general structure bones and joints
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
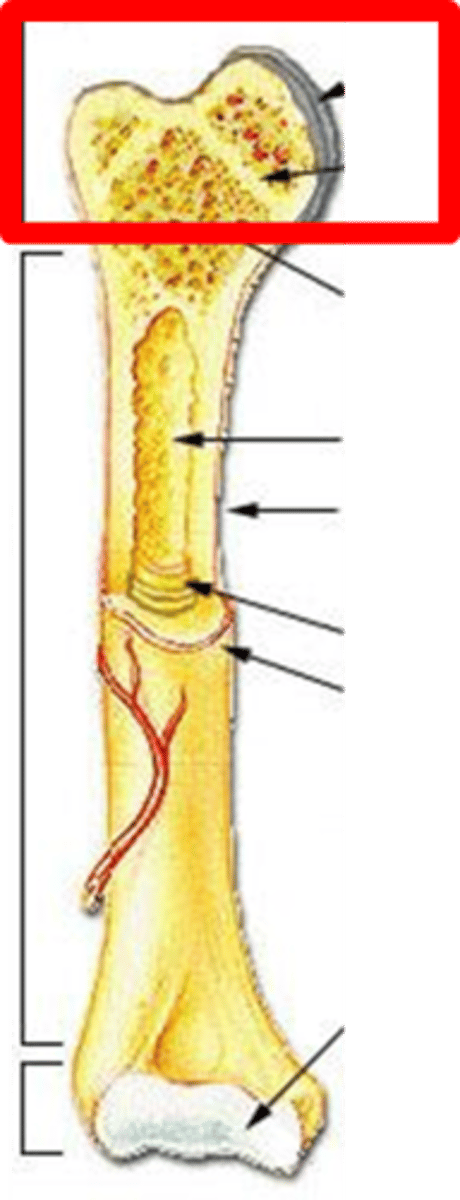
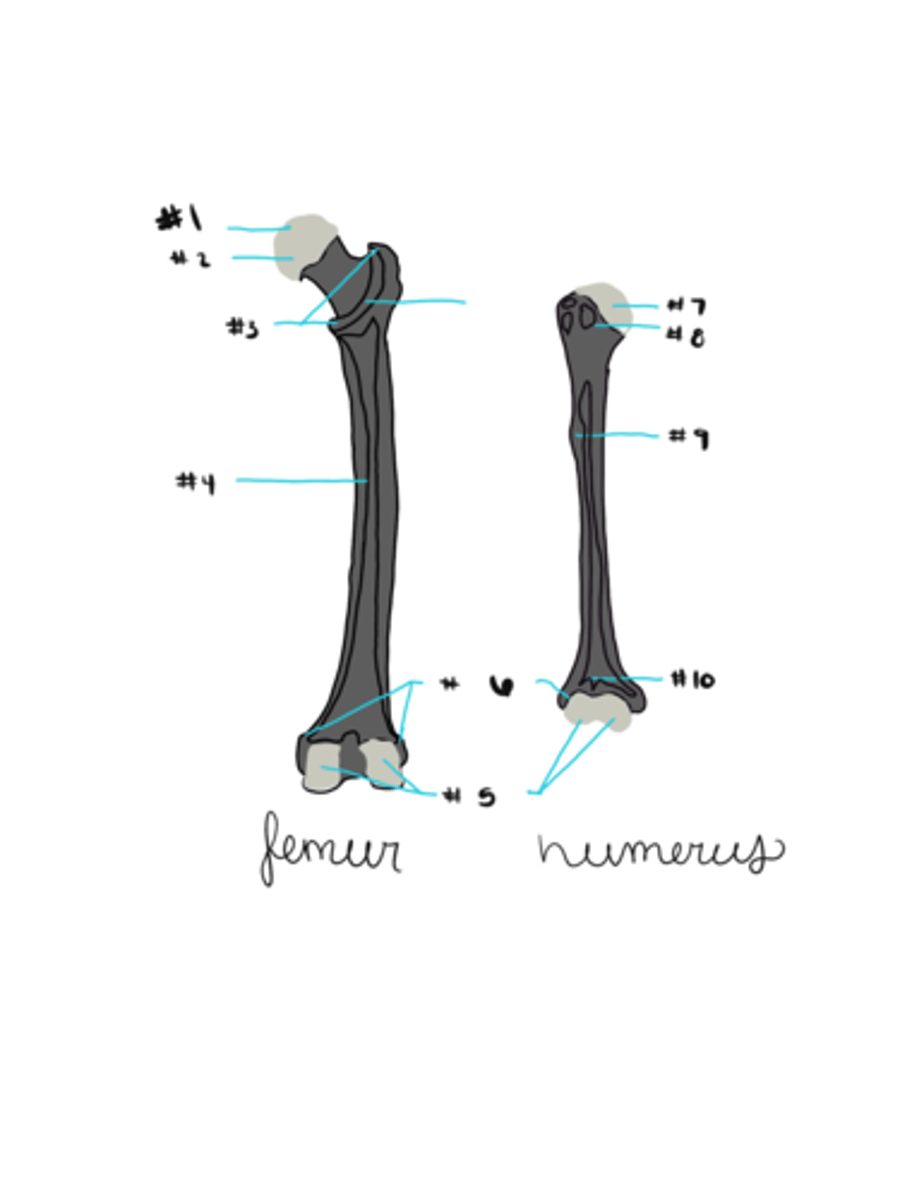
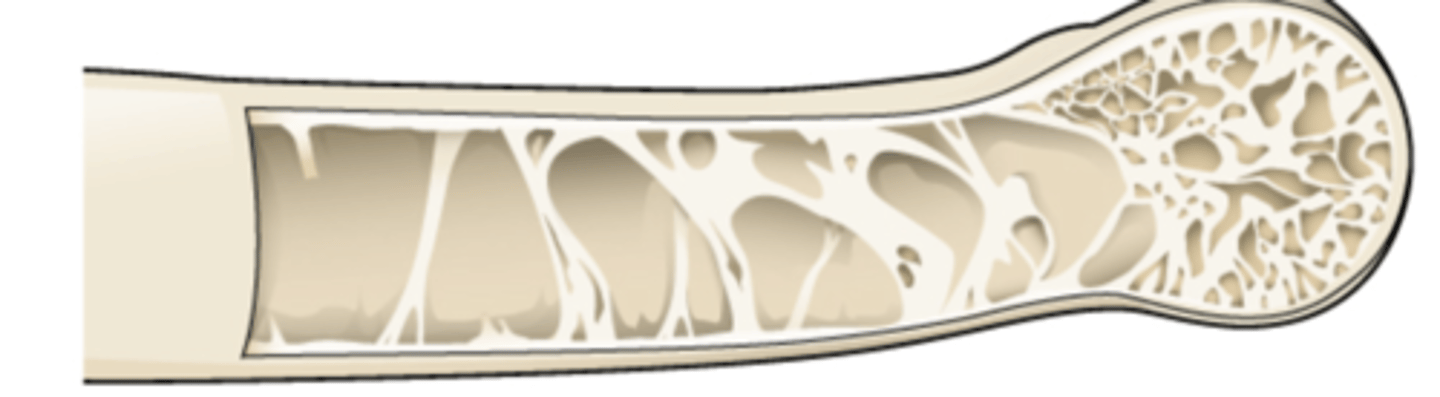
epiphysis
wide section at the end of a long bone - filled with spongy bone spaces filled with red marrow
diaphysis
middle section in long bone - medullary cavity is hollow and filled with yellow marrow
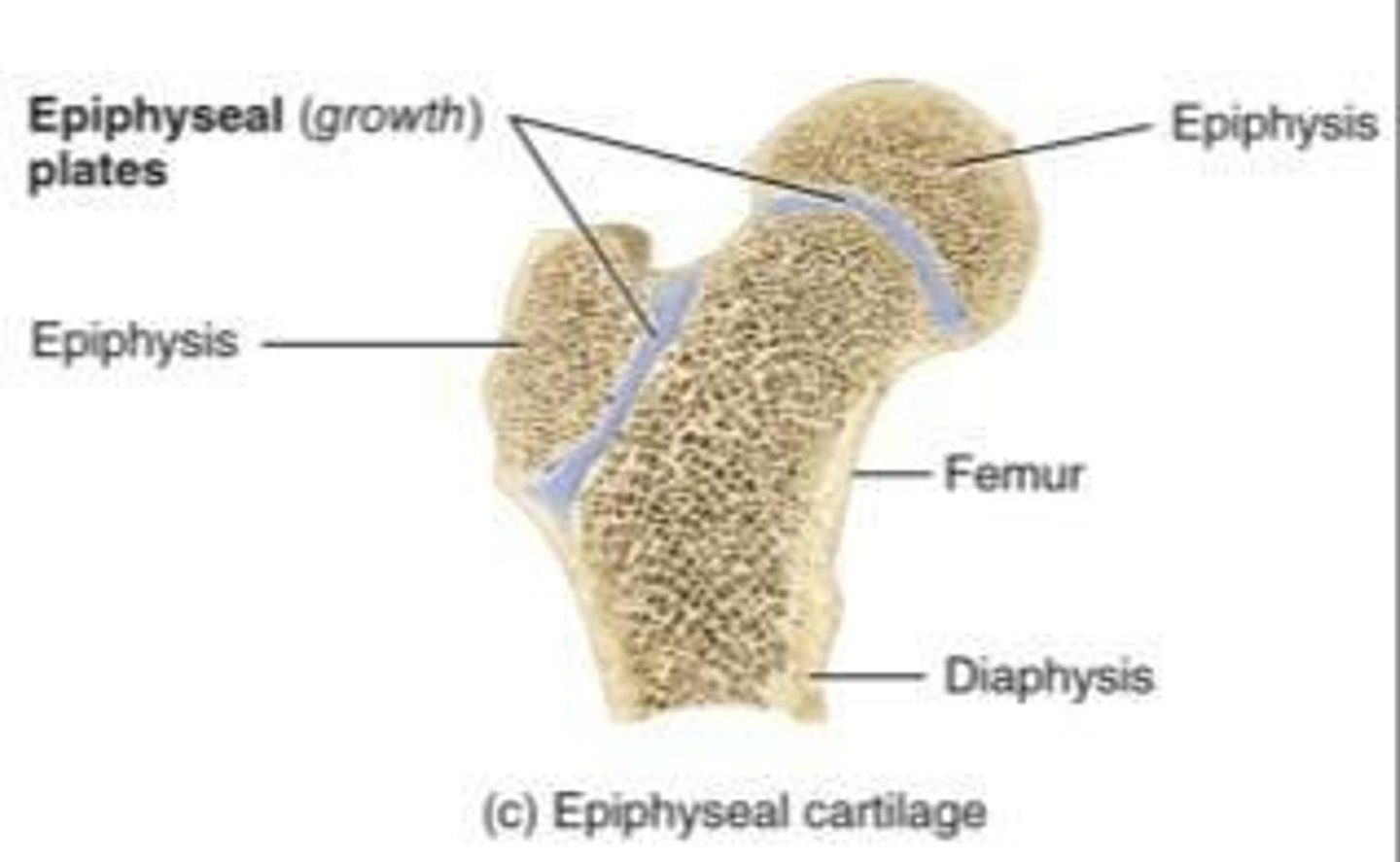
epiphyseal cartilages
between epiphysis and diaphysis in long bones
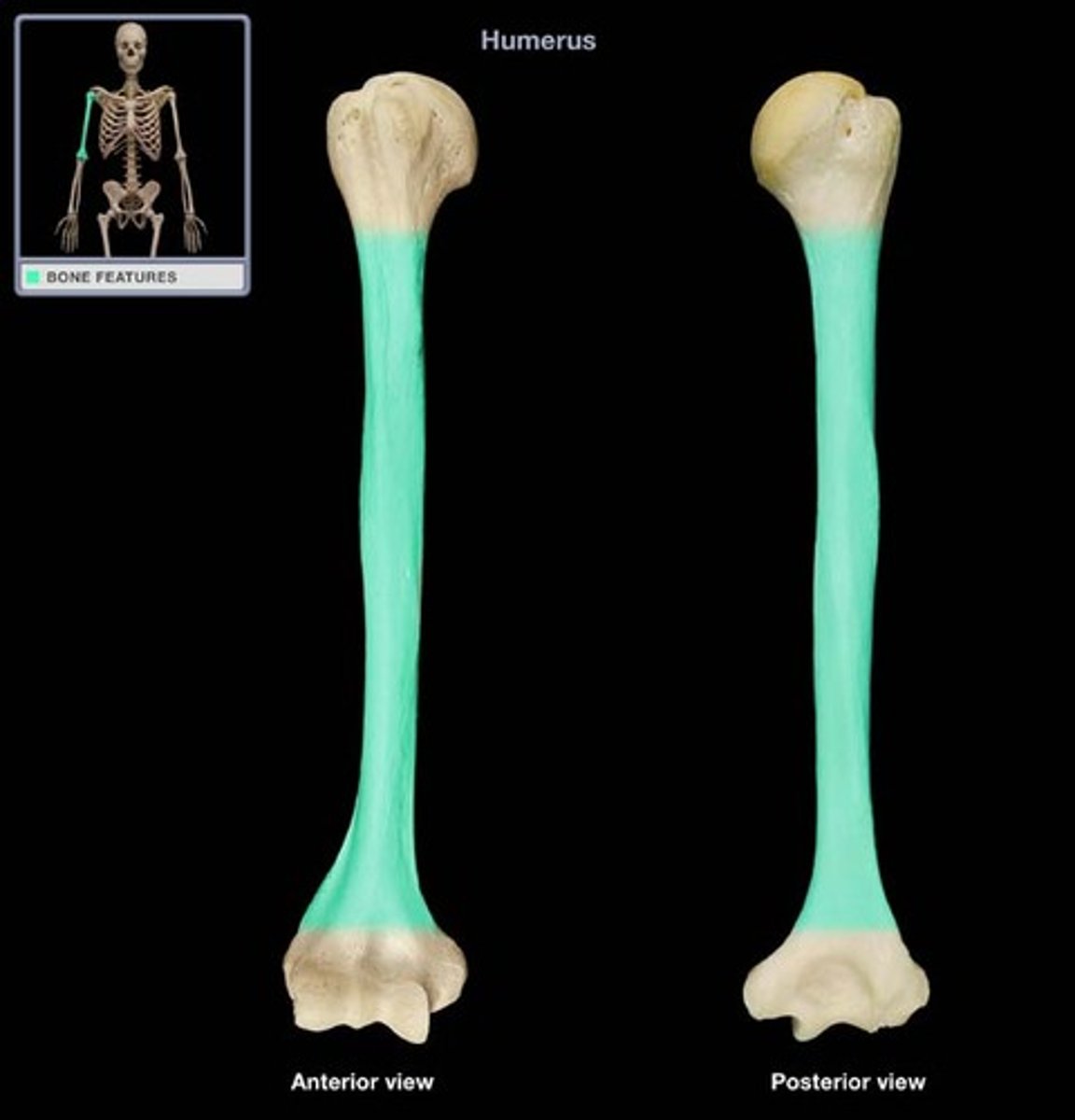
examples of long bones
femur and humerus
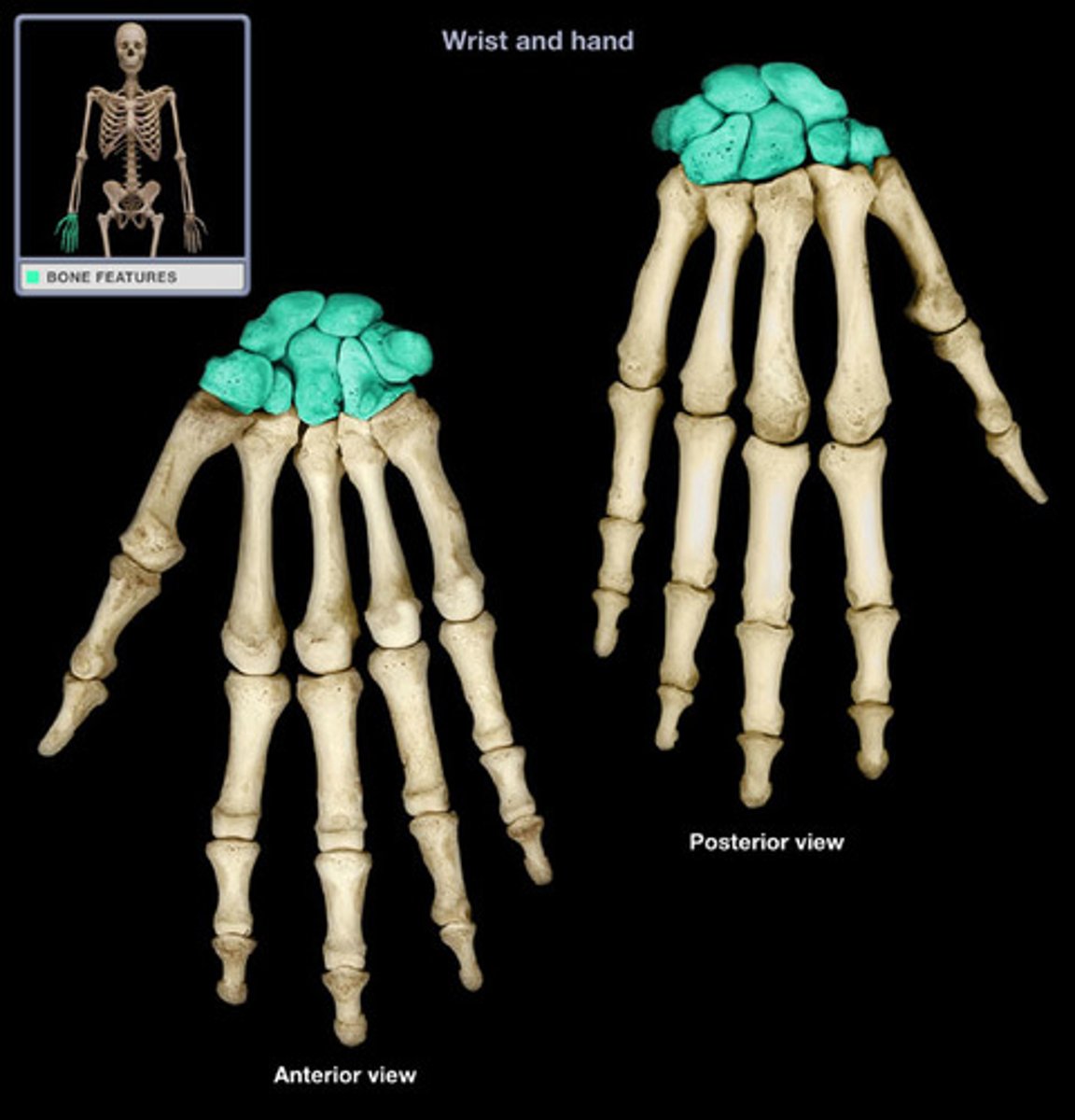
