ap world history unit 3 vocab
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:42 AM on 11/9/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
1
New cards
empiricism
an early scientific method which insisted upon the collection of date to back up
2
New cards
Peace of Augsburg
resulted in conflict between Lutherans and Roman catholic
Allowed each german state to choose wether its ruler would be catholic or lutheran
Allowed each german state to choose wether its ruler would be catholic or lutheran
3
New cards
holy synod
composed of clergymen overseen by a secular office who answered to the tsar
4
New cards
The elect
those prestined to go to heaven
ran the community which was based on plain living, simple, church buildings, and governance by the elders of the church
ran the community which was based on plain living, simple, church buildings, and governance by the elders of the church
5
New cards
serfdom
the state of being a serf (were peasant who received a plot of land and protection from a noble
6
New cards
absolutism
directed by one source of power, the king rules with complete power
7
New cards
Safavids
A Shi'ite Muslim dynasty that ruled in Persia (Iran and parts of Iraq) from the 16th-18th centuries that had a mixed culture of the Persians, Ottomans, and Arabs.
8
New cards
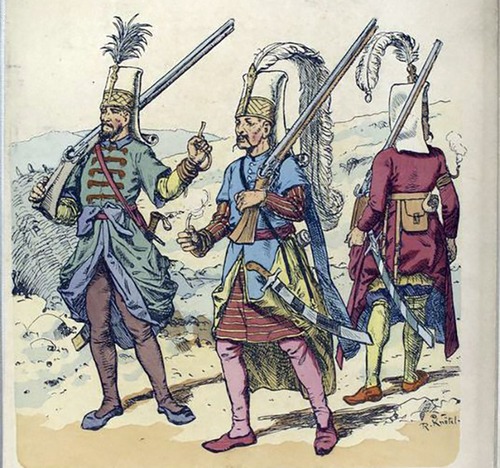
Janissary
☆ elite Ottoman guard (trained as foot soldiers or administrators) recruited from the Christian population through the devshirme system, that often converted to Islam
☆ utilized gunpowder weapons
☆ utilized gunpowder weapons

9
New cards
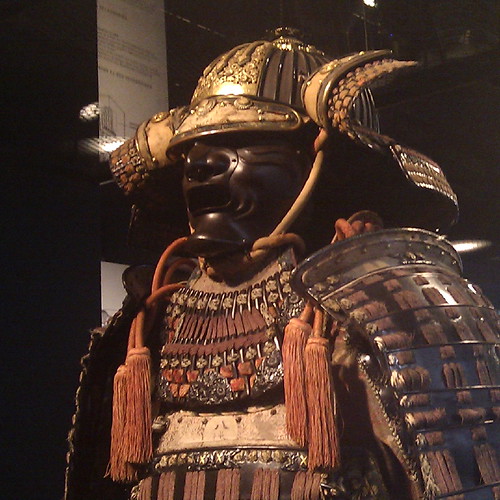
samurai
class of salaried warriors in feudal Japan who pledged loyalty to a noble called a daimyo (who in turned pledged loyalty to a shogun) in return for land or rice payments

10
New cards
Divine Right
☆ belief that a ruler's authority comes directly from God
☆ the idea that monarchs are God's representatives on earth and are therefore answerable only to God.
☆ the idea that monarchs are God's representatives on earth and are therefore answerable only to God.

11
New cards
absolute monarchy
system of government in which the head of state is a hereditary position and the king or queen has almost complete power

12
New cards
zamindars
Mughal empire's taxation system where decentralized lords collected tribute/taxes for the emperor
13
New cards
Taj Mahal
☆ beautiful mausoleum (tomb) at Agra (India) built by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan (completed in 1649) in memory of his favorite wife
☆ illustrates syncretic blend between Indian and Arabic architectural styles
☆ illustrates syncretic blend between Indian and Arabic architectural styles
14
New cards
tax farming
☆ tax-collection system utilized by the Ottoman Empire to generate money for territorial expansion
☆ the government hired private individuals to collect taxes
☆ the government hired private individuals to collect taxes
15
New cards
Protestant Reformation
☆ religious movement begun by German monk Martin Luther who began to question the practices of the Catholic Church beginning in 1519
☆ split the Roman Catholic Church and resulted in the 'protesters' forming several new Christian denominations: Lutheran, Calvinist, and Anglican Churches (among many others)
☆ split the Roman Catholic Church and resulted in the 'protesters' forming several new Christian denominations: Lutheran, Calvinist, and Anglican Churches (among many others)

16
New cards
95 Theses
☆ arguments written by Martin Luther against the Catholic church. They were posted on October 31, 1517
☆ ultimately led to Martin Luther's excommunication and the Protestant Reformation
☆ ultimately led to Martin Luther's excommunication and the Protestant Reformation
17
New cards
Martin Luther
☆ a German monk who became one of the most famous critics of the Roman Catholic Church
☆ In 1517, he wrote 95 theses, or statements of belief attacking the church practices
☆ began the Protestant Reformation
☆ In 1517, he wrote 95 theses, or statements of belief attacking the church practices
☆ began the Protestant Reformation

