Westgard, Evaluation Methods, and Reference Values
1/224
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
225 Terms
Who developed Westgard rules
James Westgard
What does Multi rule Quality Control use
a combo of decision criteria and or a combo of control rules sequentially
What type of control materials are used in Westgard rules
Level 1 and Level 2
How are decisions made in Westgard Rules
they are made in a sequential fashion
What is the main purpose of using Westgard Rules
its allows the determination of whether an analytical run is in control or out of control
How does the accuracy of Westgard Rules compare to a L-J Chart
Westgard provides better accuracy when used with single control rules
How are most quality control rules expressed in Westgard rules
they are expressed as N^L
What does N represent in Westgard Rules
the number of control observations or runs to be evaluated
What does L represent in Westgard rules
the statistical limit for evaluating the control observations
When are Multirule quality control used
when there are 2 levels of control material are being analyzed per run
What are Westgard rules designed to do
minimize false alarms or false rejections and increase error detection
What is Westgard 12S rule
The warning rule where one of the two controls results falls outside ± 2SD
What is the purpose of the 12S warning rule
it alerts techs to possible problems
Does the 12S rule automatically reject a run
No, because this deviation can happen by chance
What must be done after an 12S rule alert
The 13s rule must then be evaluated and the process of evaluation must continue sequentially
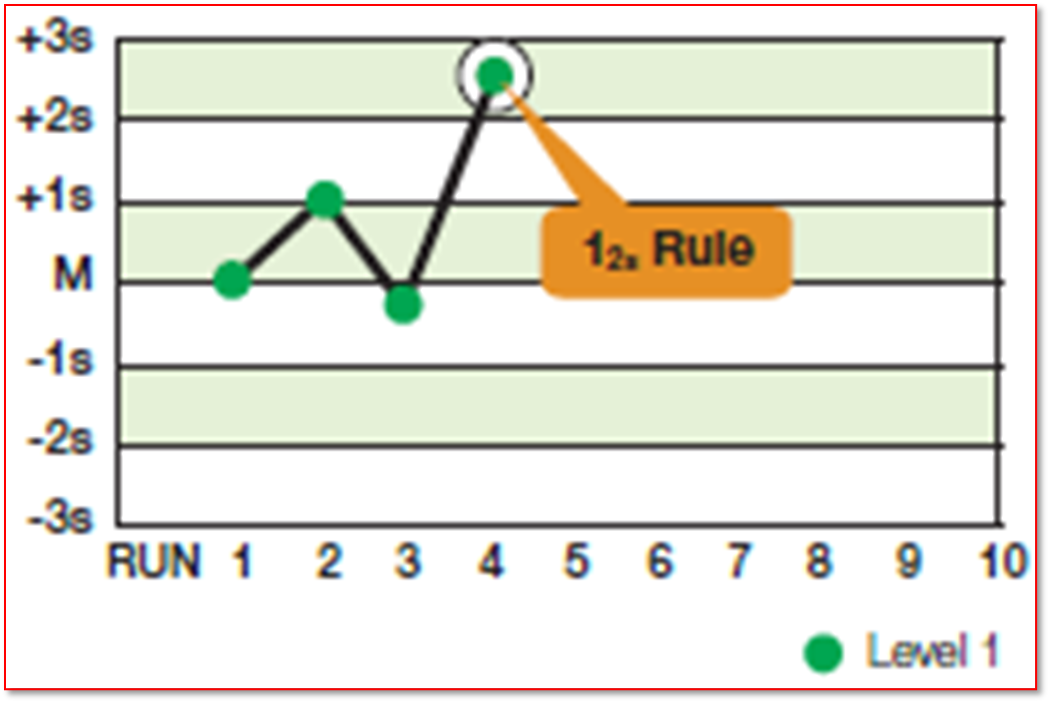
Which Westgard Rule is this
12S or Warning rule
What is the Westgard 13S rule
when either of the two control material fall outside of ± 3SD
What does a violation of rule 13S indicate
it is an indication of a random error
What should be done if rule 13S is violated
the run must be rejected
What is done if rule 13S is not violated
the next rule 22S should be checked and the evaluation should continue in a sequential order
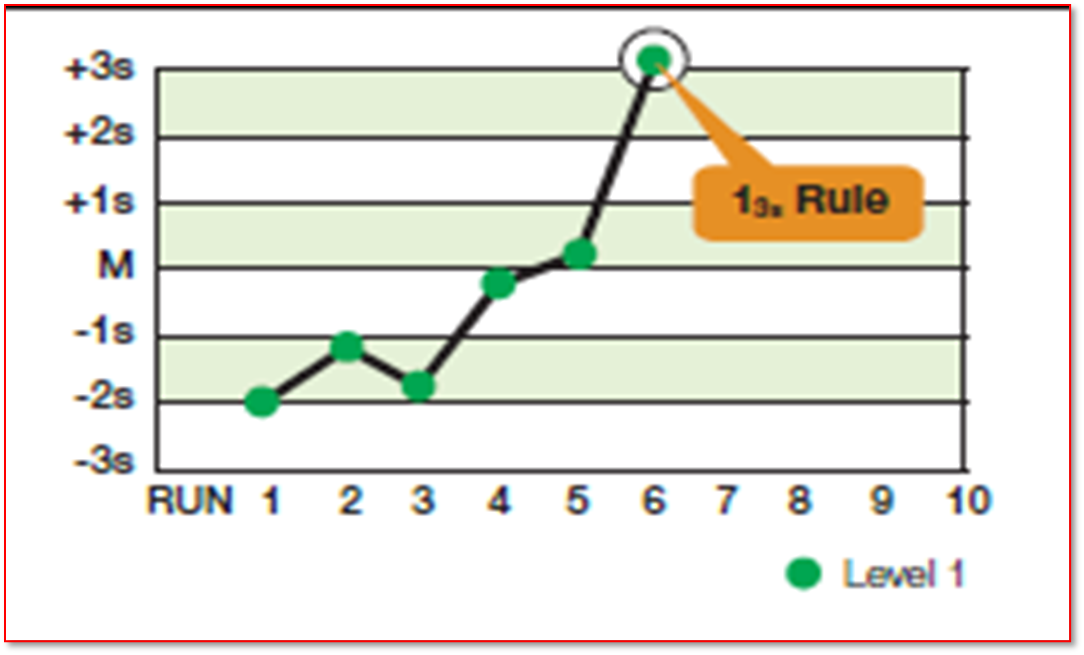
Which rule is this
13S
What is the Westgard rule 22S
when two consecutive quality control results exceed ± 2SD on same side of the mean
When can 22S rule be violated
Within the same run or across consecutive runs