short bones
cube shaped bones ex phalanges
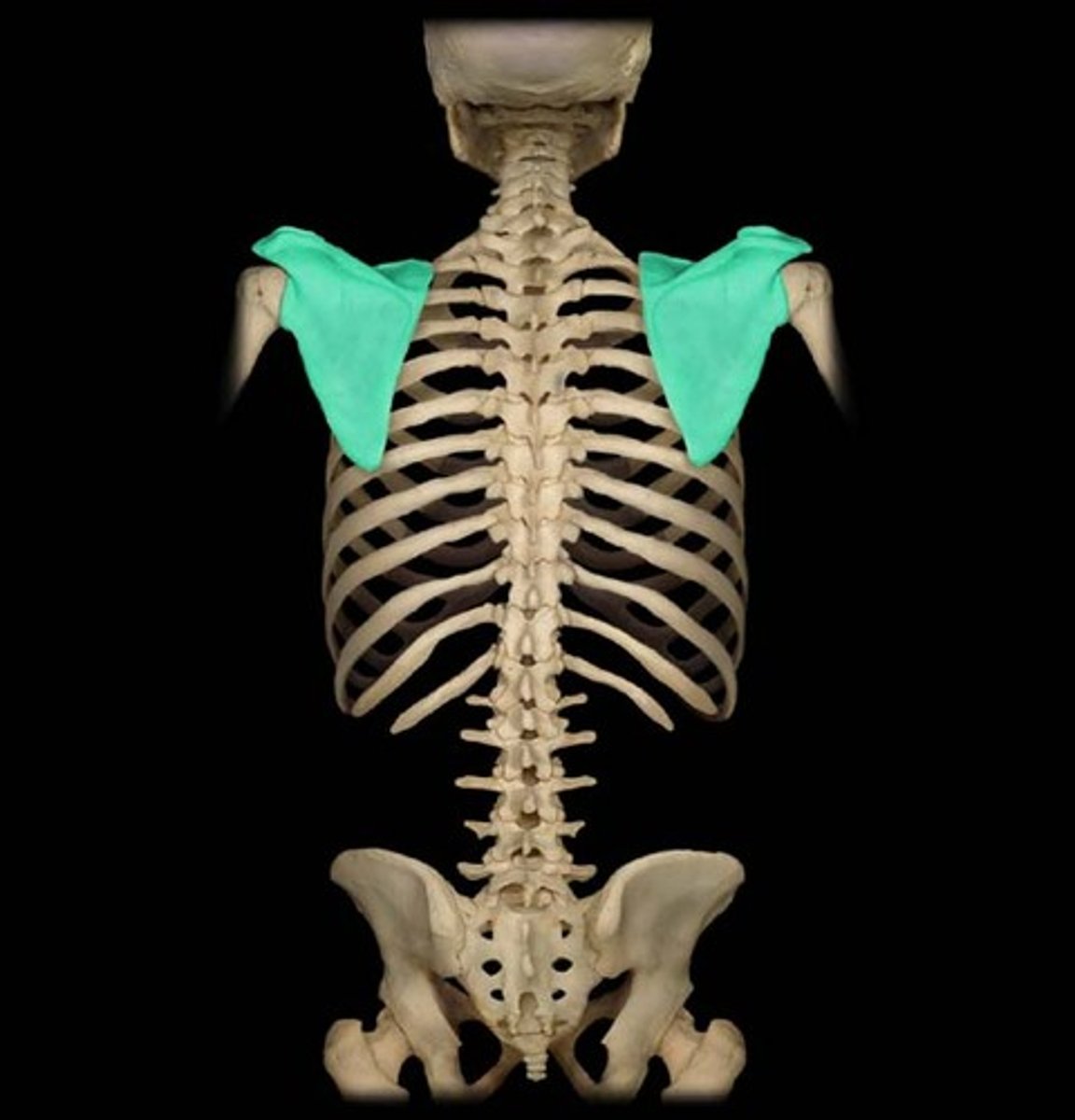
flat bones
thin or curved ex scapula
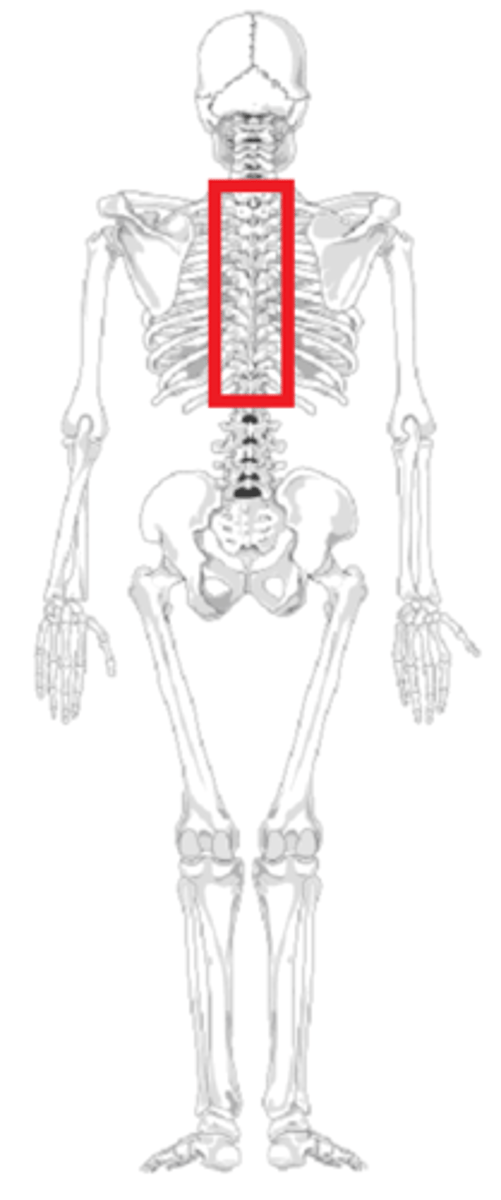
irregular bones
complex shape ex vertebrate like thoracic or cervical
sesamoid bones
Small and round bones embedded in tendons ex patella
pneumatic bones
air filled cavity lined by mucous membranes ex skull (has some) and maxilla
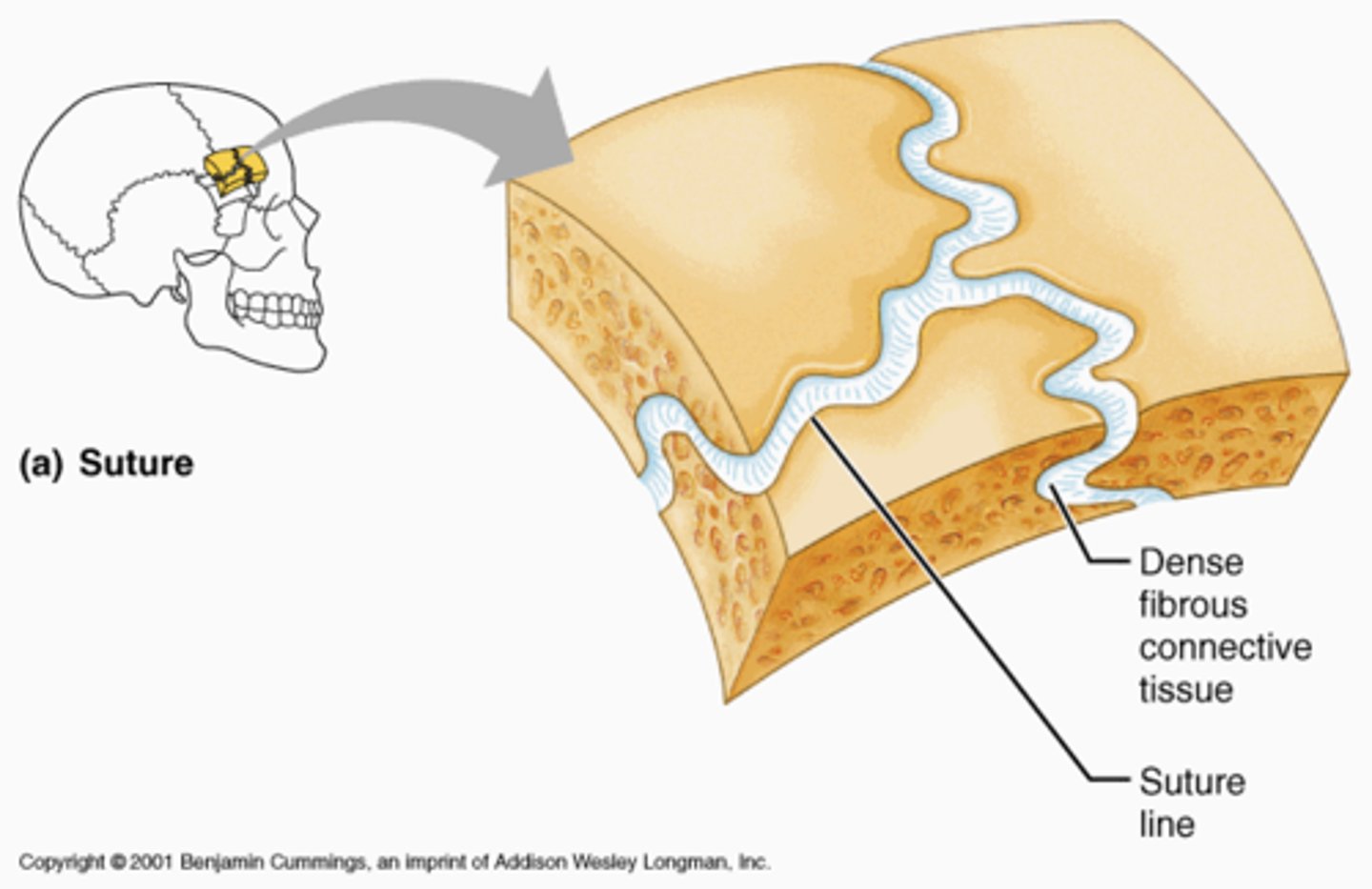
fibrous joint
adjacent bones connected by fibrous connective tissue strong not much mobility ex suture connnect scalp parts and interosseous membrane
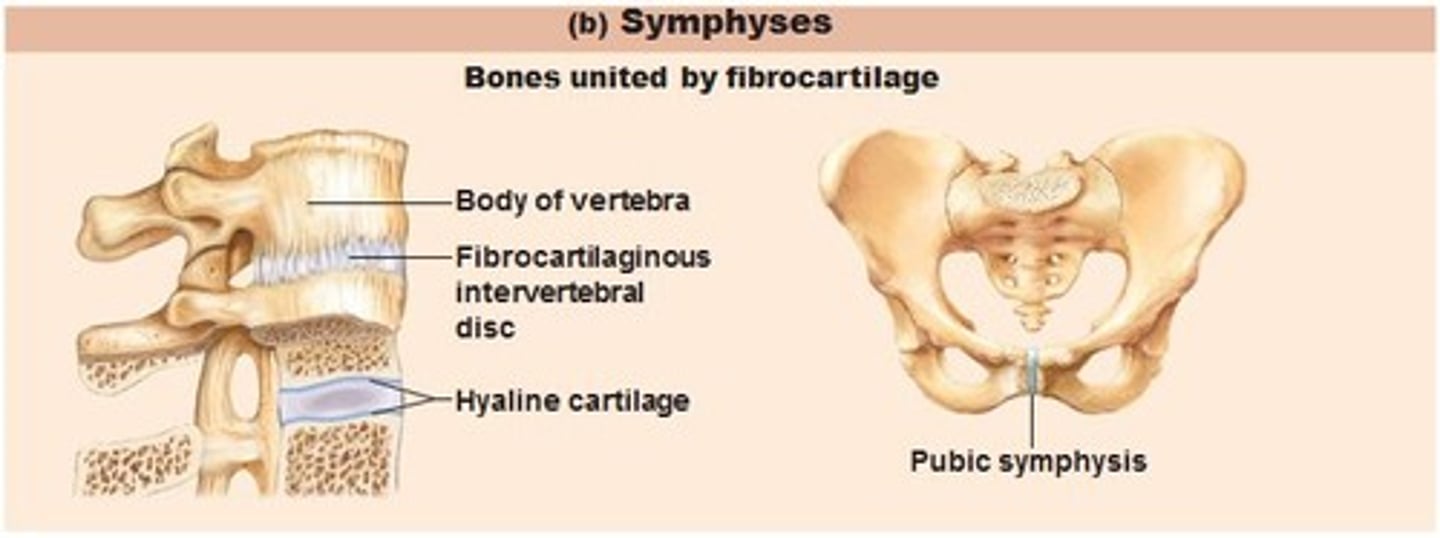
cartilaginous joint
