Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
1/49
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Heredity (inheritance)
The transmission of traits from one generation to the next

Variation
The differences in genetic outcomes between sons and daughters of parents
Genetics
The study of heredity and inherited variation
Genes
The units of heredity, made up of segments of DNA
Gametes
Reproductive cells in which genes are passed down to the next generation
Includes sperm and eggs
Somatic cells
All cells of the body except gametes and their precursors, containing 46 chromosomes
Locus
A gene’s specific position along a chromosome
Asexual reproduction
A type of reproduction where a single individual passes all of its genes to its offspring without the fusion of gametes
Clone
An individual or group of genetically identical individuals from the same parent
Sexual reproduction
A type of reproduction where two parents give rise to offspring that have unique combinations of genes inherited from the two parents
Life cycle
The generation-to-generation sequence of stages in the reproductive history of an organism
Chromosmal behavior is related to this in organisms
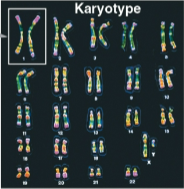
Karyotype
An ordered display of the pairs of chromosomes from a cell
Humans display 23 pairs
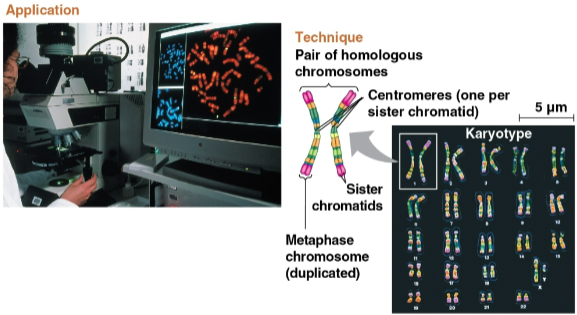
Homologous chromosomes (homologs)
The two chromosomes in each pair of chromosomes
Each has the same length, centromere position, and staining pattern with one set of chromosomes from each parent cell for inherited characteristics
Sex chromosomes
Chromosomes that determine the sex of the individual
X and Y in humans
Females have a homologous pair of X chromosomes
Males have one X and one Y chromosome
Autosomes
The remaining pairs of chromosomes that do not determine sex
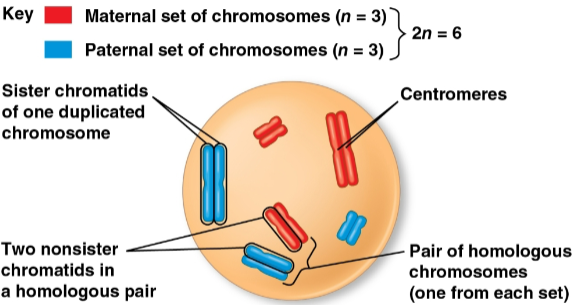
Diploid cell (2n)
A cell with two sets of chromosomes
Is 46 in humans, representing two half-sets
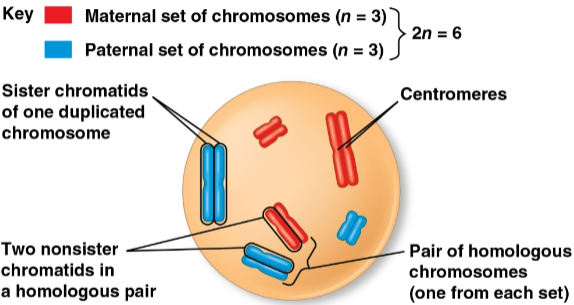
Chromosome replication
The replication of each chromosome into two identical sister chromatids
