macromolecules
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Organic Compounds
Compounds that contain CARBON are called organic.
Macromolecules are large organic molecules.
Also called POLYMERS.
Made up of smaller “building blocks” called MONOMERS.
Examples:
1. Carbohydrates
2. Lipids
3. Proteins
4. Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA)
Carbohydrates
Small sugar molecules to large sugar molecules.
Examples:
A. monosaccharide
B. disaccharide
C. polysaccharide
Monosaccharide
Monosaccharide: one sugar unit
Examples: glucose (C6H12O6)
deoxyribose
ribose
Fructose
Galactose
Disaccharide
Disaccharide: two sugar unit
Examples:
Sucrose (glucose+fructose)
Lactose (glucose+galactose)
Maltose (glucose+glucose)
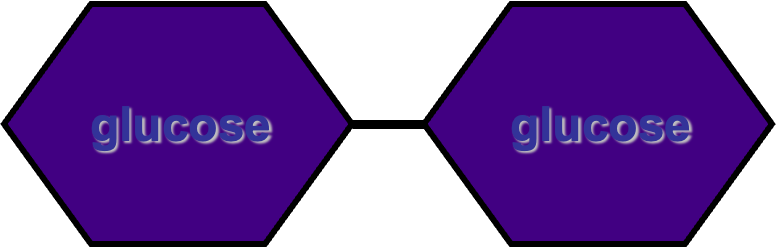
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide: many sugar units
Examples: starch (bread, potatoes)
glycogen (beef muscle)
cellulose (lettuce, corn)
Lipids
General term for compounds which are not soluble in water.
Lipids are soluble in hydrophobic (water hating) solvents.
Remember: “stores the most energy”
Examples: 1. Fats (Fatty acids)
2. Phospholipids
3. Oils
4. Waxes
5. Steroid hormones
6. Triglycerides
Six functions of lipids:
1. Long term energy storage
2. Protection against heat loss (insulation)
3. Protection against physical shock
4. Protection against water loss
5. Chemical messengers (hormones)
6. Major component of membranes (phospholipids)
Fatty Acids
There are two kinds of fatty acids you may see these on food labels:
1. Saturated fatty acids: no double bonds (bad)
2. Unsaturated fatty acids: double bonds (good)
Healthier fatty acids: unsaturated
State at room temperature: liquid (mostly)
Bonding: At least one double bond or more
Examples of food that contain FA’s:
Avocado, olive oil, natural PB
Proteins (Polypeptides)
Made of Amino acids (20 different kinds of aa) bonded together by peptide bonds (polypeptides).
Six functions of proteins:
1. Storage: albumin (egg white)
2. Transport: hemoglobin
3. Regulatory: hormones
4. Movement: muscles
5. Structural: membranes, hair, nails
6. Enzymes: cellular reactions
Four levels of protein structure:
A. Primary Structure
B. Secondary Structure
C. Tertiary Structure
D. Quaternary Structure
* Only in their tertiary and quaternary forms are they functional.
Nucleic acids
Two types:
a. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA double helix)
b. Ribonucleic acid (RNA-single strand)
Nucleic acids are composed of long chains of nucleotides linked
Nucleotides include:
phosphate group
pentose sugar (5-carbon)
nitrogenous bases:
adenine (A)
thymine (T) DNA only
uracil (U) RNA only
cytosine (C)
guanine (G)
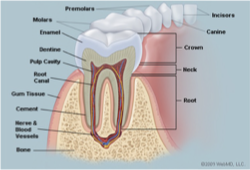
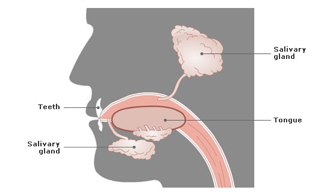
TEETH
Begin the process mechanical digestion (breaking the food down into smaller more manageable pieces) to assist in swallowing;
chopping, tearing and grinding
Each tooth is designed to complete a specific task ex. Canine as pointed and sharp to help tear, molars are flat to grind.
