Biology topic 4: Bioenergetics
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
What is the chemical equation for aerobic respiration?(1)
6 O2 + C6H12O6 → 6 H2O + 6 CO2
Name the sub-cellular structures where aerobic respiration takes place.(1)
mitochondria
Energy is released in respiration. Give two uses of the energy released in respiration.(2)
Muscle contraction, keeping warm
Describe two differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration in humans. Do not refer to oxygen in your answer.(2)
Anaerobic produces lactic acid and aerobic does not, aerobic produces carbon dioxide while anaerobic does not

What are the two products of anaerobic respiration in plant cells?(2)
carbon dioxide, ethanol
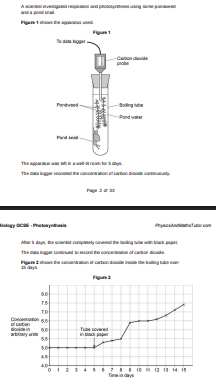
Explain why the concentration of carbon dioxide in the tube stayed the same between day 0 and day 5.(2)
The pondweed takes in CO2 for photosynthesis while snail and pondweed are respiring producing CO2.
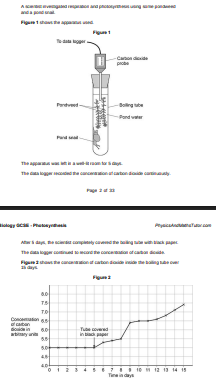
Suggest why the concentration of carbon dioxide increased between day 5 and day 10 (1)
There is no light so no photosynthesis while snail and plant are respiring releasing CO2.
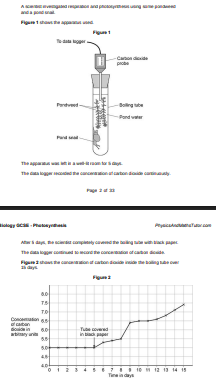
On day 10, the pond snail died. Explain why the death of the pond snail caused the concentration of carbon dioxide to increase after day 10.(3)
Snail is being decayed by bacteria therefore respiration of bacteria releases CO2.
Complete the word equation for photosynthesis. __________________ + _________________ → _________________ + oxygen (2)
carbon dioxide+water —>glucose+oxygen
Describe how energy for the photosynthesis reaction is gained by plants.(2)
Light is absorbed by chloroplasts.
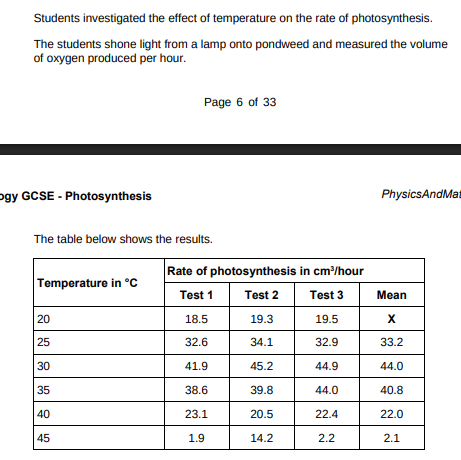
Calculate mean value X.(2)
18.5+19.3+19.5/3 = 19.1
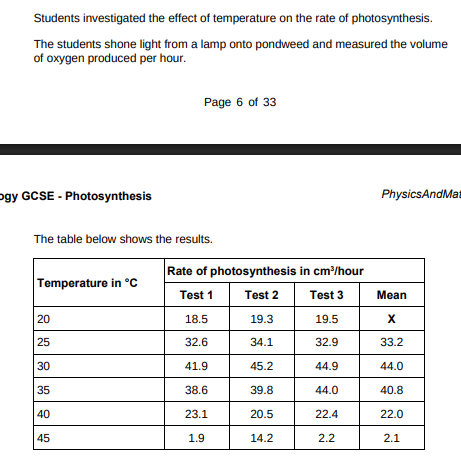
Draw a ring around the anomalous result in the table above.(1)
A ring around 14.2
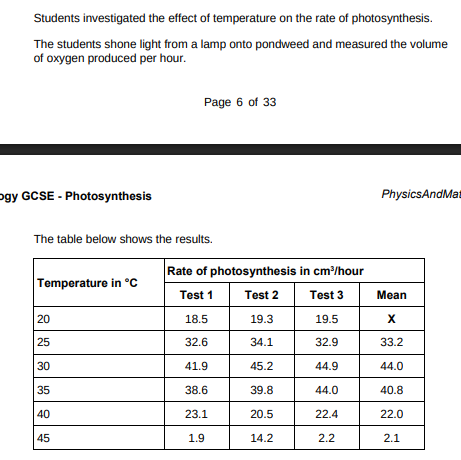
Suggest one possible cause of the anomalous result(14.2). (1)
Valaue was misread
How did the students deal with the anomalous result?(1)
Did not use it to calculate mean
Give one factor the students should have kept constant in this investigation.
pondweed species
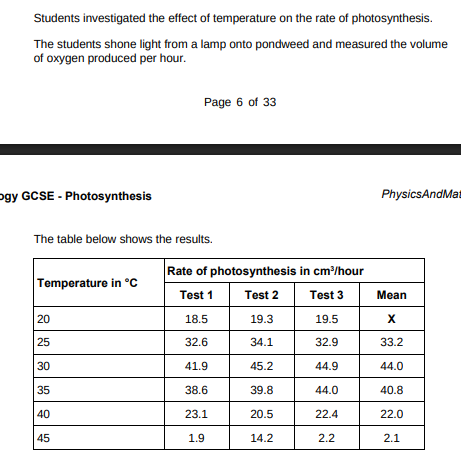
Why did the rate of photosynthesis decrease from 35 °C to 45 °C?(1)
Enzymes denature
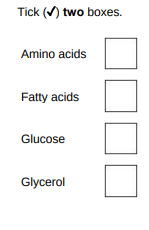
Which two products are formed when lipids are broken down?(2)
Fatty acids and glycerol
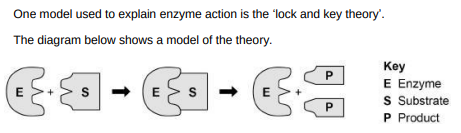
Explain the ‘lock and key theory’ of enzyme action. Use information from the diagram above in your answer.(3)
The enzyme binds to the substrate because they are complementary. The substrate is then broken down and the products are released.
There are many different types of lipase in the human body. Why does each different type of lipase act on only one specific type of lipid molecule?(1)
Because each active site has a specific shape

