Mechanical vent Chapter 11 & 12 exam review
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
The ascending ramp and sine flow waveforms are not used for positive pressure ventilation because the initial flow rate is _______ for most patients. These two waveforms may be appropriate for _______ ventilation
not sufficient, control
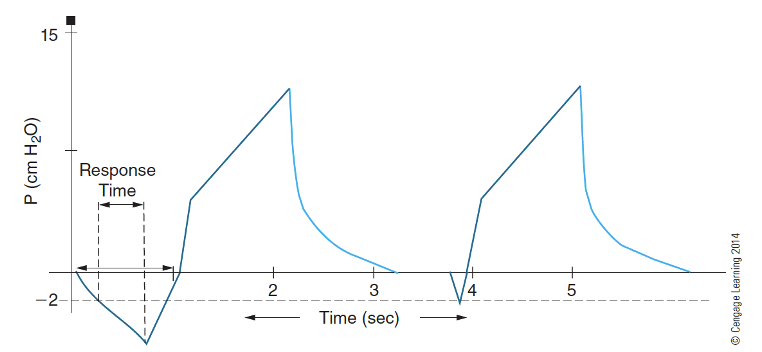
What is this waveform?
Patient triggering their own breath
In volume, pressure and flow waveforms, time in seconds is displayed along the _______ axis
x- or horizontal
The area enclosed under the expiratory flow waveform should _______ the area under the inspiratory flow waveform. If the expiratory volume is less than the inspiratory volume, _______ may be present.
be equal to, circuit leak or gas trapping.
In assist/control mode, the I:E ratio is variable because the _______ time of a breath is dependent on the beginning of the _______ breath.
expiratory, following
On a pressure waveform, PEEP is present when the end-expiratory pressure rests:
above 0 cm H2O.
On the pressure waveform, assist effort is present when the trigger pressure reaches the _______ setting.
sensitivity
In CPAP mode, there are no _______ breaths and the airway pressure is above _______ cm H2O.
mechanical, 0
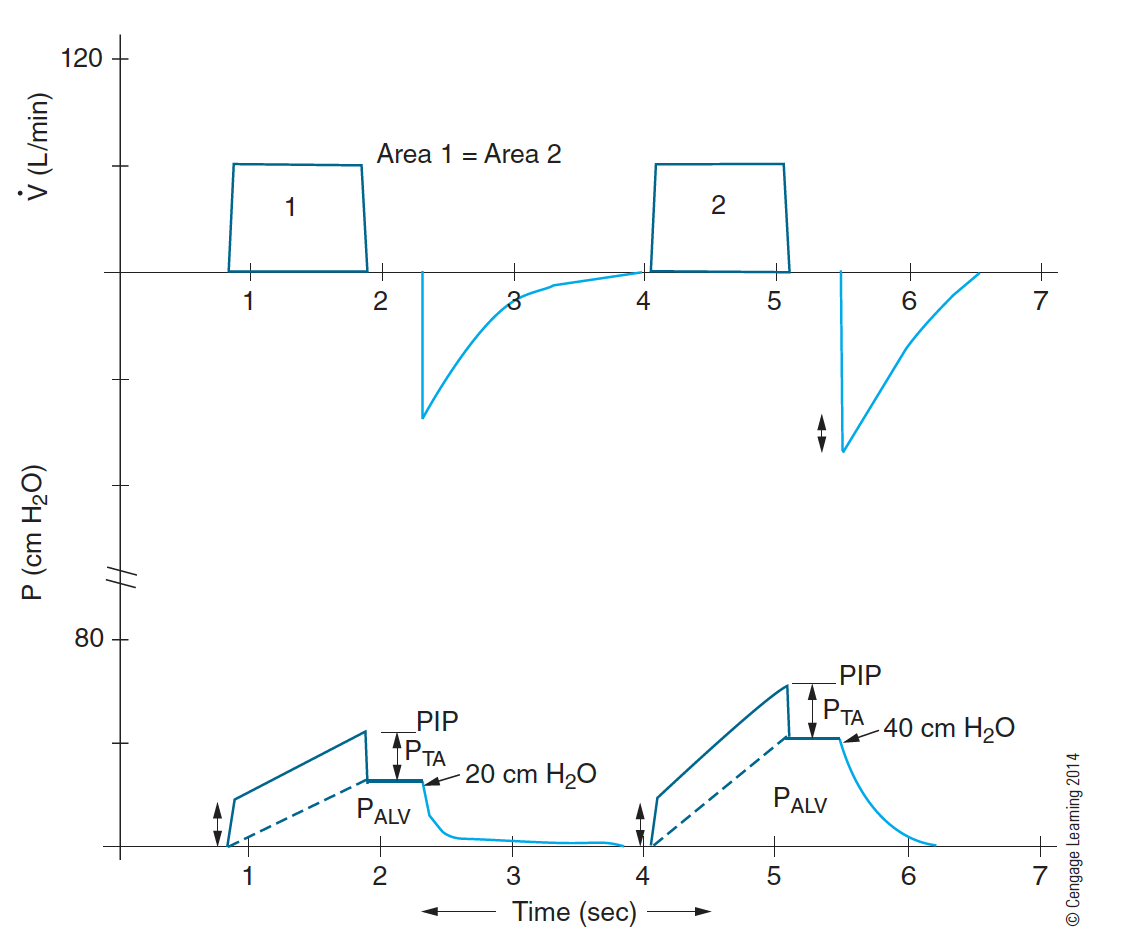
A decrease in total compliance (CLT) would show an unchanged _______ but increased _______.
