Genomics: evolution of genes and change
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
for quiz 2 of bio
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
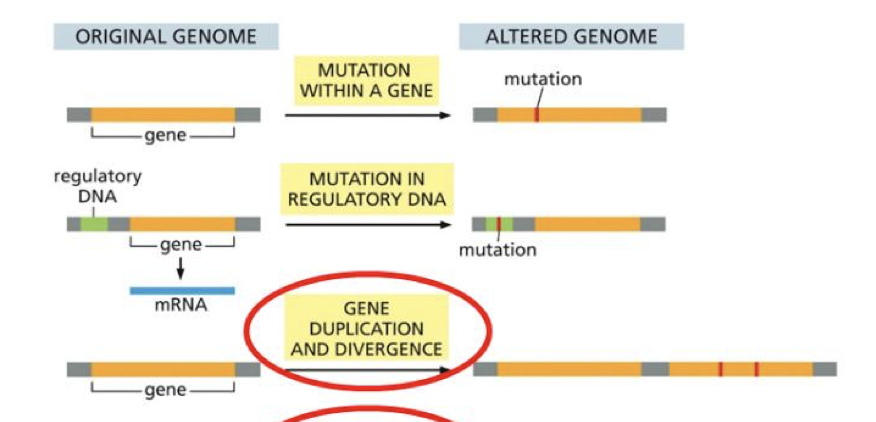
what are the first 3 ways the genome can evolve and change?
mutation in a gene
mutation in regulatory dna
gene duplication and divergence
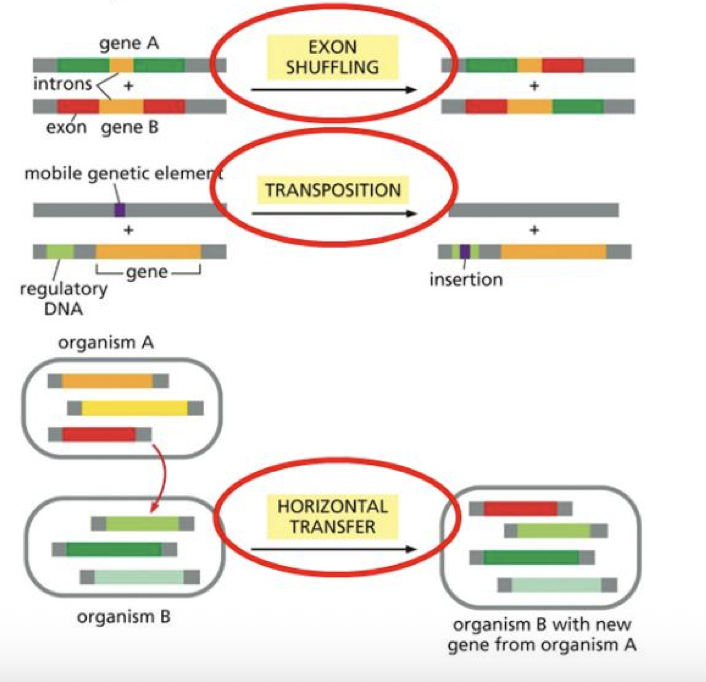
what are the next 3 ways the genome can evolve and change?
exon shuffling
transposition
horizontal transfer
how does the mutation within a gene change the genome
we have genes in the genome --> and we can get a mutation in the gene.

