topic 8 - the cell membrane
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
membrane form
double layer phospholipid; fluid mosaic model
membrane function
controls traffic into and out of the cell
selective permeability
A property of a plasma membrane that allows some substances to cross more easily than others; maintains integrity inside the cell
how many models are there of the plasma membrane?
4 models; in 1915, 1925, 1935, and 1972
1st plasma membrane model (1915)
made by Charles Overton; proposed that the membranes are made of lipids because lipids passed through (the membrane) easily
phospholipids
an amphipathic molecule; has a phosphate head and fatty acid tails
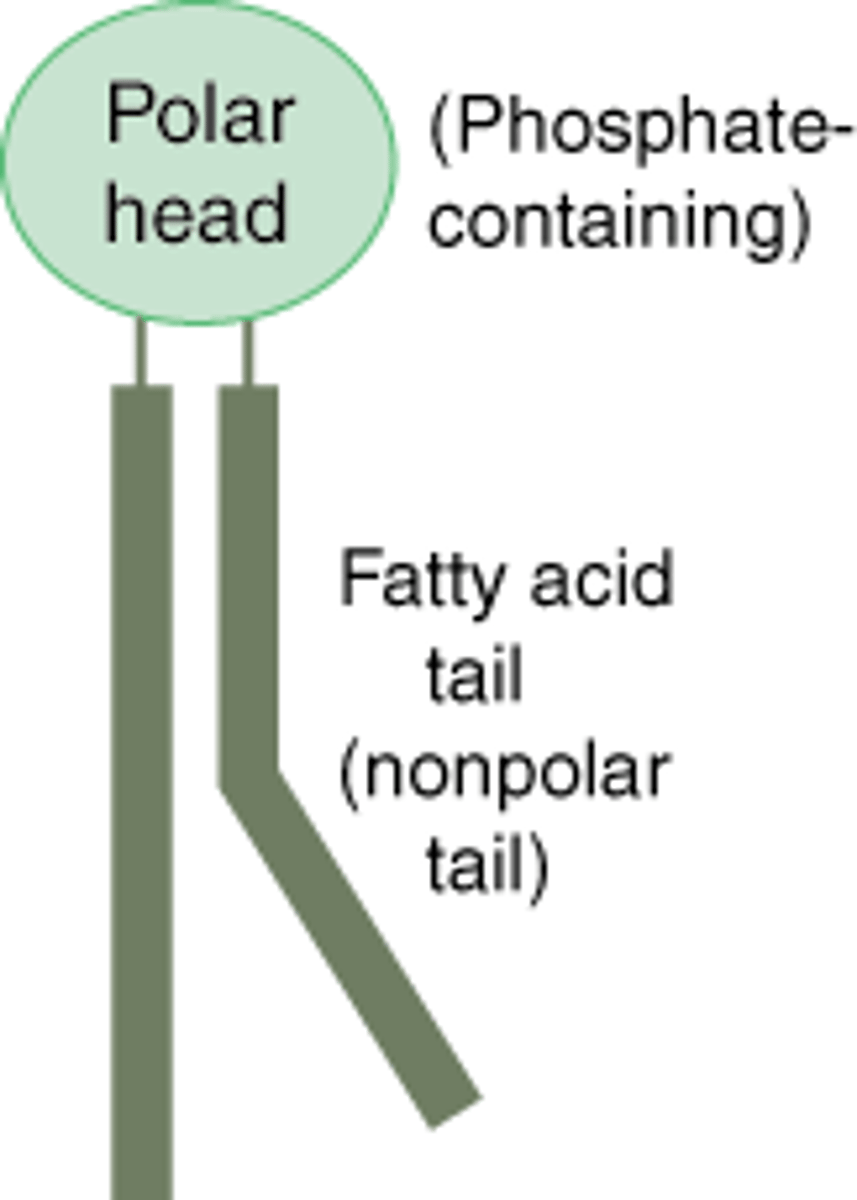
amphipathic molecule
a molecule with 2 sides: a hydrophilic & hydrophobic region
what is the phosphate head like?
it is negatively charged & hydrophilic
what is the fatty acid tail like?
it's made of nonpolar covalent bonds & is hydrophobic
2nd plasma membrane model (1925)
made by Gorter and Grendel; proposed a double layer (bilayer) of phospholipid. The outsides were philic and insides were phobic.
