Instrumentation Exam 3
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Antibody
protein made by B cells that binds to specific antigens
Antigen
foreign substances that trigger an immune response
Affinity
strength of bond between one antigen and one antibody site
Avidity
total strength of all bonds between antigen and antibody
primary reaction
First binding between antigen and antibody (immunofluorescence) = (ELISA, RIA, EMIT, FPIA)
Secondary
visible reaction (agglutination, precipitation)
Tertiary
body’s response to primary + secondary (complement activation, phagocytosis)
Quaternary
complex reactions (advanced immunoassays, molecular tests)
primary ex.
drug testing
secondary ex.
pregnancy test, latex, immunoelectrophoresis, blood typing
tertiary ex.
allergy + skin test (TB)
Quaternary ex
DNA, PCR, Chemoilluminescent, Flow cytometry
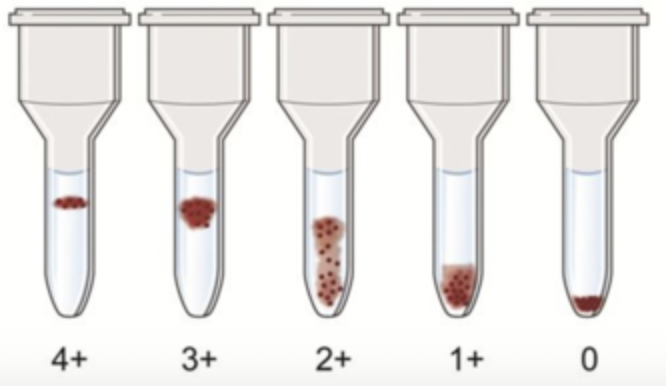
4+: strong; all cells agglutinated
3+: strong; few free cells
2+: moderate; some free cells
1+: weak; mostly free cells
0: no agglutination
Preventative Maintenance
improve product quality, lower repair costs, greater operator safety
automated clot detection
turbidimetric, nephelometric, mechanical, viscosity-based
turbidimetric
a light source used to measure opacity; less light passes as the clot forms
nephelometric
detectors used to measure light scatter due to fibrinogen forming
mechanical
the electrical circuit opened/closed when the ball moved away from the magnet because of fibrinogen forming on the ball
viscosity-based
steel ball amplitude measured, moved with magnetic field
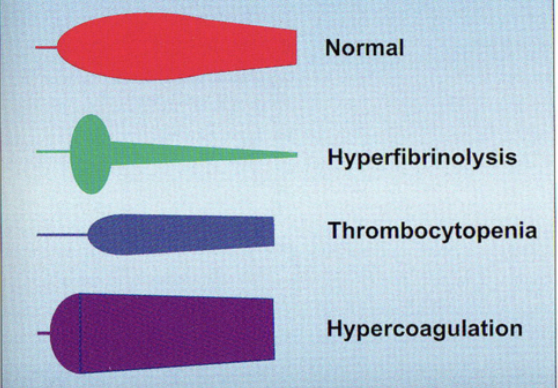
normal: balanced clotting
hyperfibrinolysis: clot breaks down too fast
thrombocytopenia: low platelet count, leading to weak clot formation
hypercoagulation: excessive clotting
Platelet aggregation reagents
ADP, Collagen, Epinephrine, Ristocetin, Arachidonic acid
ELISA enzyme labels
horseradish peroxide (HRP), alkaling phosphatase (ALP), beta-galactosidase
PCR steps summarized
denaturation- DNA strands separate
annealing- primers bind
extension- polymerase copies DNA
Long summary of PCR
enzymatically synthesizes millions of identical copies of target DNA to increase analytic sensitivity
when the target is microbial RNA or mRNA, RNA must be enzymatically converted to DNA by reverse transcriptase (RT)
latest innovation: real time RT-PCR
DNA melt curve analysis
PCR: limited by expense, need for special thermocyclers, potential aerosol contamination, nonspecific annealing & degree of stringency
Coagulation screening tests
PT, aPTT, TT, Fibrinogen, D-dimer
Bleeding time
manual method that evaluates primary hemostasis (being replaced by PFAs)
checks how long it takes for bleeding to stop after a small cut
tells you if platelets are working properly
Prothrombin time (PT)
extrinsic and common pathways
checks how long it takes blood to clot through the extrinsic and common pathways
used to monitor people taking warfarin (a blood thinner)
if PT is longer than normal, blood takes too long to clot
Activated Partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)
intrinsic and common pathways
checks the intrinsic and common pathways
used to monitor heparin therapy (another blood thinner)
if aPTT is long, problem in the intrinsic pathway or heparin effect
Thrombin Time (TT or TCT)
conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin
measures how well fibrinogen turns into fibrin, which makes the final clot
if TT is long, it means: there is a fibrinogen problem, or heparin is still in the sample
quantitative fibrinogen
determines the amount of fibrinogen
if it is low, the body can’t form a strong clot, more risk
D-dimer
detects fragments from the plasmin degradation of the fibrin clot
checks for clot breakdown products (tiny pieces left when a clot dissolves)
if high, it means the body has recently made and broken down clots
Nucleic probe testing infectious
salmonella, COVID-19, HIV, Hepatitis, Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, TB, Herpes
nucleic probe testing genetic
cystic fibrosis, sickle cell, huntington’s, Von Willebrand’s disease, Duchenne type, muscular dystrophy
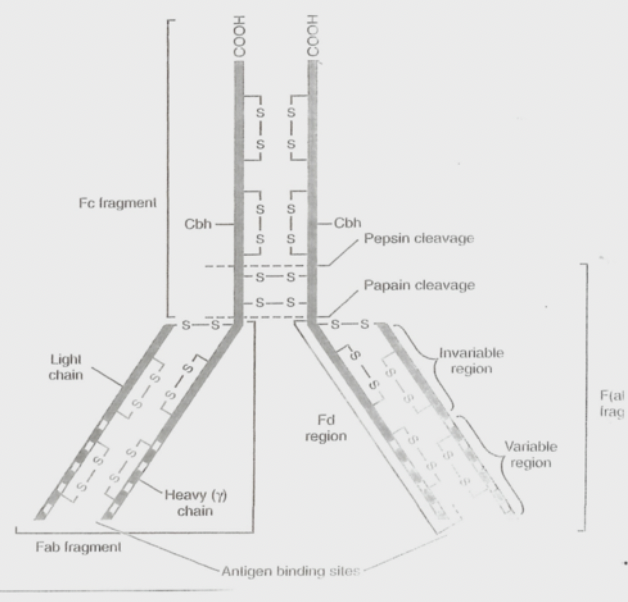
left side: 2 heavy + 2 Light chains, Fab (binds antigen), Fc (binds immune cells), Hinge (flexibility)
prozone
(antibody excess) too many antibodies= false negative
postzone
(antigen excess) too many antigens= false negative
zone of equivalence
(create insoluble complex) balanced= positive reaction
ELISA
enzyme linked immunosorbent assay
EMIT
enzyme multiplied immunoassay technique
RIA
radioimmunoassay
FPIA
fluorescence polarization immunoassay