Describe how the students would find out if the liquid from the leaf contained glucose.(3)
Add benedict’s solution to the liquid and heat. If starch is present, the blue colour changes to brick red.
Describe how the students would find out if the liquid from the leaf contained starch.(2)
Add iodine solution to liquid. If starch is present colour changes to brown-orange to blue-black.
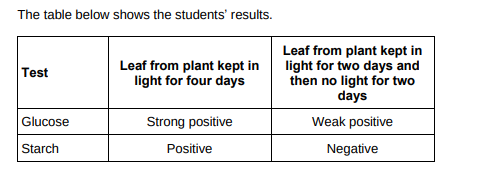
Explain why the leaf in the light for four days contained both glucose and starch.
Glucose from photosynthesis. Excess glucose is converted into starch.
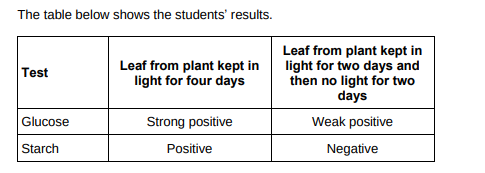
Explain why the leaf left in a cupboard with no light for two days did contain glucose but did not contain starch.(3)
Starch stores have been converted into glucose so it can be used for respiration because there is no light to make more glucose by photosynthesis.
Suggest one way the students could develop the investigation to find out more about glucose and starch production in plants.(1)
Test other species of plant
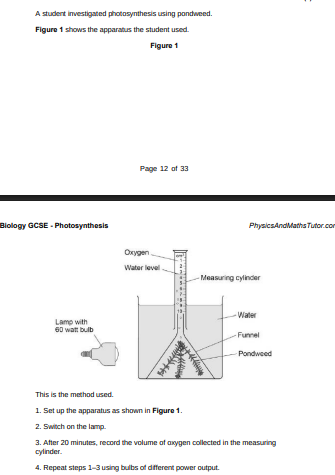
What was the independent variable in the investigation?(1)
Power output of bulb
