Psych unit 1- Ap test review
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
168 Terms
Sensation
the process of the sensory organs transforming physical energy into neurological impulses the brain interprets as the five senses of vision, smell, taste, touch, and hearing
Transduction
the process of converting outside stimuli, such as light, from a sensory signal into neural activity
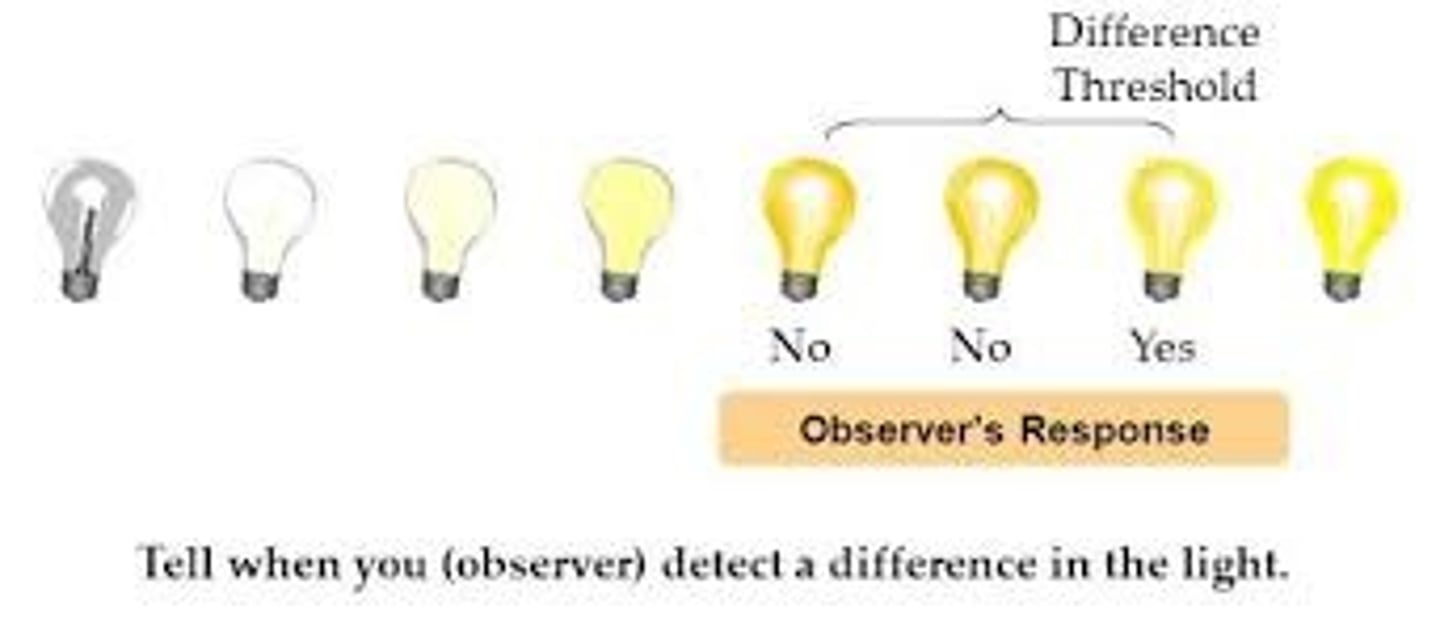
Absolute threshold
the minimum intensity of stimulation needed to detect a sensation 50 percent of the time

Just-noticeable difference
the amount a stimulus must be changed in order for a difference to be noticeable
Sensory adaptation
tendency of sensory receptor cells to become less responsive to a stimulus that is unchanging
Weber's law
to be perceived as different, two stimuli must differ by a constant minimum percentage
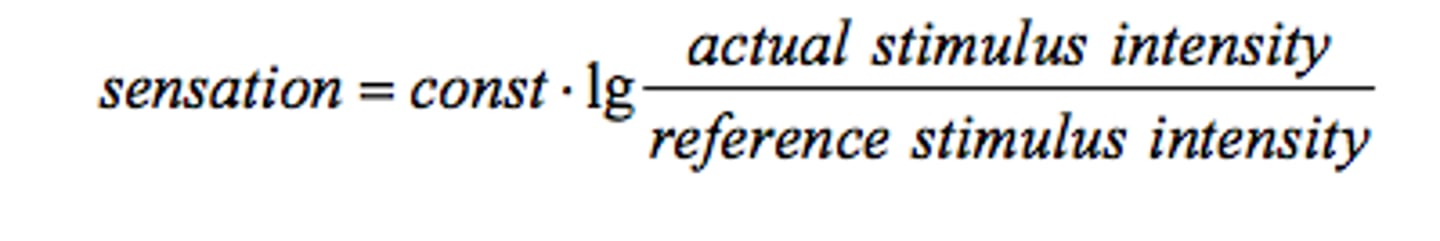
Sensory interaction
the principle that one sense may influence another, as when the smell of food influences its taste

Synesthesia
a neurological condition in which information meant to stimulate one of your senses stimulates several of your senses (e.g., hearing the word "cat" but perceiving the color green)

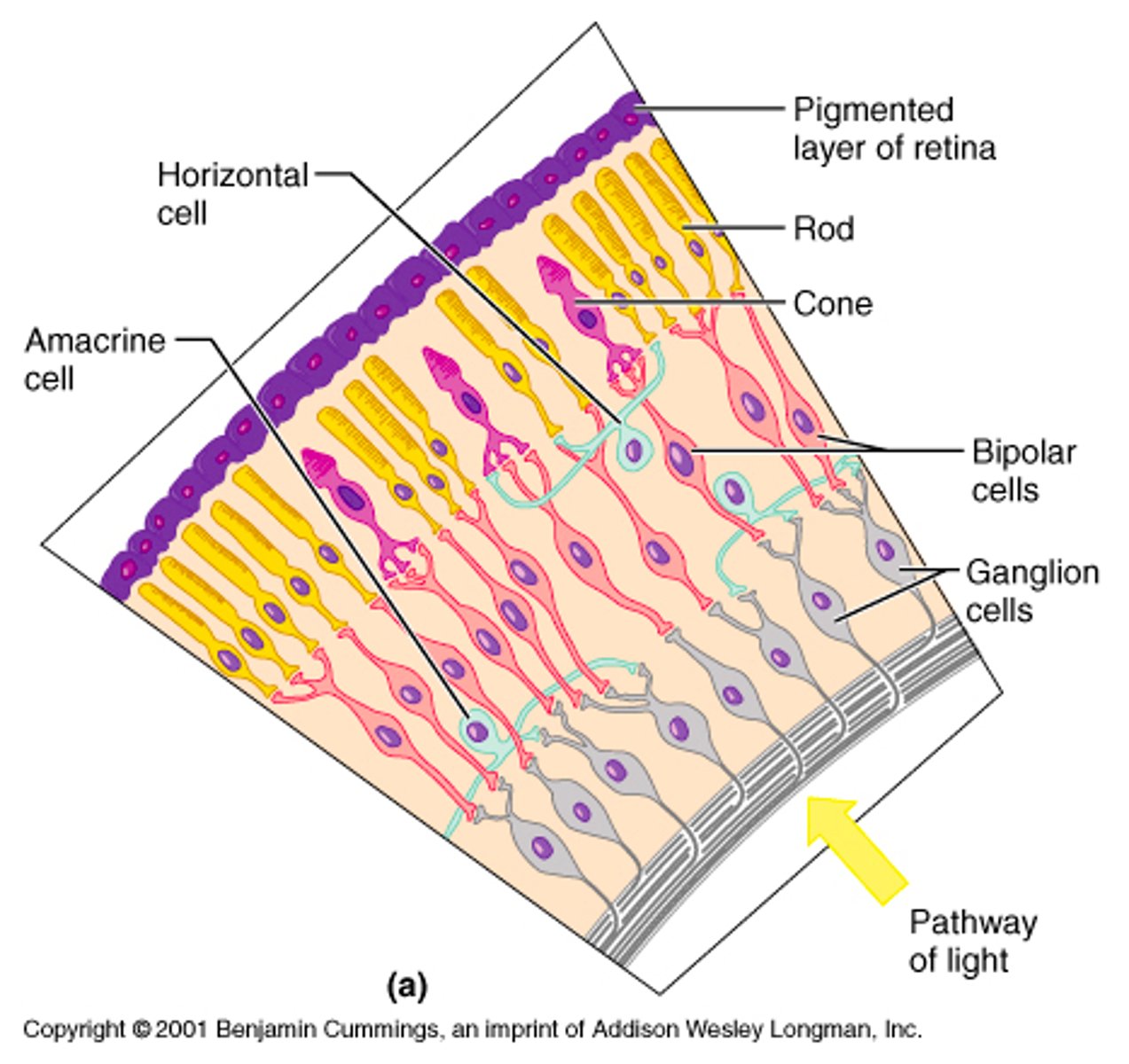
Retina
the light-sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing the receptor rods and cones plus layers of neurons that begin the processing of visual information
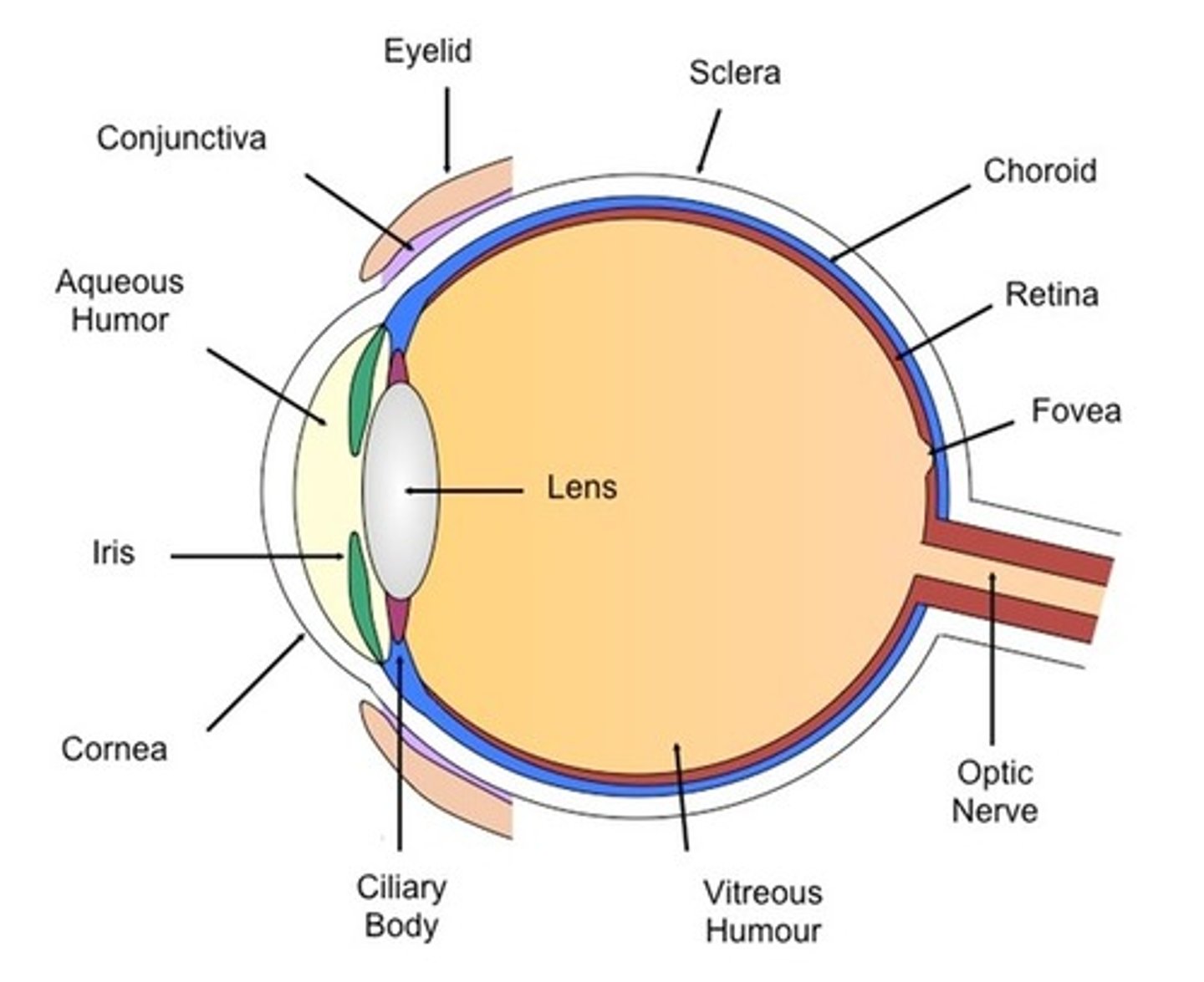
Blind spot
the point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye, creating a "blind" spot because no receptor cells are located there
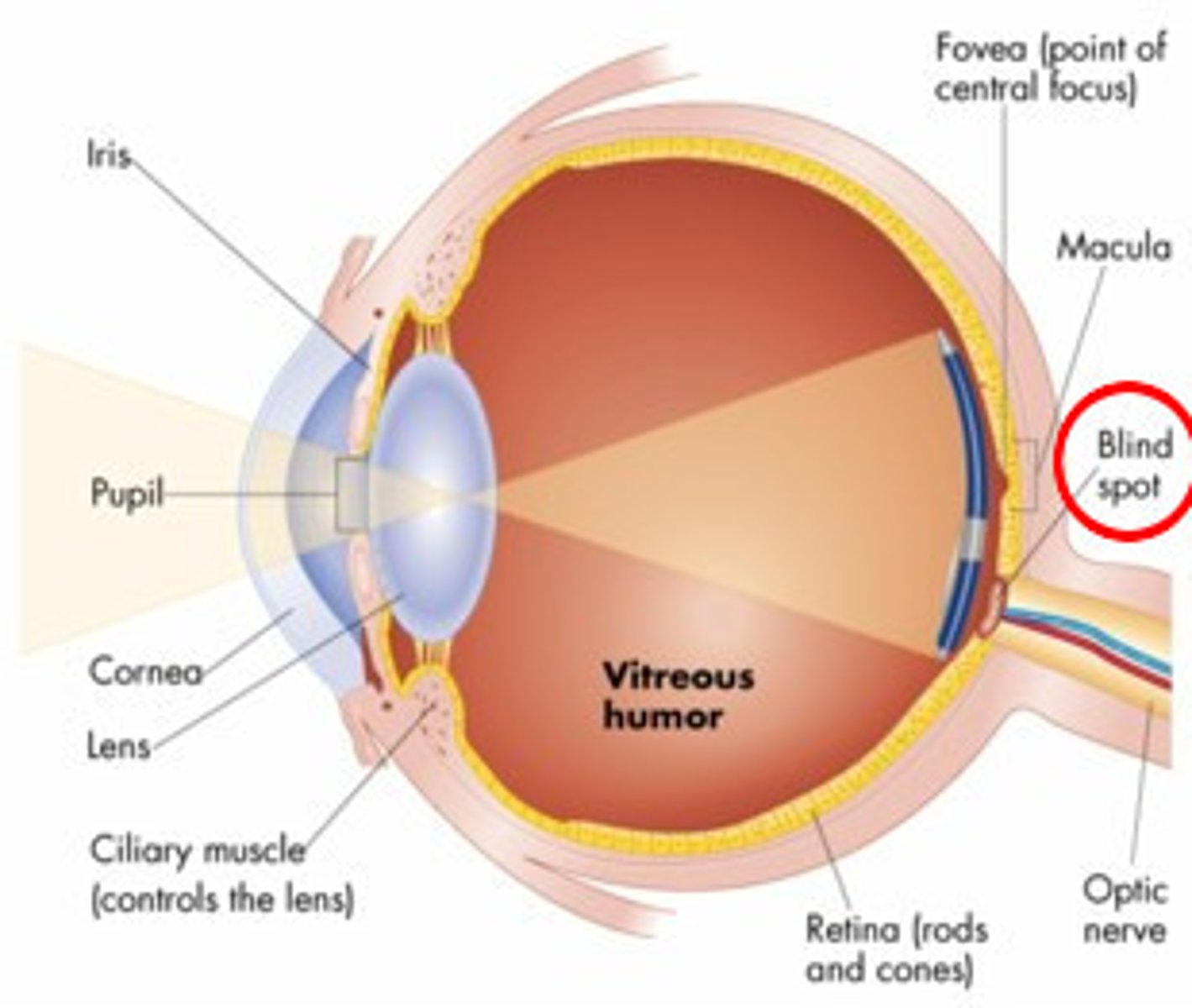
Visual nerve
the optic nerve; comprised of millions of nerve fibers that send visual messages to the brain
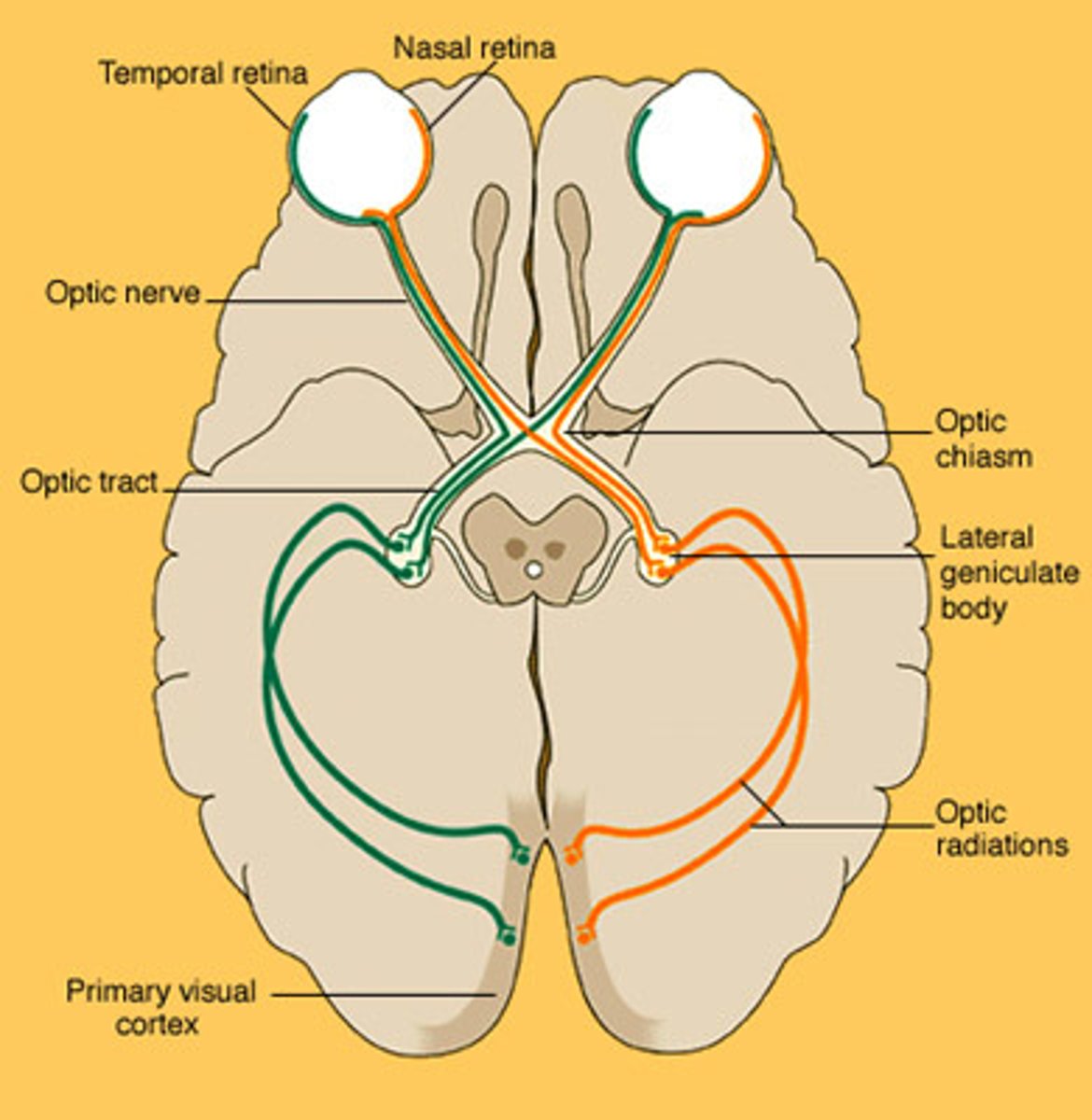
Lens
the transparent structure behind the pupil that changes shape to help focus images on the retina
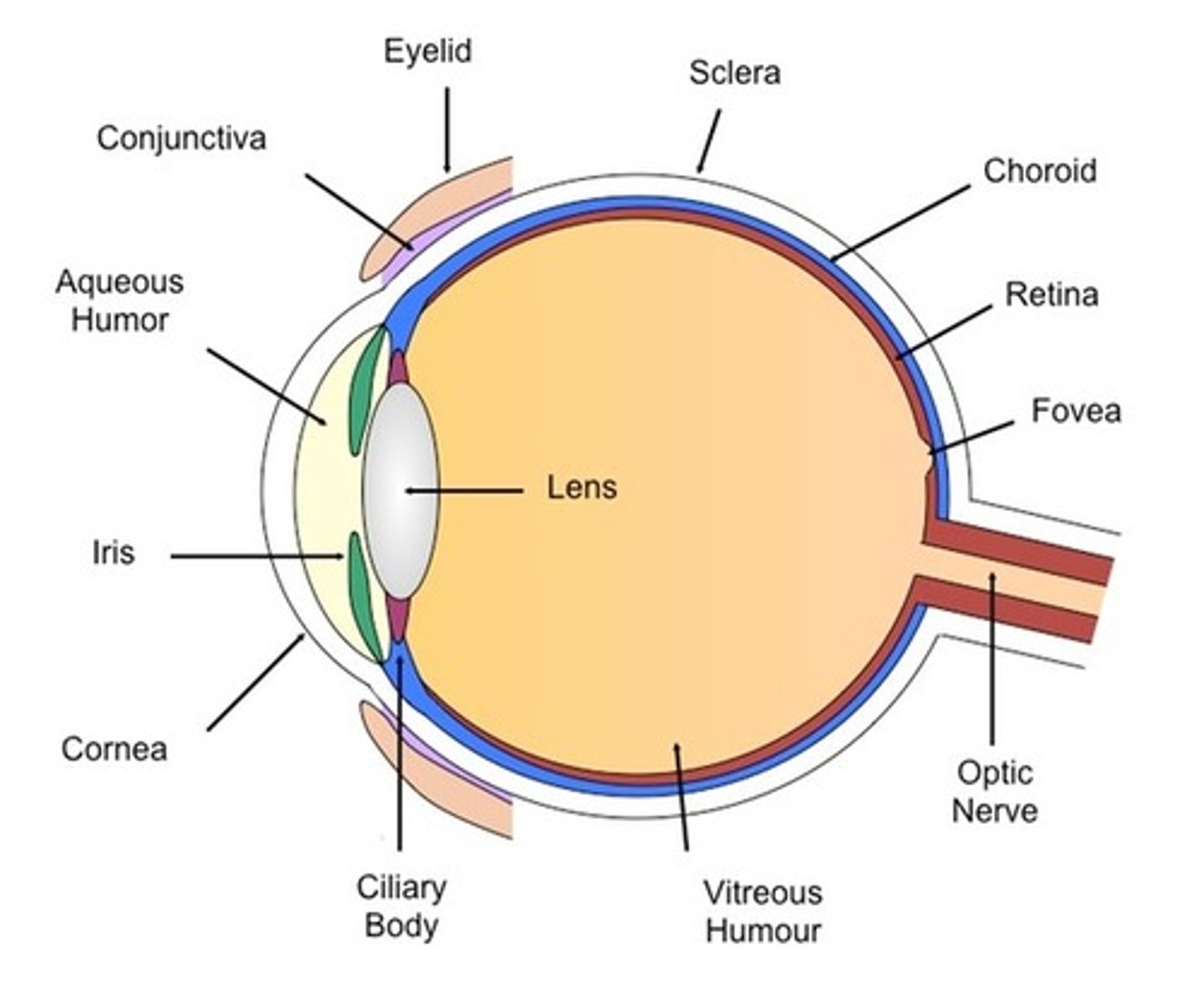
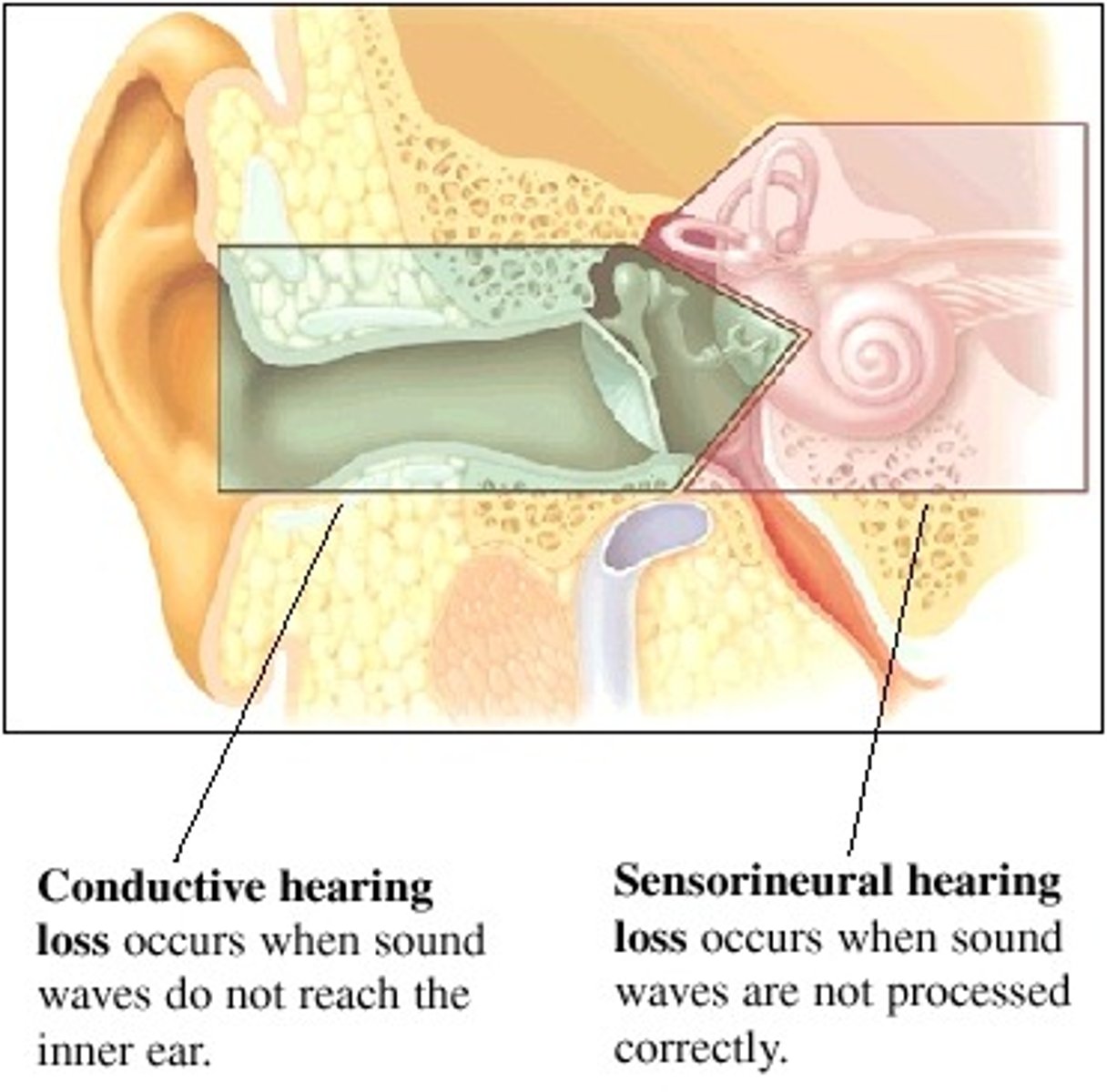
Sensorineural deafness
deafness that usually results from damage to the inner ear or to the auditory nerve
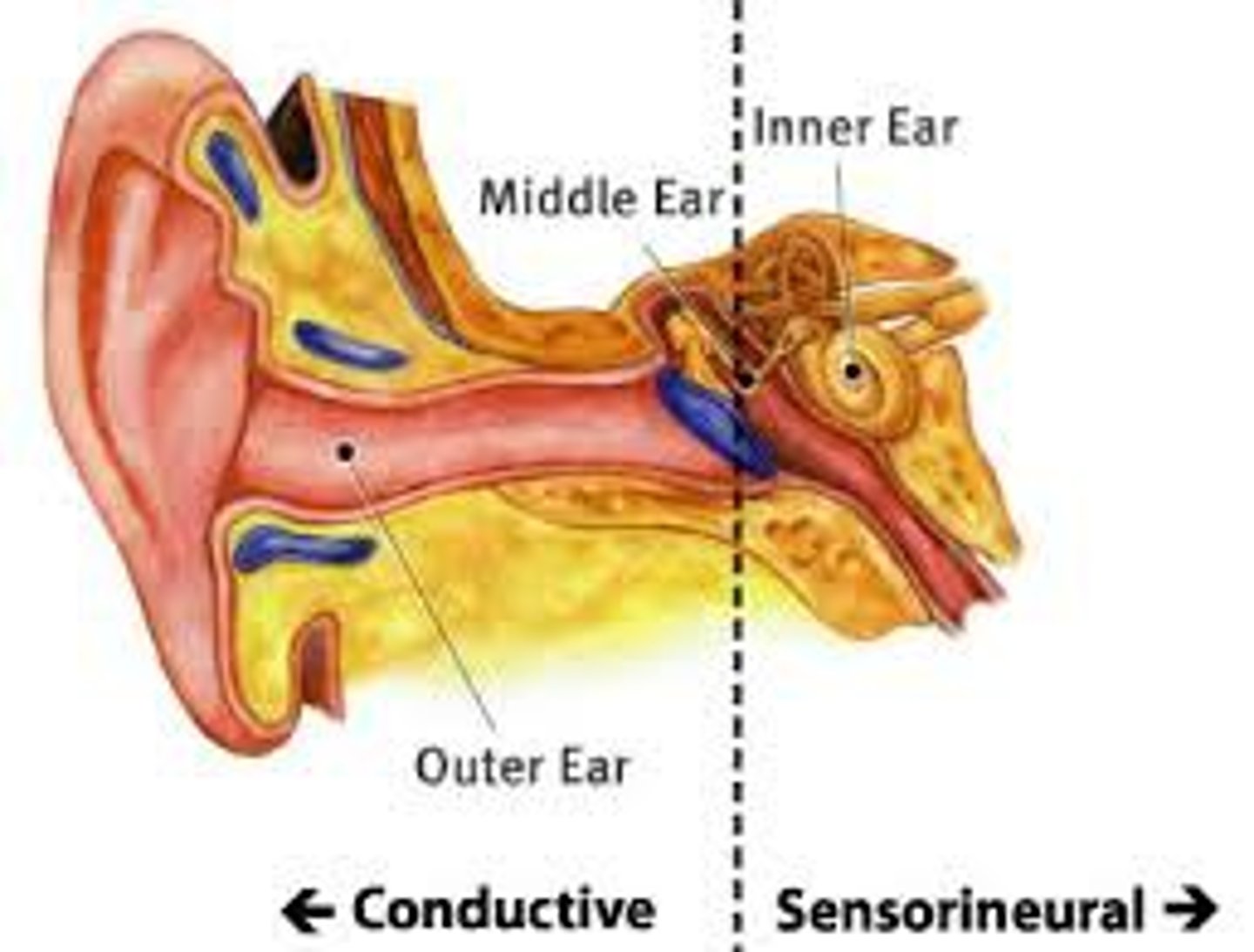
Olfactory system
the sensory system for smell
Thalamus
the brain's sensory control center, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
Pheromones
chemical signals released by an animal that communicate information and affect the behavior of other animals of the same species