Haploid cell (n)
A cell that contains a single set of chromosomes
Includes gametes (sperm and eggs)
Is 23 in humans, representing one half-set with a single sex chromosome
Eggs (ovum) have a single X chromosome
Sperm have either an X or Y chromosome
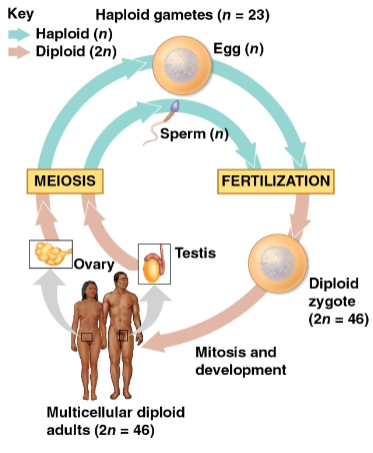
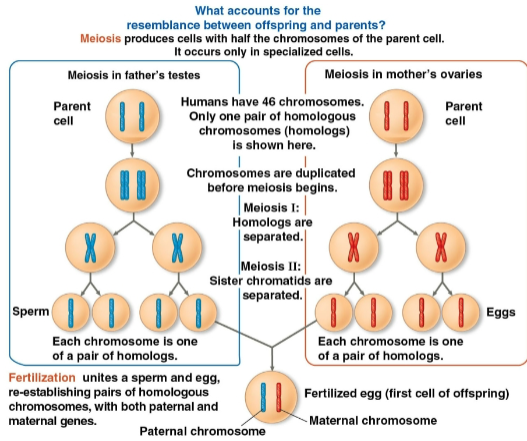
Fertilization
The union of gametes (sperm and egg) to create a zygote
Zygote
A fertilized egg with one set of chromosomes from each parent
Produces somatic cells by mitosis and develops into an adult
Often the only diploid stage in most fungi and some protists with no multicellular diploid stage; these grow by mitosis into haploid multicellular organisms
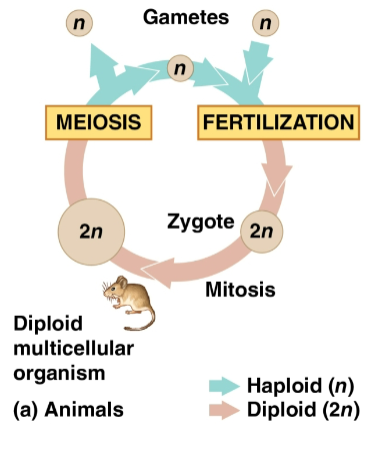
Meiosis
Type of cell reproduction that creates gametes
Found in the ovaries and testes in humans
Results in one set of chromosomes in each gamete (n) as only diploid cells can undergo this
Alternates with fertilization to maintain chromosome number
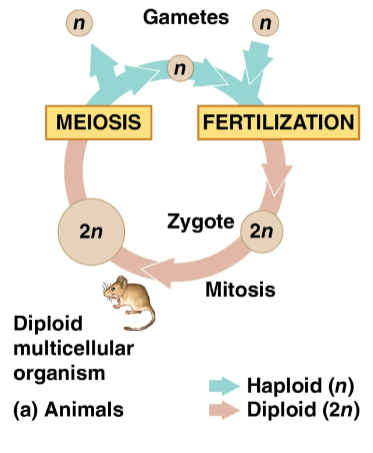
Gametes
Reproductive cells produced by meiosis that undergo no further cell division before fertilization
Often the only haploid cells in most animals
Fuse to form a diploid zygote that then divides by mitosis to a multicellular organism
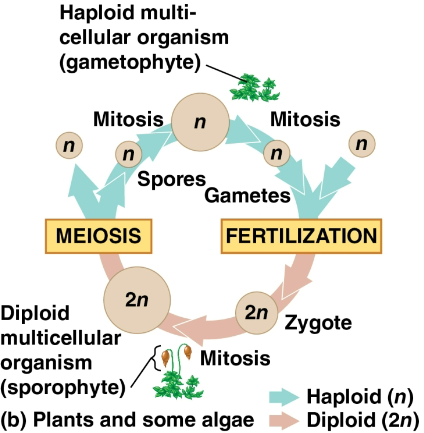
Alternation of generations
A life cycle exhibited by plants and some algae that include both a diploid and haploid multicellular stage
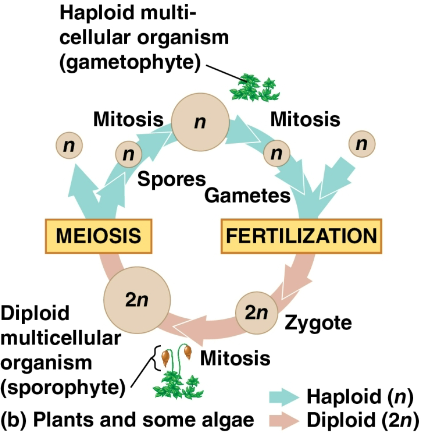
Sporophyte
A diploid organism that makes haploid spores by meiosis
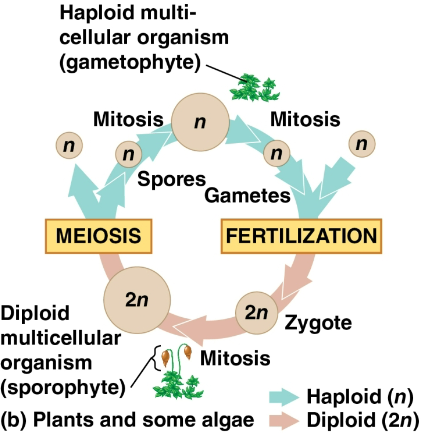
Gametophyte
A haploid organism that grew from a sporophyte by mitosis that then makes haploid gametes by mitosis
Fertilization of these gametes results in a diploid sporophyte
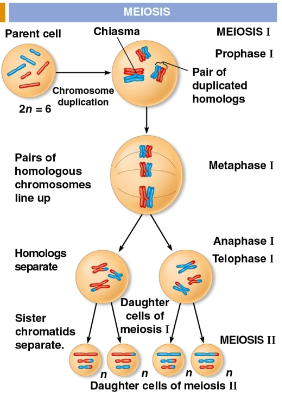
Meiosis
A method of cellular reproduction preceded by the replication of chromosomes, taking place in two stages
Results in four daughter cells with half as many chromosomes as the parent cell
Reduces the number of chromosome sets from two (diploid) to one (haploid), producing four genetically differing cells

