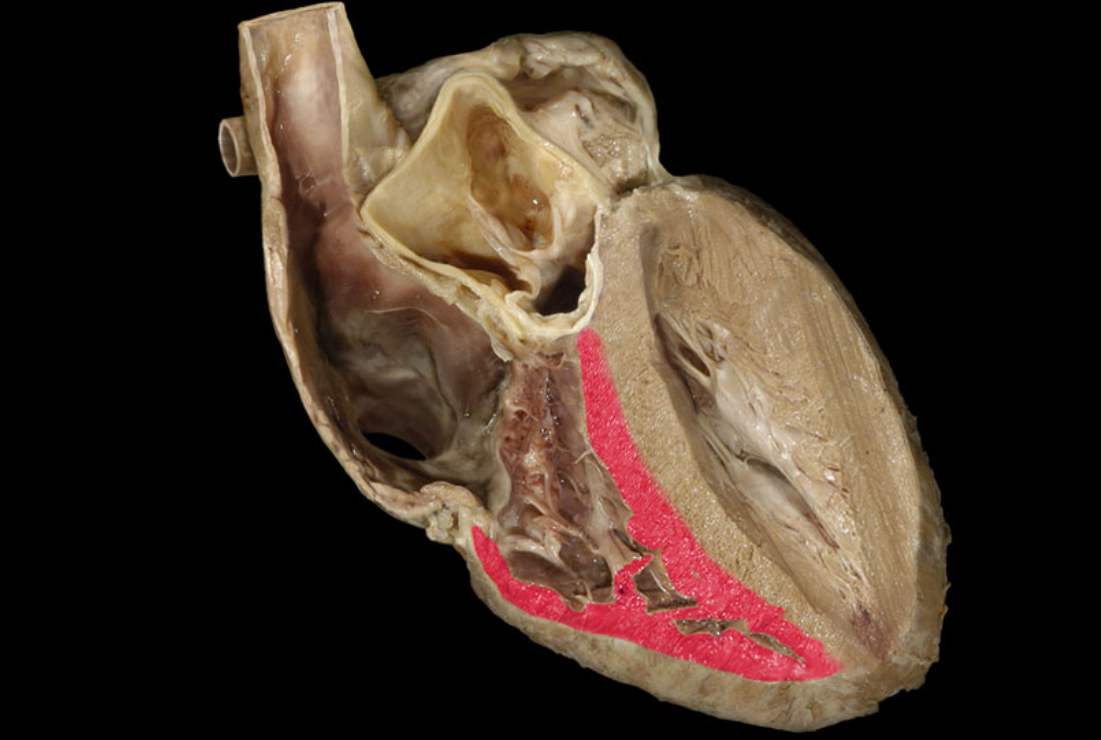
Pulmonary trunk
Pulmonary valve
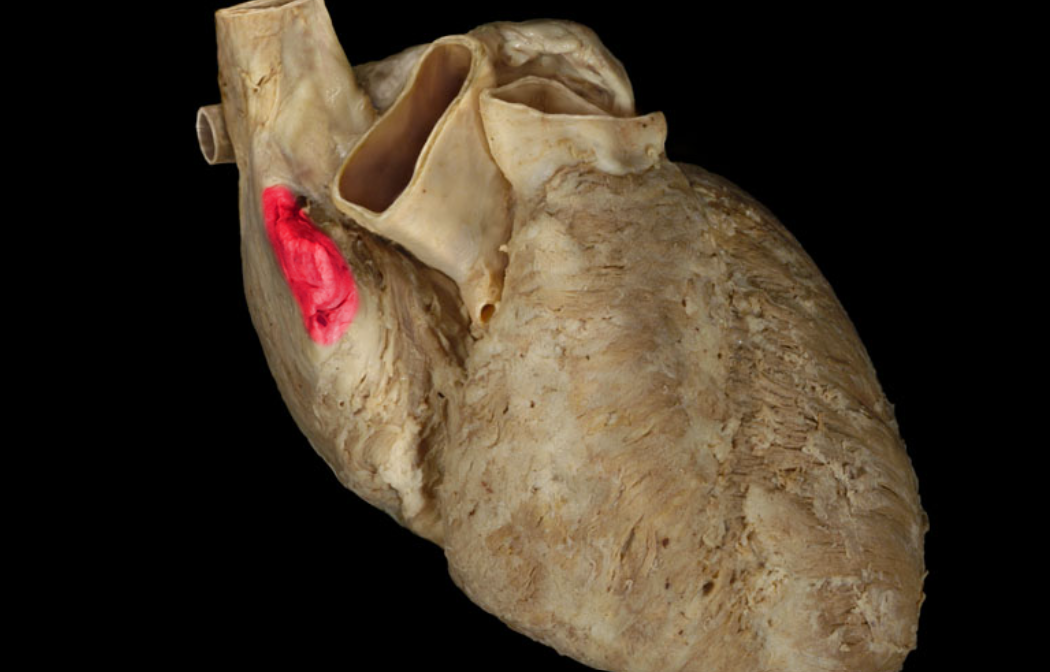
Right auricle
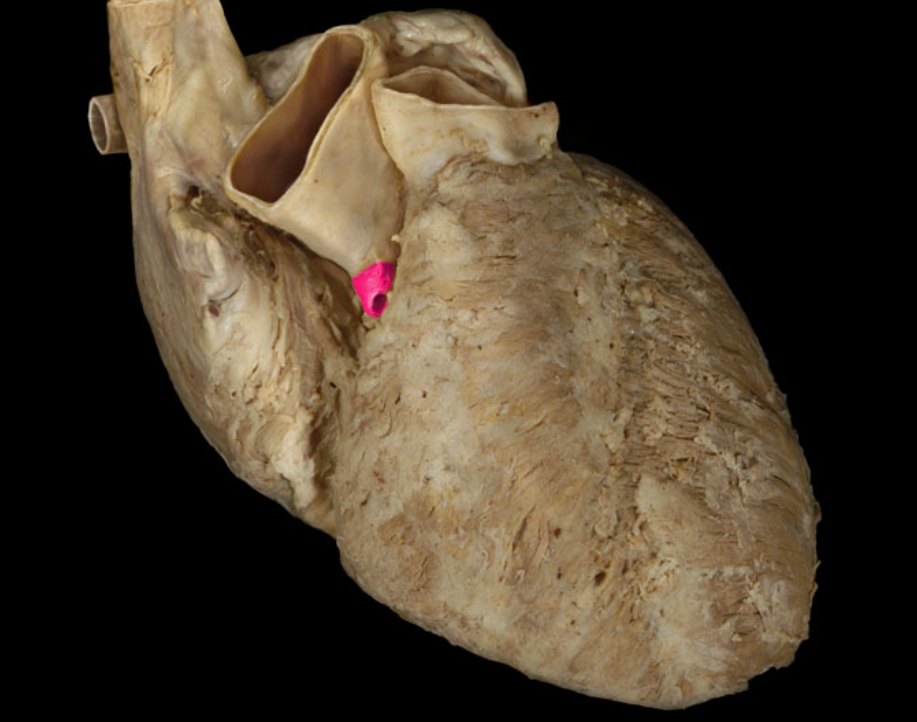
Right coronary a.
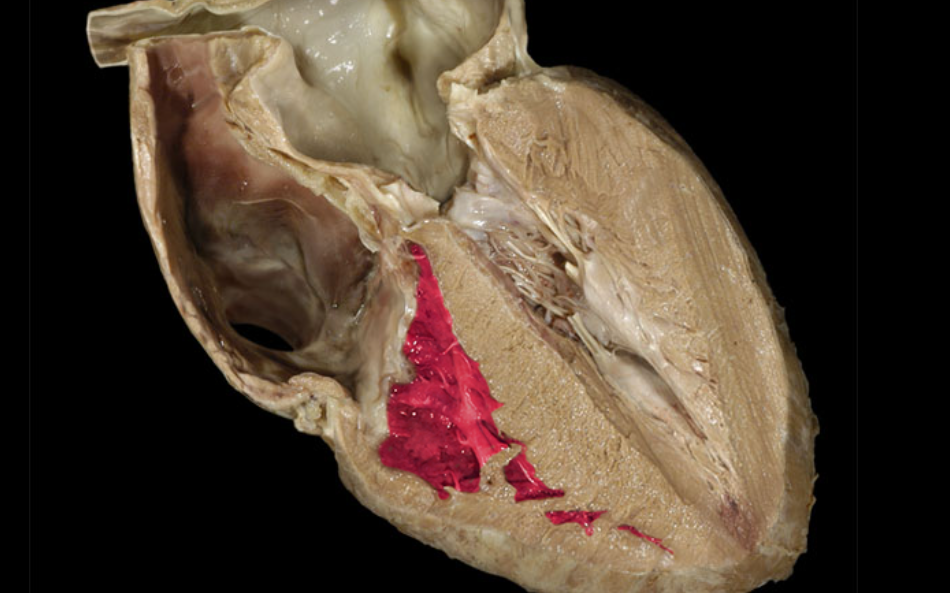
Right ventricle
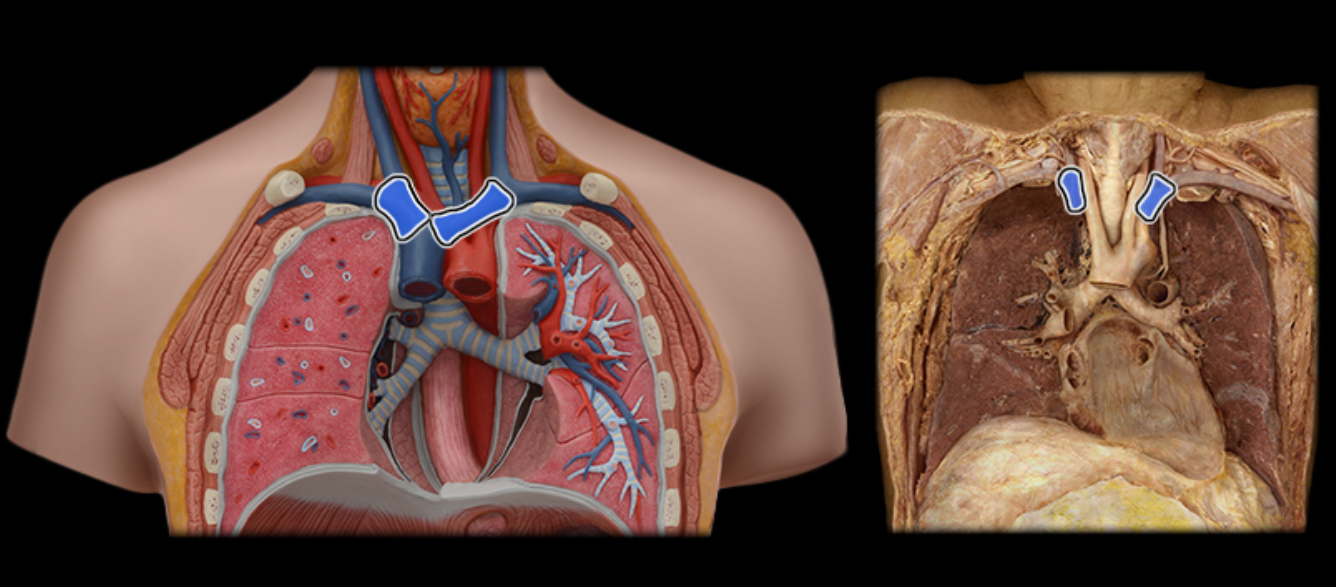
Brachiocephalic v.
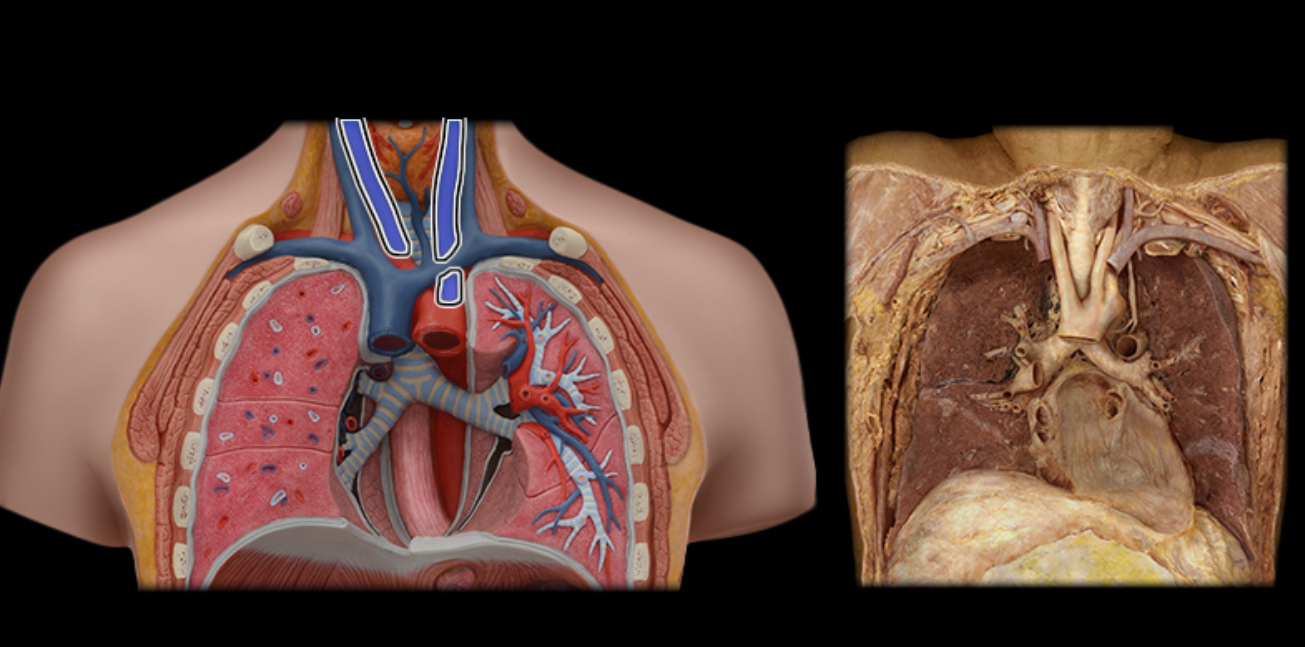
Common carotid a.