what’s one thing a mutation can do in a gene inside the genome
it can add a stop codon,
what’s another thing a mutation can do in a gene inside a genome
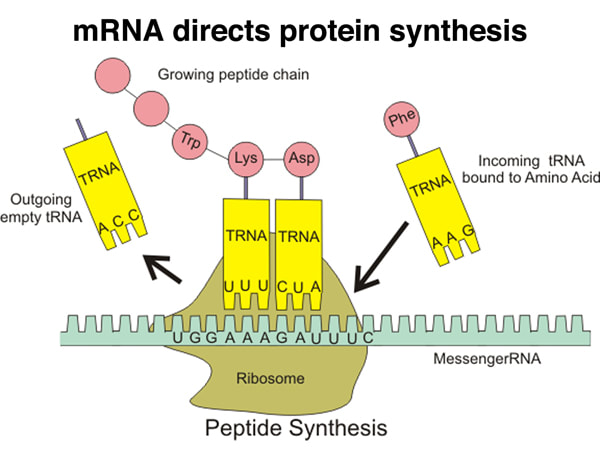
![the non-coding section of DNA that controls gene expression [cis elements]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/46f98314-20b3-4052-9468-5372c6035ec8.jpg)
by acting as binding sites for transcription factors that control the rate of transcription. .(complimentary proteins) ex. TATA BOX, TFIIH, promoters, enhancer, silencer)
activator proteins and repressor proteins that act like switches to turn genes "on" or "off,
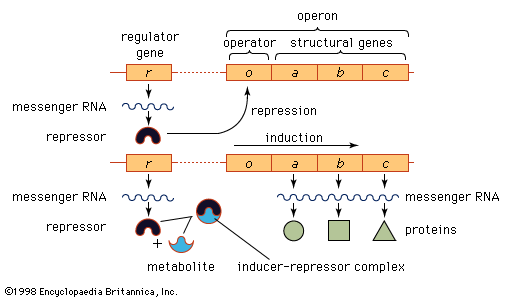
how does a mutation occur in a regulatory dna area in the genome
A gene can have a regulatory area before the gene mutation can occur in the regulatory DNA area.
in what ways can the regulatory dna be mutated .1
you can mutate the RNA site where polymerase binds).
in what ways can the regulatory dna be mutated 2.
We could mutate the TATA boxes where those enhancers and silencers are
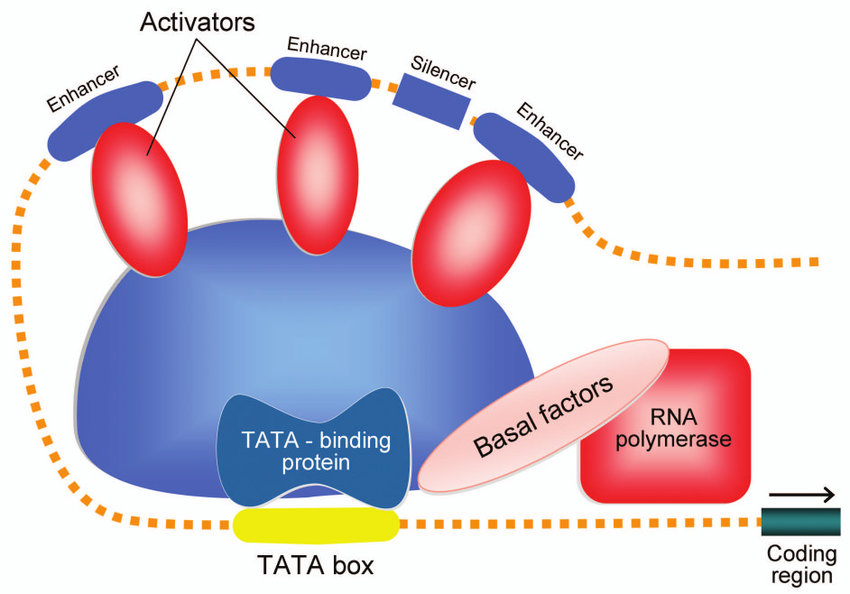
in what ways can the regulatory dna be mutated 3.
You can have a mutation that adds a stop codon, or a mutation that changes the amino acid
what can occur when you change the amino acid
you can add 1 base compared to 3 bases (very bad)
you can mutate the regulatory area
or mutate the cis elements
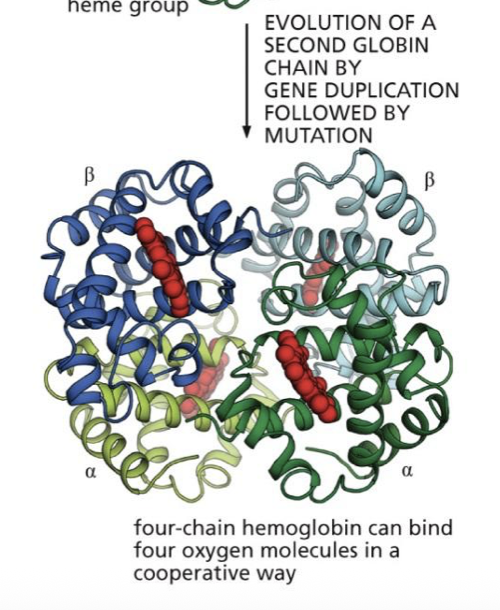
gene duplication and divergence (BIG PAPAAAA)
What occurs in Gene duplication and divergence
We can have a single gene—> and the gene duplicates with one copy being mutated and the other copy being normal.