PTA, PIP and PALV
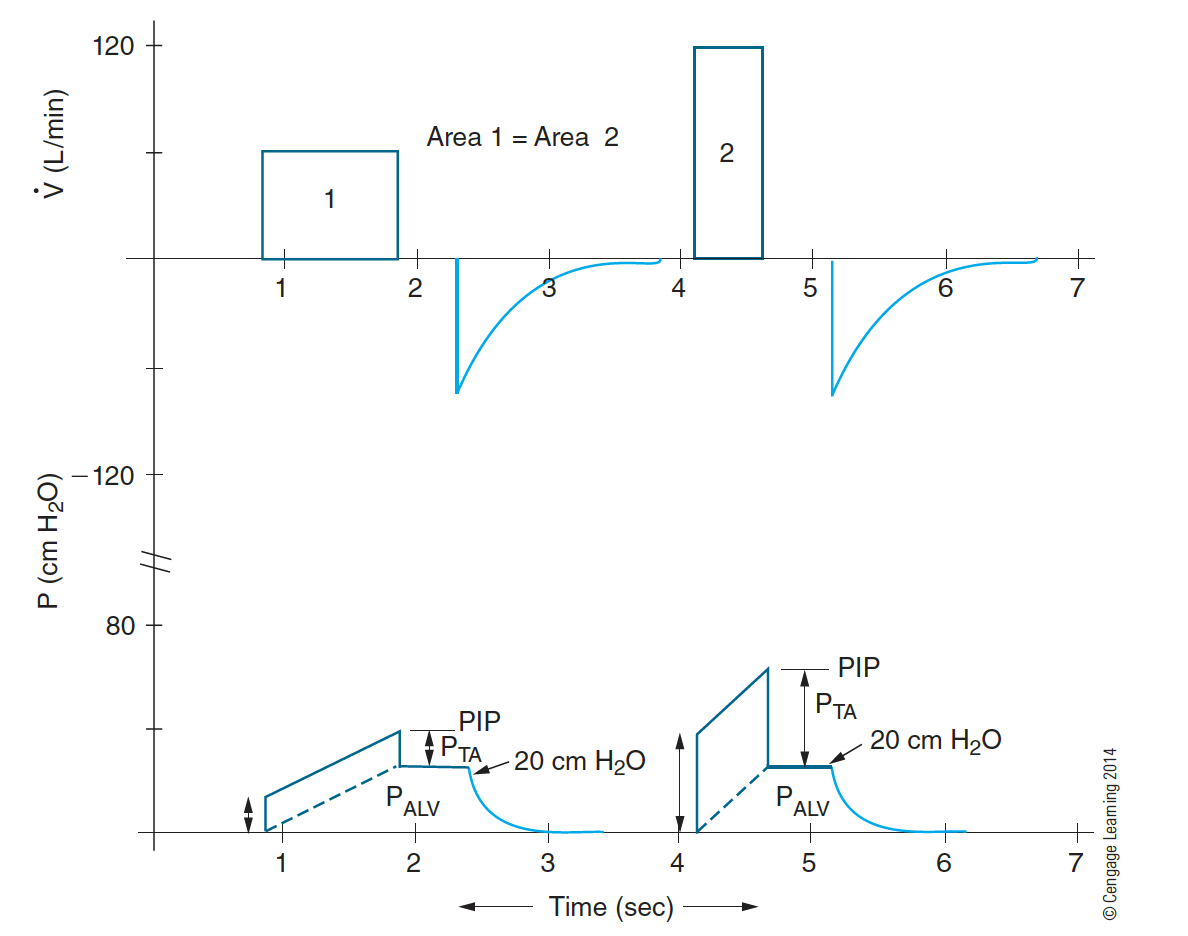
An increase in inspiratory flow or airflow resistance would show an unchanged _______ but increased
Palv, PIP and Pta
With time-limited ventilation, the higher initial peak flow for the descending ramp flow wave creates a _______ initial flow resistive pressure (PTA) than the PTA created by the constant flow.
