AP World History Unit 1 AMSCO Vocab
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms

Song Dynasty
(960-1279 CE) The Chinese dynasty that placed much more emphasis on civil administration, industry, education, and arts other than military.

Confucianism
The system of ethics, education, and statesmanship taught by Confucius and his disciples, stressing love for humanity, ancestor worship, reverence for parents, and harmony in thought and conduct.
Filial Piety (Confucianism)
a virtue of respect for one's parents, elders, and ancestors
Imperial Bureaucracy
Division of an empire into organized provinces to make it easier to control
Neo-Confucianism
A philosophy that emerged in Song-dynasty China; it revived Confucian thinking while adding in Buddhist and Daoist elements.
Buddhism in China
Spread by the Silk Roads, took form of Mahavana Buddhism. Blended with Daoism, formed 'Chan Buddhism' (aka Zen Buddhism).
Champa rice
a quick-maturing, drought resistant rice that can allow two harvests, of sixty days each in one growing season
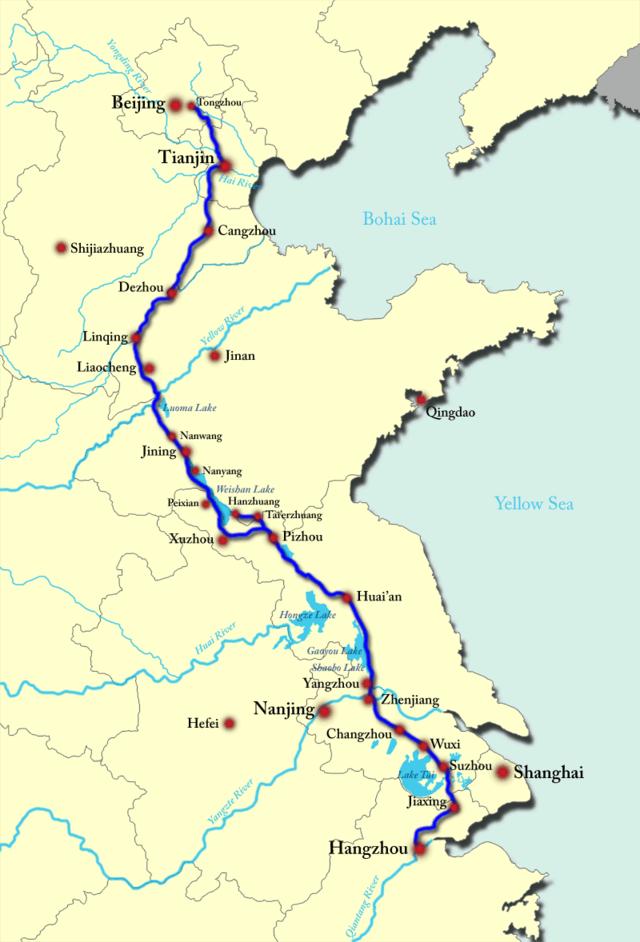
Grand Canal
Built in 7th century during reign of Yangdi during Sui dynasty; designed to link the original centers of Chinese civilization on the north China plain with the Yangtze river basin to the south; strengthened China's internal cohesion and economic development
Textile Industry
Industries primarily concerned with the design or manufacture of clothing as well as the distribution and use of textiles.
porcelain
a thin, beautiful pottery invented in China; one of China's 3 major exports
Steel and iron production
A key element during the Song Economic Revolution; helped popularize mass production and new production methods
Islam
A religion based on the teachings of the prophet Mohammed which stresses belief in one god (Allah), Paradise and Hell, and a body of law written in the Quran. Followers are called Muslims.
Judaism
A religion with a belief in one god. It originated with Abraham and the Hebrew people. Yahweh was responsible for the world and everything within it. They preserved their early history in the Old Testament.
Christianity
A monotheistic system of beliefs and practices based on the Old Testament and the teachings of Jesus as embodied in the New Testament and emphasizing the role of Jesus as savior.
