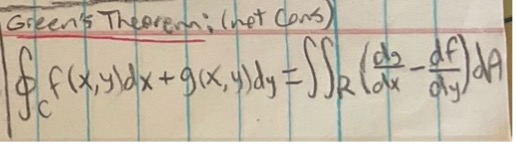Multivariable Calculus: Final Exam Review
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Distance formula
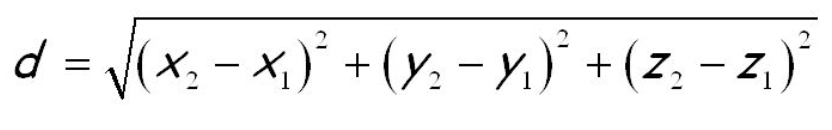
Equation of sphere of center
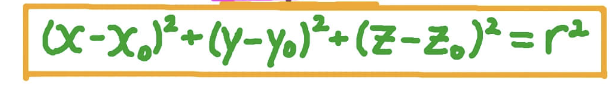
Midpoint of 2 points
can also include z for 2pts in 3-space
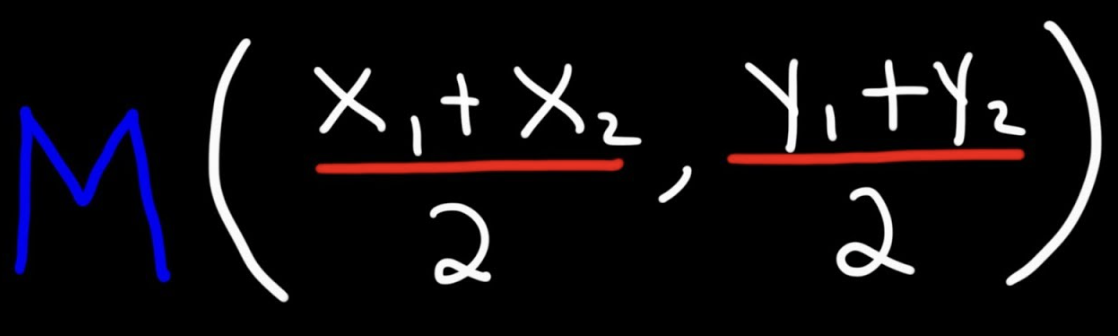
Completing the square
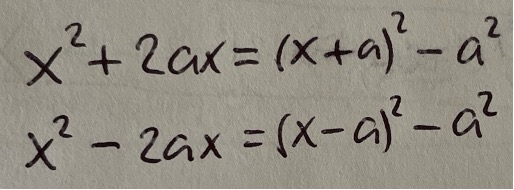
Angle b/w vectors
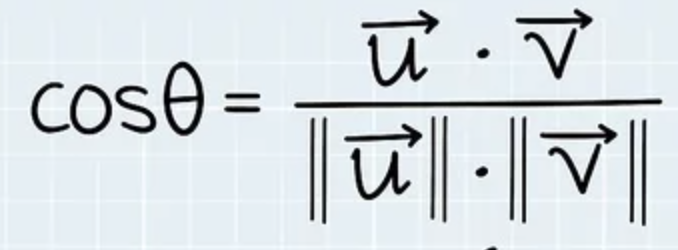
Orthagonal Projection
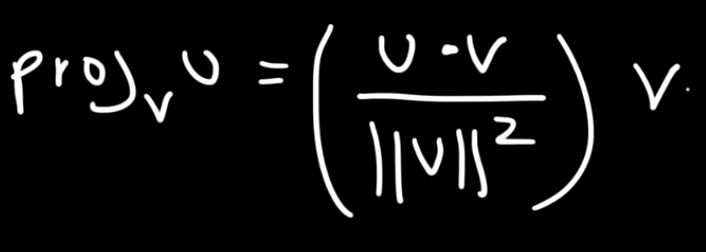
Cross Product
Area of a Parallelogram

Area of Triangle

Volume of parallepiped
or cross product of the three vectors

Parametric equation
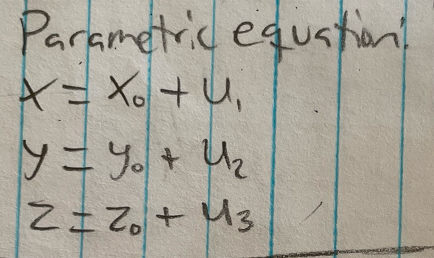
Distance b/w line and point
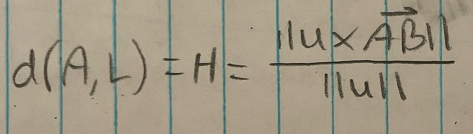
Equation of a plane in 3-space