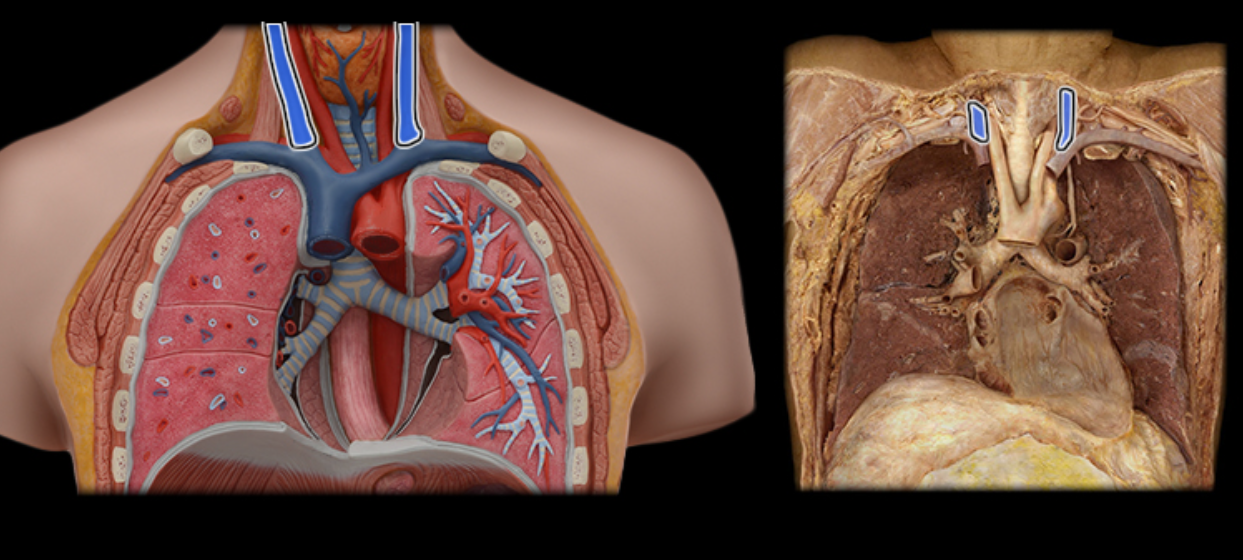
Internal jugular v.
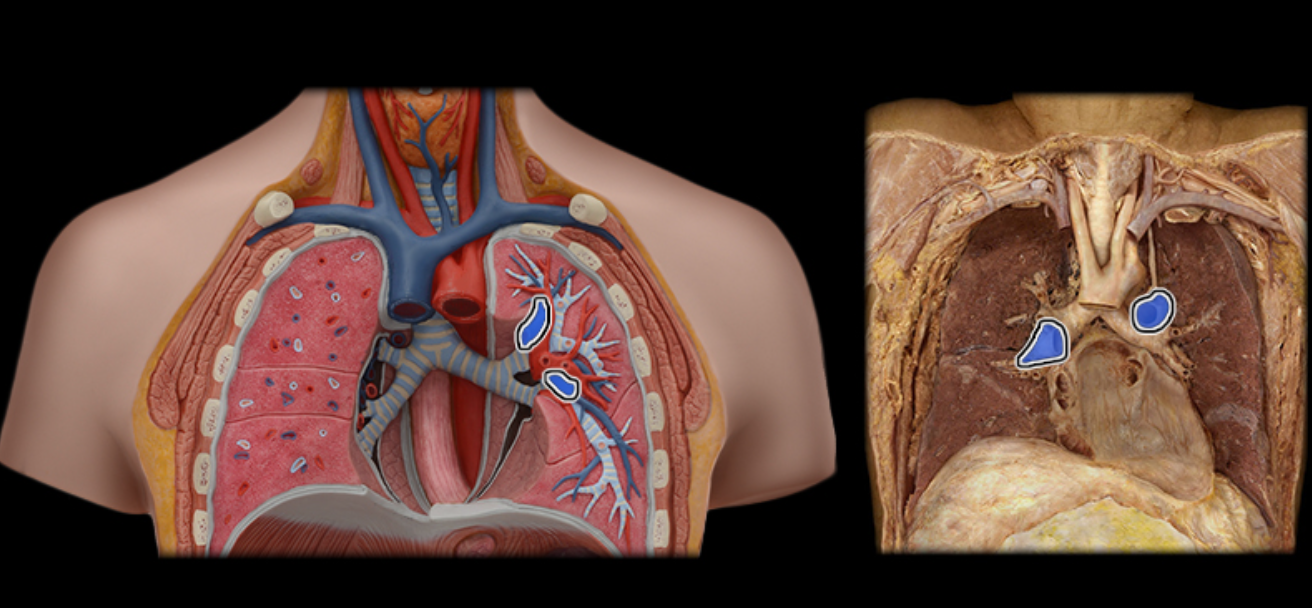
Pulmonary a.
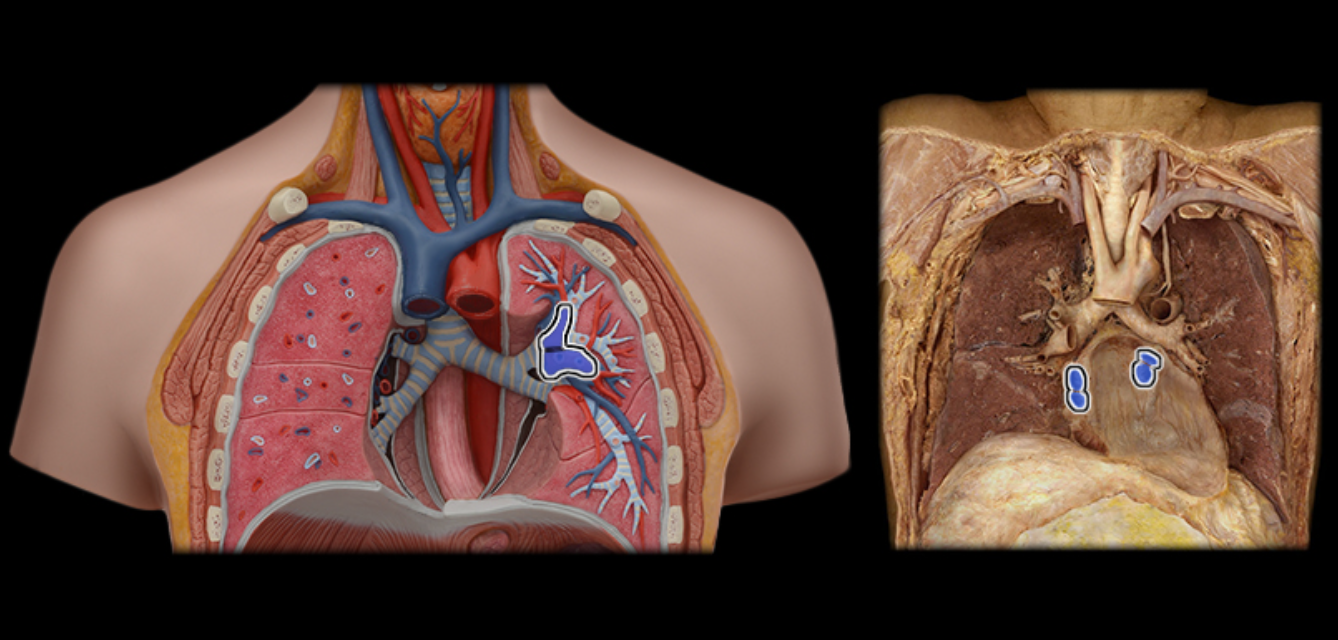
Pulmonary vv.
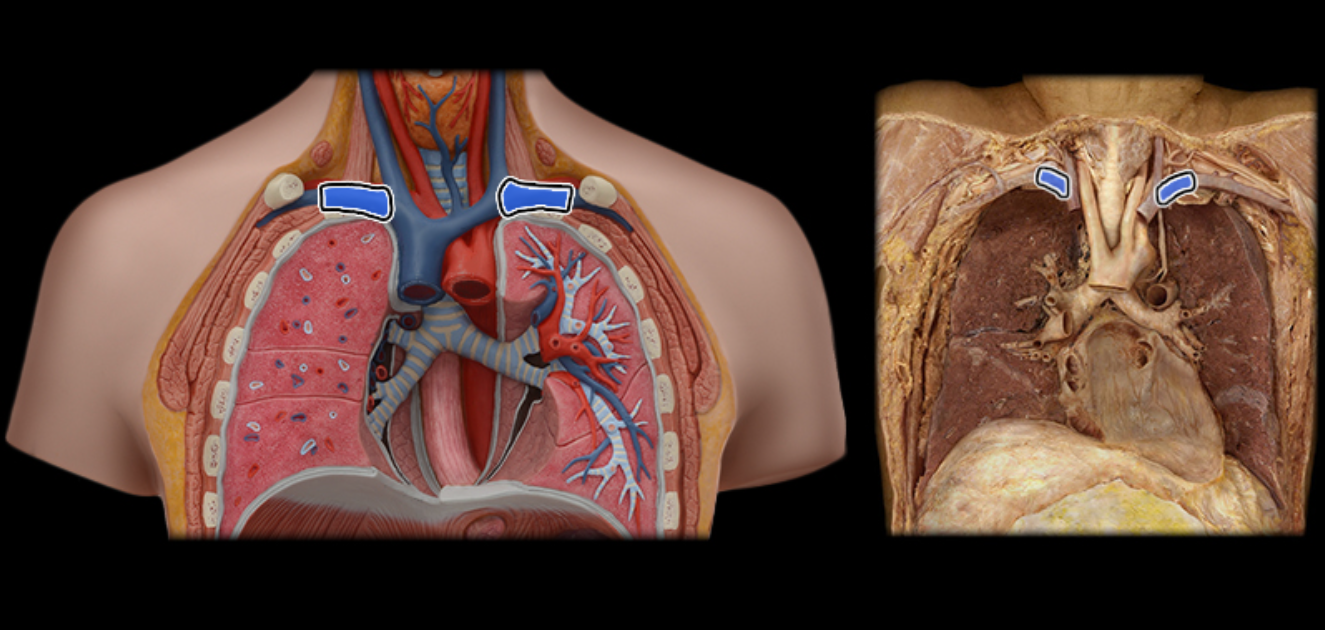
Subclavian v.
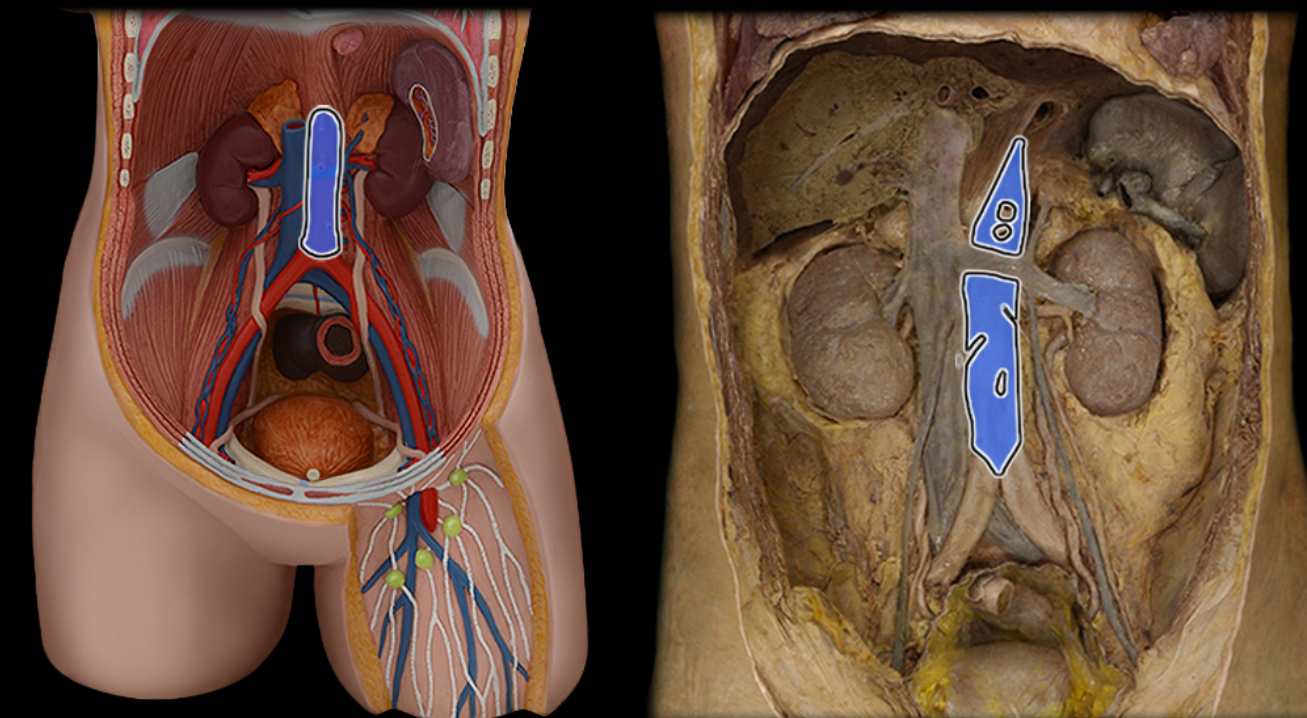
Abdominal aorta
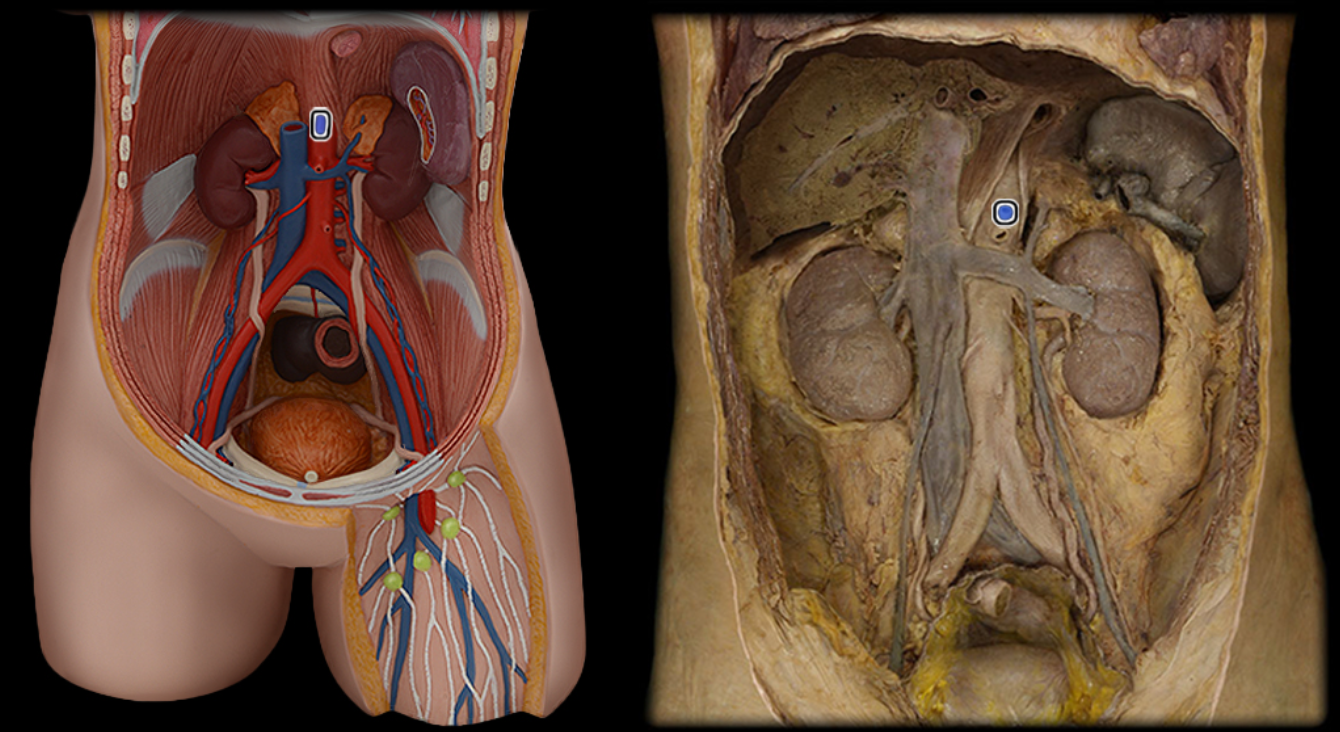
Celiac a.