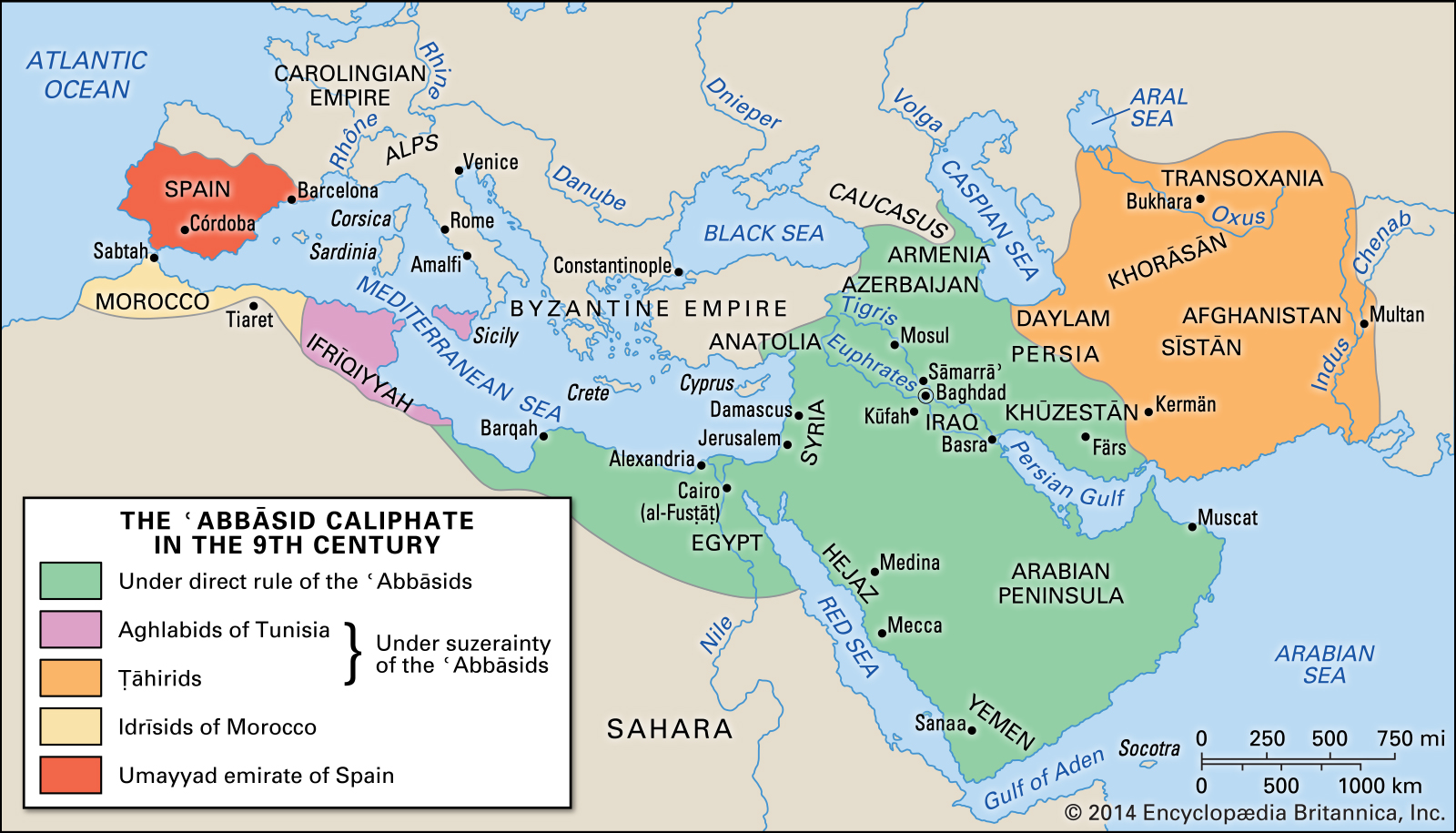
Abbasid Caliphate
third of the Islamic Caliphates of the Islamic Empire. The rulers who built their capital in Baghdad after overthrowing the Umayyad caliphs. In started in 750 CE. It flourished for two centuries, but slowly went into decline with the rise to power of the Turkish army it had created, the Mamluks. In the 13th century the Mongols displaced them.
Turks
Central Asian nomads related to the Xiongnu peoples that pressured Han China. Organized as tribes that constantly fought each other. Most converted to Islam. Most societies sought to trade with settled people. Nobles controlled absolutely in times of war.
Seljuk Empire
An empire formed by Turkish and Persian Sunnis, lasting from 1037 to 1194 A.D.
Mamluks
