Wildlife Information - Nationals 2021 Nebraska
1/190
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

191 Terms
carrying capacity
What is the term for the maximum number of animals that can live in the area sustainably for long periods of time?
Biological carrying capacity (there is also cultural carrying capacity - which is linked to how many animals can live with human impacts taken into account)
What type of carrying capacity is termed for the maximum number of animals within a given species that an area can support before that species or another species is negatively impacted?
Food
Water
Shelter/Cover
Space
What are the 4 things that determine the biological carrying capacity of a species?
Limiting Factor
The item that is in shortest supply (food, water, shelter, or space) will determine the carrying capacity of a population. What is the term of this shortest supply item?
False - it can change from season to season or year to year.
True or False - Biological carrying capacity is relatively fixed from year to year for a species.
Late spring to fall - this is when food is more abundant, as well as cover.
What times of year do we see biological carrying capacity usually the highest?
Predation
Starvation
Competition
Disease
Hunting
What are some ways that surplus animals in a population end up being lost from the population?
Cultural
In suburbs, humans feed deer. This causes more deer to live in the area and less winter mortality. This is an instance of biological carrying capacity being increased. This means there is now a ______ carrying capacity.
True. Population declines are usually now linked to other reasons. Wildlife managers will alter hunting and trapping allowances to correspond to population trends (reduce or stop hunting if population declines happen to significantly)
True or False: Hunting and trapping is seldom the reason for population declines of a wildlife species.
Loss of habitat or reduction of habitat quality
What is the main reason for population declines of wildlife species?
Migratory species - changing harvests like on waterfowl or mourning dove is linked to US Fish and Wildlife Service
What types of species cannot be managed or helped from population declines from the action of decreasing harvest (reduced hunting/fishing) by state agencies?
Predators
In rare situations, some population declines of some bird or mammal species might be due to very high amounts of _____ that are putting large pressure on the population of interest.
Decreased numbers of young bass caught
Many intermediate sized bluegill with poor health found
Lack of young bluegill seen
What are some signs that you need to decrease the harvest of bass from a waterway?
No young bass found in the waterway
Lots of young bluegill but a lot less intermediate sized bluegill
Most bass are small in size
What are some signs that you need to decrease the harvest of bluegill from a waterway?
When fish are in good condition and there are many small fish but not a lot of medium/large fish.
What is a way to know that one should decrease the amount of trout harvesting in a waterway?
Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease
What is the hemorrhagic fever that is showing up a lot in deer throughout the midwest US?
Via biting insects - biting fly/midge - they transmit the virus
How is epizootic hemorrhagic disease spread in the deer population?
Droughty - less rain means wetlands dry up a bit more - this leaves exposed mud edges of the wetland that are wet and are good habitat for the biting midges that spread the disease.
Also, as water dries up, deer congregate more around the remaining water sources and get more exposure to the midges
What type of conditions create more outbreaks of epizootic hemorrhagic disease: DROUGHTY or OVERLY WET
Bleeding (hemorrhagic) around orafices
Fever (deer go into water more to cool off when they have the disease; also many deer often die and are found in water as a result)
Lack of fear with humans
What are some symptoms of epizootic hemorrhagic disease in deer?
The cold temperatures kill off the midges that carry the disease.
Why does epizootic hemorrhagic disease significantly curtail or drop off in October?
Bluetongue
What is an alternate name for epizootic hemorrhagic disease or EHD?
False - it can affect both species of deer, but it does impact white-tailed deer more significantly
TRUE or FALSE: EHD only affects white-tailed deer and not mule deer.
False - it affects hooved animals primarily
True or False: EHD is known to infect humans.
True - but they rarely die from it
True or False: EHD is known to infect cattle.
EHD (Epizootic Hemorrhagic disease)
What disease is spread via organisms from the genus Culicoides?
White Nose Syndrome - it is a fungal disease
What disease is caused by an organism named Pseudogymnoascus destructans?
80%
What is the best estimate for the population declines in bats in northeastern US from white-nose syndrome?
30% or 55% or 80% or 95%
Because bats are K-selected species and only have 1 pup a year. So even those that survive don't usually reproduce as fast to compensate for the massive population losses
It is believed that bats impacted by white nose syndrome will not recover in their populations quickly. Why is that?
Indicator species
What term is used to describe an organism whose presence, absence, or abundance reflects a specific environmental condition?
If there is a lot of air pollution or acid rain, they don't survive well. So they indicate good air quality.
Lichens are considered to be indicator species. Why are they considered this?
False - it is fine to use indicator species. But just one species might not provide all information needed or the full story on an ecosystem. It is simply an indicator about general health.
TRUE or FALSE - Using a single indicator species represents ecosystem health well without other data.