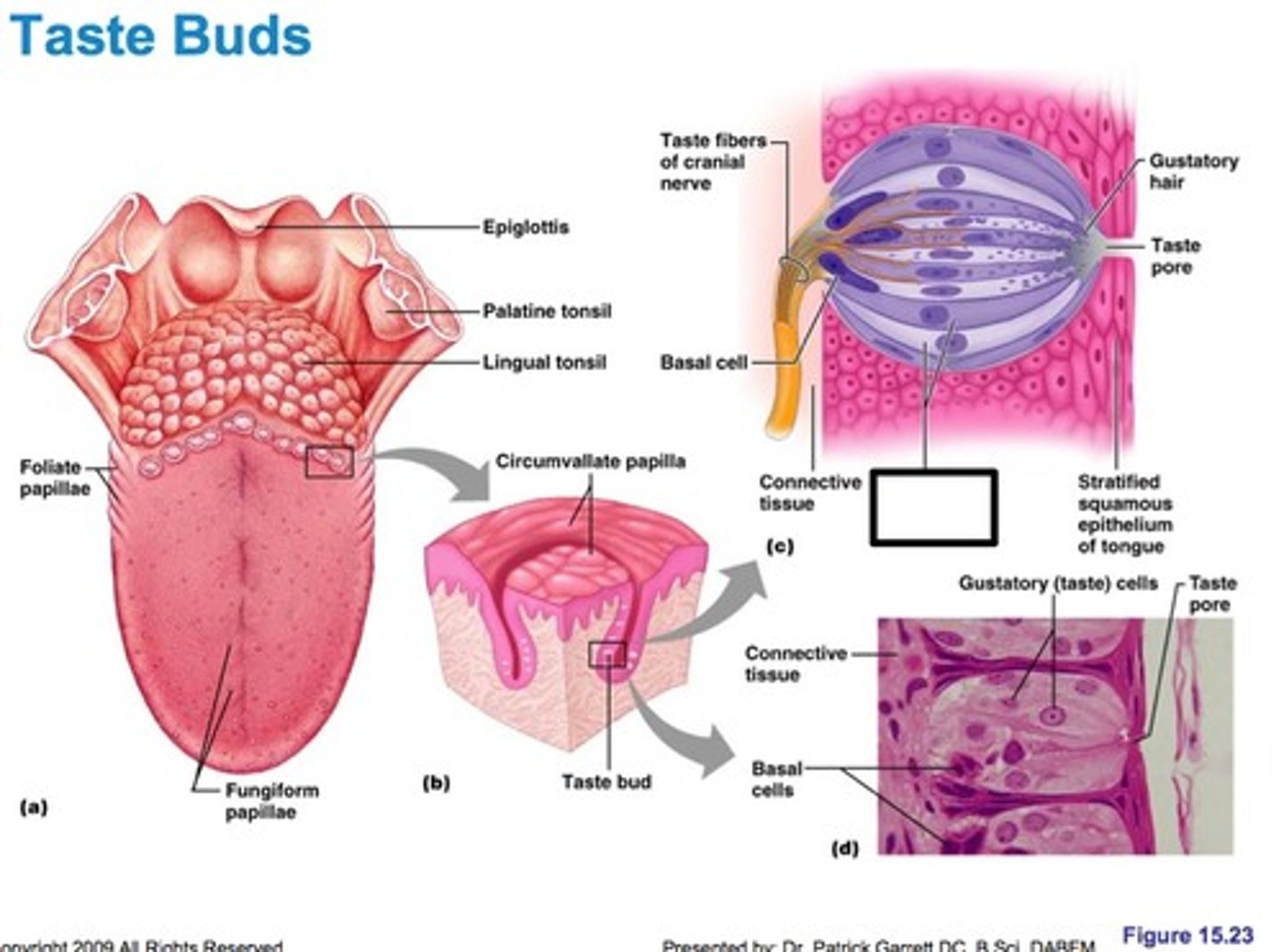
Gustation
the sensation of taste resulting from the action of chemicals on the taste buds
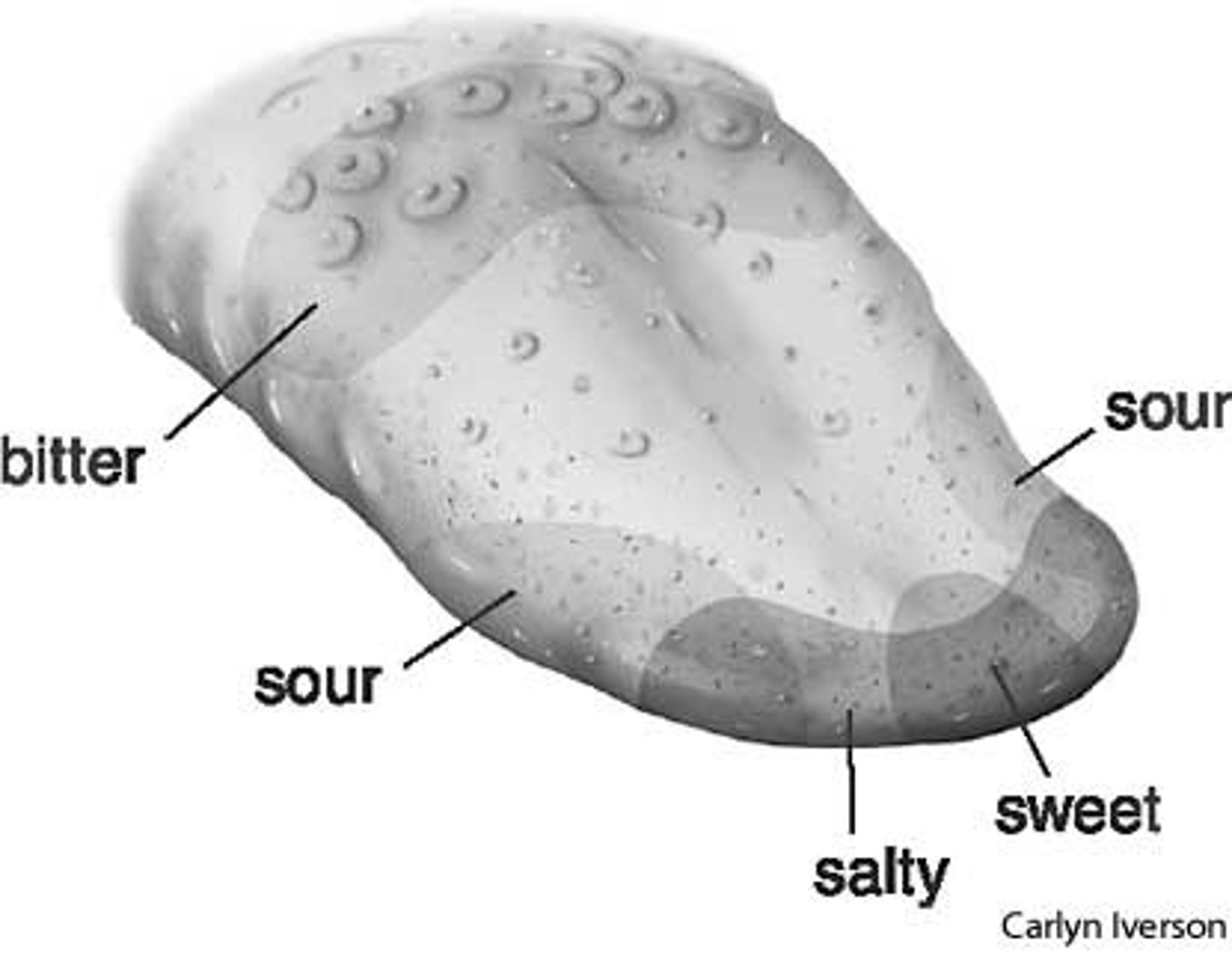
Taste receptors
chemical receptors on the tongue that decode molecules of food or drink to identify them (sweet, salty, bitter, oleogustus (oily, fatty), and umami)
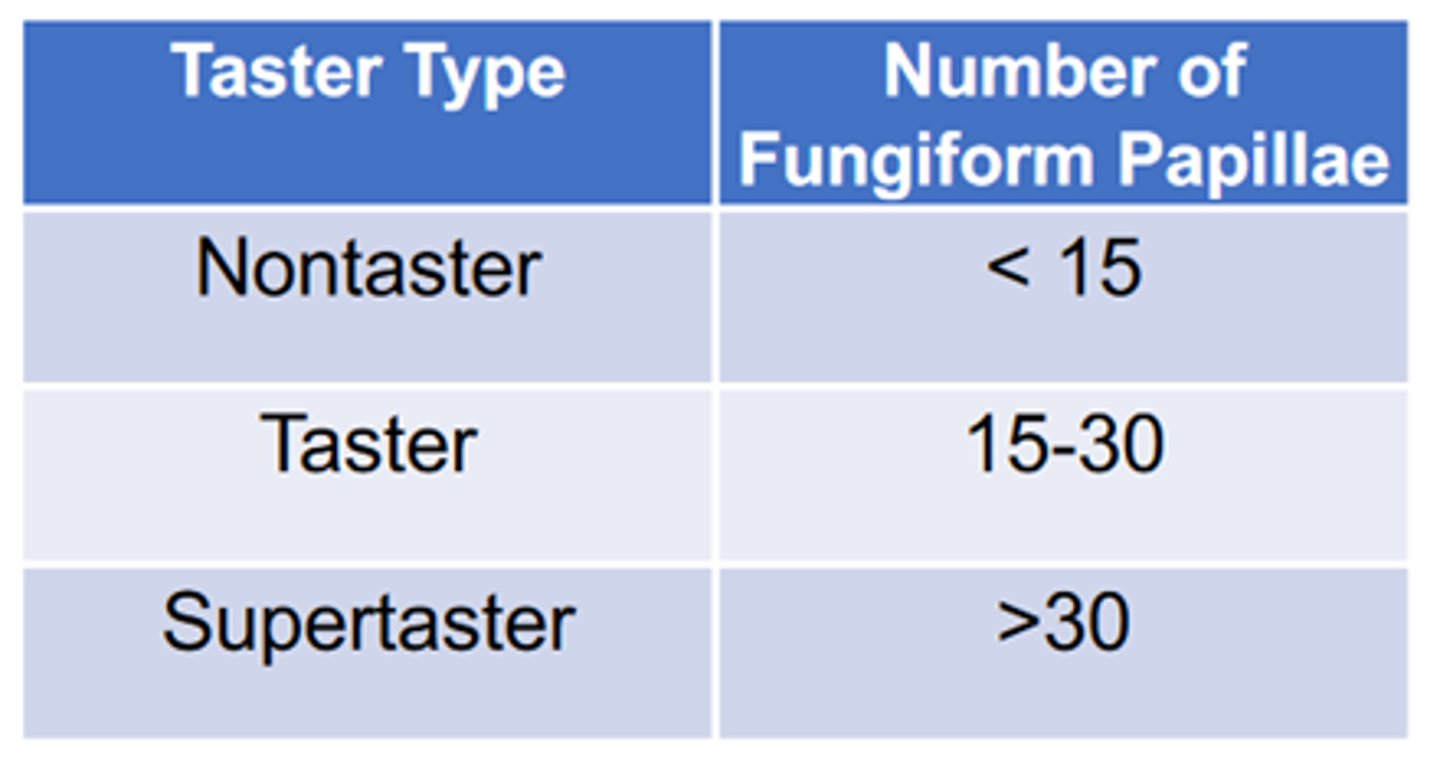
Supertasters
people with the most number of tastebuds and have the highest sensitivity to all tastes, as well as mouth sensations in general
Medium Tasters
people with an average number of taste buds; they represent 50% of the population
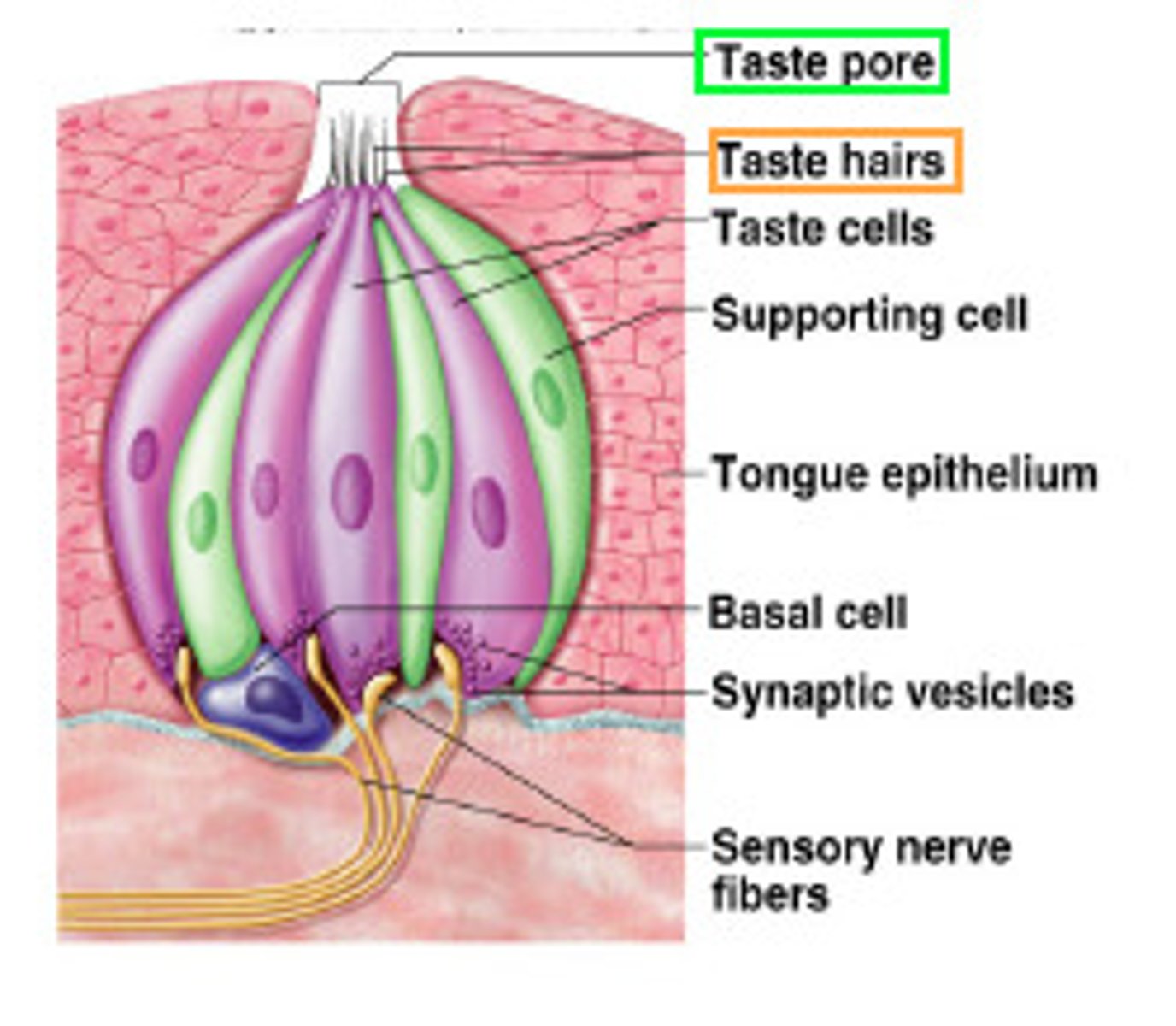
Nontasters
people with fewer tastebuds who are not so sensitive to taste; they prefer sweeter or fattier foods to maximize taste
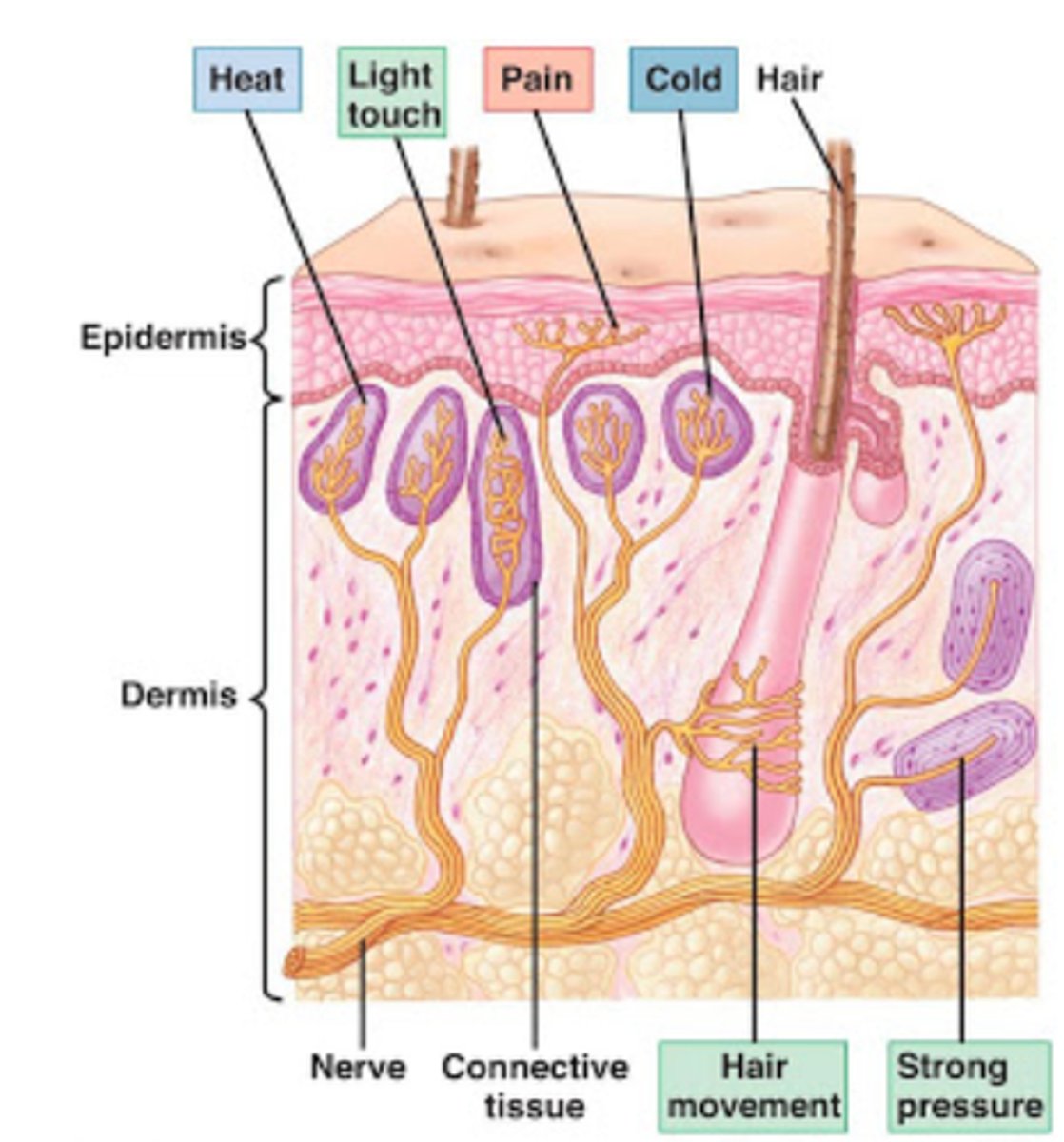
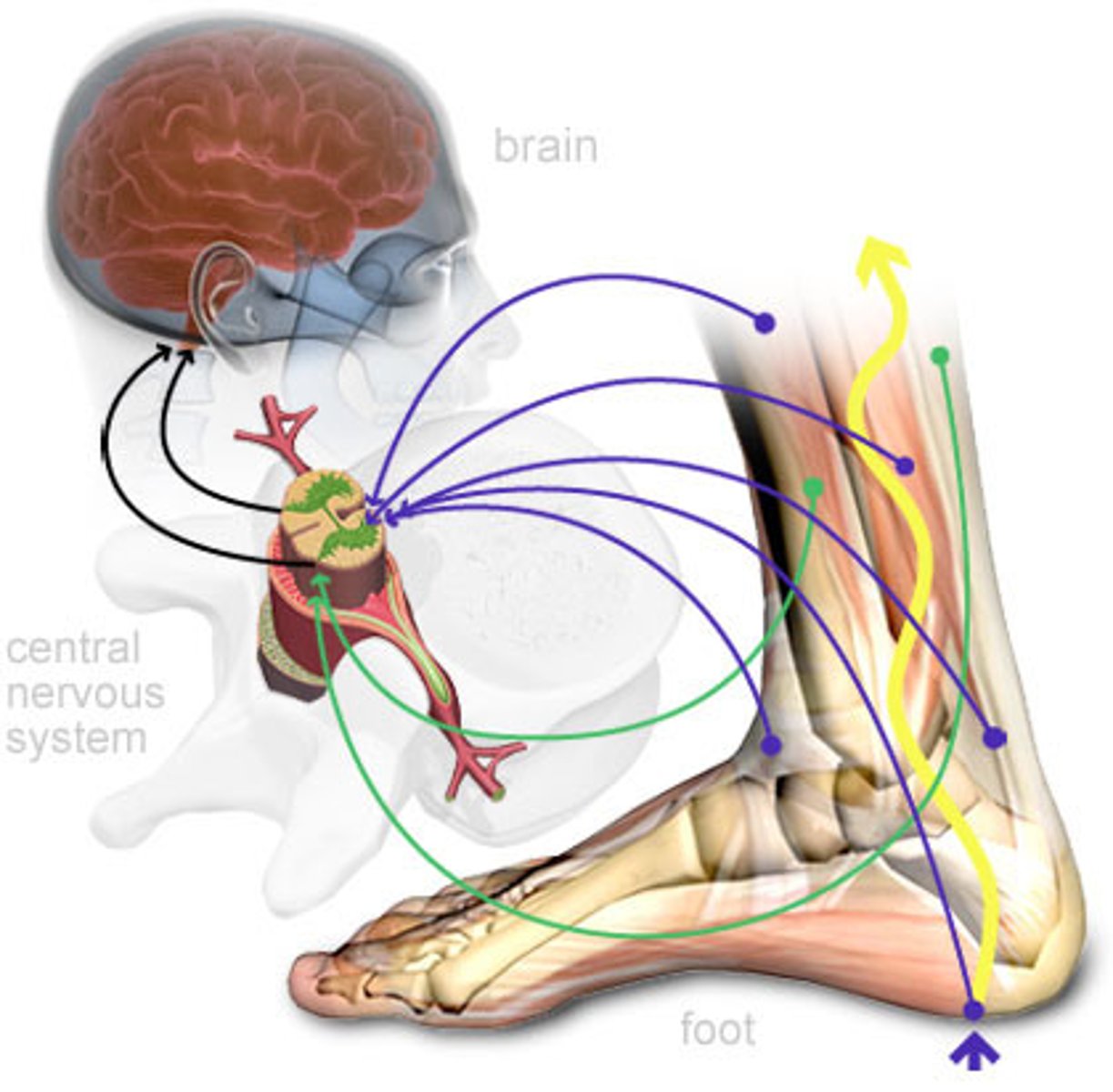
Warm/cold receptors
thermoreceptors are able to detect heat and cold and are found throughout the skin in order to allow sensory reception throughout the body
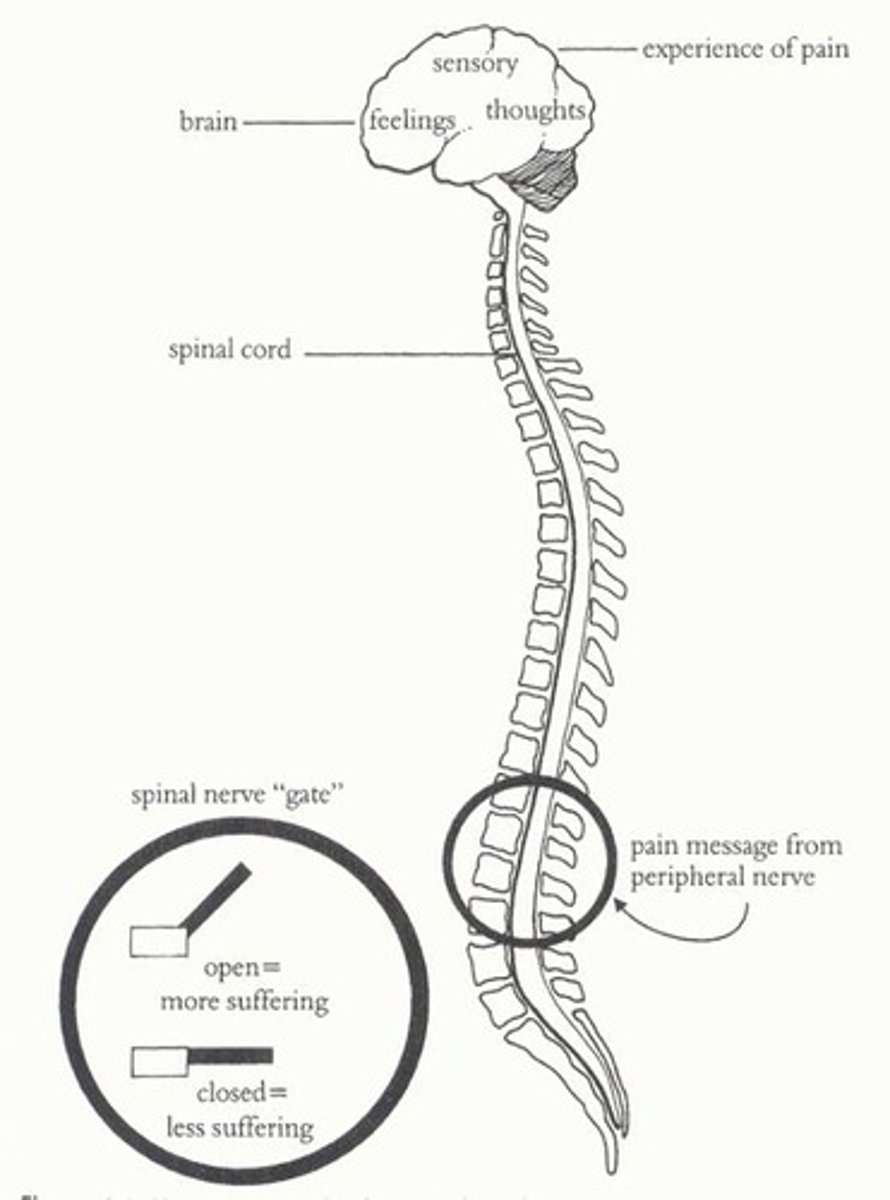
Gate control theory
theory that explains how spinal nerves block or allow pain signals to pass to the brain
Phantom limb
perceived sensation, following amputation of a limb, that the limb still exists
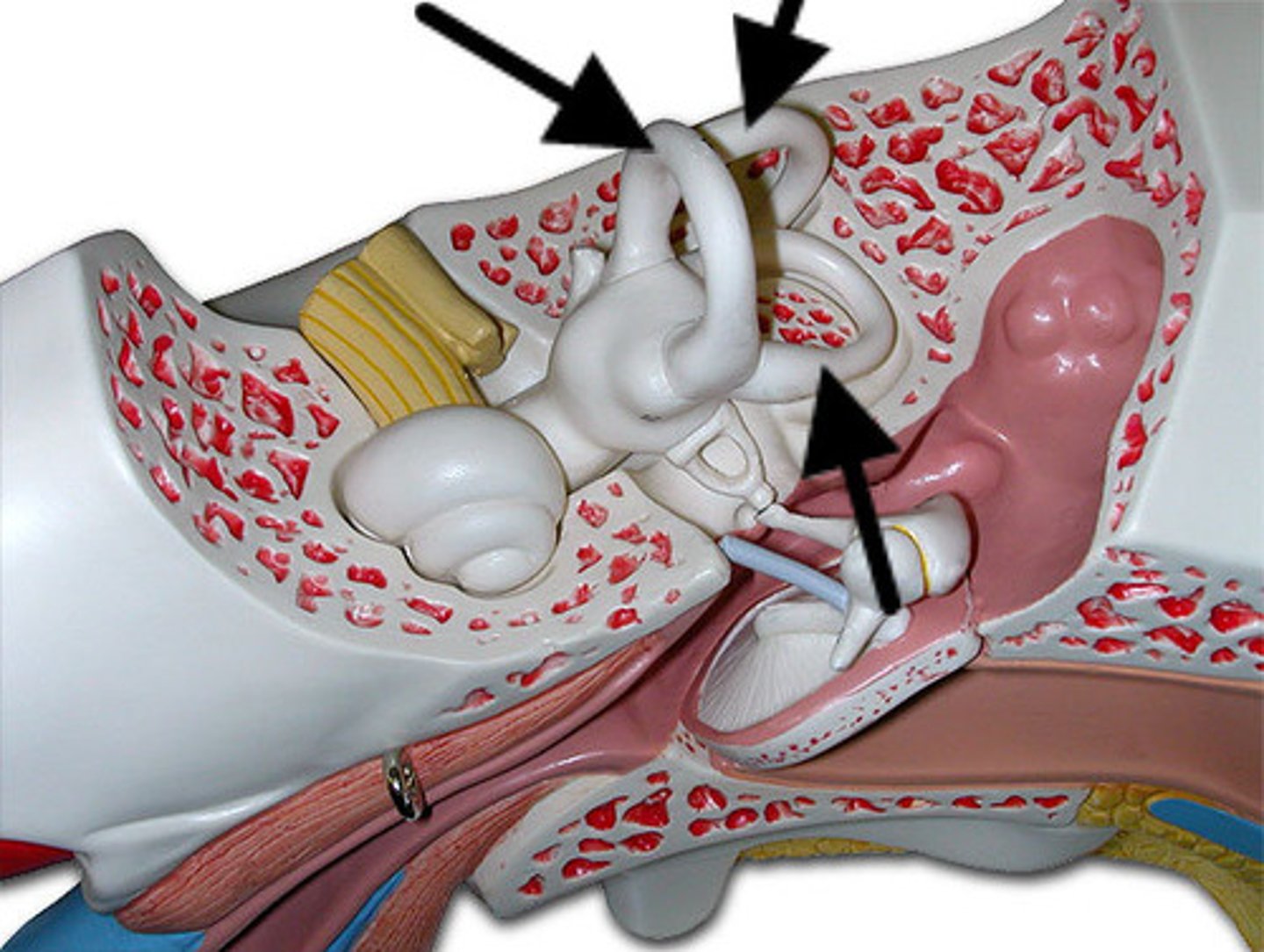
Vestibular sense
the sense of body movement and position, including the sense of balance