Under the Islamic system of military slavery, Turkic military slaves who formed an important part of the armed forces of the Abbasid Caliphate of the ninth and tenth centuries. Mamluks eventually founded their own state, ruling Egypt and Syria (1250-1517)
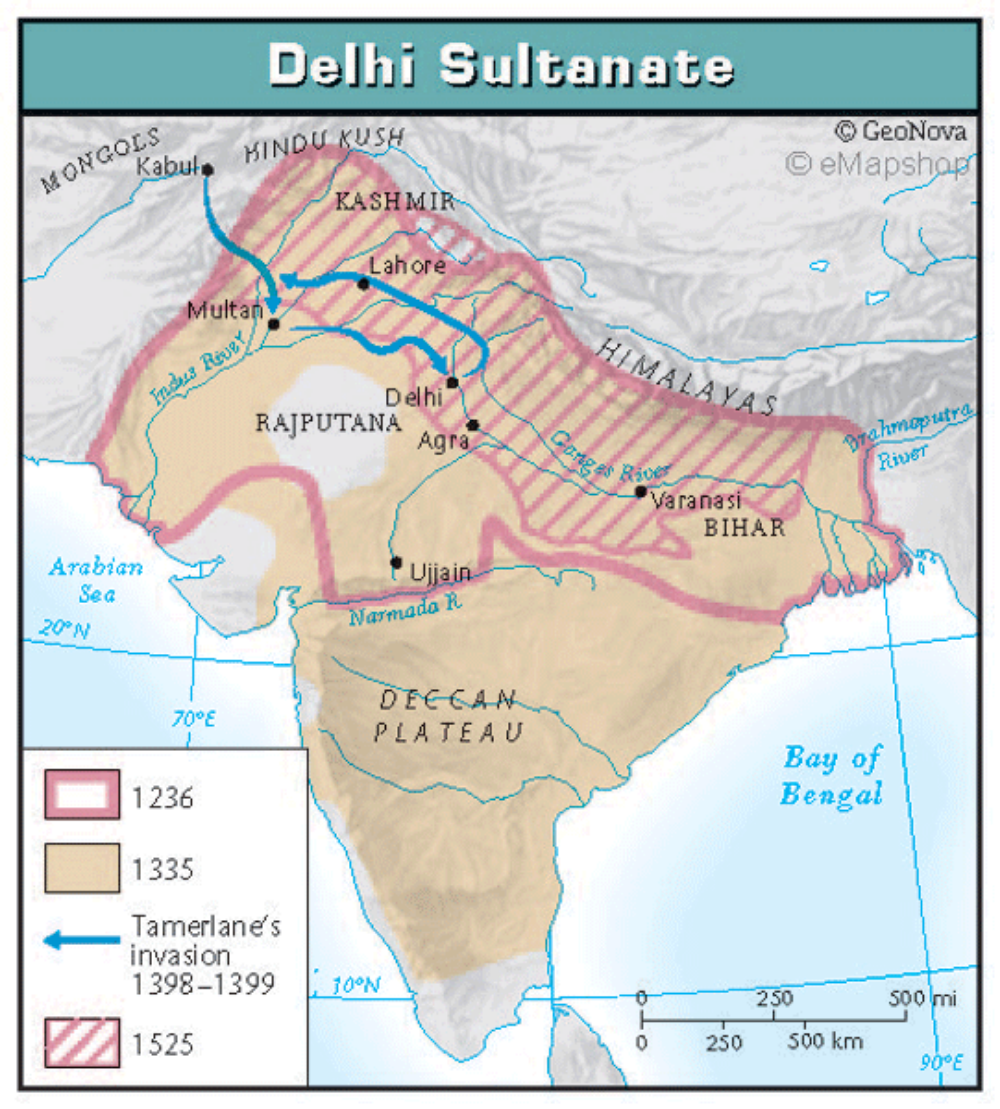
Delhi Sultanates
For about 320 years beginning in 1206, five dynasties ruled over the city of Delhi in India. A former slave named Qutb-ud-din Aibak spread Delhi's territory and influence across northern India. He also spread the influence of the Islamic religion throughout the region. After years of conquest, the Sultanate conquered and incorporated that majority of the Indian subcontinent. This resulted in a sort of unification process between the diverse peoples of the region, but also led to a split in Indian culture, as Hindus increasingly fought against the Sultanate in the 16th century, leading to its demise.
Sufis
mystical Muslim group that believed they could draw closer to God through prayer, fasting, & simple life
