Introduction to the Human Body - Anatomy & Physiology
1/192
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
193 Terms
_____ is fundamental to ALL life sciences
biology
Anatomy
study of body structure & the relationships among structures
Morphology
study of form & markings on the body’s surface
Gross Anatomy
study of structures w/o a microscope
something that can be seen (like the heart, not cells)
opposite of Histology
Systemic Anatomy
study of the body’s systems
respiratory, nervous
Histology
microscopic study of tissue structure
opposite of Gross Anatomy
Physiology
knowing the body’s (parts) functions & how they work
Cell Phsiology
study of cell specialization/differentiation (cells have different jobs)
Neurophysiology
study of nerve functions
Endocrinology
study of hormones & how they control body functions
Cardiovascular
study of functions of the heart & blood vessels (tubes)
Immunology
study of the immune system (body defense mechanisms)
Genetics..
DNA
Psychology..
Brain
Pathology..
Diseases
Biochemistry..
life
Lvls of Structural Organization: from Smallest to Largest
Chemicals, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organism
Chemical Lvl
NOT alive
in most plants and animals
Chemical Lvl: Subdivisions
subatomic particles
atoms
molecules
macromolecules
organelles
Subatomic Particles
electrons, protons, neutrons
atoms
elements
molecules
atoms tgr, compound (O2, H2O)
macromolecules
bigger compounds (DNA, proteins)
organelles
tiny parts of the cell (nucleus)
Chemical Lvl: Essential to Life
CHON: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen
Calcium
Glucose (C6H12O6)
cellular lvl
basic structural & functional unit of all life
you consist of cells, they build you
cells do the jobs
** the building AND the workers **
cell examples
muscle, nerve, blood
How many different kinds of cells are there?
260
not as many ppl would think bc the same type of cell CAN do different jobs
Cells are like humans in the fact that they..
change, develop, and die
Cells are specialized/differentiated, what does this mean?
they have developed in such a way where they are able to perform certain tasks (jobs)
cells change during embryonic development and become _______ for certain function
specialized/differentiated
Tissue lvl
groups of cells that have a common origin, appearance, & function
same type of cell comes from same clump
____ basic tissues
4
Basic tissues?
Epithelial
Muscle
Connective
Nervous
**MENC
Epithelial tissue
covers, protects surfaces (skin)
muscle tissue
allows movement
causes your body (internally & externally) to move
connective tissue
joins parts tgr & provides support
nervous tissue
responds to environment stimuli (senses) & coordinates bodily activity
feel, think
Organ lvl
structures composed of 2 or more different types of tissues, have specific functions, & have recognizable shapes
all must work together to function
organ examples??
heart, brain, liver, eyes, lungs
Organ System lvl
consists of several related organs that have a common function
organs can belong to more than one system
ex: pancreas involved in digestive AND endocrine
Organ system examples
digestive, reproductive, endocrine, respiratory, nervous
Final Level of structural organization?
organism
Life Processes of Humans (name as many as you can)
Absorption, Assimilation, Circulation, Digestion, Excretion, Growth & Development, Movement, Reproduction, Respiration, Resposiveness
RED CARD ARM**
Responsiveness
response to stimuli inside or out (brain, nerves)
Reproductions: 2 types
new organisms - meiosis
new cells - mitosis
Respiration
use of oxygen to obtain energy from food (ATP = energy)
Digestion
process to turning food to energy by liquifying food particles
Absorption
take things into body & send them places
passage of substances through sending liquids around membranes into body fluids
Assimilation
change to fit in
changing of substances into chemically different forms
Excretion
waste removal, removed from body because not needed
most of the life processes of humans are combined to get…
Metabolism
What are the 2 ideas that underlie the whole subject of anatomy and physiology?