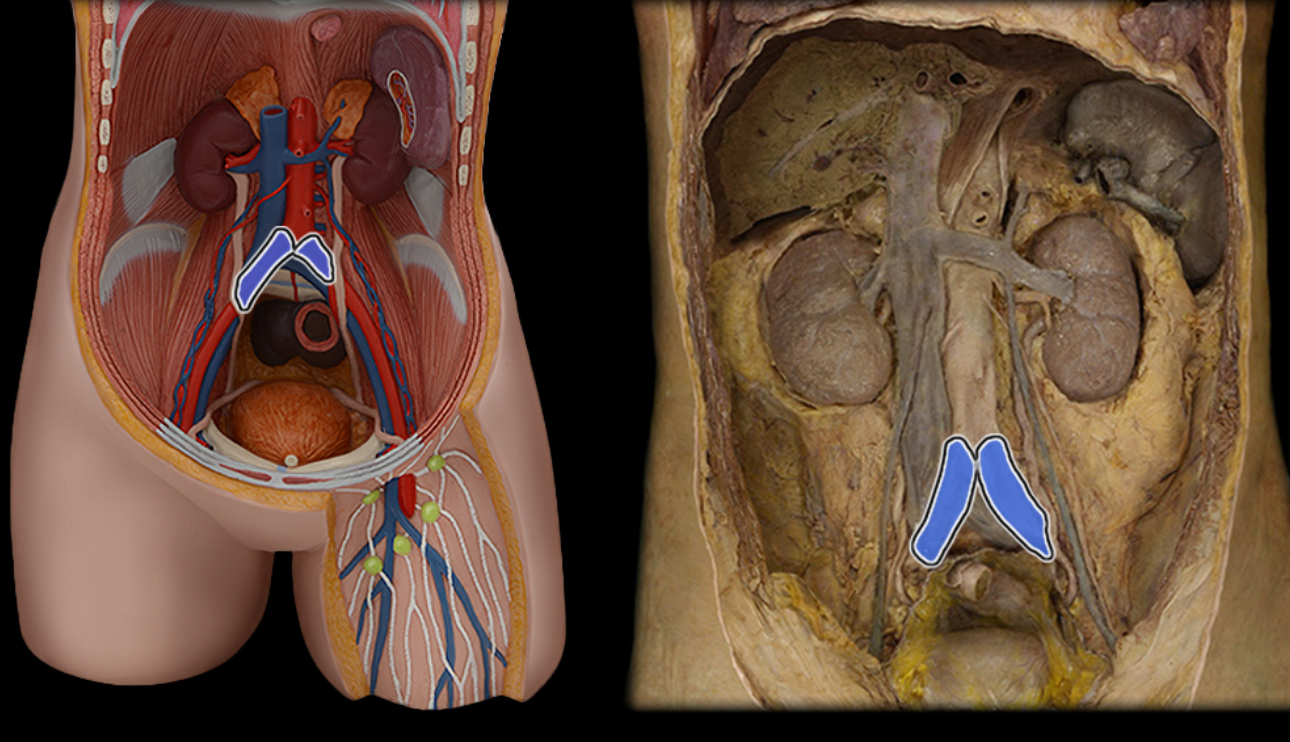
Common iliac a.
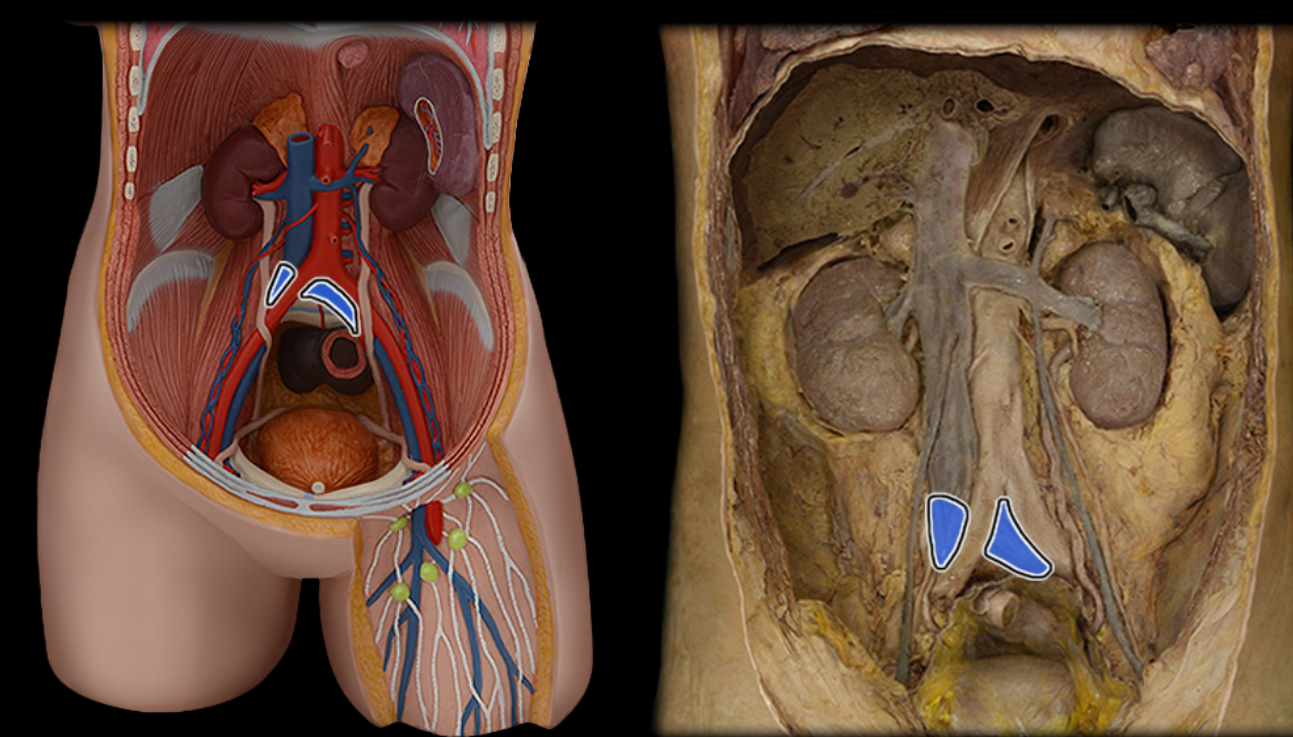
Common iliac v.

External iliac a.
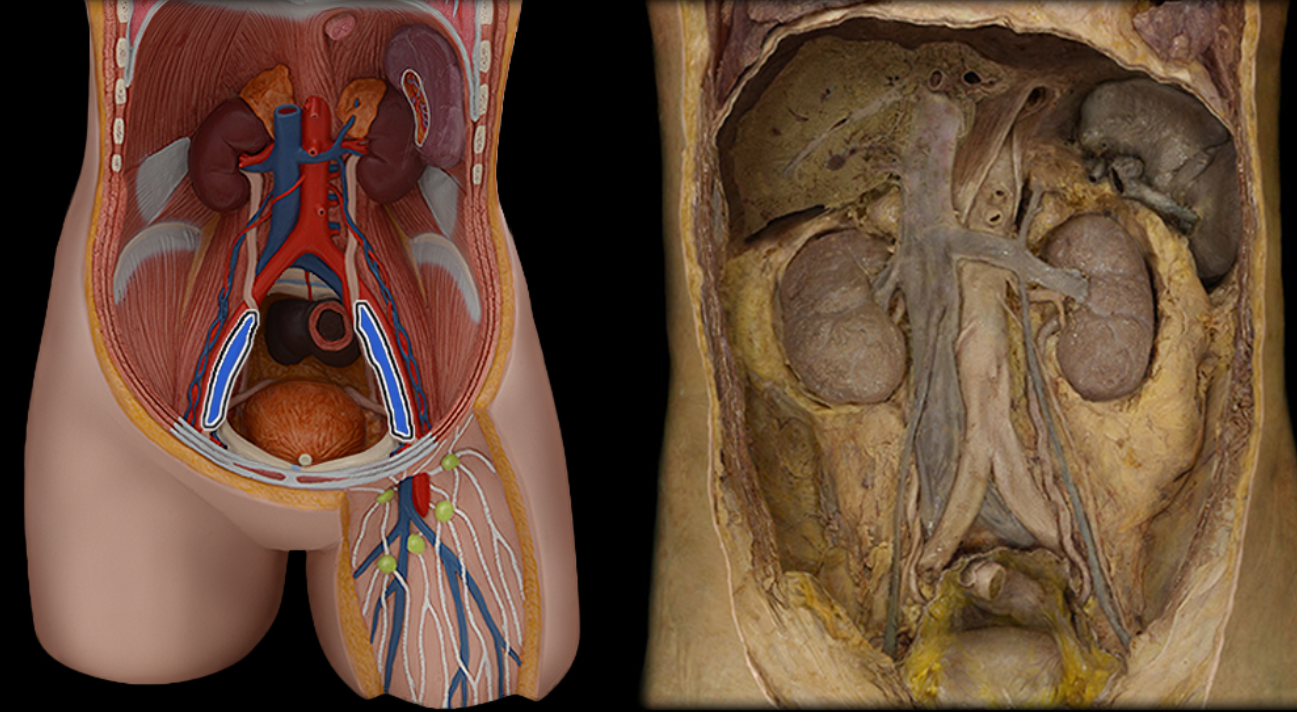
External iliac v.
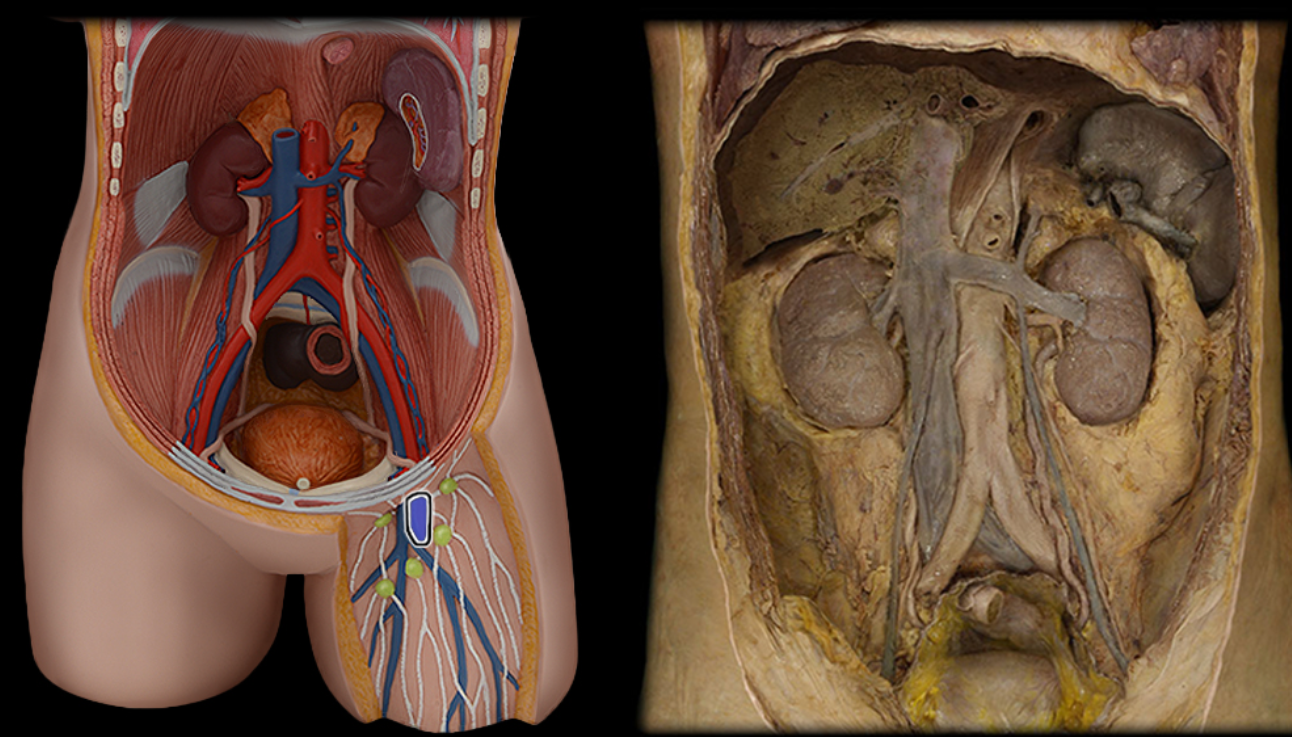
Femoral a.