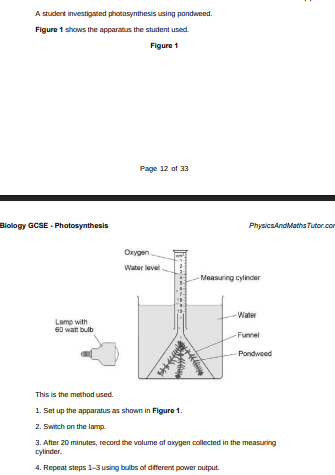
Suggest two ways the method could be improved so the results would be more valid(2)
Repeat and calculate mean, control distance of the bulb from the pondweed
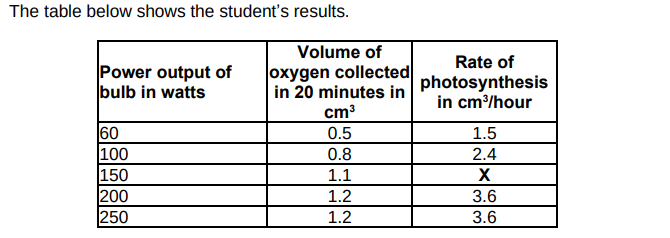
Calculate value X in the table above.(1)
3.3
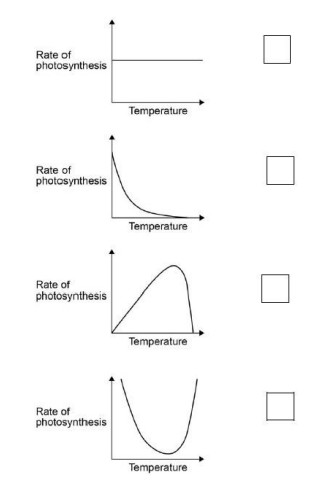
Which graph shows the effect of temperature on the rate of photosynthesis?(1)
3
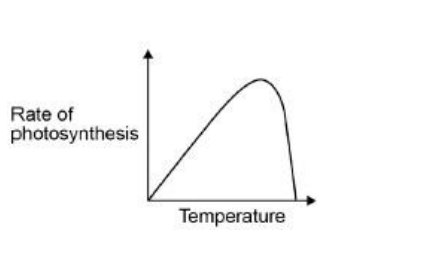
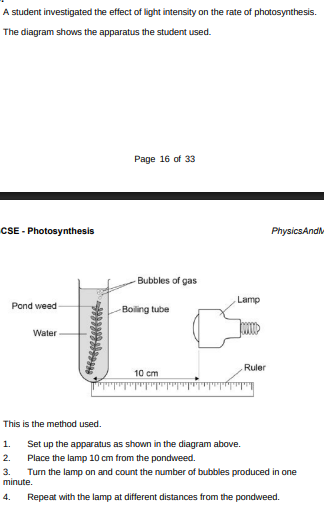
Complete the hypothesis for the student’s investigation. ‘As light intensity increases, _____________________________________ __________________________________________________________’(1)
rate of photosynthesis also increases
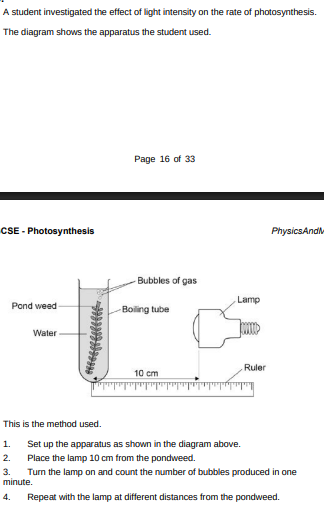
What was the independent variable in this investigation?(1)
Light intensity
The teacher suggests putting the boiling tube into a beaker of water during the investigation. Suggest why this would make the results more valid.(1)
Prevents temperature affecting photosynthesis
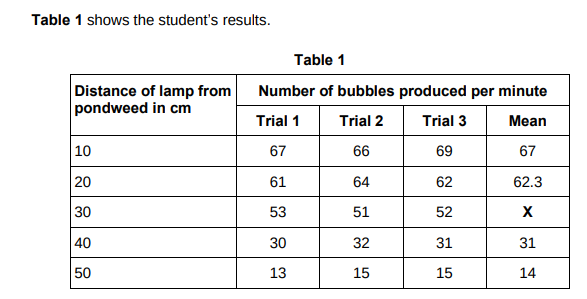
Calculate value X in Table 1.(1)
52
State one error the student has made when completing the results at 20 cm.(1)
Should be 62

