Animal Nutrition and Feeding final exam study
1/187
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
188 Terms
Which of the following best describes a key structural difference between amylose and amylopectin?
A. Amylose consists of α-1,6 glycosidic bonds, while amylopectin consists only of α-1,4 bonds.
B. Amylose is a linear polymer of glucose, while amylopectin is a branched polymer of glucose
C. Amylose is highly branched, while amylopectin is mostly linear.
D. Amylose contains fructose units, while amylopectin contains glucose units.
B. Amylose is a linear polymer of glucose, while amylopectin is a branched polymer of glucose
Which of the following are brush border enzymes involved in starch digestion? (type all that apply)
Maltase
isomaltase
pancreatic amylase
salivary amylase
sucrase
Maltase, isomaltase, sucrase
After nutrients are absorbed in the small intestine and enter the bloodstream, which organ do they travel to next for processing?
heart or lungs or liver or muscle
liver
Carbohydrates can be classified based on the number of sugars in their molecule. Please, choose the right answer for the statement.
A. Polyssacharide contain > 20 monossacharides in ther molecule
B. Oligosacharide is not a carbohydrate
C. starch is a protein
D. Monossaccharides contain 3 sugars in their molecule
A. Polyssacharide contain > 20 monossacharides in ther molecule
About alpha-amylase enzyme
A. Alpha amylase hydrolysis alpha 1-4 glycosic bond
B. Alpha amylase hydrolysis beta 1-4 glicosic bond
C. Alpha amylase breakdown starch in the stomach
D. Alpha amylase breakdown protein in the stomach
A. Alpha amylase hydrolysis alpha 1-4 glycosic bond
How many kilocalories of energy are provided per gram of lipid when metabolized?
A. 9 kcal/g
B. 2.25 kcal/g
C. 7 kcal/g
D. 4 kcal/g
A. 9 kcal/g
What is the energy density of lipids compared to carbohydrates and protein?
A. 1.5X more
B. 2.25X more
C. 2X more
D. 3X more
B. 2.25X more
Which of the following is NOT a function of lipids?
A. Absorb fat-soluble vitamins
B. Supply essential fatty acids
C. Provide energy
D. facilitate fiber degradation
D. facilitate fiber degradation
How are the fatty acids attached to the glycerol backbone in a triglyceride?
A. By ionic bonds
B. By hydrogen bonds
C. By ester linkages
D. By peptide bonds
C. By ester linkages
What is the main structural feature of a triglyceride?
A. Three fatty acid chains esterified to a glycerol molecule
B. A single glucose molecule bonded to three fatty acids
C. Three amino acids linked to a glycerol backbone
D. A ring structure composed of alternating carbon and nitrogen atoms
A. Three fatty acid chains esterified to a glycerol molecule
What is the omega classification of linoleic acid from the methyl end?
A. Omega 3
B. Omega 6
C. Omega 9
D. Omega 12
B. Omega 6
True or False
Peptides are a structure composed of a short string of amino acids, also known as the "building blocks" of proteins
True
What is the role of glycoproteins in cell interactions?
A. DNA replication
B. Cell-to-cell interactions
C. Energy production
D. Protein synthesis
B. Cell-to-cell interactions
Which fibrous protein is found in feathers, hair, wool, and hooves?
Elastin or Keratin or Resilin or Collagen
Keratin
Pepsin is a gastric enzyme that specifically cleaves which type of bonds in proteins?
A. Glycosidic bonds
B. Phosphodiester bonds
C. Disulfide bonds
D. Peptide bonds on the carboxyl side
D. Peptide bonds on the carboxyl side
What is the function of peristalsis in the digestive system?
A. To produce enzymes for digestion
B. To regulate the saliva production
C. To help break down food into nutrients
D. To move food through the digestive system
D. To move food through the digestive system
Which enzyme is responsible for breaking down carbohydrates in the digestive system?
pepsin or amylase or lipase or trypsin
amylase
True or False
Proteins can interact with other biomolecules (minerals, CHOs, lipids) to form complex compounds.
True
Which structural adaptations of the small intestine enhance its ability to absorb nutrients efficiently?
A. Extensive surface area due to villi and microvilli
B. Reducing the number of villi and microvilli
C. Having a short small intestine
D. Eating large meals
A. Extensive surface area due to villi and microvilli
What is the function of fats in the body?
