Life sci term 2 - Jonah
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Reproductive cloning
Putting the somatic cell into a pseudopregnant (induced by hormones) animal to carry the baby.
Molecular cloning
Using living cells to make many copies of a DNA fragment of interest. Inserting the fragment into the vector to make recombinant DNA.
Restriction sites
Endonuclease goes snip-snip. Dont cut the sequence of interest!!!
Antibiotic resistance gene
Important to select which bacteria will survive (the ones with the plasmid with your gene and the antibiotic resistance gene).
Selectable marker
Important to know which mammalian cells will have the gene you want being expressed (not super relevant most of the time)
Genes needed for cloning
1. Gene of interest
2. Promoter sequece
3. Restriction sites
4. Antibiotic resistance gene/selectable marker
Mature mRNA
mature mRNA has been processed, has poly-A tail (can be reverse transcribed)
Reverse transcription
Mature mRNA -> DNA
Steps for molecular cloning
1. Make cDNA
2. Bind oligo dT-primer to poly-A tail
3. Reverse-transcriptase binds to oligo dT-primer
4. Amplify cDNA (using PCR)
5. Insert amplicons into the vector using endonucleases
6. Ligate!
Plasmid
Extra circle of DNA in bacteria
Recombinant DNA
An engineered DNA molecule that comprises a target DNA sequence that has been molecularly cloned into a bacterial plasmid.
Goal of molecular cloning
Many copies of recombinant DNA using host
Recombinant DNA
Engineered DNA for some purpose or another
Gene editing
Changing genome by leveraging the cell's repair mecahnisms
Uses for gene editing
-Fix mutations
-Insert sequences
-Remove sequences
How to repair single-stranded breaks (SSB)
-Base excision repair : Just the one base
-Nucleotide excision repair : The base and it's pair or area around it
How to fix double-stranded breaks (DSB)
-Homologous recombinaition : Repair using template (if available) (must be when there are two copies present like in mitosis)
-Non-homologous end joining : Simply attach the two ends together
Zinc Finger Nucleases (ZFNs)
Nuclease that is used to guide FOK-1 (3 nucleotides at a time x 3-4 ZF in a ZFN)
FOK-1
Protein that when made a dimer, will make a double stranded cut in the DNA at a point it is guided to by TALENs or ZFNs (2 nucleases per FOK-1 snip, 4 nucleases to remove a stretch of DNA)
TALEs
Bind to one nucleotide at a time to guide FOK-1 (easily customizable: 10-12 in a TALEN)
CRISPR
Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats: Tool used to change DNA using bacterial defense mechanism that recognizes viral DNA and cuts it where CAS1 and CAS2 tell it to. (Draw this one out)
4 Steps of Cellular Respiration
1. Glycolysis (does not need O2)
2. Pyruvate processing (needs O2)
3. Krebs/Citric Acid Cycle (does not need O2)
4. Electron transport chain (needs O2)
Glycolysis
Breaking glucose into 2 pyruvate, +2 ATP, +NADH
Regulated by a negative feedback loop (More ATP, less glycolysis)
Pyruvate processing
Turning pyruvate into Acetyl-CoA, +NADH
Krebs Cycle
Turn Acetyl-CoA into CO2, +NADH, +FADH2, +ATP
Electron transport chain
Pump protons across inner mitochondrial membrane, using electrons. NADH at the start, FADH2 at Q. Proton gradient powers ATP-ase
Electron transport chain order
Complex 1 or Complex 2 -> Q -> Complex 3 -> Cytochrome C-> Complex 4
Fermentation
Anaerobic way to keep glycolysis going for a small ATP yield.
Lactic acid fermentation
More common pathway. Pyruvate -> Lactic acid
Ethanol fermentation
Less common pathway. Pyruvate -> Acetylaldehyde -> Ethanol
Photosynthesis
The process of using sunlight to produce carbohydrates. This process requires sunlight, CO2 and H2O, and produces O2 as a byproduct.
Autotrophs
Organisms that use sunlight to produce carbohydrates.
Heterotrophs
Organisms that must meet their need for nutrients by consuming other organisms.
Two linked sets of reactions
-Light-dependent reactions, first part of photosynthesis, requires light.