allow only slight movement connected entirely by cartilage ex intervertebral disc or interpubic disc
synovial joint
fluid filled joint cavity that has high mobility between two adjacent bones ex femur to patella or cervial vertebrate to skull
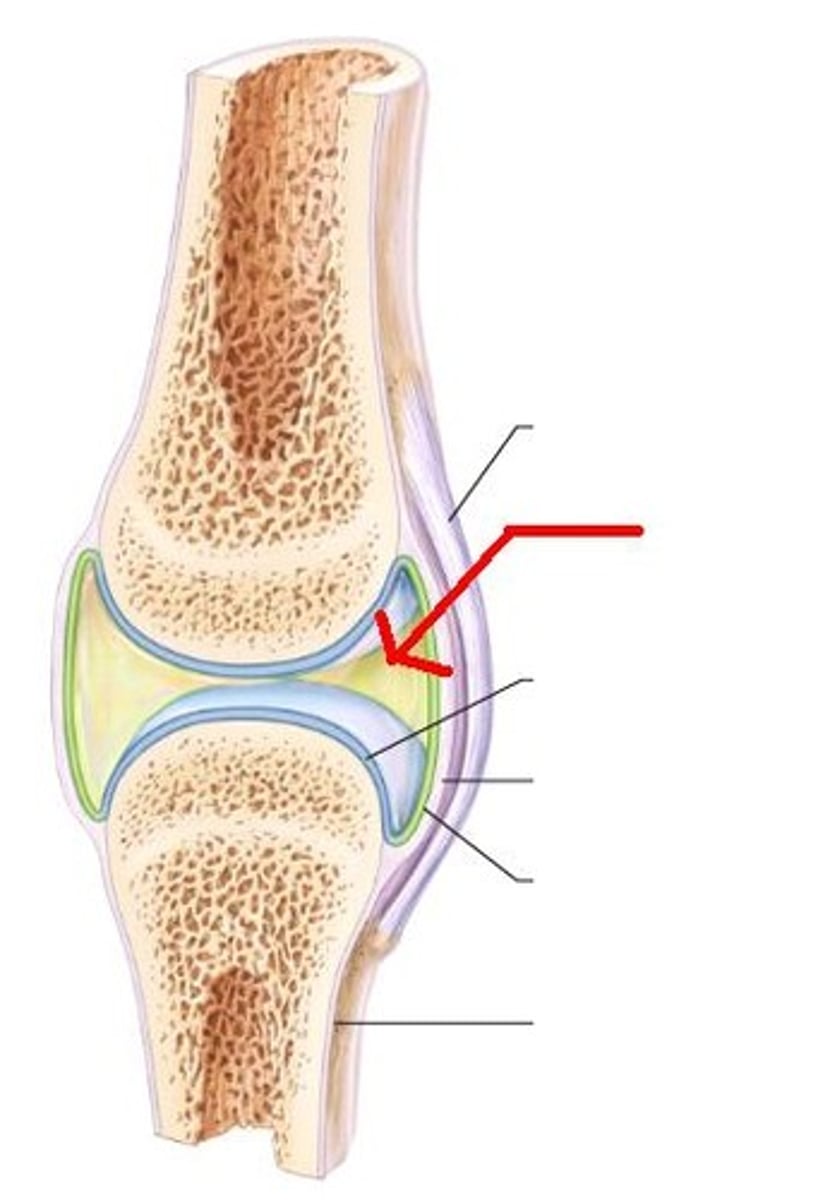
structural features of synovial joints
1 articular capsule filled by synovial fluid
2 synovial membrane make synovial fluid
3 fibrous capsule
4 articular (hyaline) cartilage covers articular surface
accessory structures synovial joint
ligaments, articular discs, articular lips, bursae
ligament
situated out or in articular capsule functions for stability and to guide or restrict movement