Some sort of environmental condition that has solid scientific backing.
To be a good indicator species, the species' presence or absence needs to be linked to what?
Amphibians
Many used decline in amphibians as a sign of impacts of climate change. However, their declines were not distinctly linked to specific environmental conditions. In fact many environmental conditions are linked to amphibian declines. So they don't make the best indicator species.
What is an example of a species or group of species being used as an indicator improperly?
Pronghorn
What is the fastest terrestrial animal in North America?
Even-toed Ungulates - hooved animals with even numbers of toes/hooves - typically 2
These include deer, sheep, cattle, pigs, pronghorn
What types of mammals are part of the Order Artiodactyla?
Members of the mammal family Cervidae. Cervids are deer. Examples in Nebraska would include white-tailed deer, mule deer, and elk.
What are cervids?
Members of the mammal family Bovidae. Bovids are usually cattle or sheep like. Examples in Nebraska would include bison and bighorn sheep
What are bovids?
Wapiti
What is the alternate name for elk that is also its name from indigenous people?
Black-tailed deer
What is another name that some people call the mule deer?
White-tailed deer are found through the whole state. Mule deer are in the western 2/3rds of the state.
Which species of deer is found across the whole state and not as restricted in its distribution compared to the other species?: White-tailed Deer OR Mule Deer
Algae
What is the main producer of a food web in an aquatic system?
Plankton is just anything that floats in water and does not really propel itself through the water.
Phytoplankton is plankton that is plant-like and does photosynthesis and is a producer.
Zooplankton is plankton that is animal-like and does not do photosynthesis and is a consumer.
What is the difference between phytoplankton and zooplankton?
Oviparous - lay eggs and eggs hatch outside body
Ovoviviparous - lay eggs but eggs kept inside body. Eggs hatch inside body and then babies come out cloaca of snake (gives the appearance of live birth but it is really not)
Viviparous - not seen in snakes - but this is live birth - no eggs involved
What is the difference between a oviparous and ovoviviparous snake?
1) Shake tail really fast on ground - it can often sound similar to a rattlesnake
2) Flatten head out to look cobra like and bigger in stature
3) Fake death by rolling over and exposing their undersides and emitting a smell of foulness
Hognose snakes are small snakes but have a couple threatening displays that are unusual and help them to avoid predation. What are these displays?
False. They are diurnal - meaning they are active during the daylight hours
True or False: Hognose snakes are nocturnal.
Puma
Mountain lion
Cougar
What are the frequently used common names for the mammal with the scientific name of Puma concolor?
They are stalking predators. So wooded areas or areas with thicker vegetation allows for hiding from prey.
Mountain lions can be found in many habitats but they tend to prefer some wooded areas. Why is this preferred for them?
White-tailed and mule deer
What is the preferred prey item of cougars?
