Rad. Physics & Imaging- Ch. 2 Study Guide
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
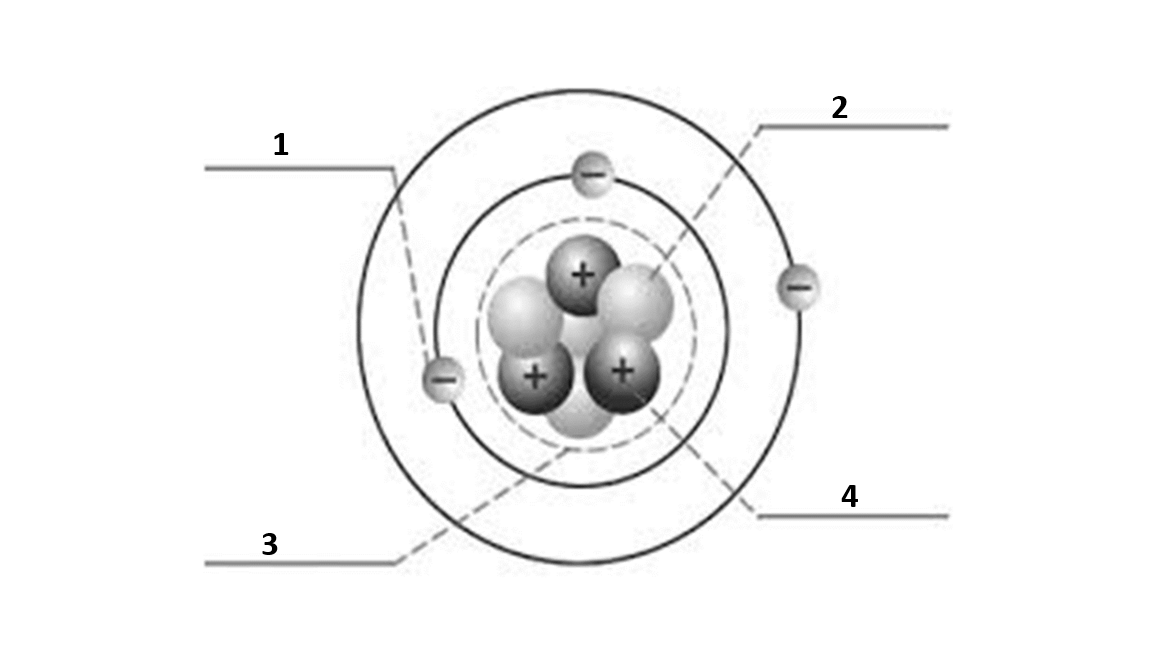
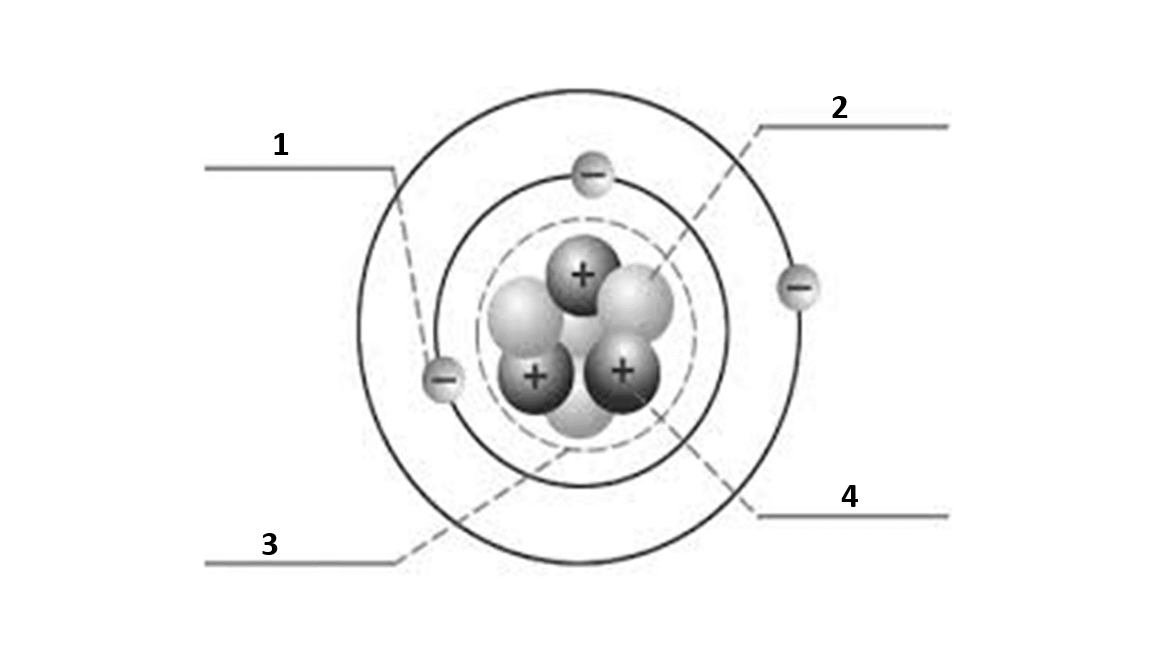
Match the number to the correct part of the atom:
Number 1 is
electron