higher
With flow-limited ventilation, the initial flow-resistive pressure (PTA) is the same for the _______ flow waves. The initial peak flow level stays the same for _______ flow during flow-limited ventilation
constant and descending ramp, constant and descending ramp
During inverse ratio pressure-controlled ventilation, the patients are usually sedated and paralyzed in order to prevent:
dyssynchrony with the ventilator
Tachypnea, agitation, accessory muscle use, active expiration, muscle fatigue, and respiratory failure are signs of:
patient-ventilator dyssynchrony
Failure of the expiratory flow to return to the zero baseline is indicative of:
gas leak or air trapping
On a pressure-volume loop, an increase in resistance would not affect the _______ while the _______ are increased
PALV; PTA, PIP, and PAO
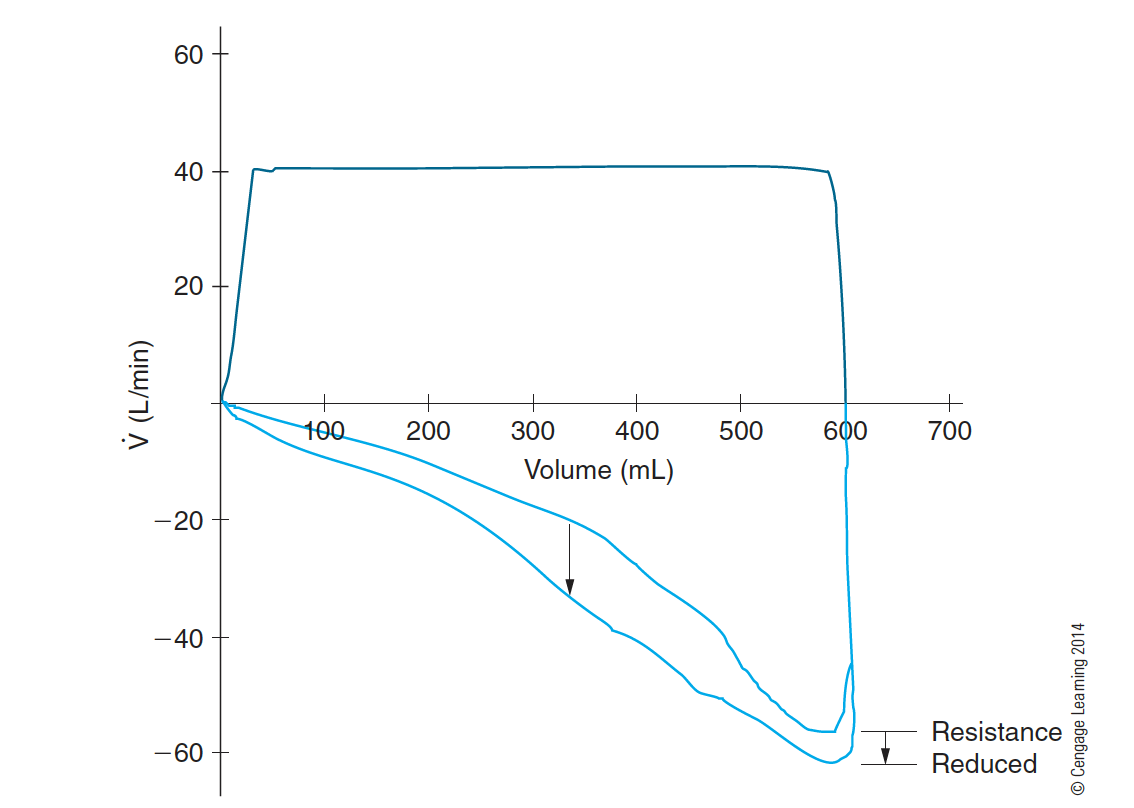
On a flow-volume loop, the expiratory flow is _______ the horizontal (volume) axis and it is usually _______ following a successful bronchodilator therapy.
below, increased
What is the TCT?
total cycle time
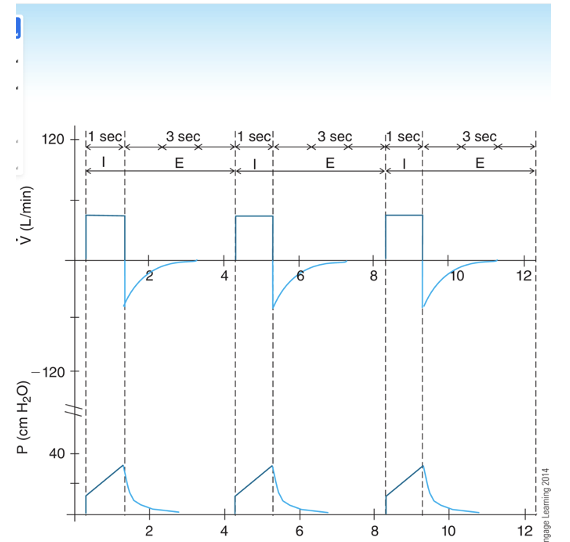
How often will the patient get a breath?
total cycle time = inspiratory time → expiratory time divided by 60 seconds
Expiration is measured from the beginning of expiration to the beginning of the next inspiration.
