BIOCH 200 - Nucleic Acids
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty
Determined that DNA was Griffith's "Transforming Factor"
Hershey and Chase
Showed that DNA was the genetic material not protein through radioactive progeny
Mononucleotides
ATP, ADP, FMN
Dinucleotides
FAD, NAD+, dCdG
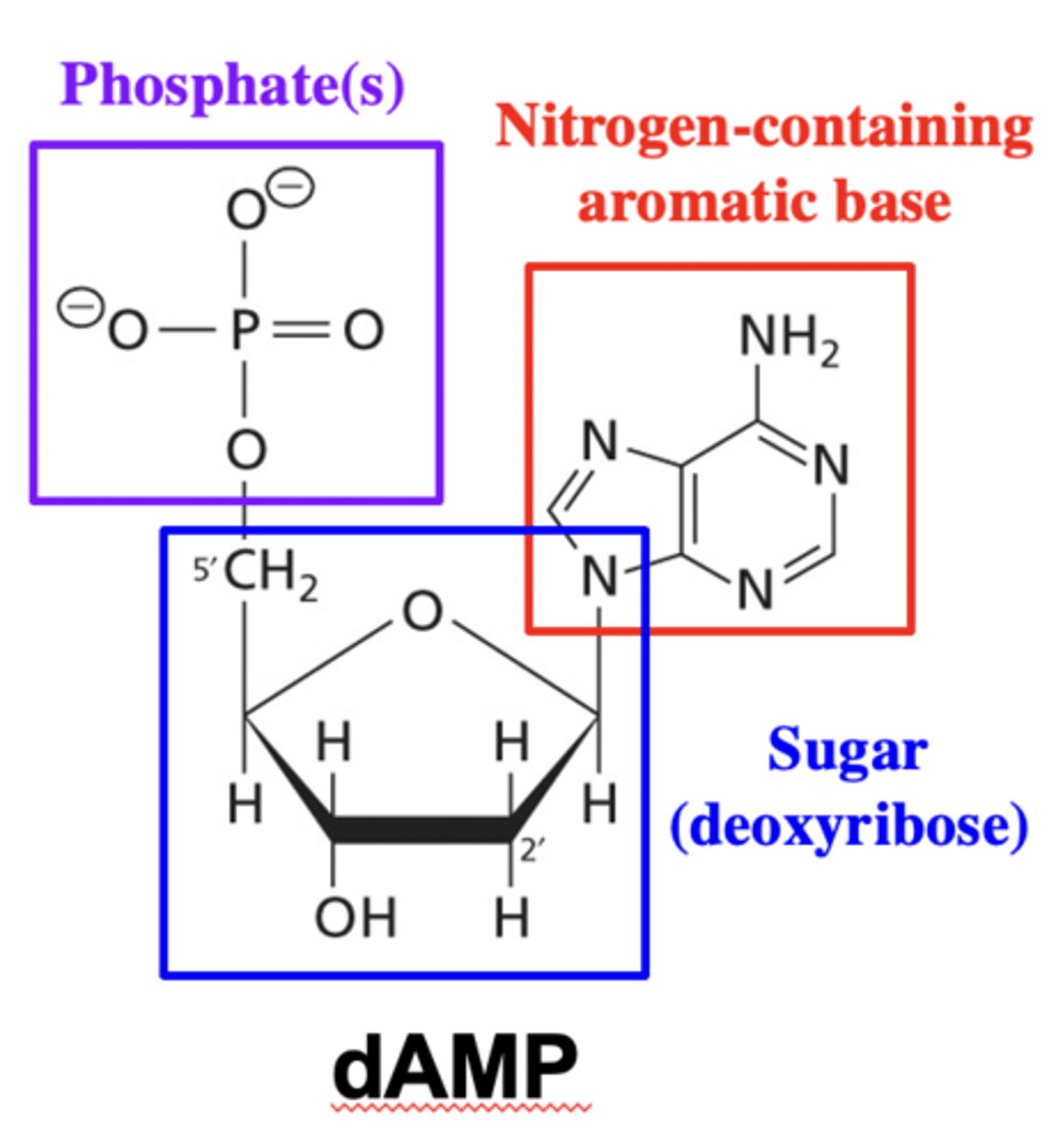
Structure of dAMP
Phosphate, deoxyribose and nitrogen-containing aromatic base
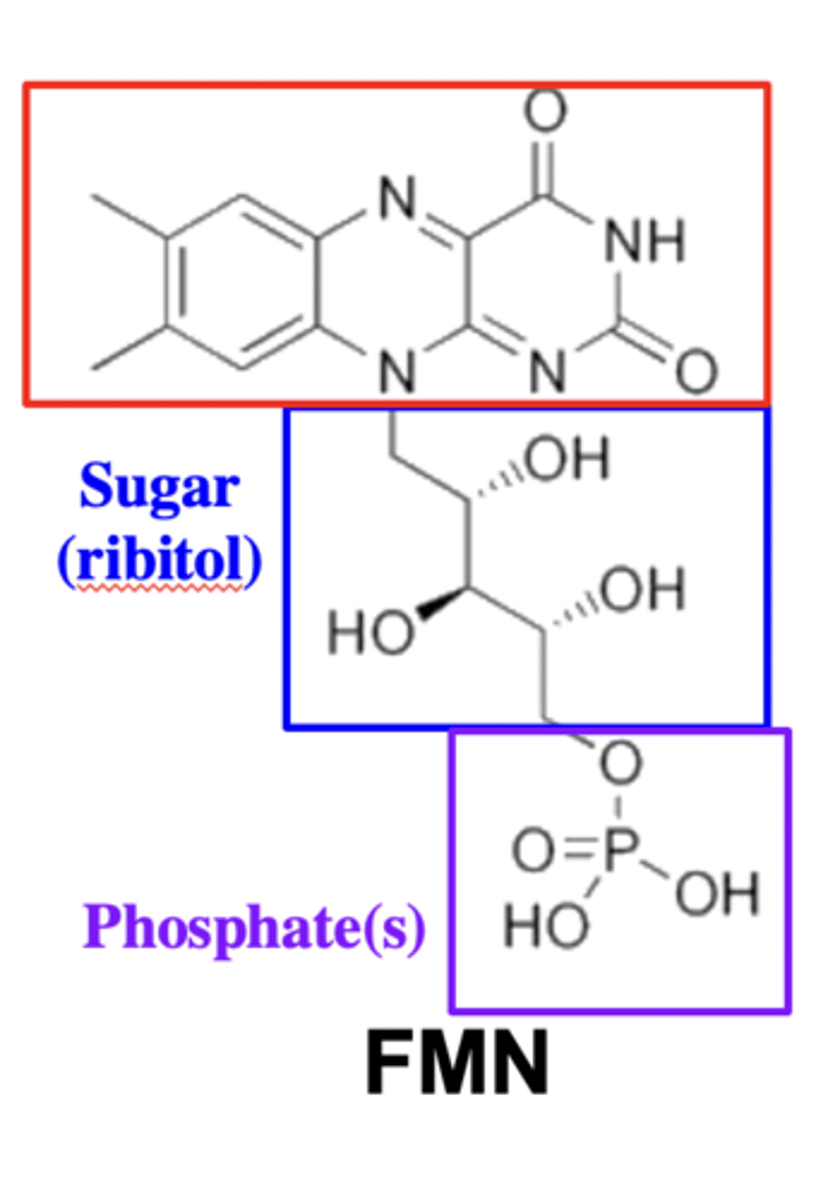
Structure of FMN
Phosphate, ribitol and nitrogen-containing aromatic base
2 Common Sugars
Deoxyribose (DNA) and Ribose (RNA)
Pyrimidine
1 carbon ring with 1N, 3N
Purine
2 carbon rings with four nitrogens
Which nitrogenous bases are pyrimidine?
Cytosine, thymine, uracil
Which nitrogenous bases are purine?