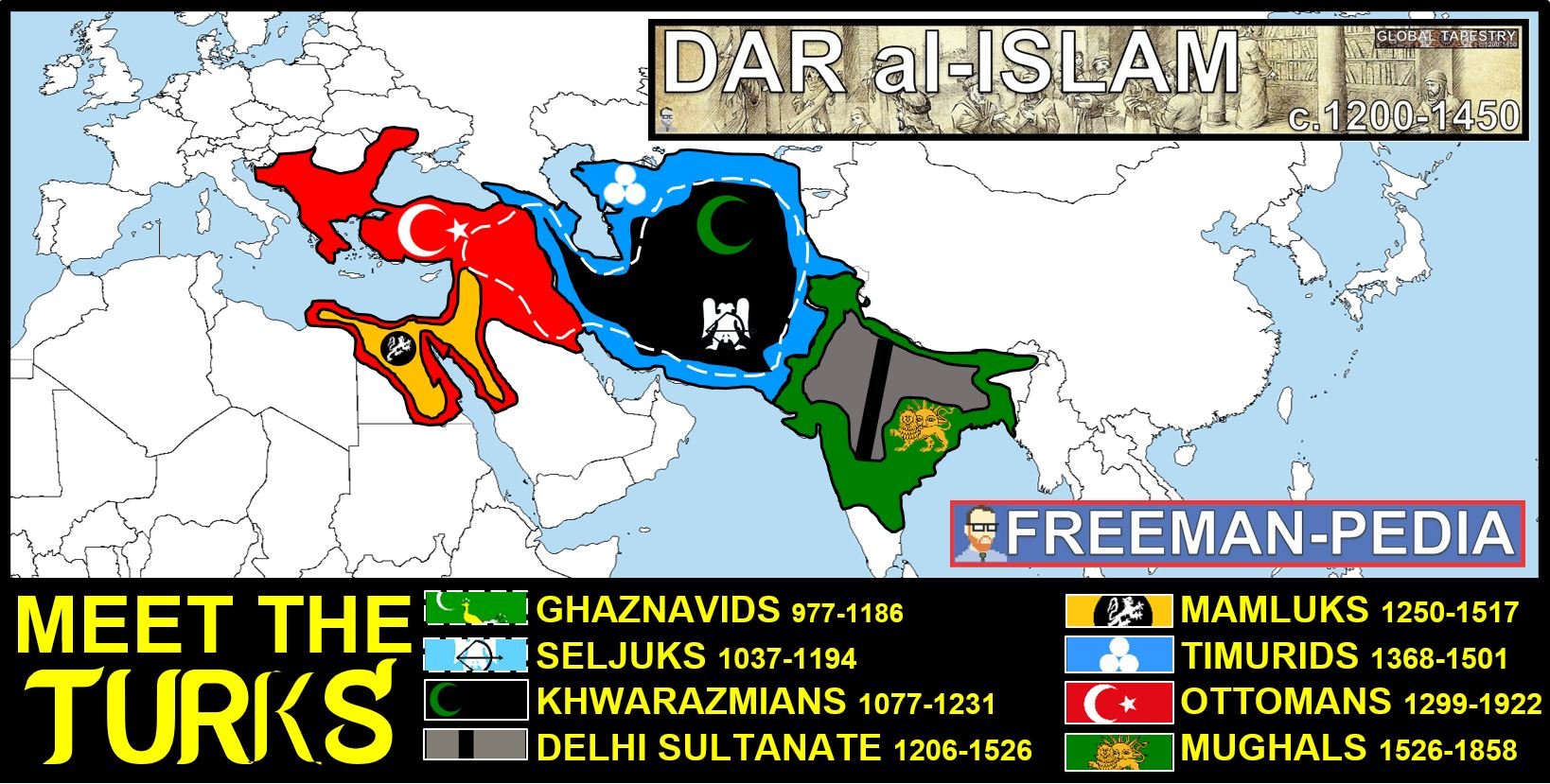
Dar al-Islam
an Arabic term that means the "house of Islam" and that refers to lands under Islamic rule
Hinduism
A religion and philosophy developed in ancient India, characterized by a belief in reincarnation and a supreme being who takes many forms
Bhakti Movement
a Hindu movement that sought to emphasize the idea of devotion to God (Salvation); women began to receive greater importance and recognition in society
Monasticism
A way of life in which men and women withdraw from the rest of the world in order to devote themselves to their faith (monetarists and nunneries)
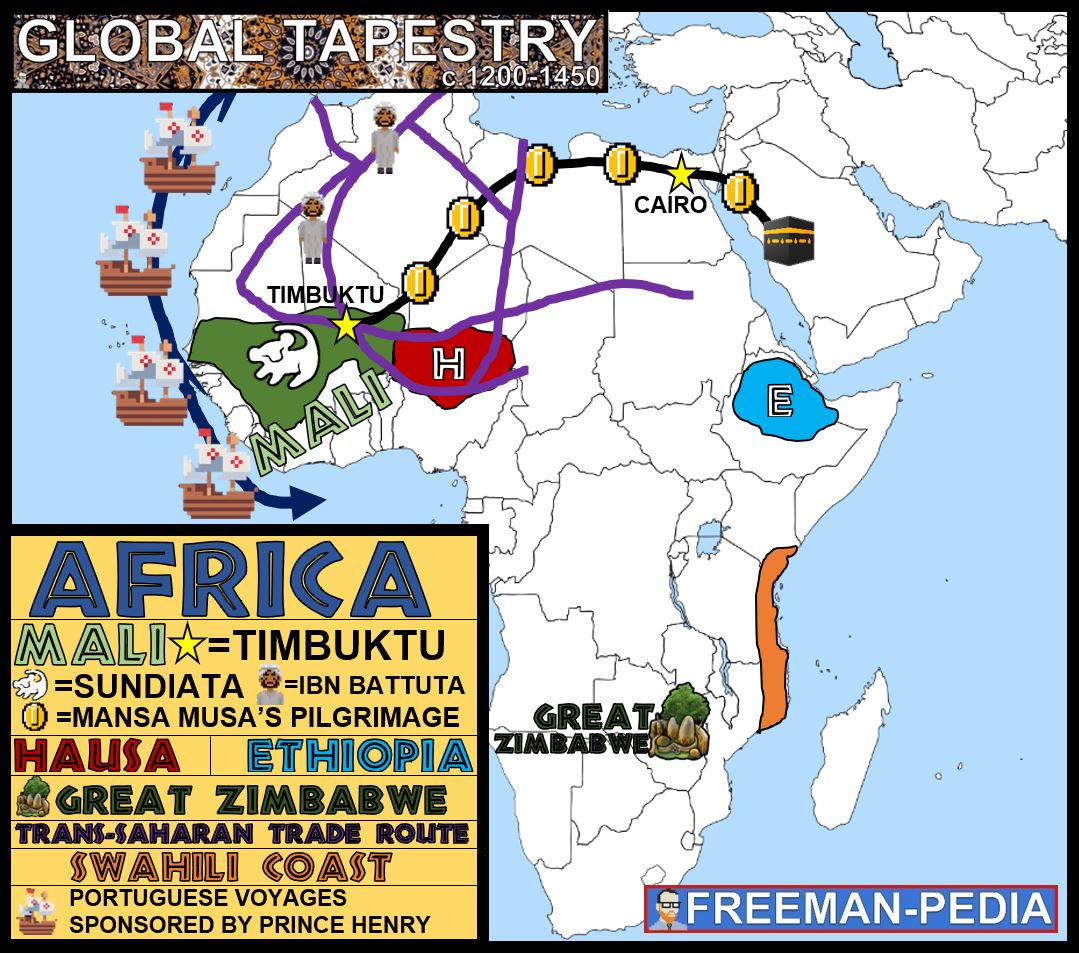
Zimbabwe
A powerful state in the African interior that apparently emerged from the growing trade in gold to the East African coast; flourished between 1250 and 1350 C.E.