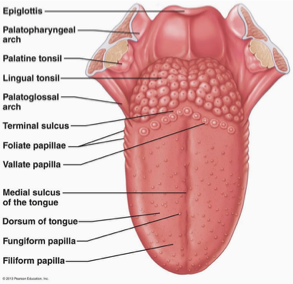
TONGUE
plays the role of moving
the food around the mouth
Taste - papillae (upper surface of the tongue, house the taste buds that allow us to taste food)
5 taste bud categories – salty, sweet, sour, bitter, umami
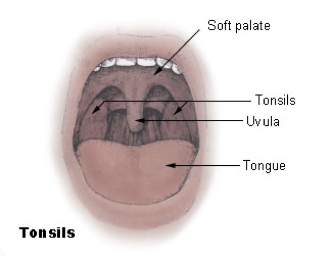
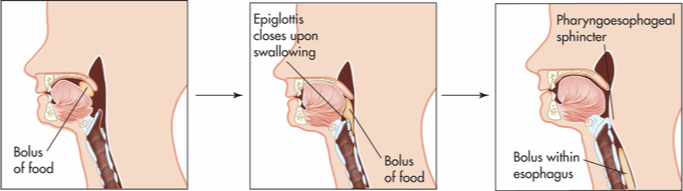
UVULA
hanging from the middle of the back edge of the soft palate
prevents food from entering the nasopharynx (or nose) during swallowing
SALIVA
clear liquid secreted into the mouth by the salivary glands and mucous glands of the mouth
moistens the mouth and lubricates food
assist in the chemical process of starch digestion by the enzyme amylase
BOLUS
round mass of food that has been chewed to the point of swallowing
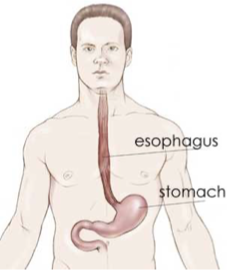
ESOPHAGUS
Tube connecting the pharynx to the stomach
approximately 24 cm long; lined with circular and longitudinal muscles which work to move food in ONE direction (down)
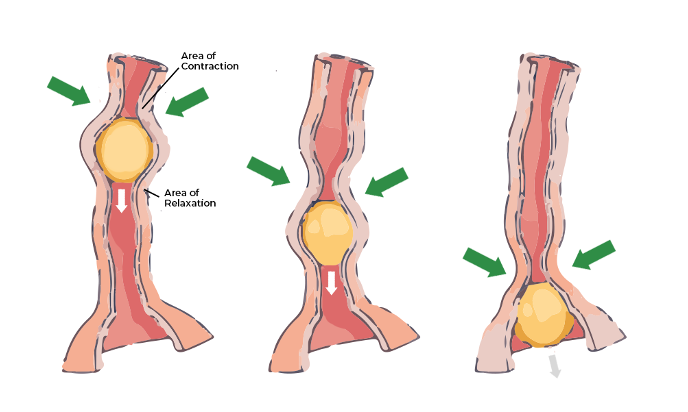
PERISTALSIS
symmetrical contraction of muscles which moves in a wave down the esophagus to help propel food through the digestive tract – uni-direction (one direction)
STOMACH
Muscular J shaped organ where food is temporarily stored while further chemical and mechanical digestion happens
walls are folded to allow distension
lined by gastric glands which secrete gastric juices that aid in chemical digestion (HCl, salts, enzymes, water and mucous) stimulated by the presence of food
mucus lines and protects the surface of the stomach from the acidic gastric juice
3 layers of muscle that relax and contract to churn stomach contents
CHYME
thick liquid of partially digested food mixed with gastric juices
CARDIAC SPHINCTER
muscular valve at the junction of the esophagus and the stomach; (top of the stomach)
controls the backflow of stomach contents back into the esophagus
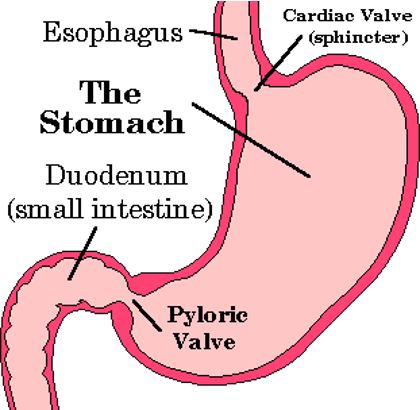
PYLORIC SPHINCTER
muscular valve at the lower end of stomach at the entrance of the small intestine.
when closed helps keep the food in the stomach

DUODENUM - SMALL INTESTINES
(the first part of the small intestine; “C” shaped)
Chemical digestion of chyme begins here
Bile from the gallbladder and digestive juices from the pancreas mix in here.
