B-Oxidation
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What is beta-oxidation of fatty acids?
The catabolic degradation of FA
What is the product of beta-oxidation?
Acetyl-CoA
NADH
FADH2
Where does beta oxidation occur?
Mitochondria
But if there are long chain FA, where will they go first before entering the mitochondria
Peroxisomes
What is the importance of beta-oxidation?
Provides energy source during fasting, exercise or when glucose is low
In which animals is beta-oxidation the most important
Ruminants and carnivores with fat-rich diets
What are the 3 steps of beta oxidation and where does it occur?
Activation of fatty acids (occurs in cytosol)
Transport into the mitochondria
Beta-Ox cycle (occurs in mitochondrial matrix)
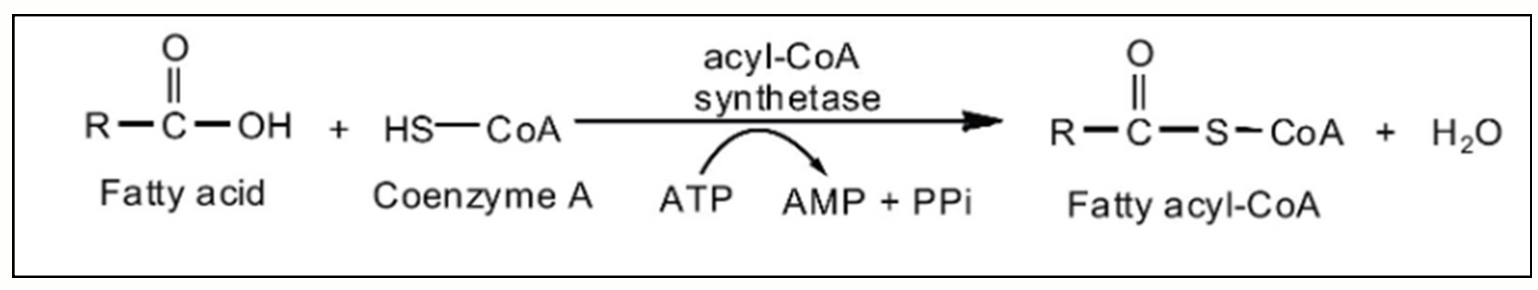
1. Activation of fatty acids
What is the enzyme needed
Why do FA need to be activated first
How are they activated
Requires
Equation
ATP converted to
Enzyme: Acyl-CoA synthetase
FA need to be activated first because: FA are inert
How activated: Converted to fatty acyl-CoA
Requires: ATP
Equation: Fatty acid + Coenzyme A + ATP —> Fatty acyl-CoA + AMP + PPi
ATP converted to: AMP which is equivalent to 2 ATP
2.Transport into the mitochondria
Can fatty acid-CoA cross the mitochondrial membrane directly
Describe the carnitine shuttle system
What converts fatty acyl-CoA to acyl-carnitine
How is acyl-carnitine transported into the mitochondria
What regenerates fatty acyl-CoA inside mitochondria
Cross directly: No fatty acyl-CoA CANNOT cross the mitochondrial membrane directly
Carnitine shuttle system:
What converts fatty acyl-CoA to acyl-carnitine:
CPT-I (carnitine palmitoyltransferase I)
How is acyl-carnitine transported into the mitochondria:
By carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase
What regenerates fatty acyl-CoA inside mitochondria:
CPT-II (carnitine palmitoyltransferase II)
3. Beta Oxidation Cycle
What are the 4 steps
Each cycle removes how many carbons from FA chain
Produces
4 steps: O-HOT
Oxidation: Converts fatty acyl-CoA into trans-Δ2-enoyl-CoA
Hydration: Converts trans-Δ2-enoyl-CoA to L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA
Oxidation: Converts L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA to B-ketoacyl-CoA
Thiolysis: Cleaves B-ketoacyl-CoA to release acetyl-CoA and shorter fatty acyl-CoA
Each cycle: Removes 2 carbons from FA chain
Produces: Acetyl-CoA and fatty acyl-CoA
In which steps of the beta oxidation cycle is FADH2 and NADH produced?
FADH2: Produced in the 1st oxidation step of converting acyl-CoA to trans-Δ2-enoyl-CoA
NADH: Produced in the 2nd oxidation step of converting 3-L-hydroxyacyl-CoA to B-ketoacyl-CoA
Between the 2 products produced, acetyl-CoA and fatty acyl-CoA which one is the main energy producing product?
Acetyl-CoA
So how does the acetyl-CoA produced be used for energy production?
Acetyl-CoA enters the TCA cycle by combing with oxloacetate to form citrate which stimulates a series of reactions
This generates NADH and FADH2 which enter the ETC to produce ATP