Hausa Kingdoms
1 kingdom divided into 7 states that were connected through kinship, blood, or ethnic ties; had no main central authority but rather ruled each state separate from one another;mainly benefited economically from the trans-Saharan trade network
Feudalism
the dominant social system in medieval Europe, in which the nobility held lands from the Crown in exchange for military service, and vassals were in turn tenants of the nobles, while the peasants were obliged to live on their lord's land and give him homage, labor, and a share of the produce, notionally in exchange for military protection.
Manorial System
self sufficient, economic structure that is the relationship between the Lord and the peasants or serfs who produced all the necessary goods to keep the manor running
Free Labor
voluntarily, wage-paying rather than slave labor
Coerced Labor
a system where the workers were forced to work based on threats, pressure, or intimidation.
Serfdom
Feudal system, the use of serfs to work the land in return for protection against barbarian invasions
Meritocracy
a system in which promotion is based on individual ability or achievement, such as in Song China where the civil service exams were used to place young men in bureaucratic jobs.
artisans
skilled craftworkers
Tribute System (China)
An arrangement in which other states had to pay money or provide goods to honor or often kowtow (bow) to the Chinese system.
scholar-gentry class
Class of men in China who were educated degree-holders and who would enjoy special privileges of dress, law and social position
Foot Binding
Chinese practice of tightly wrapping girls' feet to keep them small, begun in the Tang dynasty; an emphasis on small size and delicacy was central to views of female beauty.
woodblock printing
a type of printing in which text is carved into a block of wood and the block is then coated with ink and pressed on the page. Introduced in China during the 7th century.
House of Wisdom in Baghdad
in 830s, the Abbasids opened this renowned center of learning to meet the demand for knowledge.

Nasir al-Din al-Tusi
(1201-1274) Persian mathematician and cosmologist whose academy near Tabriz provided the model for the movement of the planets that helped to inspire the Copernican model of the solar system.
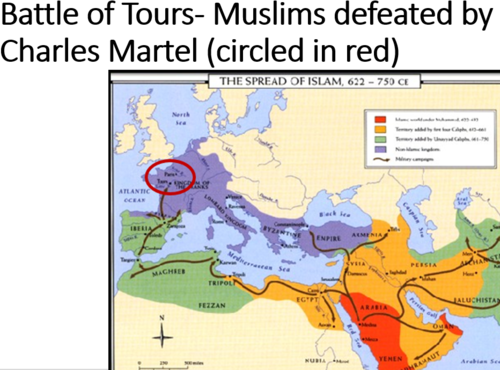
Battle of Tours (732)
Frankish army let by Charles Martel repelled a Muslim invasion of Western Europe
proselytize
to convert someone to a faith, belief, or cause
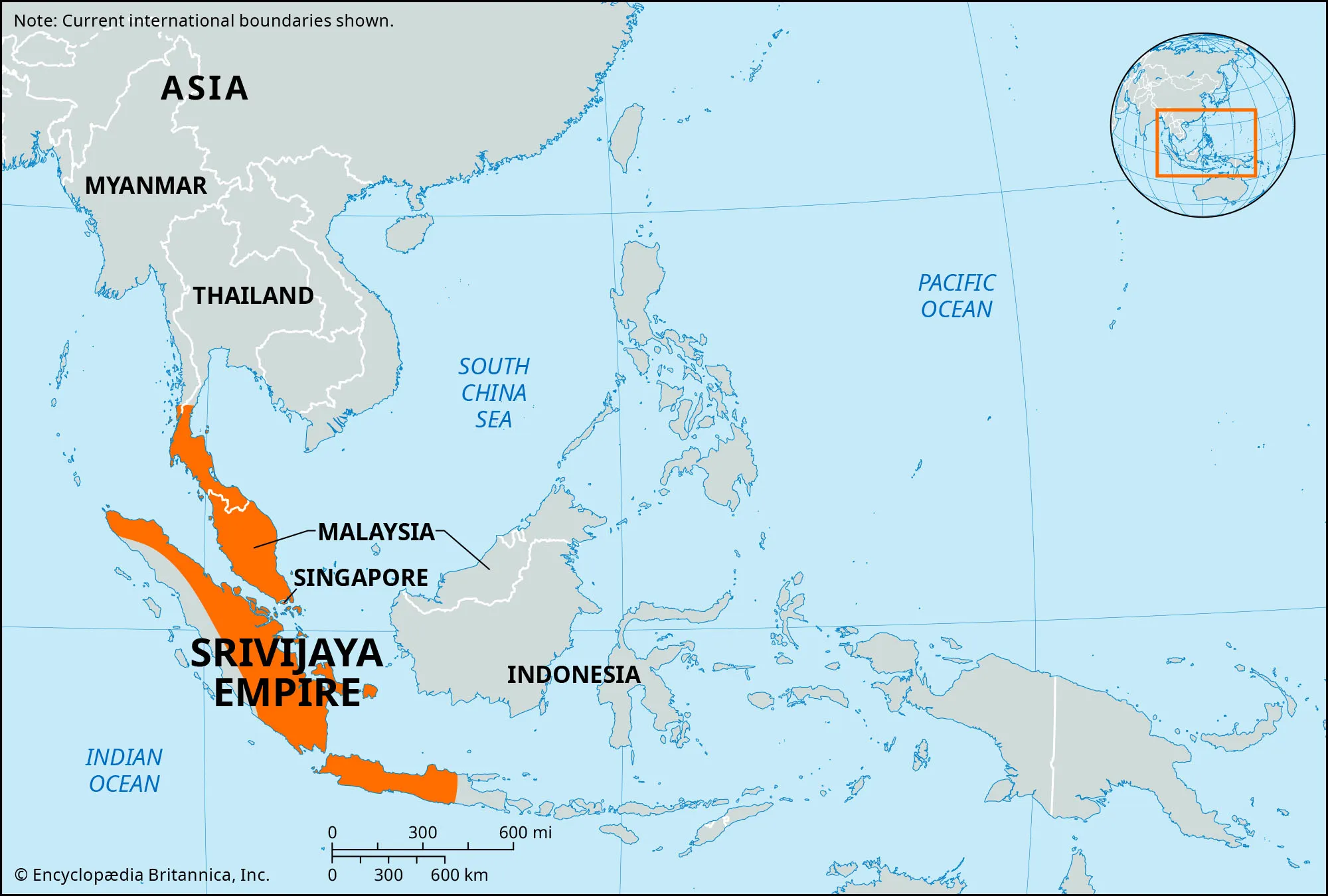
Srivijaya Empire
Hindu kingdom based on Sumatra (Indonesia). Prospered by charging fees for ships traveling between India and China (Strait of Malacca)
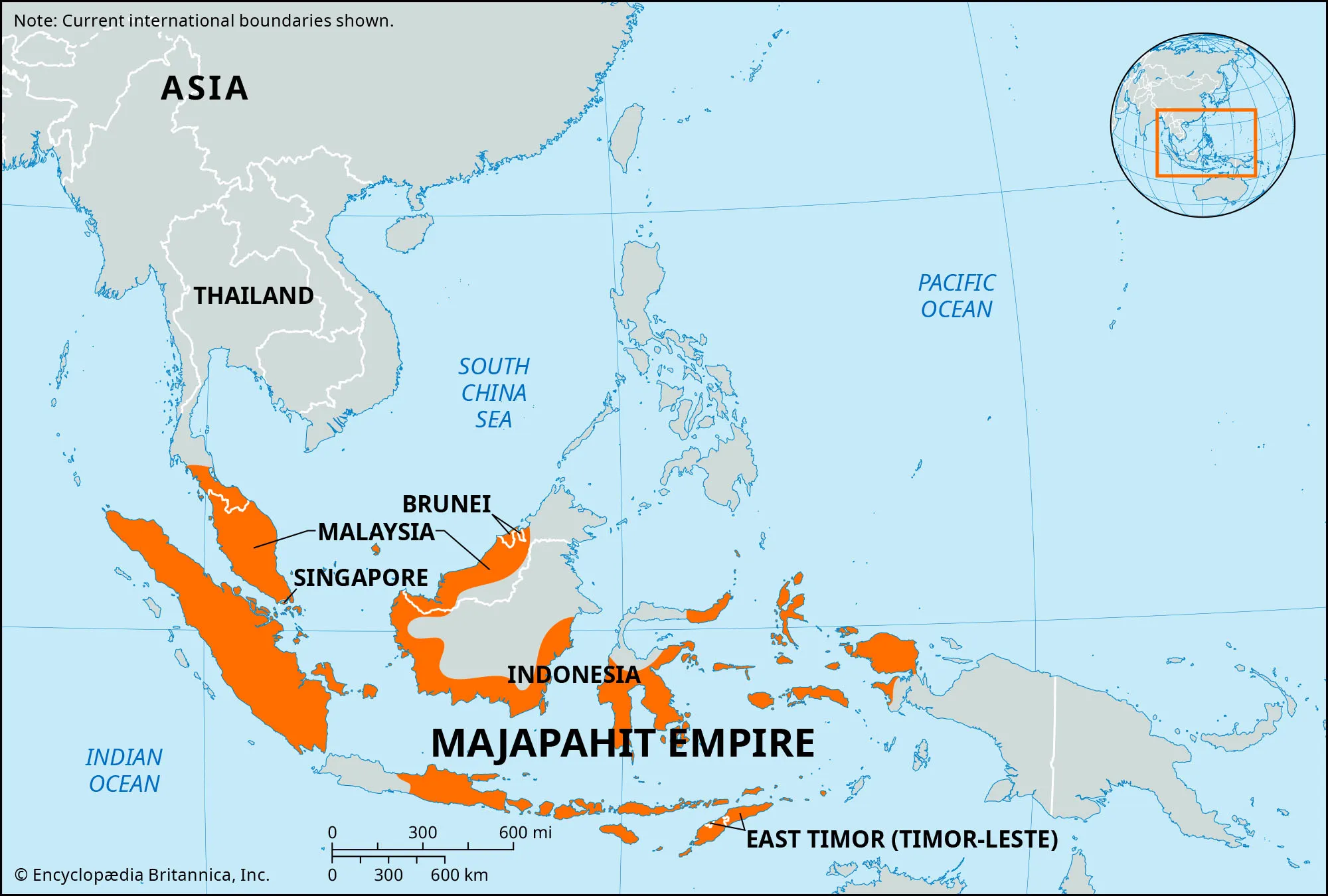
Majapahit kingdom
Like the Srivijaya Empire, the _______ prospered on controlling sea routes. It was a Buddhist kingdom.