They prefer to be active at dusk and dawn. (They will be active in the day too or can be diurnal, but they are most linked to dusk and dawn).
Mountain lions are crepuscular. What does this mean?
Young pumas tend to roam more as they look to establish their own territories - particularly young males
What types of mountain lions are most likely to travel long distances and search for new territories, allowing the species to establish new populations and increase genetic drift?
Cat - The heel pad of a cat has 2 lobes on the top and 3 on the bottom. (Dogs have one on top and two in the back)
Is this a dog or a cat track?
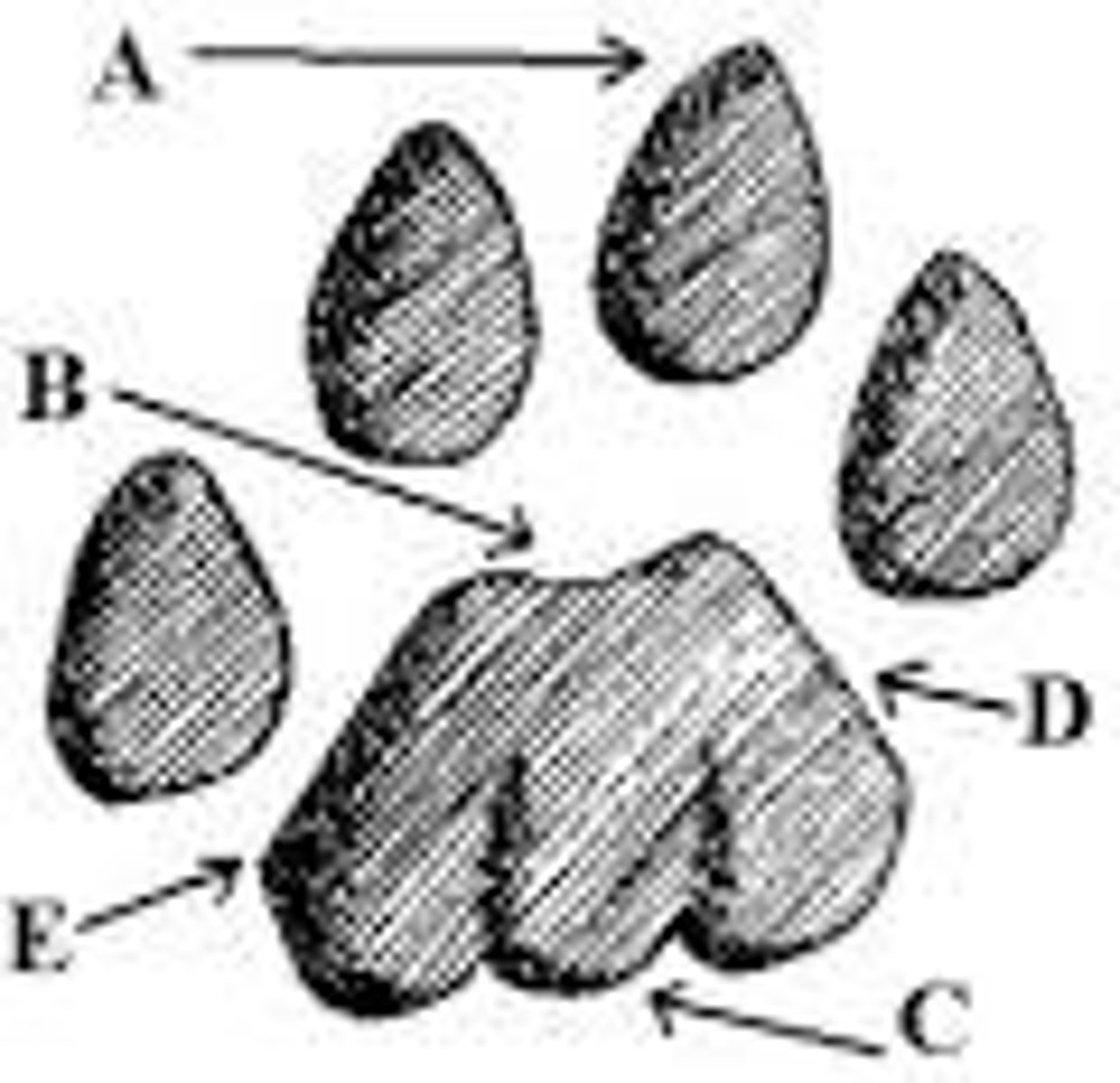
You usually should not see claw marks. The claws will be retracted.
In a mountain lion track, will you see claw marks or not?
Leave the animal a way to escape
Move slowly
Raise arms up to appear bigger
Lift up children to prevent them from running
Fight back if attacked
If you encounter a mountain lion in the wild, what are some things you should do?
Turn your back to the cat
Run away
Approach the mountain lion
Play dead if attacked (fight back - they will stop if they feel threatened based on prior attacks)
If you encounter a mountain lion in the wild, what are some things you should not do?
Poison ivy
What plant species is Toxicodendron radicans?
B) Anacardiaceae
Poison ivy is part of the plant family ____________.
A) Fagaceae
B) Anacardiaceae
C) Juglansaceae
C) Mangos and cashews
Mangos and cashews produce a compound that cause an itchy rash, just like poison ivy. (Some people who eat mangos and eat part of the skin accidentally will get rashes on their lips)
What other plants are also part of the plant family Anacardiaceae, which poison ivy is part of?
A) Corn and sugarcane
B) Walnuts and almonds
C) Mangos and cashews
It is the compound in poison ivy and plants in Anacardiaceae family that cause rashes and irritation.
What is urushiol?
False. Every part of these plants are poisonous. Burning the puts the poison compounds in the air and then they get into the lungs. This could lead to severe illness or death.
True or False: The best way to safely get rid of poison ivy, poison oak, or poison sumac in your yard is to selectively and safely burn it.
False. Really only humans get a rash (and maybe a couple of other primate species). Dogs and cats can carry the toxic compounds. So they may not get the rash but they can spread the compounds to humans that pet them.
True or False: Your pets (dogs and cats) that spend time outside can also get rashes from exposure to poison ivy.
An antimicrobial defense agent for the plant - keeping the plant safer from microbe harm/death.
Scientists believe that the development of urushiol (compound that causes rashes from poison ivy) likely did not initially evolve as a defense against humans. What is the reason it evolved that way?
The urushiol (compound of the toxins) bind to your skin's cells. It interferes with the body's ability to communicate with other cells. So it tricks your immune system into thinking your own cells are foreign and should be attacked.
Poison ivy is said to create a reaction know as a cell-mediated immune response. What does this mean it does to your cells to create the reaction it does?