Homeostasis
Feedback system
Homeostasis
the condition in which the body’s internal environment remains constant within set limits
Homeostasis: Extracellular Fluid (ECF)
internal environment consists of fluid that surrounds cells
Homeostatic Imbalances
disruptions in homeostasis that could end in illness or death
hard to keep body in same condition
our bodies are never always in homeostasis bc…
we are always exposed to stimuli
What is ICF?
fluid part of the cytoplasm
Homeostatic mechanisms have __ main components
3
none of these mechanisms think, just do what they are told
Homeostatic mechanism: Receptors
provide info from internal info
just brings in the info
Homeostatic mechanism: Control Center
decides what the response should be
decision maker
Homeostatic mechanism: Effectors
carry out responses internally to alter conditions
the do-er
Feedback System
acts that the body must perform to maintain normal anatomical & physiological conditions
can be + or - (most are -)
Negative Feedback
as the conditions are returned back to their set point, action of the effectors is reduced
** don’t realize they are fixed
** day-to-day conditions/problems
** short path back to homeostasis
examples of Negative feedback?
Body temp: shivering/sweating
Blood pressure: heart rate
Positive Feedback
process that moves conditions further away from the set point (to ult.) get back to set point — longer path
** effector action increased —more intense response
** in extreme events
** longer path to get back to homeostasis
examples of Positive feedback?