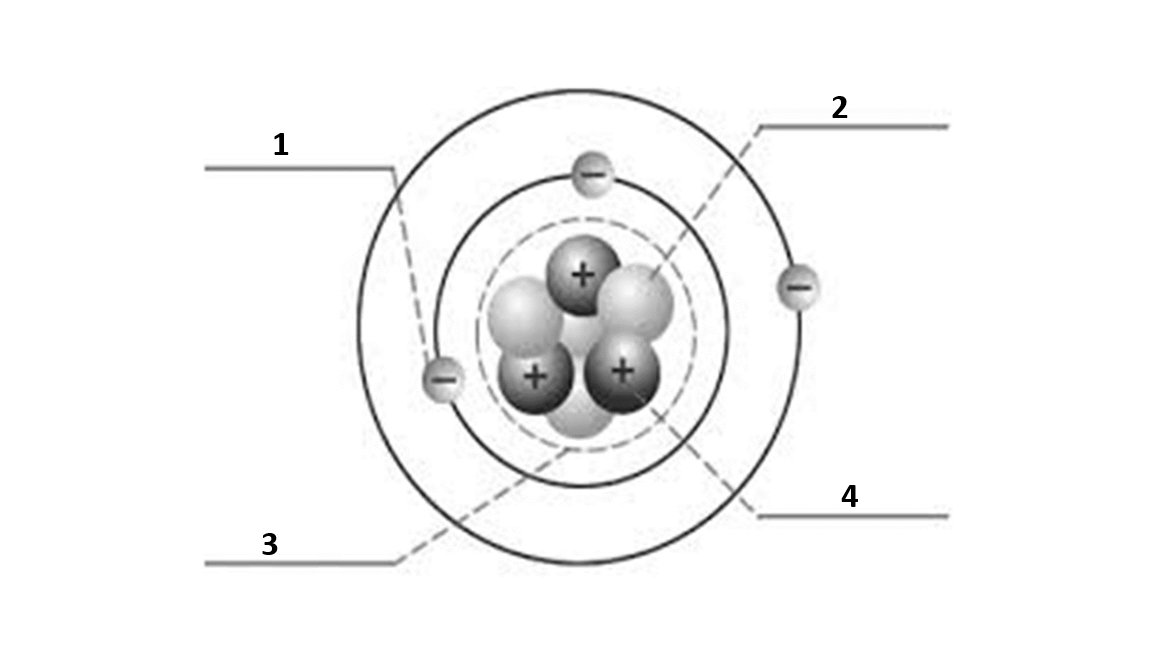
Match the number to the correct part of the atom:
Number 2 is
neutron
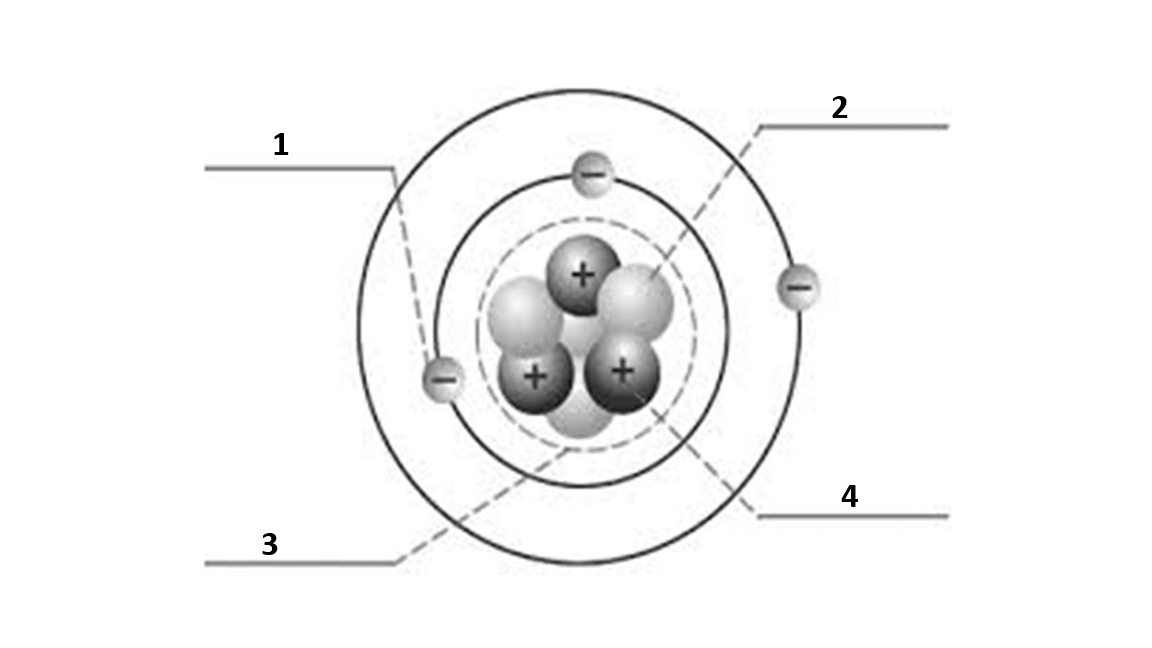
Match the number to the correct part of the atom:
Number 3 is
nucleus
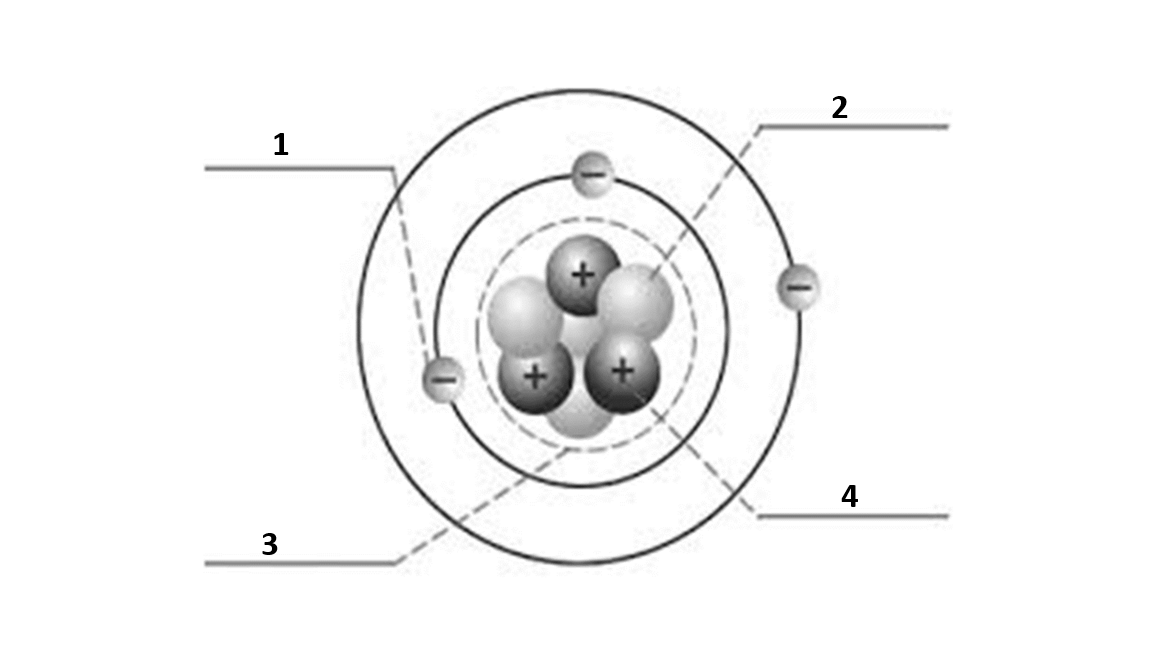