Total respiratory cycle below is 4 seconds
TCT = T1 + Te = 60sec/4 = 15 . pt gets a breath every 15 seconds.
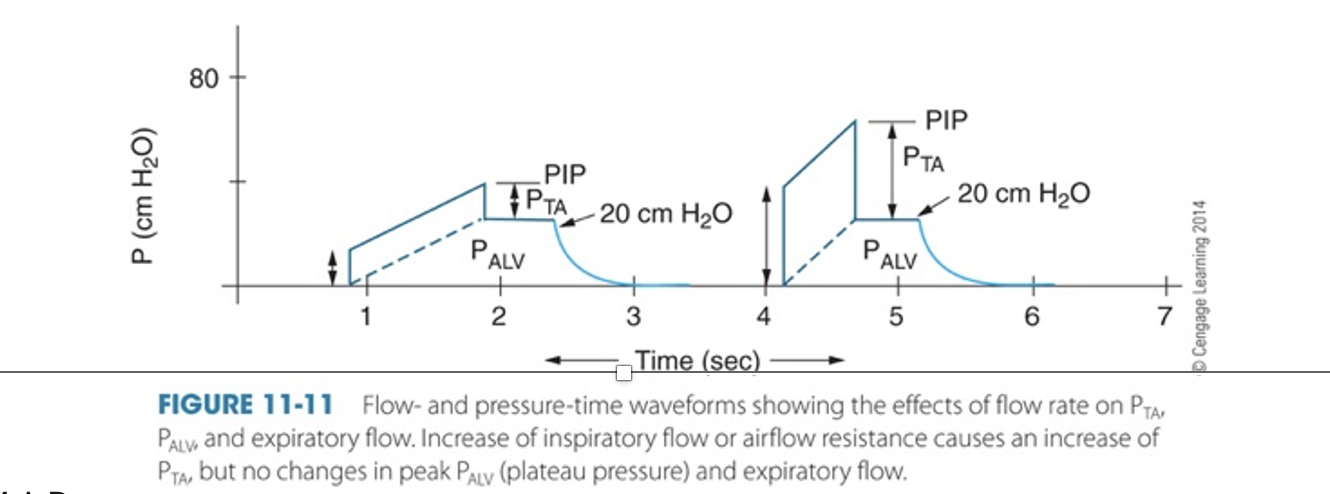
Make sure you know all of the parts of the waveform
Increase in flow or airflow resistance causes
i. An increase in transairway pressure (PTA)
ii. An increase in PIP because of the increased PTA
iii. No change in PALV (alveolar pressure) (Note: PALV is related to changes in compliance)
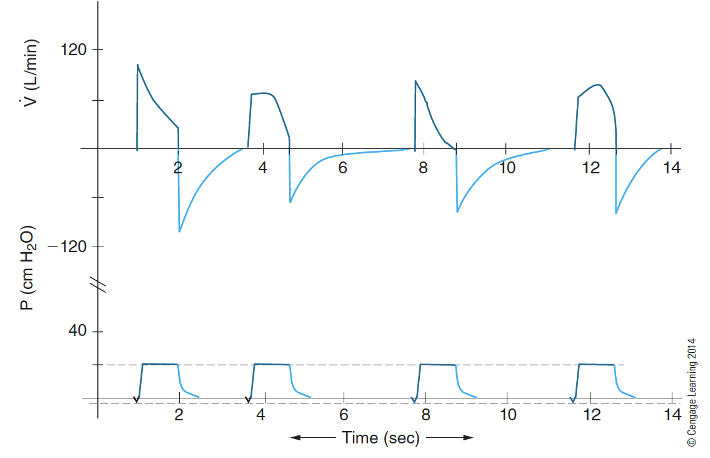
How does airway resistance/compliance affect your flow waveforms and the expiratory phase?