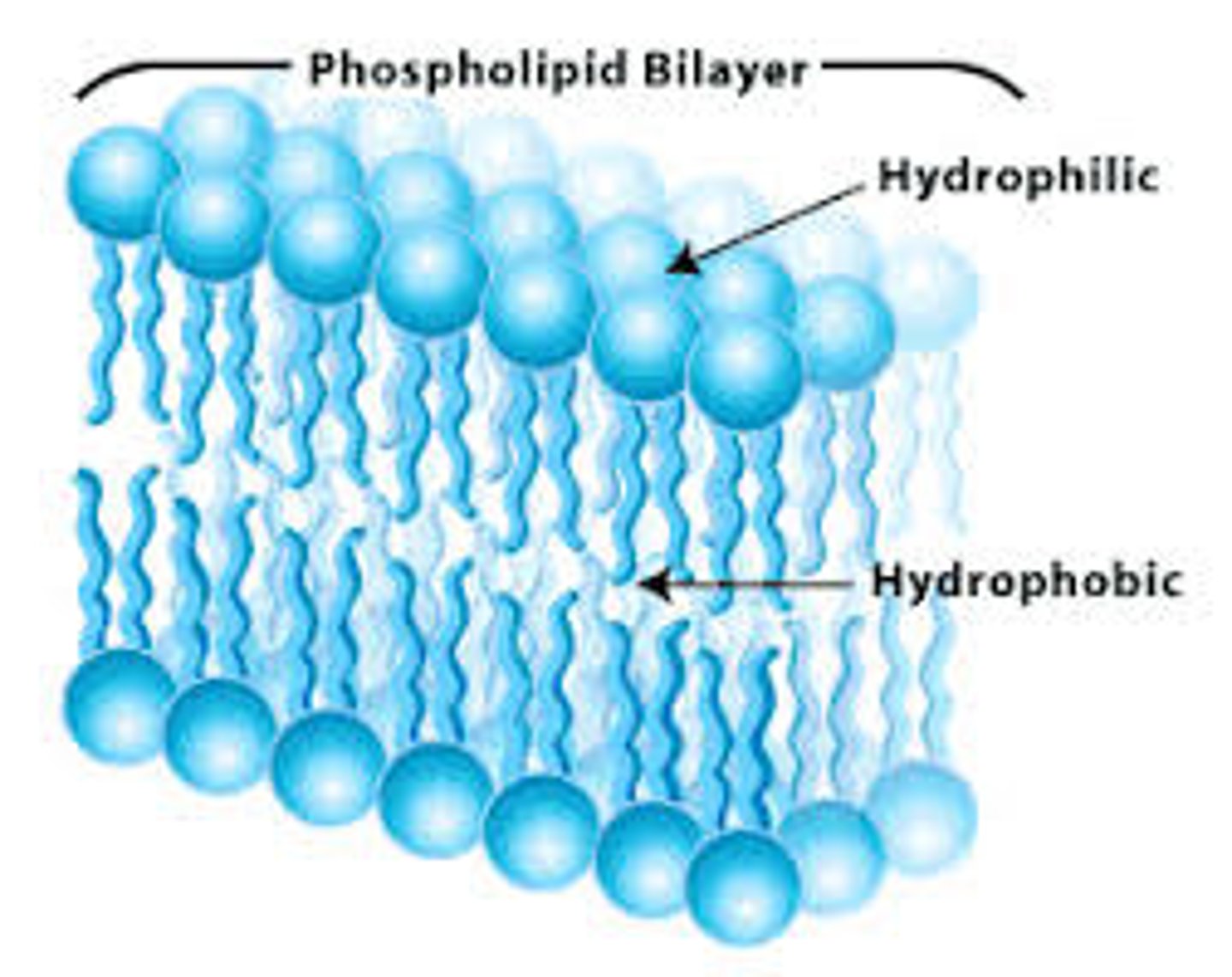
the sandwich model
the 3rd plasma membrane model made by Davson and Danielli in 1935; proposed that phospholipids may also be proteins since they don't actually adhere well to water
the fluid mosaic model
the 4th plasma membrane model made by Singer and Nicholson in 1972; proposed proteins floating in a sea of lipids but the proteins have to be amphipathic too
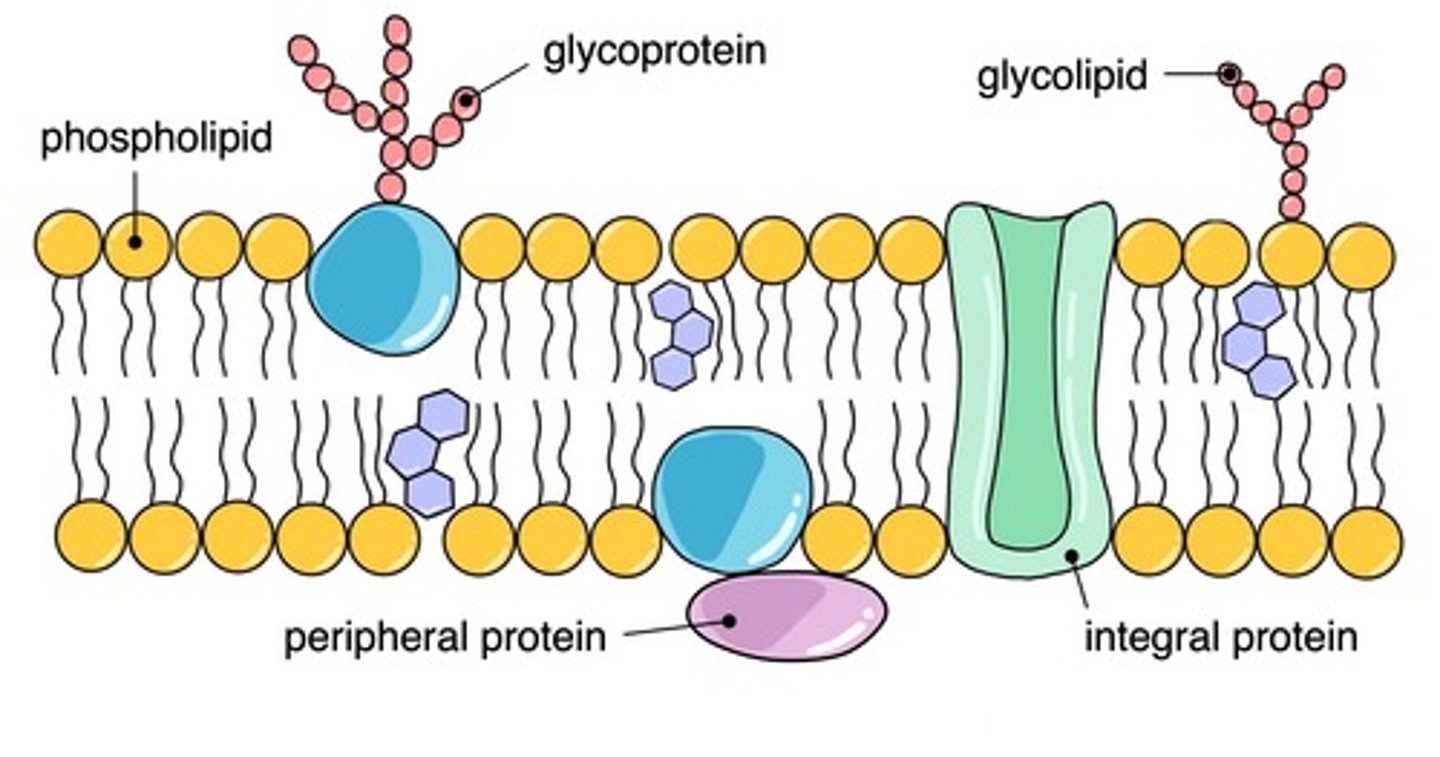
what does "fluid" mean in the fluid mosaic model?
the model shows that membranes can't be rigid, they should be "fluid" otherwise the cell wouldn't work
what does "mosaic" mean in the fluid mosaic model?
the model contains protein "tiles"
phospholipids (in FMM)
they sway back & forth. They are unsaturated in plant cells.
peripheral proteins (in FMM)
probably attached to the cytoskeleton or extracellular matrix (ECM); on edges
extracellular matrix
The substance in which animal tissue cells are embedded, consisting of protein and polysaccharides.
integral proteins (in FMM)
of several kinds: transmembrane, transport, channel, etc. They are proteins that are permanently embedded within the cell membrane. some proteins fully cross the cell membrane & others are partially in the hydrophobic section
Transmembrane (integral) proteins
cross the cell membrane & fully go through
Cholesterol
in animal cells, it prevents stiffening at low temperatures but it also helps prevent melting at high temperatures
carbohydrate tags
receptors that provide information on where a certain molecule was made to go
glycolipid
a lipid with one or more covalently attached carbohydrates
channel protein
a specialized protein that allows specific substances to enter or exit cells
transport protein
protein that moves substances or wastes through the plasma membrane