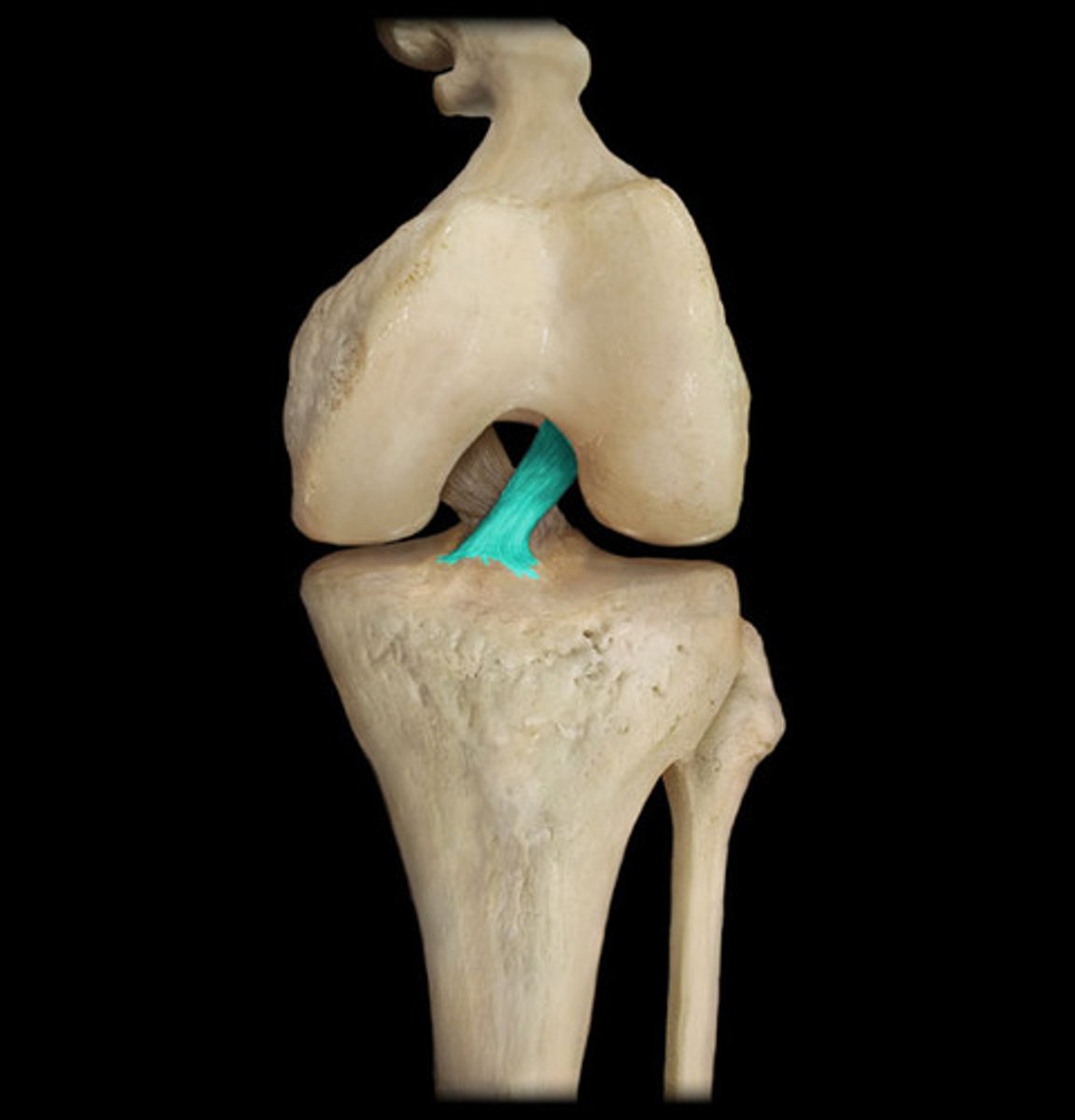
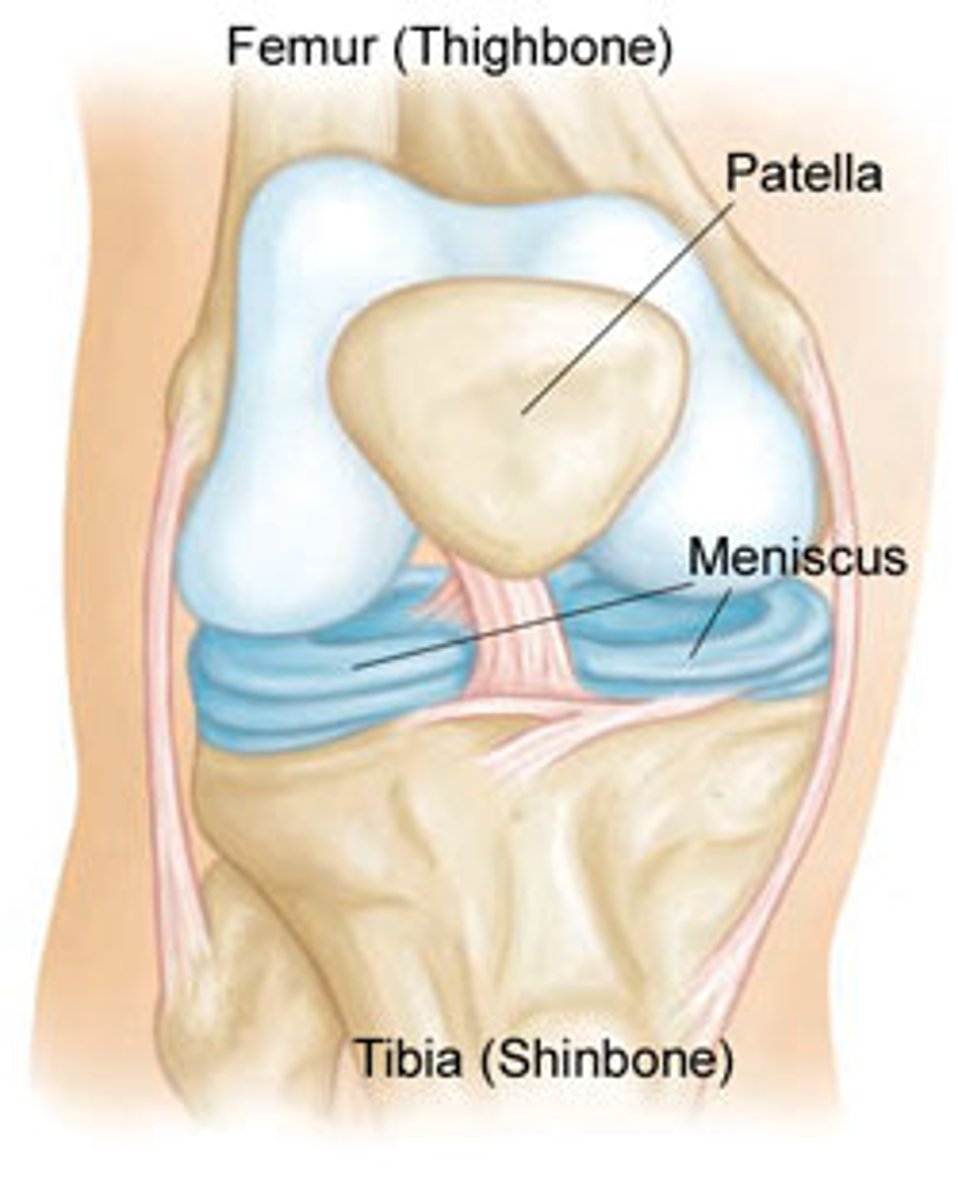
articular discs
disc - cartilaginous tissue small and oval-shaped and meniscus - large and c shaped
they both have same function which is ensure good contact, absorb shock and pressure, guide bones across eachother and stabilise joint
3 multiple choice options
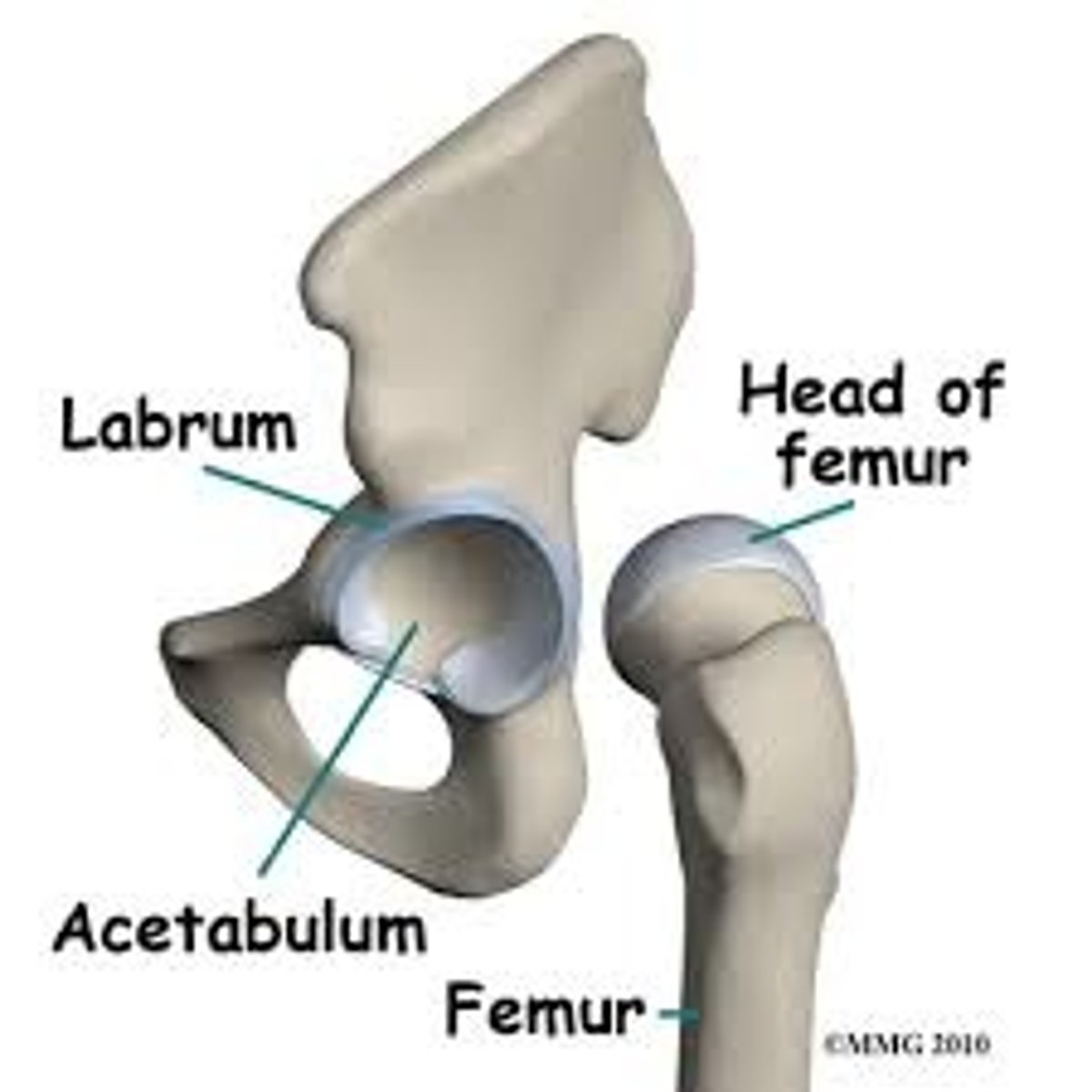
articular lip (labrum/labra)
connective tissue with cartilage on margin of articular bone its function is to enlarge surfaces and stbaility for joints
bursa
fluid filled sac that allows for easy movement of one part of a joint over another