Flow-time waveform: variable flow (top of figure)
variable flow = variable volume
What can happen if your patient is having dyssynchrony with
your settings on the ventilator?
a. Increases work of breathing
b. Increases oxygen consumption
c. Increases myocardial work
d. Prolongs weaning
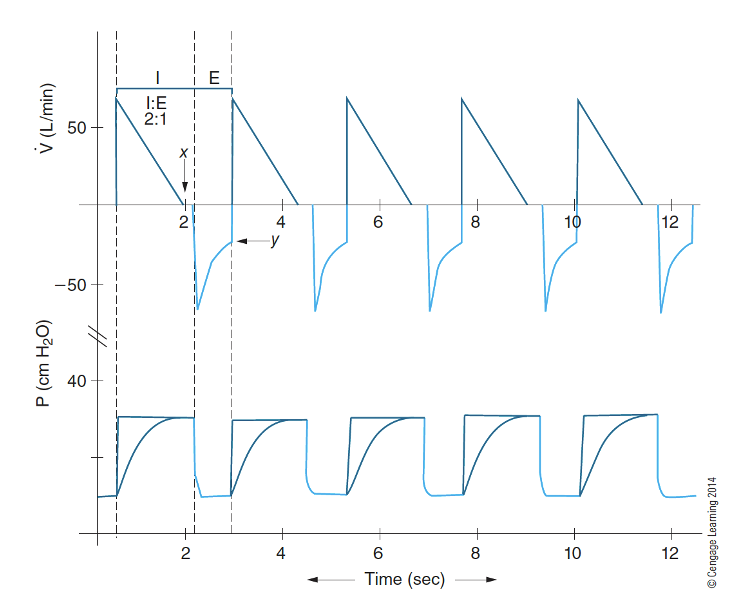
What waveform is this?
IRPCV(Inversed Ramped Pressure Control Ventilation) is characterized by a rising pressure waveform that begins at zero and gradually increases to a preset level during inspiration.
What is different about the IRV inspiratory and expiratory sizes?
The IRV (Inversely Ramped Ventilation) modality utilizes a longer inspiratory phase and a shorter expiratory phase, maximizing time for gas exchange and reducing the risk of lung overdistension.
What are some reasons that could cause dyssynchrony?
- A lack of ventilator sensitivity to the patient’s inspiratory effort
- When increased ventilatory demands are not met by a sufficient flow or volume.
What is the trigger or sensitivity?
The trigger or sensitivity is the level of patient effort required to initiate a breath on the ventilator, determining how responsive the device is to the patient's respiratory needs.
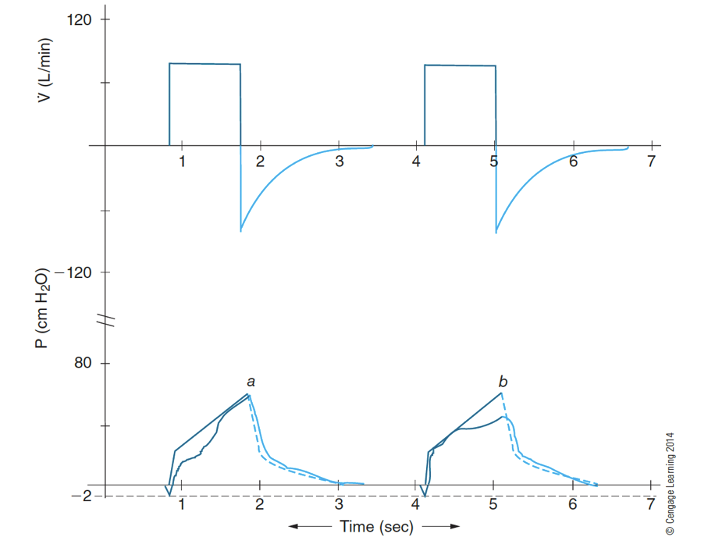
What does the waveform look like if you have inadequate flow and or volume?
Pressure-time waveform
a: drop in pressure at beginning-inspiration means more flow is needed
b: drop in pressure at end-inspiration means more volume is needed
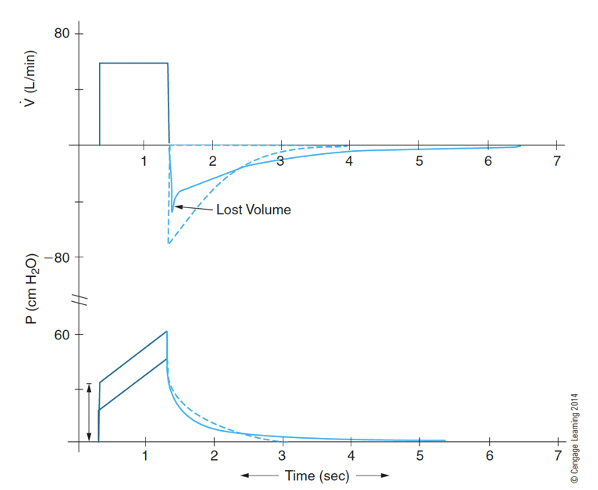
What happens to your waveform if you have increased resistance on flow and pressure waveform?