is the change caused by gene duplication big?
yes its Huge, it allows for flexibility in genes and the mutations in them
what does it mean for there to be lots of flexibility from a gene duplication
if a mutation occurs in 1 gene it wont be Lethal because we have a spare copy untouched (yay)
are all mutations bad in a gene
no, some mutations are good (ex. hemoglobin oxygen one), they can cause evolution. but some can be bad and lethal.
how big is gene duplication in evolution
big, because it allows for the cell to experiment with a variation in one gene, to see if we can get something better through variations.
what occurred in the Hemoglobin example
we originally had 1 but as we evolved we created 2
what are the 2 forms of hemoglobin called
alpha globin-
beta globin
how many copies of the forms of hemoglobin do we have now
alpha hemoglobin; has 2 copies called alpha version
beta hemoglobin: has 2 copies called beta version
so we have complex 4 chain of hemoglobin what
what do the copies in our hemoglobin useful for
since we have 2 copies of both alpha and beta hemoglobin, one can be experimented on while the other does its job. (one of the genes create the alpha one and one creates the beta)
what are the most important part of genes
exons
what is useful about EXON SHUFFLING
Instead of starting from scratch, you can take an exon and duplicate it and let it evolve.

what often occurs in the grand scheme of evolution
Exons are be moved around to create new combinations with slightly new functions.
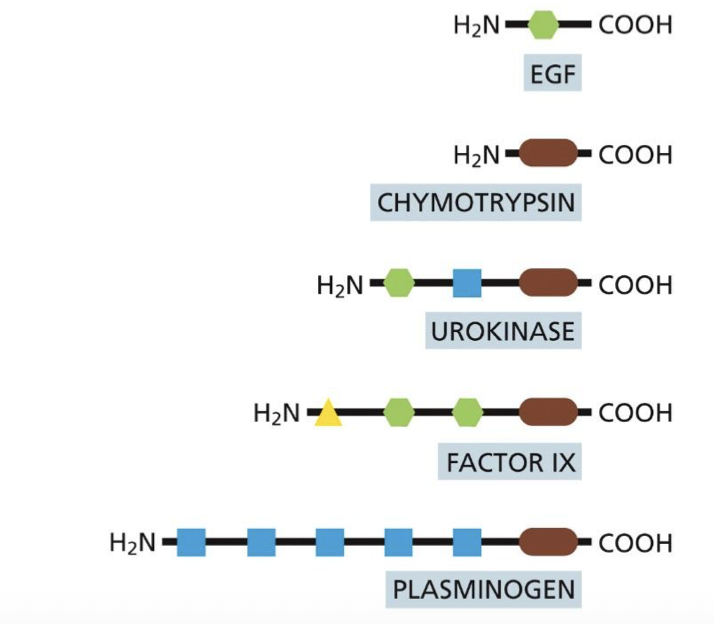
what is the context of the image
Each of the shapes represents an exon (you can have one shape that has one type of exon and another with another type and when you put them together you create a new gene with a different function.)
what occurs with a lot of evolution in the genome
moving things around (creating new combinations) and letting them evolve.
what’s the difference between exon shuffling and splicing
splicing is taking away introns, shuffling is duplicating exons inside of another gene. adding another domain
how big is exon shuffling compared to gene duplication
Similar to gene duplication it’s just a smaller scale
what consists in HORIZONTAL GENE TRANSFER
we transfer genes between speciescan you
can you do horizontal gene transfer in eukaryotes?
no, only in bacteria because It forms structures between them that pulls cells together ti exchange genes.