Can the patient results be reported if rule 22S is violated
NO
What is required if 22S rule is violated
Corrective action must be taken
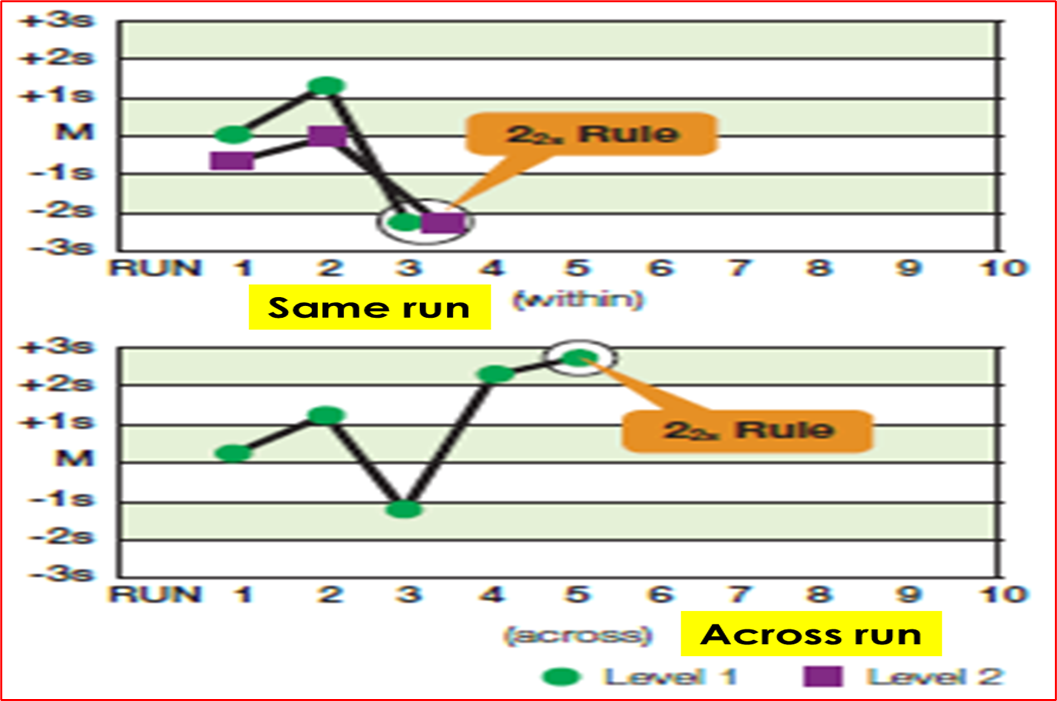
What rule is being violated
22S, the mean of level 1 and 2 are below -2SD on graph 1 and the run on the second graph exceeds +2SD across run day 4&5
What does a violation of the 22S rule indicate
a systemic error
What is the Westgard rule R4S
a range rule when one control exceeds the mean by -2SD and the other control exceeds the mean +2SD the range between the two results will exceed 4SD
What does a violation of the R4S rule indicate
a random error within the current run and not across run
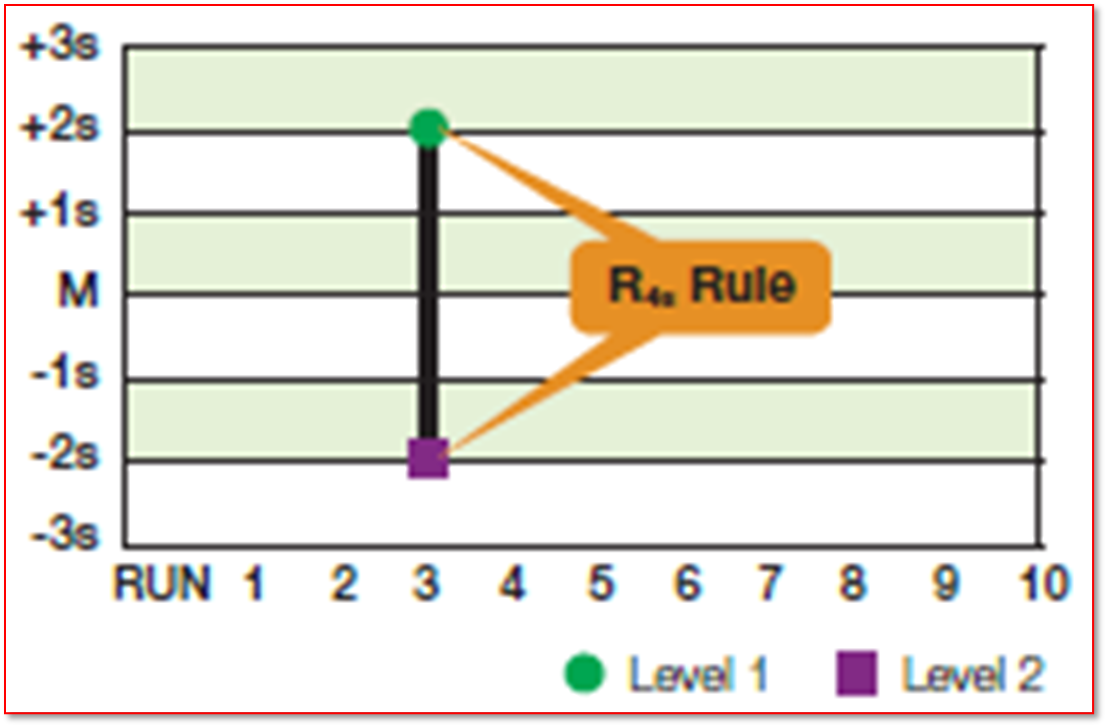
Which rule is being violated
rule R4S
What is the Westgard 41S rule
when four consecutive control rules are greater than ± 1SD on the same side of the mean
What does the 41S rule require for evaluation
control data from previous runs
How does the 41S rule apply within a single control material
it indicates systemic bias within level one control results in a single area of the method curve
How does the 41S rule apply across control materials
when applied across level one and two in combination with each showing two consecutive results greater than ± 1SD on the same side of the mean it indicates systemic error over a greater concentration
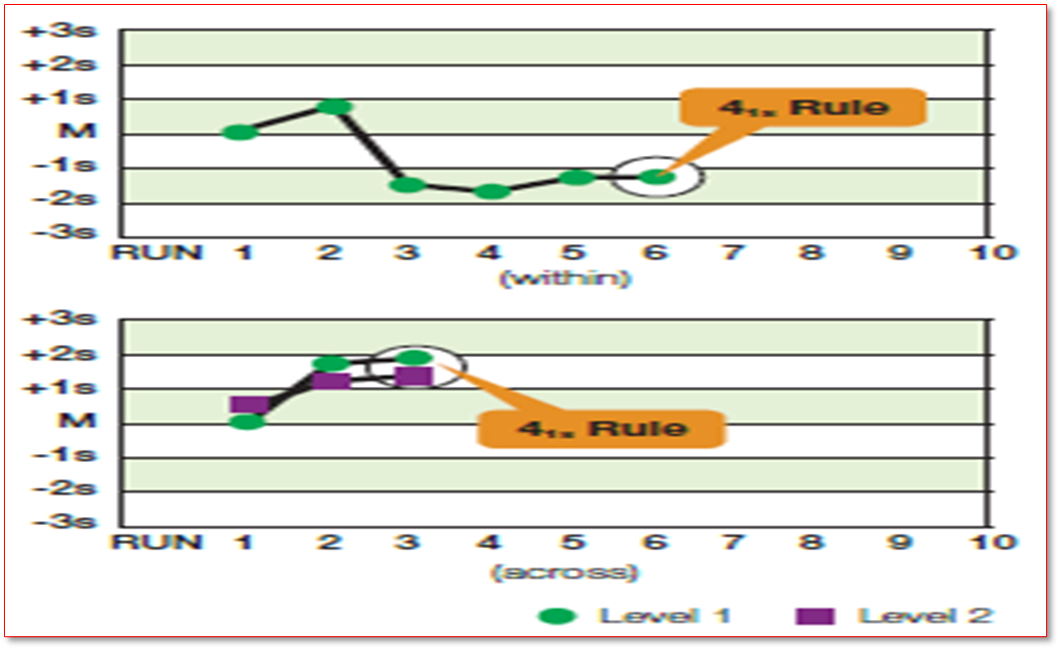
Which rule is being violated
41S where on the first graph there are 4 consecutive rules being violated only on one level indicating systemic error in one error, whereas the second graph shows 4 consecutive rules being violated in two levels which indicates systemic error in greater broad concentration
What is the Westgard 10X rule
when 10 consecutive QC results for one level of control are on one side of the mean
How does the 10X rules apply to one level of control
a violation occurs if all 10 consecutive results from that level fall on the same side of the mean
How does 10X apply to two levels of control
a violation occurs if five consecutive results from each level are on the same side of the mean
What does the 10X rule require for evaluation
it requires control data from previous runs
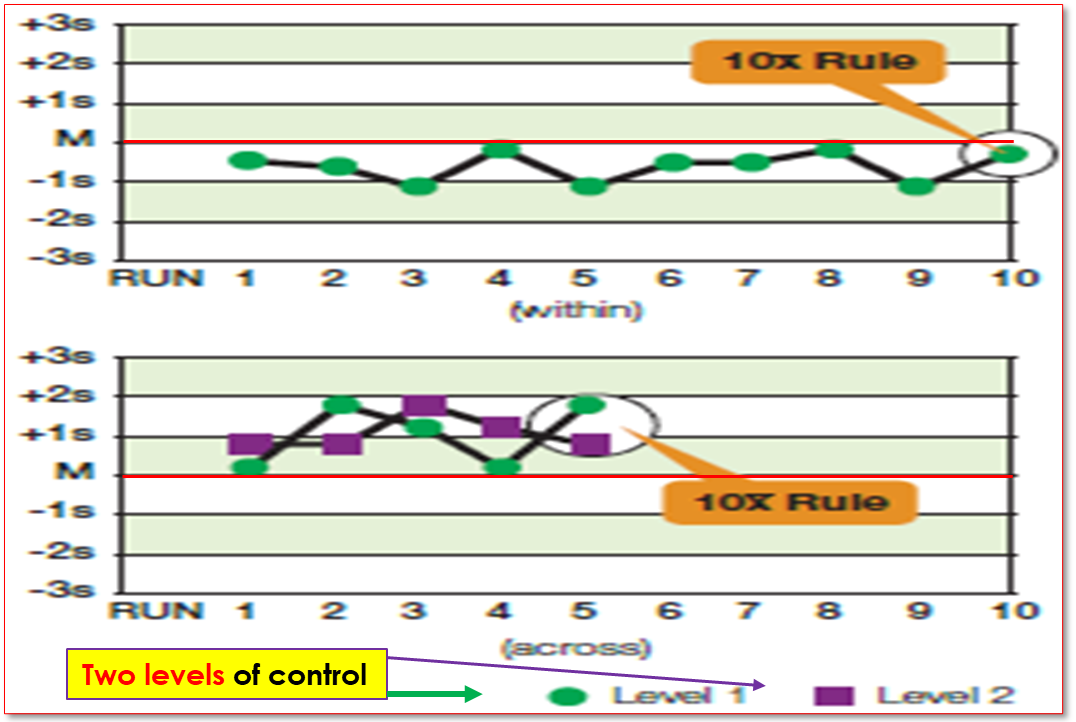
What rule is being violated