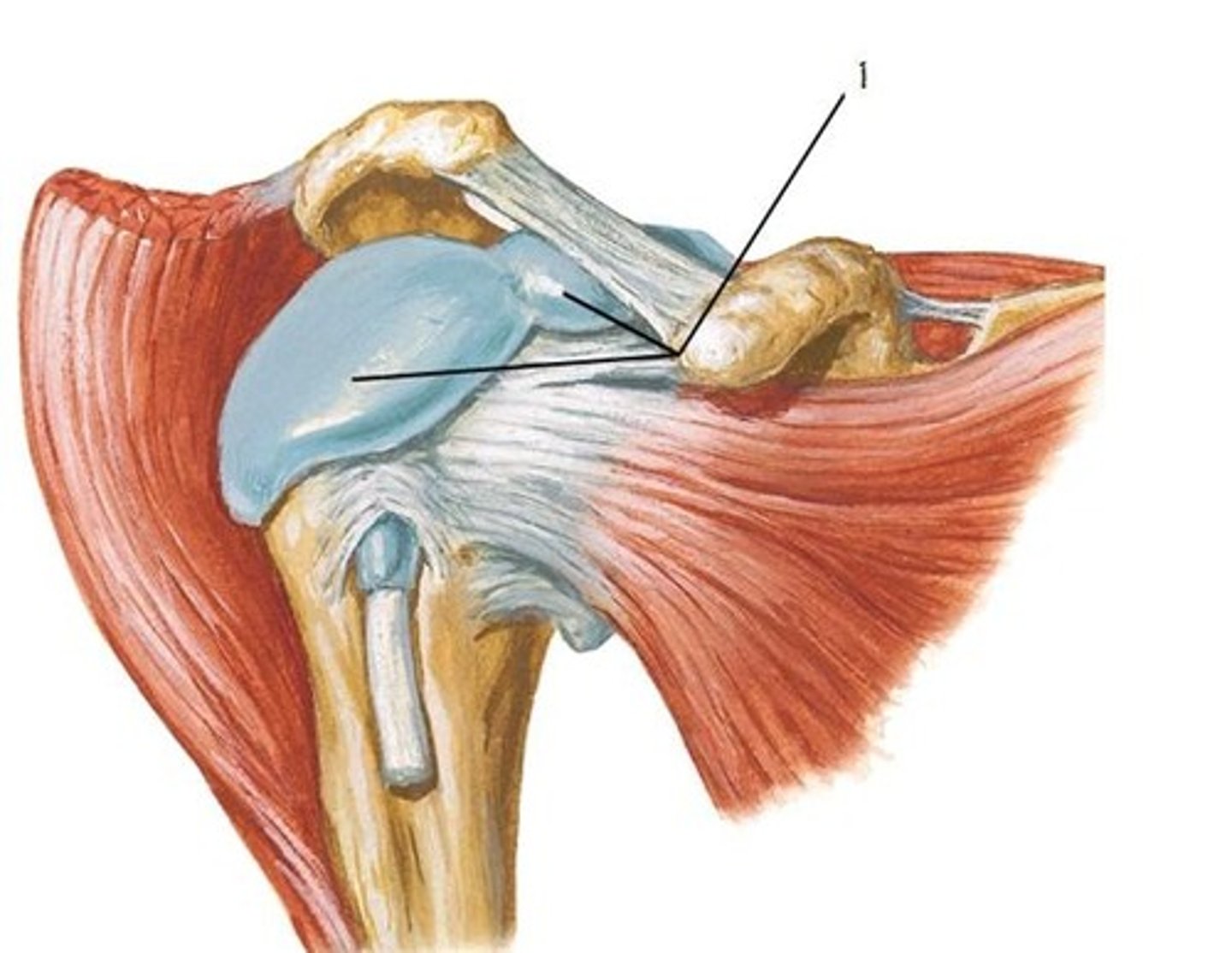
types of synovial joints
plane, hinge, pivot, condylar, saddle, and ball and socket
plane joint
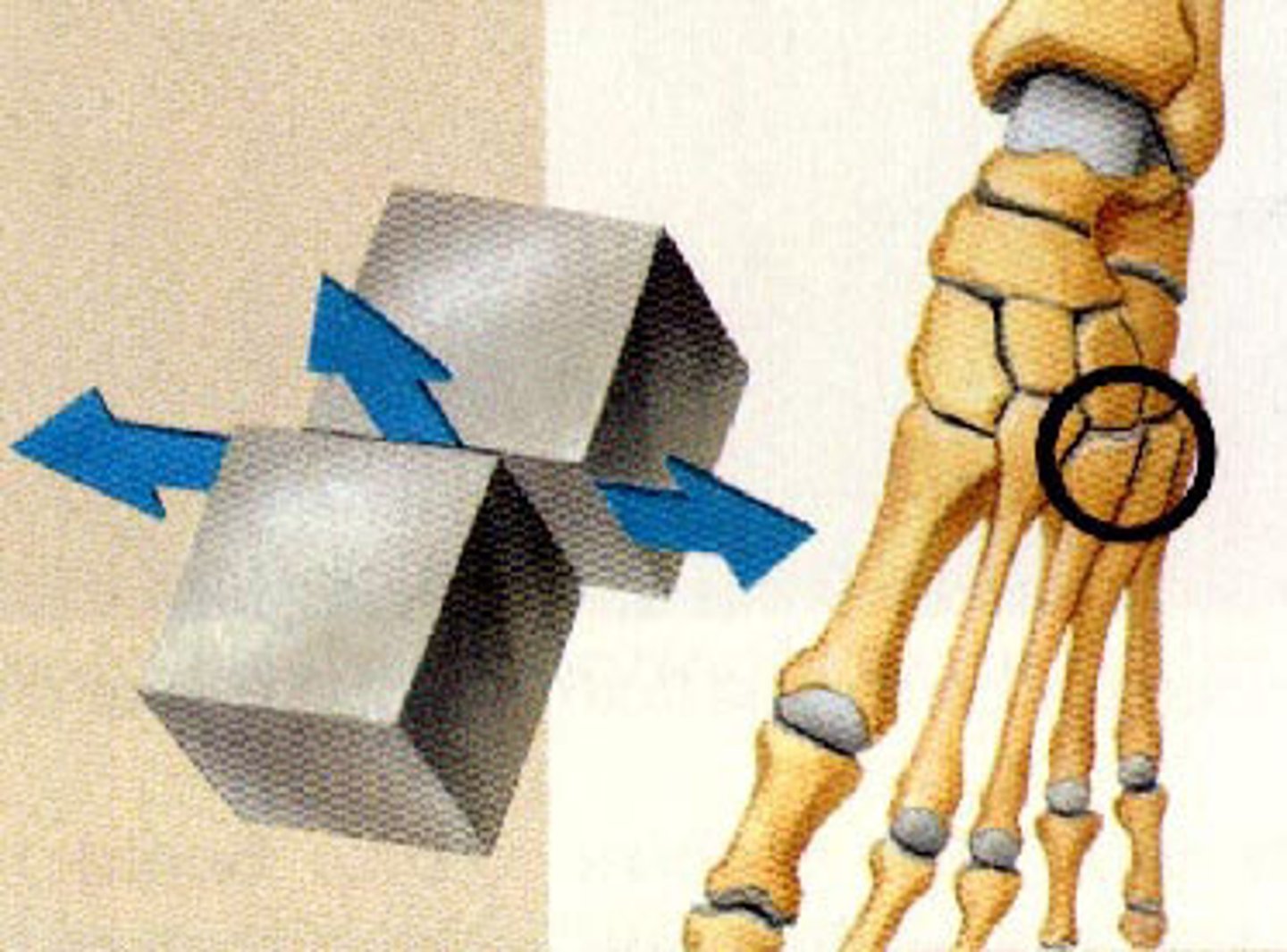
Allows gliding movements between flat surfaces ex intercarpal, intertarsal, intervertebral, sacroiliac joint
hinge joint (ginglymus)
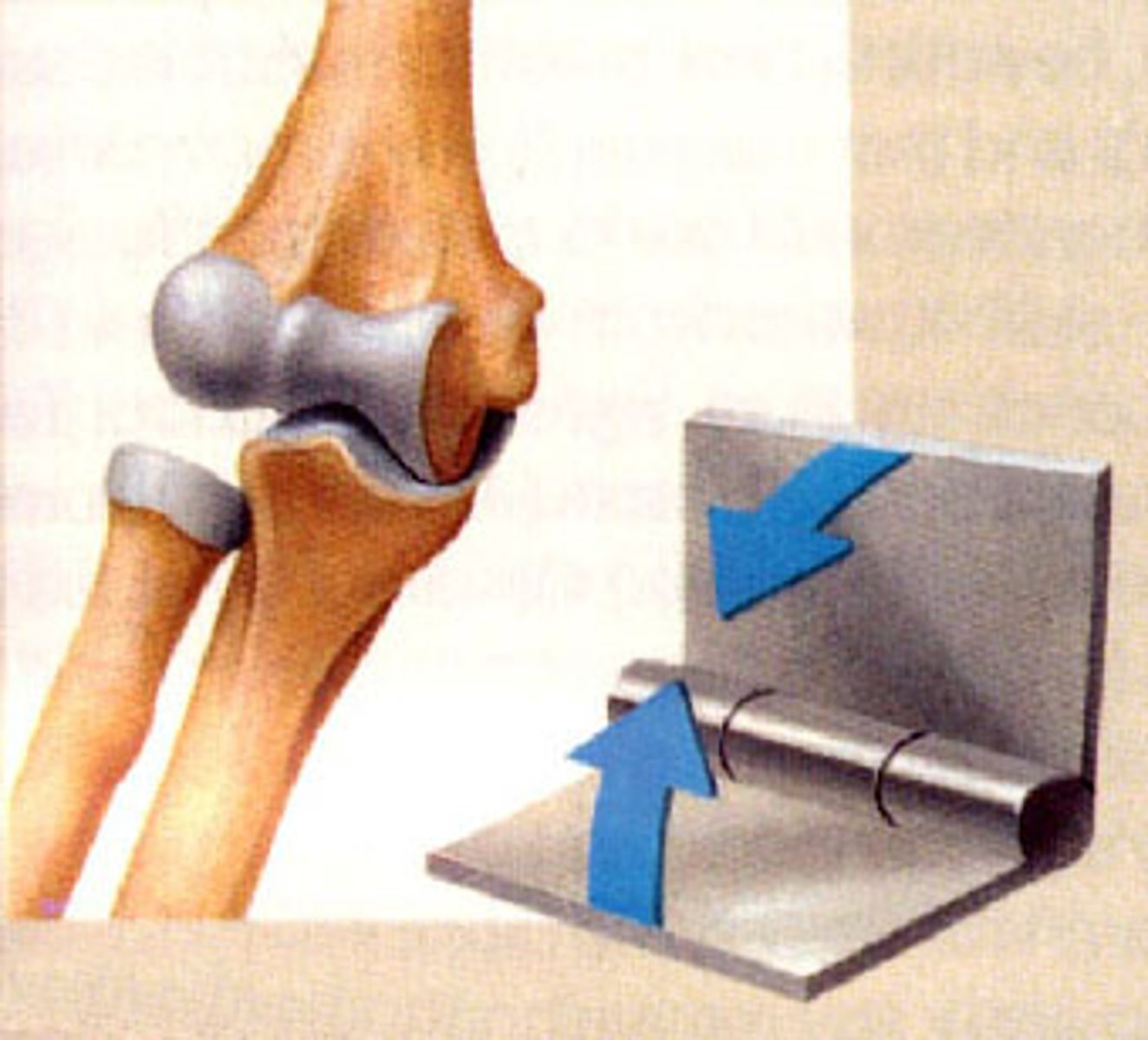
Joint between bones that permits motion in only one plane monoaxial, flexion and extension in sagittal plane ex humeroulnar and intephalangeal joint
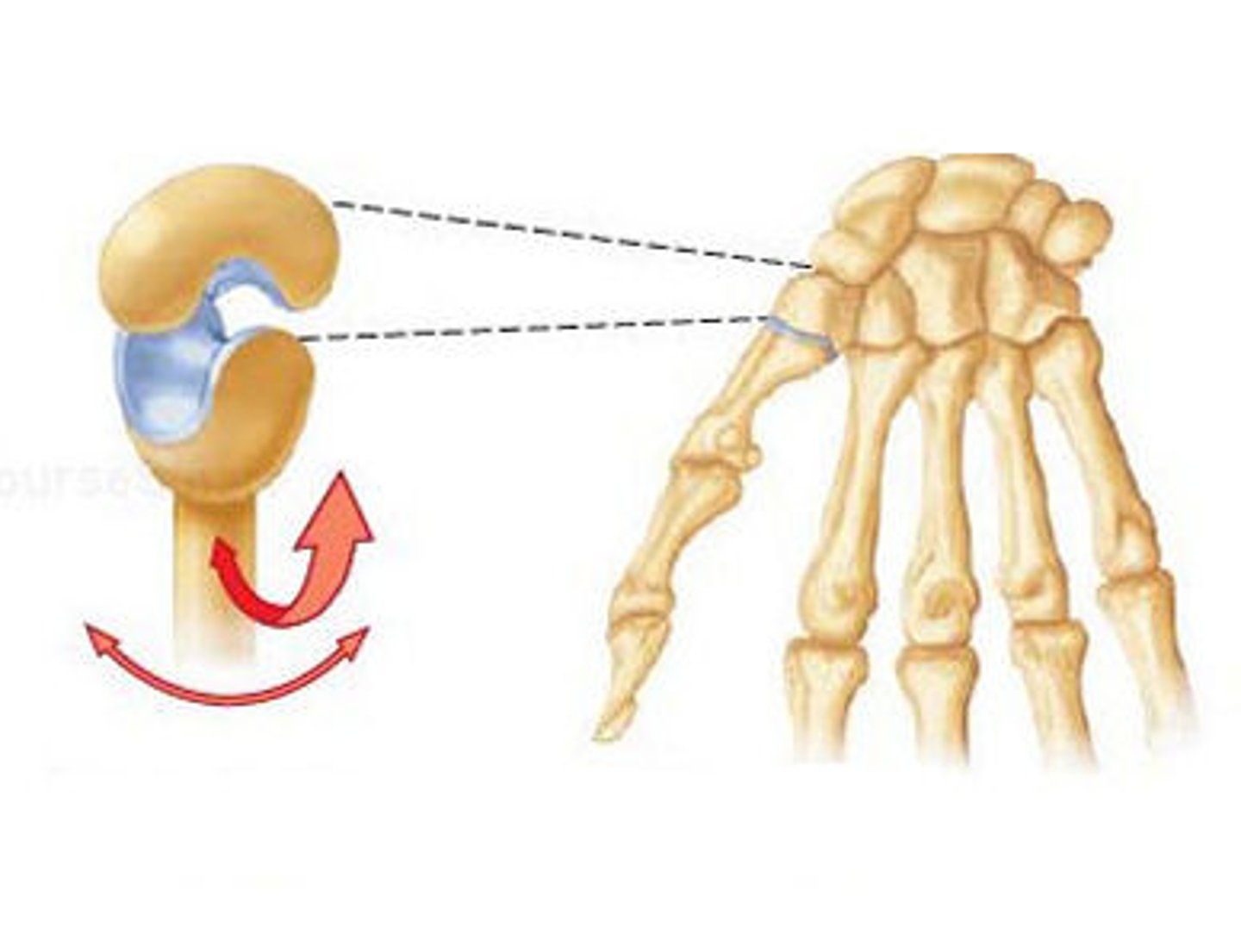
pivot joint (trochoid)
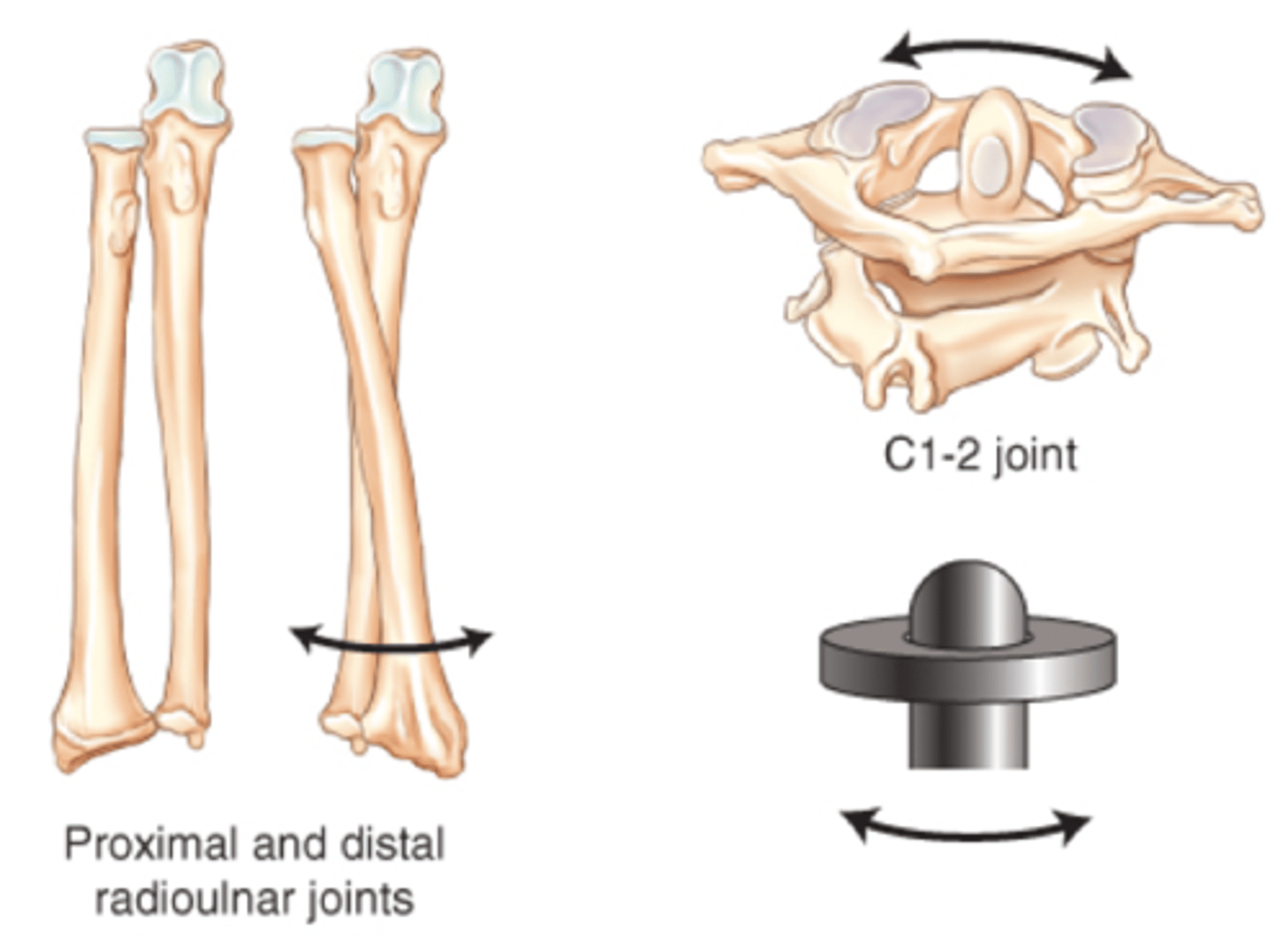