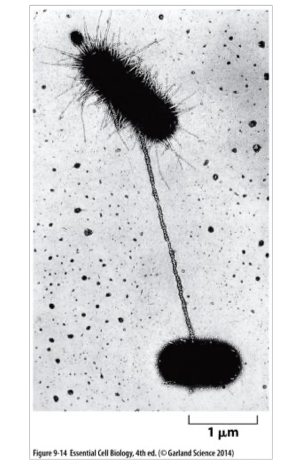
what’s the danger of sharing genes between bacteria?
they can create resistance genes for antibiotics. making it harder to create antibiotics to combat bacteria viruses
If you take the whole genome how do we make sense of it?
This is known as genomic annotation where we label the beginnings and the ends of everything, size etc..
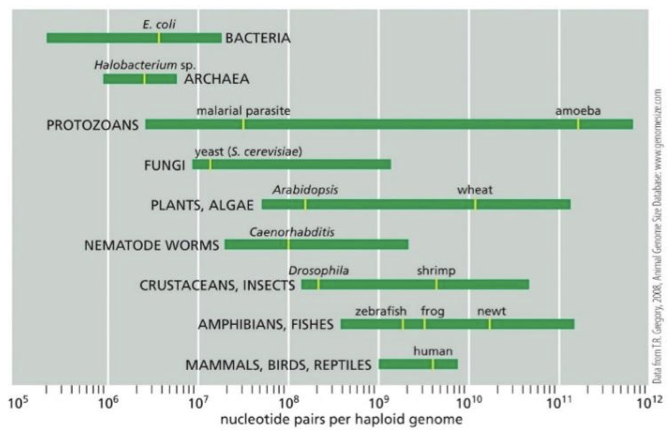
what doe the chart show
the size of genomes in organisms:
what doe the genome size chart reveal
There is not a correlation between size of the genome and complexity
how many protein coding genes are in human genome
20,000
how many pseudo genes do humans have
more than 20,000
what’s a pseudo gene
a DNA sequence that resembles a functional gene but has a lot of mutations that prevent proper expression
how do most pseudo genes arise
from the duplication of a functional gene with an accumulation of damaging mutations in one of the two copies.
what happens when a mutation is bad and causes the gene to be non-functional
the non functioning bad mutation in one of the genes copies is known as the PSEUDO GENEEEE.
do pseudo gene get expressed
no…
what is half our dna made up of that is a high copy and repetitive
transposons (junk) and 1% is exons
what are the 4 types of genetic testing
single gene testing
gene panel
whole exam sequencing
whole genome sequencing
how common is single gene testing
very common especially if there’s one genome in your family that causes a condition
example of single genome testing
1. A single gene test can be done. (Ex. Cancer runs in the family so we test a single gene of the grandson to see if he has the condition.)
what is Gene Panel often done for
often done for cancer
what is the process for gene panel in cancer
they will look at the top 2 dozen cancer genes to see if you have any of the top 2 dozen. (does not test for all genes, only the most common ones [more limited]).
what occurs in Whole Exome Sequencing
last 5 years is has become popular. They sequence the exons, which is only 1% of the genome (so it’s doable).