Match the number to the correct part of the atom:
Number 4 is
proton
What is the charge of a proton?
Positive
What is the charge of a neutron?
Neutral
What is the charge of an electron?
Negative
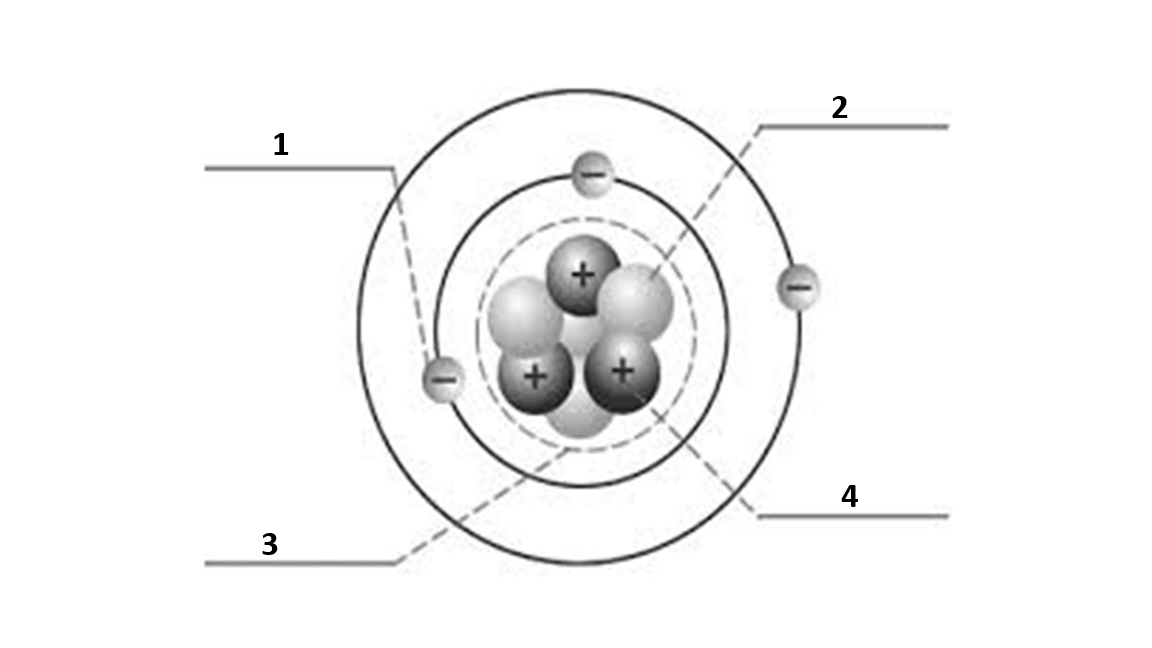
What is the atomic number of this atom?
