Chemistry Review
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
1
New cards
What is matter?
anything that takes up space and has mass
2
New cards
Mass is the ___ of matter an object has.
quantity
3
New cards
atoms
basic units of matter
4
New cards
What are atoms composed of?
protons, neutrons, and electrons
5
New cards
central area of the atom
nucleus
6
New cards
What are located in the nucleus of an atom?
protons and neutrons
7
New cards
What move around the nucleus of an atom?
electrons
8
New cards
The number of ___ is equal to the number of ___.
electrons; protons
9
New cards
How many electrons can the first orbital hold?
2
10
New cards
How many electrons can the second orbital hold?
8
11
New cards
How many electrons is the third orbital stable with?
8
12
New cards
valence electrons
the electrons on the outermost shell
13
New cards
elements
substances made up of the same type of atom
14
New cards
Which 4 elements make up around 96% of the mass of all kinds of living things?
CHON (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen)
15
New cards
Atomic Number = ___
\# of protons, # of electrons
16
New cards
Atomic Mass =
\# of protons + # of neutrons
17
New cards
\# of Neutrons =
atomic mass - atomic #
18
New cards
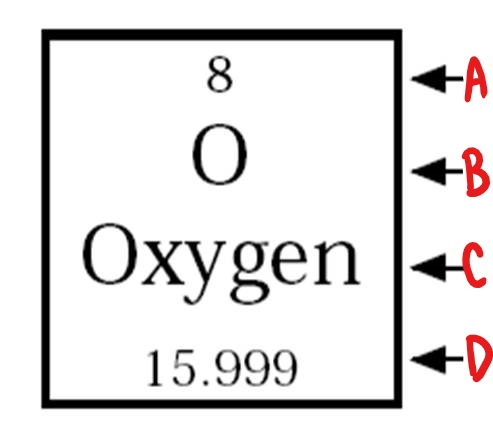
A
atomic number
19
New cards
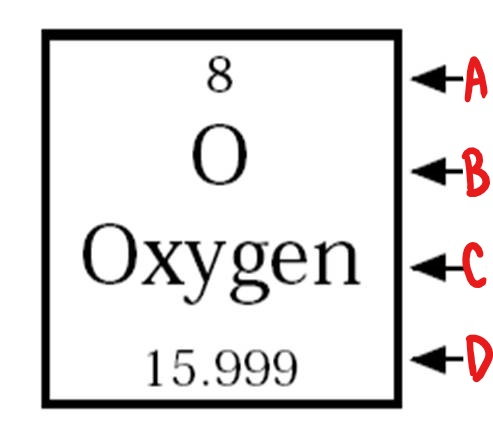
B
chemical symbol
20
New cards
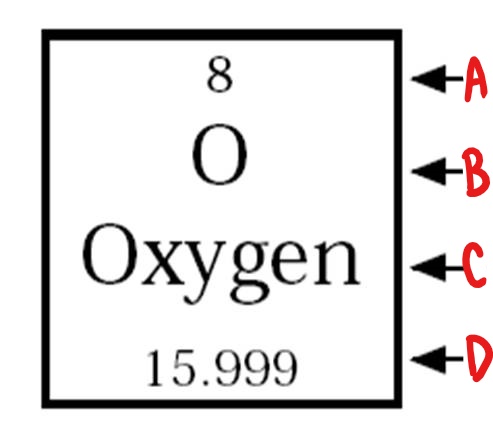
C
element name
21
New cards
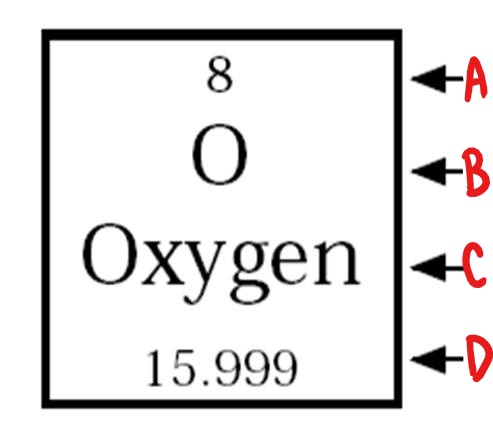
D
atomic mass
22
New cards
Elements on the periodic table are organized in order of ___.
atomic number
23
New cards
periods of elements
rows that tell you the energy level
24
New cards
group/families of elements
columns that tell you the number of valence electrons
25
New cards
What do Lewis Dot diagrams represent?
valence electrons
26
New cards
isotopes
atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons
27
New cards
compounds
substances formed by bonding two or more elements in definite proportions
28
New cards
compound examples
water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2)
29
New cards
What does the chemical formula show?
the composition of the compound
30
New cards
octet rule
When the energy levels are not filled, atoms tend to react with other atoms to fill them.
31
New cards
chemical bonds
the force that holds together the atoms that make up compounds
32
New cards
Why do atoms form bonds?
to become more stable - they need a full outer shell of electrons
33
New cards
What are the two main types of strong chemical bonds?
ionic bonds and covalent bonds
34
New cards
ionic bonds
bonds in which electrons are transferred from one atom to another
35
New cards
ionic bond example
sodium chloride (table salt)
36
New cards
ions
charged atoms that have lost or gained electrons
37
New cards
Ions of opposite charge ___, forming ionic bonds.
attract strongly
38
New cards
covalent bonds
bonds in which electrons are shared between atoms
39
New cards
covalent bond example
methane
40
New cards
polar covalent bond
non-equal sharing of electrons
41
New cards
non-polar covalent bond
equal sharing of electrons
42
New cards
hydrophilic
water loving, ionic compounds, polar covalent
43
New cards
hydrophilic examples
salt, sugar, water
44
New cards
hydrophobic
water fearing, non-polar covalent
45
New cards
hydrophobic examples
oil, fats, waxes
46
New cards
molecules
two or more atoms bonded together
47
New cards
molecule examples
O2, H2