Bacteria, viruses, protists, and fungi
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Taxonomy
The science of classifying organisms
-developed by Carolus Linnaeus
-groups organisms by physical and structural similarities
Two word naming system
Binomial nomenclature
-Genus species
-written in italics, G s
Genus Species
Genus refers to a group of organisms that are very closely related
Species is used to describe the organism and can be based on location, physical attributes, or the person that discovered the species
H. habilis=man of skill
H. erectus=upright man
H. sapien=wise man
7 levels of classification
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Domain classification
Archaea- Archaeabacteria
Bacteria- Eubacteria
Eukarya- Anamalia, Plantae, Fungi, and Protista
Phylogeny
the evolutionary history for a group of species
Cladistics
method used to make phylogenic trees, traces evolutionary history of a group by using shared traits
clade
a group of species that shares a common ancestor
derived characters
traits that can be used to figure out evolutionary relationships among a group of species are those that are shared by some species but are not present in others
node
each place where a branch splits on a cladogram
Bacteria
-eubacteria
-living
-unicellular
-cell wall (peptidoglycan)
-heterotrophic
-autotrophic (photosynthesis and chemosynthesis)
Protist
-Eukarya
-Living
-Eukaryotic
-Unicellulr and multicellular
-cell wall made of cellulose
-heterotrophic and autotrophic
-motile(move) or sessile(attatched)
Fungi
-Eukarya
-Living
-Eukaryotic
-Multicellular(except yeast)
-cell wall made of chitin
-heterotrophic
Plant
-Eukarya
-living
-eukaryotic
-multicellular
-cell wall made of cellulose
-autotrophic (photosynthesis)
Animal
-Eukarya
-living
-eukaryotic
-multicellular
-heterotrophic
Cytosol, cytoplasm, and protoplasm
cytosol- just jelly like substance
cytoplasm- jelly like substance and organelles
protoplasm- jelly like substance, organelles, and nucleus
Pathogen
An organism that causes disease, could be virus, bacteria, or fungi
Bacteria (domain characteristics)
-single celled prokaryotes
-no specialized intracellular structures
-found in large numbers everywhere on earth
Archaea (domain characteristics)
-single celled prokaryotes
-no organelles
-extremophiles, live in harsh environments such as sea vents, hot geysers, and salt lakes
Eukarya (domain characteristics)
-eukaryotes
-can be single-celled or multicellular
-contain special intracellular structures called organelles
Prokaryotic structure
-unicellular but some live in colonies
-Can be spheres (cocci), rods (bacilli), or spirals (spirilla)
-archaea vary more in shape than bacteria do
Cell walls
Eukaryotic cell walls are made of cellulose (plants or protists) and chitin (fungi)
Bacterial cell walls contain peptidoglycan (network of sugar and polypeptides)
Archaea cell walls do not have peptidoglycan
Gram stain
-helps scientists classify bacteria
-gram-negative bacteria have less peptidoglycan and stain lighter than gram-positive bacteria
Prokaryotic mobility
most move using a flagellum and pili
plasmids
small circular DNA molecules
Prokaryotic reproduction
asexually through binary fission, and exchange genetic material through conjugation
binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction in single-celled organisms by which one cell divides into two cells of the same size
Conjugation
the process where genetic material is transferred between bacterial cells
-increases genetic variation
Prokaryotic classification
obligate aerobes- require oxygen for cellular respiration (most bacteria)
obligate anaerobes- are poisoned by oxygen and use fermentation or anaerobic respiration
facultative anaerobes- can survive with or without oxygen
How do bacteria survive in harsh conditions
they can produce and endospore, a specialized thick and protective wall that is formed around DNA
Ecological roles of prokaryotes
-recycling of nutrients (recycling chemical elements, decomposing bacteria)
-nitrogen fixation (convert nitrogen in soil for plants to use)
-bioremediation (used to break down pollutants like oil)
-photosynthesis (cyanobacteria can make oxygen)
pathogenic bacteria
-cause illness by invading tissues or making toxins
Antibiotics
-work by interfering with the peptidoglycan cell walls of bacteria
How does antibiotic resistance occur
-overuse: creates selective pressure that favors the bacteria is was intended to destroy
-underuse: not completing a dose of antibiotics will only cause the weak ones to die and allows the strong ones to multiply
-misuse: mixing antibiotics with livestock food may cause bacteria within the food to become resistant
What are viruses?