a cylindrical surface rotates within a ring of bone and fibrous tissue ex the joint between the proximal ends of the radius and ulna (proximal radioulnar) and between the dens of the axis and the atlas (atlantoaxial)
condylar/condyloid joint (ellipsoid)
oval convex surface on one bone and depression on other side and is biaxial so it moves in two planes (flexion extention in saggital + abduction anddeduction in frontal = circumduction)
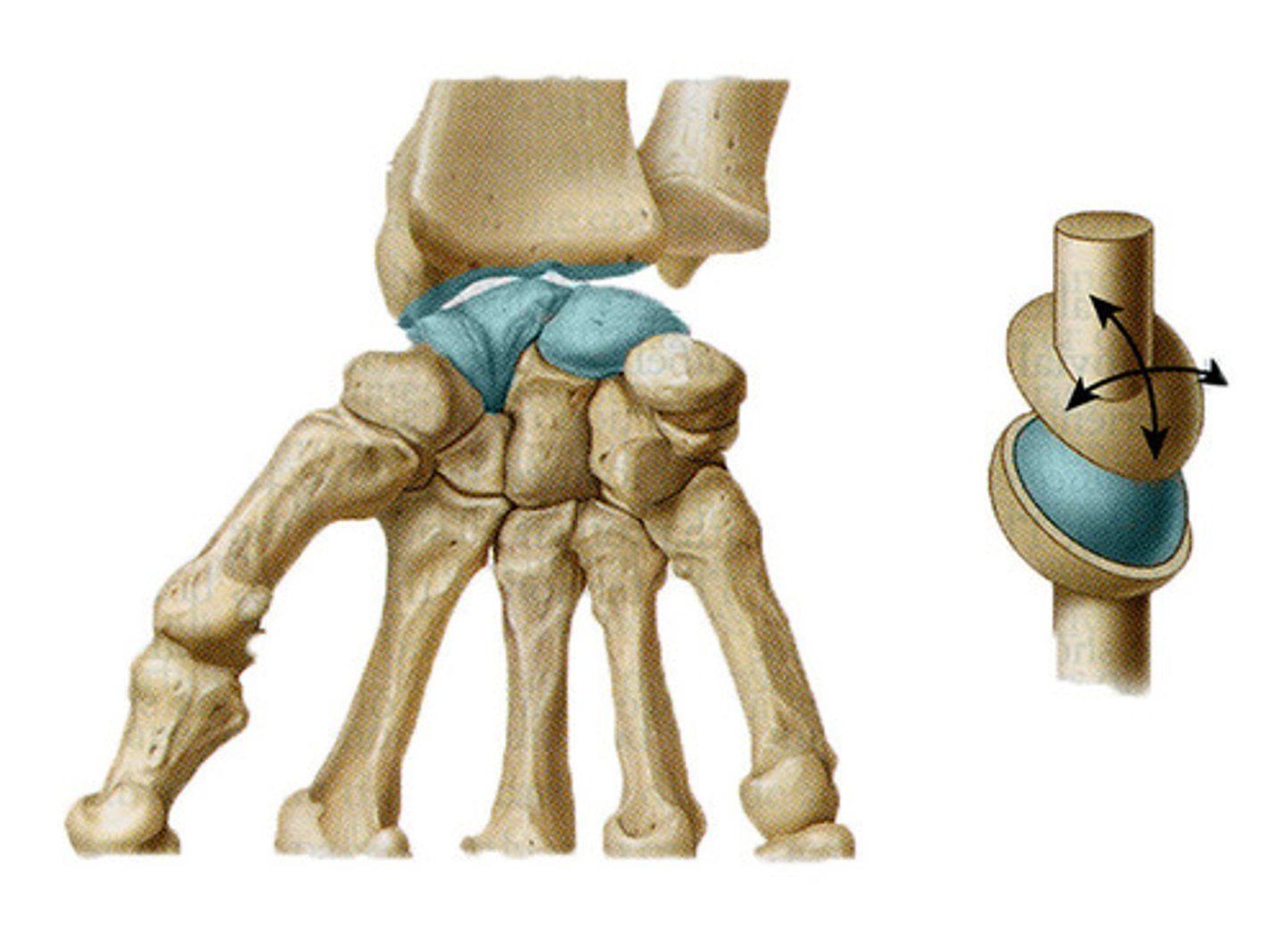
saddle joint (sellar)
both bones have saddle shaped surface - concave in one direction convex in other
biaxial
flex and ext (sagg) + abduct and adduct (frontal) = opposition
