Level 3 organic, functional groups and reagants
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
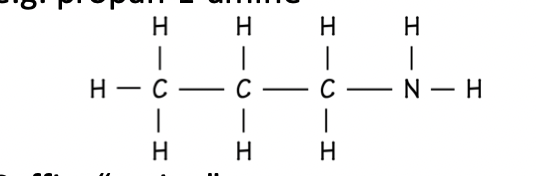
Amine
Alcohol
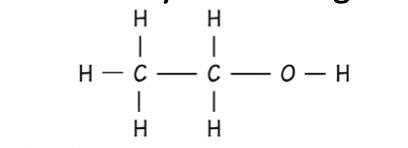
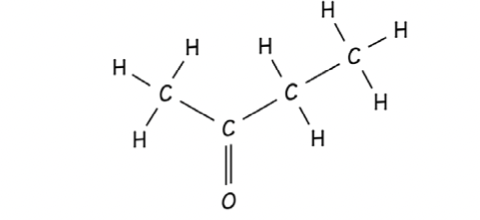
Ketone
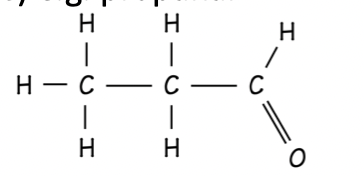
Aldehyde
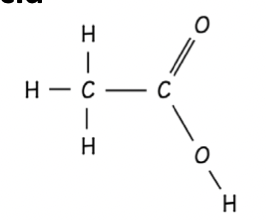
Carboxylic acid
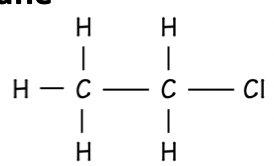
Haloalkane
Alkane
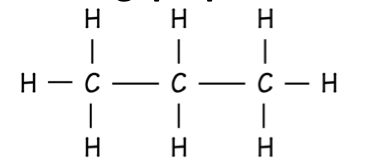
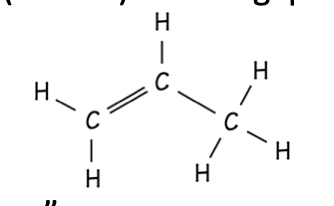
Alkene
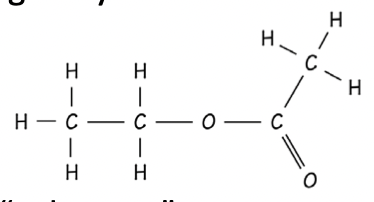
Alkyne
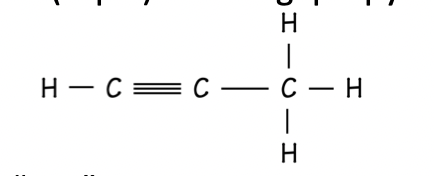
Amide
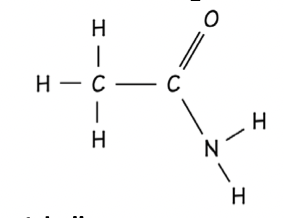
Acid chloride
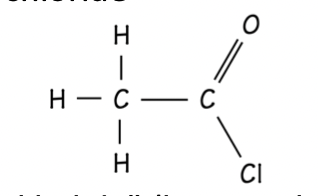
Ester
Oxidising agent (purple to colourless)
MnO₄⁻/H⁺
Oxidising agent (orange to green)
Cr₂O₇²⁻/H⁺
Reagent which converts alcohol to alkene (elimination)
conc. H₂SO₄
Reagent which converts alcohol to haloalkane (substitution)
SOCl₂/PCl₃/PCl₅
Reagent which converts haloalkane to alkene (elimination)
KOH (alc)
Reagent which converts haloalkane to alcohol (substitution)
KOH (aq)
Regent which converts aldehyde to primary alcohol (reduction)
NaBH₄
Molecule with same molecular formula but diff structural formula
Isomer
Carbon with 4 different atoms/groups attached
chiral
Optical isomers
Enantiomers
Benedict's solution
Blue to orange with aldehyde
Tollen's reagent (silver mirror)
Silver mirror formed with aldehyde
Ester
Formed when a primary alcohol and carboxylic acid combine
Acid chloride
Formed when a carboxylic acid reacts with thionoyl chloride (SOCl₂)
Addition Reacton:
The double bond breaks to a single bond to allow two new atoms/groups to be added to the carbons that were involved in the double bond.
Adding H2 to alkene reagents and reaction type.
Hydrogenation addition, Pt catalysts in high temperature and pressures. Prou
Adding halogen to alkene.
X2, the product is a di-haloalkane. If halogen is Br2, the colour changes from orange to colourless. As all the Br2 is reacted.