3
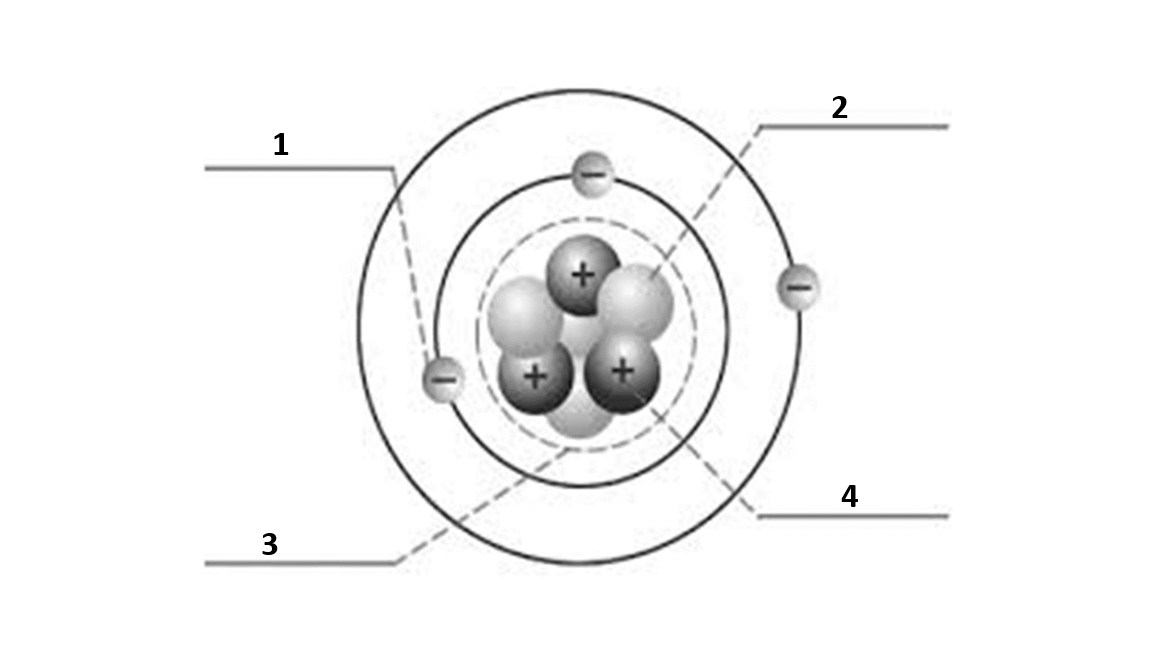
What is the atomic mass of this atom?
7
Number of electrons?
3
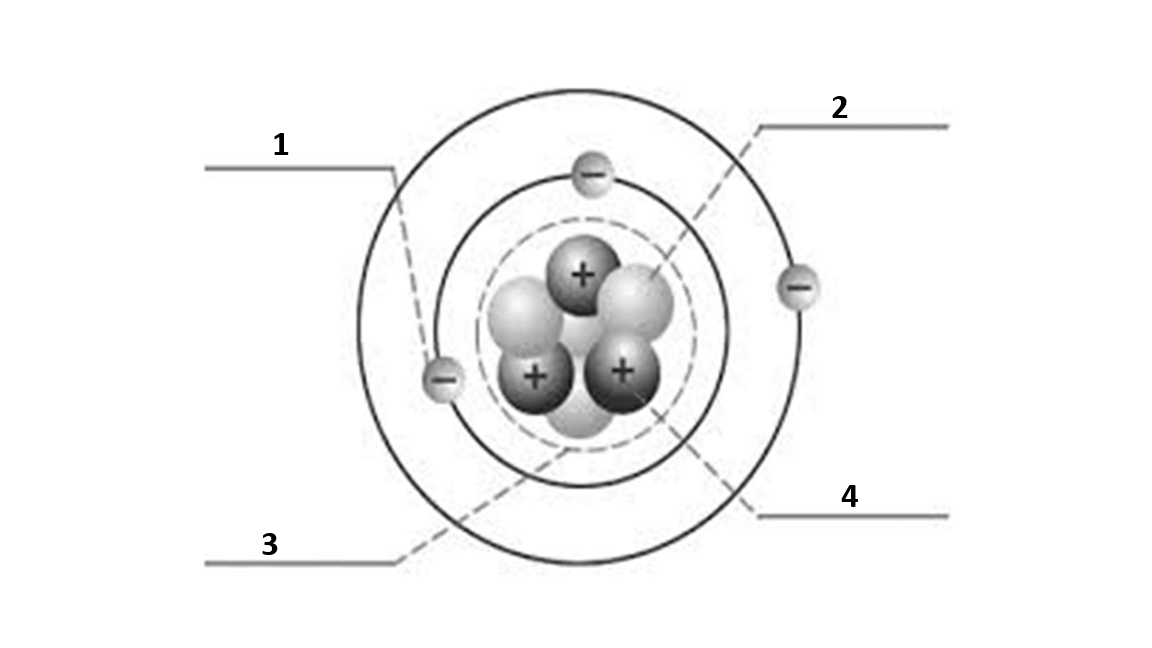
Number of protons?
