Module 2
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Business Process
collection of events, activities and decisions that collectively lead to an outcome that brings value to an organization’s customers
→ superior business processes are a way to outperform competitors
Business Process Managment
art and science of overseeing how work is performed in an organization to achieve consistent outcomes and take advantage of improvement opportunities
def: body of methods, technique and tools to discover, analyze, redesign, execute and monitor business processes (about managing the entire chain of events, not individual activities)
Common categories of business processes
order to cash
quote to order
procure to pay
issue to resolution
application to approval
order to cash
starts with customer order and ends with delivery payment
performed by a vendor
may encompass order verification, shipment, delivvery, invoicing
ex: order on amazon
quote to order
typically starts with customer requesting price quote qnd endswith customer placing order
procure to pay
start with determination that a given product or service needs to be purchased, ends with delivery and payment
may encompass obtaining quotes, approving purchase, selecting supplier
can be considered as dual to quote to cash process
issue to resolution
start: customer raising an issue
continues untill both parties agree that issue has been resolved
variant in the insurance industry relates to insurance claims
application to approval
starts with a request for certain privileges, ends with approval, denial
common in government agencies, universities,
ingredients of business process
Events happen instantaneously; they have no duration (e.g. the arrival of equipment)
Events can then trigger a number of activities (e.g. checking that equipment meets expectations); activities have duration
Decision points are points in time when a decision is made that affects business processes (e.g. the equipment should be returned)
Business Process management lifecycle
process identification
process discovery
process analysis
process redesign
process implementation
process monitoring and controlling
collect and analyze performance data on running redesigned process
correct deviations, restart cycle if major issues emerge
critical often forgotten last step
process identification
business problem is posed
process relevant to the problem are identified, defined, and related to each other
results in process architecture (collection of processes and links between them)
process discovery
current state of each process is documented
results in “as-is process models”
process analysis
identify issues with as-is-process