uterine contractions during pregnancy
blood clotting
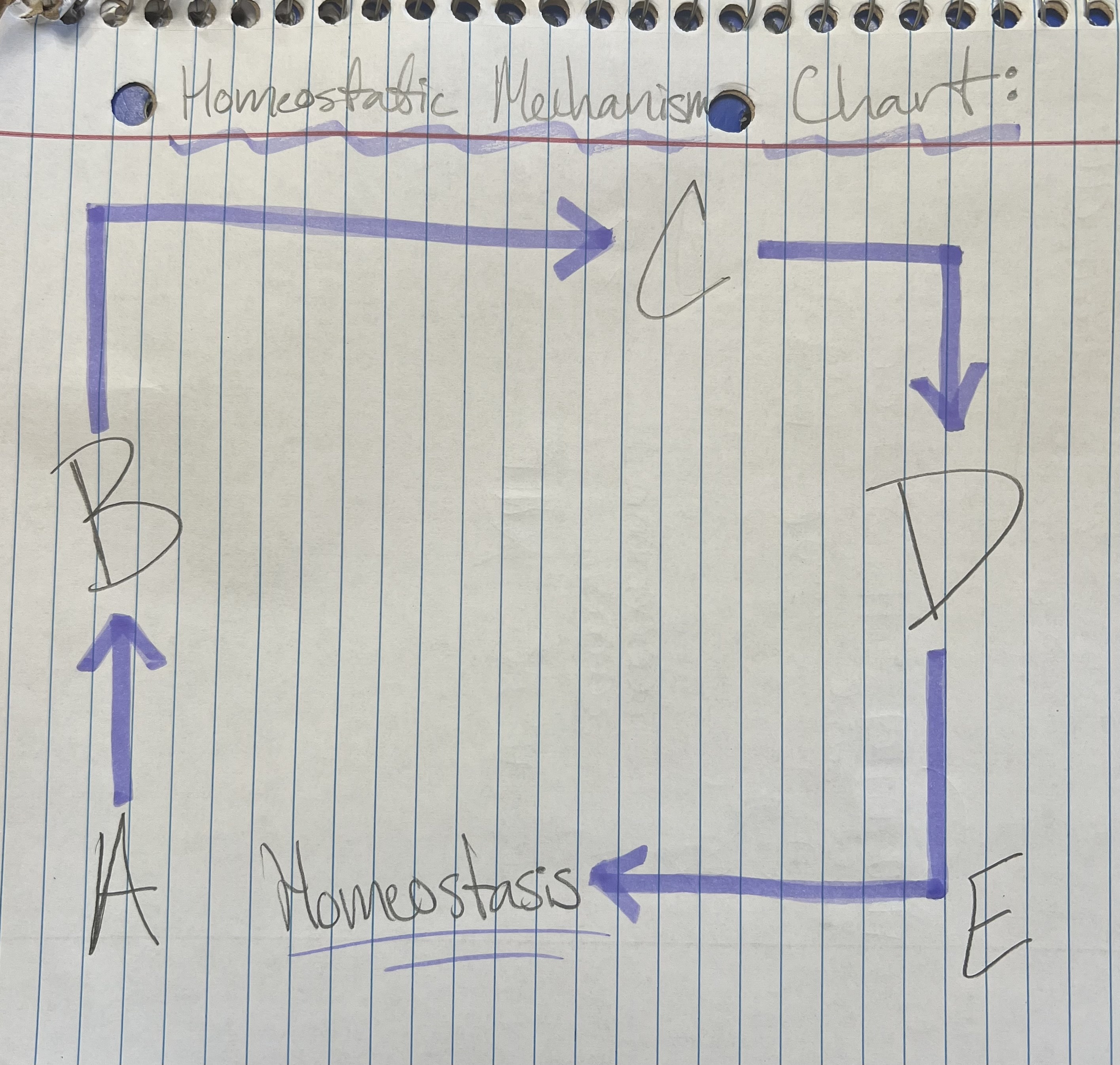
Term and Definition: A?
Stimulus: change in environment
‘cause’
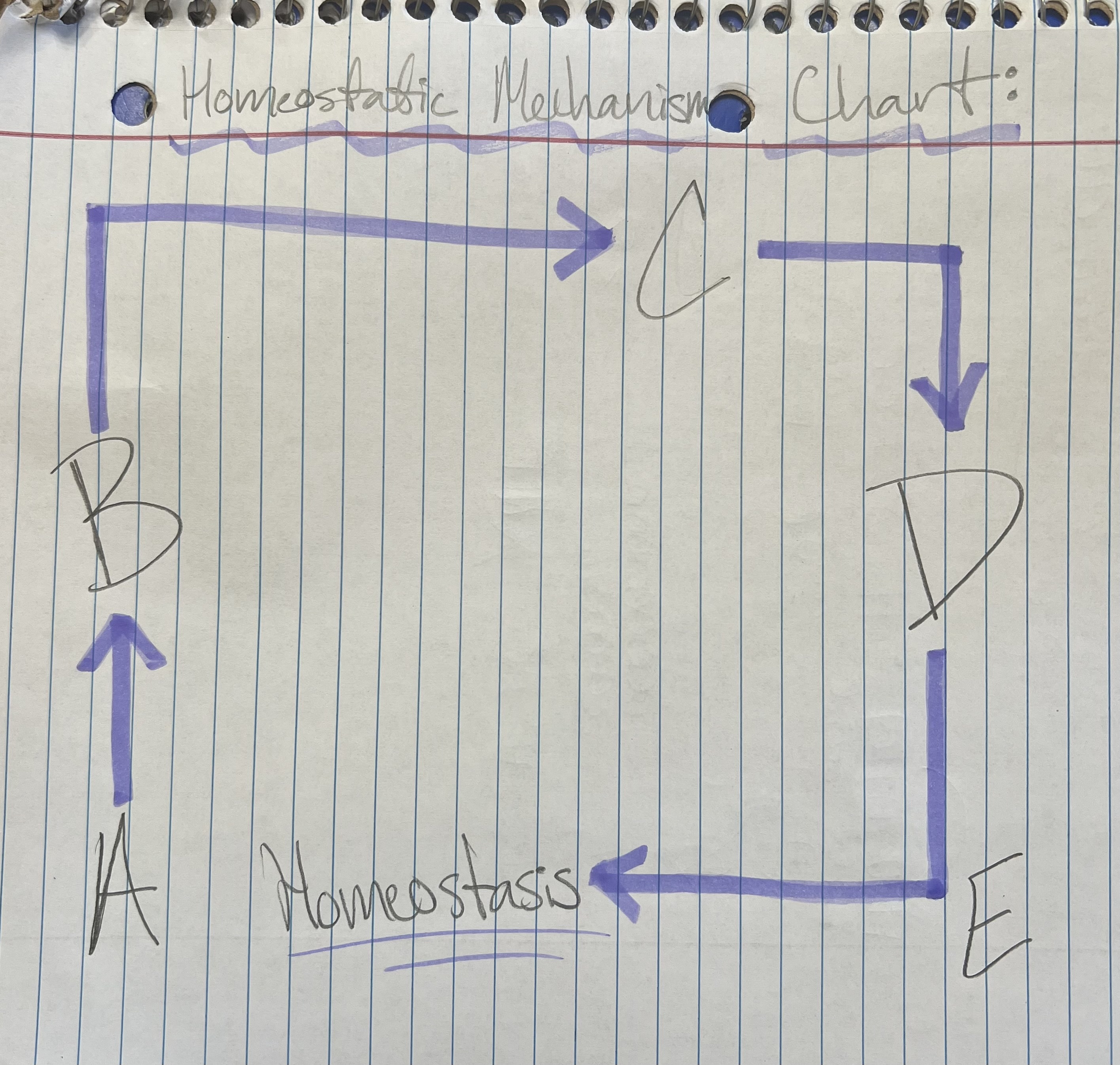
Term and Definition: B?
Receptors: grab chemical, bring it into our environment
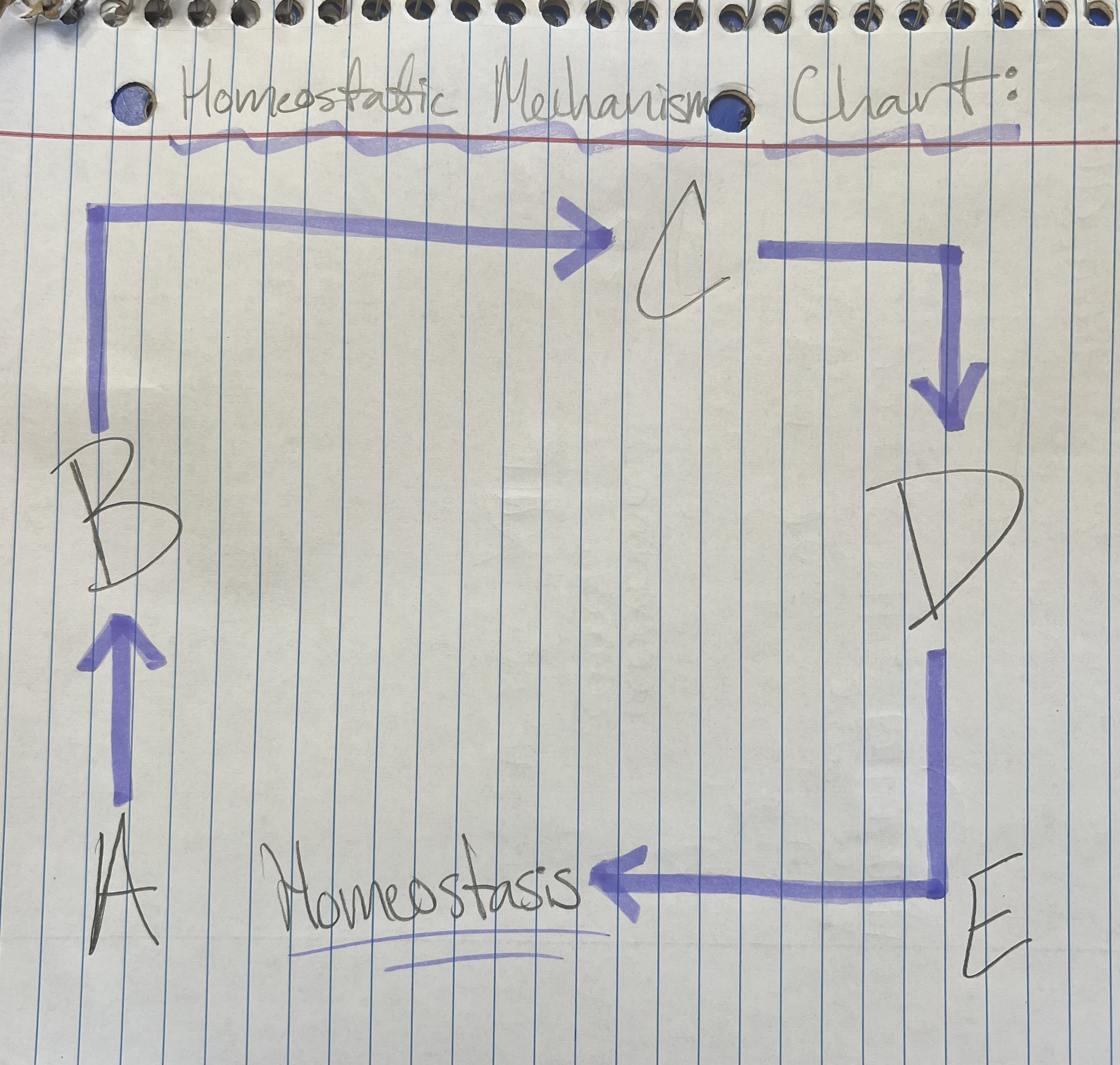
Term and Definition: C?
Control Center: interprets info from receptor
brain and spinal cord
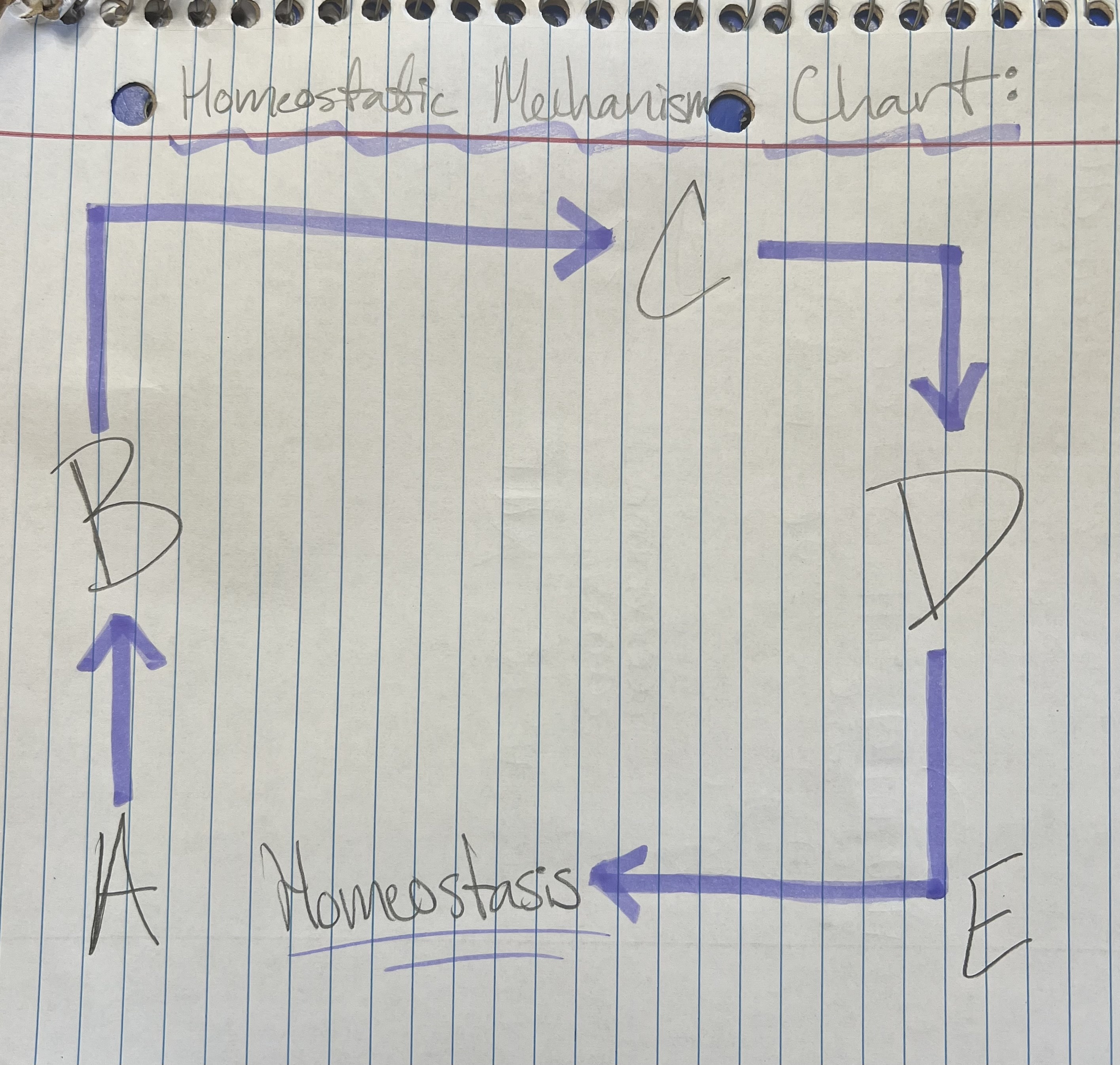
Term and Definition: D?
Effectors: directs the change
‘effect’
muscles + glands: muscles move and glands secrete chemicals
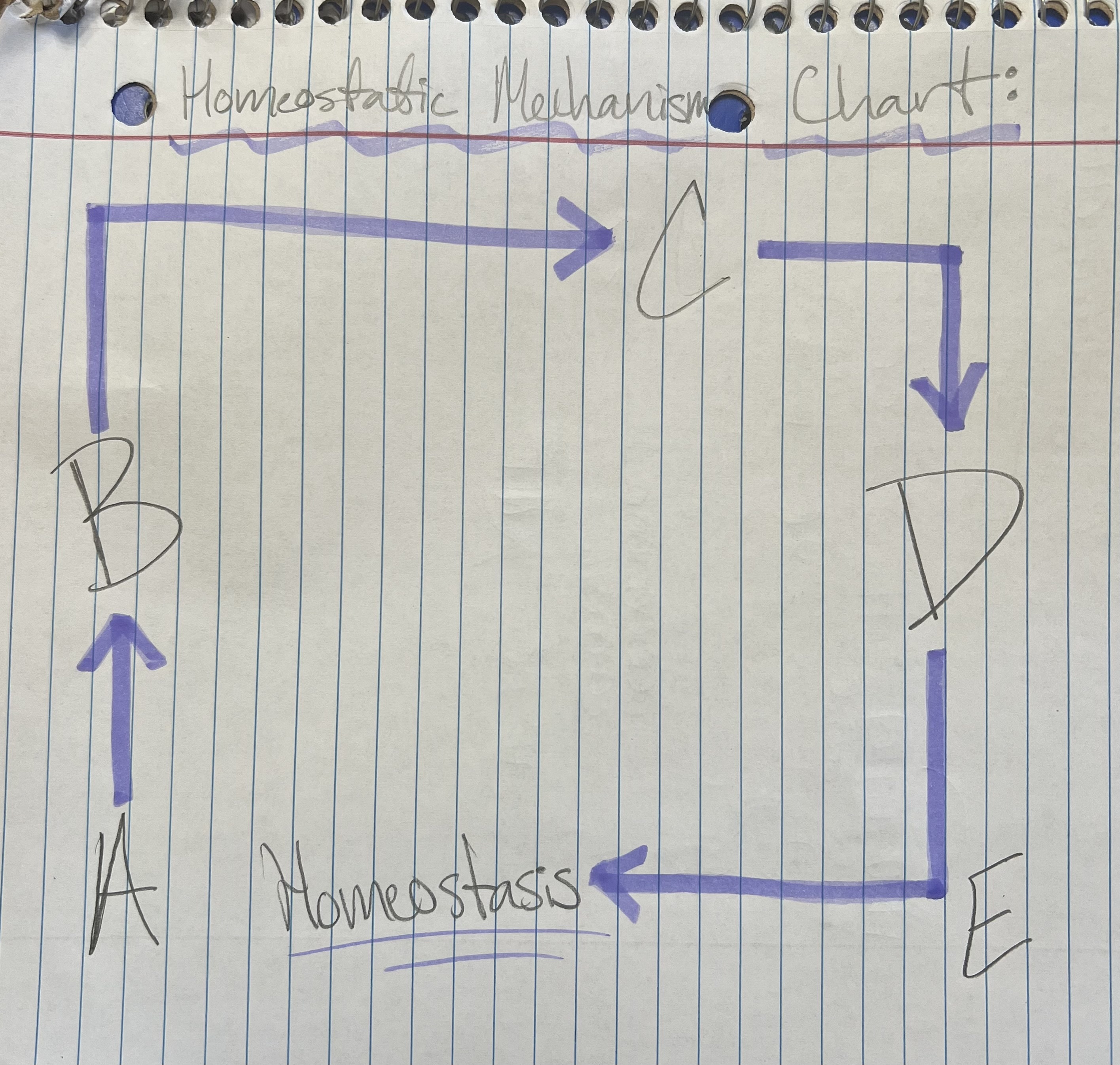
Term and Definition: E?
Response: take what brain has told me to fix problem