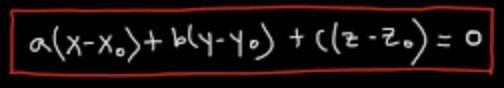
Planes given by 3-points
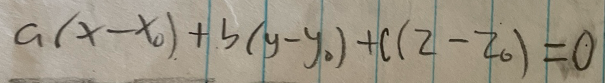
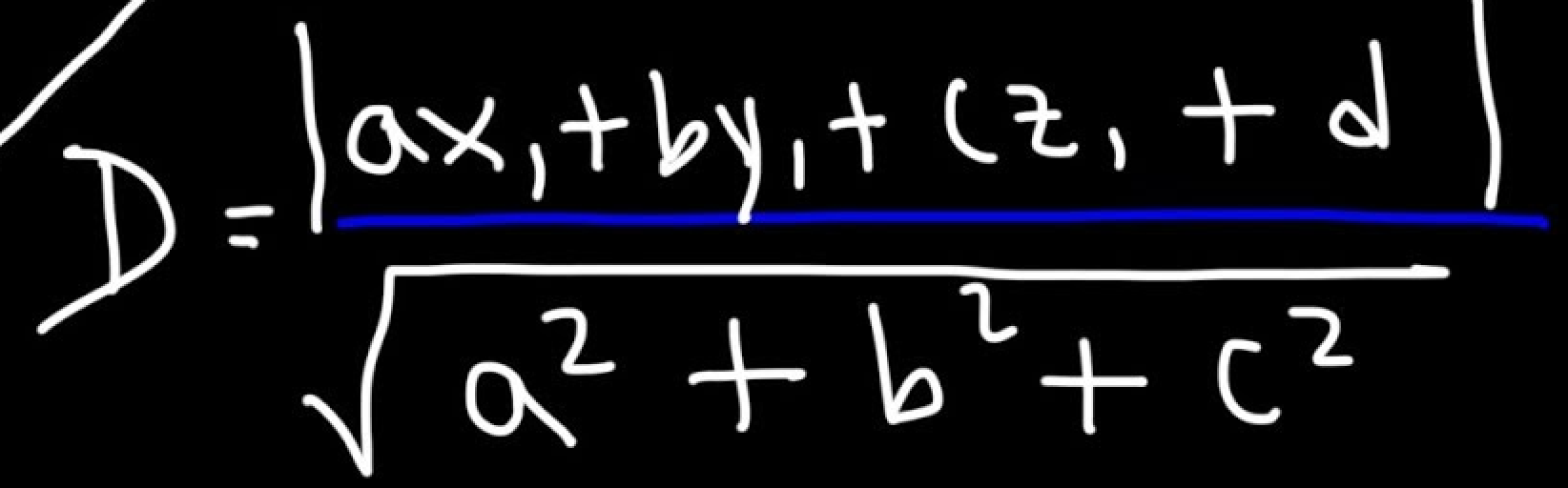
Distance b/w point and plane
ellipsoid
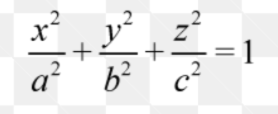
hyperboloid w/one sheet
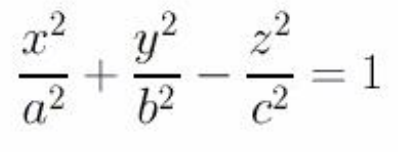
hyperboloid w/two sheets
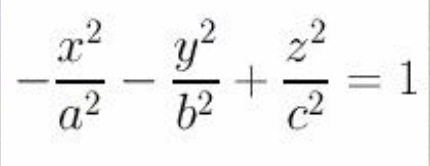
Elliptic cone
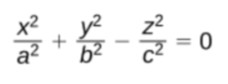
Elliptic parabaloid
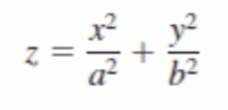
Hyperbolic parabaloid
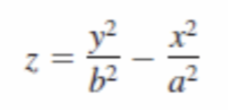
Equation of tangent line
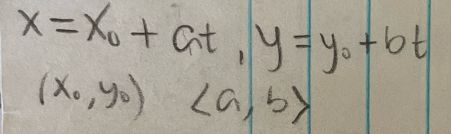
Distance
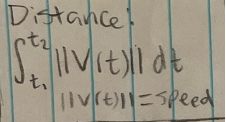
Displacement
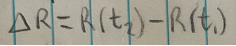
Arc length
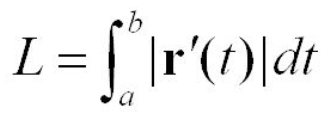
Arc length parametrization
Identify reference point (end pt) by value of pt
Use Arc length formula