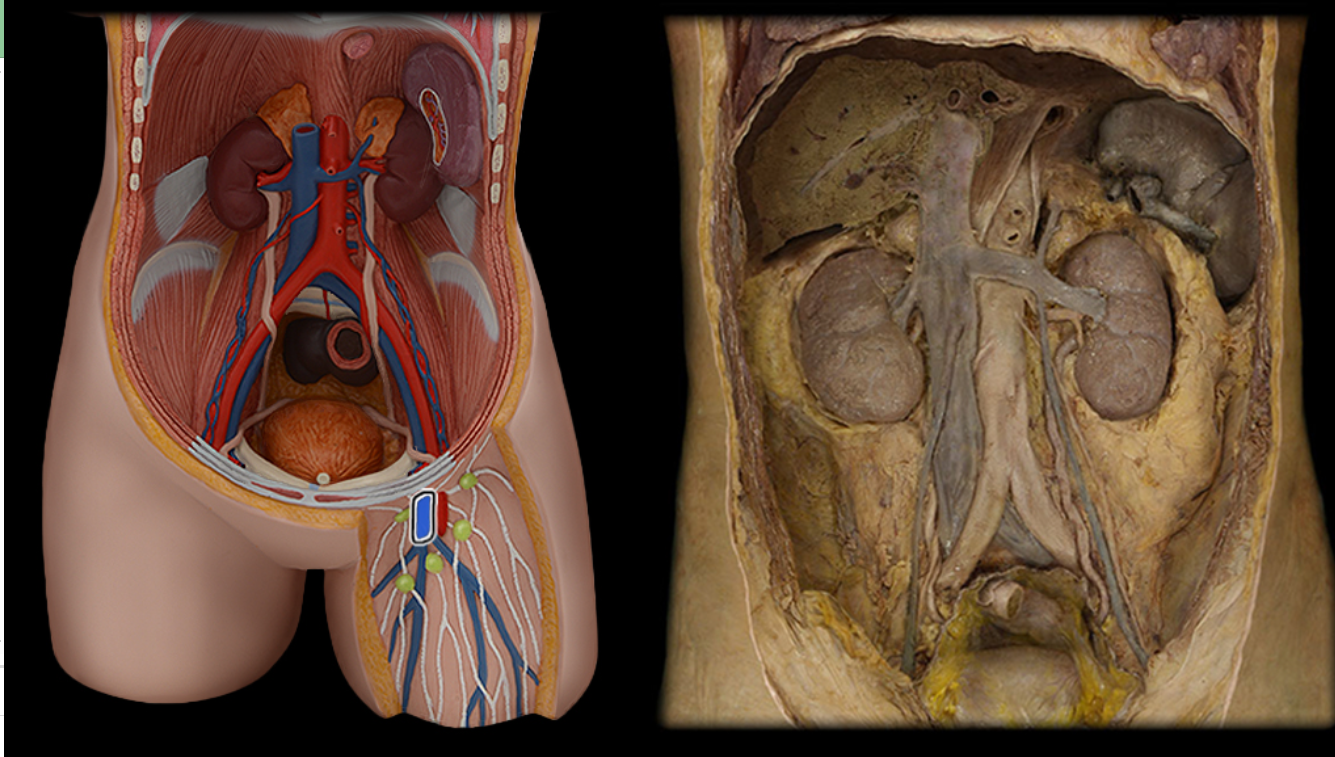
Femoral v.
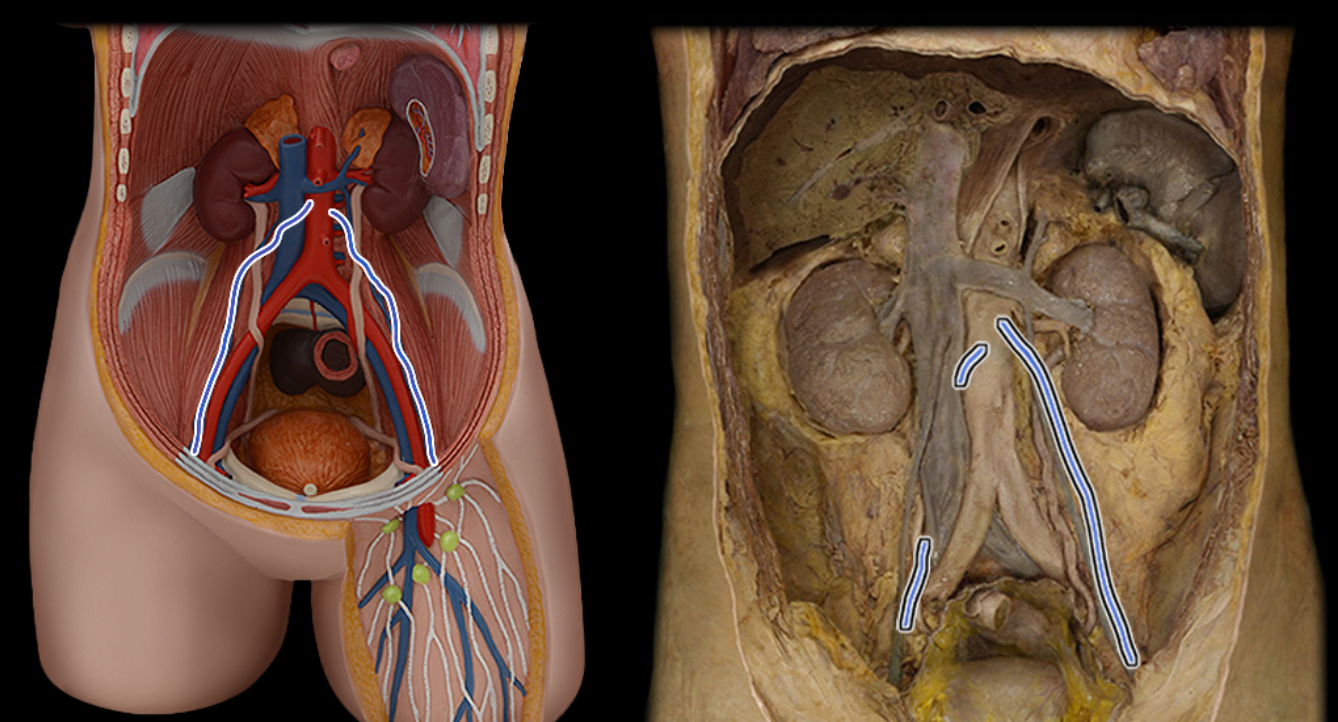
Gonadal a.
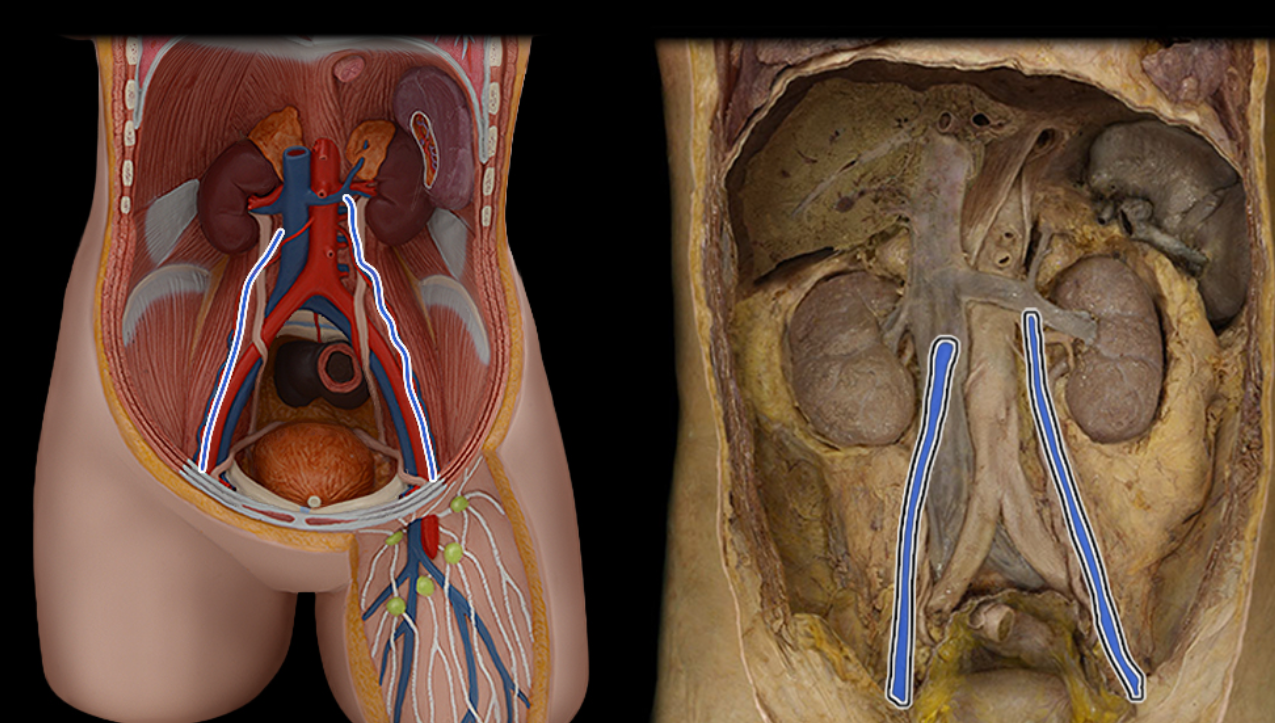
Gonadal v.
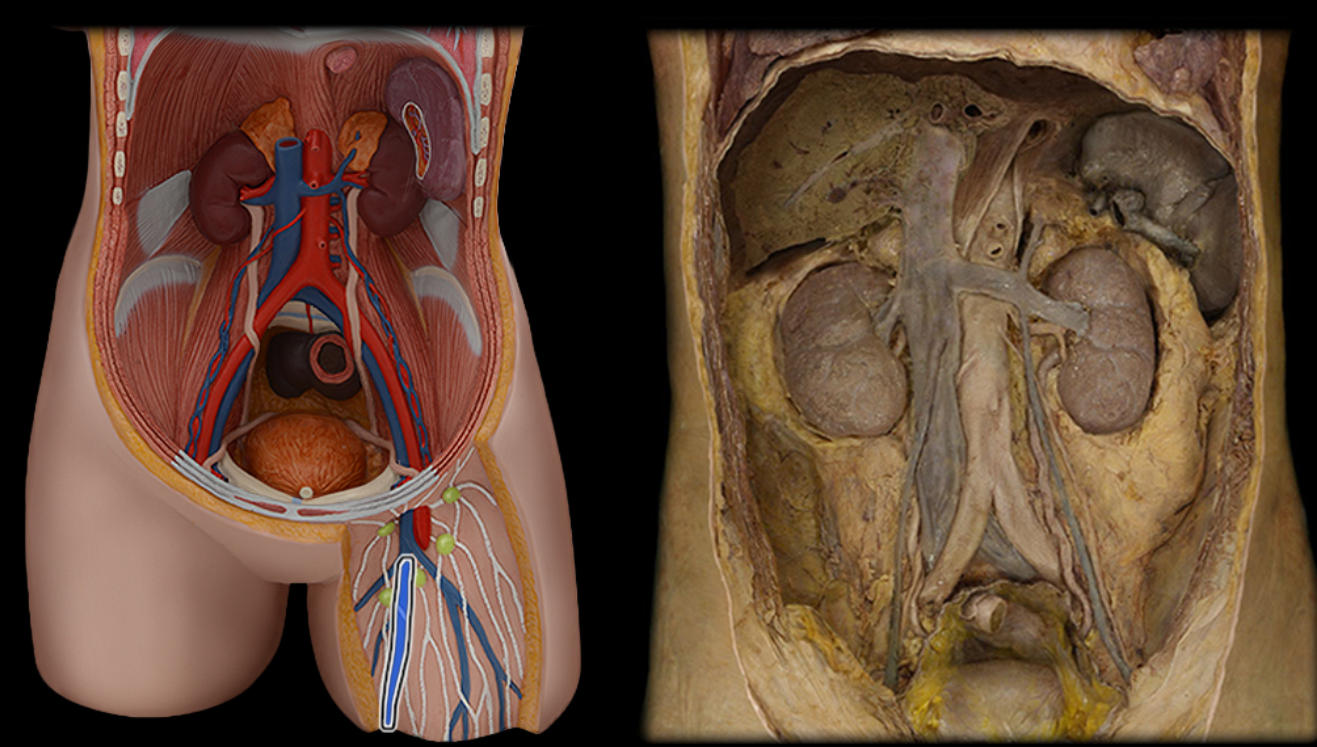
Great saphenous v.