A. Fats do not play a role in supporting cell growth or protecting organs
B. Fats are not essential for the absorption of nutrients in the body
C. Fats are only used for insulation and do not provide any energy
D. Fats provide energy, support cell growth, protect organs, and help the body absorb nutrients.
D. Fats provide energy, support cell growth, protect organs, and help the body absorb nutrients.
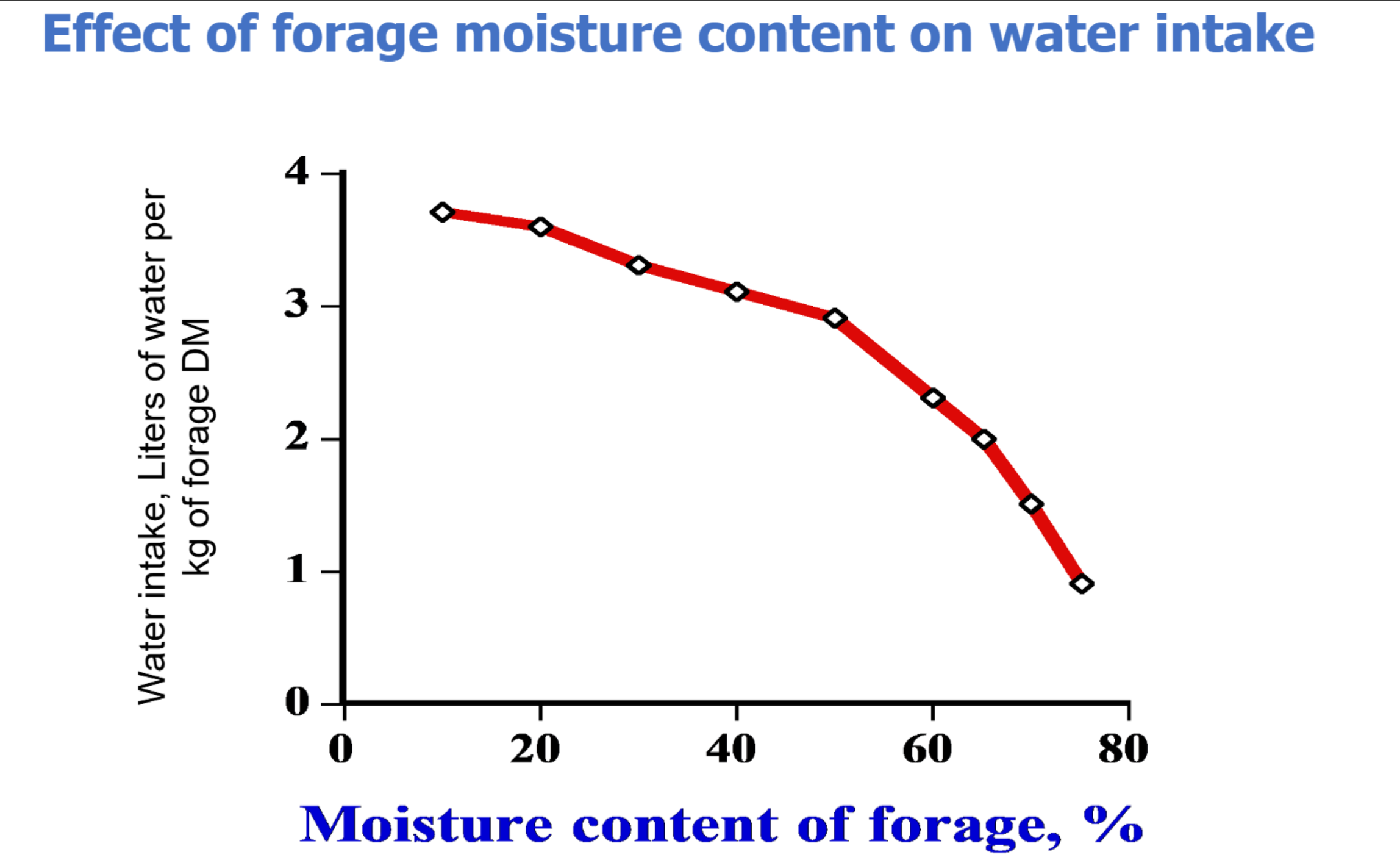
What trend is typically observed in water intake as forage moisture content increases?