find t in terms of s
In R(t) replace t value in s from step 3
Unit vectors (T(t))
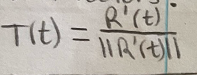
Unit vectors (B(t))
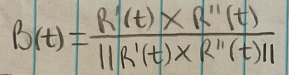
Unit vectors (N(t))
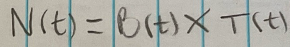
Curvature
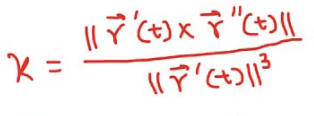
Curvature in y = f(x) form
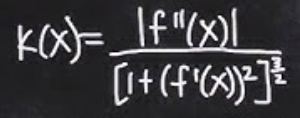
Limit and Continuity

Polar coordinates to evaluate limit
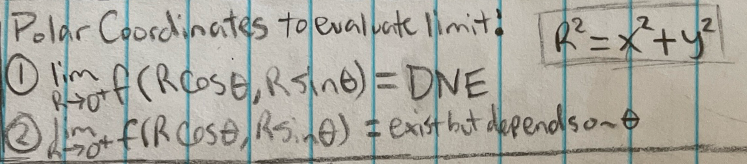
Continuity
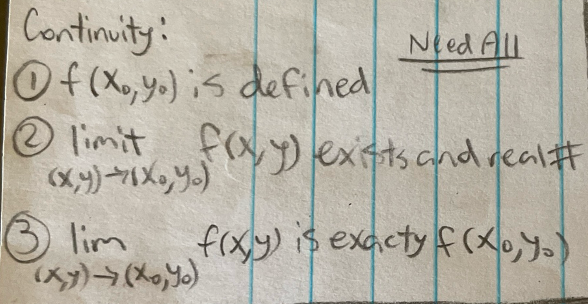
Partial derivative

Chain rule for derivative
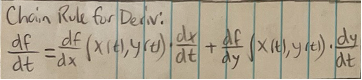
Chain rule for partial derivative
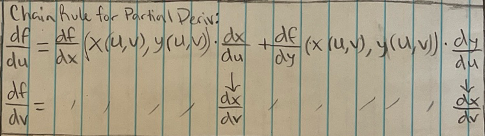
Directional derivative
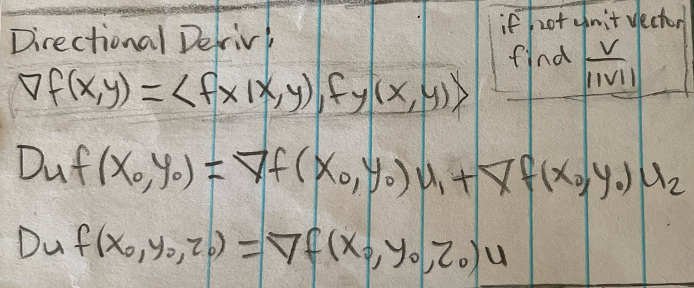
Theorem: directional derivative
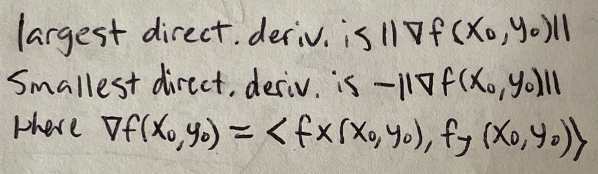
Local linear approximation