3
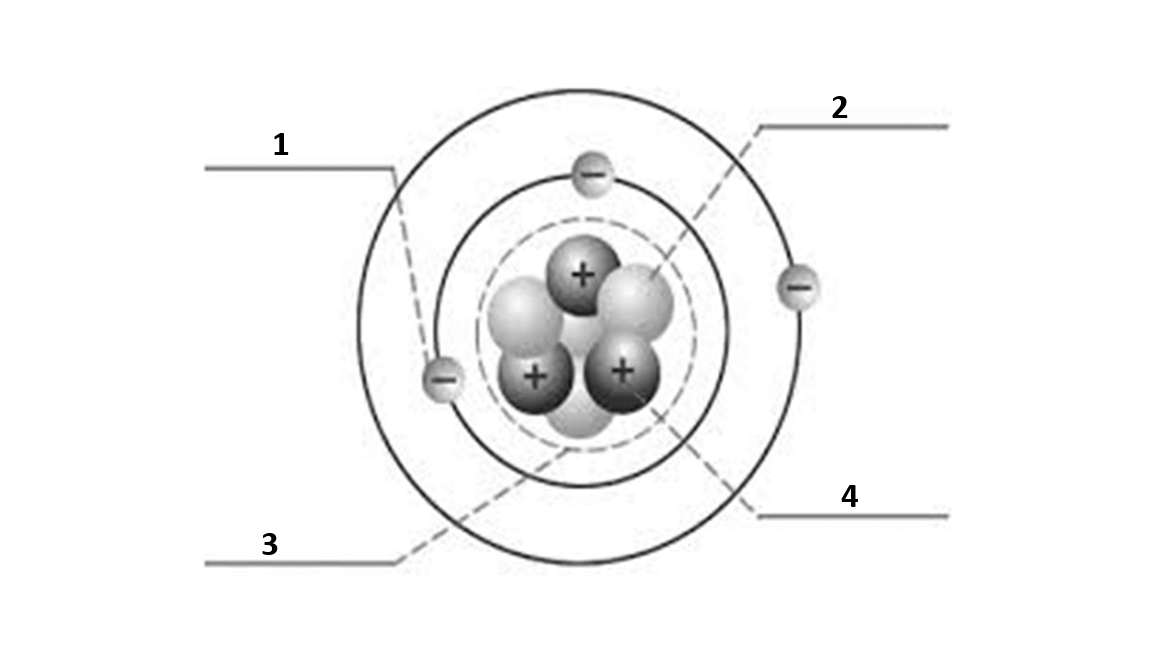
Number of neutrons?
4
Which two subatomic particles are located in the nucleus of an atom?
Protons and Neutrons
The atomic number is the number of _____
protons
The atomic mass is the number of _____ + ______
Protons + Neutrons
Elements within the same row of the periodic table have the same ______________
number of electron shells
Elements within the same group/column have the same __________