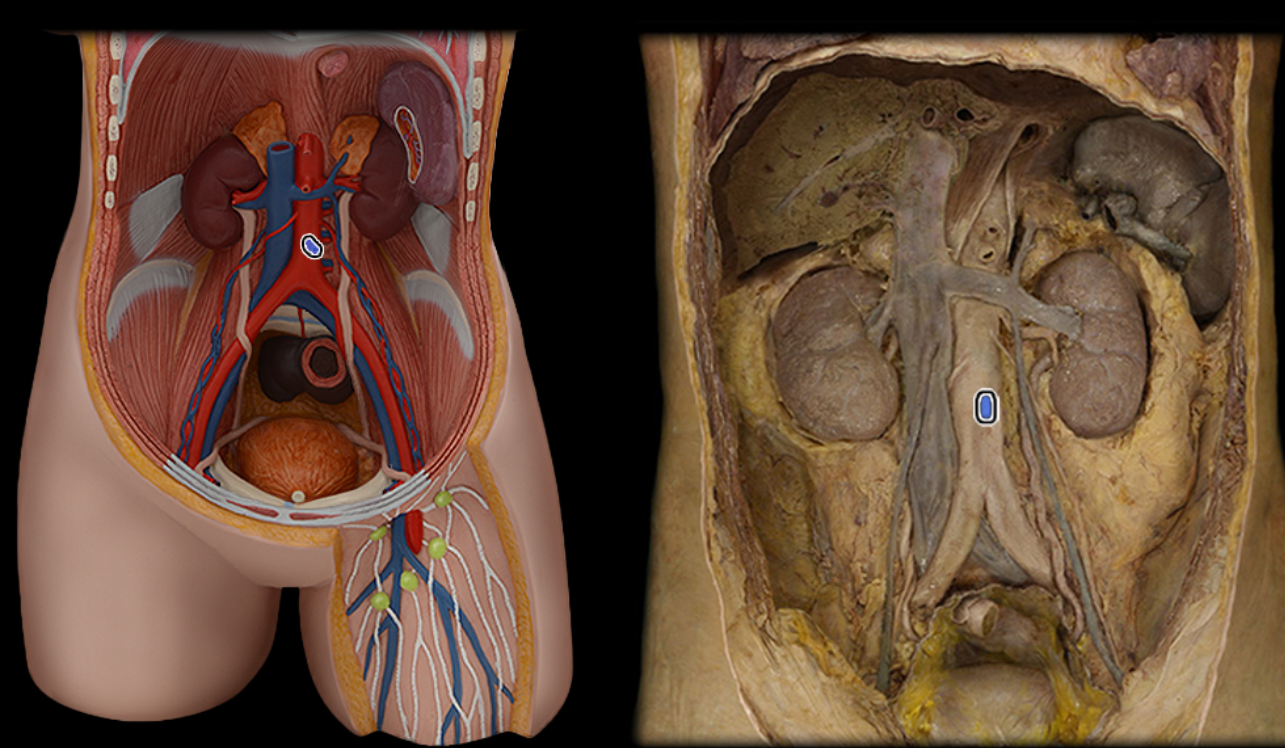
Inferior mesenteric a.
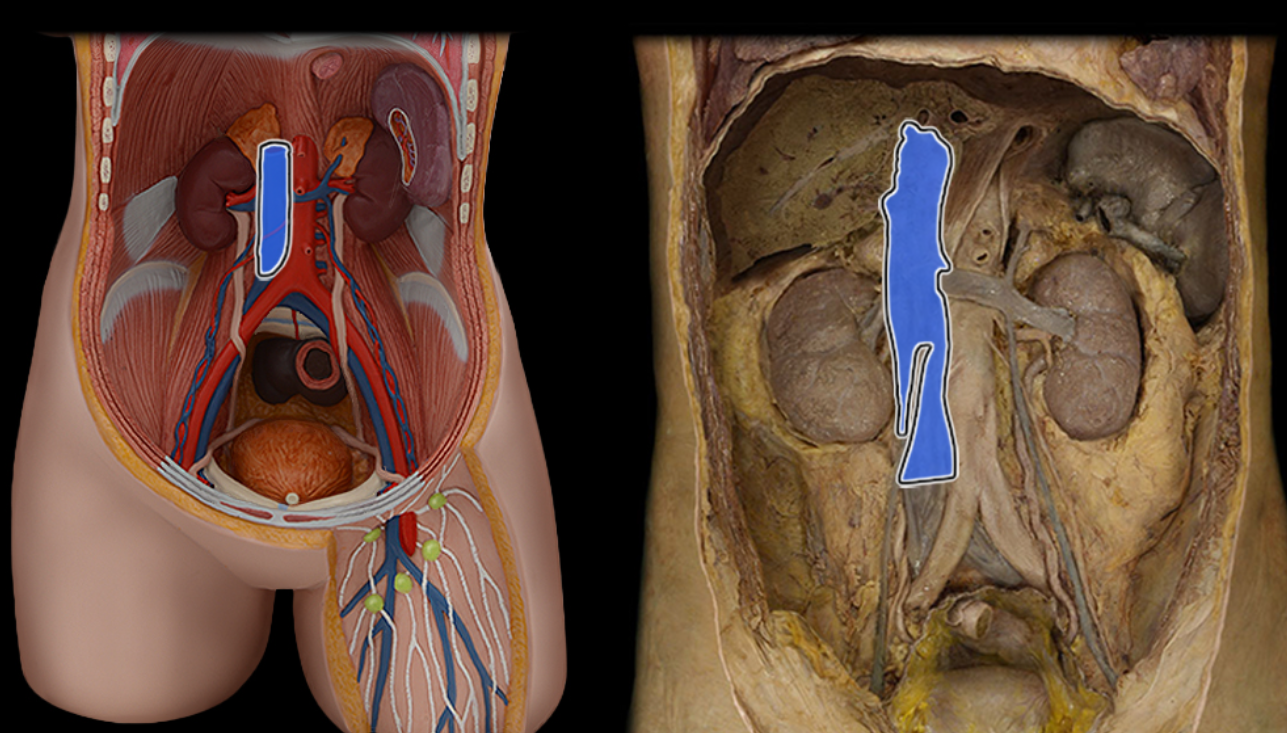
Inferior vena cava
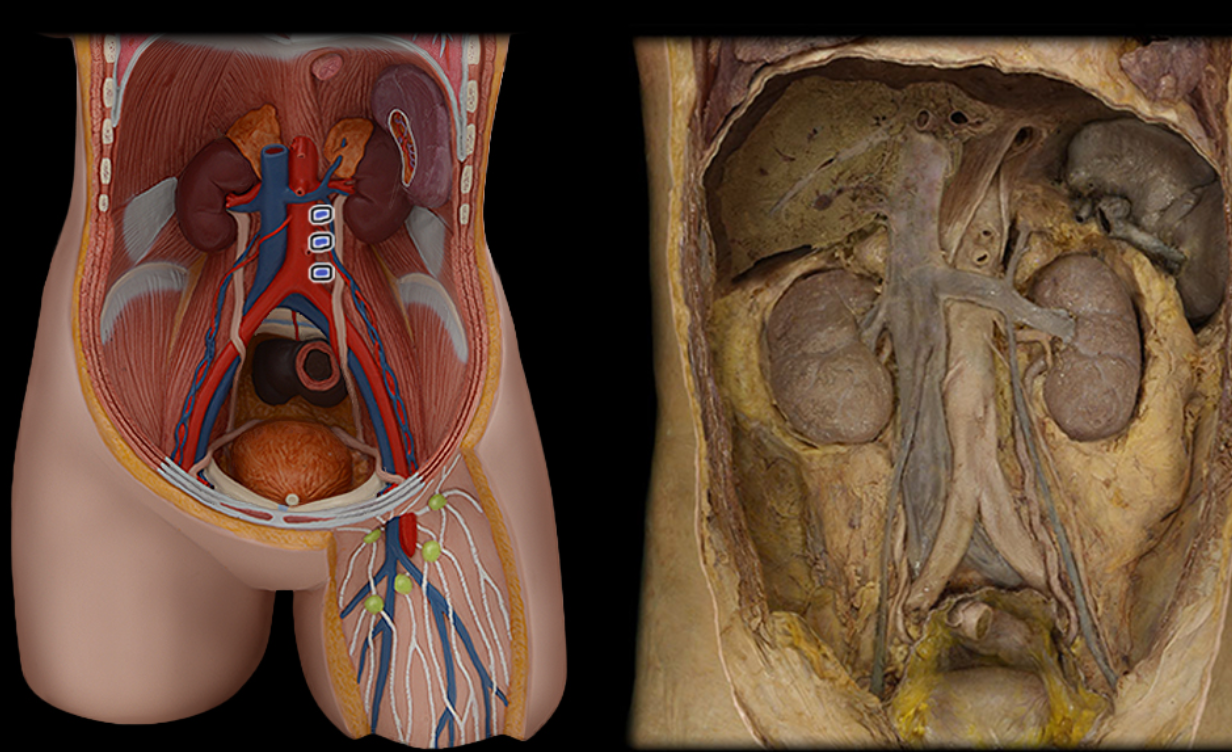
Lumbar a.

Lumbar v.
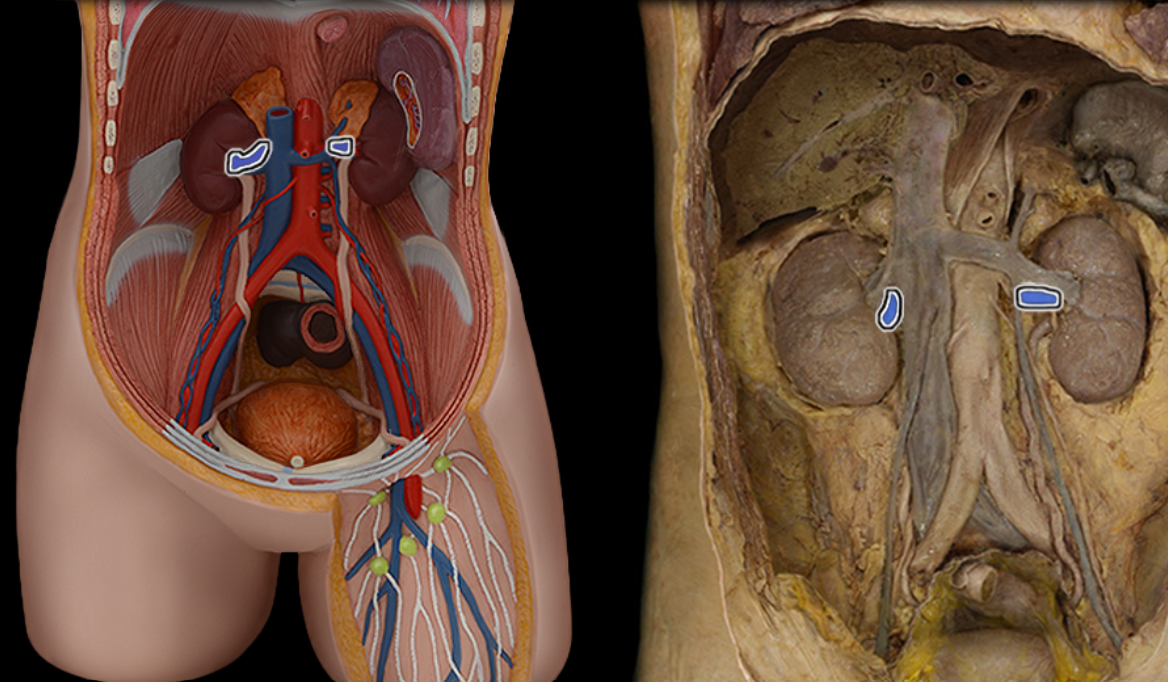
Renal a.
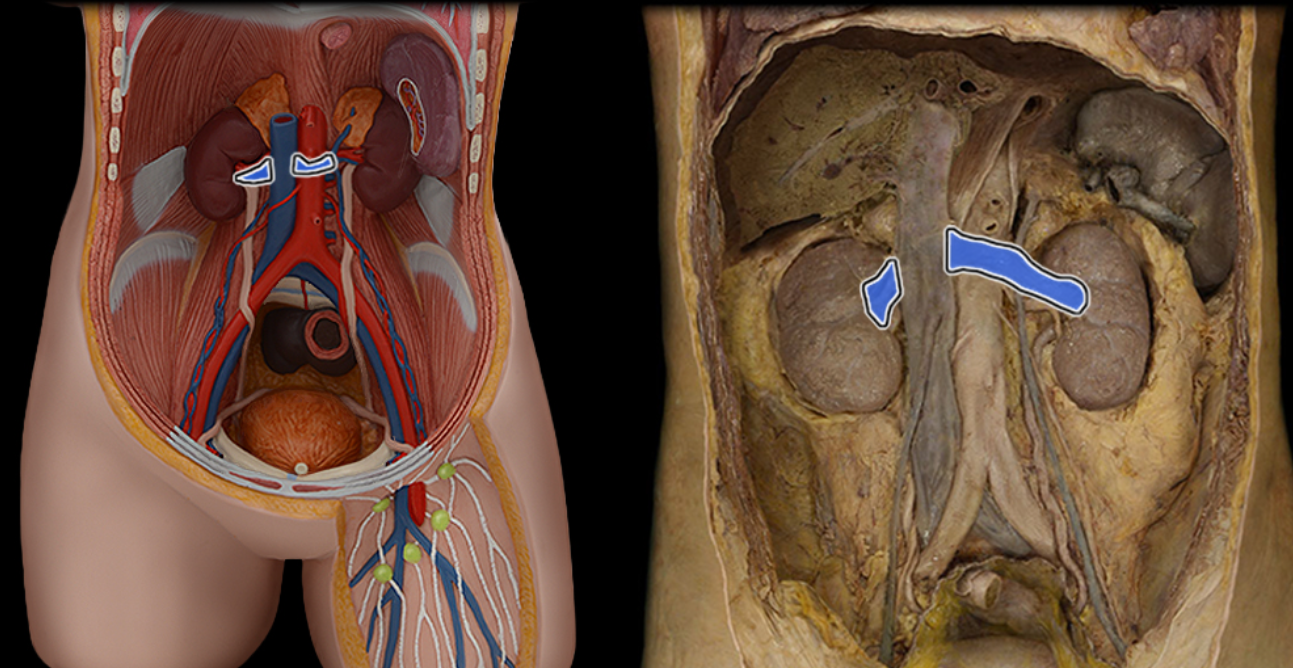
Renal v.