JEJUNUM- SMALL INTESTINES
Follows the duodenum, approximately 2.5m long, contains many more folds than the duodenum
The lining of the jejunum is specialized for absorption
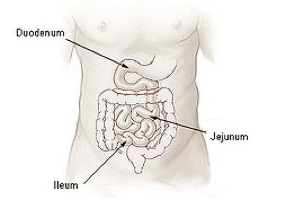
ILEUM SMALL INTESTINES
3m long, functions to absorb nutrients and to push undigested food into the large intestine
Mainly absorbs B12 and bile salts and anything left over that has not been absorbed
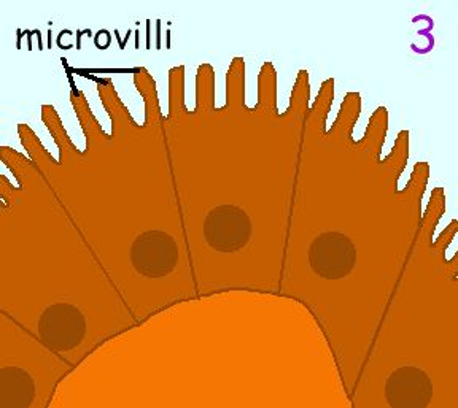
VILLI SMALL INTESTINES + MICROVILLI
tiny finger like projections that increase the surface area of the intestines.
MICROVILLI - each villi is in turn covered with many fine brush like microvilli that further increase the surface area
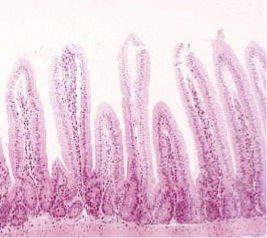
LARGE INTESTINE
absorb nearly 90% of water from the alimentary canal;
contains anaerobic bacteria to help digest undigested material;
leftover material is referred to as feces which is pushed by muscular contractions into the rectum for disposal
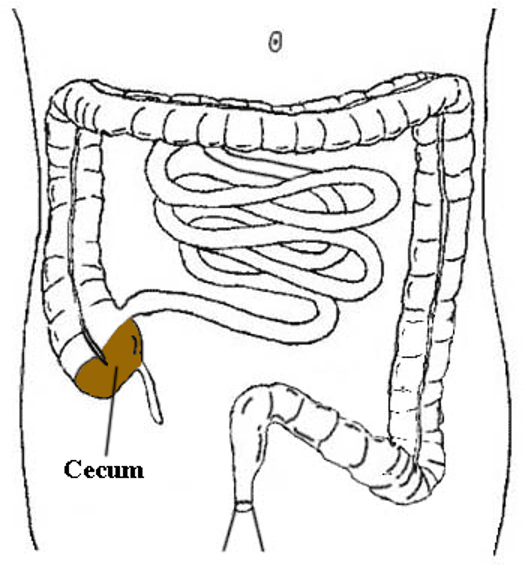
CECUM
the cavity in which the large intestine begins and into which the ileum opens; the appendix is an offshoot of the cecum
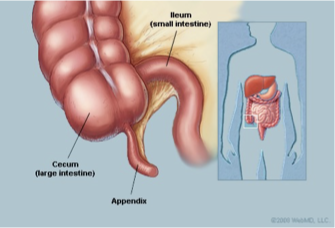
APPENDIX
finger like projection at the end of the cecum; no known function any longer
-vestigial feature
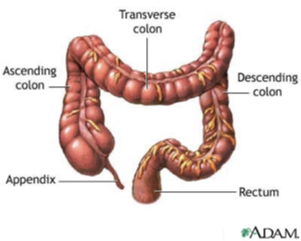
ACENDING, TRANSVERSE AND DESCENDING COLON
ASCENDING COLON - part of the large intestine that ascends from the cecum to the transverse colon
TRANSVERSE COLON - part of the large intestine that extends across the abdominal cavity and joins the ascending to the descending colon
DESCENDING COLON - part of the large intestine that descends from the transverse colon
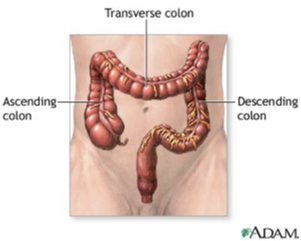
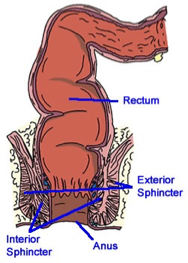
RECTUM, ANAL CANAL AND ANUS
RECTUM - the final part of the alimentary canal where waste is stored before being eliminated
ANAL CANAL - the terminal part of the large intestine
ANUS - the excretory opening at the end of the alimentary canal
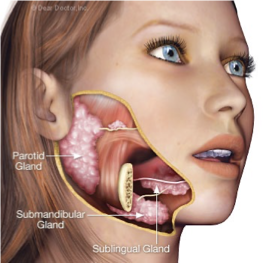
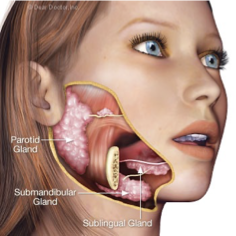
SALIVARY GLANDS` - Accessory Organs
PAROTID GLAND - the largest of the salivary glands located slightly below and in front of the 2 ears; a duct connects the gland to the oral cavity; produces the majority of saliva
SUBLINGUAL GLAND - small salivary glands located under the tongue that secrete saliva directly into the mouth through a series of pores