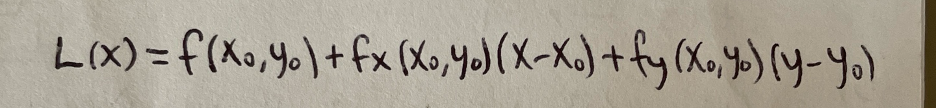
Equation of tangent plane
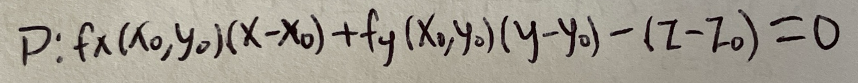
maximum/minimum
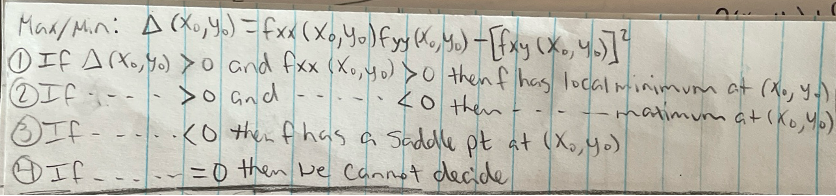
Double Integral
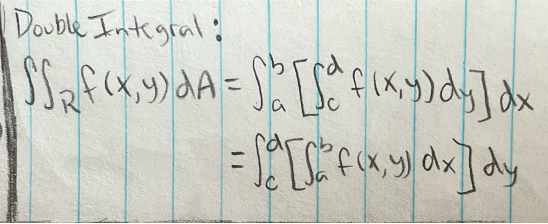
Polar Coordinates
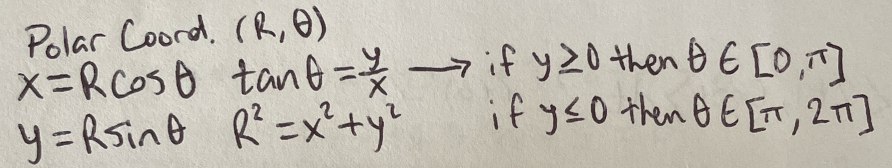
Theorem: polar coordinates
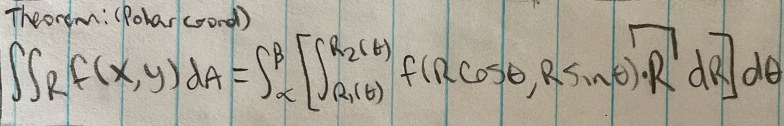
Triple Integral
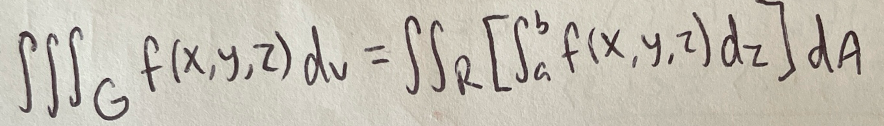
Volume (using triple integral)
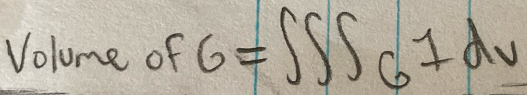
Volume (using double integral)
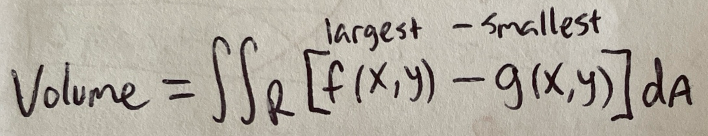
Cylindrical coordinates
same as polar coord. except z=z and integrate by z first (also has same jacobian of R)
Spherical coordinates
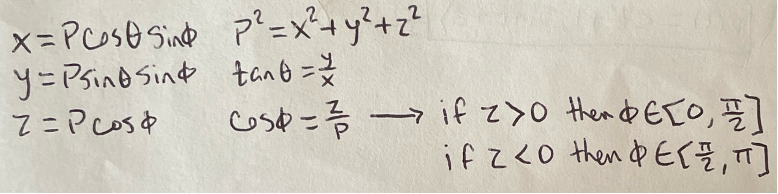
Spherical coordinates jaacobian
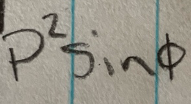
Jacobian of T
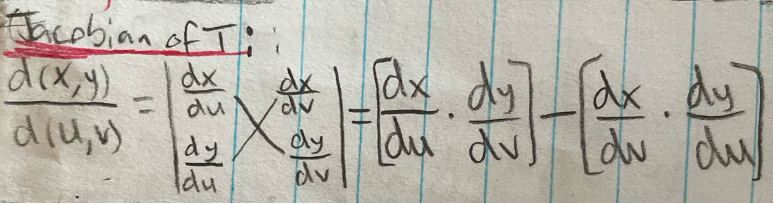