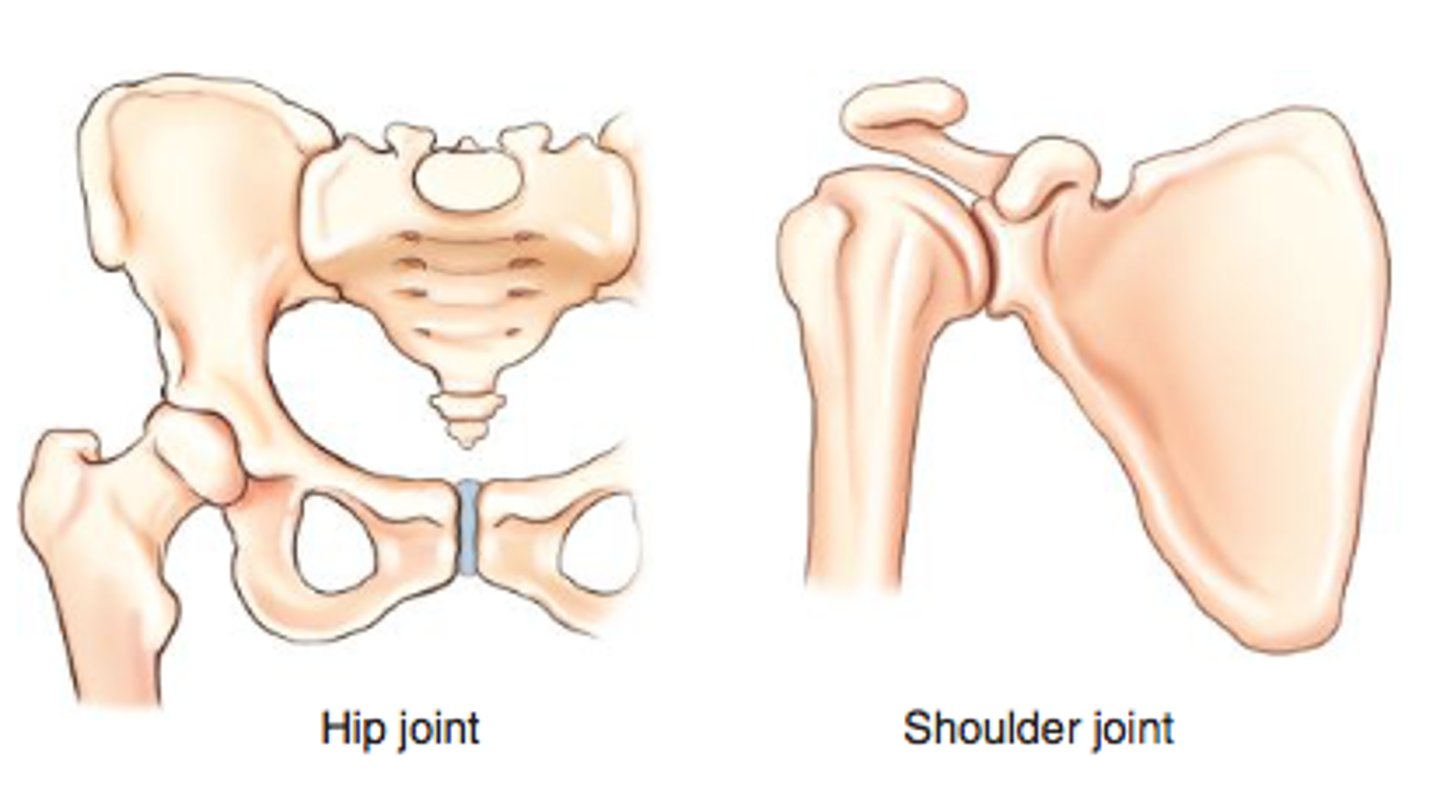
ball and socket joint (spheroidal joint)
multiaxial joint w flex and ext, abd and adduct, circumduction and medial/ lateral rotation movements ex shoulder and hip joints
uniaxial
movement in single plane around sigle axis ex hinge and pivot joint
biaxial
movement in two planes ex saddle condylar and plane joints
triaxial
movement in three planes ex ball and socket joint
sagittal plane
vertical division of the body into right and left portions

coronal plane
divides body into front and back
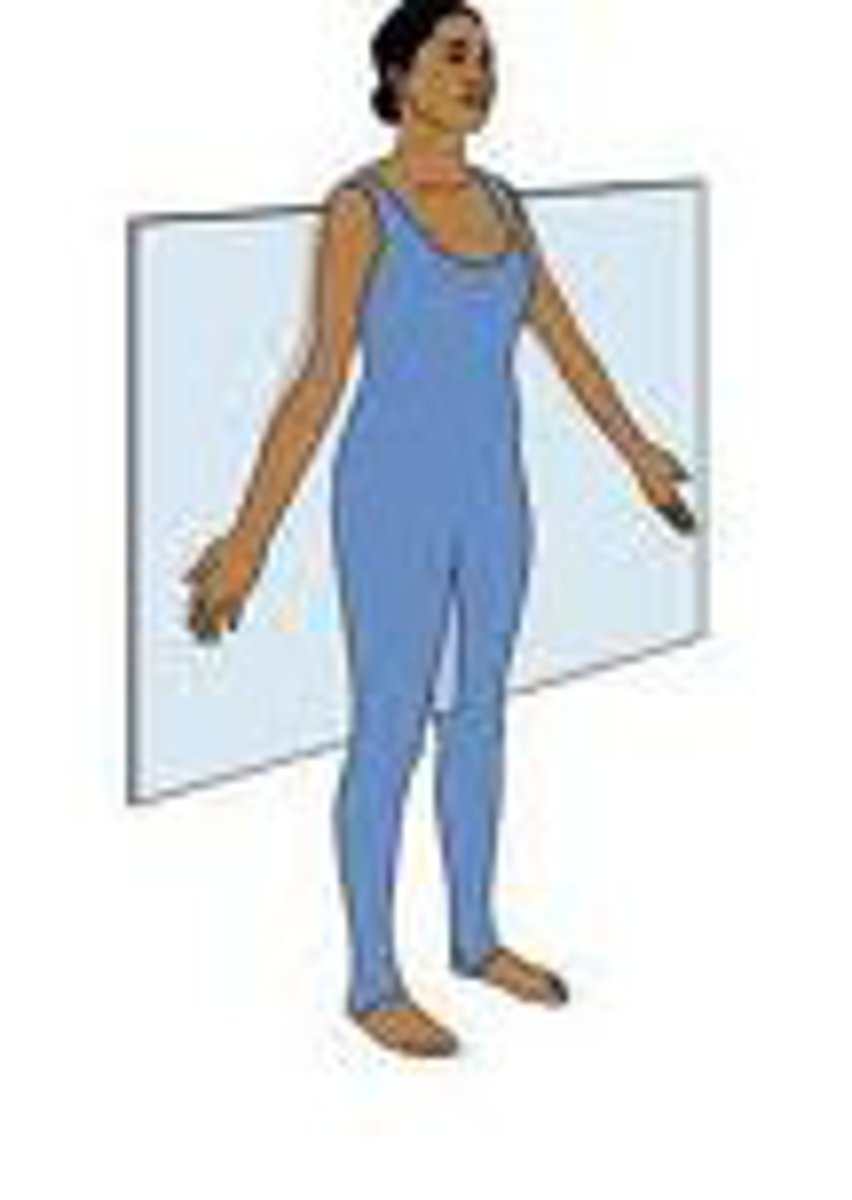

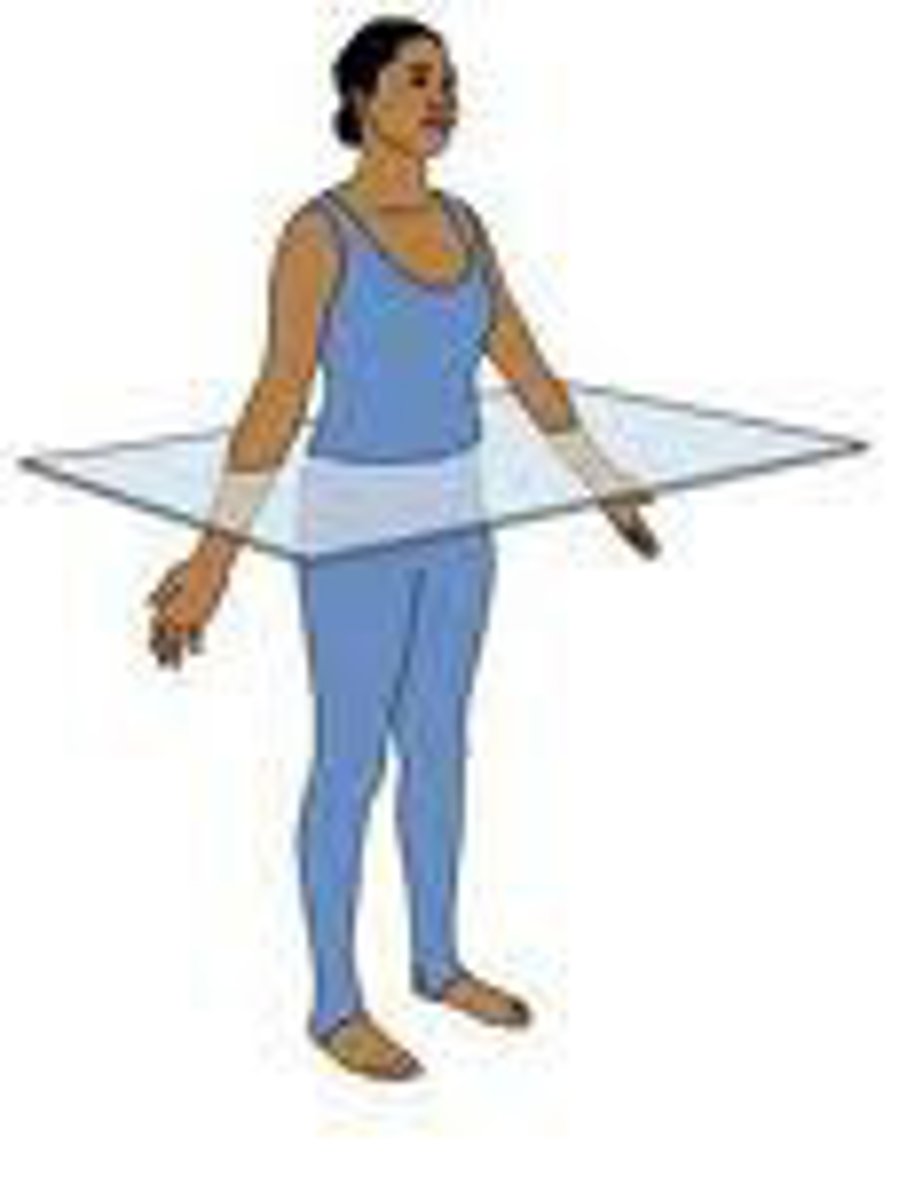
transverse plane