SUBMANDIBULAR GLAND -pair of glands located beneath the jaw which connect by a duct to the oral cavity;
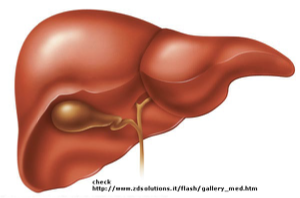
LIVER- Accessory Organs
Located in the right upper quadrant just below the diaphragm
Produces bile, an alkaline substance which aids in digestion of fats acting as an emulsifying agent (breaks fat down into smaller fat droplets that are more readily absorbed)
Some of the bile drains directly into the duodenum
GALLBLADDER - Accessory Organs
Stores and concentrates bile produced by the liver and releases it through the common bile duct to the duodenum.
Attached on underside of liver
Humans can live without a gallbladder
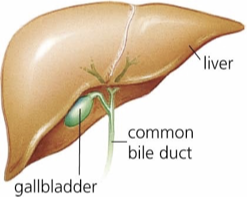
PANCREAS - Accessory Organs
Glandular organ producing several important hormones, including insulin (used to move glucose from the blood into tissues) and glucagon (used to mobilize glucose from the tissues to the blood)
Secretes pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that pass to the small intestine and break down many macromolecules.
Enzymes
* Digestive enzymes help the body break down food.
* Different enzymes, each with specific functions, are produced in various parts of the digestive tract.
* Incomplete digestion can contribute to ailments such as:
* Flatulence, bloating, belching
* Food allergies, nausea, bad breath
* Bowel problems, stomach disorders
* Digestive enzymes mainly handle the chemical breakdown of food and make up a large part of digestive secretions.
* The human body produces around 22 different enzymes involved in digestion.
Mouth
Saliva contains the enzyme salivary amylase. This enzymes breaks starch into smaller sugars and is stimulated by chewing. It is important to chew food thoroughly as this is the first stage of the digestive process.
Stomach
The stomach is responsible for the digestion of protein and ionization of minerals. The parietal cells of the stomach secrete hydrochloric acid (gastric acid).
Pepsin is secreted by the stomach and breaks up proteins
Small Intestine
The small intestine has three segments and secretes various digestive substances.
It also receives enzymes and secretions from the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder.
Duodenum – primarily absorbs minerals.
Jejunum – absorbs water-soluble vitamins, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Ileum – absorbs fat-soluble vitamins, fats, cholesterol, and bile salts.
