CH. 12 Personality
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Personality
a person's distinctive and stable way of thinking, feeling, and behaving.
behavioral genetics
the study of the impact of genes (nature) and environment (nurture) on personality and behavior.
psychodynamic theory of personality
an explanation of personality, based on the ideas of Sigmund Freud, that emphasizes unconscious forces and early childhood experiences.
psychic determinism
the belief that all thoughts and behaviors, even those that seem accidental, arbitrary, or mistaken, are determined by psychological forces.
Freudian slips
verbal or behavioral mistakes that reveal unconscious thoughts or wishes.
superego
the part of the mind that opposes the id by enforcing rules, restrictions, and morality.
ego
the part of the mind that serves as a realistic mediator between the id and superego.
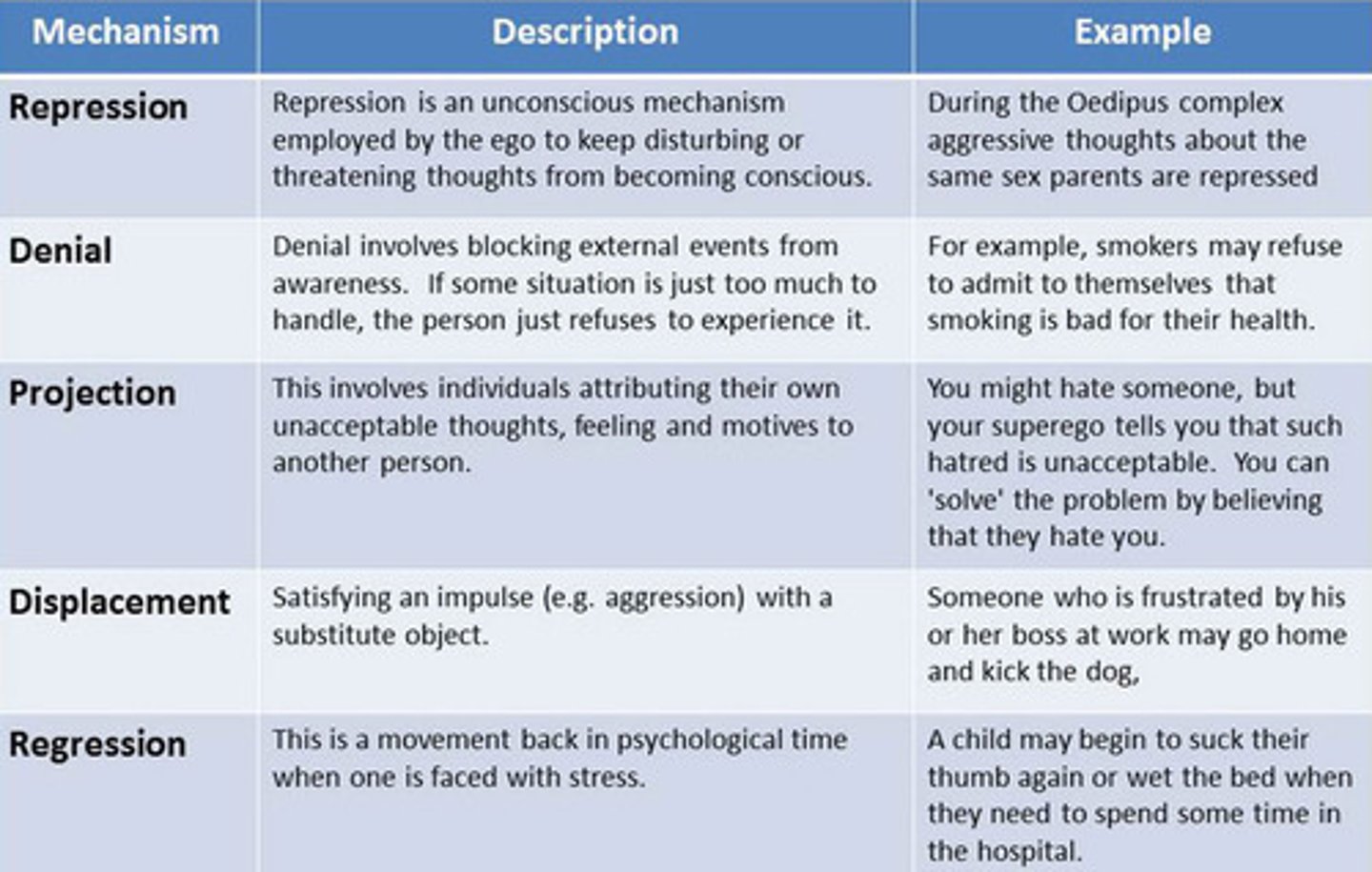
defense mechanisms
techniques used by the ego to manage conflict between the id and superego.
