Intro to Marketing - Guskey - Exam 1
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Market Segmentation
Process of dividing the market up into groups
Target Markets
Homogenous segment of the market to which a marketer directs a specific marketing program
Why Segmentation?
Everyone has different needs, you can't satisfy everyone, and it gives you a competitive edge
Mass Marketing
Hardly any product EVERYBODY would buy. There are no UNIVERSAL products
Five Ways to Segment a Market
Geographically, Demographically, Psychographically, Beneficially, and Niche
Niche Marketing/Micro Marketing
Focuses on one individual's needs such as custom suits, beds, and custom shoes
Benefit Segmentation
Consumers grouped on their reasons for using product; people use toothpaste for fresh breath, whiter teeth, fighting cavities, etc.
Psychographic Segmentation
Focuses on the Values, Importance, Attitude, and Interest of a consumer
VALS I
Focuses on the Value and Lifestyles of a consumer
Three types of consumers
Outer driven, inner driven, and need driven
Outer Driven
Belongers, Emulators, and Achievers
Inner Driven
I-am-me's, Experiential, Societally Conscious
Need Driven
Survivors and Sustainers
Demographic Segmentation
Separates market into 8 different markets
Demographic Variables
Age, Gender, Occupation, Educational level, marital status, religion, race/ethnicity, and income
Why marketers use Demographic Segmentation
It's easy to measure, use of product is related to a variable, and media schedules are calculated to demographics
Why marketers use Geographic Segmentation
It's easy, different regions use/prefer different products, and climate and seasonality play a factor
Geographic Segmentation
Dividing a market by geographic region
Marketing Concept
All of marketing revolves around the consumer; The consumer is #1
AMA- 1960 Marketing Definition
Performance of business activities that direct the flow of goods and services to the consumer
Flaws in 1960 Definition
Business- non-profits market but are not businesses; Flow- Implies it is one-way, when it is back-and-forth; Goods and Services- Ideas and concepts are marketed as well
AMA- 1985 Marketing Definition
Marketing is a process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services to create exchanges that satisfy individuals and organizational objectives.
Importance of 1985 Definition
Defined Marketing as an EXCHANGE
AMA- 2004 Marketing Definition
Marketing is an organizational function and a set of processes for creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers and for managing customer relationships in ways that benefit the organization and its stakeholders.
Flaw in 2004 Definition
It puts too much focus on the organization rather than the concept
AMA- 2007 Marketing Definition
Marketing is the activity, set of institutions and processes for creating, communicating, delivering and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners and for society at large.
Exchange Concept
Consumer provides information, money, or credit to a company in exchange for information, goods, or services
Four conditions for an Exchange
Need 2 or more parties, each parties must have something of value, each must be willing to give up thing of value, and there must be some type of communication
Marketing Eras
Self-Sufficient era, Production Era, Sales Era, Marketing Era, and New Era
Self-Sufficient era
Took place from beginning of time up to the 1800s; consumers farmed, bartered, grew, or hunted
Production era
Took place from 1800s-1920s; known for Industrial Revolution, it gave consumers an opportunity to buy stuff made by others
Sales Era
Took place from 1920s-1950s; Because of depression and war, inventory stocked up and companies tried hard to sell to consumers
Marketing era
Took place from 1950s-2000s; Known for marketing concept; determine who the consumer is and what they want
New Era
Present day; unknown if in it or not, but is characterized by major Social, Technological, and Service changes
Environmental Scanning
The process by which a firm gathers information about environmental changes in order to identify opportunities and determine threats
Three Types of Environmental Scanning
Irregular Model Reactive, Regular Model Proactive, Continuous Model
Irregular Model Reactive
Worst; Reaction to a crisis. Something happens unexpectedly and you must start collecting info
example of Irregular model
Worst; Reaction to a crisis. Something happens unexpectedly and you must start collecting info
Regular Model Proactive
will be collecting information on a regular basis/periodically
example of Regular Model
Once a year, interview customers and check on competition
Continuous Model
Best; Collect data all the time and from all types of environments
examples of Continuous Model
Social, legal, and ecological studies
Downsides of continuous model
It's expensive, takes a lot of time, not always easy
Microenvironment - Internal
Groups/individuals that have a vested interest in the product
examples of microenvironment
The supplier, distributor, stockholder, company, general public, and competition
Microenvironment -External
Deals with people, lifestyles, values, etc. as a society
Types of macroenvironments
Political, Ecological, economic, technological, etc.
Macro vs Micro Environment
In a micro, the company has some control over the groups interested in it; in a macro, the company has little to no control
Utilities
Satisfaction; Value added;
Utility values
Form showcases features and design, time gets product to consumer when they want it, place gets product to consumer where they want it, and possession allows consumer to buy/own product
Strategic Marketing
Planning according to the consumer's desires
Three ends of the marketing triangle
fit, objective, and company resources; environmental opportunities lies between company resources and objective
Company Resources
Differential advantage; what the company is good at, its specific strengths, and how it's better than competition
Environmental Opportunities
Trends; what is hot in the marketplace today?