-not cells
-particles made of nucleic acid enclosed in a protein coat
-they cannot reproduce on their own or carry out metabolic processes
-NOT LIVING OR INCLUDED IN LINNAEAN CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM
Virus structure
-capsid: protein shell that encloses the DNA
-viral envelopes: surround capsids of some viruses and help infect hosts
-surface proteins: aid in infecting host cells
Capsid shapes
rod shaped, polyhedral, complex (bacteriophages)
how does a virus identify its host
By fitting its surface proteins to receptor molecules on the surface of the host cell
Bacteriophages
A virus that infects bacteria; also called a phage.
-elongated capsid head that encloses their DNA
-protein tail piece attaches to the host and injects the phage DNA
The lytic cycle
A type of viral (phage) replication cycle resulting in the release of new phages by lysis (and death) of the host cell.
-the virus uses the hosts machinery and digests the hosts wall to create more viruses
ACTIVE
Lysogenic cycle
a viral reproductive cycle in which the viral DNA is added to the host cell's DNA and is copied along with the host cell's DNA
-DNA is incorporated into host cell and called a prophage
-dormant
DNA and RNA virus
DNA can be replicated and used for protein synthesis (DNA ->RNA->Protein)
RNA can be replicated and used for protein synthesis (RNA-> Protein)
Retroviruses
use reverse transcriptase to copy their RNA genome into DNA
-RNA->DNA->RNA->Protein
-Ex: HIV
Provirus
the viral DNA that is integrated into the hosts genome
Vaccines
harmless derivatives of pathogenic microbes that stimulate the immune system to mount defenses against the actual pathogen