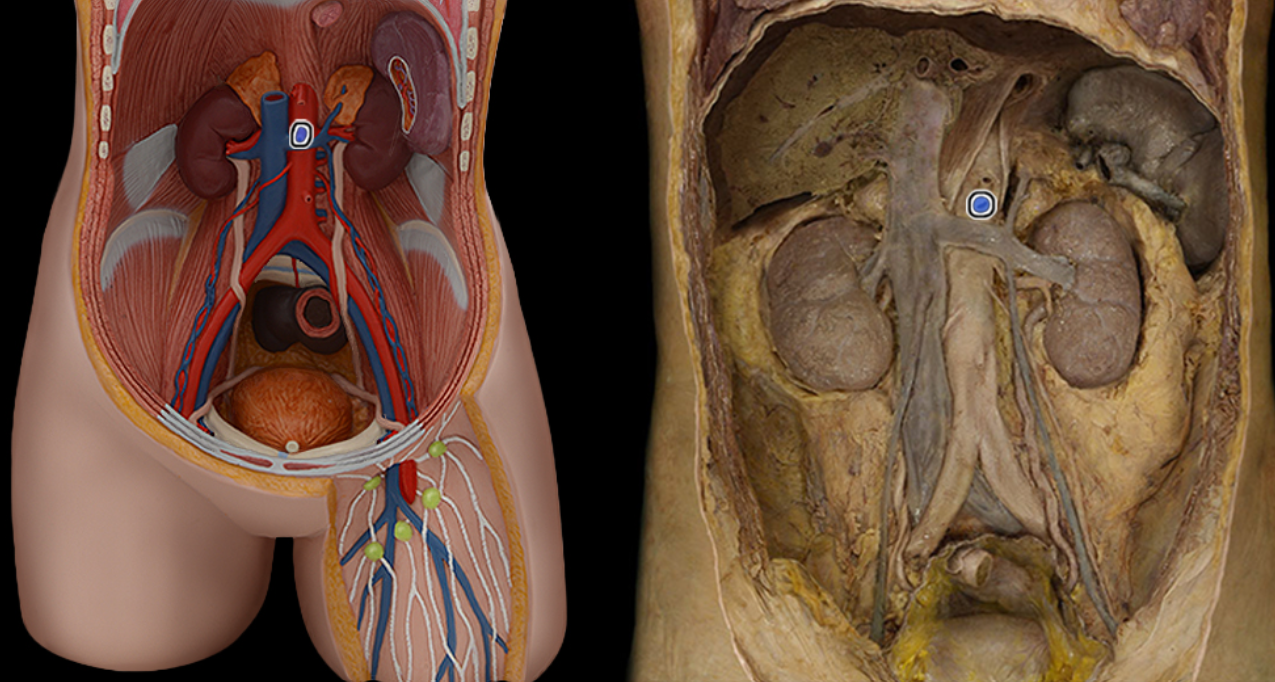
Superior mesenteric a.
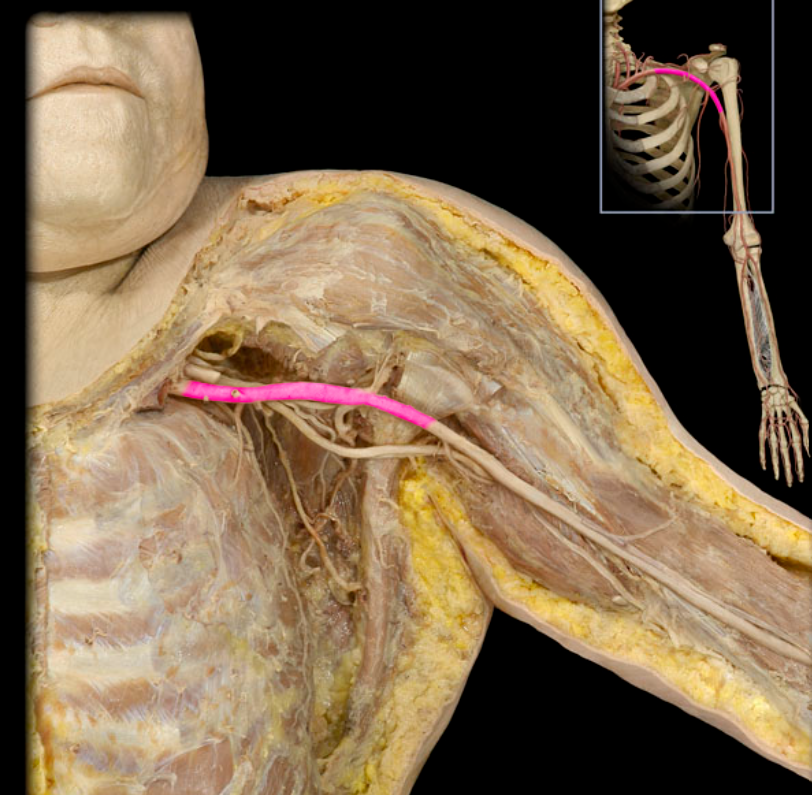
Axillary a.
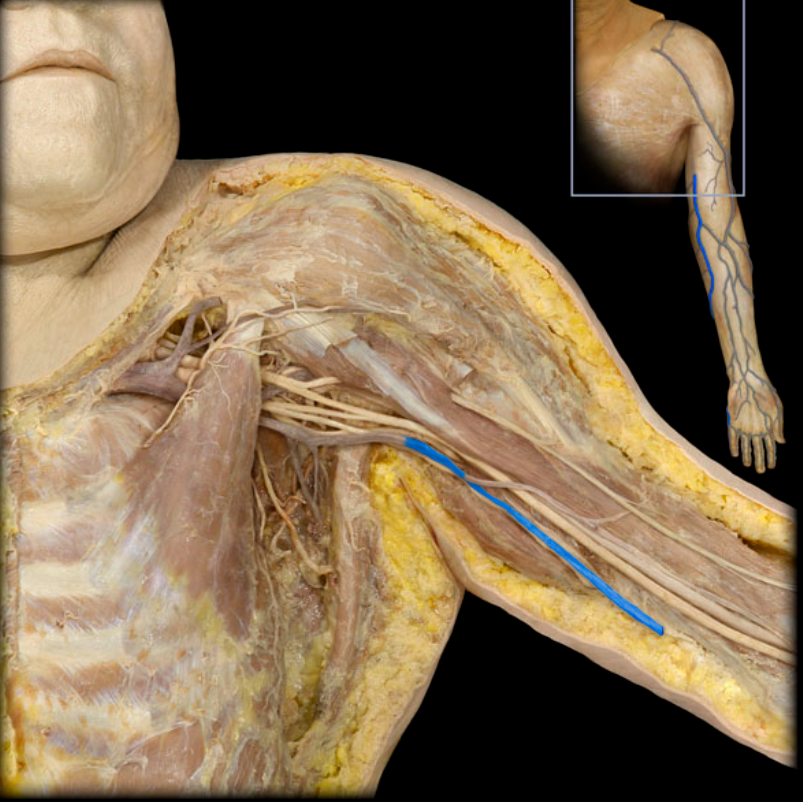
Basilic v.
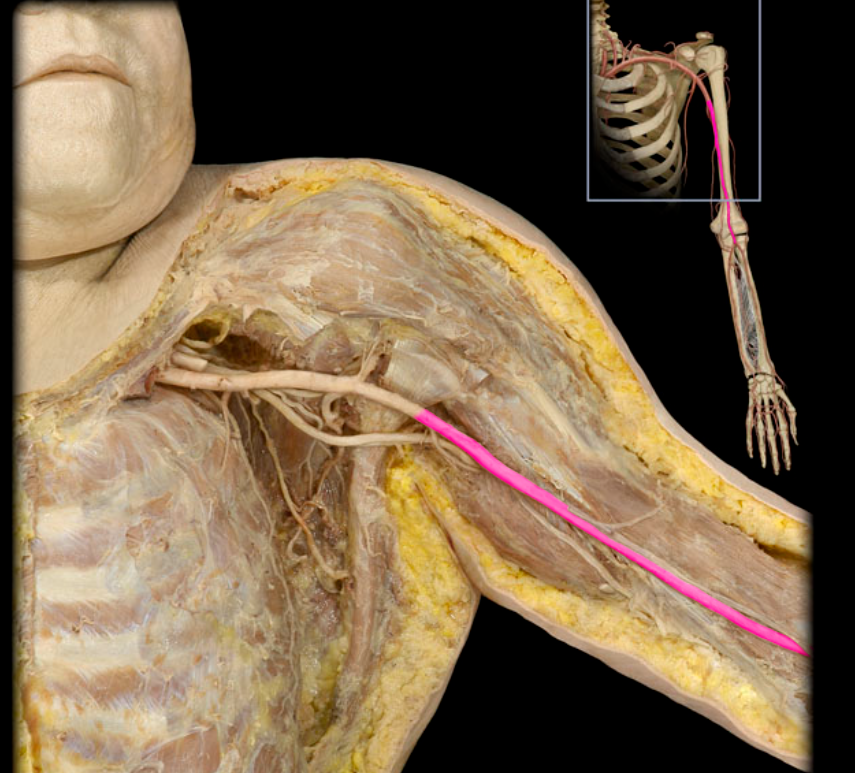
Brachial a.
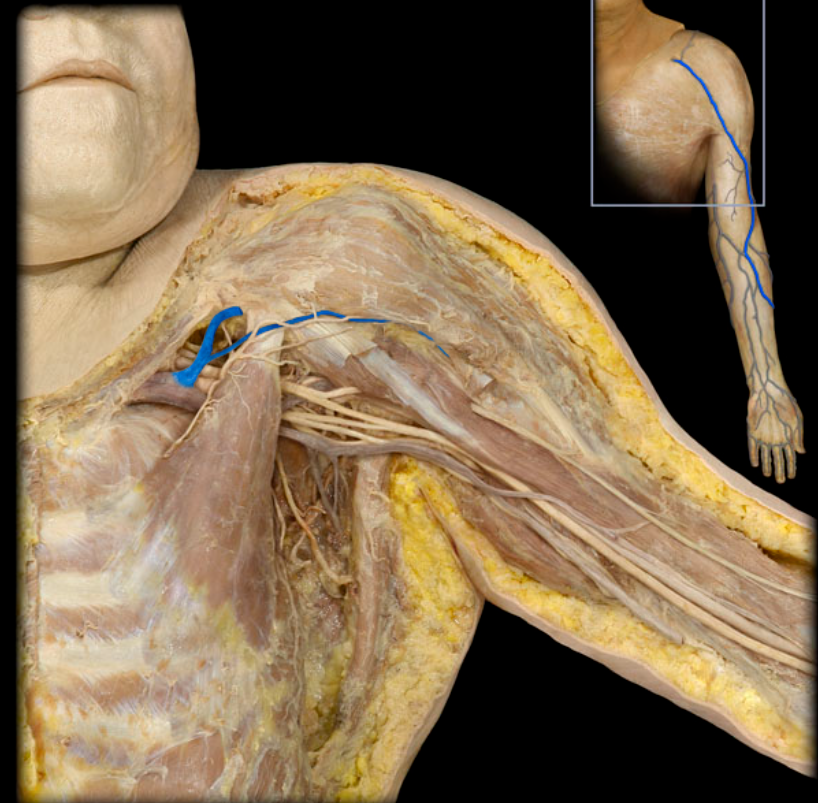
Cephalic v.
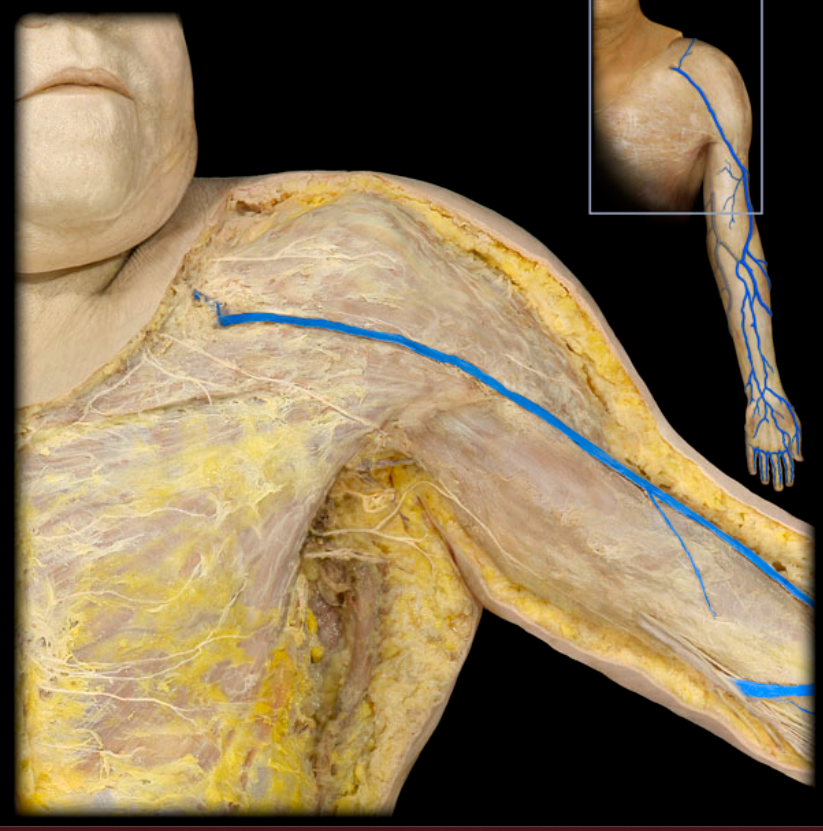
Cephalic v. and tributaries
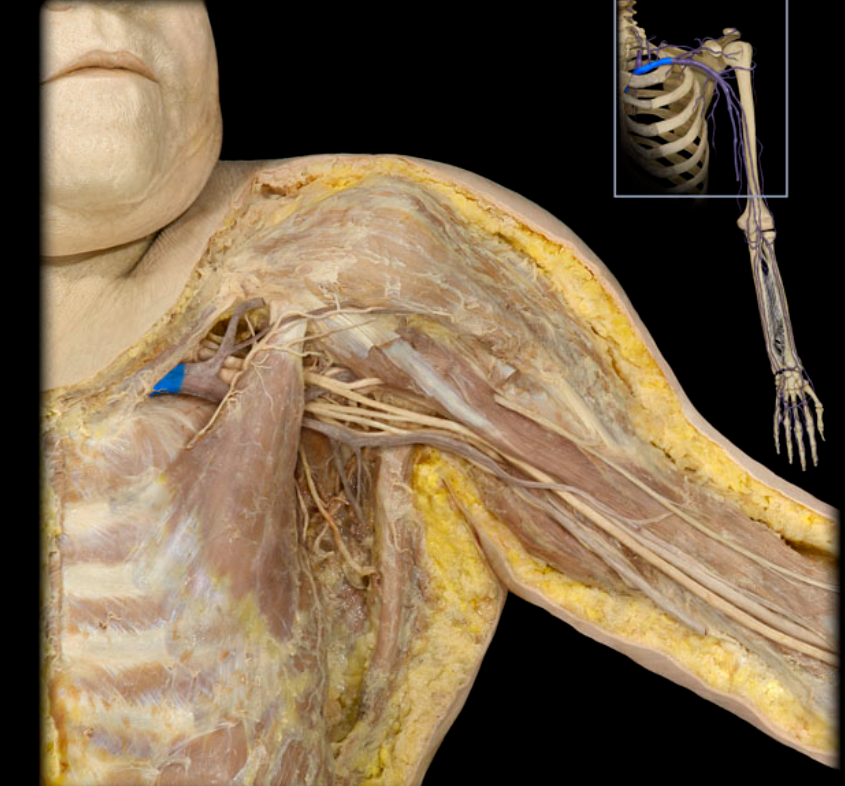
Subclavian v.