Jacobian Theorem
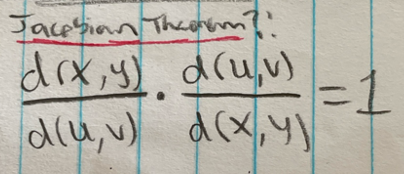
Theorem: change of variables
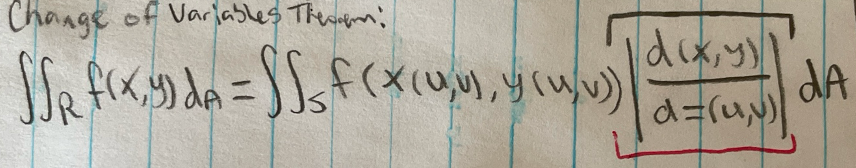
Area (with double integral)
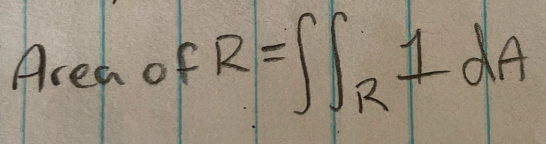
Vector field notation
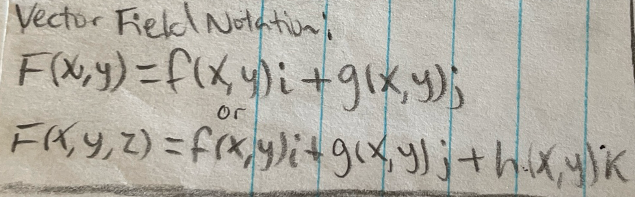
Theorem: conservative vector field in 2-space
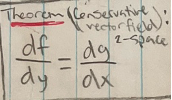
Divergence
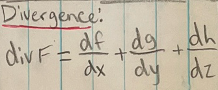
Curl of F (vector field)
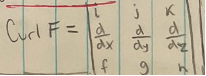
Parametric Curve
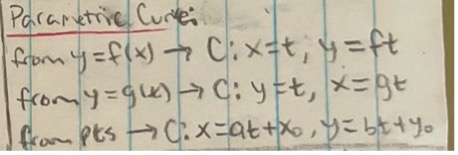
Line Integral
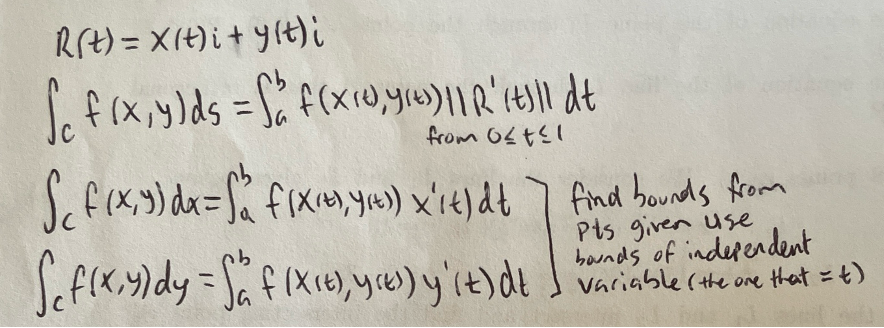
Line integral of vector valued function
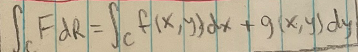
Conservative vector field (3-space)
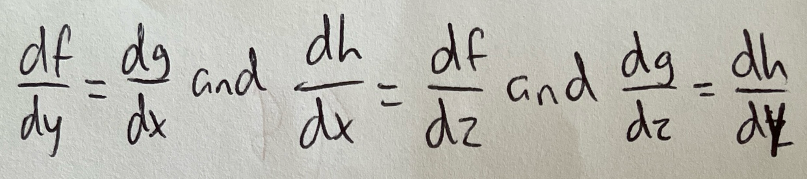
Potential function

Theorem: line integral
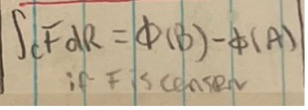
Green’s Theorem