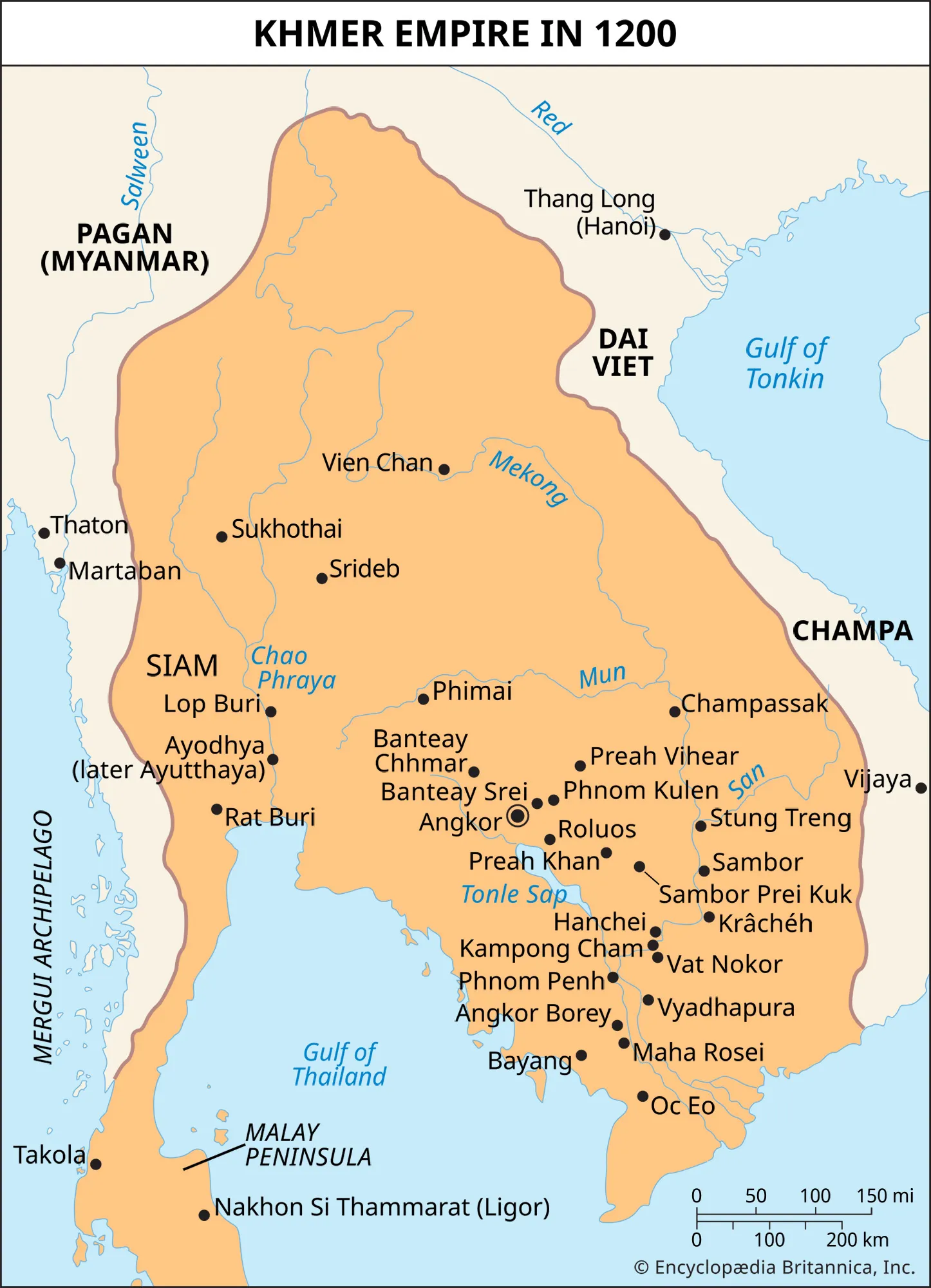
Khmer Empire
a powerful empire that lasted roughly from the 9th to the 15th centuries in what is now Cambodia. Famous for Angkor Wat, a temple complex of both Hindu and Buddhist influences.
