Medical-Veterinary Entomology – Lecture 2
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is vectorial capacity?
Equation that measures pathogen transmission by mosquitoes, defined as the average number of new vertebrate infections per day from an index case.
Factors: mosquito-to-human ratio (m), human biting rate (a), daily mosquito survival (p), and pathogen latent period (n days).
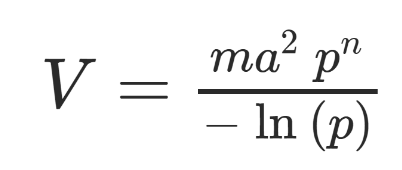
What are the 4 components of vectorial capacity?
Number of mosquitoes per person
Feeding frequency and type
Survivorship
Vector competence
What is a bridge vector?
Biting arthropod transmitting a pathogen from an animal host to a human.
What is an enzootic vector?
Biting arthropod transmitting a pathogen from one animal host to another.
What is the Risk (Probability) of human infection equation?
Risk = A x Fm x P x Cv
A = vector abundance
Fm = fraction of human blood meals
P = infection prevalence in the vector
Cv = fraction of infected mosquitos that will transmit disease by a subsequent bite = vector competence
How is MIR (minimum infection rate) calculated?
MIR = (number of positive pools ÷ total specimens tested) × 1000
Define Endemic.
Disease regularly occurring in people within a certain area/community. (Greek: endemios, native + demos, people)
Define Epidemic.
Rapid spread of disease to many people in a population within a short time. (Greek: epi = upon/above + demos = people)
Define Pandemic.
Epidemic spread across multiple regions/continents, affecting many individuals. (Greek: pan = all + demos = people)
Define Enzootic.
Disease in non-human animals that is constantly present in a specific area at low incidence.
Define Epizootic.
Rapid spread of disease among non-human animals in a population within a short time. (Greek: epi = upon + zoon = animal)
Which invasive mosquitoes drive most recent epidemics?
Culex pipiens,
Cx. quinquefasciatus,
Aedes albopictus,
Aedes aegypti.
Diseases: Yellow fever, Dengue (DHF), West Nile encephalitis, Rift Valley fever, Chikungunya, Zika fever, Urban malaria.
what is the Mosquito (Culicidae) taxonomy?
Kingdom Animalia → Phylum Arthropoda → Class Insecta → Order Diptera → Family Culicidae → Subfamilies Anophelinae, Culicinae
Morphological difference in eggs between Anophelinae vs Culicinae
Anophelinae: visible lateral floaters.
Culicinae: no floaters.
Morphological difference in larvae between Anophelinae vs Culicinae
Anophelinae: no respiratory siphon.
Culicinae: highly visible siphon.
Morphological difference in adult females between Anophelinae vs Culicinae
Anophelinae: palps as long as proboscis.
Culicinae: palps smaller than proboscis.
Morphological difference in adult males between Anophelinae vs Culicinae
Anophelinae: palps rounded extremities.
Culicinae: palps tapered extremities.
Morphological difference in resting position between Anophelinae vs Culicinae
Anophelinae: oblique to surface.
Culicinae: parallel to surface.
Diseases transmitted by Anopheles gambiae complex
Malaria, human filariasis. A. gambiae (endophilic, endophagic), A. arabiensis (drier climates).
Diseases transmitted by Culex pipiens group
West Nile, St. Louis encephalitis, bird malaria.
Temperate: Cx. pipiens form molestus (underground, autogenous)
Tropical/subtropical: Cx. quinquefasciatus
Diseases transmitted by Aedes spp.
Dengue, Chikungunya, Zika, Yellow fever.
Ae. aegypti: feral form (formosus) vs domestic form.
Ae. albopictus: Asian tiger mosquito, cold-hardy, invasive.
Define Anthropophilic.
Preferring human hosts over animals (e.g., Anopheles gambiae).
Define Endophilic.
Mosquito that tends to rest indoors.
Define Endophagic.
Mosquito that feeds indoors.
Name three globally invasive Aedes mosquitoes and expansion timeline.
Aedes aegypti: worldwide after 1500s (tropical)
Aedes albopictus: worldwide after 1960s (tropical & temperate)
Aedes japonicus japonicus: worldwide after 1990s (temperate)
How are anopheles eggs laid?
Later floats - eggs laid individually on water
How are aedes eggs laid?
No floats - eggs laid individually beside water
How are culex eggs laid?
no floats - eggs laid in rafts on water
How do anopheles larvae rest?
No siphon- rest parallel to water surface
How do aedes larvae rest?
Siphon - rest at an angle to water surface,
How do culex larvae rest?
Siphon - rest at an angle to water surface
What is the culex life cycle?
Eggs laid in raft at water surface
Larvae has a siphon and rest at an angle to water surface
Pupa takes air from water surface
Adult emerges at water surface from pupa