What evidence in Table 1 shows that the data is repeatable?
The number of bubbles at each distance are similar.
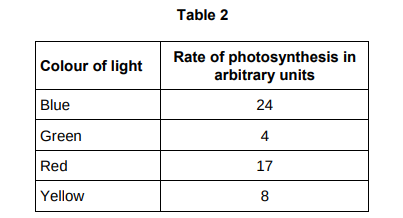
Give two conclusions from the table above (2)
Blue light gives the highest rate of photosynthesis, green light gives the lowest rate of photosynthesis.
The glucose produced in photosynthesis can be converted into amino acids to make new proteins for the plant.
Complete the sentences.
The glucose produced in photosynthesis can also be used in other ways. Glucose can be used in respiration to release _________________ . Glucose can be converted to cellulose to strengthen the _________________ . Glucose can be stored as _________________ .
energy, cell wall, starch
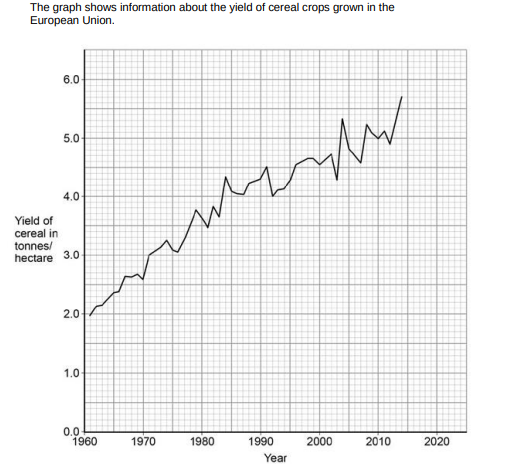
Calculate the increase in the yield of cereal between 1970 and 2010.(2)
5-2.6 = 2.4
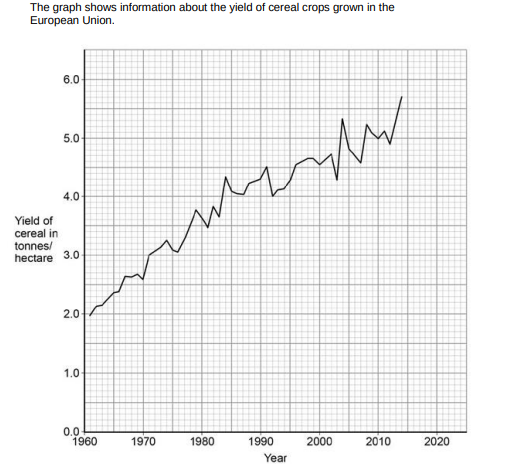
Estimate by what fraction the yield of cereal increased between 1971 and 1992. 1/10,1/3.1/2 or ¾ ? (1)
1/3
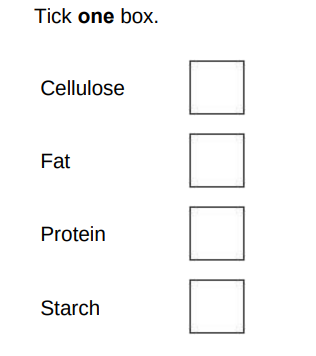
Which substance do plants make using nitrate ions?(1)
Proteins