-Light-independent reactions, second part of photosynthesis, does not require light (Calvin cycle)
What is transferred between light and dark reactions
Chemical energy (NADPH, ATP)
Where does photosynthesis take place
Chloroplasts.
Chloroplast
Cell organelle with a double membrane, filled with granum which are stacks of pancakes (thylakoids), inner fluid is stroma.
Granum (grana)
Stack of pancakes (thylakoids)
Chlorophyll (a and b)
Pigments that absorb red and blue light, reflect green light
How does Photosystem 1 work
-Pass excited electrons to ferredoxin
-Ferredoxin reduces NADP+ to NADPH
-NADPH goes to Calvin cycle
Photosystem 2
-Feeds an ETC that pumps protons to produce ATP
-Photophosphorylation
Z-Scheme
Model of how photosystems I and II interact
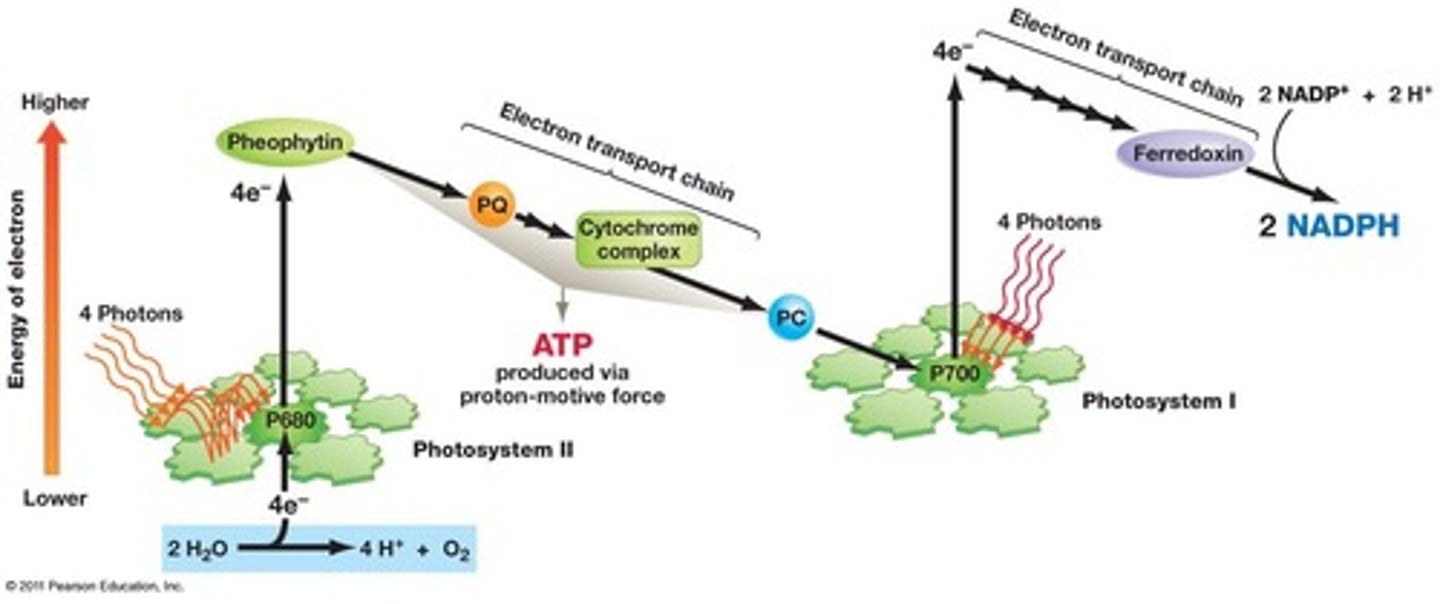
Enhancement effect
Effect where when combiend, PS 1 and PS 2 produce more energy than their independent sums.