– Leads to a lower expiratory flow (top figure, solid line)
• (Note: inspiratory flow is preset on ventilator)
– Leads to a higher peak inspiratory pressure (bottom figure, solid line)
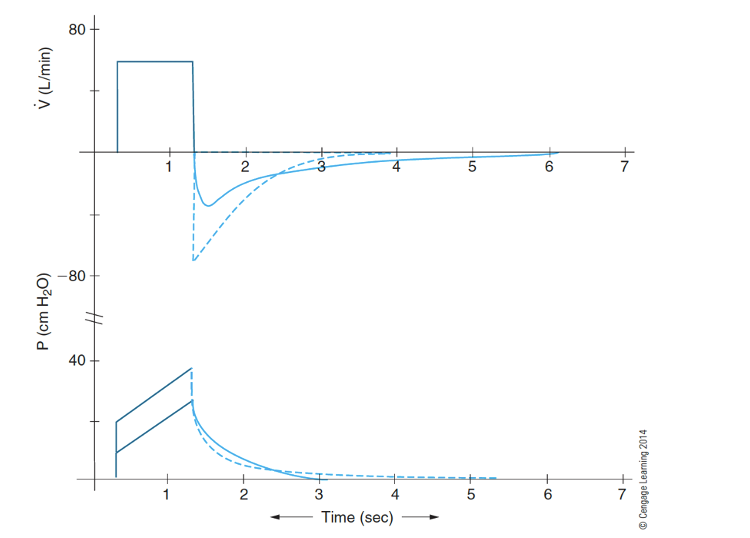
What does loss of elastic recoil mean? What does that look like on a waveform?
Loss of elastic recoil (high compliance)
a. Leads to a lower expiratory flow (top figure, solid line)
i. (Note: inspiratory flow is preset on ventilator)
b. Leads to a lower peak inspiratory pressure (bottom figure, solid line)
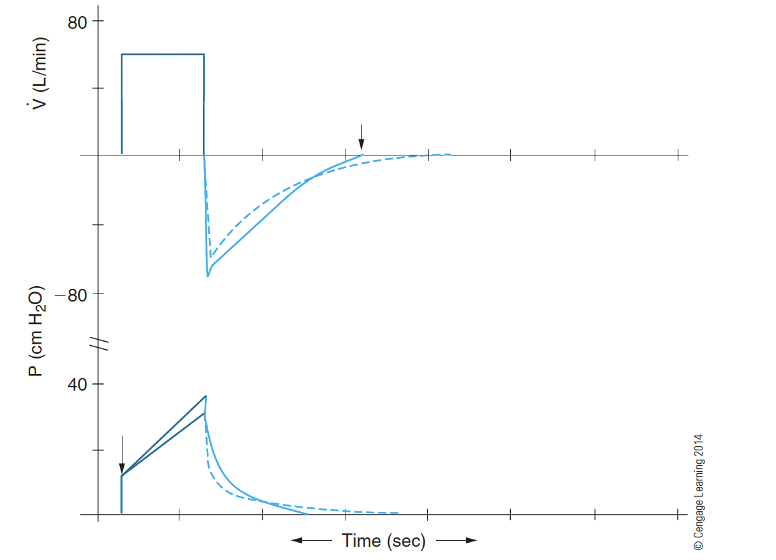
What does decreased compliance look like?
Decreased lung-thorax compliance (CLT)
– Leads to a higher expiratory flow (top figure, solid line)
• (Note: inspiratory flow is determined by ventilator)
– Leads to a higher peak inspiratory pressure (bottom figure, solid line)
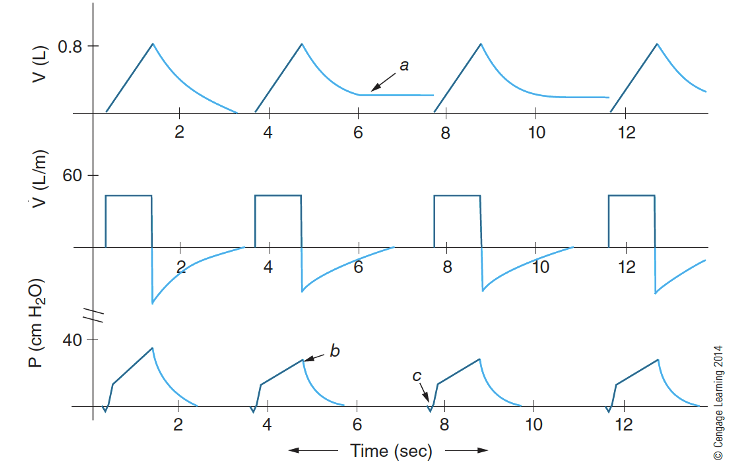
What does a circuit leak look like?