Adenine and Guanine
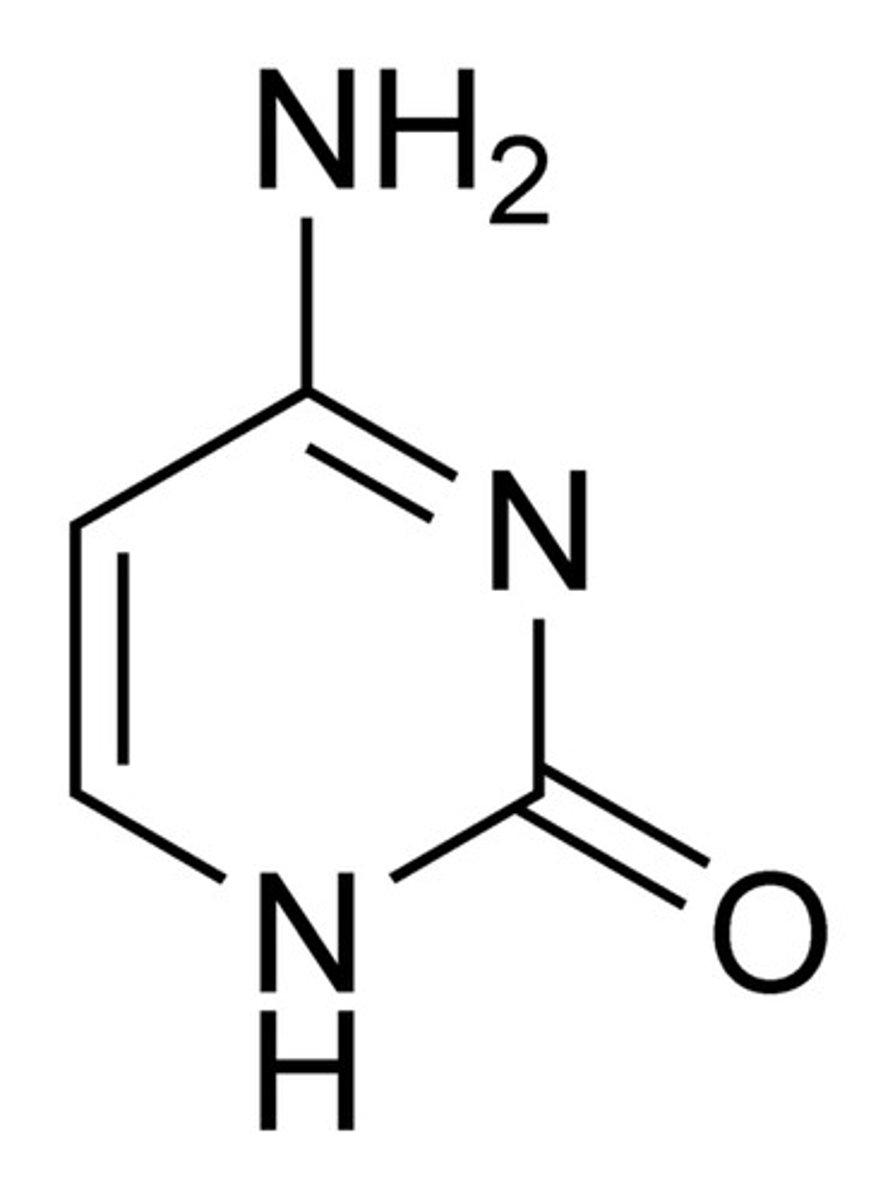
Structure of Cytosine
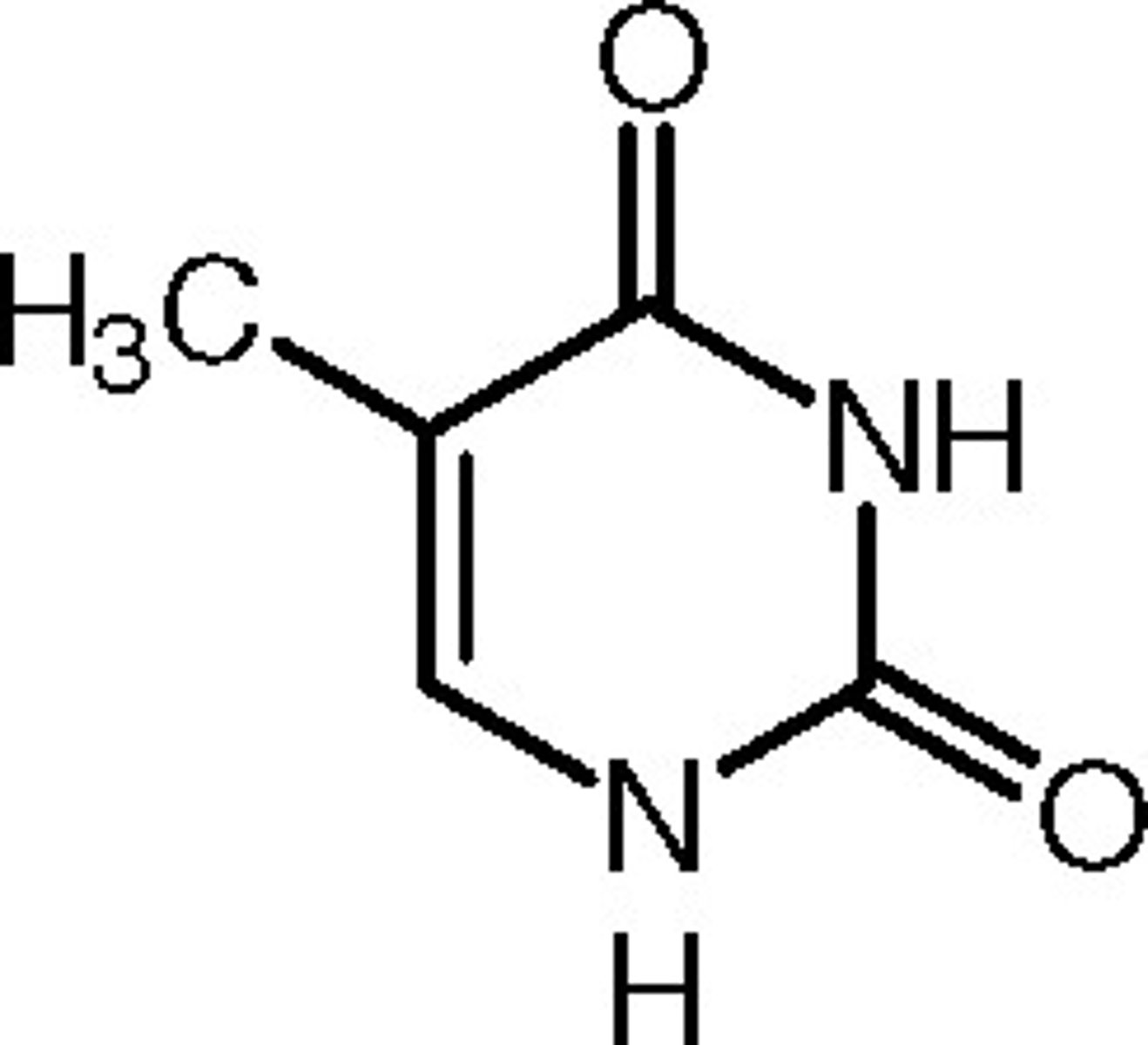
Structure of Thymine
Structure of Uracil
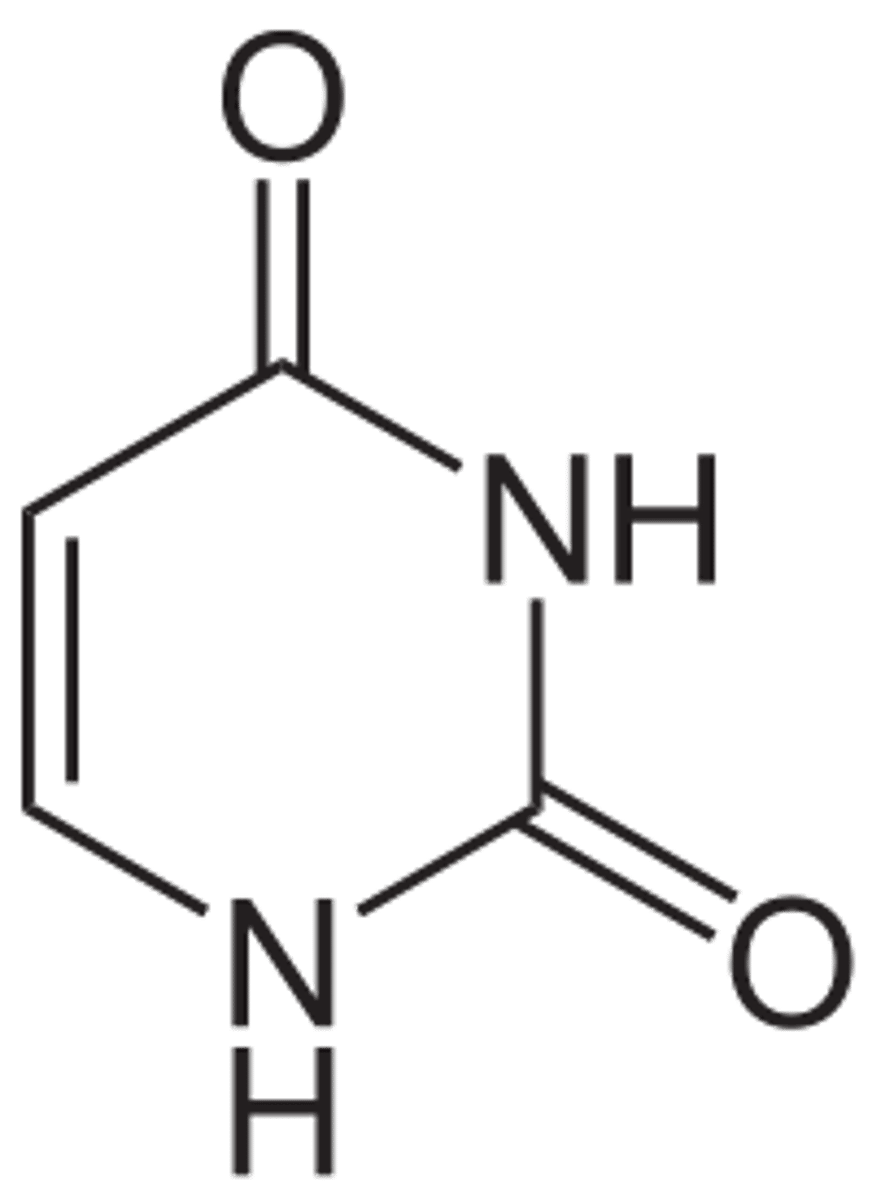