A. Water intake has a negative correlation with water intake; where the higher the feed moisture% the higher the intake in liters of water per kg of feed
B. Water intake has a positive correlation with water intake; where the higher the feed moisture% the lower the intake in liters of water per kg of feed
C. Water intake has a positive correlation with water intake; where the higher the feed moisture% the higher the amount of liters of water per kg of feed
D. Water intake shows a negative correlation with forage moisture content—as the percentage of moisture in feed increases, the amount of drinking water consumed (in liters per kg of feed) decreases.
D. Water intake shows a negative correlation with forage moisture content—as the percentage of moisture in feed increases, the amount of drinking water consumed (in liters per kg of feed) decreases.
What is the implication of water samples exceeding the maximum upper limit for sodium?
A. Potential health risks for livestock
B. Increased water availability
C. Improved water quality
D. increased water intake
A. Potential health risks for livestock
Which of the following is NOT typically considered a factor that affects water requirements in animals?
A. Environmental temperature
B. Salt intake
C. Feed moisture content
D. Hair color
D. Hair color
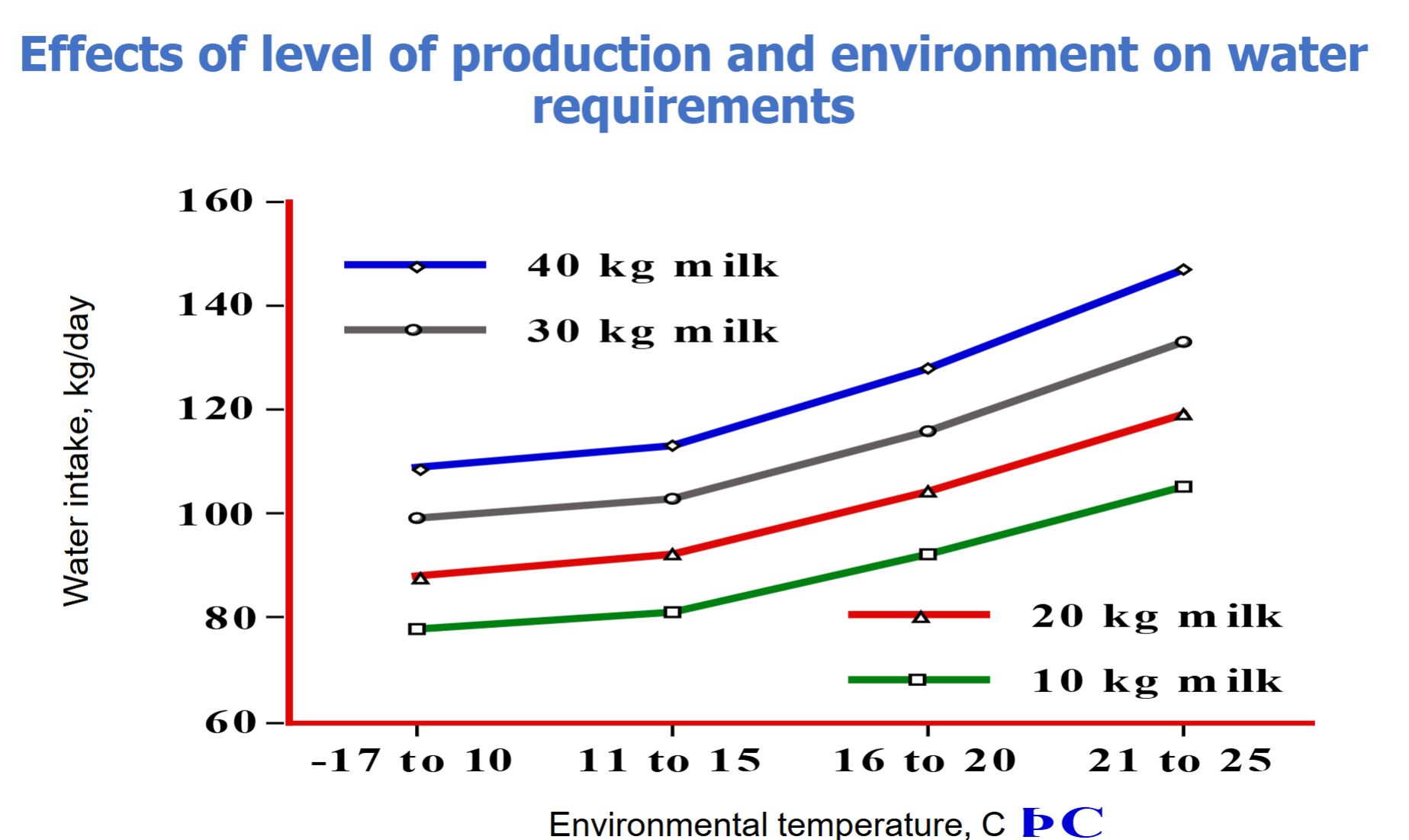
Choose the correct correlation and explanation between water intake, environmental temperature and milk production.