number of valence electrons
A cation has a ____ net charge
positive
A anion has a _____ net charge
Negative
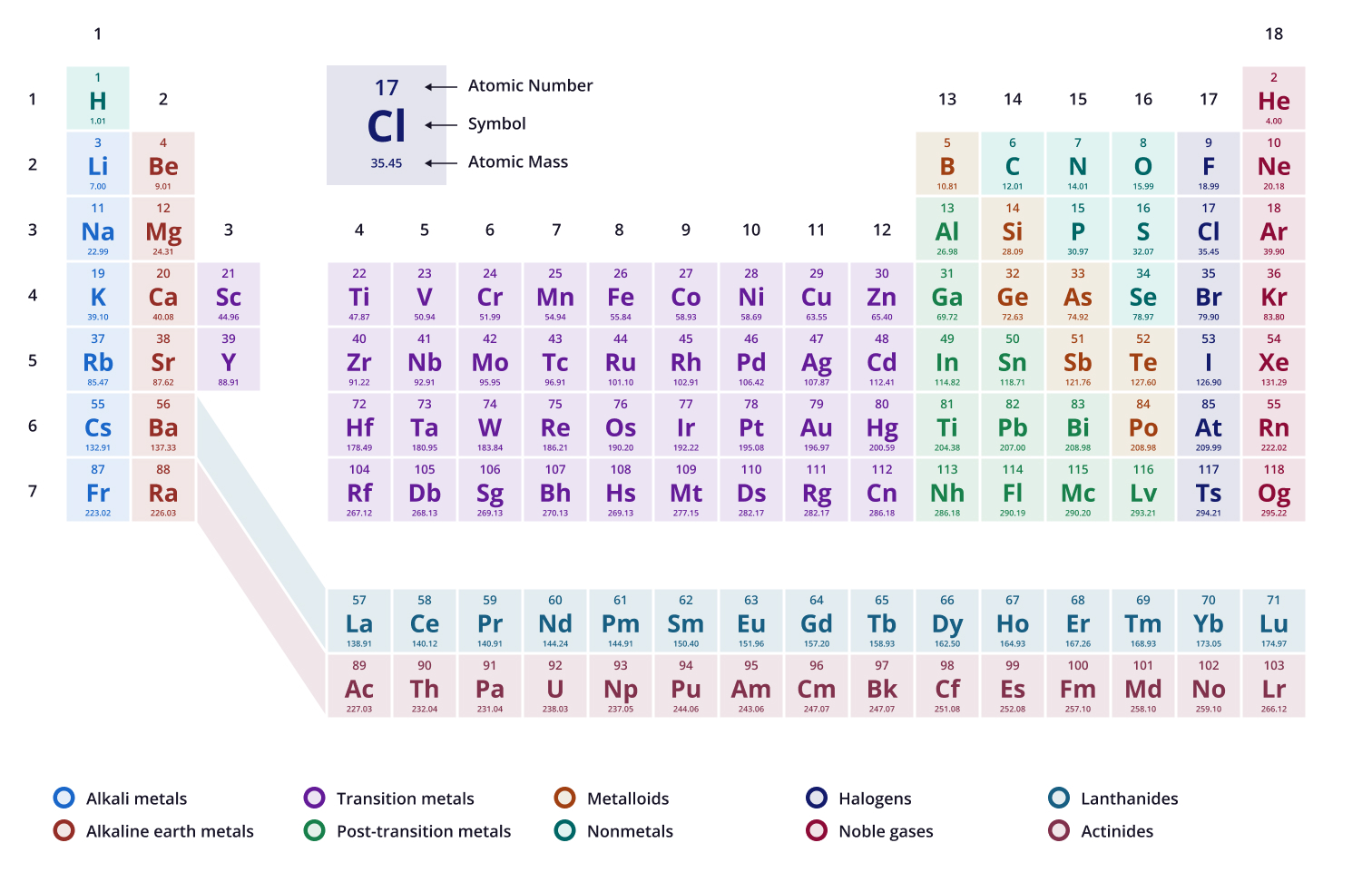
Sodium (Na) has ___ neutrons
12
There are ____ protons found in the element “oxygen”
8
There are ____ protons found in the element “tungsten” with the chemical symbol “W"
74
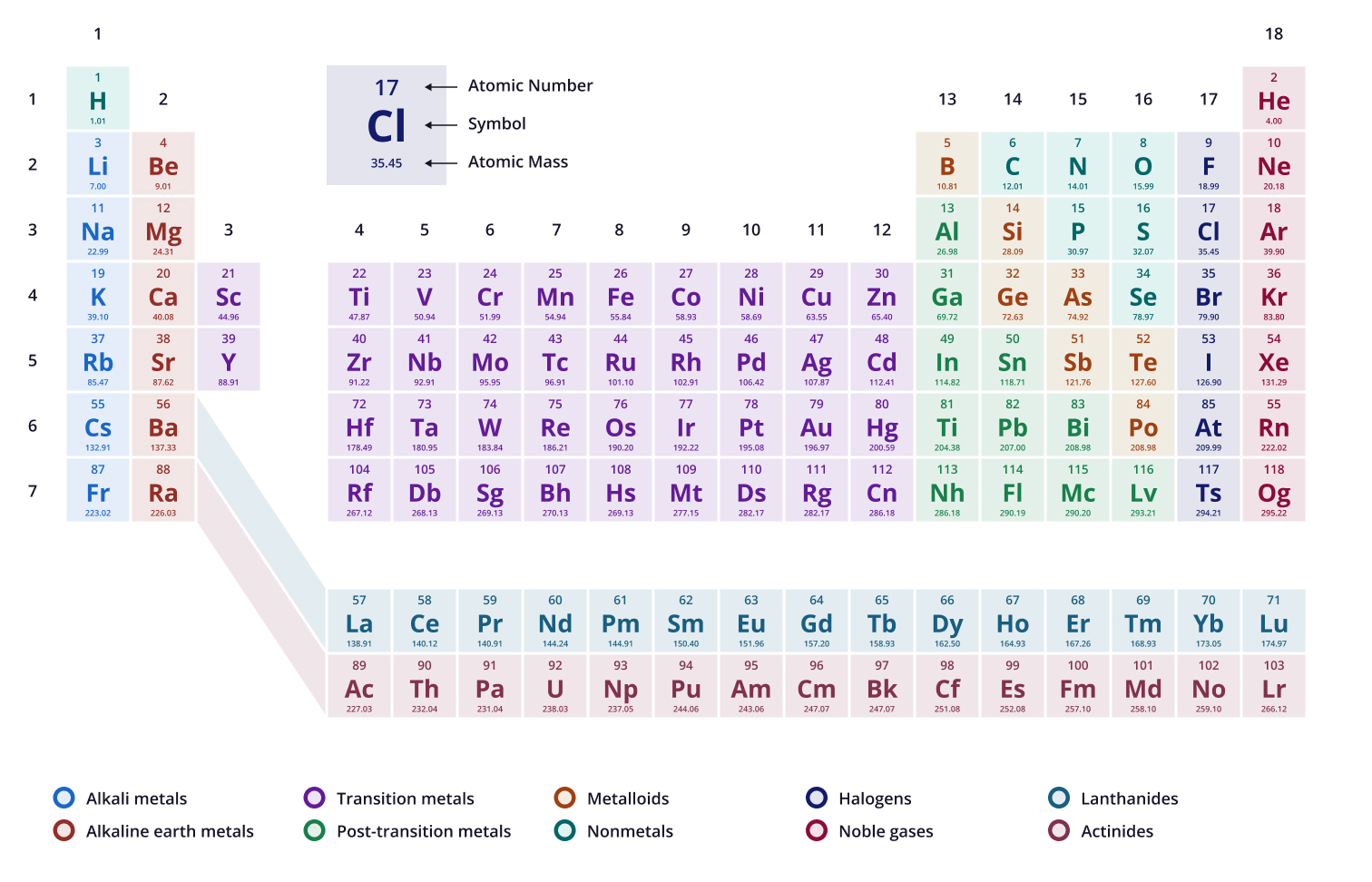
Based on the periodic table, which of the following has the highest number of electrons?