Semicircular canals
three tiny, fluid-filled tubes in the inner ear that help a person maintain balance
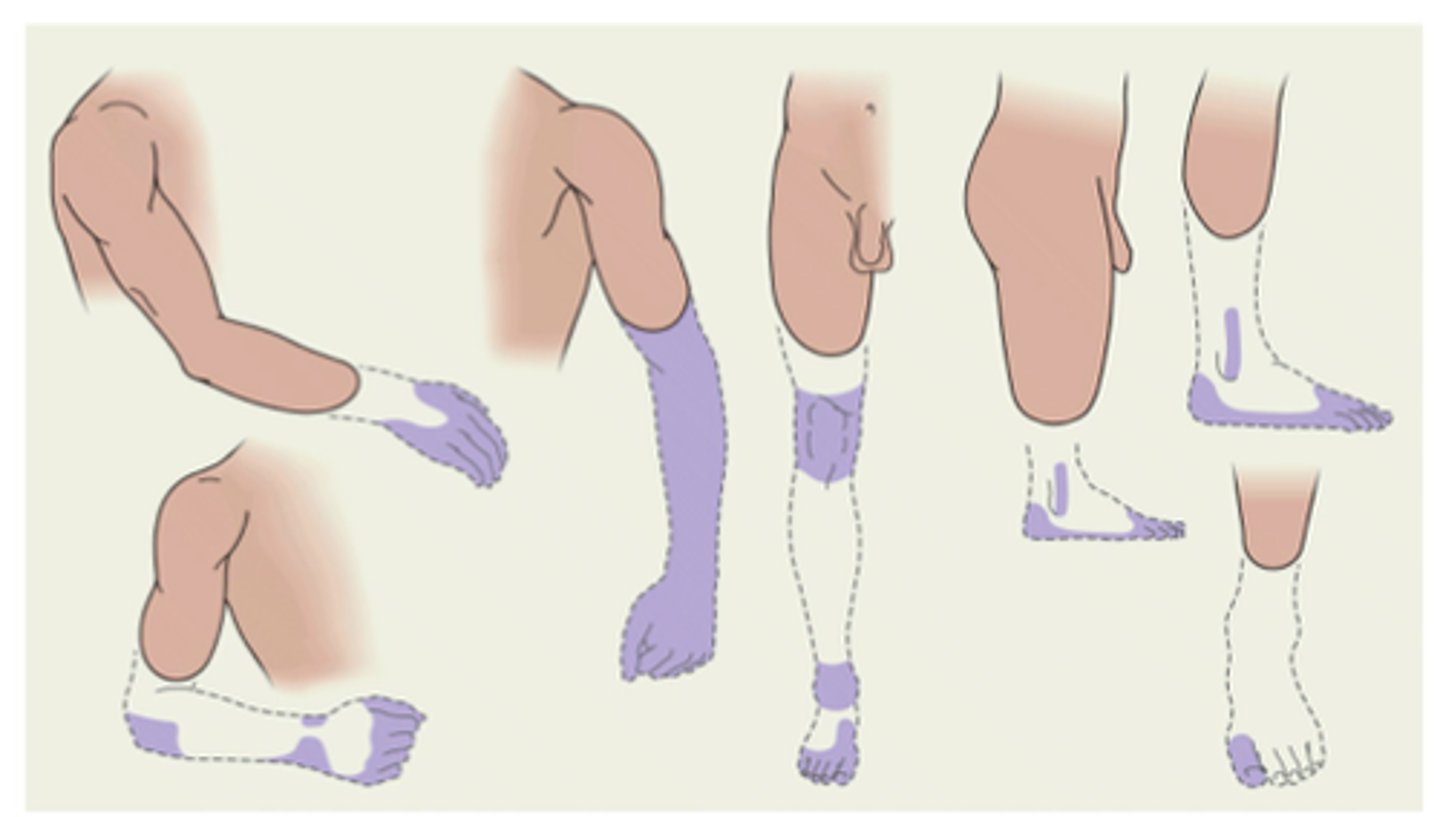
Kinesthesis
the sense that provides information about the position and movement of individual body parts
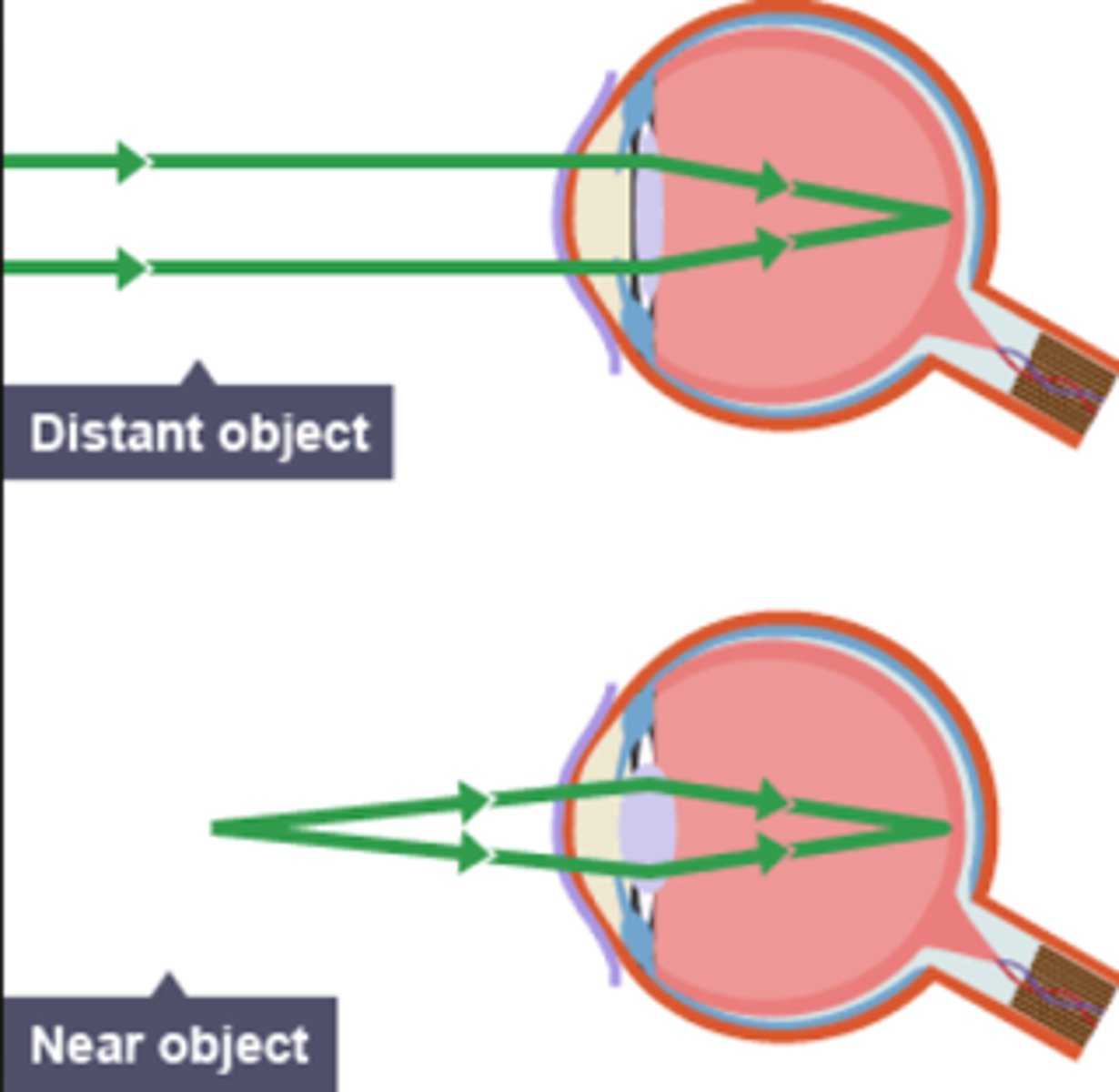
Accommodation
the process by which the eye's lens changes shape to focus near or far objects on the retina
Nearsightedness
a condition in which nearby objects are seen more clearly than distant objects because distant objects focus in front of the retina
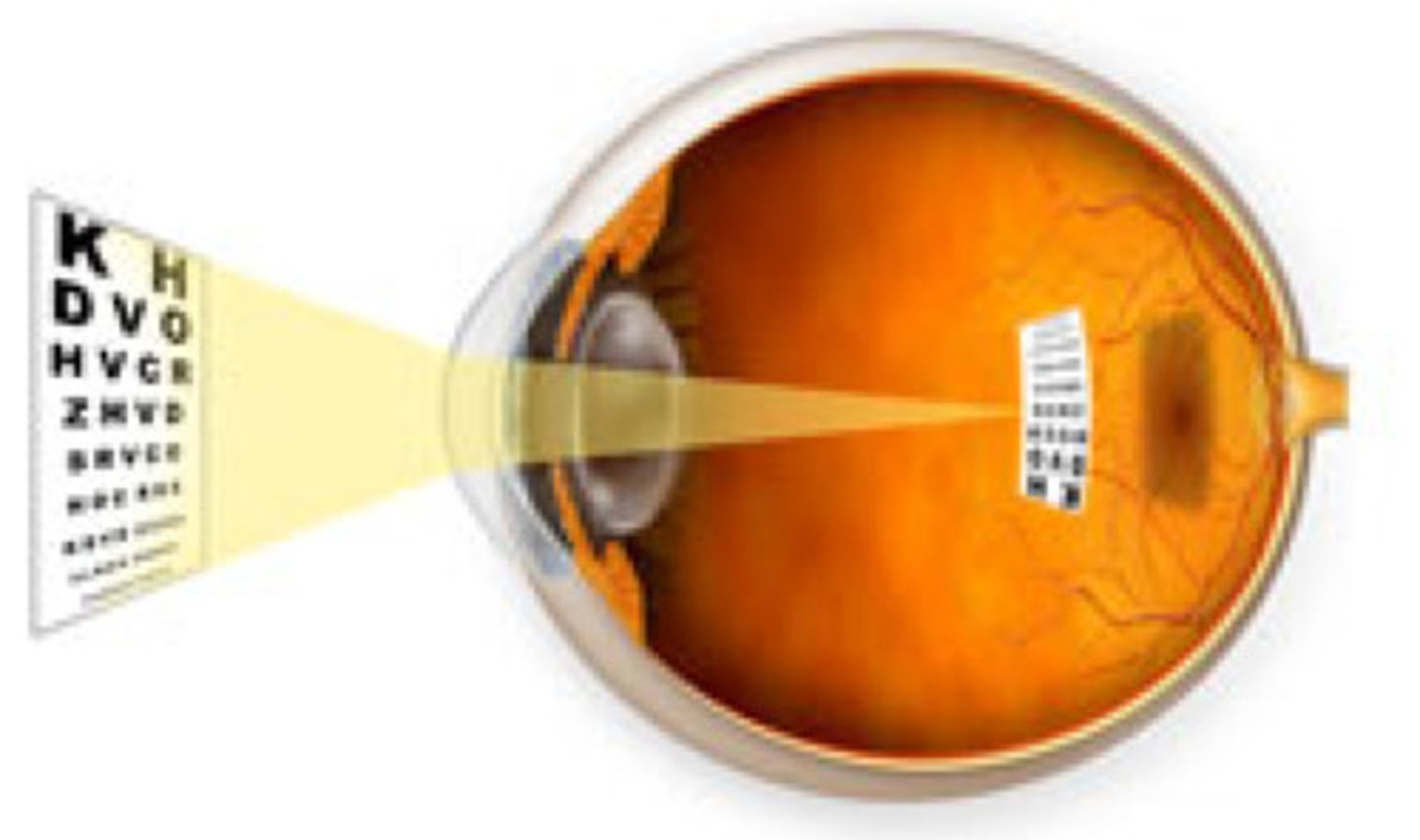
Farsightedness
a condition in which faraway objects are seen more clearly than near objects because the image of near objects is focused behind the retina