A. Water intake remains constant regardless of changes in temperature or milk production.
B. Water intake decreases as environmental temperature and milk production increase, due to reduced metabolic demand.
C. Water intake is positively correlated with both environmental temperature and milk production—as temperature and milk output increase, animals require and consume more water to support thermoregulation and lactation.
D. Water intake is negatively correlated with both environmental temperature and milk production—as temperature and milk output increase, animals require and consume more water to support thermoregulation and lactation.
C. Water intake is positively correlated with both environmental temperature and milk production—as temperature and milk output increase, animals require and consume more water to support thermoregulation and lactation.
In hind gut fermenters, water from the undigested food is absorbed mainly in the _____ ________
Large Intestine
What percentage of an animal's body weight is typically made up of water?
A. 40-50%
B. 50-60%
C. 80-90%
D. 60-70%
D. 60-70%
Which digestive process involves microorganisms breaking down food components?
A. Mechanical digestion
B. Microbial fermentation
C. Chemical digestion
D. Enzymatic hydrolysis
B. Microbial fermentation
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of monogastric herbivores?
A. Possess a single-chambered stomach
B. Rely heavily on microbial fermentation in the hindgut
C. Efficiently digest cellulose without microbial assistance
D. Consume plant-based diets
C. Efficiently digest cellulose without microbial assistance
True or False
Bulk/roughage grazers have wide muzzle structure so they can graze without selecting the food.
True
What is the pH range of the stomach?
A. 2.5 to 4.5
B. 1.5 to 3.5
C. 3.5 to 5.5
D. 4.5 to 6.5
B. 1.5 to 3.5
Which of these species below is a hindgut fermenter?
A. giraffe
B. rabbit
C. llama
D. cow
B. rabbit
Gastrin produced by the gastric epithelium is stimulated by the presence of _______ in the stomach
proteins
True or False
Non-protein nitrogen sources, such as urea, can be used to support microbial growth in ruminants; however, the amount of urea added to the diet must be carefully regulated
True
Which cell produces pepsinogen?
A. mucous cells
B. chief cells
C. enteroendocrine cells
D. parietal cells
B. chief cells
True or False
Biological Value (BV) is % of digested & absorbed protein that is retained in body for productive functions
True
Which of the following is NOT digested by enzymatic digestion in mammals?
Cellulose or Proteins or Starch or Fats
Cellulose
As food travels through the digestive system, it is exposed to a variety of pH levels. The stomach has a pH ranging from 1.5 to 3.5 due to the presence of hydrochloride acid (HCl), and the small intestine has a pH ranging from 7 to 8. HCl converts pepsinogen into pepsin, an enzyme that digests proteins in the stomach. Which of the following most likely happens to pepsin as it enters the small intestine?
A. It's activity increases to digest more proteins.
B. pepsin is converted into trypsin
C. It's shape changes to engulf large proteins
D. It becomes inactive
D. It becomes inactive
True or False
Vitamins such as C and E are natural antioxidants and can aid on the prevention the rancidity in oils
True
Which of the following amino acids is classified as essential in nutrition?
Alanine or Glutamine or Methionine or Tyrosine
Methionine
Dietary lipids are absorbed in the small intestine and packaged into ____________, which enter the ______ ________, bypassing the liver initially.
Chylomicrons, Lynfatic system
Which of the following dietary changes is most likely to lead to acute rumen acidosis in cattle?