Mitosis
A method of cellular reproduction that conserves the number of chromosome sets
Produces two cells genetically identical to the parent cell
Sister chromatid cohesion
The close association of sister chromatids as chromosomes duplicate before meiosis and sorting
Cohesins are cleaved at the end of metaphase in mitosis
Cohesins are cleaved along the chromosome arms in anaphase I (separation of homologs) and at the centromeres in anaphase II (separation of sister chromatids)

Cohesins
Proteins that hold together sister chromatids after interphase
Nonsister chromatids are broken at precisely matching points
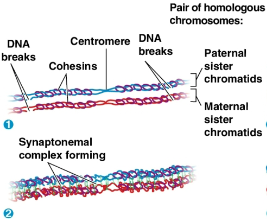
Synaptonemal complex
A zipper-like structure that holds the homologs together tightly in prophase I
Synapsis
Process where DNA breaks are repaired and DNA is joined from one nonsister chromatid to the corresponding segment of another
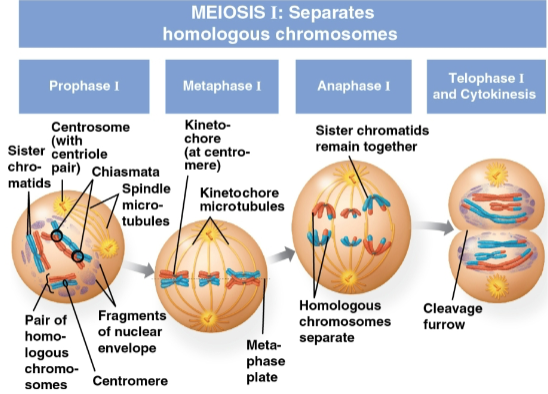
Meiosis I
The first stage of meiosis with four phases:
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Telophase I and cytokinesis
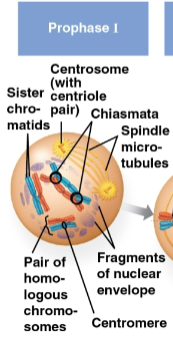
Prophase I
First stage of meiosis I where each chromosome pairs with its homolog and crossing over occurs at chiasmata
Crossing over occurs for each sister chromatid within each chromosome, resulting in genetic variation for all four
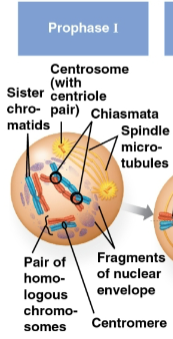
Chiasmata
X-shaped regions on chromosomes where crossovers occur
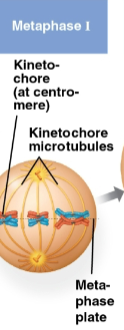
Metaphase I
Second stage of meiosis I where pairs of homologs line up at the metaphase plate, one chromosome facing each pole
Microtubules from the poles are attached to the kinetochore of each chromosome
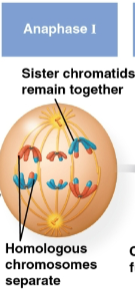
Anaphase I
Third stage of meiosis I where pairs of homologs separate as one chromosome of each pair moves towards opposite poles
Sister chromatids remain attached at the centromere and move as one unit toward the pole
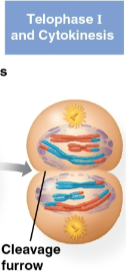
Telophase I
Fourth and last stage of meiosis I where each half of the cell has a haploid set of duplicated chromosomes
Each chromosome still consists of two sister chromatids
Cytokinesis occurs simultaneously with this, forming two haploid daughter cells with either a cleavage furrow or cell plate forming
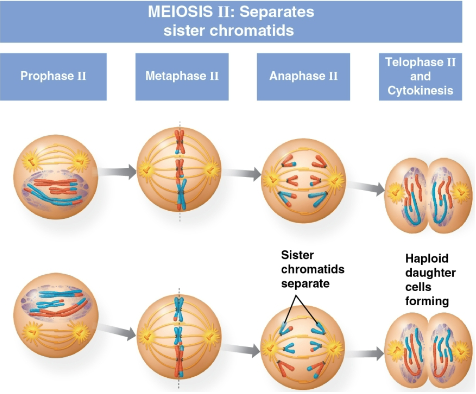
Meiosis II
The second stage of meiosis with four phases:
Prophase II
Metaphase II
Anaphase II
Telophase II and cytokinesis
Is very similar to mitosis
Prophase II
First stage of meiosis II where a spindle apparatus forms
Chromatid pairs move toward the metaphase plate later in this stage