Photoreceptors
rods and cones in the eye; they respond to light
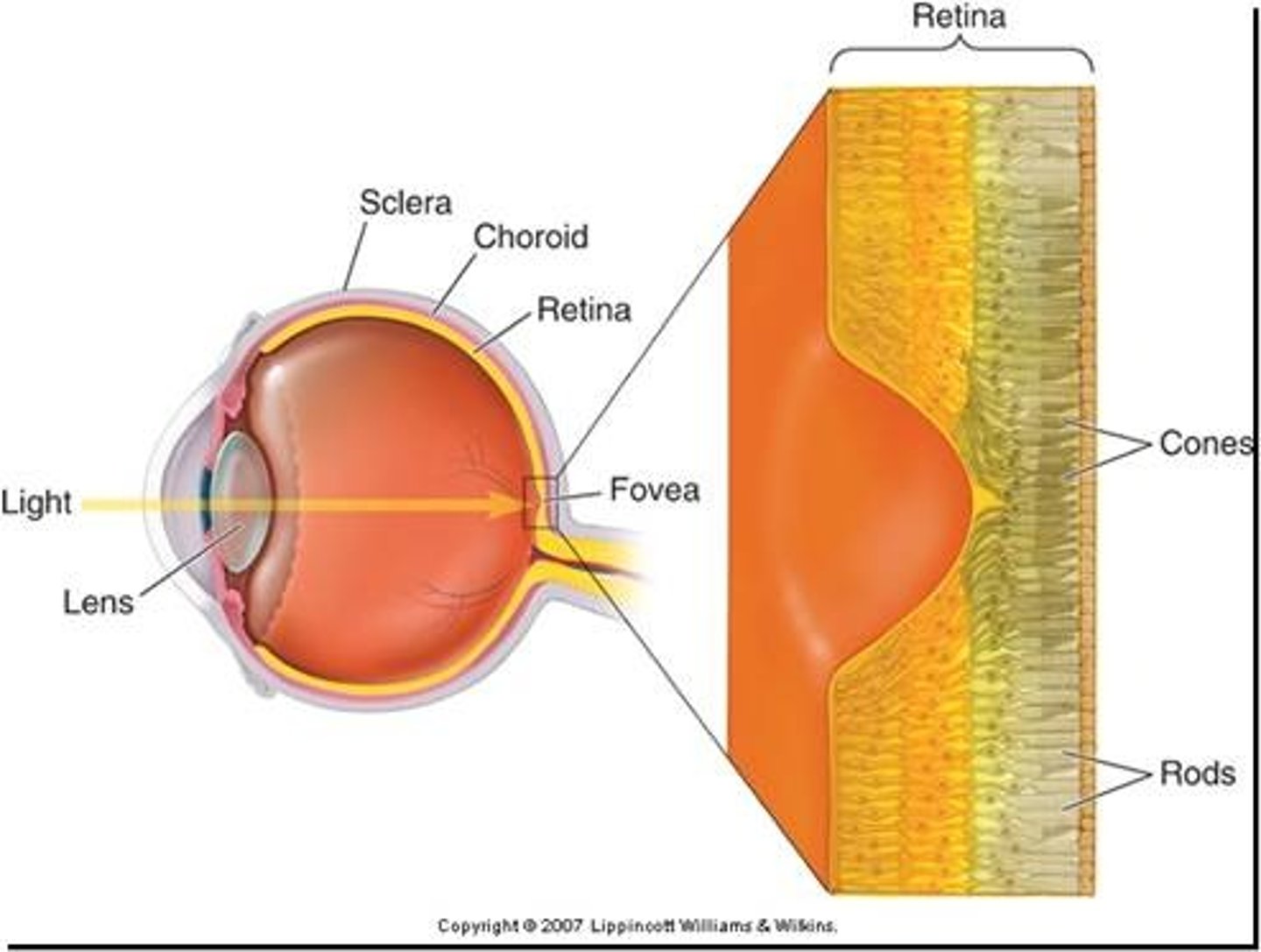
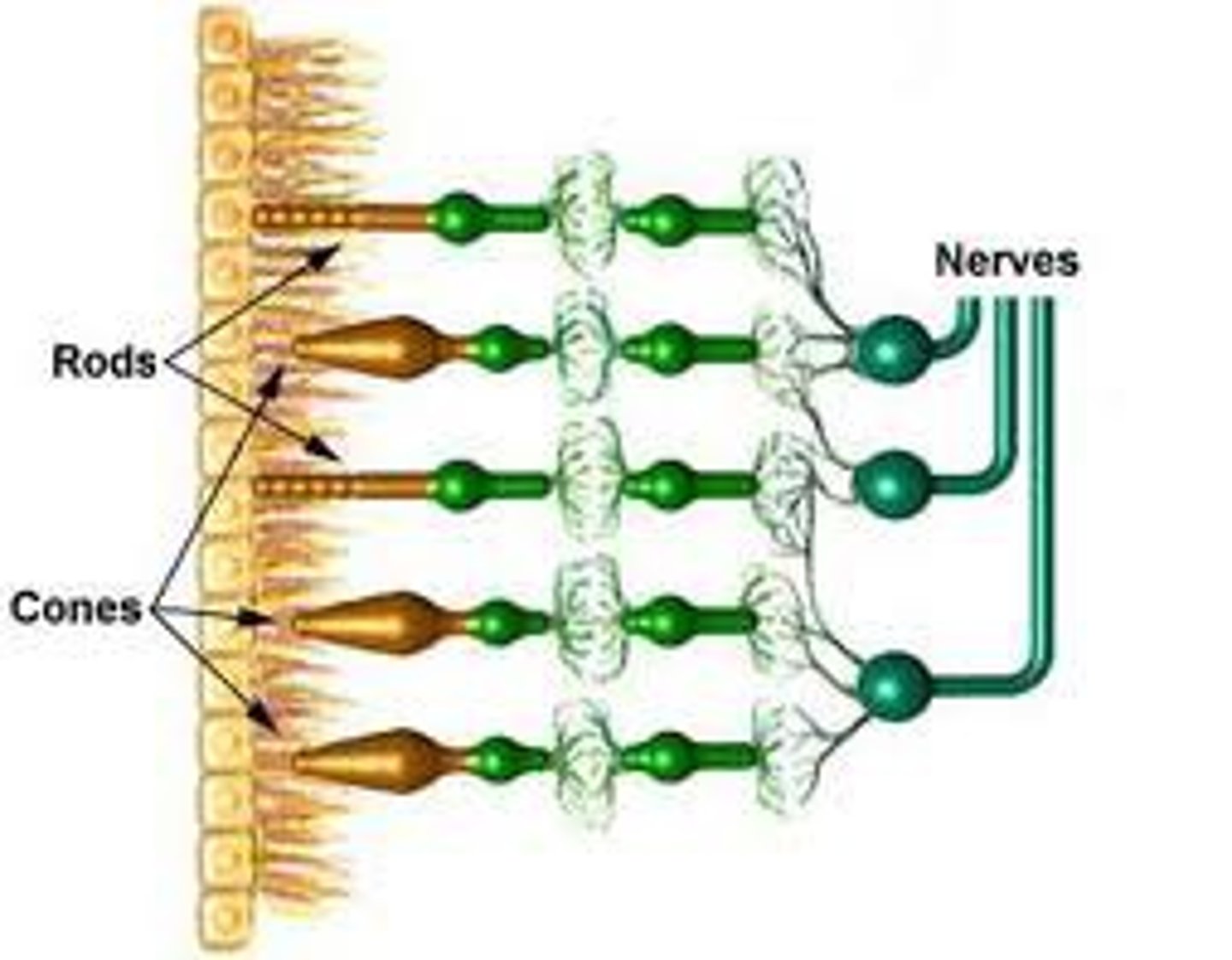
Rods
retinal receptors that detect black, white, and gray; necessary for peripheral and twilight vision, when cones don't respond
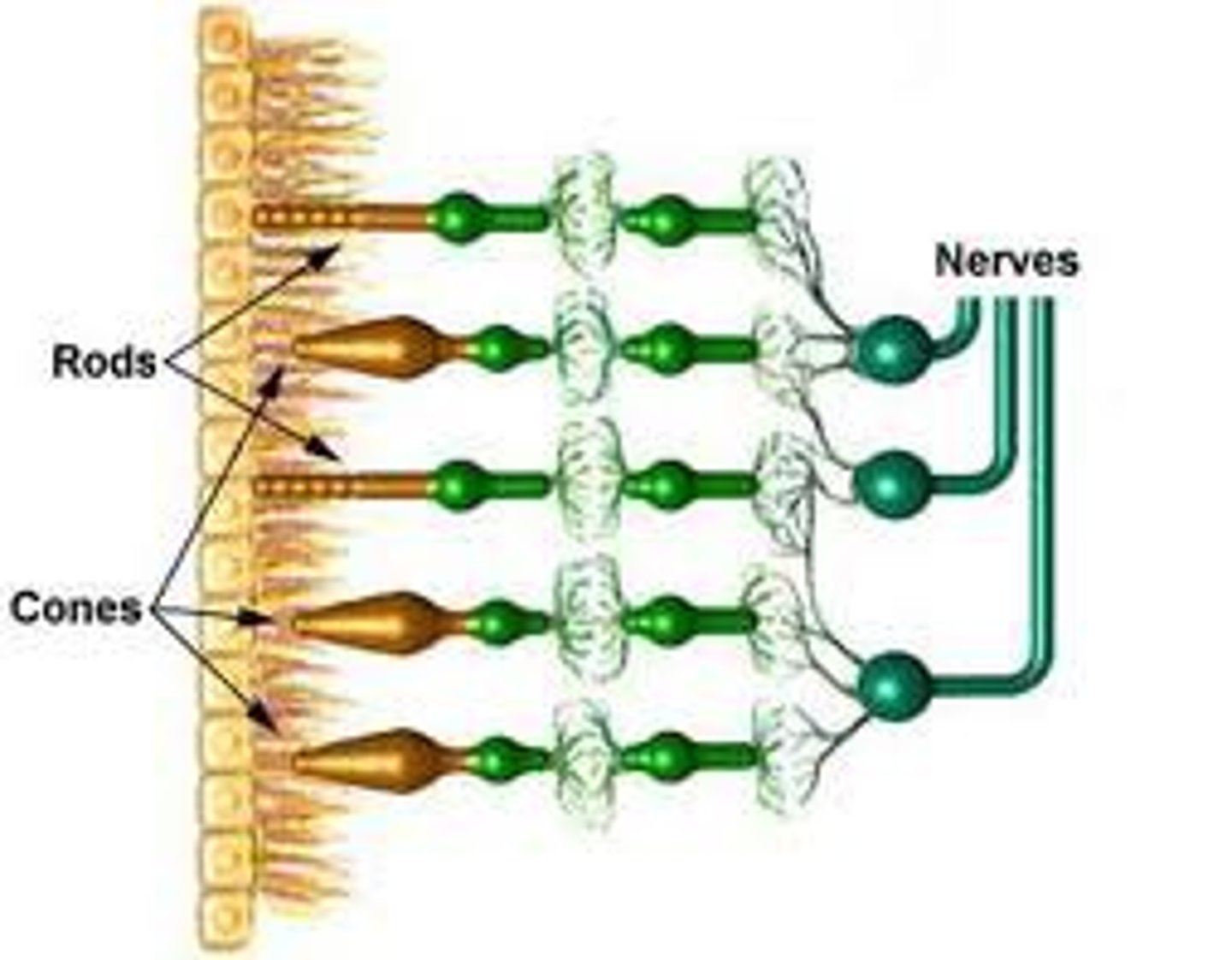
Cones
three types of photoreceptors (blue, green, red) responsible for color vision and color sensitivity
Trichromatic theory
the theory that human eyes only perceive three colors of light: red, blue, and green
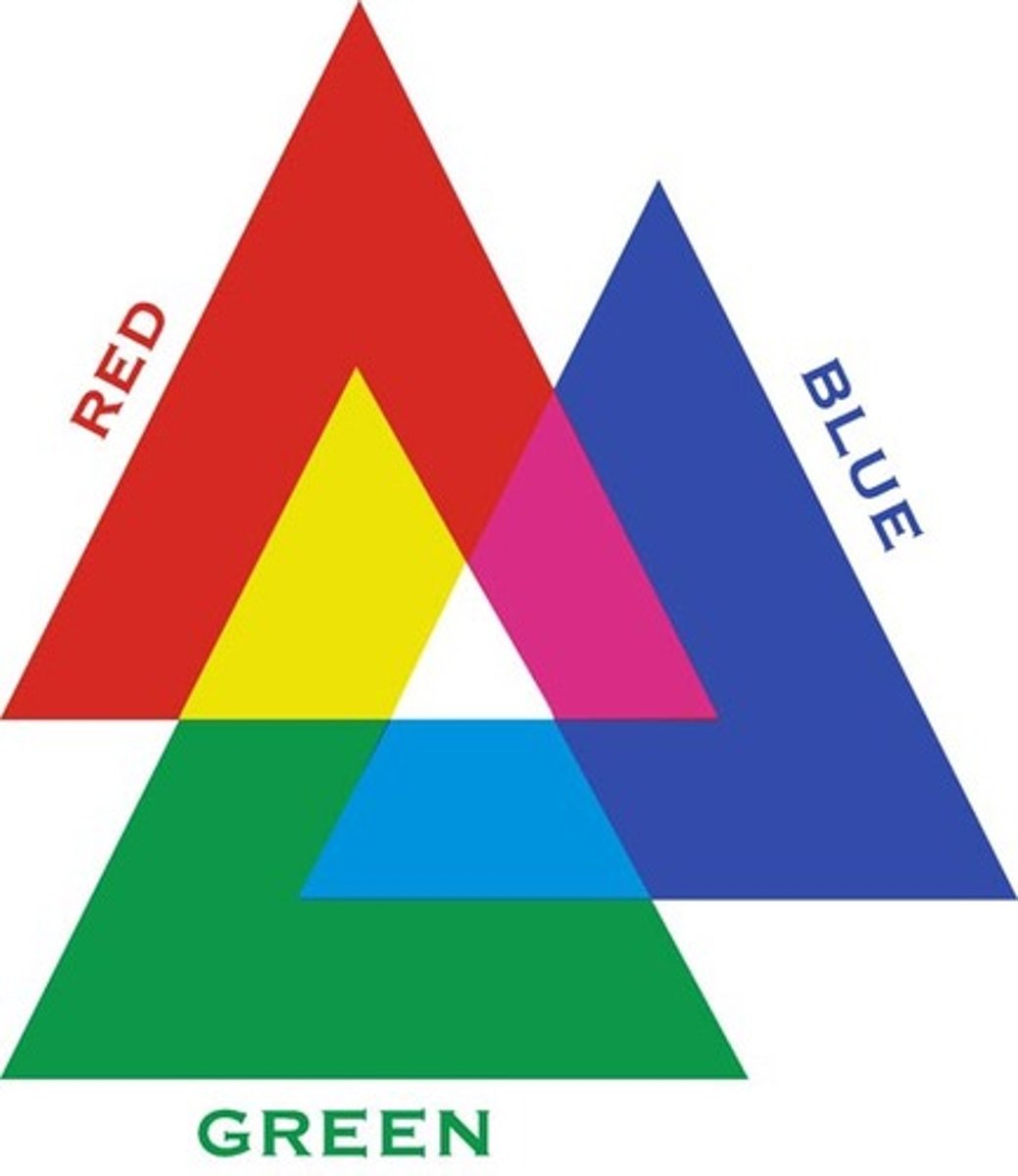
Opponent-process theory
the theory that opposing retinal processes (red-green, yellow-blue, white-black) enable color vision (e.g., some cells are stimulated by green and inhibited by red; others are stimulated by red and inhibited by green)
Afterimages
images that occur when a visual sensation persists for a brief time even after the original stimulus is removed
Ganglion cells
specialized cells behind the bipolar cells whose axons form the optic nerve which takes the information to the brain
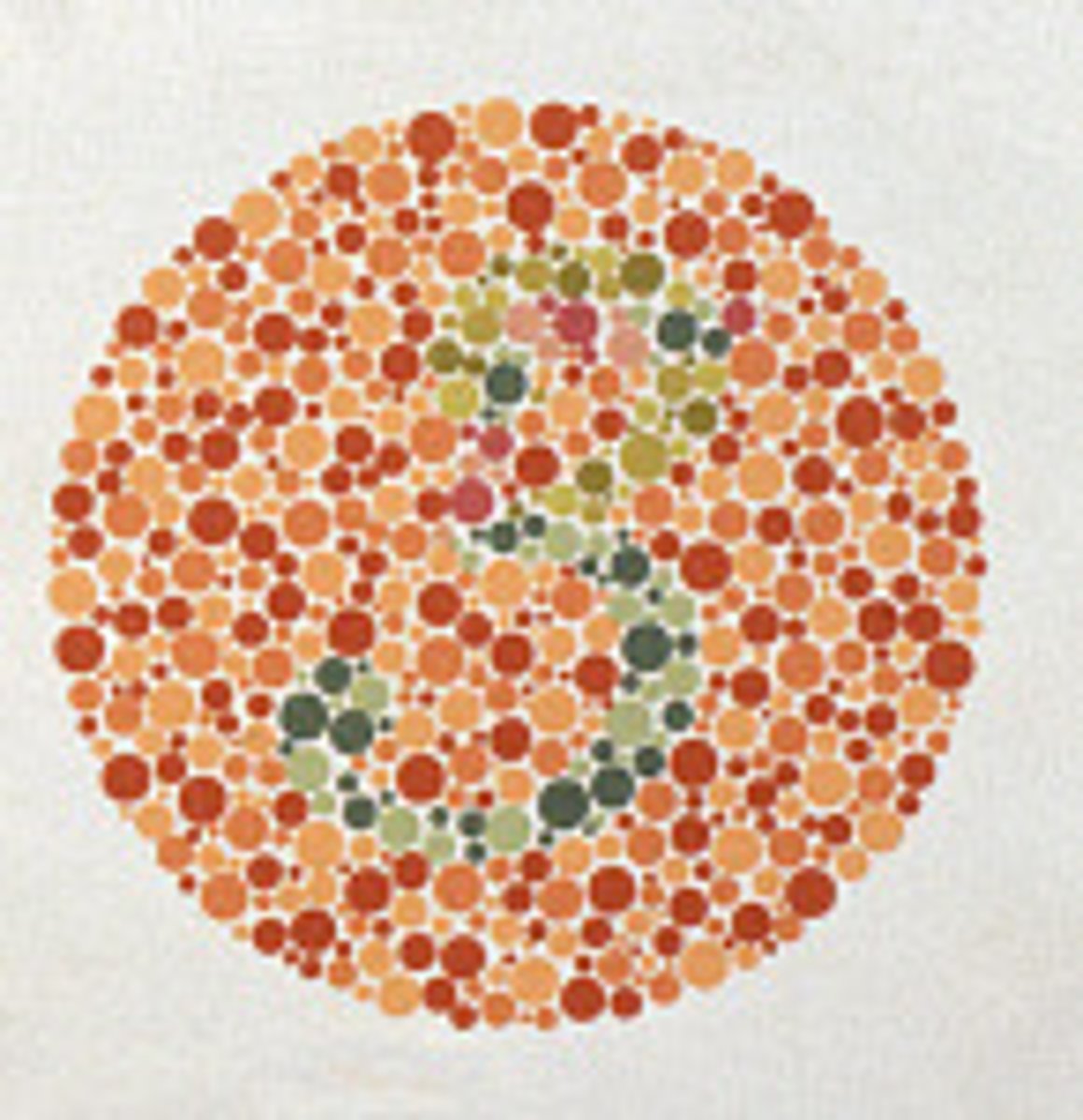
Dichromatism
when only two of the three cone types are present or functional; red and green, for example, may appear the same
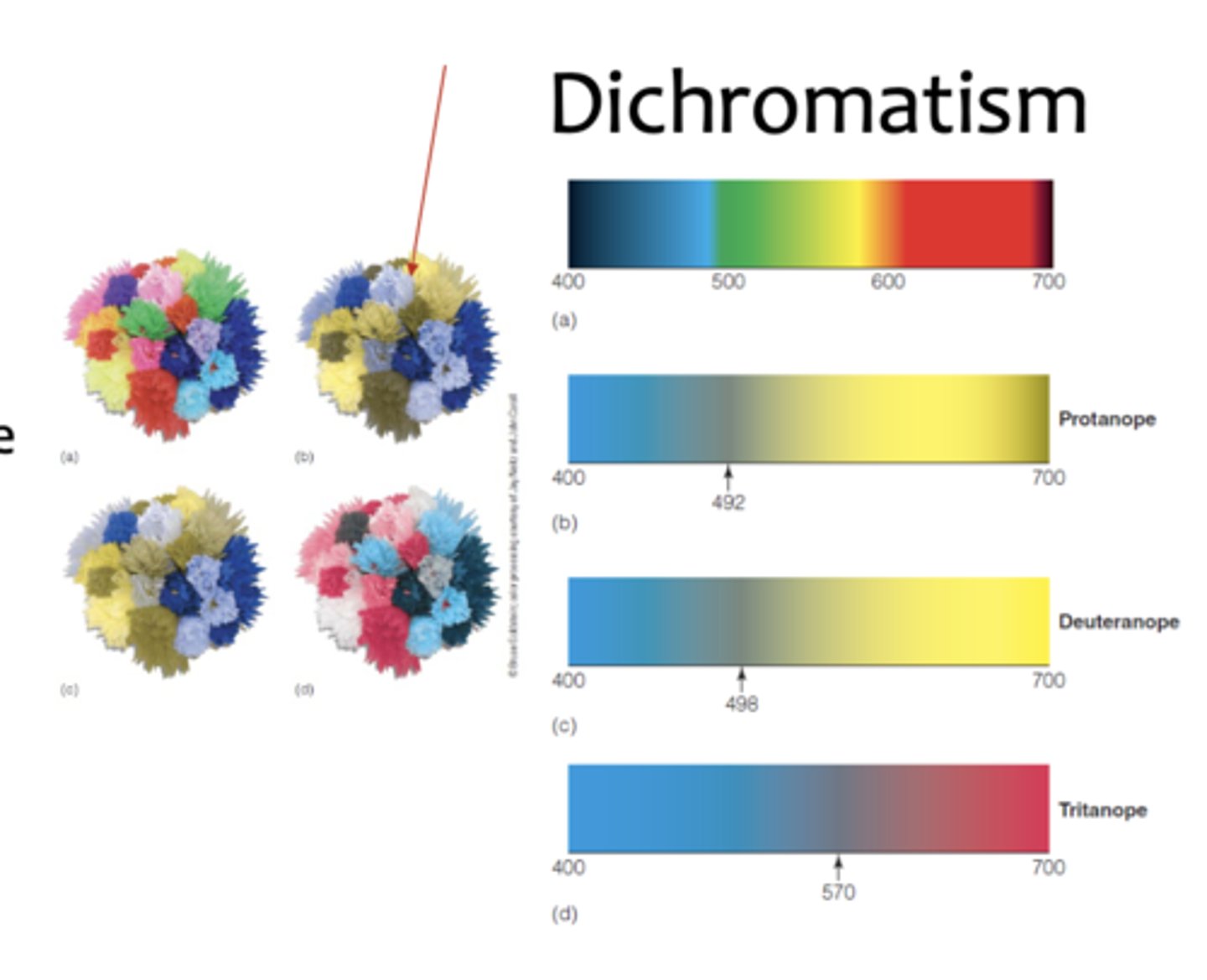
Monochromatism
when only one of the three cone types is present or functional; no color can be perceived (colorblindness)
Prosopagnosia
inability to recognize faces (face blindness)