Structure of Adenine
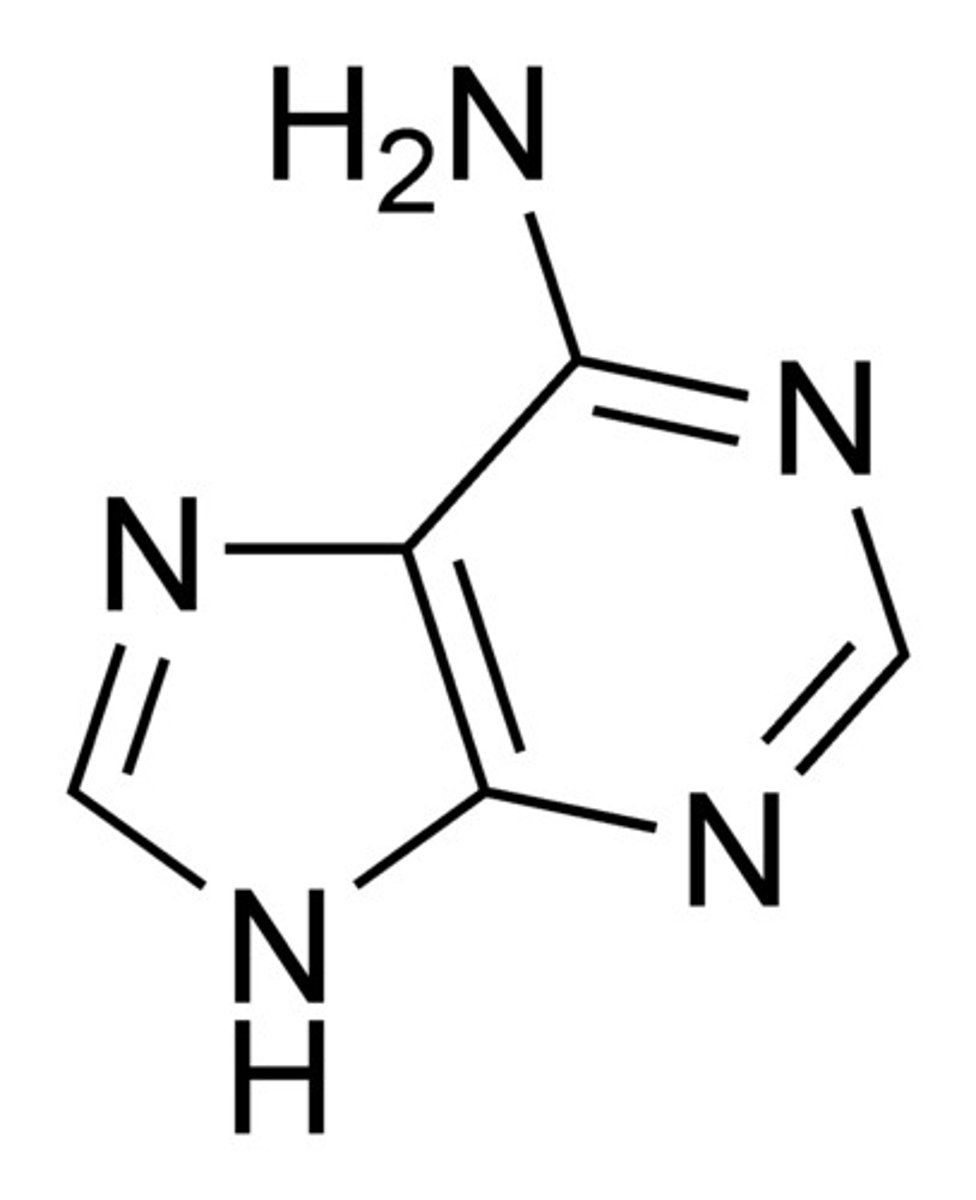
Structure of Guanine
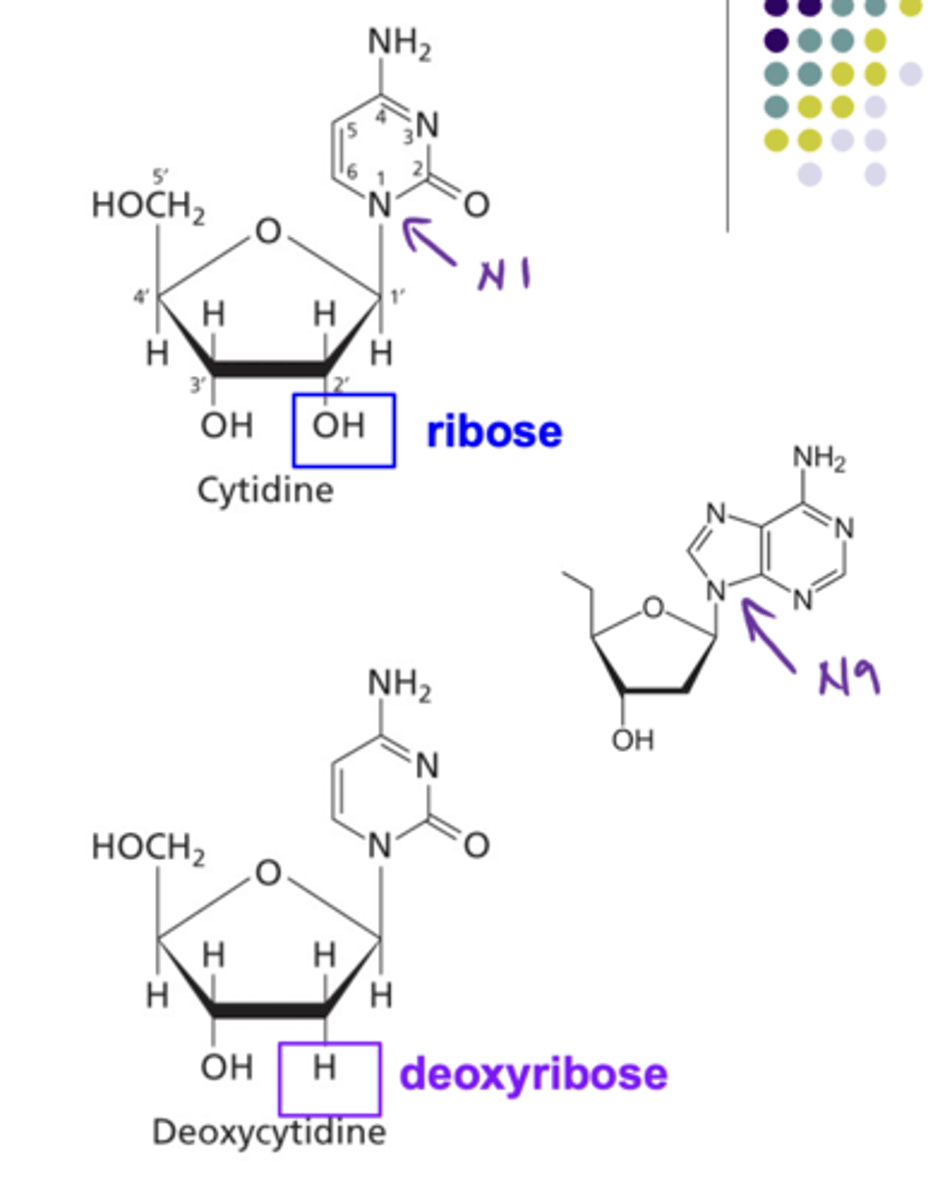
Where are purines and pyrimidines connected to their sugars within nucleotides?