10X rule where graph one shows that all 10 consecutive runs are all on the same side of the mean on one level, and the second graph shows two levels running 5 consecutive runs each on the same side of the mean
What are indicators of systemic error in quality control
the two main indicators are Trends and Shifts in control data
What are trends in systematic errors
they are gradual increase or decrease in control values over time similar to a chronic condition
What are causes of trends in systematic errors
Reagent of standard deterioration
Gradual accumulation of debris in the sample or reagent delivery system
Deterioration of the instrument light source or performance
Aging or deterioration of QC materials
What direction can trends take
upward or downward
What are shifts in systematic errors
a sudden change in values in one direction, similar to an acute condition
What are some causes of shifts in systematic errors
Use of new reagents
Malfunction in the instrument or major maintenance
Inaccurate calibration or recalibration
Failure in sample/reagent delivery system
What direction can shifts take
negative or positive deviation
What is the traffic light rule
warning rule means to use other rules to inspect control points for further evaluation, and rejection rule indicates that the process is out of control, requiring immediate corrective action
What should be done if a rejection rule is violated
stop testing immediate
Identify, correct and document the problem
Repeat testing on patient samples and controls
Do not report results
When can you report results when a rule is rejected
until the problem is solved
until controls indicate proper performance
When should you follow policies and procedures
for remedial action and troubleshooting
What does solving “out of control” problems include
Retest the same control
Retest a fresh aliquot of the same control material
Reconstitute/thaw a new vial of control material and retest
Replace faulty reagents/ check reagent lot
Look for instrument - related mechanical faults
Recalibrate the assay ( asses linear response which is the signal or absorbance/concentration)
Consult the QC officer and/ or supervisor for further direction
What organizations set quality control standards
JCAHO, CLIA, and CAP
What do JCAHO, CLIA, and CAP stand for
Joint Commission on Accreditation of Health Organizations
Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments
College of American Pathologist
What QC requirements are set by JCAHO, CLIA, and CAP
The number of control value run/day (CLIA guidelines)
Documentation of QC results
Proficiency testing as part of quality assessment
Standard operating procedures (SOPs) for testing
Training and refresher courses for staff
What is the minimum number of control materials that must be run each day according to CLIA guidelines
according to CLIA 88’ at least two control samples of different concentrations must be tested every 24 hours
What are examples of QC guideline for blood gas testing
Test both high/low blood gas control materials
This must be tested every 24 hours
At least one blood gas control sample must be tested every 8 hours
At least one control must be tested each time a patient sample is tested
What should be included in QC documentation
Record all information good/bad
Record all corrective action
What is proficiency testing
a QC requirement process by which stimulated patient specimens made from a common pool are used to validate a laboratory performance in testing process
Who requires proficiency testng
CAP, CLIA, and JCAHO
What is the purpose of proficiency testing
to maintain lab accreditation
What are the steps for proficiency testing
A series of unknown samples is sent to lab from program
Samples are analyzed in the same manner as patient samples
Results are reported to program
Results are complied with results from all other labs participating in survey
Performance report is sent back to each participating lab
What are strict requirements for proficiency testing
Labs must incorporate PT into its routine workflow as much as possible
Test values/samples must not be shared with other labs at any time
PT samples are tested by bench technical staff only who normally do patient testing and should be completed within usual time
What is personnel competency and training apart of
QC requirement
What do personnel competency and training address
the importance of people training and education
What are CLIA’S components for laboratory competency assessment
Timing of training and guidelines for competence assessment (frequency/Interval)
Design of in service training program (workshop) via internet/ zoom conferencing