The yield of cereal in 2004 was much greater than the yield in 2003. Suggest three possible reasons for the increased yield in 2004.(3)
a genetically-modified variety of seed was sown in 2004, more rain fell in spring and early summer in 2004, the mean summer temperature was lower in 2003
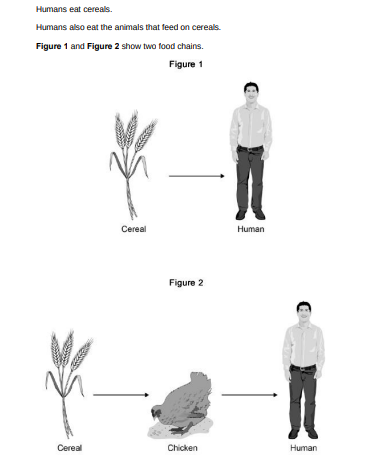
In Figure 1, 1 hectare of cereal crop would provide enough energy for 8 people for a year.
In Figure 2, 10 hectares of cereal crop would be needed to provide enough energy for only 1 person for a year.
It is much more efficient for humans to get energy by eating cereals than by eating chickens. Calculate how many times more efficient.(1)
80

In Figure 1, 1 hectare of cereal crop would provide enough energy for 8 people for a year.
In Figure 2, 10 hectares of cereal crop would be needed to provide enough energy for only 1 person for a year.
Why is it more efficient for humans to get energy by eating cereals than by eating chickens?(2)
chickens use energy for movement and for keeping warm, much of the food eaten by chickens is wasted as faeces

The algae make glucose by photosynthesis. Which two substances do the algae need for photosynthesis?(2)
carbon dioxide, water
What is the source of energy for photosynthesis?(1)
light
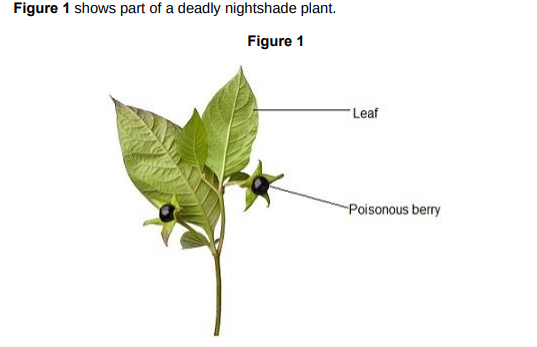
How will the poisonous berries help the deadly nightshade plant to survive?(1)
It will stop animals eating it

Suggest how the gorse plant is adapted to defend itself.(1)
thorns

The green leaves of the gorse plant make glucose for the plant to use. What are two uses of glucose in the gorse plant?(2)
For respiration, to store as starch
A student wanted to show that the leaves of a gorse plant contain glucose. The student crushed the leaves to extract the liquid from the cells. Describe the method the student could use to test the liquid from the cells for glucose. Include the result if glucose is present.(3)
Add Benedict’s solution and heat. If glucose is present, solution changes from blue to brick red.
The roots of the gorse plant have bacteria that turn nitrogen gas into nitrate ions. Explain why nitrate ions are needed by the gorse plant.(2)
Nitrate ions are needed to make amino acids which are neede for new cells.
The roots of gorse plants can be infected by honey fungus. The honey fungus produces tiny spores underground. Suggest how the honey fungus spores travel from the roots of an infected gorse plant to the roots of a healthy gorse plant.(1)
on the soil water
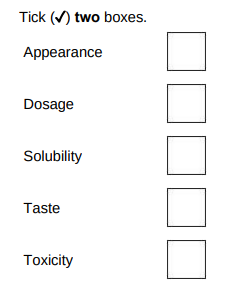
A drug can be extracted from gorse seeds. Doctors want to trial the drug from gorse seeds to see if it can treat diarrhoea. Which two factors must the doctors test the drug for in the trial?(2)
dosage, toxicity

In the trial some patients will take tablets made from gorse seeds and some patients will take tablets made from sugar. What are the tablets made from sugar called?
Placebos
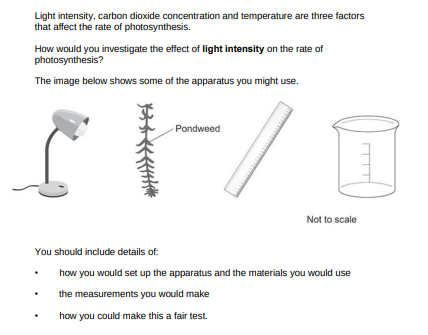
(6)
1)Set up by having the weed inside the water inside the beaker with light shining on it from a light at the closest distance possible.
2)Give the plant about 5 mins to get accustomed to the surroundings then count the amount of bubbles produced in the water during 1 minute.
3)After step 2, move the light back a small specific distance with the help of a ruler and repeat counting the bubbles for a minute after letting the plant accustom for 1 minute.
4)Move the lamp further again the same distance moved during step 3 and repeat.
P.S. Use same pondweed every time during the process and consider using a water bath to keep the temperature a control variable