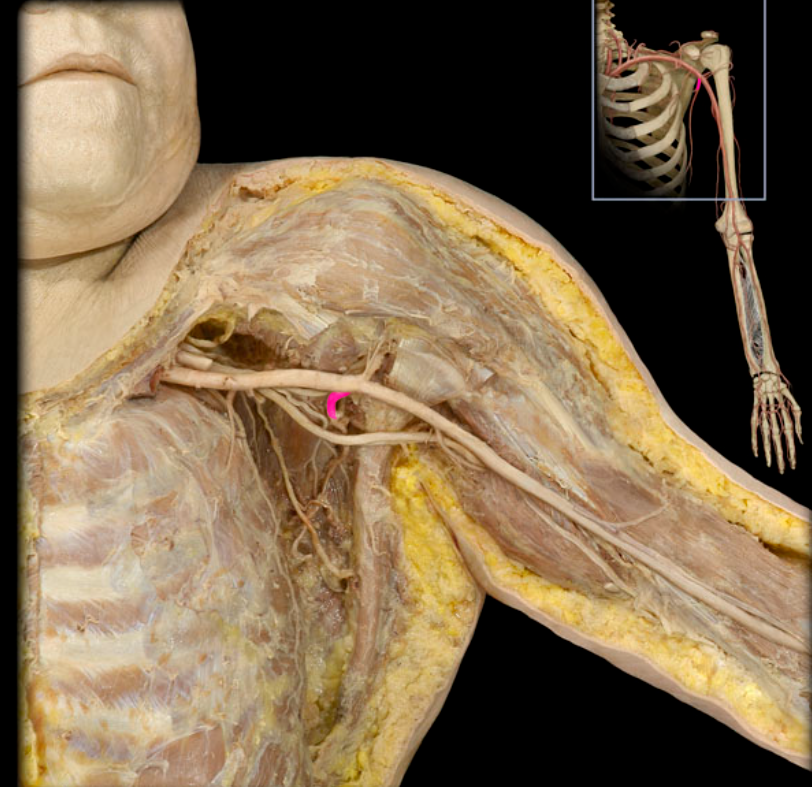
Subscapular a.
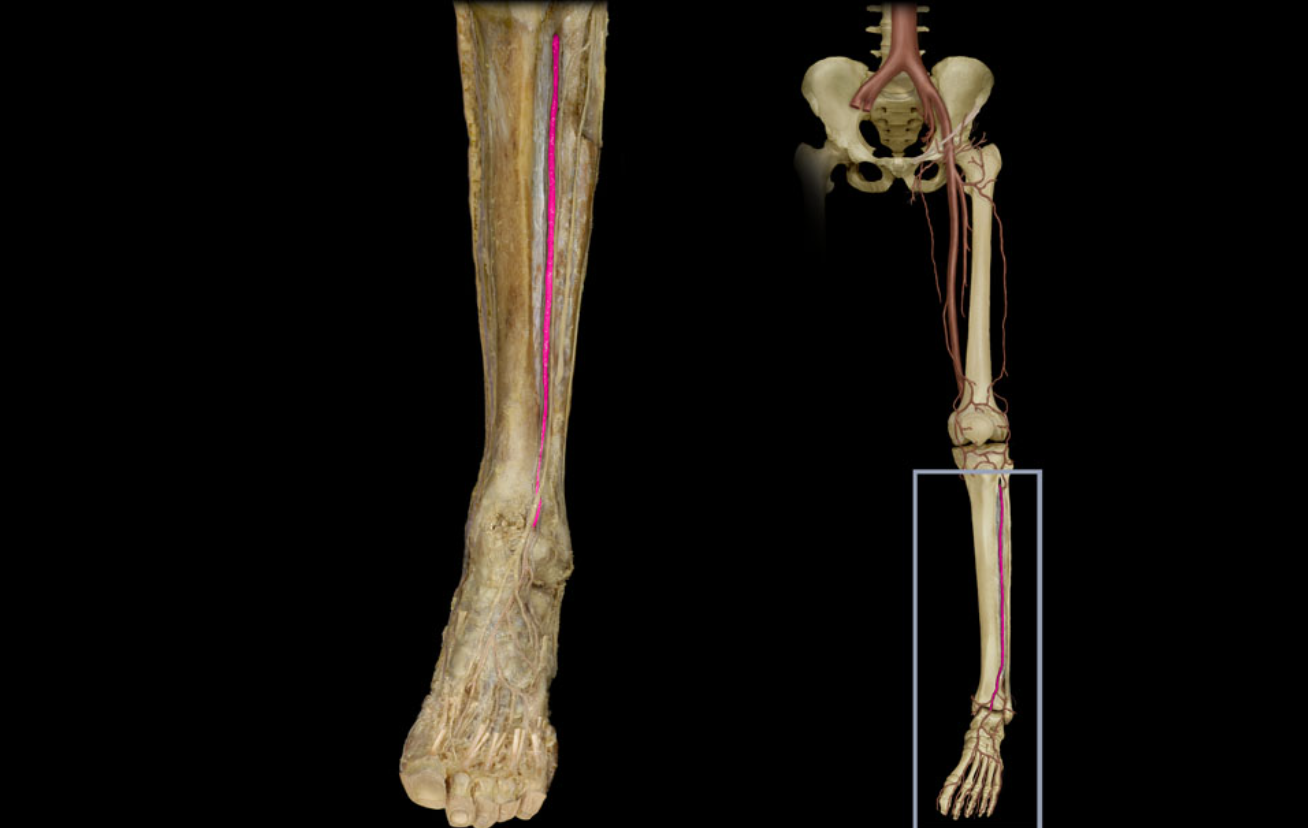
Anterior tibial a.
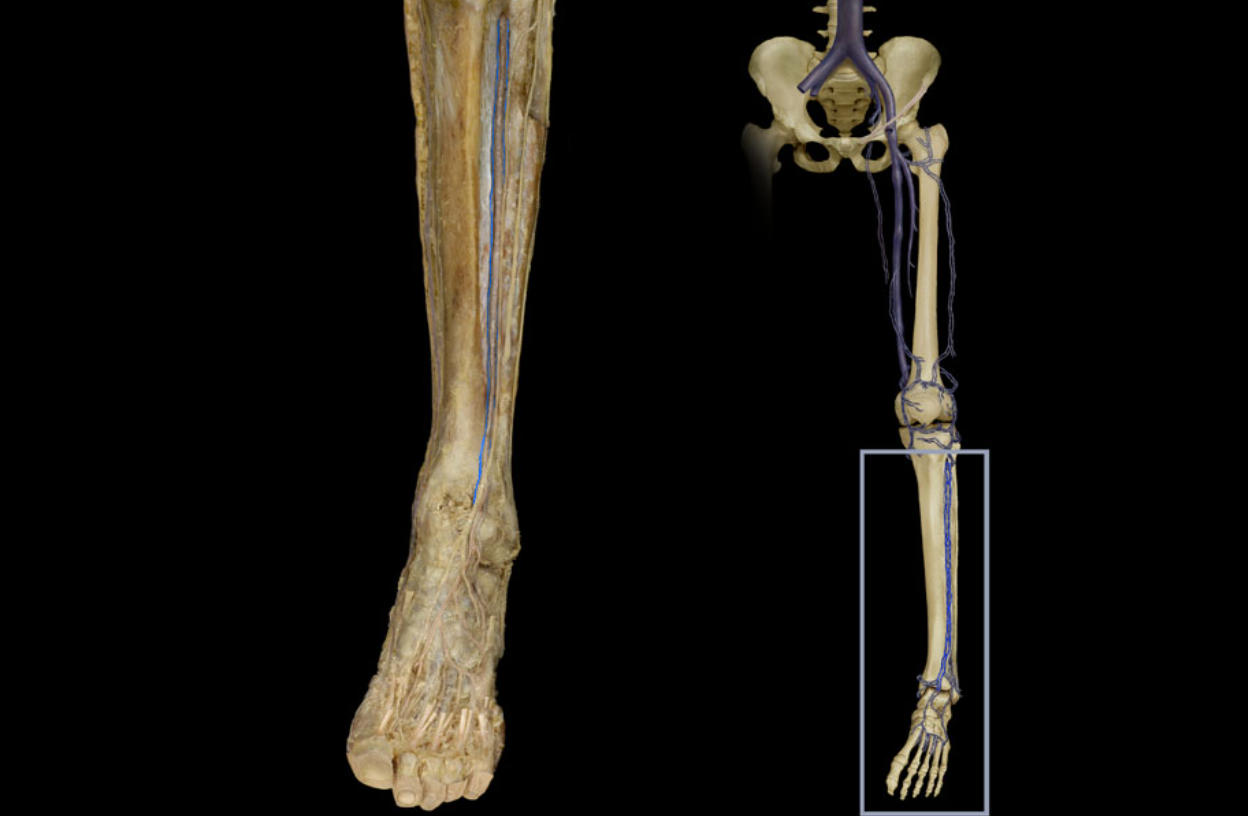
Anterior tibial vv.
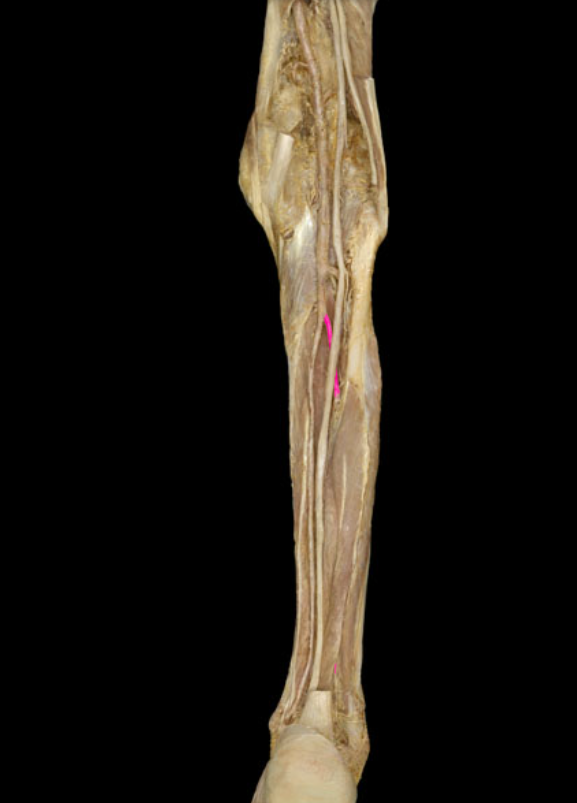
Fibular a.
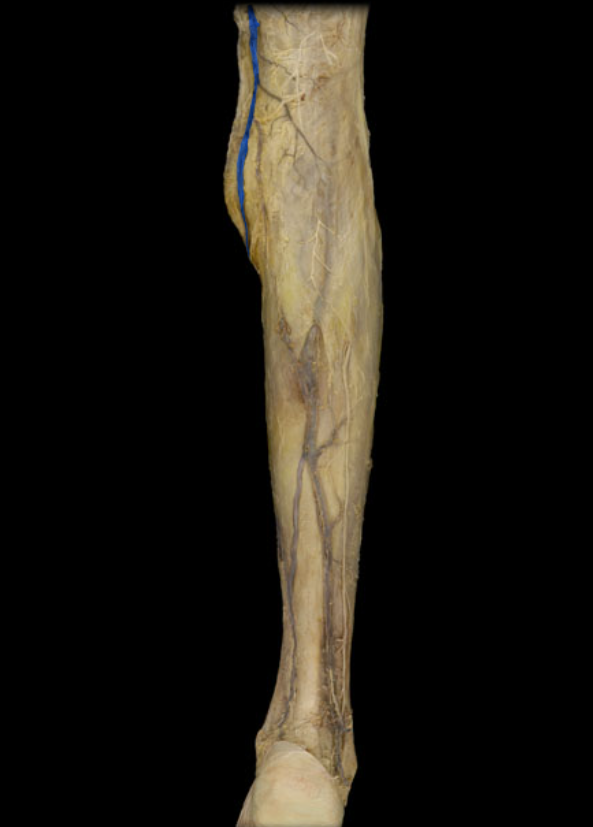
Great saphenous v.
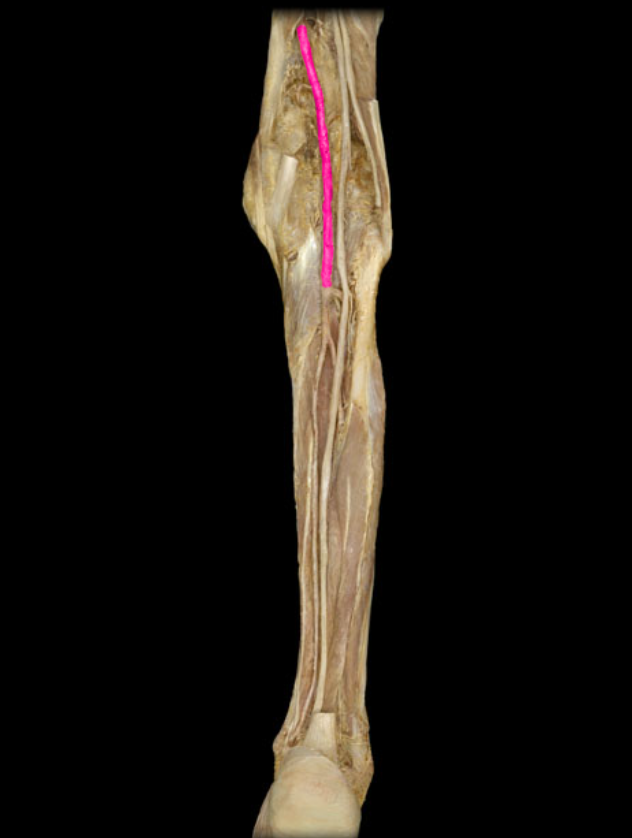
Popliteal a.