Needs assessment of gap analysis (area of defect)
Utility and economy of internet based in service training
What is the purpose of a CLSI (clinical and lab standards institute) defined procedure document
it is a QC requirement document of an analytical procedure and promotes development and use of consensus standards
What should a SOP document include
Test name
Method principal
Significance of test
Patient preparation
Test specimen requirements
Equipment and materials needed
Reagent preperation
Test procedure
Calculations
Quality control procedures
Reference intervals
Panic values
Limitations of the procedure
References (including the instrument user’s manual)
How often should the procedure be reviewed, signed, and dated
annually
What are new quality initiatives
programs used to ensure incorporation of QM and QA principals into daily operations
What is the purpose of New Quality initiatives
eliminate defects and improve processes
What is the relationship between QM and QA in these initiatives
they are a continuous improvement process
What is SIX SIGMA
a QC process that business use to eliminate defects and improve processes
What are other examples of New Quality intiaitve
Lean Production -used in manufacturing to eliminate defects and improve processes
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 9000
Joint Committee for Traceability in Laboratory Medicine
Why do we evaluate method performance in clinical laboratories
to assess how well new methods compare to existing methods
Why is it important to evaluate method performance
because the agreement between clinical lab test results and the clinical diagnosis is indispensable
Why do we evaluate laboratory test methods
To assess clinical performance of methods
To assess characteristics of the test methods
How well they detect disease when disease is present (Sensitivity)'
How well they do not detect when disease is absent (specifically)
What does the agreement between clinical lab test result and clinical diagnosis ultimately establish
definitive diagnosis
What is an important consideration during evaluation of test methods
it will ensure achievement of definitive diagnosis using reliable clinical methods
What do evaluation of test methods provide
an indication of test performance
What is the “million dollar question” in clinical testing