Krypton
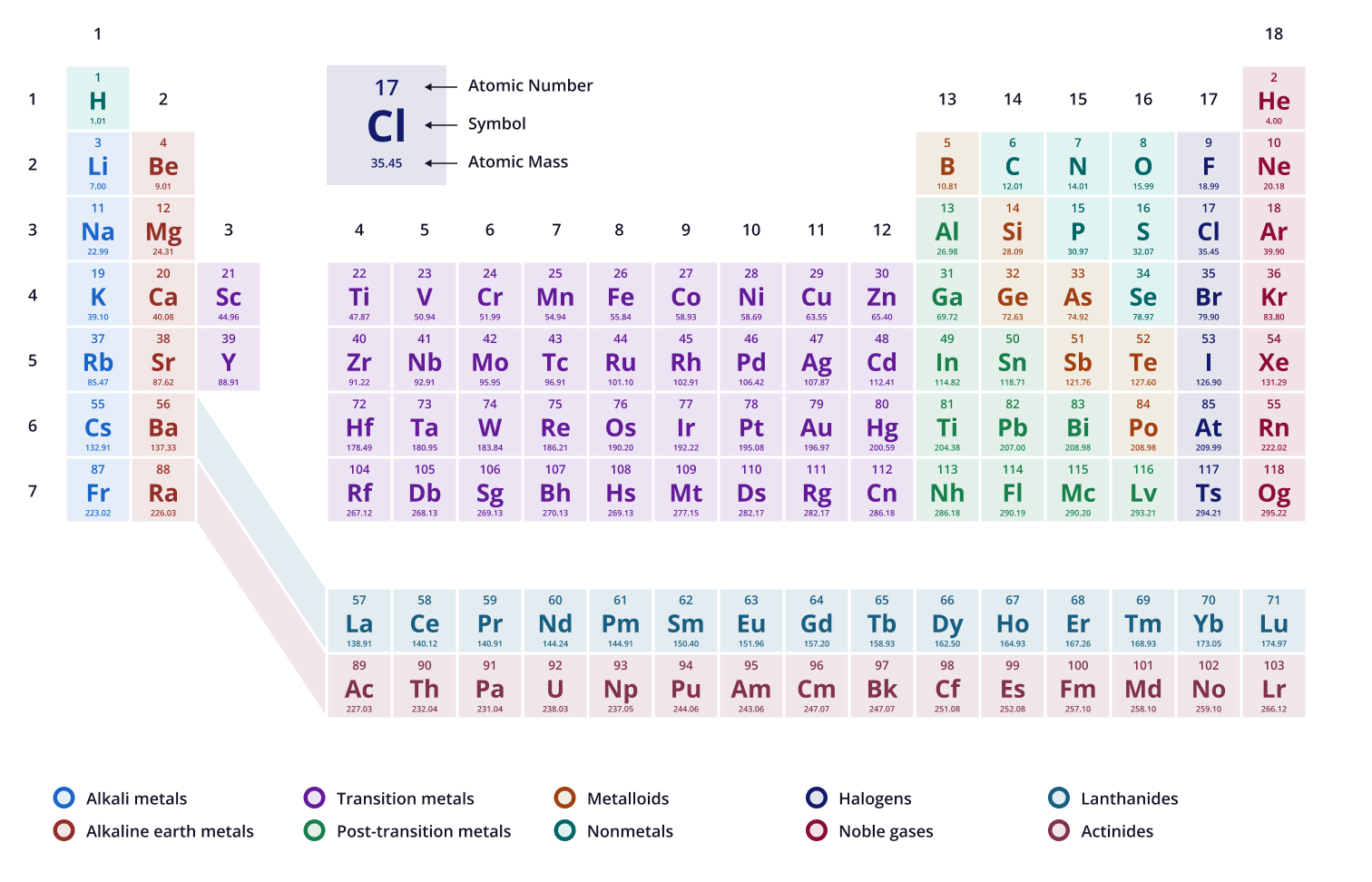
![<p>Potassium[19] has ____ electron(s) in the outermost orbital shell</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3861ca71-0a9f-421e-8875-b1618c6e2741.jpg)
Potassium[19] has ____ electron(s) in the outermost orbital shell
1
Hydrogen has _____ neutrons
0.0078
![<p>Phosphorus [15] has ____ neutrons within the nucleus</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1621f987-e71c-422b-a753-97330fa5e4eb.jpg)
Phosphorus [15] has ____ neutrons within the nucleus
16
![<p>Which iso is this Kr [36]-81; Kr[36]-81m</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/50af0eb9-70ad-4cfa-af83-aabef036903b.jpg)
Which iso is this Kr [36]-81; Kr[36]-81m
isomers
![<p>Which iso is this K[19]-40; Ca[20]-40</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f4799a33-fd41-41ca-ab32-841956626ff7.jpg)
Which iso is this K[19]-40; Ca[20]-40
isobars
![<p>Which iso is this Tc[43]-99; Tc[43]-99m</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1185b028-6608-446f-b9b0-1f41d65ea401.jpg)
Which iso is this Tc[43]-99; Tc[43]-99m
isomers
![<p>Which iso is this C[6]-14; N[7]-14</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0d17a84d-b978-4f86-bb3c-179deccb193e.jpg)
Which iso is this C[6]-14; N[7]-14
isobars
![<p>Which iso is this O[8]-16; O[8]-17</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/706f791e-d6e1-4d0d-a5b7-0e85c3a3be59.jpg)
Which iso is this O[8]-16; O[8]-17
isotopes
![<p>Which iso is this B[5]-12; C[6]-13</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1a6885b3-af54-4d2c-8117-d51de15e91b7.jpg)
Which iso is this B[5]-12; C[6]-13
isotones
![<p>Which iso is this Cl[17]-37; Ar[18]-38</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/adfa3ecf-2d74-40a4-bcd3-60a54a8adedf.jpg)
Which iso is this Cl[17]-37; Ar[18]-38
isotones
![<p>Which iso is this H[1]-1; H[1]-3</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2f1c2bb6-7749-4ffe-afbc-fa805294985d.jpg)
Which iso is this H[1]-1; H[1]-3
isotopes
O2 is an example of a/an:
molecule only
H2O is an example of a/an:
compound and molecule
![<p>Carbon[6] has ____ electron(s) in its outermost orbital shell</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/22b34baa-e99b-4aff-a39b-47f89adfa5fe.jpg)
Carbon[6] has ____ electron(s) in its outermost orbital shell
4
![<p>Magnesium[12] has ____ electron orbital shells</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/70023ad2-bb85-412f-8a49-2e4bcb9c2166.jpg)
Magnesium[12] has ____ electron orbital shells
3
![<p>Chlorine[17] has ____ electron(s) its outermost shell</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/732fd1b8-21b5-4895-89dc-1f418b285918.jpg)
Chlorine[17] has ____ electron(s) its outermost shell
7
![<p>Iodine[53] has ____ electron orbital shells</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0e1cbecc-bdbf-4e04-a968-284fbe02a8e7.jpg)
Iodine[53] has ____ electron orbital shells
5
Decreased wavelength, increased frequency=
increase in energy
How many photons in the x-ray beam
Beam Quantity
Average energy of x-ray photons on the x-ray beam
Beam Quality
Beam Quantity is controlled by what?
mAs
Beam Quality is controlled by what?
kVp
Increasing mAs, increases what?
Increases number of photons in the x-ray beam
Increasing kVp, increases what?
Increases the average energy of photons in the X-ray beam
In beam Quality, Long wavelength =
Low energy
In Beam Quality, High frequency =
high energy
Isotropic means
Photons diverge in all directions
Differential absorption means
Different tissues require different amounts of energy for penetration/absorption
What is the maximum number of electrons that will occupy the outermost shell of an atom?