Strategic Business Units (SBU) goals
Single or related business with its own competitors, goals, and resources
Mission statement
How a company broadly defines itself to its employees, consumers, and the public
Marketing Strategy P's
Product, Price, Promotion, and Distribution (Price/Placement)
Growth-share matrix

Star
Sustains differential advantage despite rising competition; Uses its own financing to grow; HIGH market share and HIGH growth
Question Mark
LOW Market Share but HIGH growth; could do well or bad, unknown how it will perform
Cash Cow
HIGH market share but LOW growth; has loyal customers but don't tend to grow
Dogs
LOW market share and LOW growth; not performing well and not expected to do well anytime soon
Growth Opportunities Model
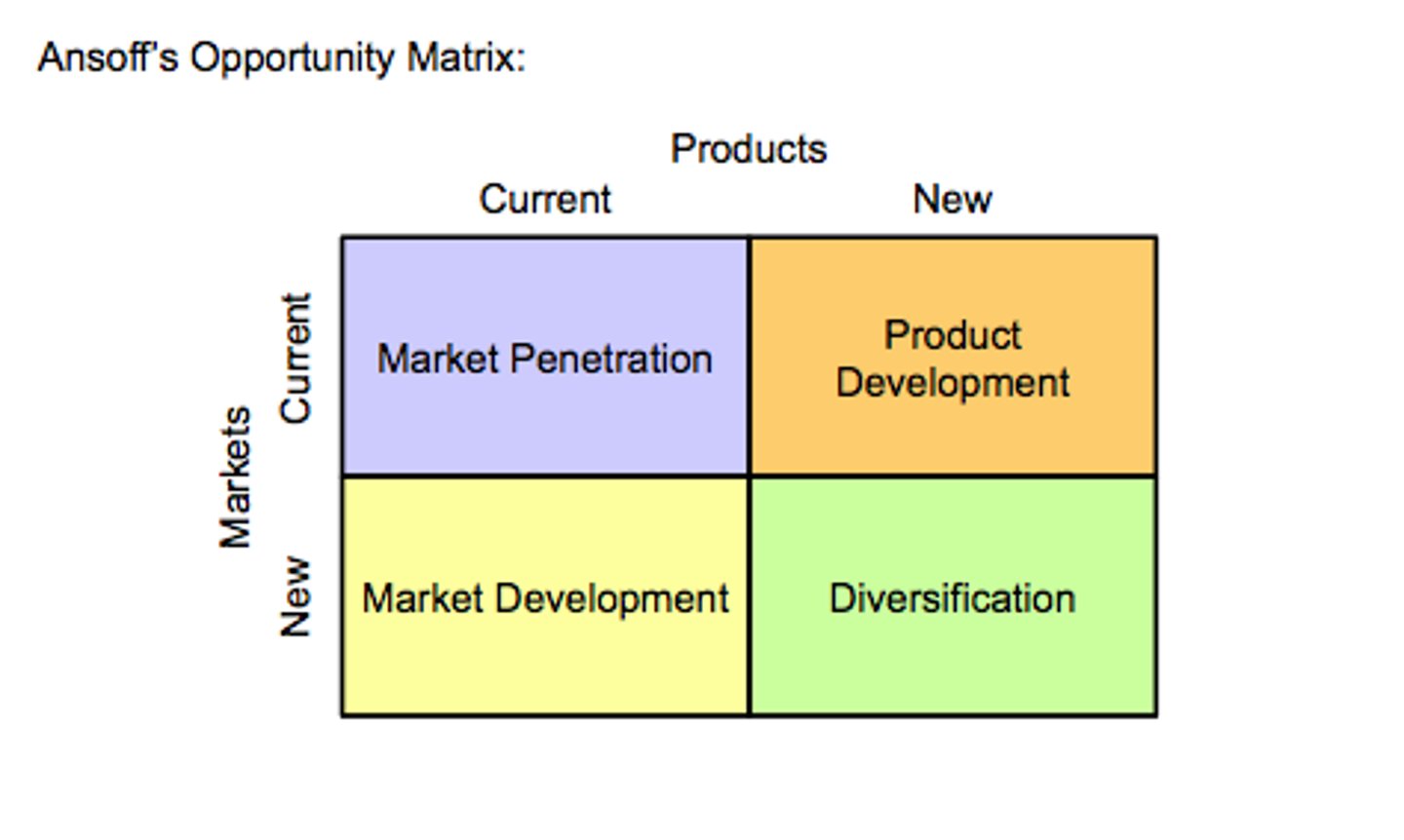
Market Penetration
Sell the same product to the same consumer, albeit with different uses
Product Development
New product, but sell to the same consumers as original product
Market Development
Same product, but sell to new people
Diversification
New product sold to an entirely new market