CCMA Exam
1/221
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
222 Terms
advance beneficiary notice
a form provided to the patient when the provider believes Medicare will probably not pay for services recieved
allowed amount
the maximum amount a third-party payer will pay for a particular procedure or service
copayment
an amount of money that is paid at the time of medical service
coinsurance
a policy provision frequently found in medical insurance whereby the policyholder and the insurance company share the cost of covered losses in a specified ratio, such as 80:20
deductible
a specific amount of money a patient must pay out of pocket before the insurance carrier begins paying
explanation of benefits
a statement from the insurance carrier detailing what was paid, denied, or reduced in payment; also contains information about amounts applied to the deductible, coinsurance, and allowed amounts
participating provider (PAR)
providers who agree to write off the difference between the amount charged by the provider and the approved fee established by the insurer
medicare
generally covers patients age 65 and older by Part A (hospitalization) or Part B (routine medical office visits) benefits
tricare
authorizes dependents of military personnel to receive treatment from civilian providers at the expense of the federal government
CHAMPVA
covers surviving spouses and dependent children of veterans who died as a result of service-related disabilities
medicaid
provides health insurance to the medically indigent population through a cost-sharing program between federal and state governments for those who meet specific eligibility criteria
managed care
an umbrella tern for plans that provide health care in return for preset scheduled payments and coordinated care through a defined network of providers and hospitals
workers’ compensation
products wage earners against the loss of wages and the cost of medical care resulting from an occupational accident or disease as long as the employee is not proven negligent
CMS-1500 Form
claims submitted by a provider or supplier
CMS-1500 Form Section 1
carrier block
contains the address of the insurance carrier and is located at the top of the form
CMS-1500 Form Section 2
patient/insured section
contains information about the patient or insured
includes boxes 1 through 13
CMS-1500 Form Section 3
physician/supplier section
contains information about the physician or suppler
includes boxes 14 to 33
Supine
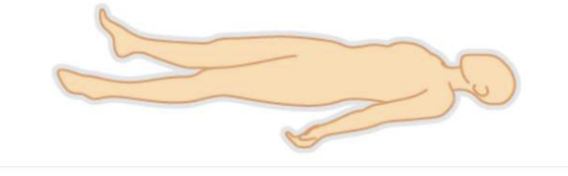
Dorsal Recumbent position
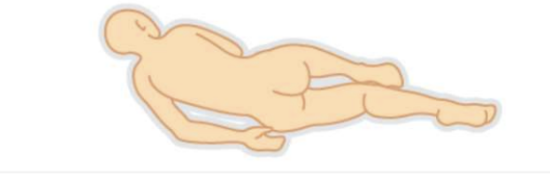
SIms’ position
Knee-elbow position

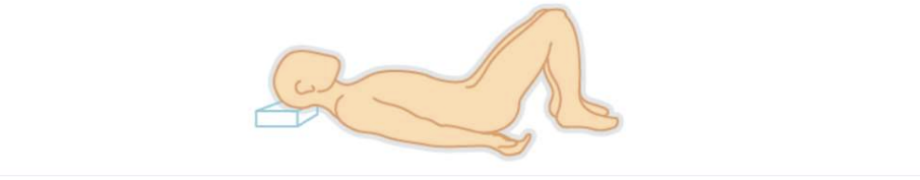
Fowler’s Position
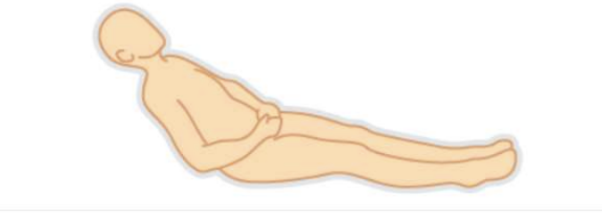
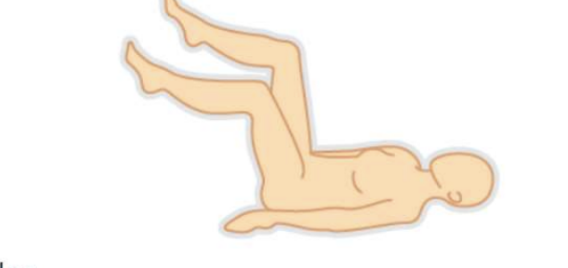
Lithotomy position
Schedule 1 drugs
high potential for abuse and no approved medical use in the United States
heroin, mescaline, and lysergic acid diethylamide
includes marijuana
Schedule 2 Drugs
substances that have a high potential for abuse, are considered dangerous and can lead to psychological and physical dependence
morphine, methadone, oxycodone, hydromorphone, hydrocodone, fentanyl, and methamphetamine
handwritten prescription with no refills
Schedule 3 drugs
moderate to low potential for physical and psychological dependence
ketamine, anabolic steroids, and testosterone
handwritten prescription and can be refilled five times in 6 months
Schedule 4 drugs
low potential for abuse and dependence
diazepam, zolpidem, eszopiclone, alprazolam, chlordiazepoxide, and clonazepam
can refill five times in six months and refills can be authorized over the phone
Schedule 5 drugs
substances that contain limited quantities of some narcotics
usually for antidiarrheal, antitussive, and analgesic purposes
atropine, pregabalin, lacosamide, and opium/kaolin/pectin/belladonna
can refill five times in six months and refills can be authorized over the phone
Epidural
epidural space
injectable liquid
not permitted to administer
intra-arterial
arteries (to break up clots)
injectable liquid
not permitted to administer
intra-articular
within a joint space
injectable liquid
not permitted to administer
intradermal
within a joint space
injectable liquid
permitted to inject
intramuscular
deltoid, vastus lateralis, ventrogluteal muscles
injectable liquid
not permitted to administer
introaosseous
bone marrow
injectable liquid
not permitted to administer
intraperitoneal
peritoneal cavity (abdomen)
injectable liquid
not permitted to administer
intrapleural
pleural space (lungs)
injectable liquid