Metaphase II
Second stage of meiosis II where the sister chromatids are arranged at the metaphase plate
Crossing over in meiosis I means the two sister chromatids are no longer genetically identical
Kinetochores attach to microtubules extending from opposite poles

Anaphase II
Third state of meiosis II where the sister chromatids separate
Each sister chromatid now moves as two newly individual chromosomes toward opposite poles

Telophase II
Fourth and last stage of meiosis II where the chromosomes arrive at opposite poles
Cytokinesis occurs shortly after as nuclei form and chromosomes decondense
Mutations
Changes in an organism’s DNA that are the original source of genetic diversity
Creates different versions of genes called alleles
Alleles
Different versions of genes created by mutations
Reshuffling these during sexual reproduction produces genetic variation
Chromosomal behavior
What is responsible for most of the variation that arises in each generation during meiosis and fertilization, including:
Independent assortment of chromosomes
Crossing over
Random fertilization

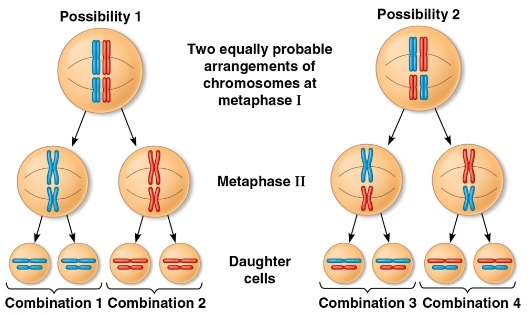
Independent assortment
The sorting of maternal and paternal homologs into daughter cells independently of the other pairs with random orientations
n
The haploid number
2 to the power of this represents the number of combinations possible when they assort independently into gametes
This is 23 in humans, leading to 223 (over 8 million) possible combinations
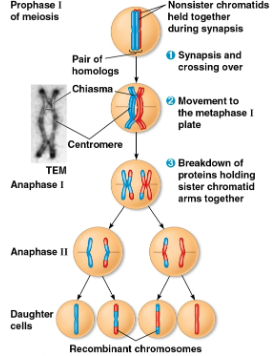
Recombinant chromosomes
Chromosomes that combine DNA inherited from each parent during crossing over, allowing for variation within a single chromosome
1 to 3 crossover events occur per chromosome in humans
Random fertilization
The fact that any sperm can fuse with any ovum (unfertilized egg)
The fusion of two gametes (8.4 million possible combinations) produces a zygote with any of about 70 trillion diploid combinations, adding a unique genetic identity
Genetic variation
Created through natural selection, mutations, and meiosis
Asexually reproducing organisms increase this by incorporating foreign DNA from the environment