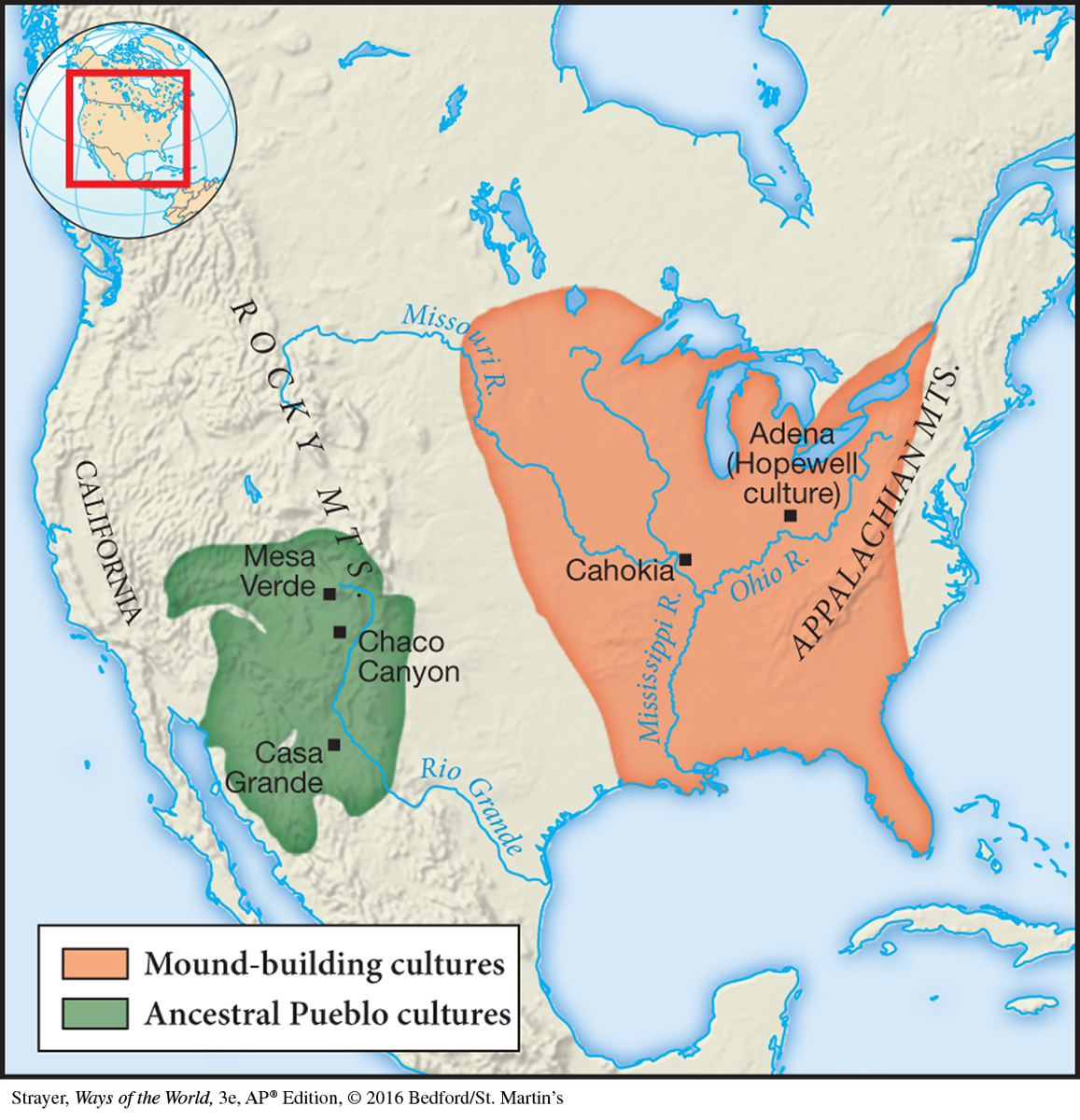
Cahokia
Mississippian settlement near present-day East St. Louis, home to as many as 25,000 Native Americans
city-state
a city that with its surrounding territory forms an independent state. Examples include the Maya, the Ancient Greeks, and the Swahili city-states of East Africa.
Chinampas
Raised fields constructed along lake shores in Mesoamerica to increase agricultural yields, famously used by the Aztecs.
Theocracy
A government controlled by religious leaders
Pachacuti
Inca ruler (1438-1471); began the military campaigns that marked the creation of an Inca empire.
Mit'a System
economic system in Incan society where people paid taxes with their labor and what they produced
Animism
The belief that bodies of water, animals, trees, and other natural objects have spirits, similar to Shinto in Japan
Kingdom of Ghana
powerful West African kingdom (7th–13th century) that thrived through control of the trans-Saharan trade, particularly gold and salt, and was located in what is now southeastern Mauritania and part of Mali
Kingdom of Axum (Aksum)
In northern Africa-Christians. Good Trading location=Lots of Money
Griots
Professional oral historians or storytellers who served as keepers of traditions in Africa
three-field system
a system of farming developed in medieval Europe, in which farm land was divided into three fields of equal size and each of these was successively planted with a winter crop, planted with a spring crop, and left unplanted.
Lay Investiture Controversy
A power struggle over whether a secular leader (king, emperor), rather than the pope, could invest bishops with the symbols of office.
Hundred Years War
War between France and Britain, lasted 116 years, mostly a time of peace, but it was punctuated by times of brutal violence (1337 to 1453). Began the decline of knights and the rise of nationalism.
Great Schism of 1054
the official split between the Western Roman Catholic Church and the Orthodox Church in the East
Primogeniture
A system of inheritance in which the eldest son in a family received all of his father's land. The nobility remained powerful and owned land, while the 2nd and 3rd sons were forced to seek fortune elsewhere.
Crusades (1095-1291)
Series of wars and pilgrimages with the goals of retaking the Holy Land for Christians; originally called in 1095 by Pope Urban II after a request from the Emperor of Byzantine and the Patriarch of the Eastern Orthodox church
Marco Polo
Venetian merchant and traveler. His accounts of his travels to China offered Europeans a firsthand view of Asian lands and stimulated interest in Asian trade.
Renaissance
"rebirth"; following the Middle Ages, a movement that centered on the revival of interest in the classical learning of Greece and Rome
Humanism (Renaissance)
A Renaissance intellectual movement in which thinkers studied classical texts and focused on human potential and achievements