A. Sudden introduction of high-concentrate grain diet
B. Gradual increase in forage intake
C. Supplementation with rumen buffers
D. Increased access to pasture with high fiber content
A. Sudden introduction of high-concentrate grain diet
What is a common clinical sign of subacute ruminal acidosis (SARA) in dairy cows?
A. Reduced feed intake and loose feces
B. Elevated rumen pH
C. Severe dehydration and recumbency
D. High milk fat percentage
A. Reduced feed intake and loose feces
What is a significant environmental concern when feral horses and beef cattle share the same grazing land?
A. Increased milk production in cattle
B. Improved biodiversity due to mixed grazing patterns
C. Overgrazing leading to soil erosion and vegetation loss
D. Enhanced soil fertility from manure
C. Overgrazing leading to soil erosion and vegetation loss
Which management strategy can help reduce land degradation when feral horses and beef cattle coexist in the same rangeland?
A. Implementing rotational grazing and population control
B. Allowing unrestricted access to riparian zones
C. Increasing grain supplementation for both species
D. Encouraging competition to improve forage utilization
A. Implementing rotational grazing and population control
True or False
Ketosis in dairy cattle is caused by an energy imbalance, typically occurring when energy demands exceed intake during early lactation.
True
Vitamin K is usually synthesized by _________ in ruminants.
microbes
What is the major antagonist for trace minerals?
A. Molybdenum
B. all trace minerals have antagonistic effects
C. Sulfur
D. Iron
B. all trace minerals have antagonistic effects
What factors should we consider for balancing mineral requirements to prevent a potential deficiency?
A. all answers are correct
B. production status
C. drinking water and forage mineral content
D. animal category
A. all answers are correct
True or False
Minerals do not interfere with each other
False
True or False
Selecting a mineral source for a diet is based on cost and bioavailability
True
True or False
The only mineral that animals have ‘nutritional wisdom’ (consume adequate amounts on their own or even excessive amounts) is salt.
True
True or False
Relative bioavailability of trace minerals does not vary with its respective inorganic chemical forms (e.g., sulfate, carbonate, etc.).
False
True or False
The ideal ration of Calcium (Ca) and Phosphorous (P) is 2:1.
True
True or False
Vitamins A, D, E and B are common limiting fat-soluble vitamins in formulating diets
False
A trace mineral linked with an organic compound is known as
A. hydroxychloride source
B. Organic source
C. Inorganic source
D. sulfate source
B. Organic source
_______, Trace mineral required for rumen microbe to synthesize Vitamin B
Cobalt
Which of the following statements is NOT an overall goal of feed processing?
A. Increase animal selectivity
B. Ensure feed intake is possible and efficient
C. Store and preserve feeds effectively
D. Improve feed acceptability
E. Enhance nutrient digestibility
A. Increase animal selectivity
[____________] can be found in high concentration in forage
Calcium or Selenium or Phosphorus or Iron
Calcium
__________ can be found in high concentration in grains
phosphorus
Which of the following feed processing methods involves heat during the process?
A. Grinding
B. Steam rolling
C. Reconstitution
D. Rolling
B. Steam rolling
What is the most abundant mineral in the body?
Iron or Phosphorus or Calcium or Potassium
Calcium
True or False
Flaking is a thermal treatment that alters the chemical structure of starch, making it more accessible to the animal.
True
Green forages have high concentration of carotene, which is a precursor to _______.
A. Vitamin C
B. Vitamin A
C. Vitamin D
D. Vitamin B
B. Vitamin A
[__________] minerals are generally shown in rations as a % of the diet.
A. micro
B. trace
C. macro
D. organic
C. macro
True or False
Vitamin E deficiency can cause muscle and heart disease
True
True or False
Horses are less efficient in synthesize Vitamins K and complex B when compared to ruminants.
True
True or False
In ruminants, mineral solubility in the rumen has a positive correlation with its bioavailability.
False
Which of the following is NOT a function of calcium in the body?
A. Bone formation
B. Oxygen transport
C. Muscle contraction
D. Blood clotting
B. Oxygen transport
Selenium and Vitamin D are closely linked, and they both play a role in the immune function of animals.
True or False
False
True or False
Ionophores are additives used to gram negative bacterial growth and have hydrophilic membranes in their composition
False
Which of the following is a primary benefit of pelletizing animal feed?