What are the tools for representing extent of agreement
The extent of agreement of test results with patient diagnosis or clinical diagnosis is represented in which ways or how well does the test results agree with the doctors diagnosis
Clinical sensitivity
Clinical specificity
Efficiency
Predictive values
Positive Predictive Value
Negative Predicative Value
Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) charts
Odds ratio
Likelihood ratios (LH)
Positive LH
Negative LH
What does sensitivity measure in clinical testing
how well a test detects the presence of disease in people who actually have it.
How is sensitivity related to disease
it is the percentage of people with a disease
What does sensitivity detect
the true positive or TP
What is FPR
the quantity 1-specficity
What is FNR
the quantity 1-sensitivity
What is the formula for Specificity
TRUE NEG/ TRUE NEG + FALSE POS
What is the formula for Sensitivity
TRUE POS/ TRUE POS+ FALSE NEG
What is a sensitive test (method)
one that rarely miss people who have the disease which means it will have few false negatives
Why is sensitive testing important in Cushing Syndrome
because the syndrome is caused by excess cortisol it can be fatal if misdiagnosed
Therefore, in order to avoid misdiagnosis the sensitive test method must have …
high sensitivity with few false negatives
How is specificity related to health
it is the percentage of people without the disease when correctly predicted by the test
What does specificity measure
how well the test is at calling uninfected people negative
What does specificity detect
it detects true negative or TP
A specific test will…
rarely misclassify people without the disease and will have few false positives
Why is specificity important in cystic fibrosis
the disease is serious and is not curable (affects babies) and if a FP is obtained it can lead to psychological and economic trauma to the patient and parents
Therefore, in order to avoid misdiagnosis the specific test method must have …
the highest specificity with few false positives
Clinical sensitivity and specificity test can be
Dichotomous (qualitative or binary, descriptive) or Continuous (quantitative data)
What is a dichotomous test
a type of test that has defined variables (two possible outcomes or results), such as pos/neg, 1 or 0, or present or absent