Pyrimidine = N1
Purines = N9
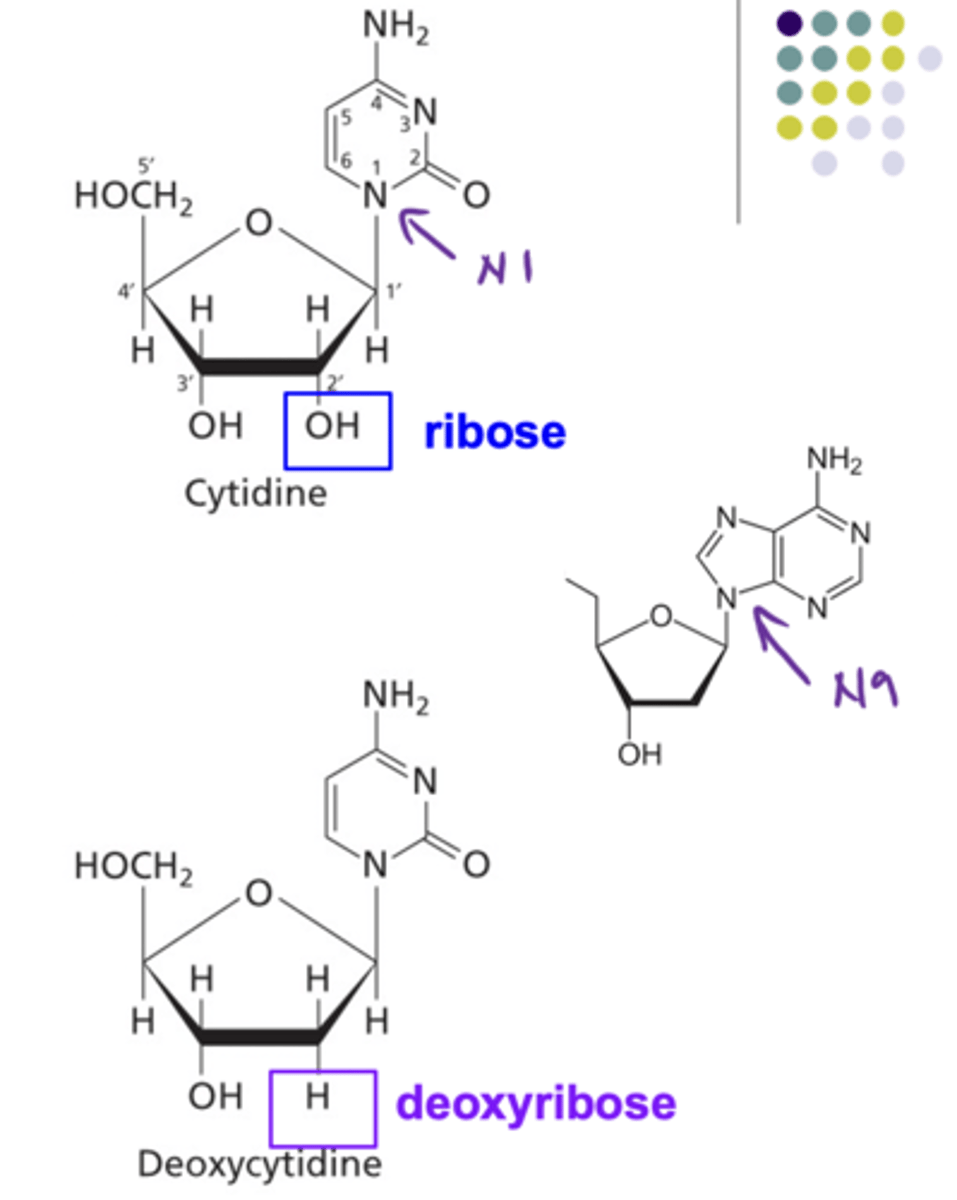
Structure of a Ribose vs Deoxyribose
Ribose has as hydroxyl on carbon 2 while deoxyribose does not
Naming Purines
-ine become -osine
Naming Pyridimidines
-ine become -idine