8
Atoms that share an electron that orbits both nuclei form:
Covalent bonds
The horizontal periods (Rows) of the periodic table contains elements with:
The same number of electron shells
As the frequency of electromagnetic radiation decreases, wavelength will:
Increase
What are the three fundamental particles of an atom?
electrons, neutrons, and protons
If an atom has an equal number of protons and electrons, it has what amount of net charge?
No net charge
If the negative charge outnumber the positives, the atom is called a
negative ion; anion
If the positive charges outnumber the negatives, the atom is called a
positive ion; cation
Binding energy
Holds the protons and neutrons together to form the nucleus
How are electrons held in their orbits?
electron-binding energy
What are the key determinants of X-ray production?
Nuclear binding energy and electron binding energy
What are the two types of atomic interactions in the X-ray tube that produce X-rays?
Characteristic and Bremsstrahlung
Electron shells
The energy levels or orbits around the nucleus where electrons are found.
Atomic number
Number of protons an atom contains in its nucleus
Atomic mass number
Number of protons and Neutrons an atom has in its nucleus
Elements
The simplest forms of substances that compose matter
Molecule
Two or more atoms bonded together
Compound
A molecule that contains atleast two different elements. Thus, all compounds are molecules, but not all molecules are compounds.
Chemical symbol
Abbreviation of the element
Iso means same; IsotoPes
The SAME number of PROTONS but a different number of neutrons (H-1, H-2, H-3)
Iso means same; IsotoNes
The SAME number of NEUTRONS but a different number of protons (O-16, C-14, F-17). To find the number of Neutrons, subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass number.
Iso means same; isobArs
A different number of protons but the SAME total number of protons AND neutrons (ATOMIC Mass Number) (O-16, C-16, F-16)
Iso means same; IsoMers
The SAME number of protons and neutrons, but different amounts of energy within their nuclei (Molecular Formula)
Ionic Bonding
Based on the attraction of opposing charges. One atom gives up an electron, and one atom takes an extra electron
Covalent Bonding
Based on two atoms sharing electrons that then orbit both nuclei. (Figure 8 pattern)
The horizontal rows in the periodic table are called
Periods
When two atoms are bonded together by an electron orbiting both atoms, it is known as a:
Covalent bond
When two atoms are bonded together by one atom giving up an electron and the other atom gaining an electron, it is known as a:
Ionic Bond
If an atom gains or loses an electron, it is called a what?
ion
If it says electron orbital shells, you will:
Count the # of rows from the top to the desired elements row.
When you see this “Electrons are in its outermost shell” in the question you should…
Use formula 2n²
Two atoms sharing electrons that orbit both nuclei
covalent bond
electron creates a figure 8 as it orbits the two nucei
covalent bond
the attraction of opposing charges
ionic bond
Atoms
Tiny indivisible structures that make up all things
Who discovered electrons
Joseph John J.J. Thomson
Alpha Particles
Made up of two protons and two neutrons and have a positive charge.
Bremsstrahlung interactions involve….
Attraction to the nucleus of the atom
How many periods are arranged as rows on the periodic table?
7
How many groups are arranged as columns on the periodic table?
8
Atoms in each period have the same number of what?
electron shells
Atoms in each group have the same number of what?
electrons in the outermost shell