ap psych unit 2 - perception, processing, thinking - lessons 1-3
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
top-down processing
a cognitive process where the brain uses prior knowledge, experiences, and context to interpret information.
ex. recognizing jumbled letters in a word using prior knowledge.
bottom-up processing
data-driven approach, meaning it begins with the individual components and uses them to create a larger picture or solution.
ex. learning to read by first recognizing letters and words.
selective attention
focusing on a specific stimulus while filtering out other distractions and irrelevant information.
inattentional blindness
person doesn’t notice unexpected but visible objects because their attention is focused on something else.
change blindness
someone fails to notice significant changes in their visual environment, even when changes are obvious.
binocular cues
depth cues that require the use of both eyes to perceive depth and distance.
monocular cues
depth cues that only need one eye to perceive.
retinal disparity
different images captured by each eye due to their different positions, which the brain uses to create a 3D perception.
convergence
2 or more things coming together or approaching a limit, resulting in a single point.
texture gradient
monocular cue where the change in the texture of a surface provides information about distance, with textures appearing less detailed as they go into the distance.
interposition
monocular cue where an object that blocks the view of another object is perceived as closer.
linear perspective
monocular cue where parallel lines look like they’re coming together because they’re heading farther away.
ex. train tracks in a painting
relative clarity
monocular cue where objects that are clearer are perceived as closer, while blurrier and more dull-colored objects seem farther away.
relative clarity vs texture gradient
relative clarity is the perception of depth based on how sharp an object appears.
texture gradient is the perception of depth based on the detail of an object's surface
relative size
monocular cue where you perceive an object’s size in comparison to other objects in the same visual field.
heighth in vertical plane
monocular cue that when something looks higher in a vertical plane, it seems farther away.
visual perception constancies
color constancy, size constancy, shape constancy
(tendency of perception to remain consistent with change)
gestalt perception
emphasizes that we perceive whole objects(gestalts) rather than bits of sensory info.
law of figure ground
part of what we see is the center of our attention and the rest is the background.
law of continuity
objects arranged in either a straight line or a curve are seen as a unit.
law of proximity
things that are close together are perceived as belonging together.
law of similarity
similar things are perceived as being related.
law of closure
incomplete figures tend to be perceived as complete wholes.
stroboscopic movement
illusion that objects are moving slower or stationary when they’re actually moving continuously under flashing lights.
phi phenomenon
illusion where stationary objects blinking rapidly appear to be in motion.
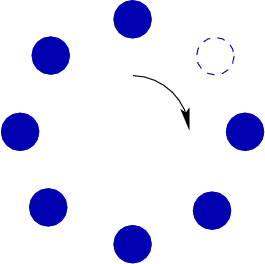
autokinetic effect
perception where a point seems to move after looking at it for a while.
inductive/informal reasoning
type of thinking that draws conclusions from observations or everyday knowledge.
ex. seeing a series of white swans and concluding all swans are white.
deductive/formal reasoning
type of thinking that uses general principles to draw conclusions.
ex. if it is raining, the ground will be wet. It is raining outside. Therefore, the ground is wet.
algorithm
step-by-step procedures that guarantee a solution. it’s the “long way.”
ex. using every key to open a door.
concept
category used to group stuff that shares similar characteristics.
ex. different kinds of chairs.
natural concept
concept that’s formed naturally based on experience.
formal concept
concept that’s formed by memorizing rules.
schema
cluster of knowledge about something based on previous experience.
assimilation
new information is incorporated into pre-existing schemas.
accommodation
existing schemas might be altered or new schemas might be formed with new experiences.
cognitive dissonance
discomfort experienced when holding 2 or more conflicting beliefs or when your beliefs don’t match your actions.
ex. a smoker knowing that smoking is harmful, but does it anyway.
prejudice
schema that stops people from seeing the world as it is and stops them from taking in new information. “putting their beliefs over anything else.”
prototype
generalized “best example” of a category.
ex. calling a crow a bird more than a penguin, because a crow matches the prototype of a bird better.
exemplar
something that’s a perfect and specific example or a model of a category.
heuristic
informal reasoning strategy or guide that saves time-decision-making shortcut.
ex. consistency, representative, or availability
consistency heuristic
“just do what you always do”
representative heuristic
judge something based on how close it is to your prototype[“best example”], often ignoring statistical base rates.
availability heuristic
judge a situation based on examples of similar situations that initially come to mind.
analogy
judge a situation based on similar situations.
cocktail party effect
ability to attend to only one voice within a sea of many as you chat with a party guest(example of selective attention).
perceptual set
to perceive one thing and not another based on our expectations.
divergent thinking
creative thought process used to form ideas by exploring many possible solutions.
ex. brainstorming uses for an object like a paperclip.
convergent thinking
seeking the “single solution” for a problem.
functional fixedness
when someone can’t think of a new use for an object because they only see it in terms of their original purpose.
the sunk cost fallacy
someone is reluctant to abandon a strategy because they’re invested in it, even if abandonment is more beneficial.
ex. reading a bad book, but still finishing it.
the gambler’s fallacy
belief that past events influence future ones, causing someone to believe an outcome is more likely to happen after it has occurred less frequently.
ex. believing a coin is “due” for heads after landing on tails more frequently.
cognition
all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating.
metacognition
cognition about our cognition; keeping track of and evaluating our mental processes.
ex. realizing you have forgotten the key points of an article and deciding to reread it.
insight
a sudden realization of a problem’s solution.
mental set
tendency to use a previously successful solution to solve a new problem, even if a different approach is needed.
ex. pulling a push door
belief perseverance
the tendency to hold onto one's beliefs even when presented with evidence that contradicts them.
blindsight
a neuropsychological condition where individuals with damage to the primary visual cortex can respond to visual stimuli without consciously seeing them.
ex. if an object was moved to the left and a person who was looking at the object, but cortically blind, somehow knew it was moved to the left, even though they could not see it.