Blindsight
the ability of individuals with blindness to detect and respond to visual stimuli despite lacking awareness of having seen anything

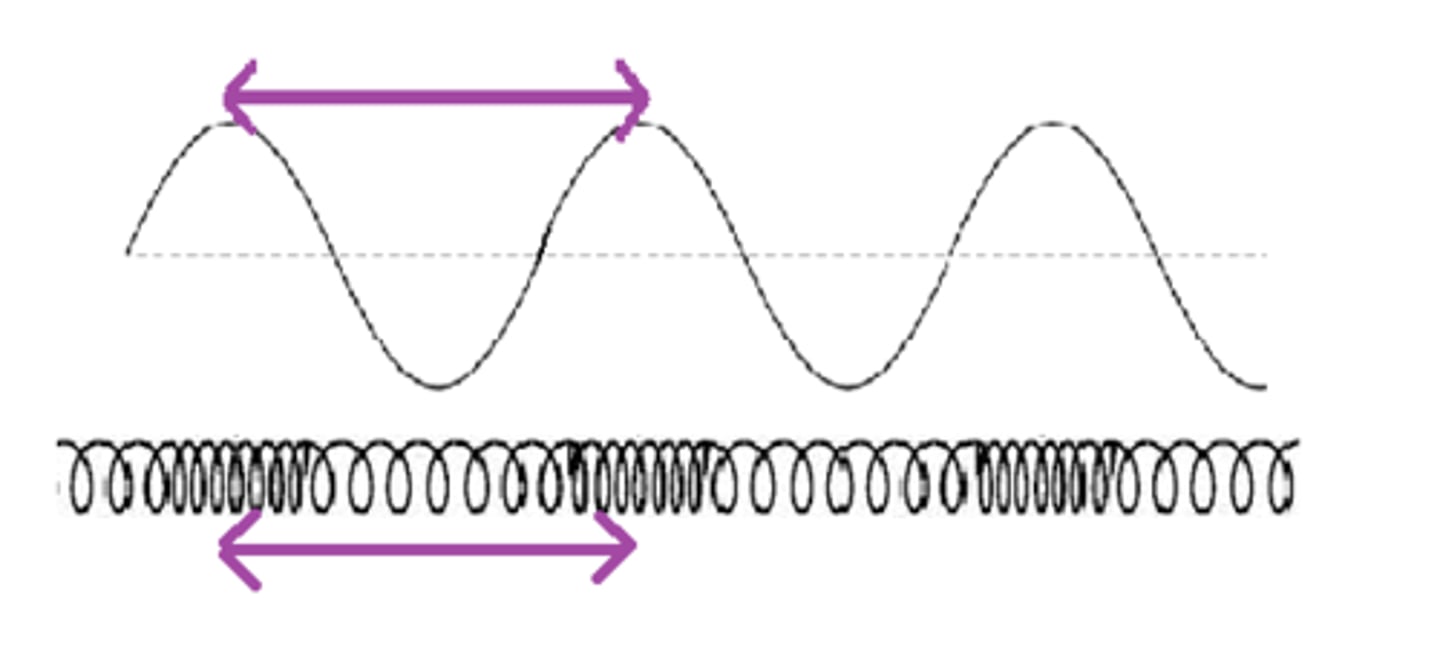
Wavelength
the distance between two corresponding parts of a wave
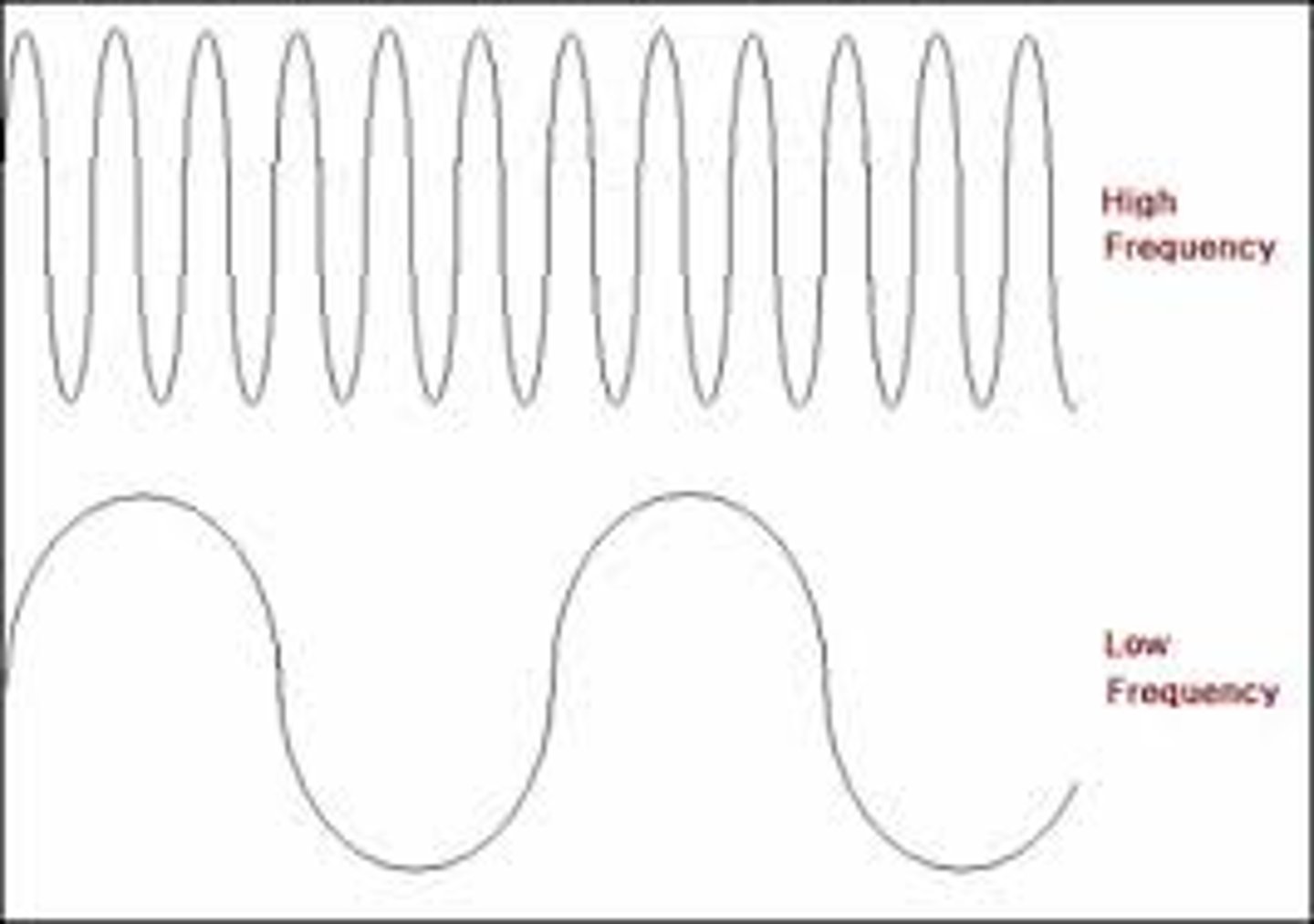
Pitch
the highness or lowness of a sound, as determined by the frequency of the sound waves
Amplitude
the height of a wave's crest
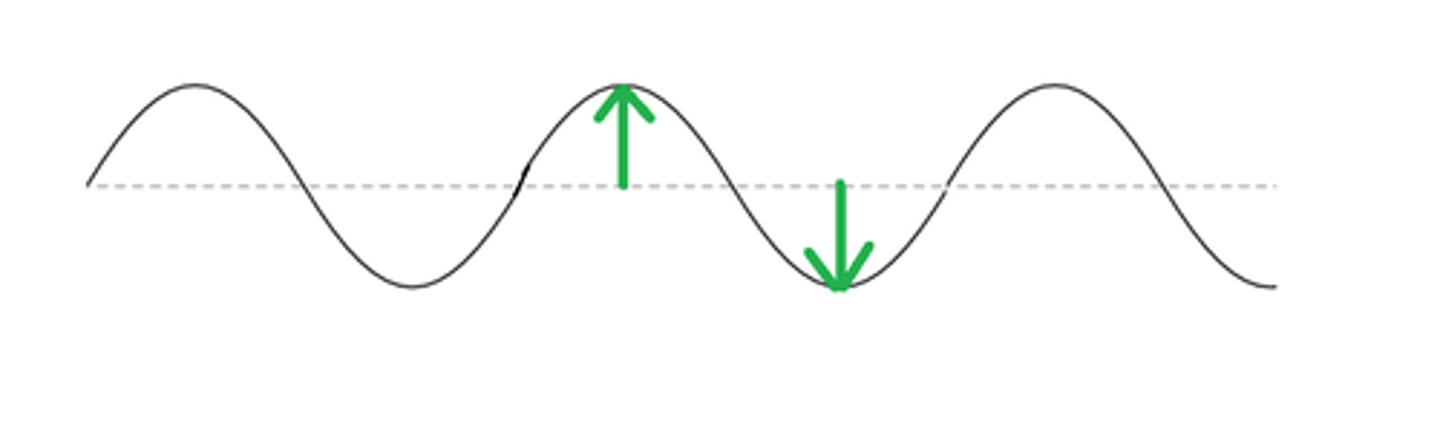
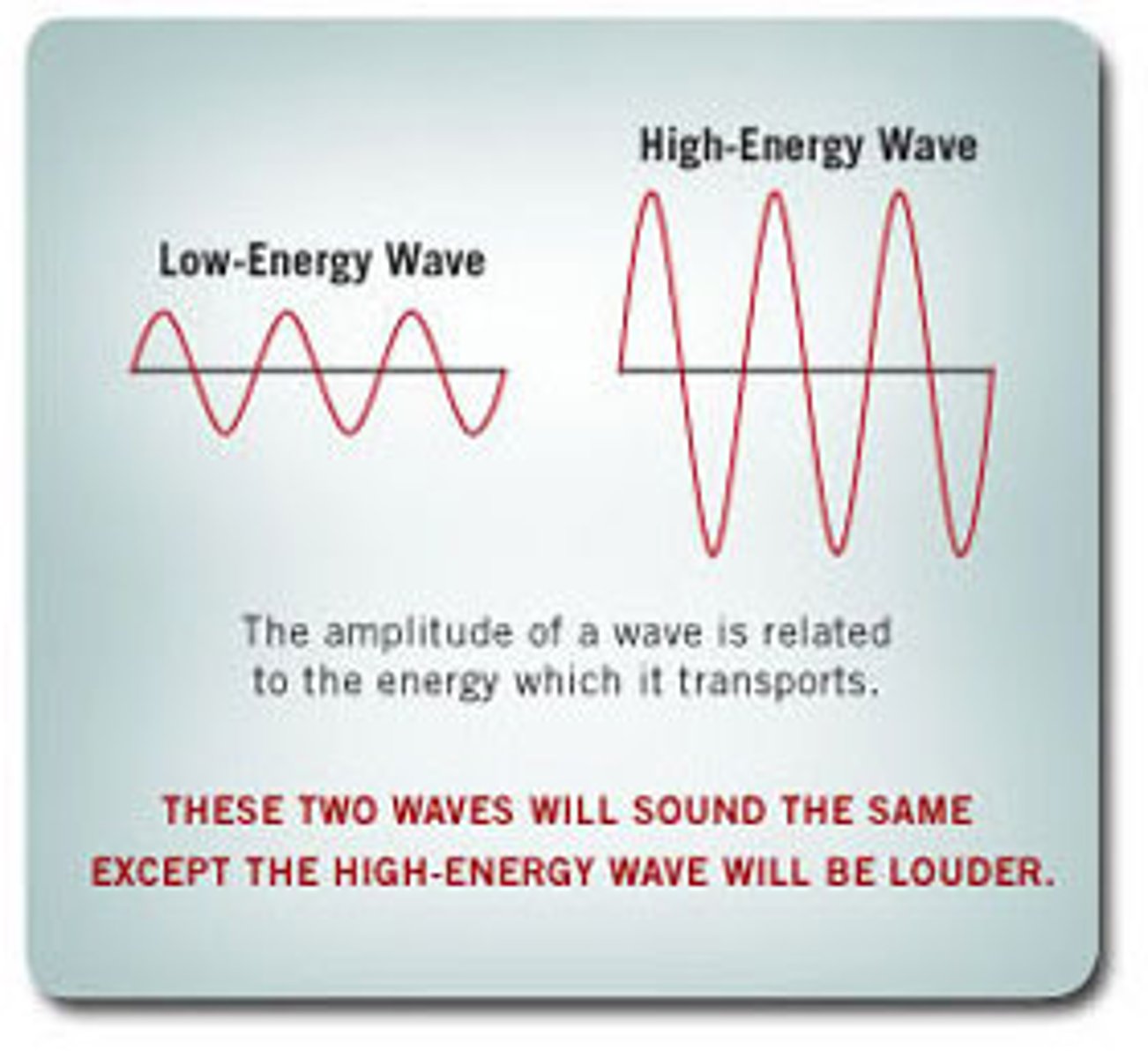
Loudness
how strong or soft a sound seems to a listener; determined by the intensity or amount of energy
Pitch perception
the aspect of hearing that allows us to tell how high or low a given tone is
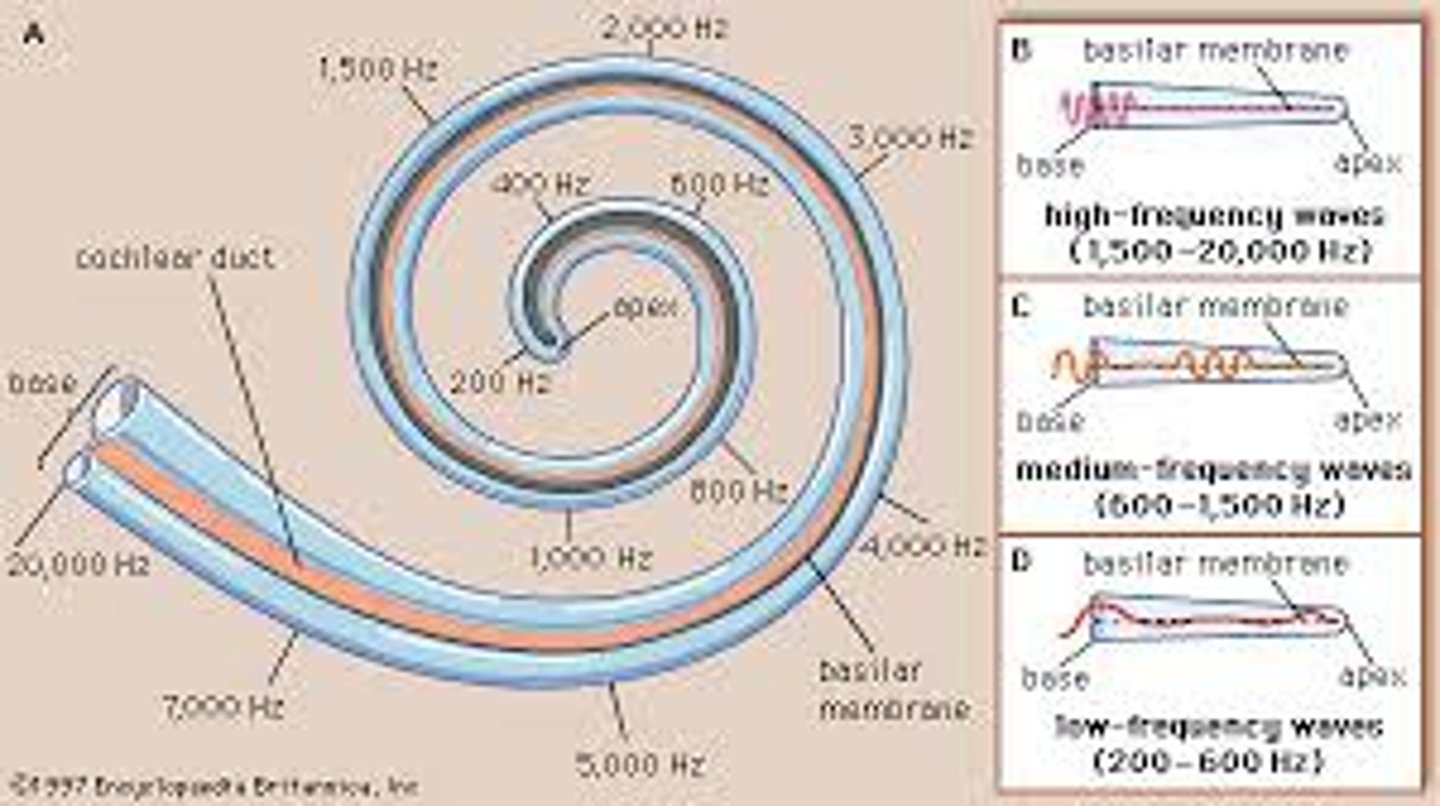
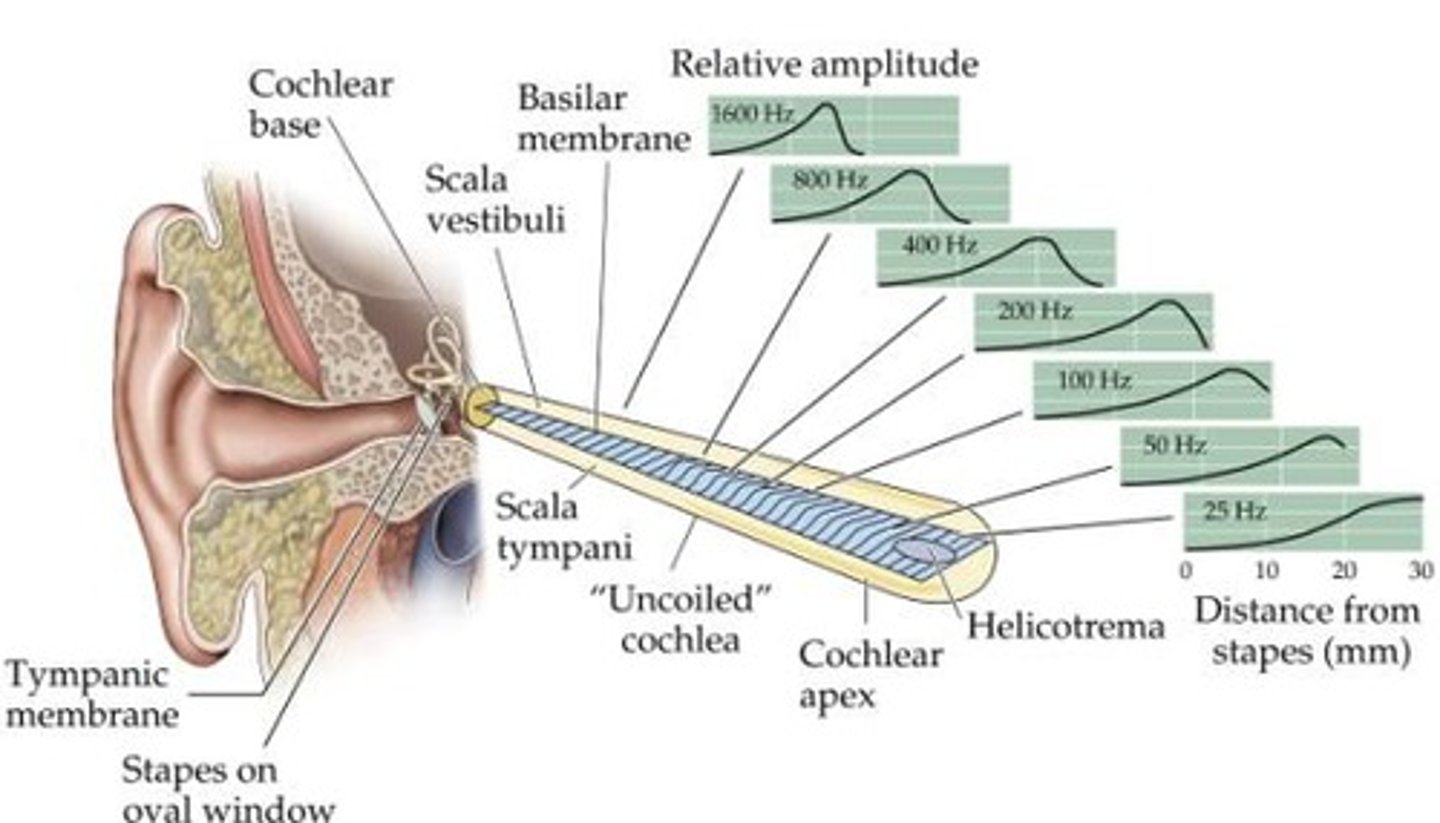
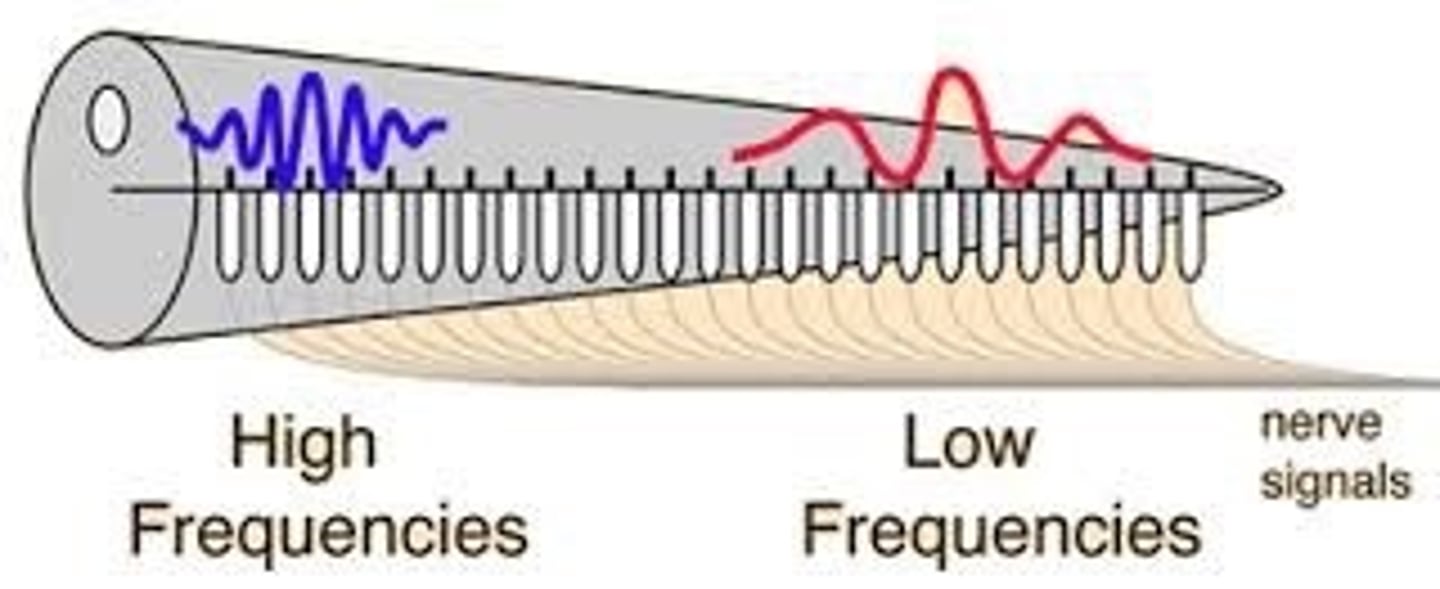
Place theory
the theory that a person hears different pitches because of vibrations in specific places on the basilar membrane of the cochlea
Volley theory