Structure of ATP
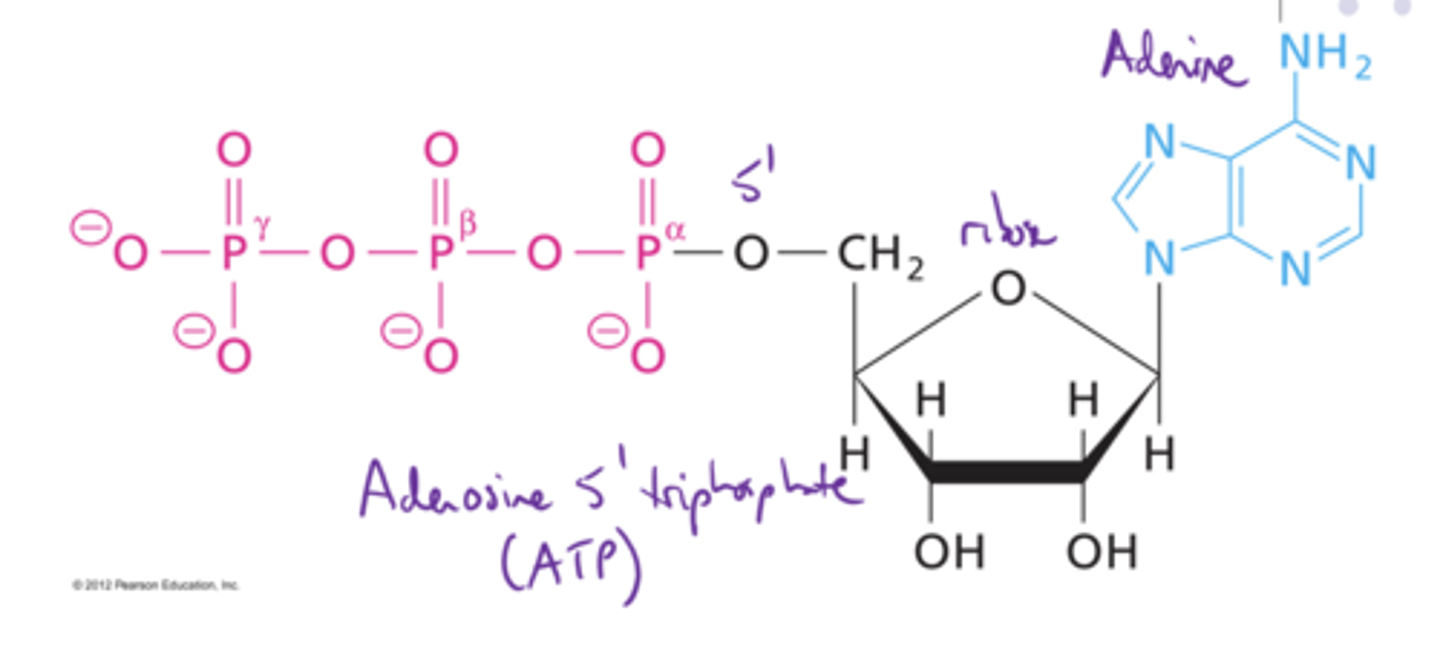
Structure of dATP

T/F. Phosphate is usually at the 5' position
True
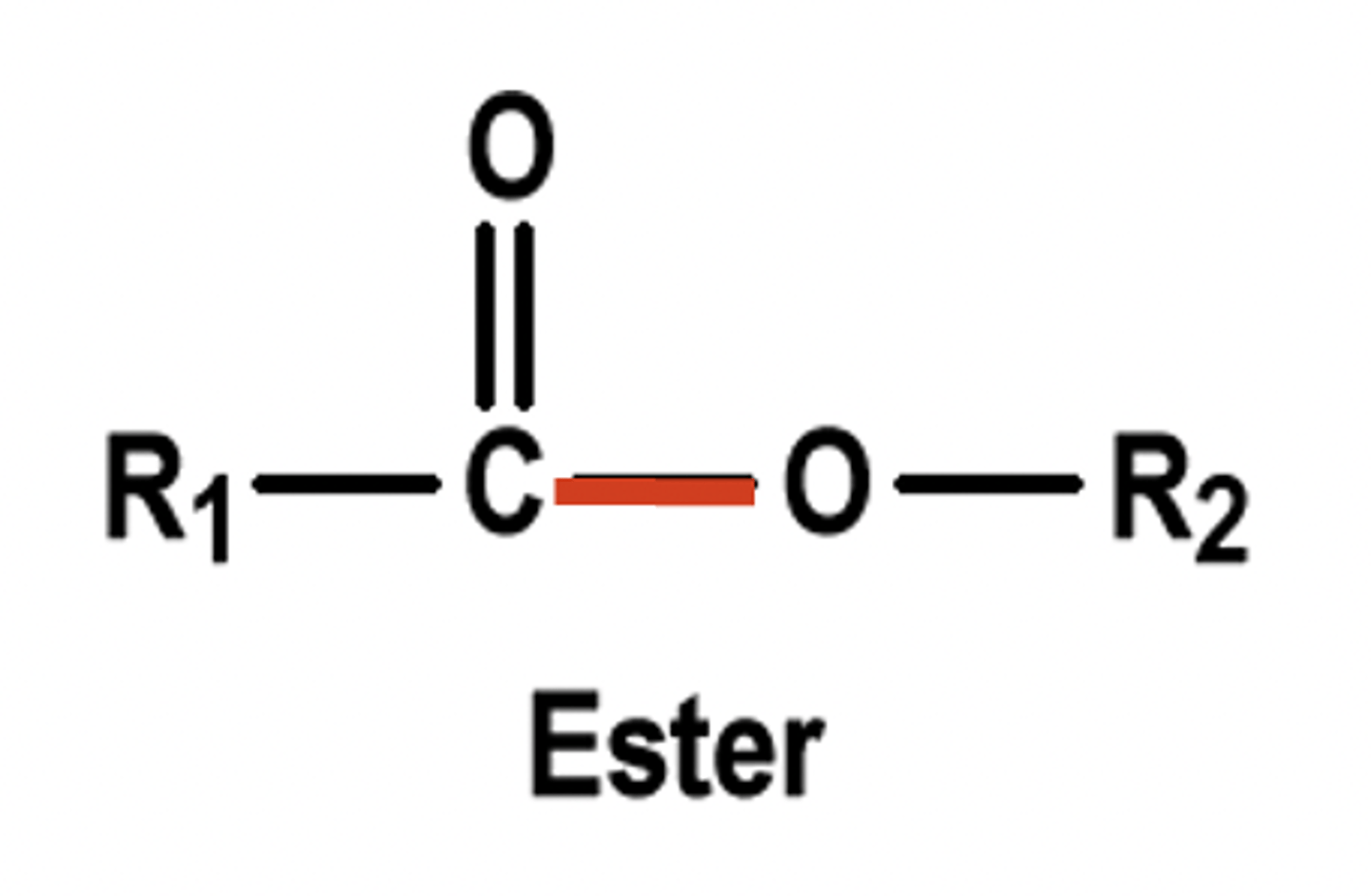
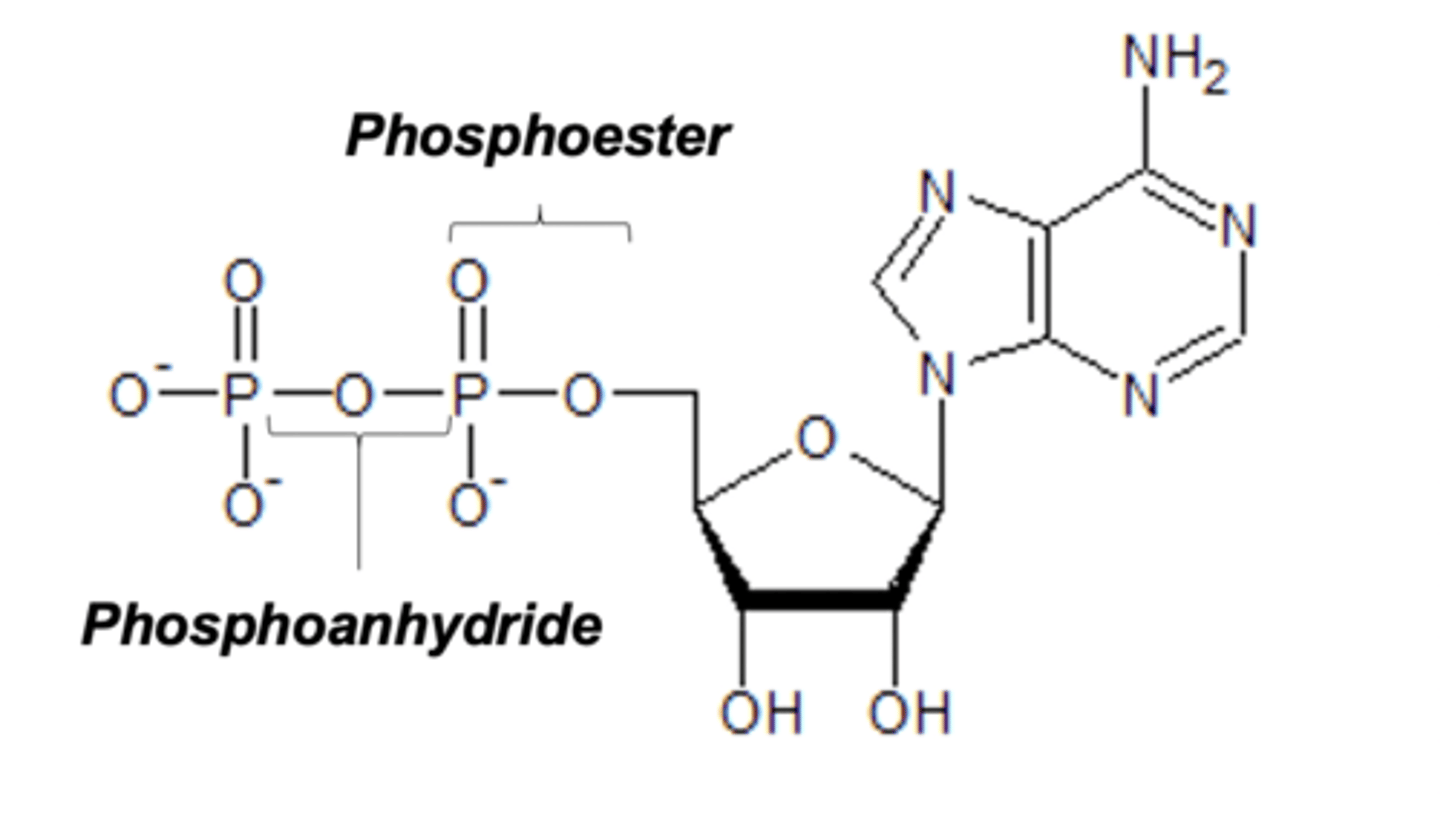
Ester
RCOOR