horizontal division of the body into upper and lower portions
transversal axis
pependicular to sagittal plane
sagittal axis
perpendicular to coronal plane
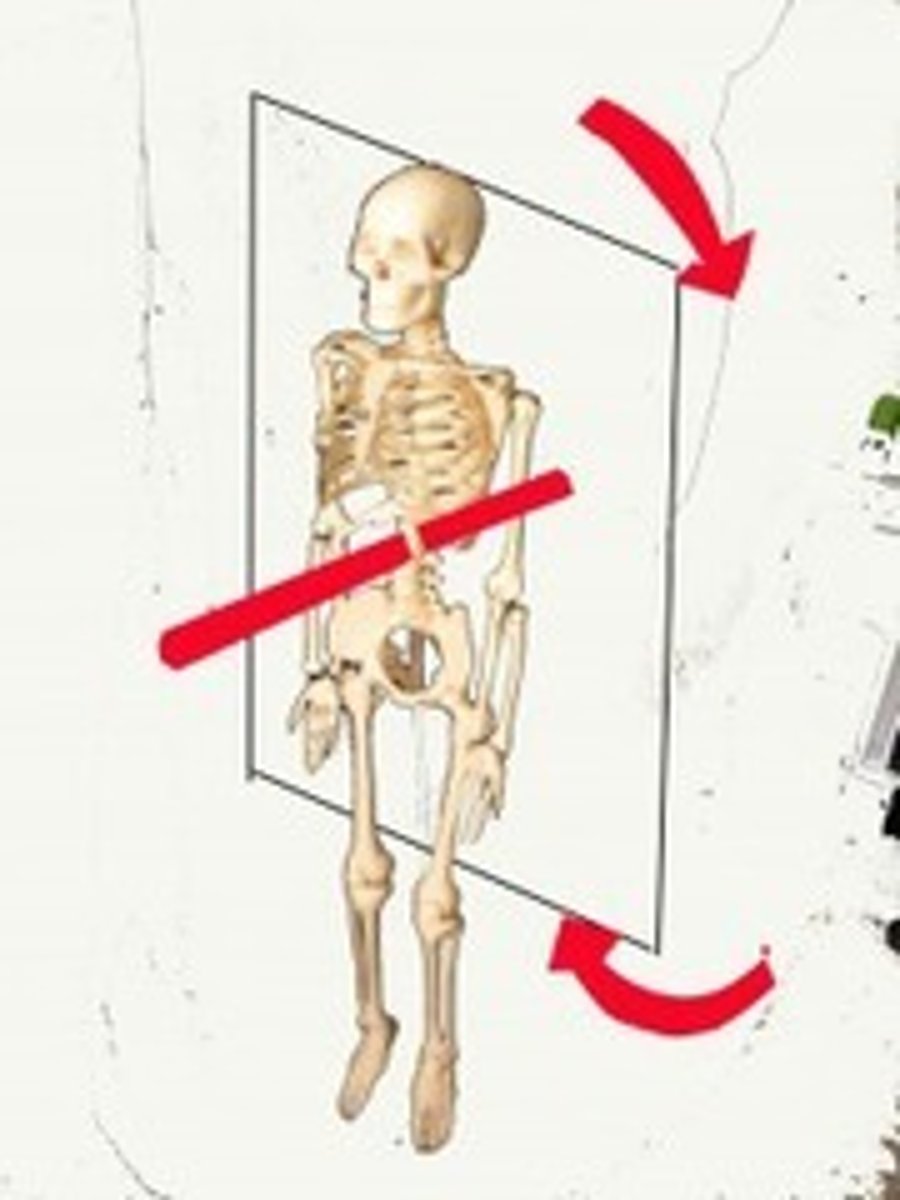
longitudinal axis
perpendicular to transverse plane
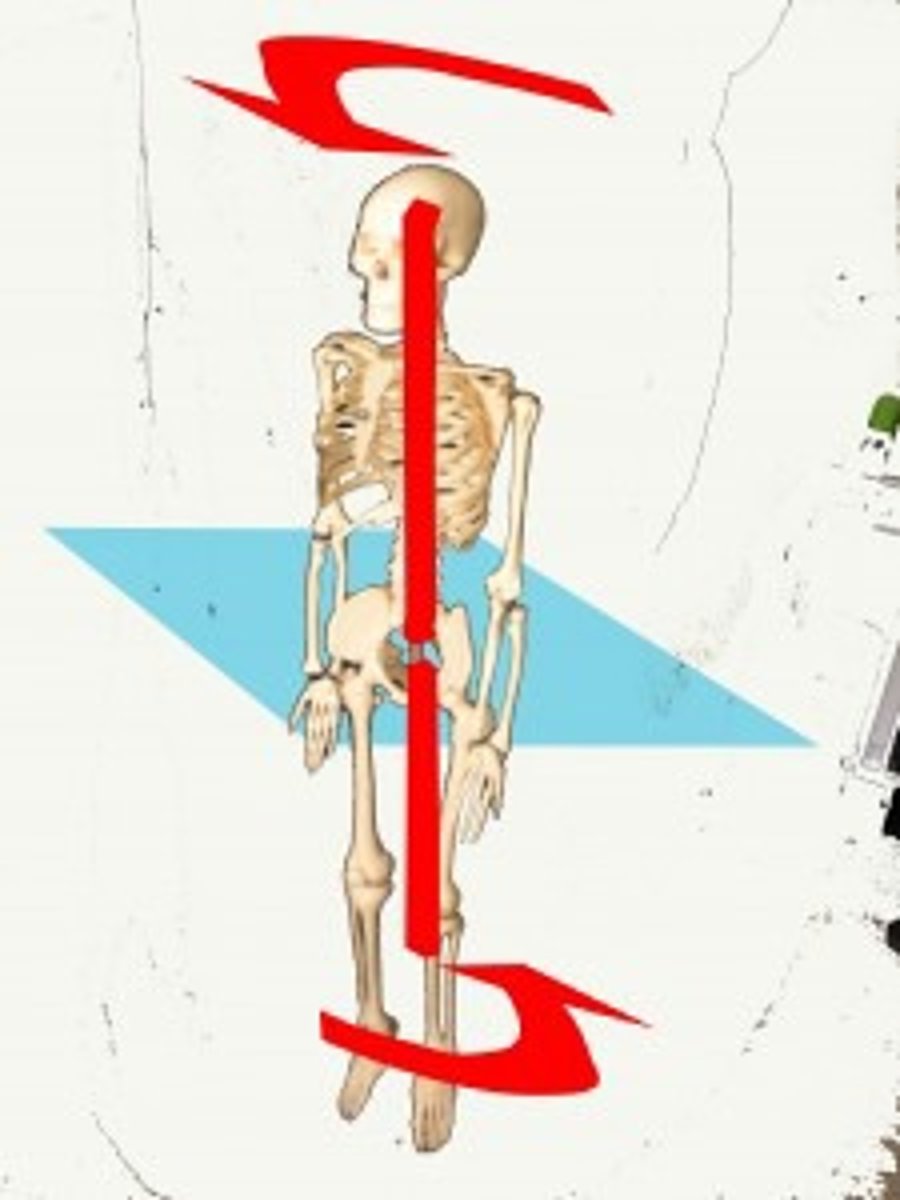
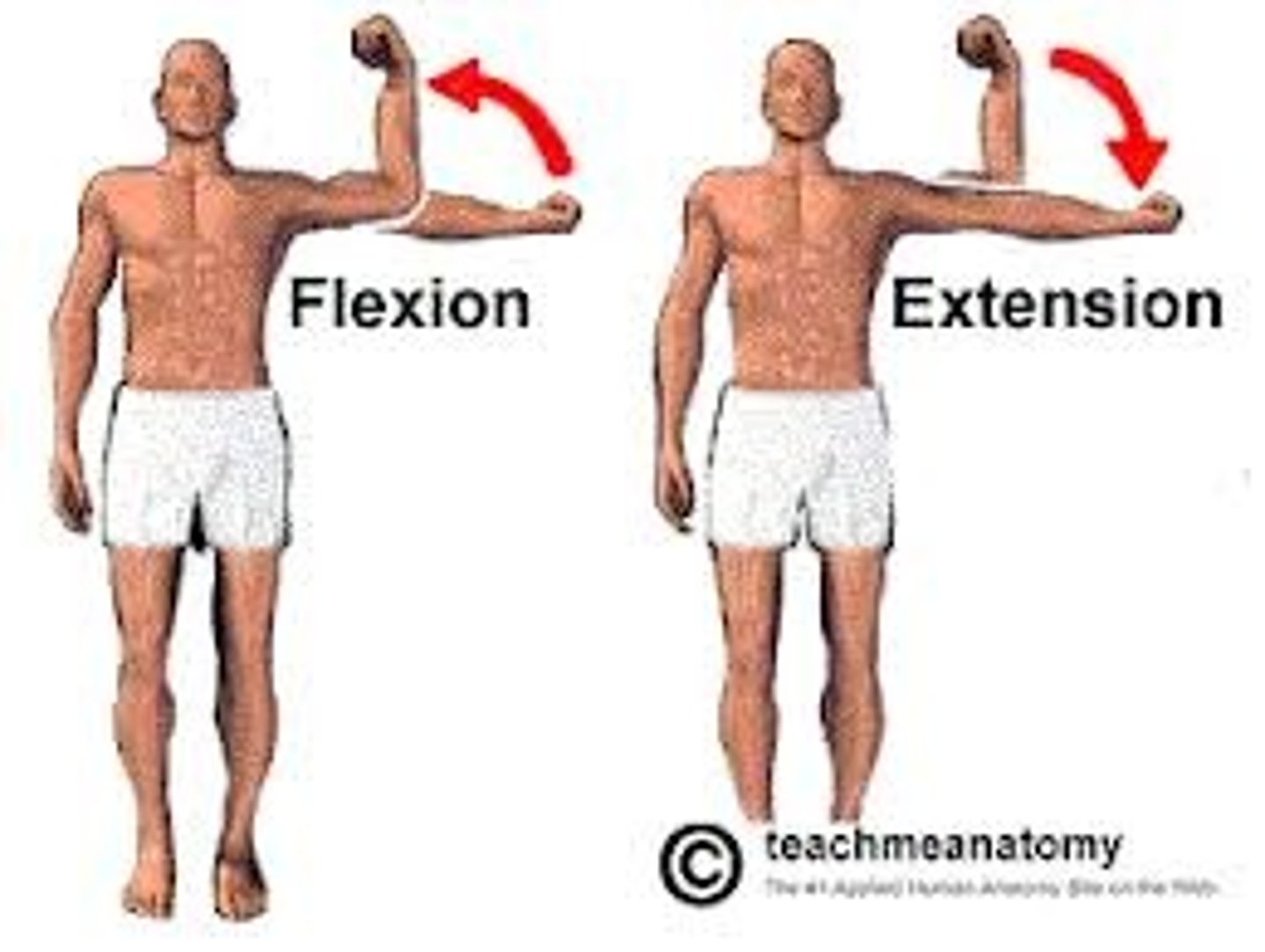
flexion and extension
flex - decrease (anterior) / extend - increase (posterior) in joint angle
abduction/adduction
coronal plane on sagittal axis - movement away (laterally) /into (medially) from the midline

rotation
horizontal plane on longitudinal vertical axis

circumduction
combine flex + adduct + extend + abduct to rotate a joint