Smaller less complex entities that cause disease in plants and animals
viroids (RNA molecules that infect plants and disrupt their growth) and prions (slow-acting, virtually indestructible infectious proteins that cause brain disease in animals)
What is Protista compared to?
a kitchen junk drawer
Ameboid motion
motion with the use of pseudopods (cytoplasmic extensions)
Cilia motion
short and numerous, used like oars on a boat
flagella motion
long, 1-2 per cell, wavelike or propeller motion
How do protists reproduce?
-many use mitosis which can limit genetic diversity
-some can preform conjunction
-many protists have life cycles where they switch between sexual and asexual reproduction depending on the conditions (alternation of generations)
Autotrophic protists
They can perform photosynthesis and mainly consist of unicellular algae. they form the base of the food chain in aquatic enviornments
mutualistic protists
-many protists are involved in mutualistic symbiosis where both they and their host benefit
parasitic protists
-responsible for causing some of the worlds most dangerous diseases
-Malaria, Sleeping sickness, Ameobic Dysentery
Ameobas
use false feet to move, pseudopodia, heterotrophic
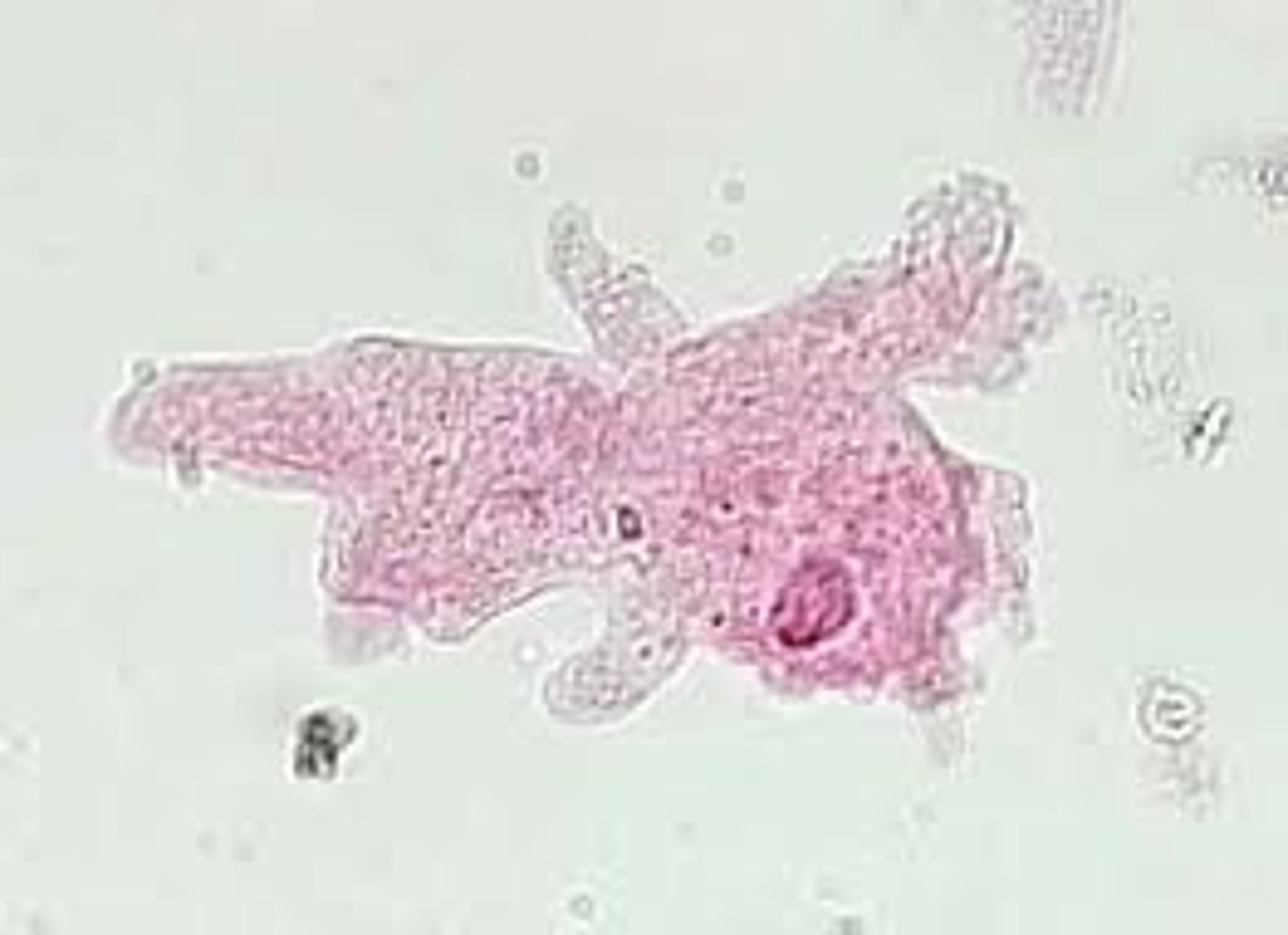
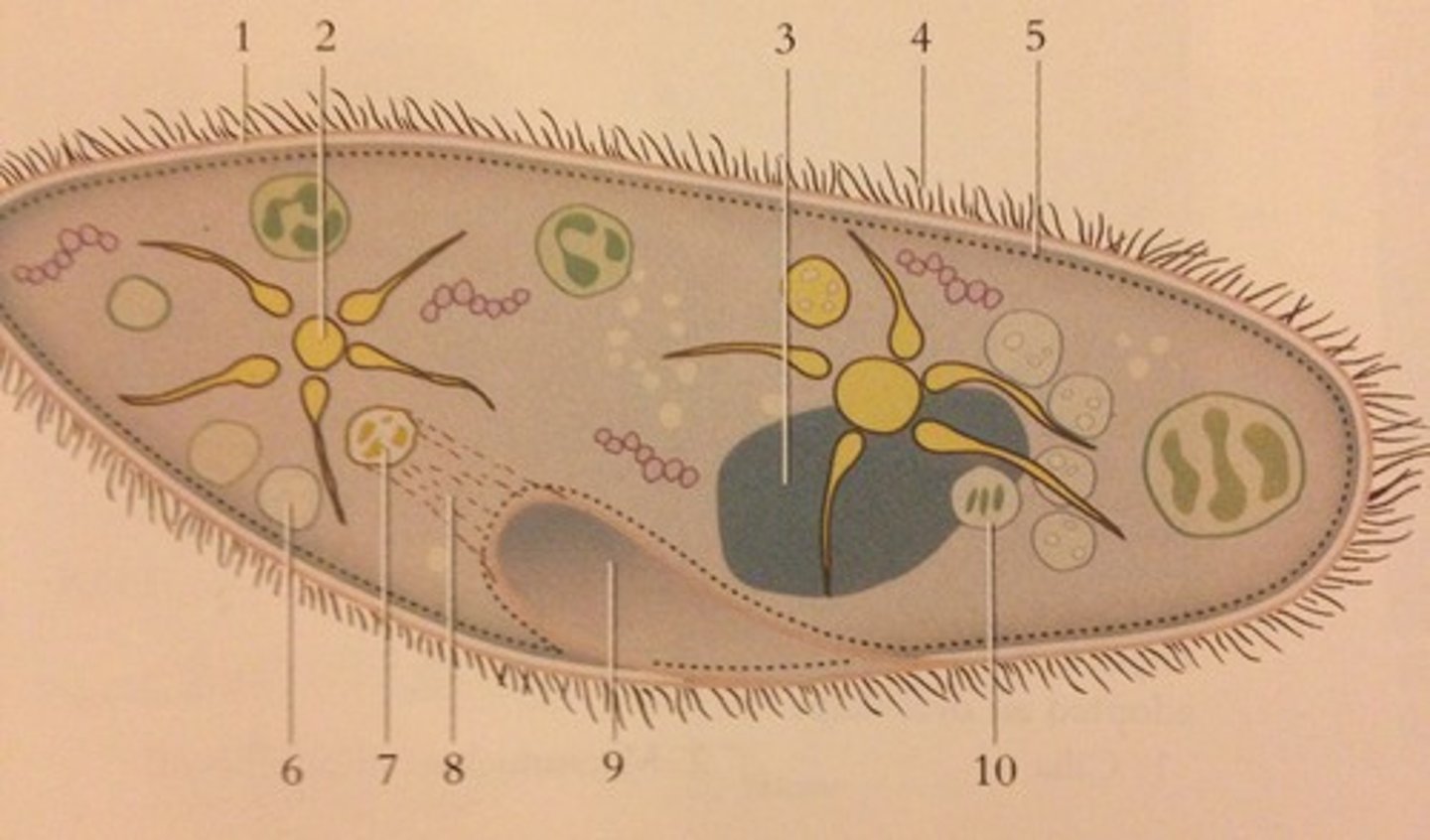
Paramecium
use cilia to move, heterotrophic
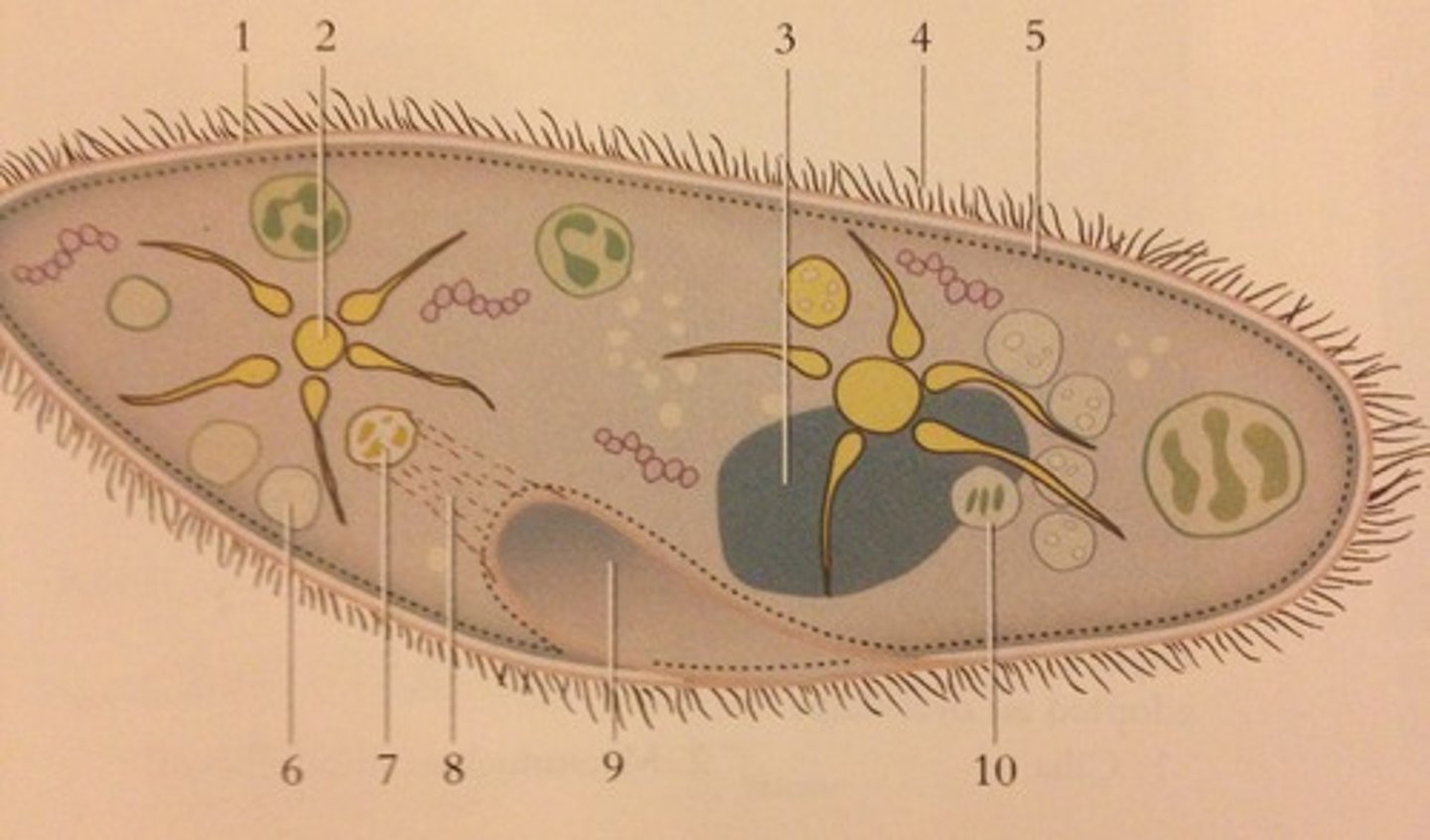
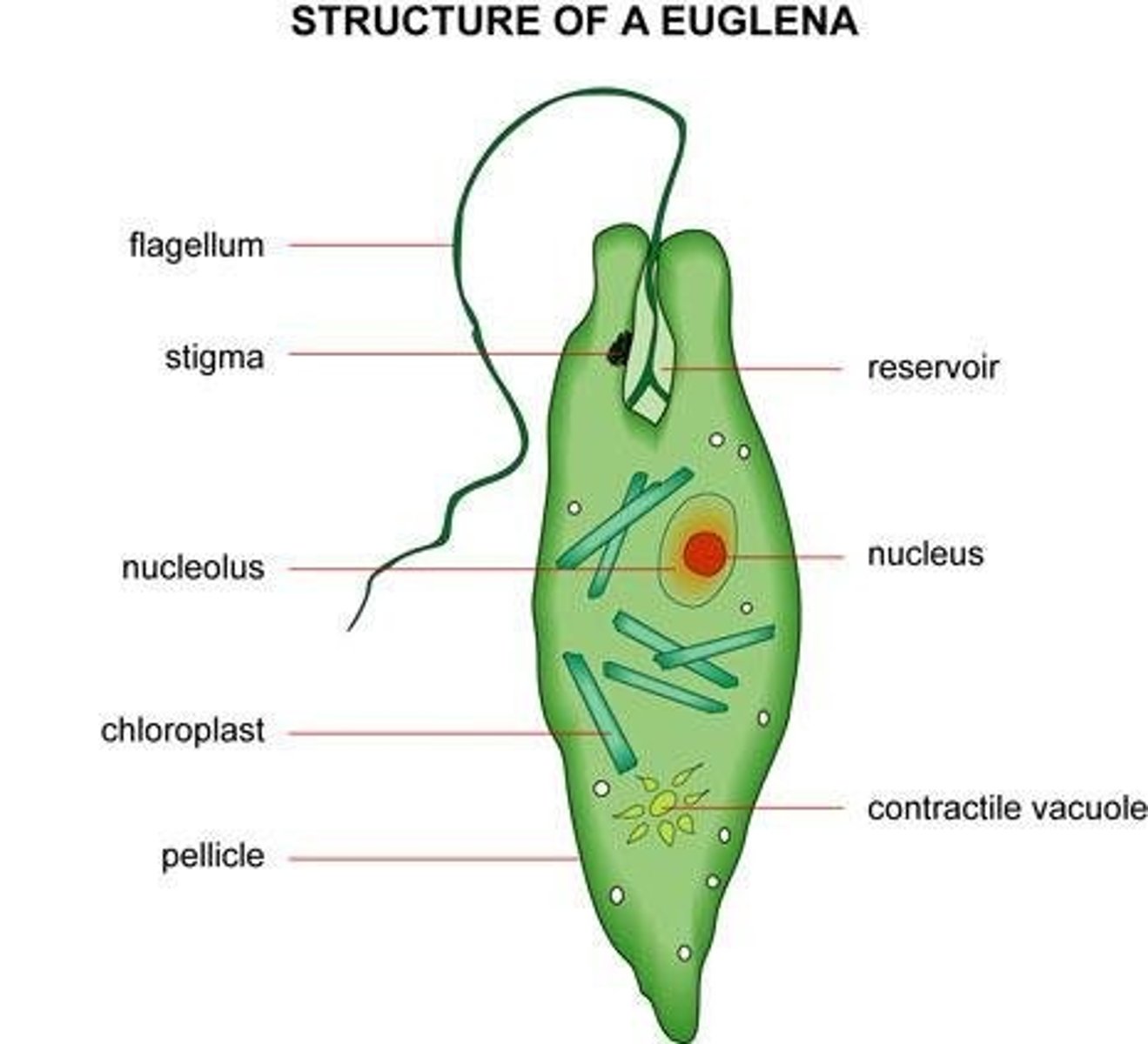
Euglenoids
use flagella to move, both autotrophic and heterotrophic
How do fungi differ from plants