Photosystem 2 mechanism
-Feed high energy electron to pheophytin (chlorophyll is oxidized)
-Electrons from pheophytin go to ETC in thylakoid membrane
-Plastoquinone (PQ) shuttles electrons across thylakoid membrane, to ETC
-Standard ETC from there on
-*Proton transport increases proton concentration by 1000x
How does photosystem 2 recharge
Get electrons by splitting water (oxygenic hydrolysis) (only way to split water naturally)
P680
Photosystem 2
P700
Photosystem 1
Plastocyaninin
Protein that carries electrons from PS2 to PS1
Calvin cycle phases
1. Fixation (3 RuBP + 3 CO2 -> 6 PEG)
2. Reduction (6 PEG + 6 ATP + 6 NADPH -> 6 G3P)
3. Regeneration (5 G3P +3 ATP -> 3RuBP)
Fixation
First step in Calvin cycle. Fixing carbon to ribulose bisphosphate to make phosphoglycerate.
Reduction
Second step in Calvin cycle. Using ATP and NADPH to turb phosphoglycerate to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
Regeneration
Using ATP to regenerate ribulose-bisphosphate from glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to run the cycle again
How to make G3P
3 Turns of Calvin cycle
Rubisco
-Most abundant protein, fixes carbon to RuBP
-Sluggish
-Photorespiration
Photorespiration
Rubisco uses O2 as a substrate, causes net loss of C fixed, net loss of ATP
Stomata
-Leaf pores for gas exchange
-Normally open during the day, closed at night
C3
Normal pathway (Calvin cycle)
C4
-Photorespiration fix for hot climates
-CO2 fixed to 4-C organic acids in mesophyll cells
-4-C organic acids transported to bundle sheath cells
-4-C releases CO2 then travels back to mesophyll cells
-CO2 used for the Calvin cycle
-Separated by space
CAM
-Photorespiration fix for incredibly hot climates
-Crassulacean Acid Metabolism
-CO2 fixed to 4-C organic acids at night
-4-C releases CO2 for Calvin cycle during the day
-Separated by space and time
Starch
Glucose storage molecule in plants
Difference between fundamental and realized niche