not permitted to administer
intrathecal
subarachnoid space (brain)
injectable liquid
not permitted to administer
intravenous (IV)
Major veins, most often in the arms and hands or via central venous access devices
injectable liquid
not permitted to administer
subcutaneous
under the skin of the abdomen, anterior thighs, upper outer arm, upper back (under the shoulder)
injectable liquid
permitted to administer
Fat soluble vitamins
a
d
e
k
water-soluble vitamins
B1
B2
B3
B6
folate
B12
pantothenic acid
biotin
C
Erikson’s stage of psychosocial development
trust/mistrust
autonomy/shame and doubt
initiative/guilt
industry/inferiority
identity/role confusion
intimacy/isolation
generativity/stagnation
ego integrity/despair
Stages of grief
denial
anger
bargaining
depression
acceptance
apathy
indifference
lack of interest, feeling, concern, or emotion
compensation
a method of balancing a failure or inadequacy with an accomplishment
conversion
transformation of an anxiety into a physical symptom that has no cause
denial
avoidance of unpleasant or anxiety-provoking situations or ideas by rejecting them or ignoring their existence
displacement
the redirection of emotions away from its original subject or object onto another less threatening subject or object
disassociation
a disconnection of emotional importance from ideas or events from compartmentalizing those emotions in different parts of awareness
identification
the attribution of characteristics of someone else to oneself or the imitation of another
intellectualization
analysis of a situation with facts and not emotions
introjection
adoption of the thoughts or feelings of others
physical avoidance
keeping away from any person, place or object that evokes memories of something unpleasant
projection
transference of a person’s unpleasant ideas and emotions onto someone or something else
rationalization
an explanation that makes something negative or unacceptable seem justifiable or acceptable
reaction formation
belief in and expression of the opposite of one’s true feelings
regression
the reversion to an earlier, more childlike, developmental behavior
repression
the elimination of unpleasant emotions, desires, or problems from the conscious mind
sarcasm
the use of words that have the opposite meaning, especially to be funny, insulting, or irritating
sublimation
rechanneling unacceptable urges or drives into something constructive or acceptable
suppression
voluntarily blocking of an unpleasant experience from one’s awareness
undoing
canceling out an unacceptable behavior with a symbolic gesture
verbal aggression
a verbal attack on a person without addressing the original intent of the conversation
superior
above or closer to the head
inferior
below or closer to the feet
anterior
toward the front of the body
posterior
toward the back of the body
medial
closer to the midline of the body
lateral
further away from the midline of the body
proximal
closer to the trunk of the body
distal
farther away from the trunk
superficial
closer to the surface of the body
deep
farther from the body’s surface
travel of electrical impulse
sinoatrial node (SA)
atrioventricular node (AV)
bundle of His
purkinje fibers
homeostasis
body’s systems and biological processes maintain stability
chain of infection
infectious agent
reservoir host
portal of exit
mode of transmission
portal of entry
susceptible host
conditions for growth
moisture
warmth
oxygen
food
time
average heart rate
newborn (birth to 1 month) 120 to 160/min
infant (1 to 12 months) 80 to 140/min
toddler (1 to 3 years) 80 to 130/min
Preschool (3 to 5 years) 80 to 120/min
school-age (6 to 15 years) 70 to 100/min
Adult (older than 15 years) 60 to 100/min
Pulse Oximetry
A probe is attached to the finger that incorporates an infrared light
reading of 95% or higher is considered a normal result
blood pressure
A sphygmomanometer is used to determine the blood person
millimeters of mercury
systolic pressure is recorded when the first sharp tapping sound is heard, which is when the blood begins to surge into the artery that has been occluded by the inflation of the blood pressure cuff
diastolic pressure is noted when the last sound disappears completely and blood is flowing freely
diastolic and systolic are stage 1 and 5 of korotkoff sounds
phase 2 there is a swishing sound as more blood flows through the artery
phase 3 sharp tapping sounds are noted as more blood is surging
phase 4 the sound changes to a soft tapping sound
hypertension
high blood pressure
anything above 140/90 mmhg
prehypertension
120-139/80-89 mm Hg