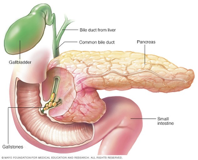
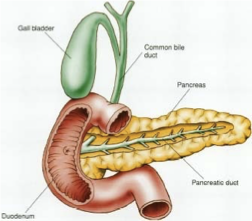
Pancreas
The pancreas produces digestive enzymes that act in the small intestine and play a major role in digestion.
It secretes about 1.5 litres of pancreatic juice per day.
Pancreatic enzymes include:
Lipases – digest fats, oils, and fat-soluble vitamins.
Amylases – break down starches and carbohydrates into smaller sugars like maltose.
Proteases – break down proteins into smaller amino acids.
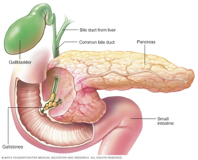
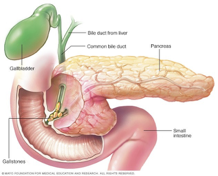
Liver and Gall Bladder
The liver produces bile that is either stored by the gallbladder or secreted into the small intestine.
Bile emulsifies fats and fat-soluble vitamins.
It also helps keep the small intestine free from parasites.
The liver metabolises proteins, carbohydrates and cholesterol and is responsible for the detoxification of toxins, drugs and hormones.
Peptic Ulcers
Ulcers occur when stomach or duodenum tissues become inflamed due to a weakened mucous lining.
Most ulcers are caused by Helicobacter pylori, an acid-resistant bacterium that prevents mucus production.
Symptoms: abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, loss of appetite.
Treatment: antibiotics to eliminate bacteria and medications to reduce acid production.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): general term for diseases causing intestinal inflammation.
Chronic conditions that cannot be cured but can be treated.
Crohn’s disease – can affect any part of the digestive tract
Symptoms: diarrhea, abdominal cramping, fatigue, blood in stool, reduced appetite
Treatment: medications to reduce signs and symptoms
Ulcerative colitis – affects the colon
Symptoms: loose/bloody stool, cramps, abdominal pain
Treatment: surgery to remove affected colon section, medications to reduce symptoms
Constipation
Bowel movements are reduced to 3 or less per week. Stools are dry, small and difficult to eliminate.
Can be caused by inadequate water intake, lack of physical activity or healthy diet, and lack of good nerve and muscle function in the bowel
Treatment: Increase hydration and fiber
Hepatitis
Hepatitis: inflammation of the liver; three types – A, B, and C.
Symptoms: fever, malaise, loss of appetite, diarrhea, nausea, abdominal discomfort, dark urine, jaundice (yellowing of skin/eyes).fever, mal
Treatment: no specific cure; manage symptoms.
Hepatitis C:
Caused by the Hepatitis C virus, a bloodborne virus.
Transmission:
Sharing injection equipment (drug use)
Reuse/inadequate sterilization of medical equipment (syringes/needles)
Transfusion of unscreened blood products
Vaccine: none available
Hepatitis A:
Contracted from contaminated food or water.
Vaccine: available
Hepatitis B:
Potentially life-threatening liver infection.
Transmission: infected bodily fluids
Vaccine: available
Cirrhosis
Chronic disease of the liver that occurs when scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue and prevents the liver from functioning properly.
Chronic alcoholism and hepatitis C are most common causes
Treatment: liver transplant
Gall bladder Stones
Cholesterol in the bile can precipitate out of the bile and form crystals. These crystals grow and become gall stones
Factors that can cause stones are obesity, heredity and alcohol intake
Can be treated with medications or ultrasound shock waves
If the gallstone problem is serious, the entire gall bladder may need to be surgically removed.
Common Procedures
Barium swallow:
X-ray using liquid barium to visualize the esophagus and upper digestive tract (throat, esophagus, stomach)
Helps detect swallowing issues, blockages, ulcers, or tumors
Endoscopy:
Medical procedure using an endoscope (thin, flexible tube with light and camera)
Can visualize:
Enzyme activity
Structure of digestive tract
Digestion in action
Can also remove polyps or take samples for biopsy