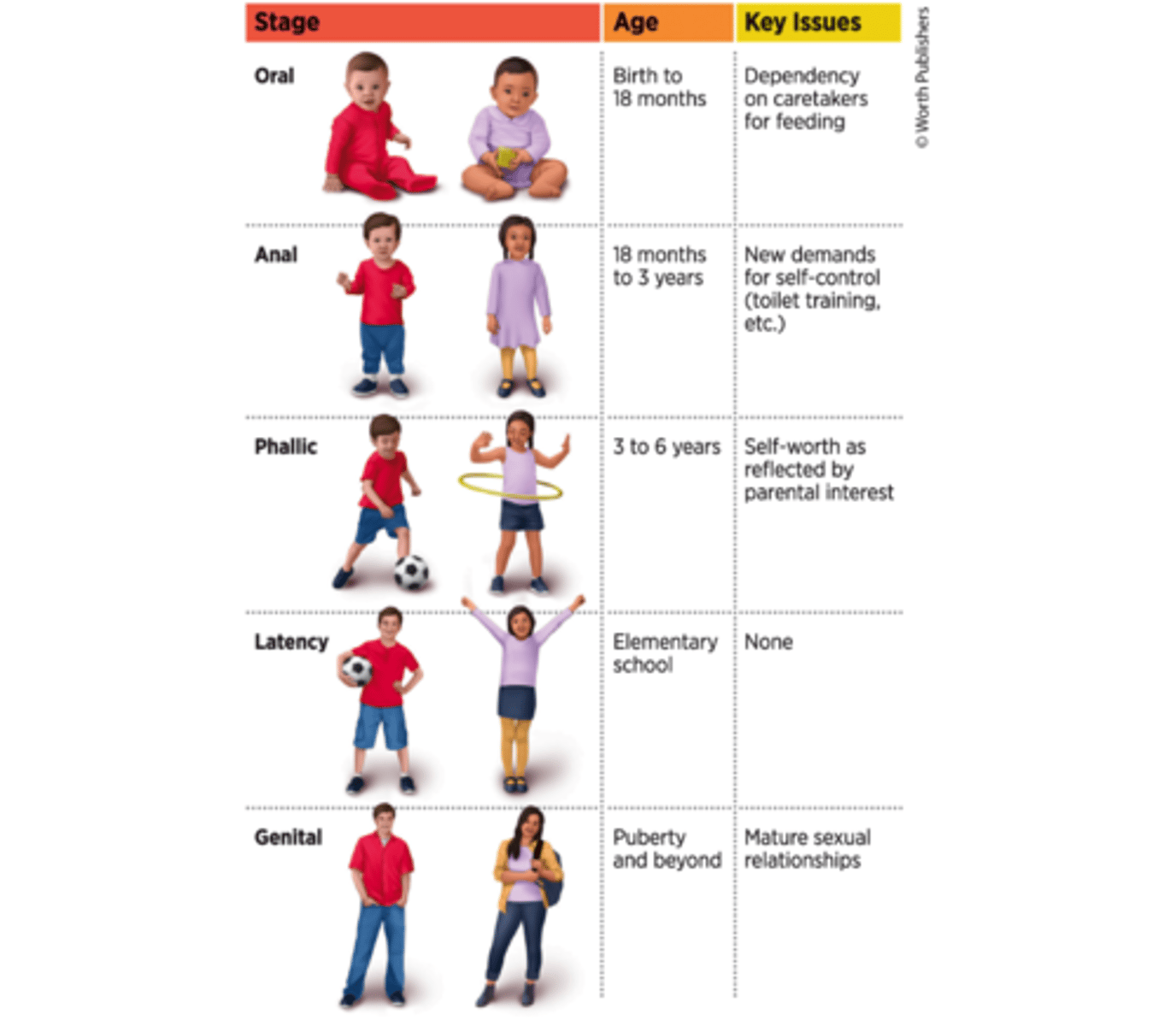
psychosexual stages
the five biologically based developmental stages of childhood during which personality characteristics are formed.
fixation can occur
a lingering psychological difficulty directly related to unsuccessful experience of a particular psychosexual stage.
oral stage
The first of Freud's psychosexual stages, which takes place from birth to about 18 months and focuses on the psychological consequences of feeding behavior.
anal stage
lasts from about age 18 months to about age 3, and focuses on the psychological consequences of toilet training.
phallic stage
runs from approximately 3 to 6 years old and focuses on the psychological consequences of attraction to the opposite-gender parent/caregiver.
Oedipus complex
the childhood experience of desiring the mother and resenting the father.