average blood pressure rates
infants and children 60-100/30-80 mm Hg
adults 100-140/60-80 mm Hg
respiration rates
28/min
breathing pattern and depth describe how much air is inhaled
newborn average 30 to 50/min
adult rate 12 to 20/min
heart rate
radial pulse most common site for taking an adult pulse
brachial pulse most common for children
carotid most common for use in emergency procedures
deltoid muscle injection
1 to 2 inches below the acromion
90 degree angle
do not aspirate vaccines
aspirate most other types of medications administered via this route
do not use for infants or children under 3 years old
should not exceed 1 mL
massaged after medication is administered
ventrogluteal muscle injection
place heel of the hand on the greater trochanter (right hand placed on left hip and left hand placed on right hip), middle finger is placed on the iliac crest and the fingers are spread, where the V is made is where the injection goes
90 degree angle
do not aspirate vaccines
aspirate most other types of medications administered via this route
deep IM injections are prescribed or when larger quantities of medicines are needed
viscous medications
vastus lateralis muscle injection
mid to upper outer thigh
90 degree angle
do not aspirate vaccines
aspirate most other types of medications administered via this route
vaccines and medication for people under 3 years old
subcutaneous injection
multiple subcutaneous tissue sites are readily available for injections
45 degree angle
do not aspirate for vaccines, insulin, or heparin
aspirate for most other types of medications administered via this route
when administering insulin or heparin, site should be massaged
sites should be rotated
common sites upper outer arm, abdomen, and thigh
intradermal
for the forearm, one hand width from the wrist and one hand width from the elbow
any area within the anterior forearm visible is acceptable for the injection
upper back may be used
10 to 15 angle
do not aspirate
used for testing
presence of a wheal is expected
do not massage or apply pressure
most common site for TB testing is mid forearm
allergy testing is done on back
oral medications
in the mouth
solids: for multiple-dose bottles, pour pills into the lid first, then the medicine cup
liquids: read liquids at the lowest point of the curve of the liquid and “palm” the label to prevent distortion if medication drips down the bottle
buccal
between the cheek and gums resulting in rapid absorption
medication bypasses the digestive system, resulting in smaller doses required for therapeutic effects
medication is designed to melt while held in the cheek area
eating, drinking, or smoking can influence the absorption rate
sublingual
under the tongue
nitroglycerin tablets and spray are common forms of medication via this route
because the medication bypasses the digestive system, smaller doses are require for therapeutic effects
solids: medication melts and absorbs into the bloodstream rapidly
liquids: sprays are occasionally used to deliver sublingual medications
eating, drinking, or smoking can influence absorption rates
inhalation
typically used for targeted areas such as bronchial passages
can be delivered via a nebulizer
patient must hold the medication in lungs as long as possible
topical medications
designed to react locally and systematic absorption is minimal
can serve as a barrier to prevent irritants from damaging the skin or can be used to treat a local condition
typically oil-or-water-based products
monitor for skin irritation or reaction
mucosal
designed to absorb into and through mucous membranes
medications can be administered in the vagina, rectum, eye, or ear
can cause irritation to the mucosas
transdermal
for continuous slow absorption of various medications
used for smoking cessation, pain medication, hormone delivery
avoid touching the medication when applying the patch
dispose of the patch in a container that is not accessible to children
monitor skin for irritation
cryosurgery
process of exposing tissues to extreme cold temperatures to destroy cells
may be performed for conditions such as warts or cervical dysplasia
canister with liquid nitrogen, cryoprobe
colposcopy/hysteroscopy
using an instrument to inspect the vaginal area and cervix or the uterus and deliver treatments or perform diagnostic testing
cannot be performed if woman is on period
electrosurgery or electrocauterization
a pulse of electrical current is sent through tissue to cauterize
used to minimize or stop bleeding, destroy small polyps, or break scar tissue