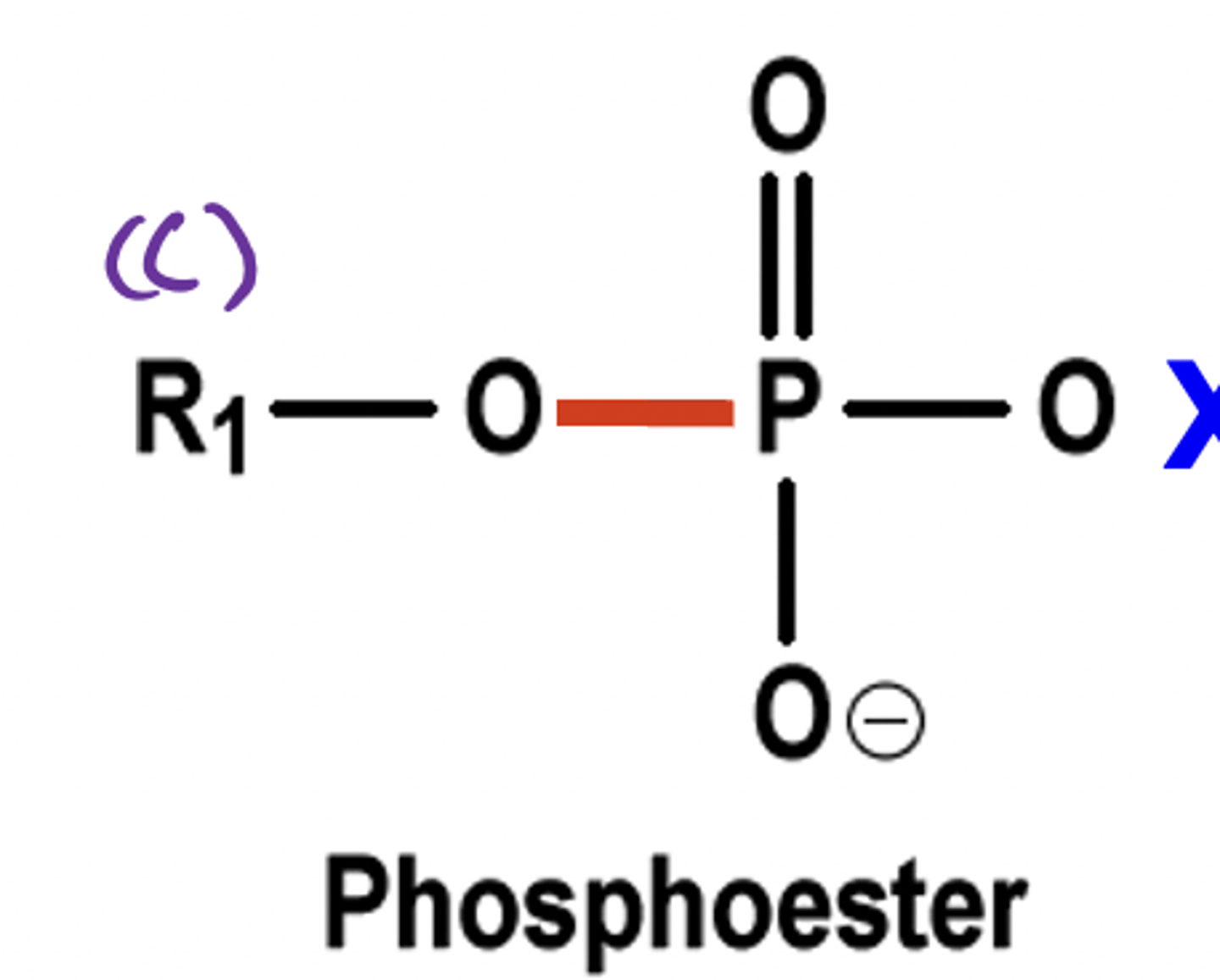
Phosphoester
Link carbons to phosphate groups
Phosphodiester
Link two different carbons to one phosphate group
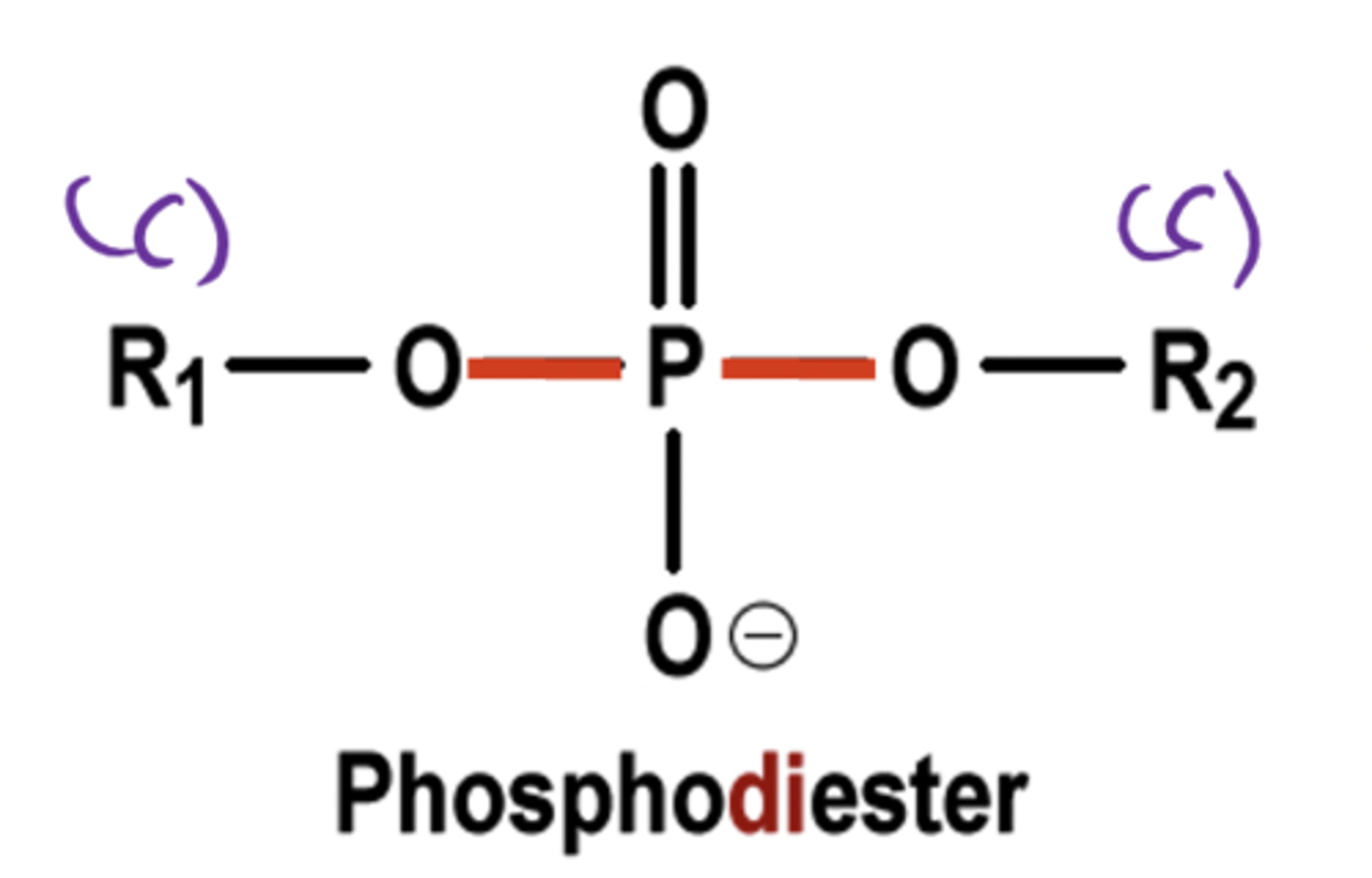
How are nucleotides linked to form nucleic acids?