A. Eliminates the need for forage in the diet
B. Improves feed intake and reduces wastage
C. Reduces the need for grinding grains
D. Increases the moisture content of the feed
B. Improves feed intake and reduces wastage
What is one of the main advantages of using extrusion in pet food manufacturing?
A. It improves texture, digestibility, and shelf life of the final product.
B. It eliminates the need for packaging and storage.
C. It allows for the inclusion of raw meat without any safety concerns.
D. It reduces the need for grinding grains before feeding.
A. It improves texture, digestibility, and shelf life of the final product.
True or False
Toasting is a feed processing method commonly used for oilseeds to de-activate antinutritional factors such as trypsin inhibitors in soybeans.
True
True or False
Iron deficiency is a common deficiency in livestock, and it's usually associated with beef cattle and swine.
False
True or False
Vitamin C is an important antioxidant that can be synthesized in all mammals.
False
True or False
Syndrome of PICA is more closely related to a deficiency of phosphorus in livestock
False
True or False
Vitamin A, itself, is not found in plants, but only in animal tissues
True
True or False
Processing of grains decrease its rate of digestion in the rumen.
False
Match the macro minerals and their main symptoms when animals have severe deficiency.
Rickets in young or the adult form of osteomalacia
Calcium and phosphorus
Match the macro minerals and their main symptoms when animals have severe deficiency.
Grass tetany
Magnesium
Match the macro minerals and their main symptoms when animals have severe deficiency.
PICA syndrome
Sodium and Chlorine
Match the macro minerals and their main symptoms when animals have severe deficiency.
Muscle necrosis (rhabdomyolysis)
Potassium
Match the macro minerals and their main symptoms when animals have severe deficiency.
Shedding of wool/hair and reduced wool growth
Sulfur
True or False
Propionate is the only glucogenic VFA in the liver
True
True or False
When ruminal pH goes bellow 5, there is a shift of production between lactic acid and acetic/propionic acid.
True
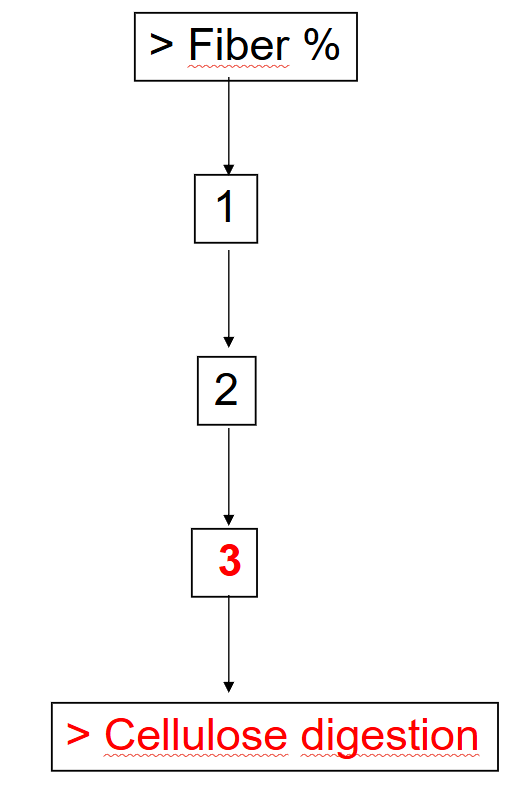
Fill in the blank
_______________ (< Rumination time, > Rumination time), _______________ (> salivation, < salivation), _____________ (> Ruminal pH, < Ruminal pH)
> Rumination time, > salivation, > Ruminal pH
why would a younger animal (smaller) be more feed efficient?