change is corrected
major features of the human body include…
cavities, membranes, and organ systems
Body Cavity
confined spaces within the body that contain internal organs
holes, usually lead to organs
what do body cavities do? (their purpose?)
protect, separate, & support organs
body cavities are separated by..
bone, muscle, or ligaments
Human body is divided into 2 parts, the ____ and the ____
Axial, Appendicular
Axial
includes head, neck, & trunk
Axial: Cranial Cavity
formed by skull & contains the brain
Axial: Spinal cavity
formed by vertebrae & contains the spinal chord
Axial: Thoracic cavity
superior portion containing lungs, and their air passages, esophagus, heart, and major blood vessels
chest area
Mediastinum
space btwn right and left lungs in thoracic cavity
heart, aorta, esophagus, & bronchi
Axial: Abdominopelvic Cavity
inferior portion
lower, digestion
Abdominopelvic cavity: Abdominal Cavity
upper part of abdominopelvic cavity
contains stomach, spleen, kidneys, liver, pancreas, small intestine, etc
Abdominopelvic cavity: pelvic cavity
contains bladder, reproductive organs, rectum, parts of large intestine
lower part of abdominopelvic cavity
Axial: Organs housed in the thoracic & abdominopelvic cavity are known as ______
viscera
Axial: Diaphragm
strong muscle that forms the floor of the thoracic cavity
mainly used in respiration
Axial: Cavities also found within the head…
nasal, oral, orbital, middle ear, sinus
Appendicular
includes the lower & upper limbs
why does the Appendicular contain no true cavities?
No organs are stored here
no organs → not a cavity
Appendicular: Serous membranes
line the walls of the thoracic & abdominal cavities
covers the organs here
Serous membranes: Pleural membranes
surrounds the lungs
Pleural membranes: Parietal pleura
covers right & left thoracic walls
Pleural membranes: visceral pleura
covers right and left lungs
Pleural membranes:
covers lungs and chest cavity
Pericardial Membranes
surrounds the heart
Pericardial Membranes: Parietal pericardium
lines the walls
Pericardial Membranes: visceral peritoneum
covers organs
Integumentary System
skin & structures grow from it
hair, nails, oil glands
Integumentary System purpose?
protection