plants contain chlorophyll and photosynthesize which fungi do not photosynthesize and absorb their energy from the environment
plants have true roots while fungi do not
plant cell walls are made of cellulose while fungi cell walls are made of chitin
anatomy of fungi
hyphae- long filaments that make up the bodies of fungi
mycelium- hyphae that grow together into a tangled mass found underground
fruiting body- reproductive structures found above ground
How do fungi obtain nutrients?
by secreting chemicals that break down food and then absorbing it
-hyphae extend into the food source and release enzymes that break down food that is then absorbed across cell walls
-high surface area= larger amounts of nutrients taken in
classifying fungi
they are classified by their mode of sexual reproduction
Sac fungi (Ascomycota)
-during sexual reproduction they form a sac called an ascus that contains spores for reproduction
-include yeast, certain molds, morels, and truffles
Bread Mold (Zygomycota)
-during sexual reproduction they form a structure called an zygospore that gives rise to a sporangium which releases spores
-most spoil food
-ex mycorrhizae
club fungi (basidiomycota)
-during sexual reproduction they form structures called basidia that contain spores for reproduction
-ex: mushrooms, puffballs, and bracket
Fungi reproduction
-reproduce in vast numbers
-usually haploid except when they are in the sexual reproduction stage and they are diploid
-sexual reproduction requires the fusion of two haploid cells followed by meiosis
-sexual reproductions during favorable conditions and asexual reproduction when conditions are harsh
ecological roles of fungi