the theory that groups of neurons of the auditory system respond to a sound by firing action potentials slightly out of phase with one another so that when combined, a greater frequency of sound can be encoded and sent to the brain
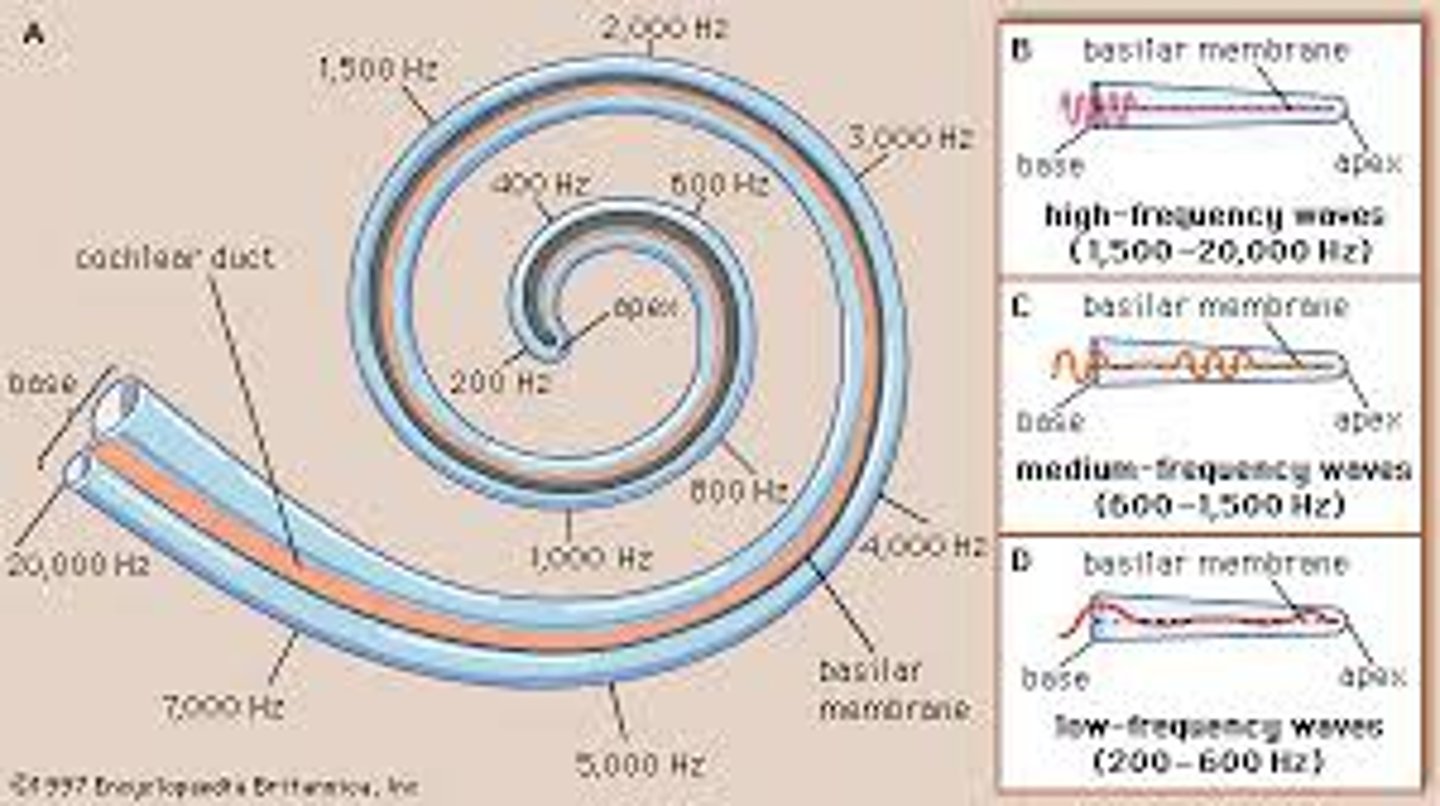
Frequency theory
the theory that the rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of a tone (e.g., a tone measuring 600 hertz will be transduced into 600 nerve impulses a second)
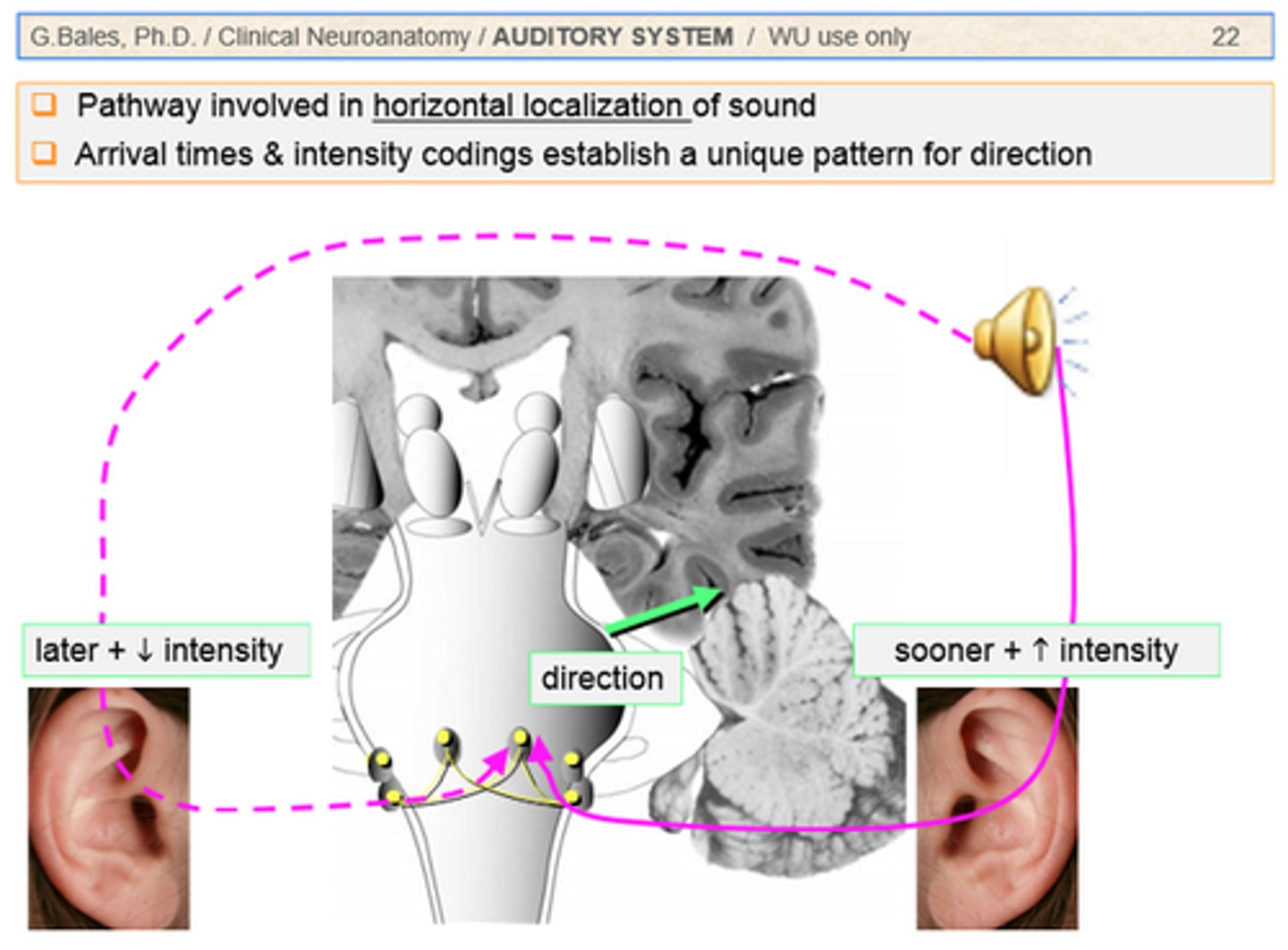
Sound localization
when the brain locates the direction a sound originated from based on which ear the sound strikes first
Conduction deafness
hearing loss caused by damage to the mechanical system that conducts sound waves to the cochleaConduction deafness
Consciousness
awareness of unique thoughts, memories, feelings, sensations, and environments
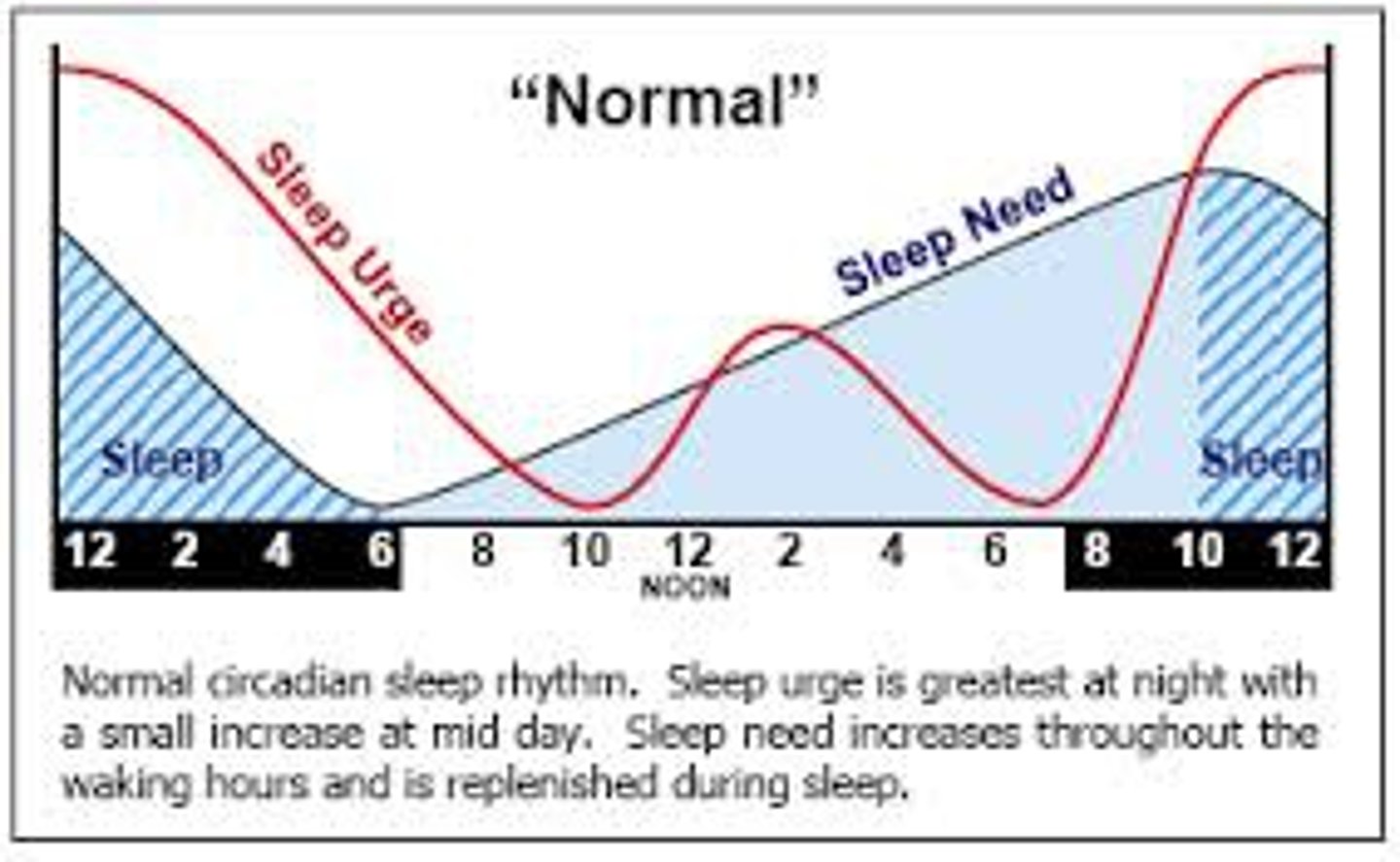
Circadian rhythm
the biological clock; regular bodily rhythms that occur on a 24-hour cycle
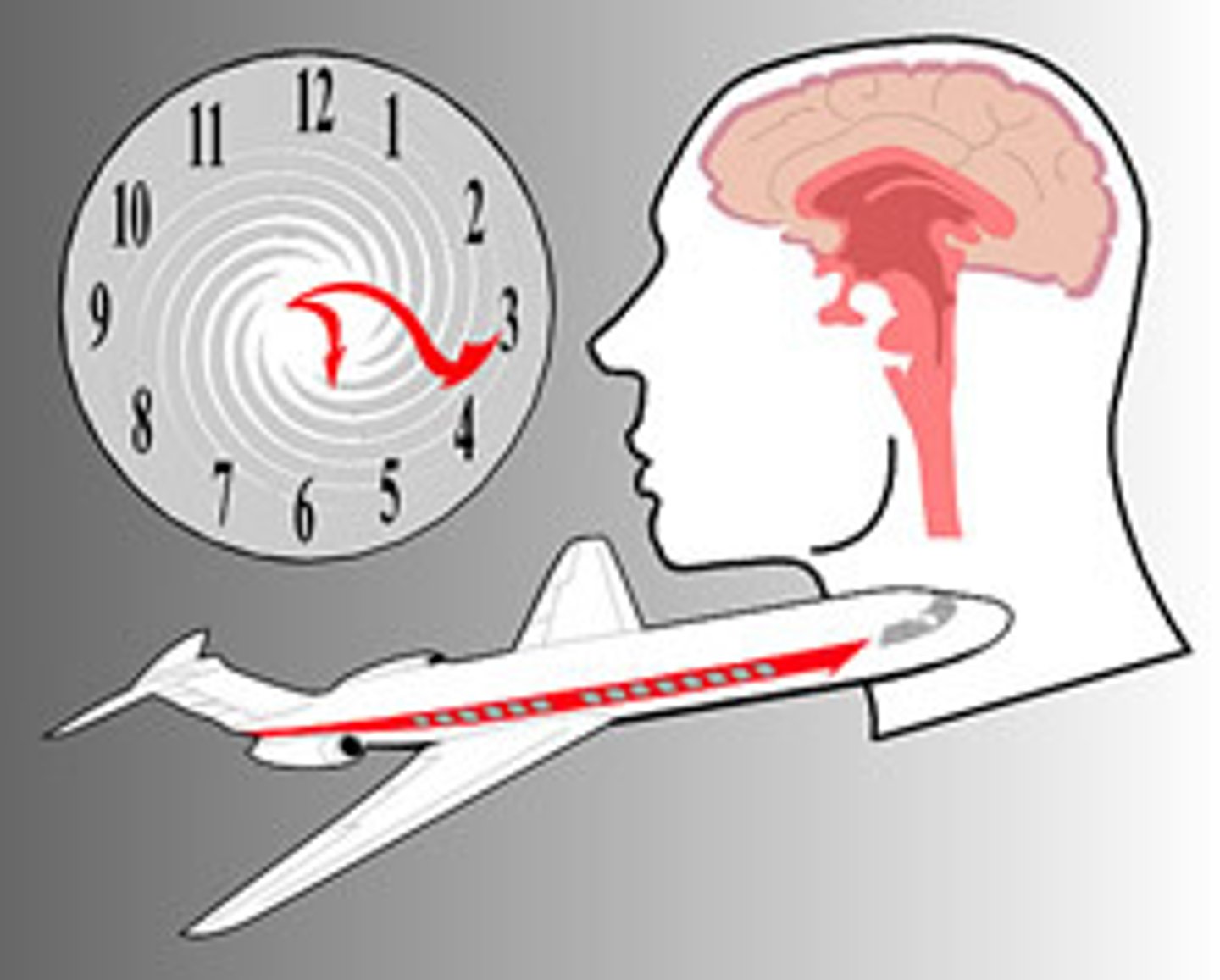
Jet lag
a disruption of circadian rhythms due to crossing time zones
Shift work
a pattern of work in which a person sometimes works during the day and sometimes during the night