Electra complex
the childhood experience of desiring the father and resenting the mother.
latency stage
lasts through roughly age 6 to 11 or 12, when puberty has not yet kick-started the child's sexual drive, and the child's energies are focused primarily on school and other tasks that have little to do with the sexual or bodily issues that are so prominent in other stages.
genital stage
lasts from puberty through adulthood and focuses on mature, adult sexual relationships.
neo-Freudian theories
A revised theory that did not entirely reject the basics of Freud's original psychodynamic theory.
collective unconscious
common, inherited memories that are present in the minds of people of every culture.
archetypes
specific symbols or patterns within the collective unconscious that appear consistently across cultures and time periods.
DEFENSE MECHANISM WHAT THE EGO DOES EXAMPLES
Repression: Hides your id impulse in the unconscious to keep you unaware of it You have an id impulse to insult your parent/caregiver, but it never reaches consciousness.
Denial: Blocks external events from consciousness because they are too threatening You learn that your good friend has a fatal disease but act as if everything is OK.
Regression: Retreats to an earlier time in your life when the current stressor was absent Soon after you take a stressful new job, you find yourself craving the comfort foods and TV shows you enjoyed as a kid.
Projection: "Projects" your id impulse onto others, so it appears they have it rather than you You have an id impulse to cheat on your partner, but you accuse your partner of wanting to cheat on you.
Rationalization: Comes up with seemingly acceptable explanations for behaviors actually based on id impulses You give in to your impulse to order (and eat) many boxes of Girl Scout cookies, but tell yourself that you only did so to support a worthy cause.
Reaction formation: Overreacts against the id impulse by doing the exact opposite, as if overcompensating You have an id impulse to damage your friends' new house, but instead you buy them a housewarming gift.
Displacement: Redirects the id impulse toward a safer target in order to minimize the consequences to you You have an id impulse to scream at your supervisor, but instead you scream at your dog.
Sublimation: Redirects the id impulse in a way that actually benefits others You have an id impulse to hurt other people, so you become a soldier who can do so for the sake of national security.
psychosexual stages of development
stages of child development in which a child's pleasure-seeking urges are focused on specific areas of the body called erogenous zones
humanistic theory of personality
based on the ideas of Carl Rogers, emphasizes our inherent tendencies toward healthy, positive growth and self-fulfillment.
self-actualization
fully becoming the person you have the potential to become.
positive regard
warmth, acceptance, and love from those around you.
conditions of worth
requirements that you must meet to earn their positive regard.
the ideal self
the self-actualized version of yourself that you naturally strive to become
incongruence
— a mismatch between your real self and your ideal self — leads to unhappiness and mental illness.
congruence
a match between your real self and your ideal self.
self-concept
your view of who you are. The way important people in your life treat you, particularly how they respond to your self-actualization tendencies, has tremendous power in shaping that view of yourself.
behavioral theory of personality
emphasizes the influence of the environment and the importance of observable, measurable behavior.
social-cognitive theory of personality
emphasizes the interaction of environment, thought processes, and social factors.
reciprocal determinism
the theory that three factors — your behavior, your environment, and your cognitions — continually influence each other.
self-efficacy
your beliefs about your own capabilities
locus of control
your belief about how much control you have over what happens to you.
internal locus of control
the belief that your life is under the control of forces inside of you
external locus of control
the belief that your life is under the control of forces outside of you
trait theory of personality
emphasizes the discovery and description of the basic components of personality. All other personality theories attempt to explain why personality develops the way it does.
traits
stable elements of personality that influence thoughts, feelings, and behavior across most situations.
five-factor model of personality (the Big Five)
an explanation of personality that emphasizes five fundamental traits present in all people to varying degrees.
Neuroticism
the tendency to experience negative emotions such as anxiety, depression, and stress
Extraversion
the tendency to be socially outgoing
Openness to experience — the tendency to be receptive to new or unconventional ideas
Conscientiousness
the tendency to be organized, responsible, and deliberate
Agreeableness
the tendency to cooperate and comply with other people
multimethod assessment
an approach to personality assessment that emphasizes the use of multiple methods rather than only one method.
cultural competence
the ability to work sensitively and expertly with members of a culturally diverse society.
clinical interview
a method of personality assessment in which the psychologist engages in conversation with the client.
objective personality tests
the client responds to a standardized set of questions, usually in multiple-choice or true-false format.
Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory-2 (MMPI-2)
a widely used and respected objective personality test that emphasizes mental disorders.
NEO-Personality Inventory-3 (NEO-PI-3)
an objective personality test that measures the Big Five personality factors
projective personality tests
clients respond to ambiguous stimuli in a free-form way.
Rorschach inkblot technique
a projective personality test in which the client responds to 10 inkblot images.
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
a projective personality test in which the client creates stories in response to cards that show people in undefined situations.
behavioral assessment
an approach to assessment that assumes client behaviors are themselves the problems, rather than signs of deeper problems.
What are the big 5 personality traits?
openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, neuroticism