(a) demonstrates that a leak has developed, since the volume never returns to the zero baseline. The ventilator still delivers the same flow pattern.
(b) shows that the PIP for ventilation has been reduced, since less volume is being delivered to the patient’s lungs.
(c) is used to emphasize that the negative pressure to trigger the sensitivity threshold may appear the same (although sometimes the descent to the sensitivity threshold may be prolonged)
What are the two different volume loops?
Pressure-volume loop (PVL)
flow-volume loop (FVL)
What can volume loops tell us?
Volume loops can provide insights into lung mechanics, including compliance and resistance. They help assess how effectively the lungs are filling and emptying during ventilation.
Effects of airflow resistance on Pressure-Volume loop (PVL)
Increase in airflow resistance - PTA, PIP, and PAO are increased. No change in PALV
Decrease in airflow resistance - PTA, PIP, and PAO are decreased. No change in PALV
What does beaking (duck bill) of the PV loop tell us?
Beaking of the PV loop indicates increased airway resistance or reduced compliance, suggesting difficulty in airflow during expiration. It demonstrates that peak pressures are higher due to limitation in lung inflation and deflation.
What specifically do flow volume loops tell us?
Flow volume loops depict the relationship between airflow and lung volume, providing information on airflow obstruction or restriction. They help assess peak expiratory flow rates and evaluate the quality of airflow during forced maneuvers.
Effects of airway status on flow-volume loop (FVL)
A decrease in airflow resistance (e.g., bronchodilator, secretions clearance) increases the peak expiratory flow
An increase in airflow resistance lowers the peak expiratory flow
Note: peak inspiratory flow is preset on the ventilator
Strategies that are useful to improve ventilation include all of the following except:
increase mechanical deadspace.
Dr. McFarland asks the therapist to adjust the ventilator in order to improve the oxygenation status of the patient with normal V/Q status. Which of the following ventilator adjustments would have the most direct effect on oxygenation?
increase oxygen concentration (FIO2)
When the ventilator frequency is over 20/min, the incidence of ________ is increased, especially when the pressure support ventilation is also used.
Auto-PEEP
An endotracheal tube is sometimes shortened because a shorter ET tube:
facilitates airway management and secretions removal.
A patient has alveolar hypoventilation. Will this cause acidosis or alkalosis? What will it lead to if supplemental oxygen is not provided to the patient?
Alveolar hyperventilation due to hypoxia,
improper ventilator settings,
or metabolic acidosis,
can lead to : respiratory muscle fatigue, worsening outcomes.
The primary purpose of permissive hypercapnia is to reduce the patient’s _______ during mechanical ventilation.
pulmonary pressures
Permissive hypercapnia is a technique in which the mechanical _______ is reduced. This change is done intentionally to increase a patient’s _______.
tidal volume, PaCO2
CPAP and PEEP may be used to reduce or correct refractory hypoxemia caused by:
intrapulmonary shunting.
The PaO2 of a spontaneously breathing patient has been deteriorating while on 60% of oxygen via a partial-rebreathing mask. The physician asks the therapist to suggest the best solution for this problem. The therapist should recommend the following procedures in the order provided:
CPAP, mechanical ventilation with PEEP, inverse ratio ventilation.
Compensated respiratory acidosis and compensated metabolic alkalosis have similar blood gas characteristics:
normal pH, high PaCO2, and high HCO3 -. One useful clue to differentiate these two conditions is that in compensated:
respiratory acidosis, the pH is on the acidotic side of normal range.
A patient’s low pressure alarm is triggered persistently. The likely causes of this condition include all of the following except:
A. disconnection of ventilator circuit.
B. kinking of endotracheal tube.
C. power failure.
D. leakage of endotracheal tube cuff.
kinking of endotracheal tube.
During patient rounds in the ICU, the high pressure alarm of a ventilator is triggered. This condition is likely caused by:
A. disconnection of ventilator circuit.
B. low pressure limit set too high.
C. loose ventilator humidifier fitting.
D. patient coughing.
patient coughing.
Analysis of sputum samples by the culture and sensitivity method is _______. It provides information on the type of _______ that the microbes are sensitive to.
time-consuming, antibiotics
The urine output of a patient is about 15 mL/hour. This volume of urine output is _______ than normal and it implies that there is too _______ fluid in the extracellular fluid compartment.
lower, little
In replacing fluids to a volume-depleted patient, it is not safe to administer fluids that have no sodium because _______ movement of sodium-free fluid into the brain and kidney cells may cause _______ of these organs.
rapid, swelling
Decreased muscle function, flattened T wave and depressed ST segment on the electrocardiogram, and diminished bowel sounds are some signs of:
hypokalemia.