Whole genome Sequencing
very expensive, debate if it’s worth it,
how much of a difference is there with genome of chimps and humans
1.2% difference, You don’t need a huge change in genome to get a drastic change in the gene
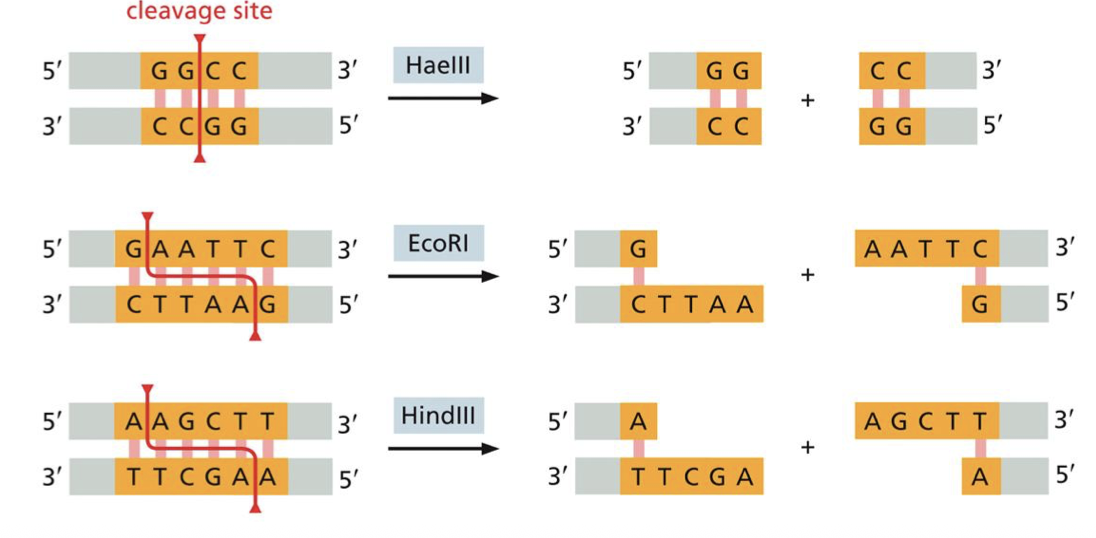
What do Restriction Enzymes do
They recognize at a specific site in the dna cut it to open it up to study,They cut unique sequences In a unique ways
where do the restriction enzyme cut and how
cuts at cleavage site, just cutting up and down ‘straight line’ is called a BLUNT END, if not straight down its called a STICKY END(sticky ends can be easier to work with)
what are PLASMIDSSS
- Plasmids are circular piece of DNA that’s not part of the genome
- Plasmids are something extra, in addition to the regular chromosomes
PLASMIDSSS AGHHH. what are plasmids used for
We usually use plasmids in a research lab to move DNA around.It’s a circle and we put important things in it that we want in the lab.
Ex. If we want bacteria to grow faster or change its shape we would add this
what do we often do to the plasmid
We also often cut it open and put in a new gene that we want to study.
(we use it like a tool to engineer what we want in them and put in what we want to study in them)
what do you work with plasmids in
in a tube where we add cells to see how they react
what are the 3 important areas to the plasmid
polylinker
orgin of replication
anti-biotic resistance
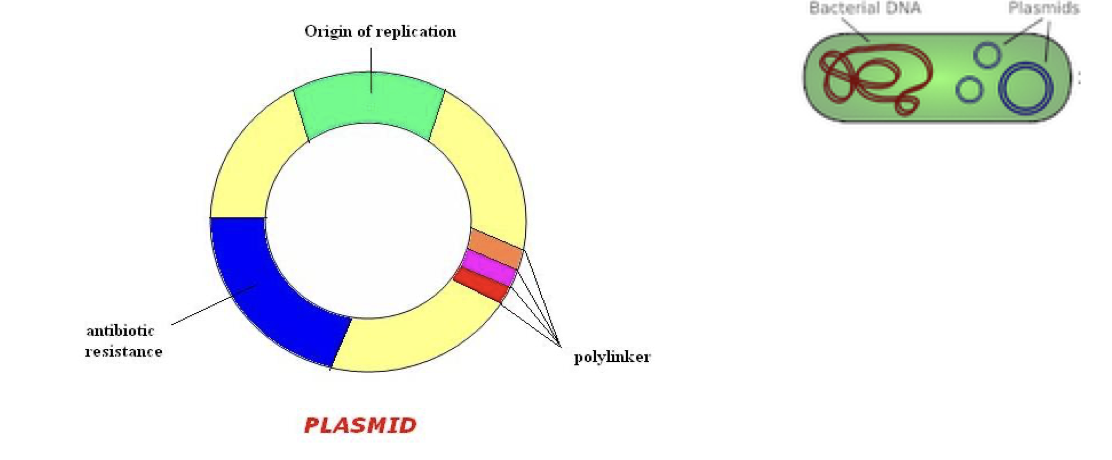
what’s the polylinker
it has lots of restriction enzyme sites.