Fundamental niche is the entire set of conditions under which an animal (population, species) can survive and reproduce itself. Realized niche is the set of conditions actually used by given animal (pop, species), after interactions with other species (predation and especially competition) have been taken into account.
Ecology
Science of interactions
Is ecology scale dependent
Yes, ecology is very scale dependent. It can be observed within a petri dish, in a field or in a province.
Structural questions in ecology
What is it, how does it work
Dynamical questions in ecology
How do things change over space and time
Perspectives in ecology
Physiological
Population
Community
Landscape
Ecosystem
Evolutionary (its a loop)
Community in ecology
How populations interact with each other
Population
Individuals of the same species interacting at the same spatial and temporal scale.
Population dynamics
How do populations change over time, what causes them to change
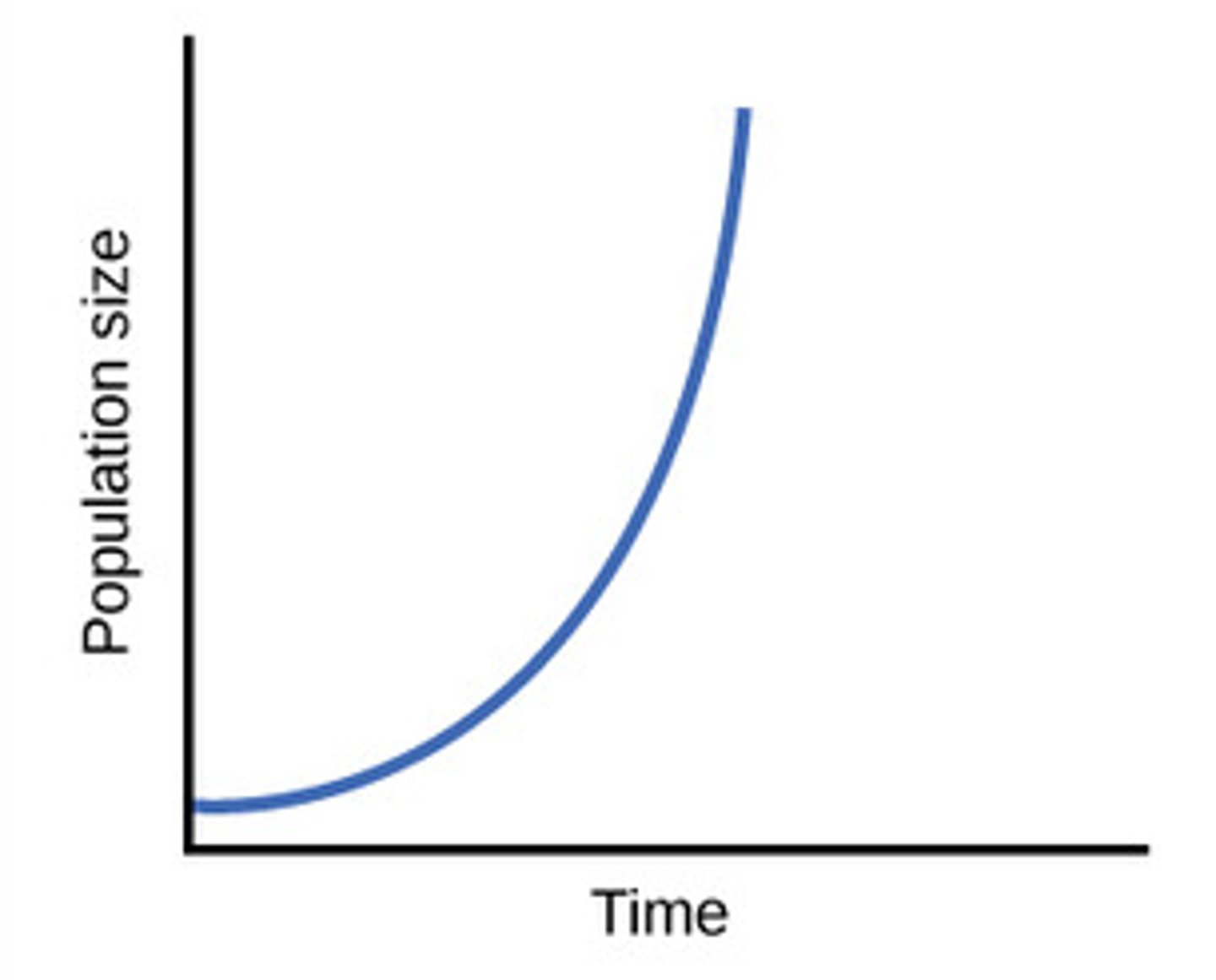
Exponential growth
dN/dt = rN (r = per capita growth rate)
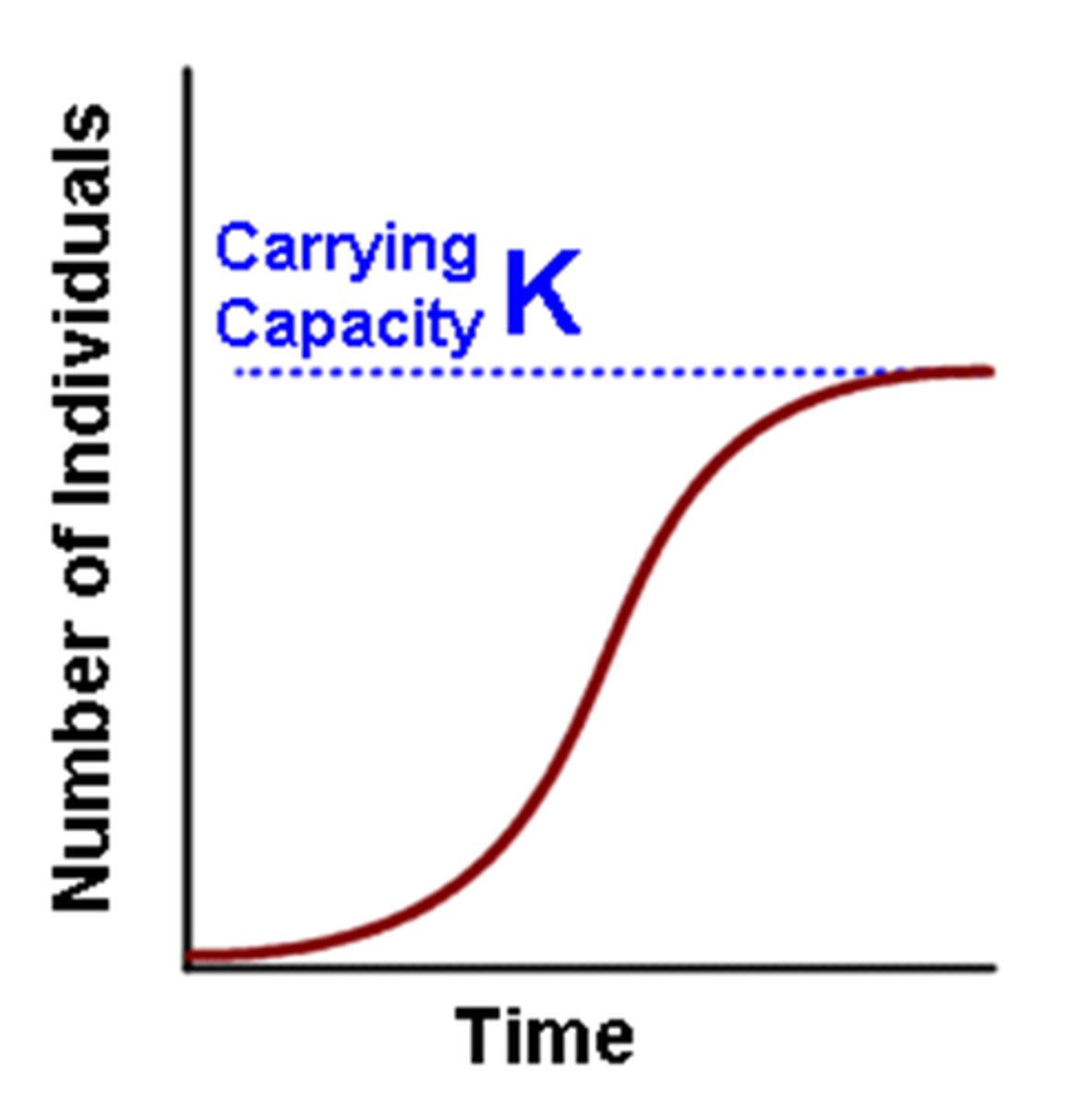
Logistic growth
dN/dt = rN(K-N)/K (K = carrying capacity)
Meta-population dynamics
Interaction of a population through time and space (including immigration and emigration)
Meta-population
Small isolated populations, some movement between them
Population regulating factors
Any parameter (intra or extra) that prevents a population from growing exponentially
Community
An interaction through periodic occupancy of space (interaction, not presence)
Types of interactions
Competition
Consumption
Mutualism
Commensalism (not real)
Competition
Negative - Negative interaction
Consumption
Negative - Positive interaction
Mutualism
Positive - Positive interaction
Competition defn
Any interaction between two spp. where an increase in density of one spp. causes a decrease in per capita population growth rate of the other.
A struggle for limited resources
Mechanisms of competition
Consumption of a resource
Preemption (space)