Nucleotides are linked by 3'-5' phosphodiester bonds
Phosphoanhydrides
Links two phosphates to each other
What directionality are nucleotide sequences written in?
5' to 3'
Primary Structure of DNA
Sequence of nucleotide residues (i.e. AGTC)
Secondary Structure of DNA
Chains of nucleotides - double helix
Is the sugar-phosphate backbone polar or non-polar?
Polar
Is the sugar-phosphate backbone in RNA or DNA more polar?
It is more polar within RNA
Nucleotide Nomenclature - Phosphates attached to a single carbon/OH groups
Mono-/di-/tri-
Nucleotide Nomenclature - Phosphates attached to multiple carbon/OH groups
Bis-/tris-
T/F. RNA is more susceptible to hydrolysis of phosphodiester bond than DNA. Why or why not?
True, the presence of the 2C' OH group makes it more susceptible (DNA is more stable)
Cytosine Deamination
Spontaneous uncatalyzed reaction that converts the NH2 to a carbonyl group forming a uracil
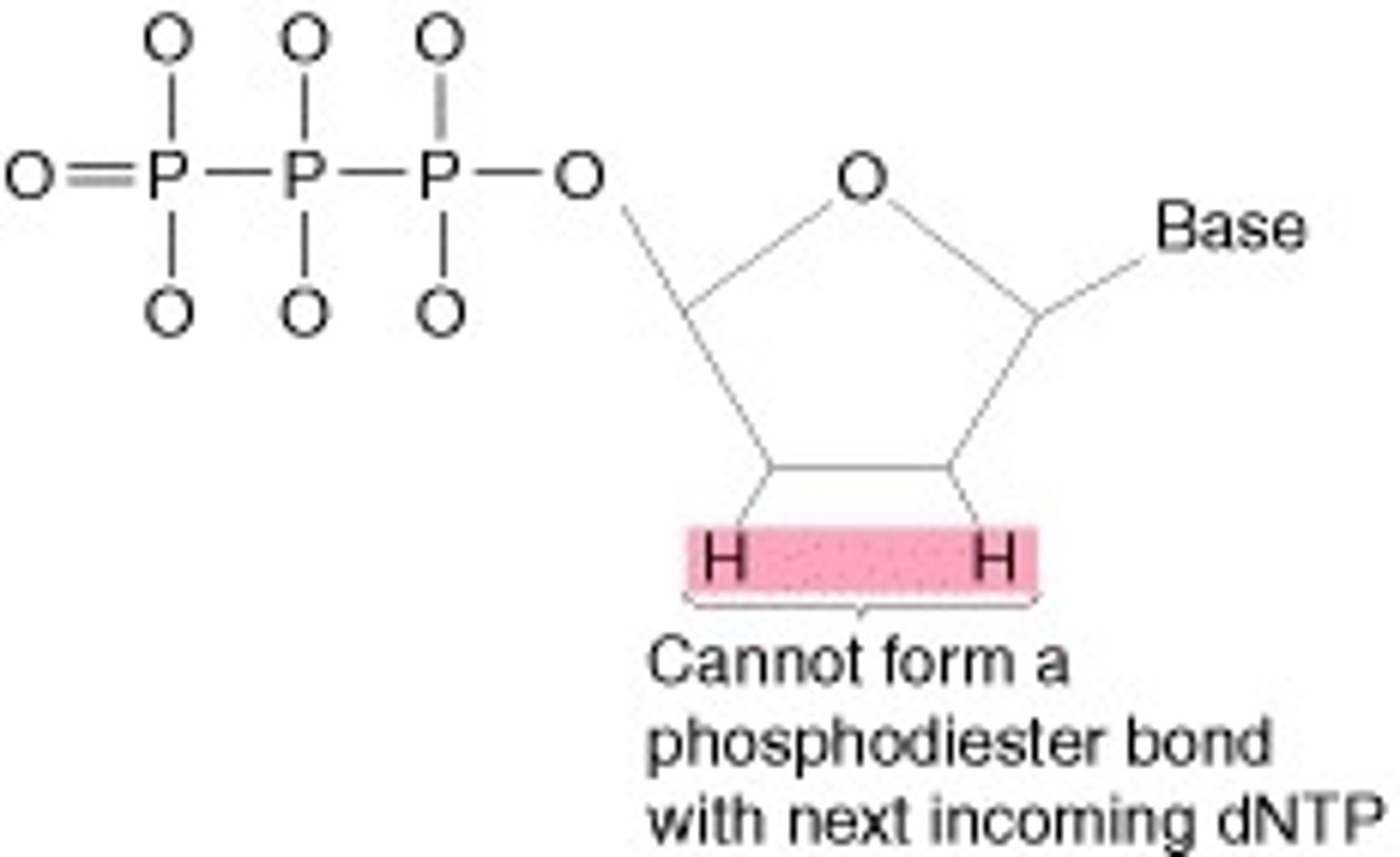
Dideoxynucleotide
Missing a hydroxyl group (-OH)
Properties of the Bases
Heterocyclic, aromatic, electron delocalization, planar, poorly soluble in water, largely hydrophobic
Beer-Lambert Law
Used to relate the concentration of nucleic acid to the absorbance
Erwin Chargaff (Chargaff's Rule)
Discovered that DNA composition varies, but A = T and G = C (chargaff's rule)
B-form DNA
Antiparallel strands with a right-handed twist stabilized by base stacking and hydrogen bonds
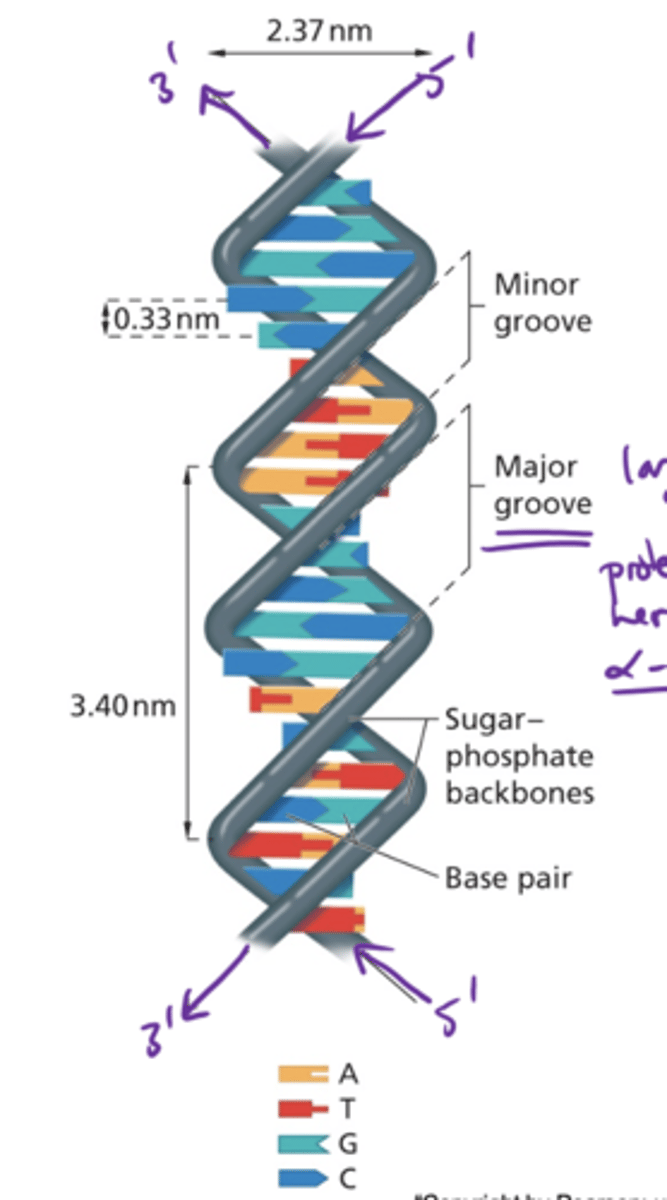
Base Stacking
Van der Waals interactions and hydrophobic forces
Complementary Sequences
Poly nucleotides are non-identical and are anti-parallel however they obey chargaff's rule
DNA Denaturation
1. Separation of DS to SS
2. Disruption of non-covalent forces (base stacking and HB)
3. Essential for some cellular processes
4. Changes in absorption properties occurs
Relative Absorbance of Double Stranded vs Single Stranded DNA
SS have a higher absorbance due to more bases (which absorb UV) exposed
Tm of AT vs GC pairs
AT pairs have a lower melting point (2HB) while GC pairs have a higher melting point (3HB & strong base stacking interactions), therefore higher GC content = higher Tm
Tm
Midpoint of melting
T/F. AT pairs tend to separate first during denaturation.