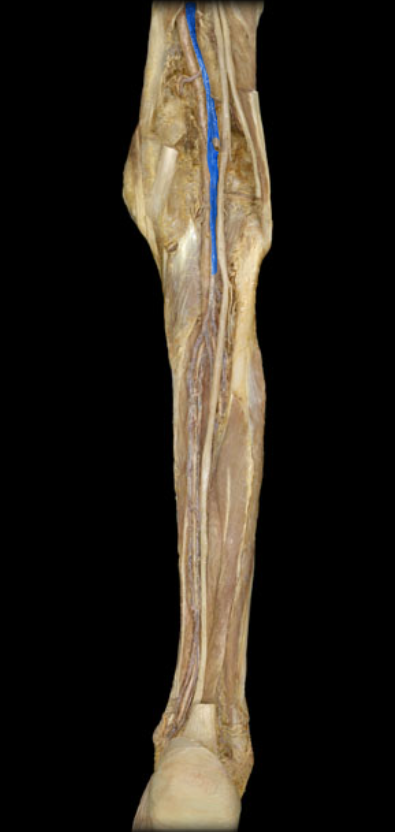
Popliteal v.
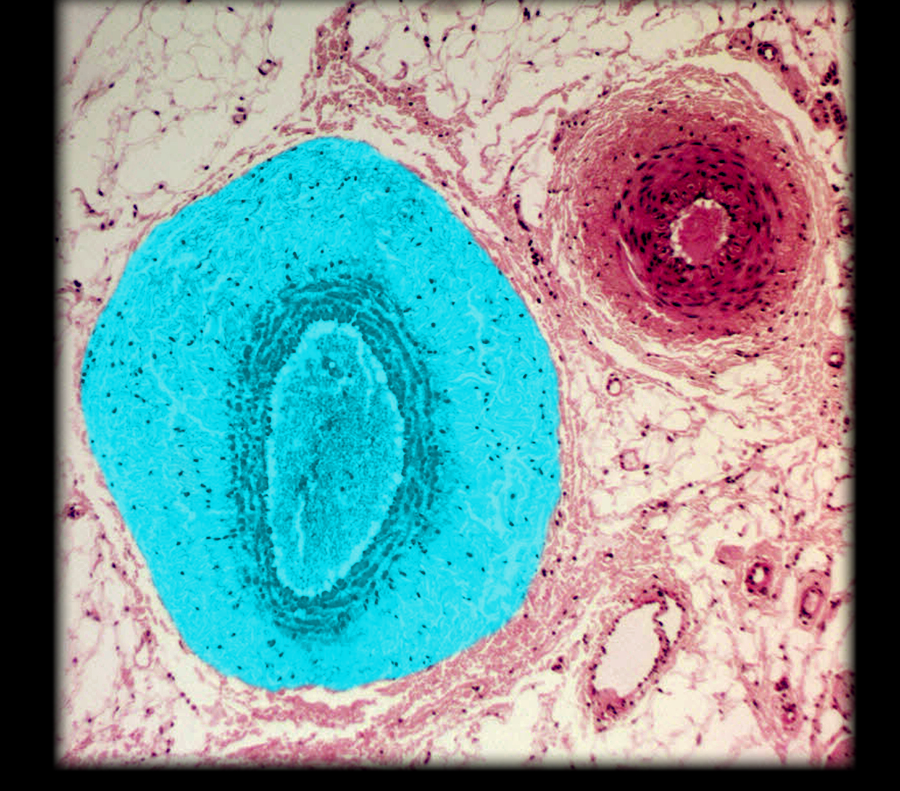
Medium-sized v.
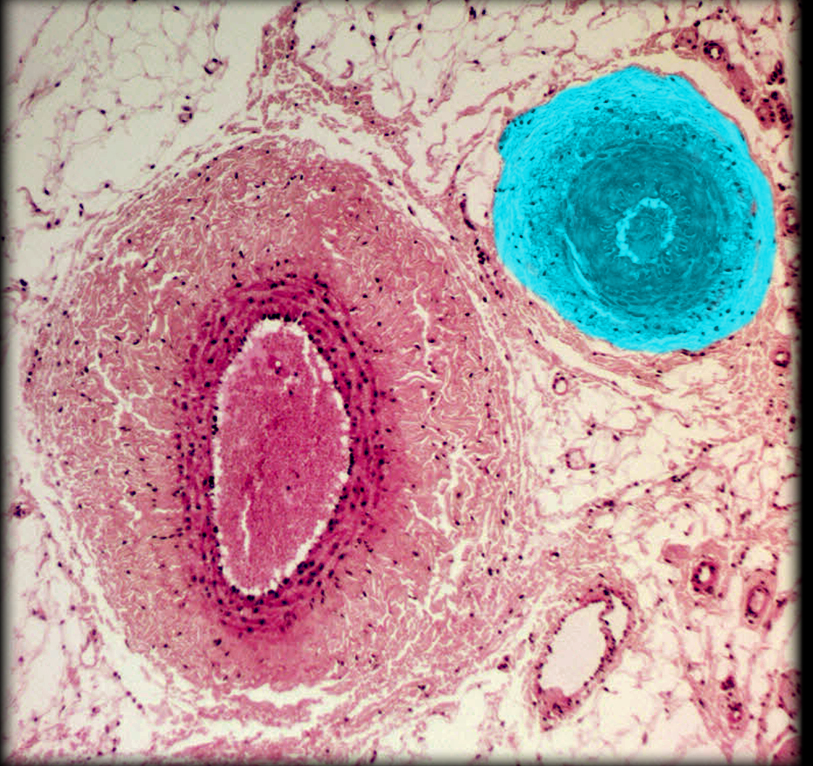
Muscular a.
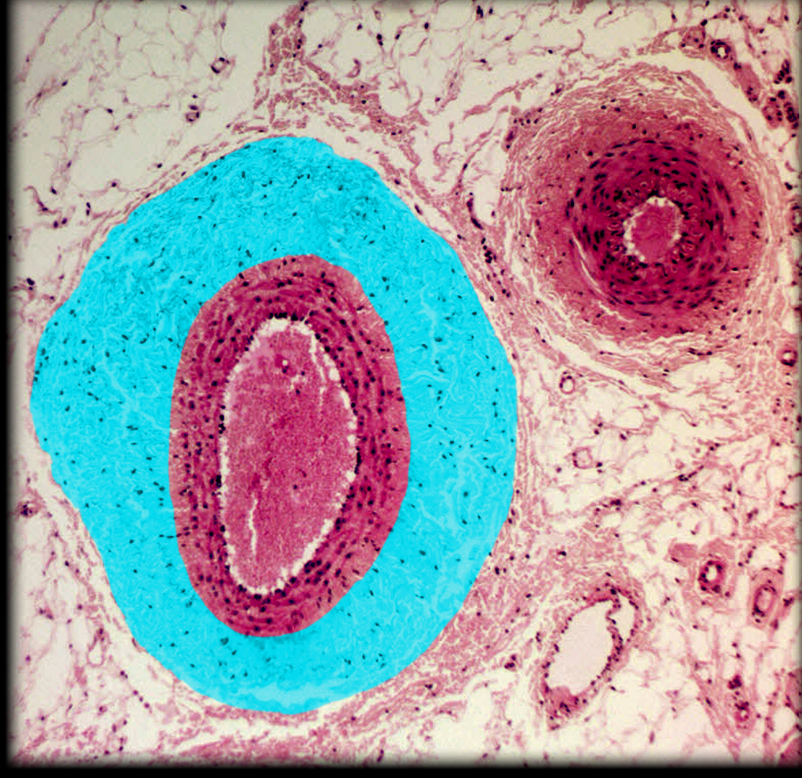
Tunica externa of medium-sized v.
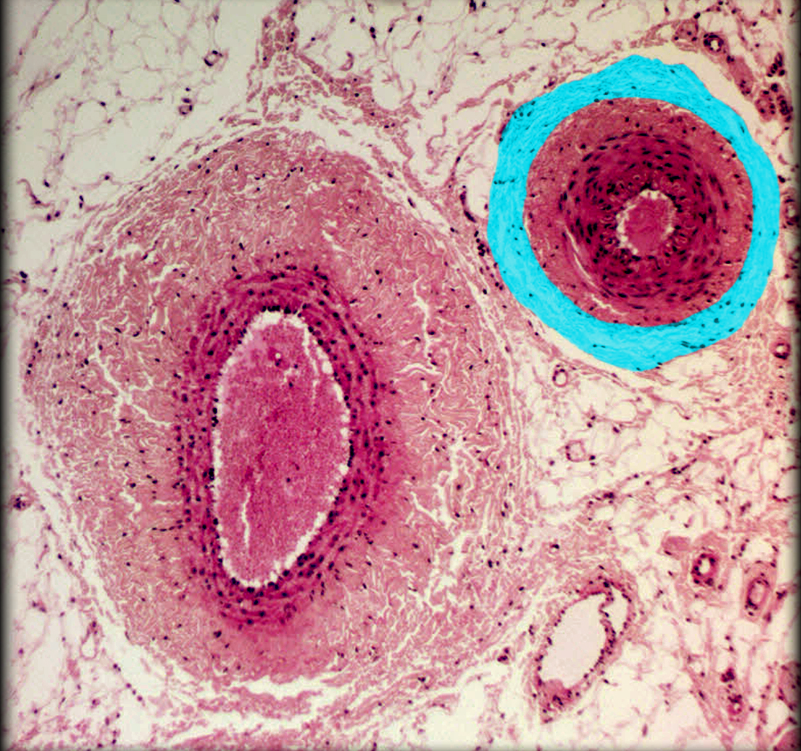
Tunica externa of muscular a.
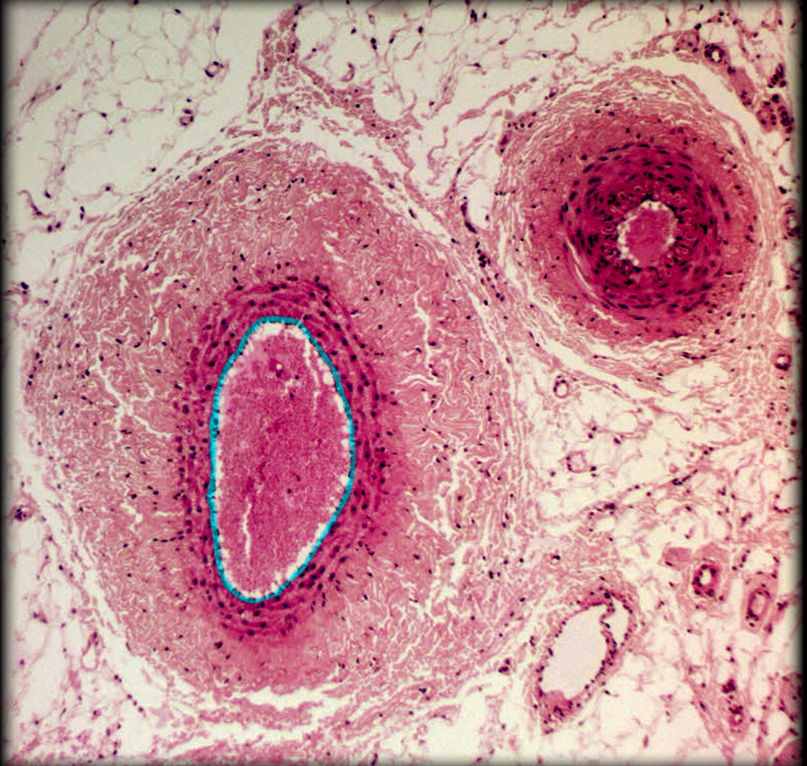
Tunica intima of medium-sized v.
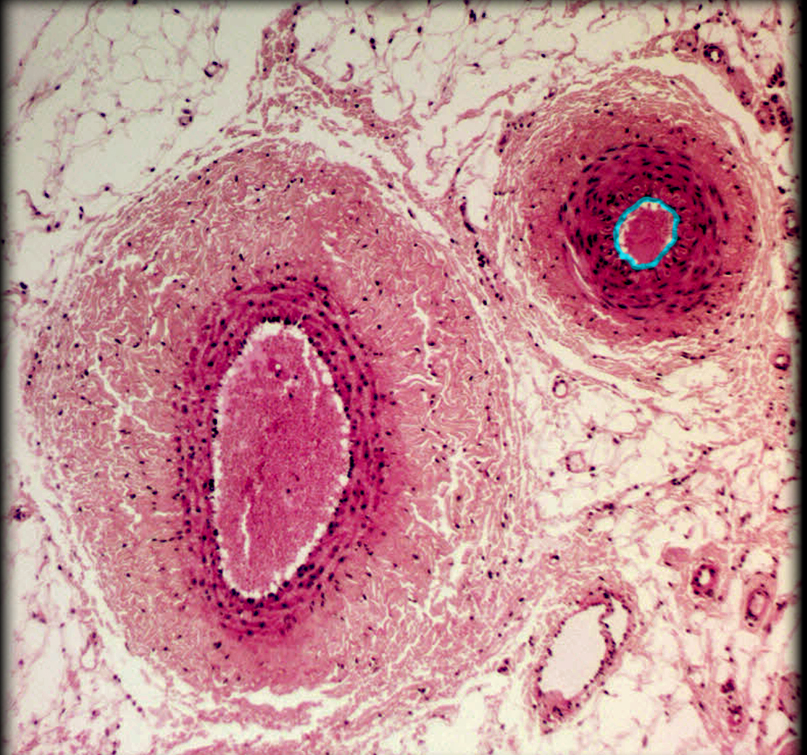
Tunica intima of muscular a.