____ maintenance, → ____ feed can go to growth
Exception is animals small due to being ___
Chickens are more feed efficient → more _________ feeds
Less, more, sick, concentrate
Applied Equine Nutrition Fall
Forage/roughage
• Hay
• PastureConcentrate (concentrated sources
of nutrients)
• Compounded grains, protein sources,
micronutrients_________ crude protein
10 – 16%
Applied Equine Nutrition Fall
________________
• Hay
• Pasture___________ (concentrated sources
of nutrients)
• Compounded grains, protein sources,
micronutrients10 – 16% crude protein
Forage/roughage, Concentrate
Applied Equine Nutrition Fall
Roughages
Consume at least 1 pound per 100 pounds of bodyweight
(___)1.5% is ideal
Maximize time spent eating
__ hours per day in nature
Prevent boredom
Prevent gastric ulcers
1%, 16
Applied Equine Nutrition Fall
Roughages
Consume at least 1 pound per 100 pounds of bodyweight
(1%)____ is ideal
Maximize time spent eating
16 hours per day in nature
Prevent boredom
Prevent gastric ulcers
1.5%
Applied Equine Nutrition Fall
Roughages- Hay
Desirable attributes
___ in dust or mold
Cut ____ and leafy (____ to the
touch) instead of stemmy and
______Green = ______ __
Types
Legume- higher in crude
protein, calcium, energyAlfalfa, clover, perennial
peanut
Grass- lower in crude protein
and energyOrchardgrass, Timothy,
coastal bermudagrass...
Low, early, soft, coarse, vitamin A
Applied Equine Nutrition Fall
Roughages- Hay
Desirable attributes
Low in dust or mold
Cut early and leafy (soft to the
touch) instead of stemmy and
coarseGreen = vitamin A
Types
_______- higher in crude
protein, calcium, energy______, clover, perennial
peanut
_____- lower in crude protein
and energyOrchardgrass, Timothy,
coastal bermudagrass...
Legume, Alfalfa, Grass
Applied Equine Nutrition Fall
Roughages- Pasture
Higher ________ and
_______ content than hayAllows horses to ___
and ________Horses require 1-10
acres of pasture to
satisfy their nutritional
requirements1 = well cared for
pasture and soil10= unmanaged
pasture and soil
vitamin, mineral, walk, exercise,
Applied Equine Nutrition Fall
Roughages- Pasture
Higher vitamin and
mineral content than hayAllows horses to walk
and exerciseHorses require ____
acres of pasture to
satisfy their nutritional
requirements_ = well cared for
pasture and soil__= unmanaged
pasture and soil
1-10, 1, 10
Applied Equine Nutrition Fall
Feedstuffs
Concentrate- a concentrated form of nutrition or nutrients
“grain, pellets, sweet feed”
Sometimes necessary in diet, sometimes not
The non-forage part of the diet
Typically fed at 0.5 (0.2-0.7)% of bodyweight
0.5 pounds per 100 pounds bodyweight
Should NEVER exceed 50% of diet
Racehorses
Lack of owner knowledge
Lack of forage access
Applied Equine Nutrition Fall
Feedstuffs
__________- a concentrated form of nutrition or nutrients
“grain, pellets, sweet feed”
Sometimes necessary in diet, sometimes ___
The _________ part of the diet
Typically fed at 0.5 (______)% of bodyweight
___ pounds per 100 pounds bodyweight
Should _______ exceed 50% of diet
Racehorses
Lack of owner knowledge
Lack of forage access
Concentrate, not, non-forage, 0.2-0.7, 0.5, NEVER
Applied Equine Nutrition Fall
Feedstuffs
Concentrate- a concentrated form of nutrition or nutrients
“_____, ______, _____ ____”
Sometimes necessary in diet, sometimes not
The non-forage part of the diet
Typically fed at 0.5 (0.2-0.7)% of bodyweight
0.5 pounds per 100 pounds bodyweight
Should NEVER exceed 50% of diet
___________
Lack of owner _________
Lack of _____ access
grain, pellets, sweet feed, Racehorses, knowledge, forage
Applied Equine Nutrition Fall
Concentrates- Grains
Grains- ___, corn, barley
High in energy (_____)
Not balanced for _____ ____, vitamins, minerals
Require supplemental ______ and _______
Processed
________, rolling, _______, steam flaking, __________
Increased ________ (instant oats vs. traditional oats)
Reduced _____ life span
oats, starch, amino acids, vitamin, mineral, Cracking, crimping, micronizing, digestibility, storage
Applied Equine Nutrition Fall
Concentrates- Grains
Grains- oats, ____, ______
High in ______ (starch)
Not balanced for amino acids, _______, ______
Require _________ vitamin and mineral
Processed
Cracking, _____, crimping, _____ ________, micronizing
Increased digestibility (______ oats vs. _______ oats)
Reduced storage life span
corn, barley, energy, vitamins, minerals, supplemental, rolling, steam flaking, instant, traditional