This is where you add the gene you want to study as well.
what’s origin of replication
once the plasmid enters the cell you can make hundreds of copies of it instead of just one copy.
what do plasmids have a high number of when it comes to origin of replication
they have a high copy number of origin of replication making It be able to make so many copies. (plasmids can copy themselves all the time.)
what is anti-biotic resistance
it works as a tracker to weed out the cells that have the plasmid insertion to study those genes and kills off the cells that do not. (the anti biotic kills the other cells)
how do you begin cloning in a plasmid
you add the restriction enzyme to cut open the gene
what do we hope to achieve by cutting open the plasmid with the restriction enzyme
that our gene is inserted into the plasmid through its sticky ends and they line up in the circle and are bonded by ligase.
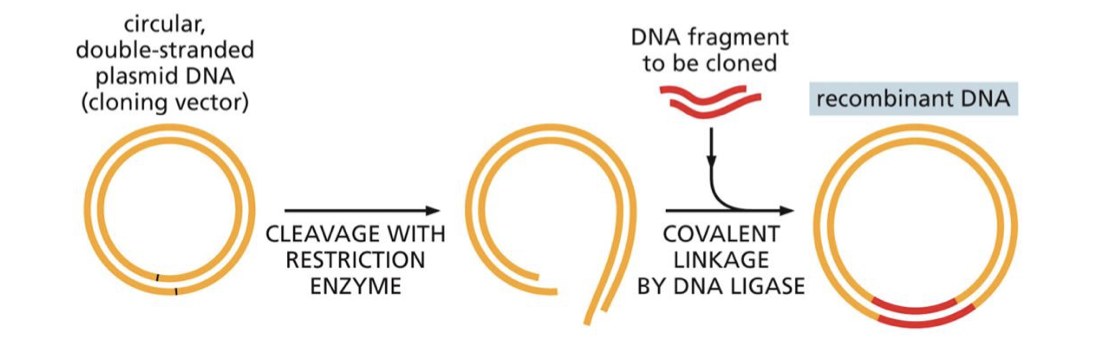
why do we add the target gene to the plasmid in the first place
because the gene alone is not stable enough and will degrade so this is why we put it into a plasmid.
what occurs after the target gene is aligned with the plasmid
we add ligase on the ends to bind the gene and plasmid.
what is the new plasmid dna with the new dna fragment inside called
recombinant dna
what could be the next step after creating the recombinant DNA plasmid
to insert the plasmid into cells where the cells with divide and the plasmid will replicate on its own, weeding out the target DNA that was added to it. So that we can study the target DNA.
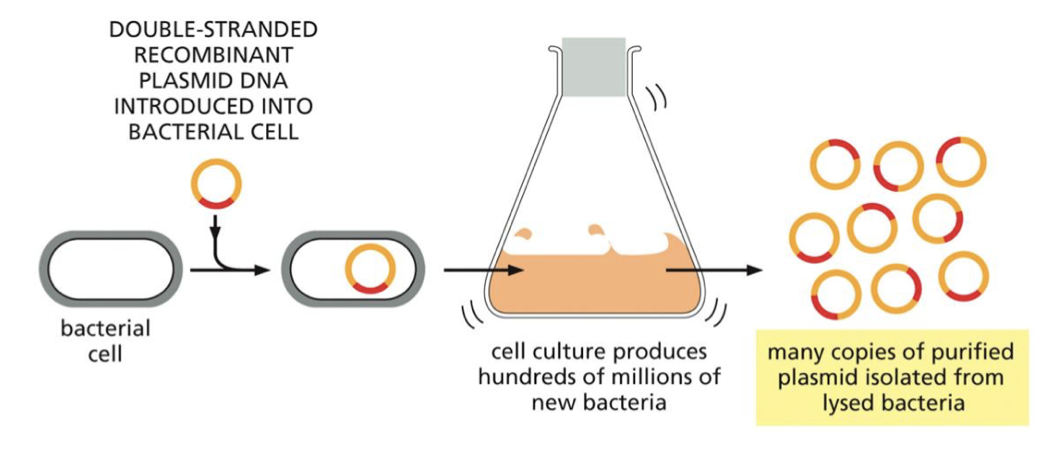
The DNA fragments that are cloned in the plasmid can be:
a normal version of the gene
a mutated version (to see how the mutated gene would affect the nucleus )
a gene tagged with a GFP
ETC.
what is something you can do to the gene that is being cloned
you can add a GFP tag to it to monitor movement
when you take a gene from one plant and put it in a new plant its known as what
a transgenic plant