Allelopathy (using chemicals to compete)
Territoriality
Consumption competition
One species inhibits another by consuming a shared resource
Preemptive competition
Mainly among sessile organisms, where the mere presence of one species reduces a shared resource for another (competition for space)
Allelopathic competition
One species inhibits another by changing the chemical composition of a resource
Territorial competition
One species inhibits access of another species to a resource via behavioral aggression
Competitive exclusion principle
Two species cannot use the same resource in the same way and coexist
For two species to exist, what must be true
intraspecific competition > interspecific competition
If interspecific competition > intraspecific competition
One species is competitively excluded
Classical definition of consumption
Any interaction between two spp. where
-A density increase in spp. i causes an increase in the per capita population growth rate of spp. j
-A density increase in spp. j causes a decrease in the per capita population growth rate of spp. i
Consumption types
Predation
Parasitism
Herbivory
Seed predation
Competition coefficient (aij)
The sp. i proportional effect that sp. j has on sp. i
Predator functional response
Per capita consumption rate of a predator given prey density.
Often becomes saturated. 3 types, first, half and logistic
Zero growth isoclines
Where the population is not growing or shrinking
Disturbance
Any factor which causes a decrease in the number of individuals in a population.
Intermediate disturbance hypothesis
States that areas with intermediate disturbance will have the greatest biodiversity
Niche
The place a species occupies in a community
The environmental requirements of the species
An n-dimensional hypervolume where 'n' equals the number of physical and biological factors important to the survival and reproduction of a species
N-dimensional hypervolume
Fundamental niche
N-dimensional hypervolume + ineractions
Realized niche