results in structured collection of issues
process redesign
identify changes that address uncovered issues
analyze and compare change options with respect to performance measures
results in a redesign process (“to-be process model”) that combines most promising changes
process implementation
prepare and perform changes required to move from as-is to to-be process
covers organisational change management (changes required to way of working of involved participants) and process automation (development and deployment of supportive IT systems)
process monitoring and controlling
collect and analyze performance data on running redesigned process
correct deviations, restart cycle if major issues emerge
critical often forgotten last step
role of algorithms
can assign tasks
can make processes more efficient
can reduce costs
ex: uber dynamic pricing
BPMN: events and activities
naming conventions:
Events usually begin with a noun (e.g. purchase order received)
Activities usually begin with a verb in imperative form (e.g. approve order)
To name a process model, we use a noun, potentially preceded by an adjective (e.g. “claim handling process”)

tokens
illustrate the progress of a given instance of the process - they outline the currents ate of that instance
depicted as colored dots on top of a process model
branching and merging
gateways:
gating mechanisms that allows or disallows the pasage of tokens
represented by diamonds
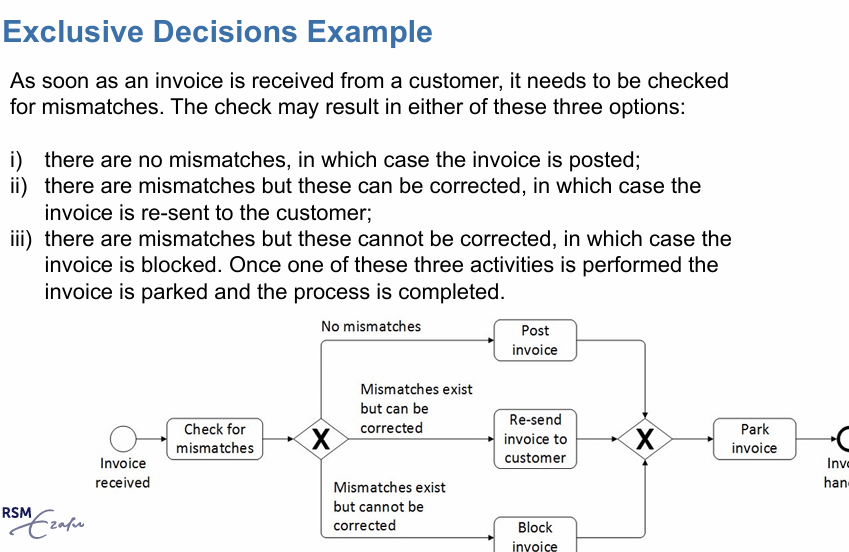
exclusive decisions: XOR gateway
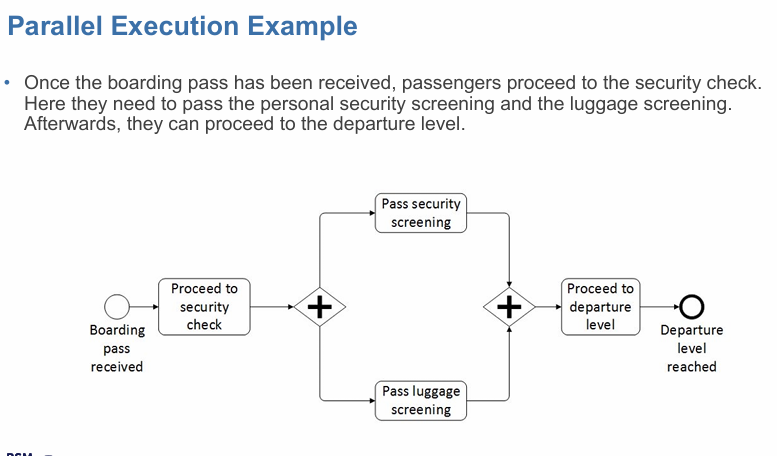
parallel execution
AND gateway
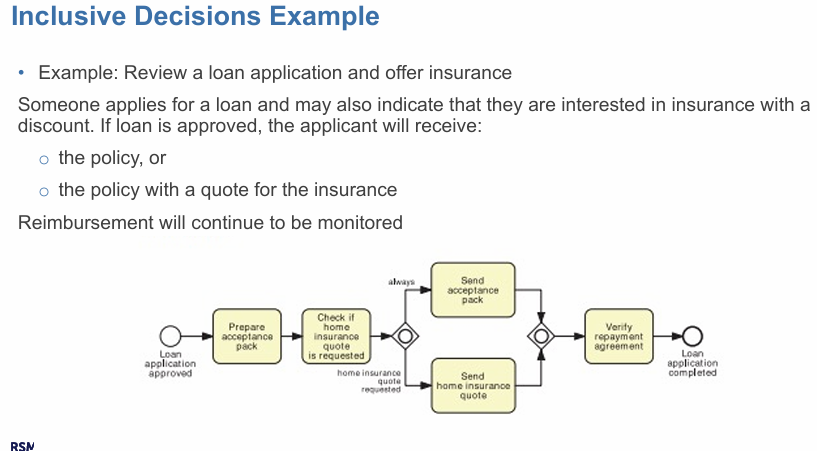
inclusive decisions
OR gateway
resources
anything or anyone involved in the performance of a process activity, such as participants, software, or equipement
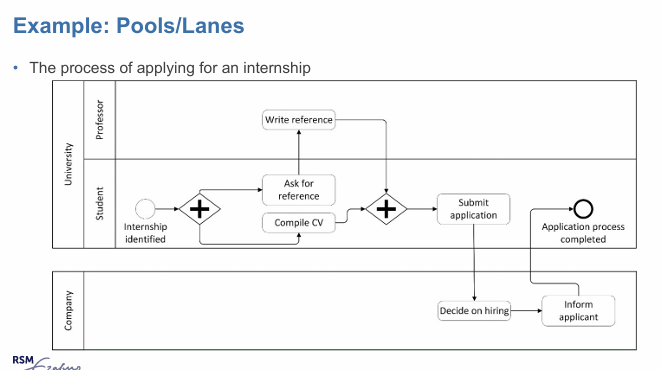
BPMN provides two constructs to model resources aspects: pools and lanes
pools
generally used for resources classes
business oarties, such as sellers, buyers, supliers
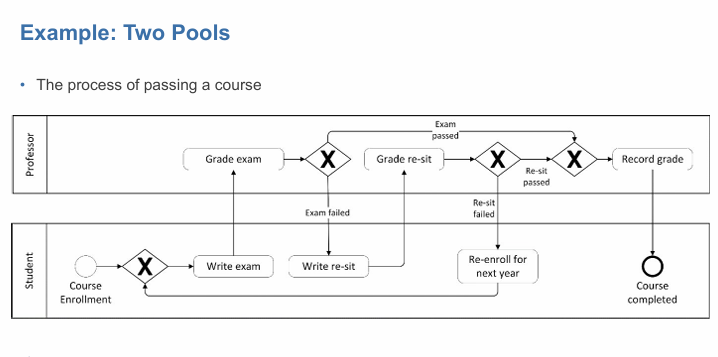
lanes
used to partition a pool into sub-classes or individual resources, department unit, teams, software system
can be nested in multiple levels
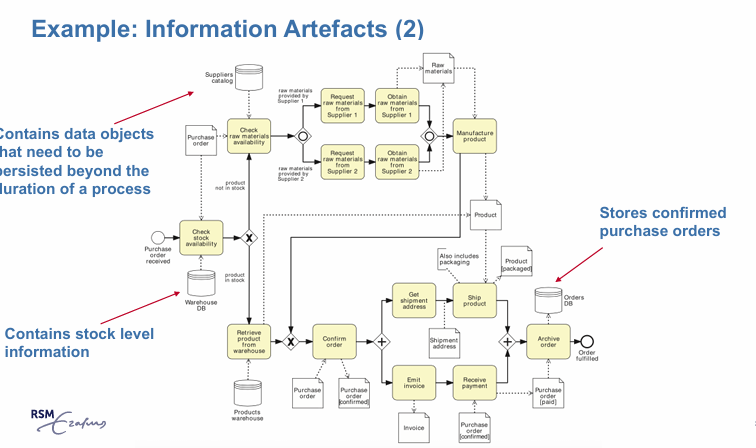
BPMN: information artefacts
data perspective
indicates which information artifacts are required to perform an activity
data objects
represents the information that flows in and out of activities in a business process
notation: documents with upper right corner folded over , linked to activities with a dotted arrow with open head
data stores
places where data objects are stored and need to be persisted beyond the duration of a single process instance
noted as empty cylinders