-decomposers: decompose the dead and decaying organic matter, return nutrients back into the soil
-pathogens: illnesses in humans such as ringworm and athletes food, illnesses and plants such as Dutch elm disease
Relationships in fungi
-Mutualists:
Mycorrhizae, symbiotic relationship- where fungus transfer minerals to a plants roots and plant roots supply carbohydrates to fungus
Lichens, symbiotic relationship- fugus protects photosynthetic partner providing minerals, and photosynthetic partner provides carbohydrates to fungus
ameoba
animal like
Phytoplankton
plant-like
water molds
fungi like
zooplankton
animal-like
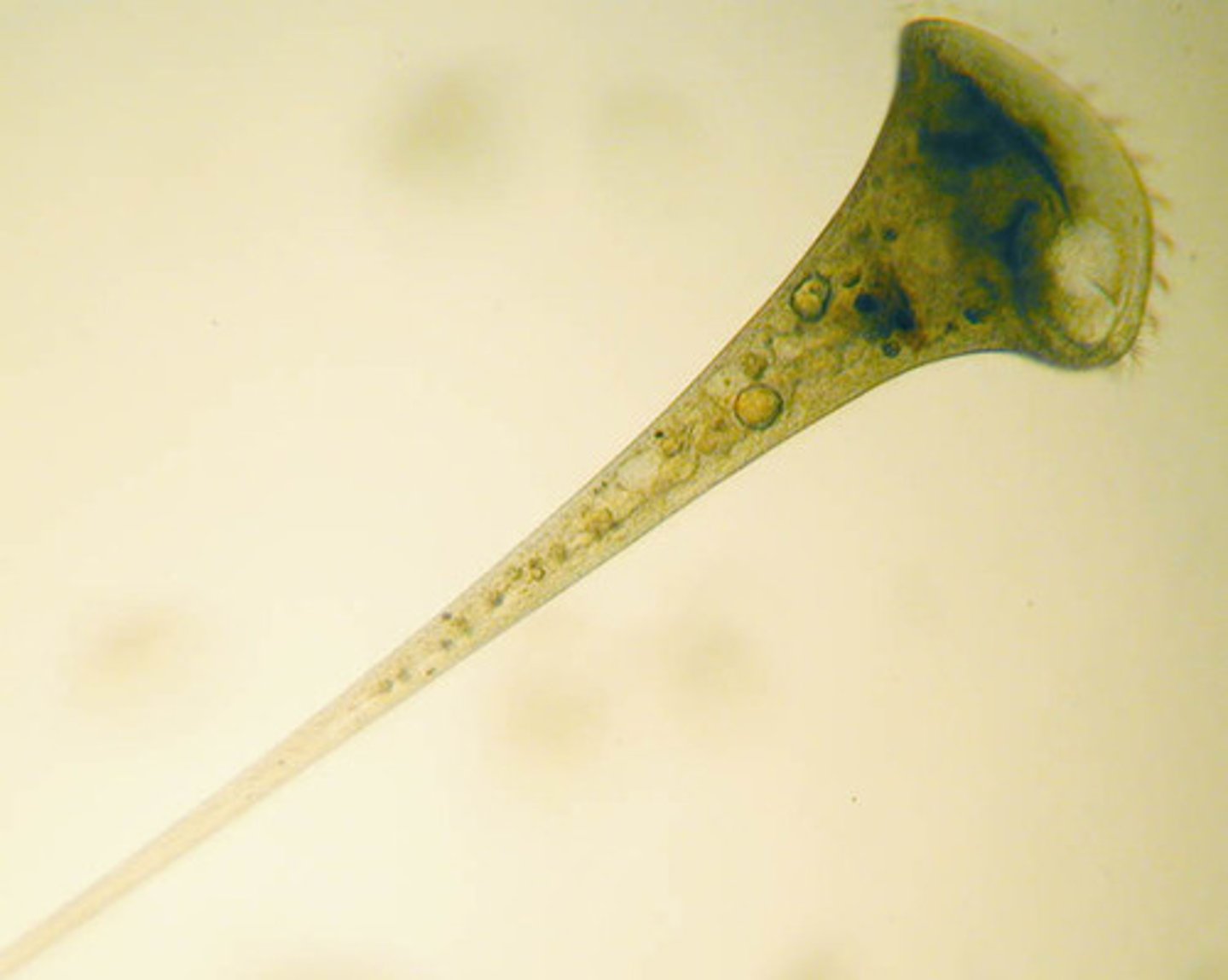
stentor
Paramecium
euglena
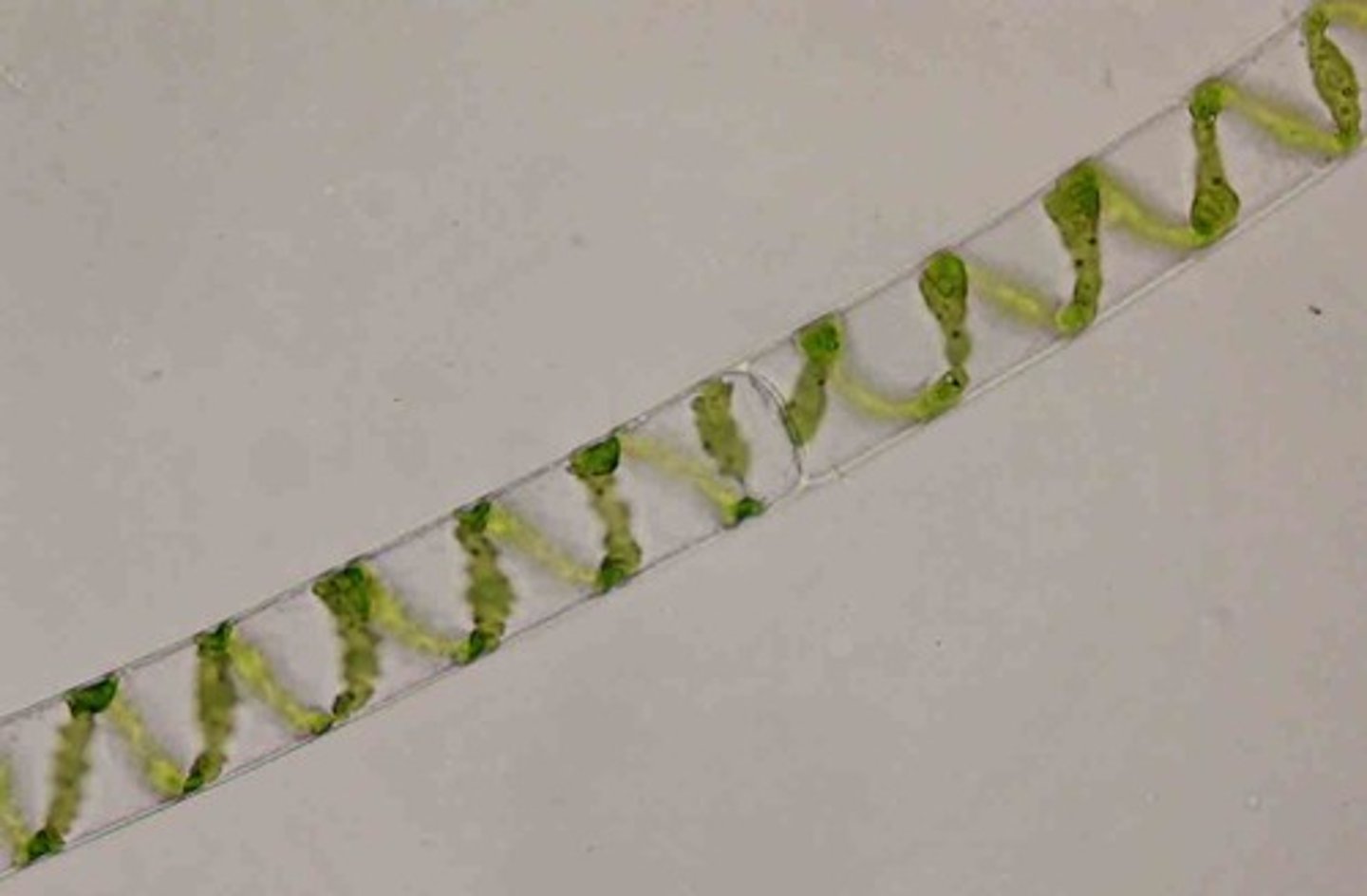
spyrogyra

Derived characteristics
characteristics that arise as lineages evolve over time