Immunity to poison ivy
10-15% of people have _______ in association with poison ivy.
False. Actually, increased exposures will make it more likely that outbreaks will occur and be worse.
True or False. If you are not immune to poison ivy initially, repeated exposures to it over time will build you up an immunity to it.
False. It is typically found in early successional habitats in areas with disturbance or habitat edges
True or False. Poison ivy is typically found in mid- to late-successional plant communities
True. Birds eat berries. Deer and insects eat the leaves.
True or False. Poison ivy is a widely used food by forest wildlife like birds, deer, and various insects.
True!
True or False. Poison ivy comes in 30-40 different species in North America which means it can be found in leave, vine, small plant varieties.
True. Some individuals will climb right away as they grow from seedlings while others do not.
True or False. Scientists are not sure why poison ivy climbs like a vine.
Bur oak - (Quercus is the genus name for oaks and macrocarpa is latin for "large fruit" - referencing how it has a large acorn and acorn cap)
What is the plant known by the scientific name of Quercus macrocarpa?
False. It does tolerate wildfires better than other tree species. However, this is due to its thick and corky bark
True or False. Bur oak has a thin bark that makes it tolerate wildfires better than other trees.
Mast is food sources from trees/plants. Hard mast means it has hard texture. A good example is an acorn. It is a widely used food and is hard.
What is hard mast and what are examples of it?
Mast is food sources from trees/plants. Soft mast means it has soft texture. A good example is a berry. It is a widely used food and is soft in texture.
What is soft mast and what are examples of it?
4
How many chambers are found in a deer's stomach?
Rumen
Reticulum
Omasum
Abomassum
What are the names of the chambers of a deer's stomach?
An animal that has a 4 chambered stomach.
Deer and cow families are ruminants.
What is a ruminant?
Cud
Chewing your own cud means that the animal eats grass, swallows it and lets it digest a bit, then regurgitates it and chews it again (the cud)
A ruminant is also described as an animal that chews their own ____.
Grass is the main diet. This is a hard compound to digest to gain nutrients from it. This is because plants have lots of cellulose and their digestive system cannot break it down well. So they have to "eat" it twice to gain more nutrients from it and break it down.
Why does a ruminant chew its cud?
B) 1-2 hours
How quickly can a ruminant fill its stomach?
A) 20 -30 minutes
B) 1-2 hours
C) 24-30 hours
Rumen (the first chamber)
Which chamber of a ruminant is used for storage of recently eaten food?
Bacteria in its digestive system. The bacteria gain shelter and some nutrients from the animal. The animals gets nutrients from the grass that the bacteria was able to actually break down.
Ruminants cannot directly digest cellulose in plants themselves. However, the animal can still breakdown the cellulose. This is because the ruminant animal has a mutualistic relationship with _______.
Fermentation - they ferment sugars in the plant material. This is done in low oxygen. Amino acids are released.
What biological process is primarily being used by the bacteria in the digestive system of a ruminant to get them to breakdown cellulosic plant material?
Methane (fermentation occurs in low oxygen). So breaking down organic materials in low to no oxygen means making methane instead of carbon dioxide
In fermentation in a ruminant stomach, what major gas is made and expelled?
Reticulum - more nutrients will get absorbed here and more fermentation will occur
After grass is fermented in the rumen a bit, it is regurgitated as cud and the animal chews it more. What chamber of the stomach will the material go to after its second chewing?
Omasum
After the reticulum, the fine particles left over will now enter what stomach chamber?
Water
What is the main item now removed and absorbed from the materials in the omasum?
Abomasum - gastric juices continue to digest plant material
What is the final stomach chamber that material will enter and what happens here?
Small intestine
After the abomasum, where does the plant material move to next in the digestive system?
Rumen
Which stomach chamber is the largest of the 4?
Community
What is the term for all populations of different species found in an area?
Species richness
What is known as the number of species found in a community?
Species diversity
What is known as measuring both species richness and the relative number of each species?
Foundation species
What is the term for a species that plays an essential role in creating a community?
Keystone species
What is the term for a species that has a disproportionately large effect on the community compared to their relative abundance?
Invasive species
What is the term for a non-native species whose introduction causes environment and/or economic harm?
Ecological succession
What is the term for progressive changes in the composition of an ecological community over time?
Pioneer species
What is the term for the first species to populate an area during succession?
Climax community
What is the term for a community that has reached a steady state after ecological succession?
Equator
Communities near the _____ usually have the highest species richness across the globe.
Primary succession
If a plant community establishes in newly formed soil where plants were not established there prior, this is called _____ succession.
Secondary succession
If a plant community establishes in areas where it was previously occupied by living things prior to the disturbance, this is called _____ succession.