During mechanical ventilation weaning attempts, which setting is primarily used to overcome ETT resistance?
Pressure support ventilation
When pressure support ventilation is used properly, it reduces the work of breathing by increasing what?
Spontaneous Vt
What is the benefit to prone positioning?
has been used as a “stop-gap” strategy to improve the
ventilation,
oxygenation,
and pulmonary perfusion status of patients with acute respiratory failure and ARDS.
What negative effects will hyperkalemia have on your patient?
Increased neuromuscular conduction
elevated T wave and depressed ST segment on ECG (mild)
cardiac arrest (severe)
increased bowel activity
diarrhea
Name some reasons why we do VAP prevention:
Patients who are intubated and on mechanical ventilation are more prone to develop nosocomial pneumonia than nonintubated patients.
Some sources for VAP: Patient
Health care provider
Equipment and supplies
how we can prevent VAP
proper handwashing techniques,
closed suction systems,
continuous-feed humidification systems,
change of ventilator circuit only when visibly soiled,
and elevation of head of bed to 30 degrees to 45degrees
What is autopeep?
unintentional PEEP associated with pressure support ventilation, high tidal volume and frequency, inadequate inspiratory flow, excessive I-time, inadequate E-time, and air trapping
how to trouble shoot Auto-PEEP
may be reduced or eliminated by
↑ flow rate to decrease I-time
↓ VT to decrease I-time
↓ f to increase E-time
Keep PS frequency less than 20/min
↓ air trapping with bronchodilator
Apnea/low frequency alarm may be triggered due to:
Circuit disconnection
Oversedation
Prolonged neuromuscular block
Respiratory center dysfunction
Respiratory muscle fatigue
If your patient has very thick secretions and you cannot get them out, what is another option?
Occasionally, humidification and removal of
the secretions are supplemented by use of a saline solution or mucolytic agent via a small volume nebulizer.
Patency of the endotracheal tube
Use largest size appropriate for patient
Remove secretions from ET tube on an as-needed basis
Monitor and avoid
Kinking of ET tube
Biting on ET tube
ET tube malfunction (e.g., herniated cuff)
When would you need to change your vent circuit?
Maximum time interval for circuit change is unknown
Weekly circuit change has been shown to be an optimal interval
Circuit should be changed when it is visibly soiled
Benefits of Initiate extracorporeal membrane oxygenation ECMO:
a. An option for some neonates who do not respond to conventional mechanical ventilation
b. Oxygenation occurs outside the body
c. ECMO is most suitable for neonates
d. Refer to Chapter 17 for more information on ECMO
Benefits of Initiate Inverse ratio ventilation (IRV)
e. I-time longer than E-time
f. Inspiratory flow is reduced to achieve an inverse I:E ratio
g. IRV reduces or corrects refractory hypoxemia that is nonresponsive to conventional mechanical ventilation with PEEP
h. IRV
i. Overcomes noncompliant lung tissues
j. Expands collapsed alveoli
k. Increases time for gas exchange
What is optimal peep?
lowest pressure level that offers the most benefits with the least side effects
what fixes refractory hypoxemia
Increase inspired oxygen fraction (FIO2)
a. Improve ventilation is the priority if hypoxemia is caused by hypoventilation (↓PaO2 with ↑PaCO2)
b. Consider PEEP if refractory hypoxemia is present (e.g., PaO2/FIO2< 200 mm Hg)
What fixes oxygen toxicity
Keep PaO2 < 80 mm Hg (<60 mm Hg for COPD) or FIO2 <60% to prevent oxygen toxicity
Increase in airflow resistance: patient factors
Bronchospasm
Coughing
Patient-ventilator dyssynchrony
Secretions in ET tube
Biting on ET tube
Mucus plug
Conditions that Decrease in lung or chest wall compliance
Tension pneumothorax
Atelectasis
ARDS
Pneumonia
What is normal hemoglobin level?
more than 10 g/100 mL
What is permissive hypercapnia
Permissive hypercapnia is a strategy used to minimize the incidence of ventilator- induced lung injuries caused by positive-pressure ventilation
What type of patient would need permissive hypercapnia
beneficial strategy in the management of patients with status asthmaticus and adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
How to calculate ventilator frequency needed to achieve a certain PaCO2
Frequency x PaCO2 / Desired PaCO2
New frequency: Ventilator frequency needed for a desired PaCO2
Frequency: Original ventilator frequency
PaCO2: Original arterial carbon dioxide tension
Desired PaCO2: Desired arterial carbon dioxide tension