True
Why is DNA denaturation measured at 260mm?
UV is most strongly absorbed at this wavelength
Hyperchromicity
Increase in UV absorbance when DS => SS
Hypochromicity
Decrease in UV absorbance when SS => DS
T/F. Denaturation must occur for replication or transcription.
True
As the temperature increases....
DS begins to denature, hydrogen bonds break causing separation forming SS and INCREASES UV ABSORPTION
As the temperature decreases...
SS begins to anneal and form hydrogen bonds through fast zippering and DECREASES UV ABSORPTION
Renaturation
Reformation of dsDNA through proper base pairing, nucleation and zippering so it regains its native conformation
Steps of Renaturation
1. Nucleation (slow)
2. Zippering (fast)
Factors that Affect Tm
1. pH
2. Salt concentration
How does pH affect Tm?
Very low or very high destabilizes DNA, lowering the Tm
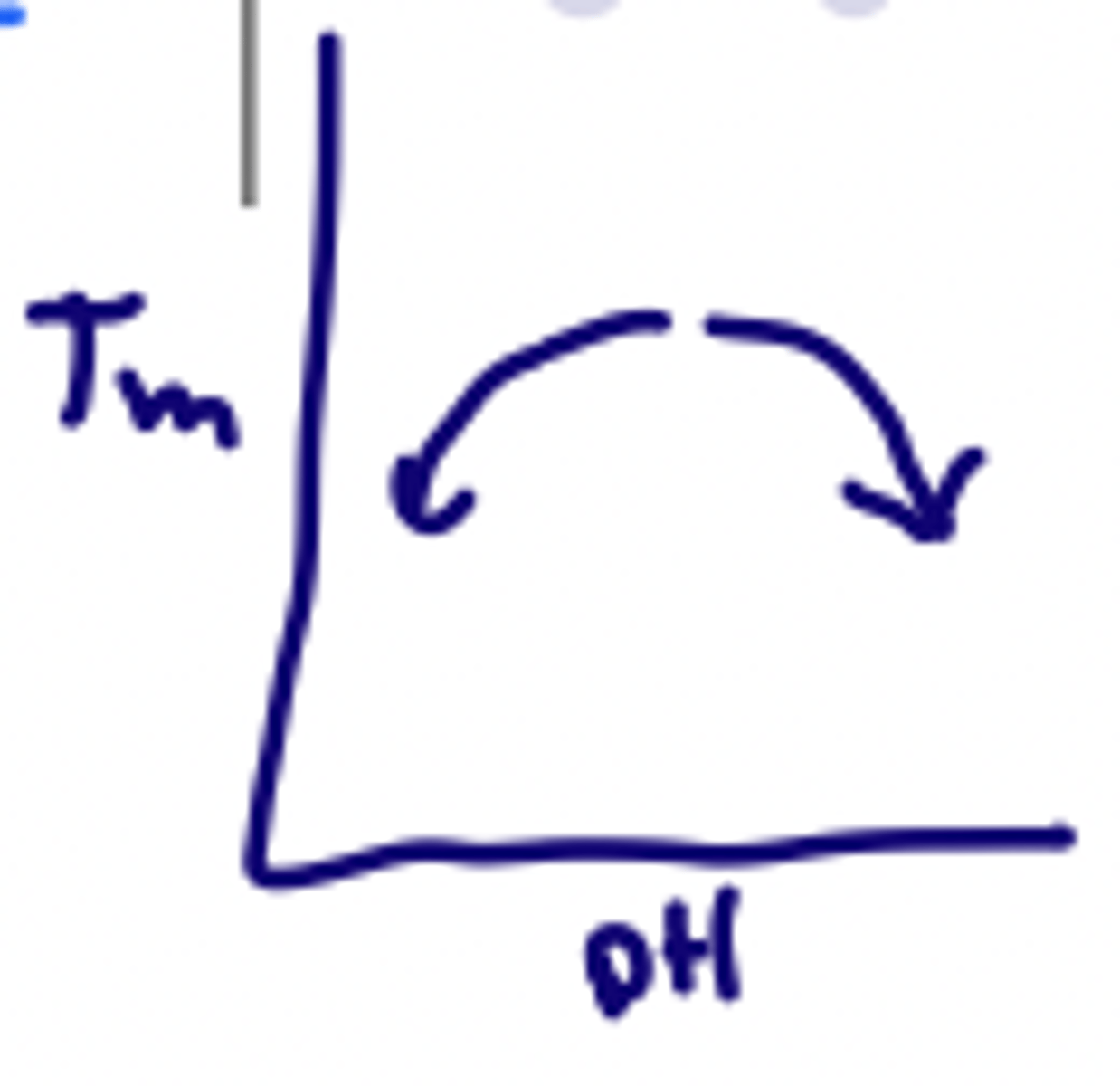
How does salt concentration affect Tm?
Salt ions shield negative charges on phosphate reducing repulsion and stabilizing the double helix
Increase salt = ___ Tm
Increase Tm
(Stabilizes double helix)
Decrease salt = ___ Tm
Decrease Tm (destabilizes double helix
T/F. Denaturation and renaturation behaviour of nucleic acids enables hybridization.
True
What determines the Tm of a hybrid?
How well they match
More similar match = ____ Tm
Higher Tm
Worse match = ____ Tm
Lower Tm
Intrastrand Base Pairing
Hydrogen bonding between bases on the same strand of nucleic acids
Interstrand Base Pairing
Hydrogen bond forming between complementary bases
T/F. The structure of RNA is LESS dependent on nucleotide sequence than double stranded DNA.
False, RNA is MORE dependent on nucleotide sequence
What type of base pairs can RNA form?
G = C (triple bond)
A = U
G = U
What is the usual max absorbance for DNA and RNA?
~260nm
What is the usual max absorbance for protein?
~280nm
What is the ideal ratio for pure DNA and RNA?
DNA = 1.95
RNA = 2.1
What does it mean when the ratios are lower than the ideal ratio?
Potential protein contamination
Order the following from highest to lowest absorption A260nm.
DS, Free nucleotides, SS
Free nucleotides > SS > DS
Dinucleotide
two nucleotides covalently bonded together by a single phosphate