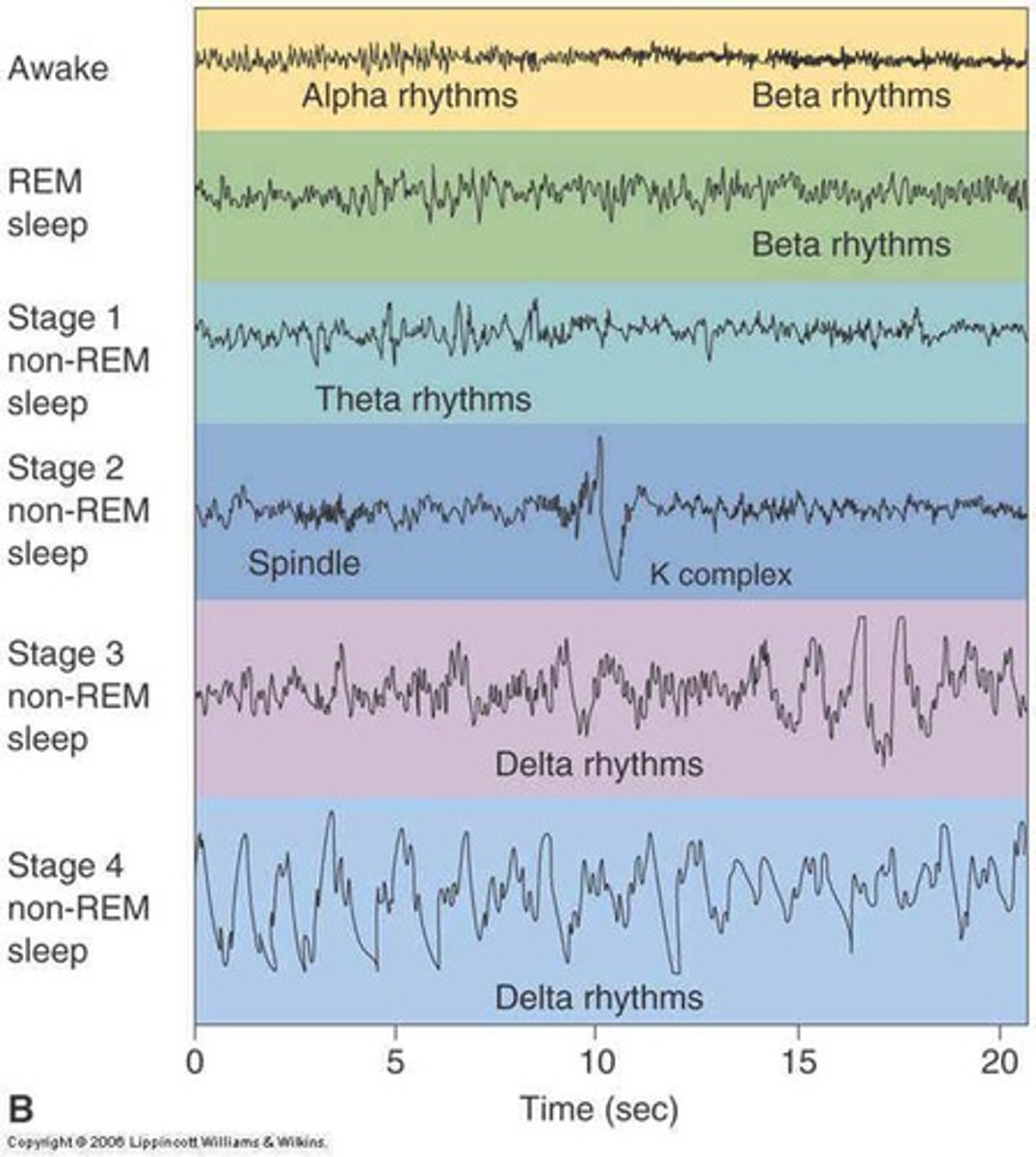
REM sleep
characterized by rapid eye movements and a high level of brain activity; accounts for about 25% of a person's total sleep
REM rebound
the tendency for REM sleep to increase following REM sleep deprivation (created by repeated awakenings during REM sleep)
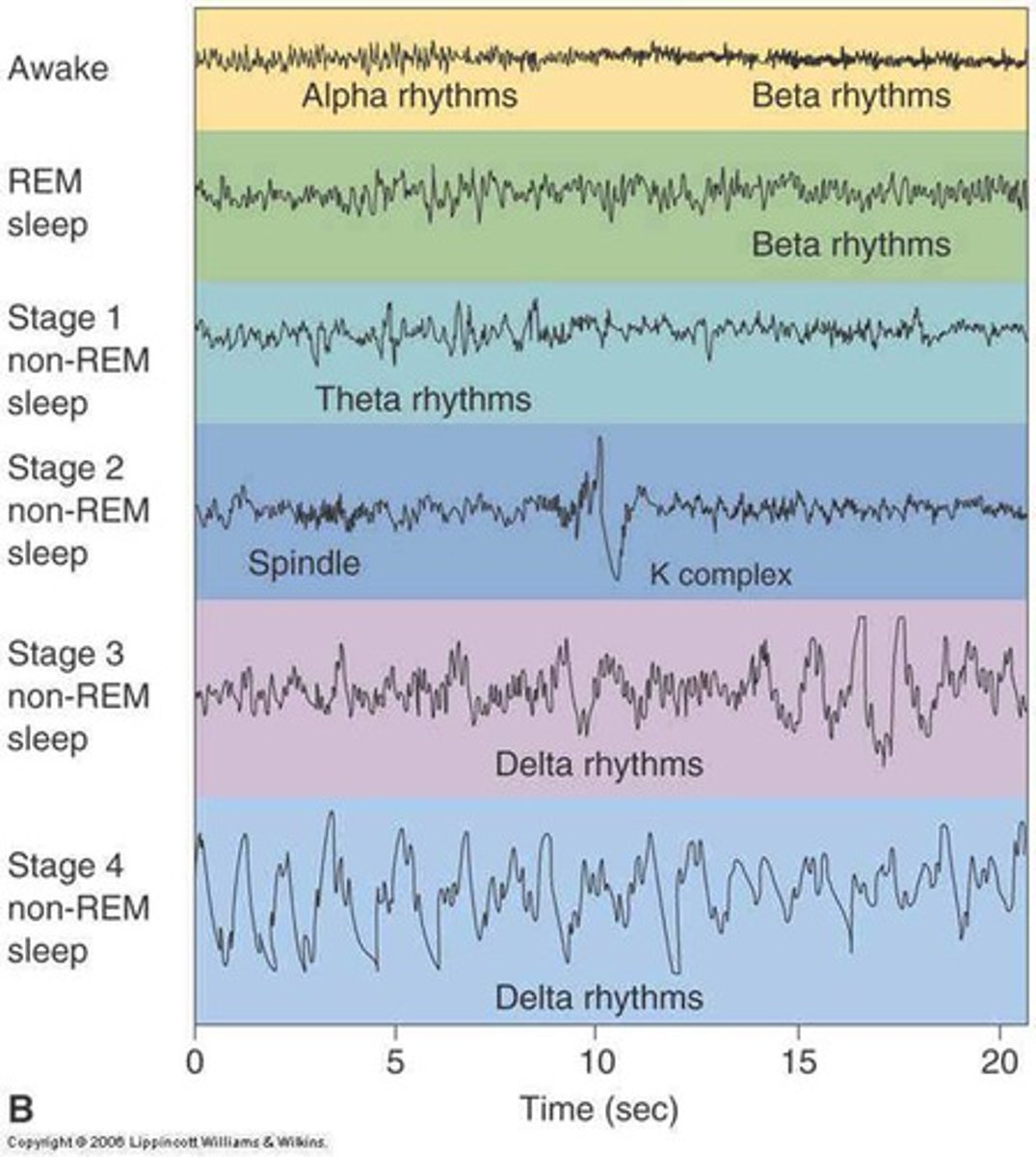
NREM stage 1
a transition period between wakefulness and sleep ("nodding off") characterized by relaxation and easy arousal
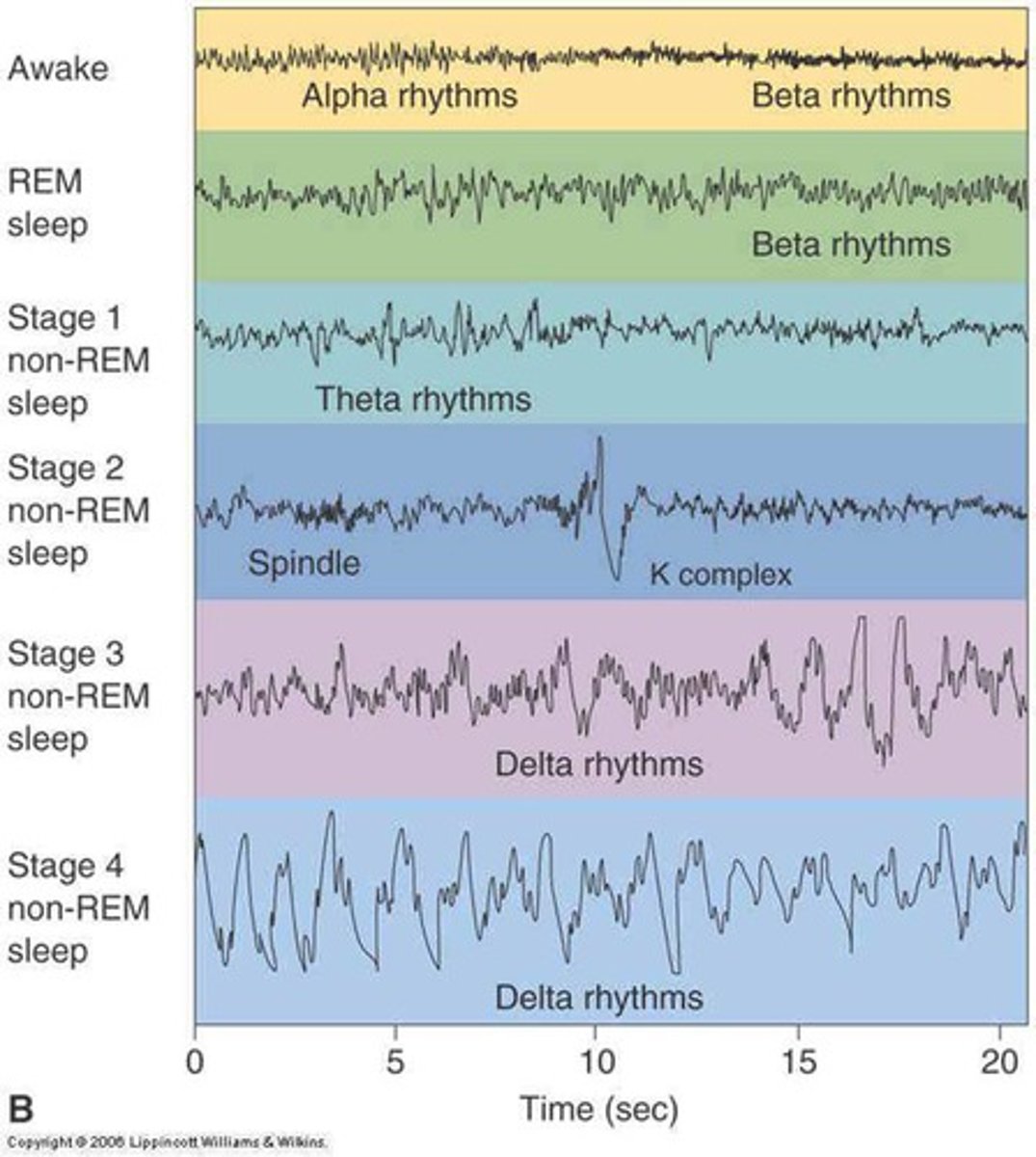
NREM stage 2
characterized by continued slowing of heartbeat, breathing, muscle activity, and eye movements; accounts for about half of a person's total sleep
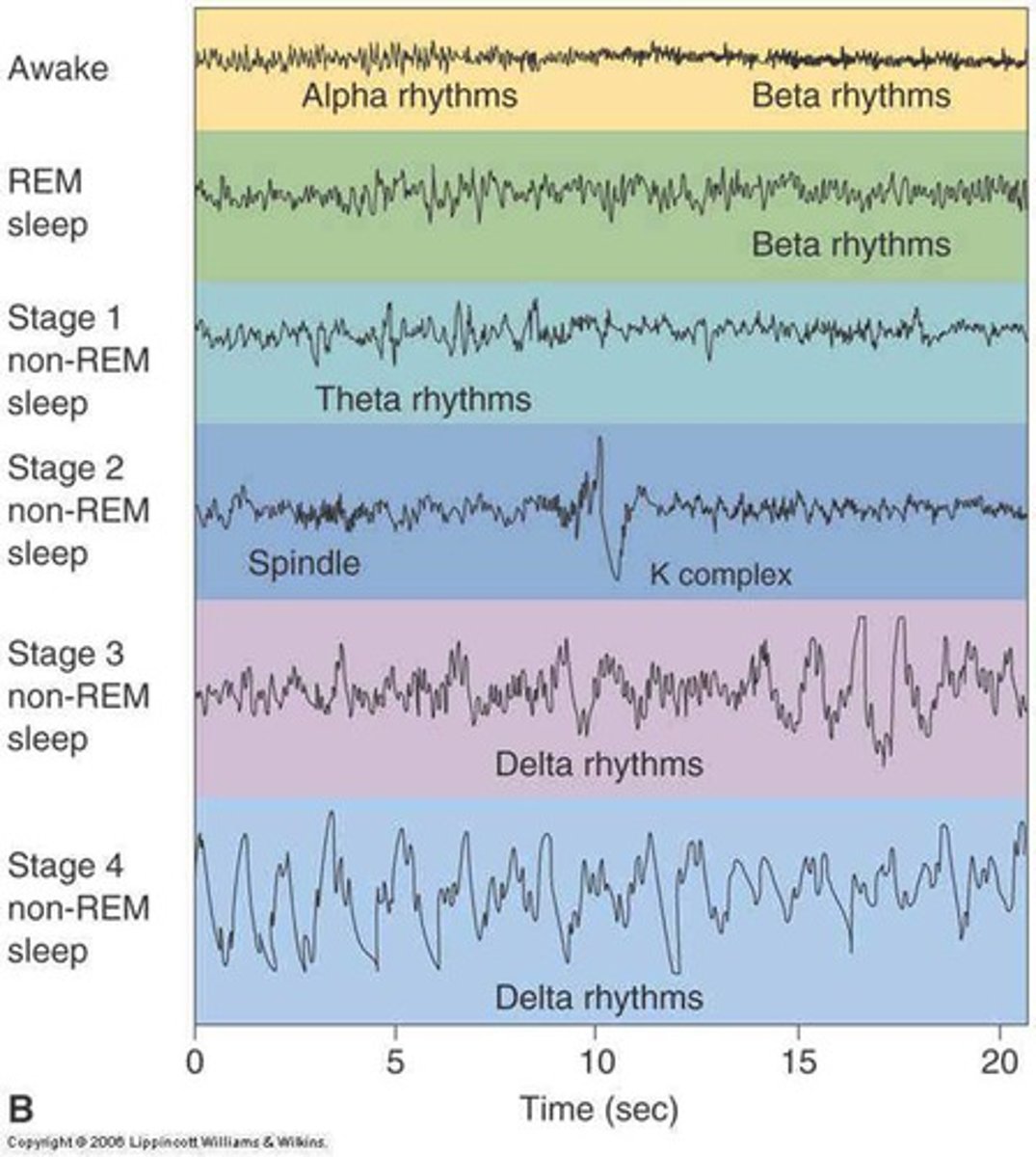
NREM stage 3
characterized by muscle relaxation, lowered blood pressure, and slower breathing; deepest sleep occurs in this stage
Hypnagogic sensations
imaginary images or sensations (e.g., falling or floating) that seem real and occur as a person is falling asleep