18
New cards
Counter/Catholic Reformation
☆ the reaction of the Roman Catholic Church to the Protestant Reformation
☆ reaffirming the veneration of saints and the authority of the Pope (to which Protestants objected), ended sale of indulgences and simony, created Jesuits missionaries, but also the began the Inquisition
☆ reaffirming the veneration of saints and the authority of the Pope (to which Protestants objected), ended sale of indulgences and simony, created Jesuits missionaries, but also the began the Inquisition
19
New cards
Jesuits
☆ also known as the Society of Jesus; a teaching and missionary order to resist the spread of Protestantism (a result of the Counter Reformation)
☆ sent to China, Japan, and the New World to gain Catholic converts
☆ sent to China, Japan, and the New World to gain Catholic converts

20
New cards
indulgence
☆ a pardon given by the Roman Catholic Church in return for repentance for sins and payment
☆ "a way to reduce the amount of punishment one has to undergo for sins"
☆ "a way to reduce the amount of punishment one has to undergo for sins"

21
New cards
Simony
the buying and selling of church offices, seen as a corrupt practice, this practice was outlawed by the Catholic Church during the Counter Reformation
22
New cards
Thirty Years War
☆ a war that resulted from the Protestant Reformation (1618-1648 CE)
☆ occurred in the Holy Roman Empire between German Protestants and their allies (Sweden, Denmark, France) and the emperor and his ally, Spain who supported Roman Catholicism
☆ ended in 1648 after great destruction with Treaty of Westphalia
☆ occurred in the Holy Roman Empire between German Protestants and their allies (Sweden, Denmark, France) and the emperor and his ally, Spain who supported Roman Catholicism
☆ ended in 1648 after great destruction with Treaty of Westphalia
23
New cards
John Calvin
☆ 1509-1564
☆ french theologian who developed the Christian theology known as Calvinism
☆ attracted Protestant followers with his teachings
☆ believed in predestination
☆ french theologian who developed the Christian theology known as Calvinism
☆ attracted Protestant followers with his teachings
☆ believed in predestination

24
New cards
Shogunate
Japanese system of government under a shogun (military warlord), who exercised actual power while the emperor was reduced to a figurehead

25
New cards
Daimyo
Japanese feudal lord who commanded a private army of samurai; owed allegiance to the shogun

26
New cards
Ivan IV (the Terrible)
☆ Confirmed power of tsarist autocracy by attacking the authority of the boyars
☆ continued policy of expansion
☆ established contacts with western European commerce and culture.
☆ continued policy of expansion
☆ established contacts with western European commerce and culture.
27
New cards
justices of the peace
English local officials in the shires appointed by the crown and given wide authority in local government.
28
New cards
English Bill of Rights
It guaranteed certain rights to English citizens and declared that elections for Parliament would happen frequently. By accepting this document, they supported a limited monarchy, a system in which they shared their power with Parliament and the people.
29
New cards
Louis XIV
☆ (1638-1715) Known as the Sun King, he was an absolute monarch that completely controlled France
☆ One of his greatest accomplishments was the building of the palace at Versailles.
☆ One of his greatest accomplishments was the building of the palace at Versailles.
30
New cards
Romanov Dynasty
Dynasty that favored the nobles, reduced military obligations, expanded the Russian empire further east, and fought several unsuccessful wars, yet they lasted from 1613 to 1917.
31
New cards
daimyo
A Japanese feudal lord who commanded a private army of samurai
32
New cards
Tokugawa Ieyasu
☆ founder of the Tokugawa Shogunate which lasted from 1603 to 1867
☆ reunified Japan and established political unity in Japan
☆ reunified Japan and established political unity in Japan
33
New cards
Period of Great Peace
The Tokugawa Shogunate created this period in Japan known as the Edo Period by adopting a policy of isolation
34
New cards
Askia the Great
☆ Songhai ruler who made Islam official religion to unite his empire
☆ oversaw Songhai at its height
☆ oversaw Songhai at its height
35
New cards
tributes
wealth sent from one country or ruler to another as a sign that the other is superior
36
New cards
Henry VIII
☆ (1491-1547) King of England from 1509 to 1547
☆ his desire to annul his marriage led to a conflict with the pope, England's break with the Roman Catholic Church, and its embrace of Protestantism
☆ established the Church of England (Anglican) in 1532
☆ his desire to annul his marriage led to a conflict with the pope, England's break with the Roman Catholic Church, and its embrace of Protestantism
☆ established the Church of England (Anglican) in 1532

37
New cards
Edict of Nantes
document that granted religious freedom to the Huguenots
38
New cards
shariah
Islamic law