Activation-synthesis (dreams)
the theory that dreams are the result of the cerebral cortex interpreting and organizing random flashes of brain activity, originating in the lower brain structures, especially the pons
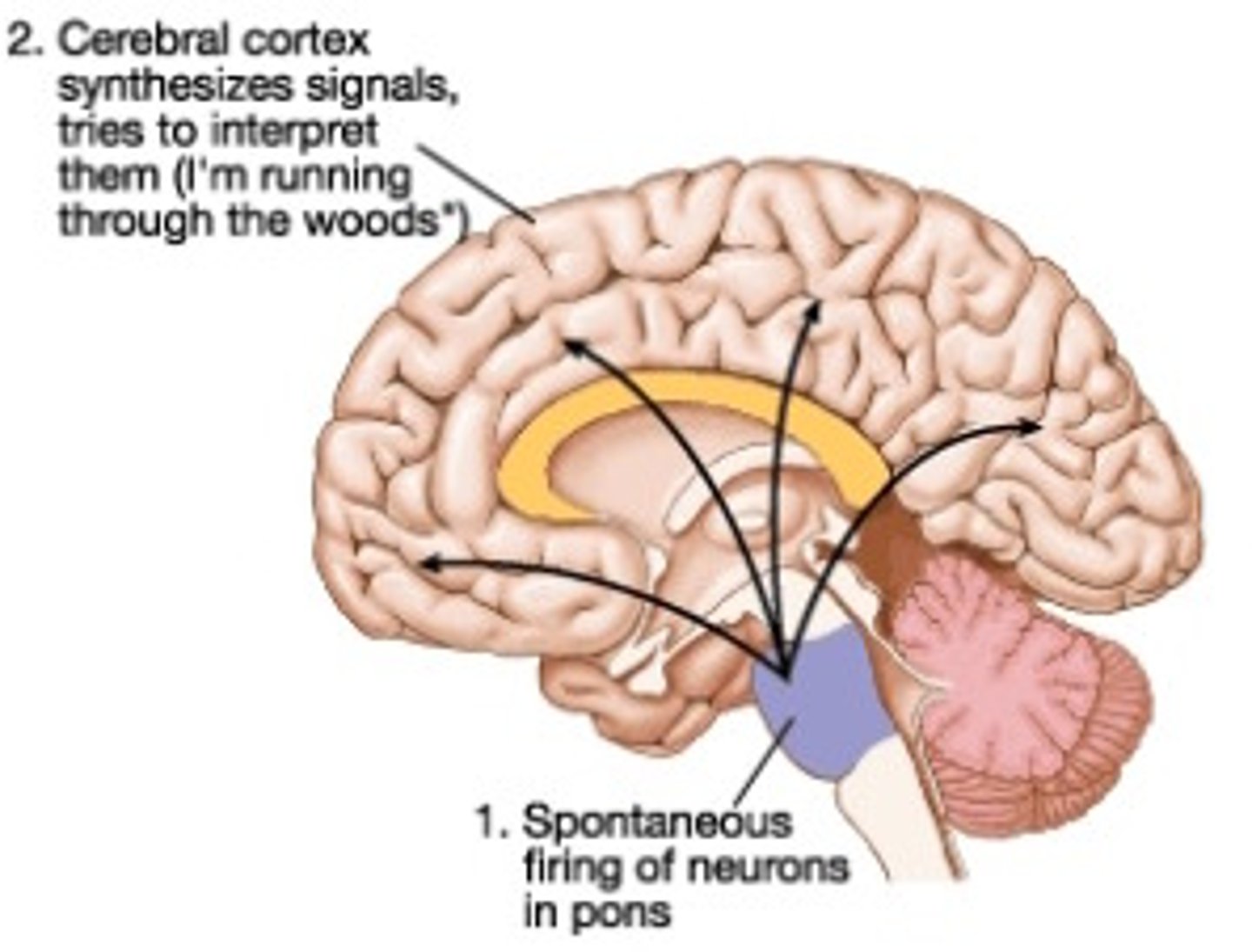
Consolidation theory (dreams)
the theory that during sleep, the brain is best able to integrate newly encoded memory into long-term store and that dreaming is influenced by this process

Restoration of resources
the theory that people need rest to recover energy lost throughout the day in order to be productive and healthy

Insomnia
recurring problems in falling or staying asleep. (Myers Psychology for AP 2e p. 238)

Narcolepsy
a sleep disorder characterized by unmanageable drowsiness and/or uncontrollably falling into REM sleep during the day

REM sleep behavior disorder
a disorder in which a person physically acts out vivid, often unpleasant dreams with vocal sounds and sudden, often violent, arm and leg movements during REM sleep

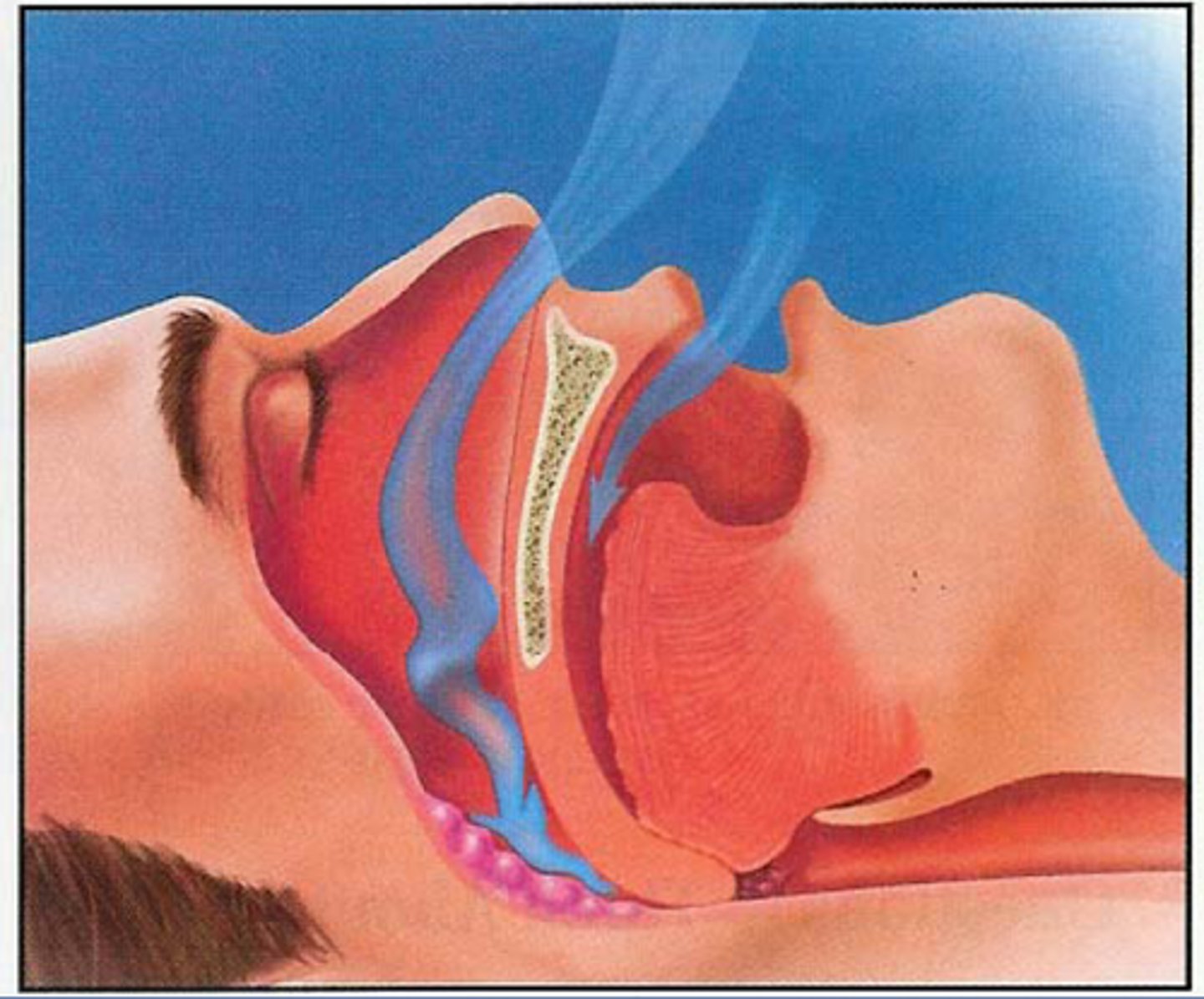
Sleep apnea
a disorder in which a person stops breathing for brief periods while asleep
Somnambulism
the condition of walking or performing some other activity without awakening; also known as sleepwalking
Cerebral cortex
outermost part of forebrain; controls voluntary muscular movements as well as sensation, movement, memory, emotions, and executive function
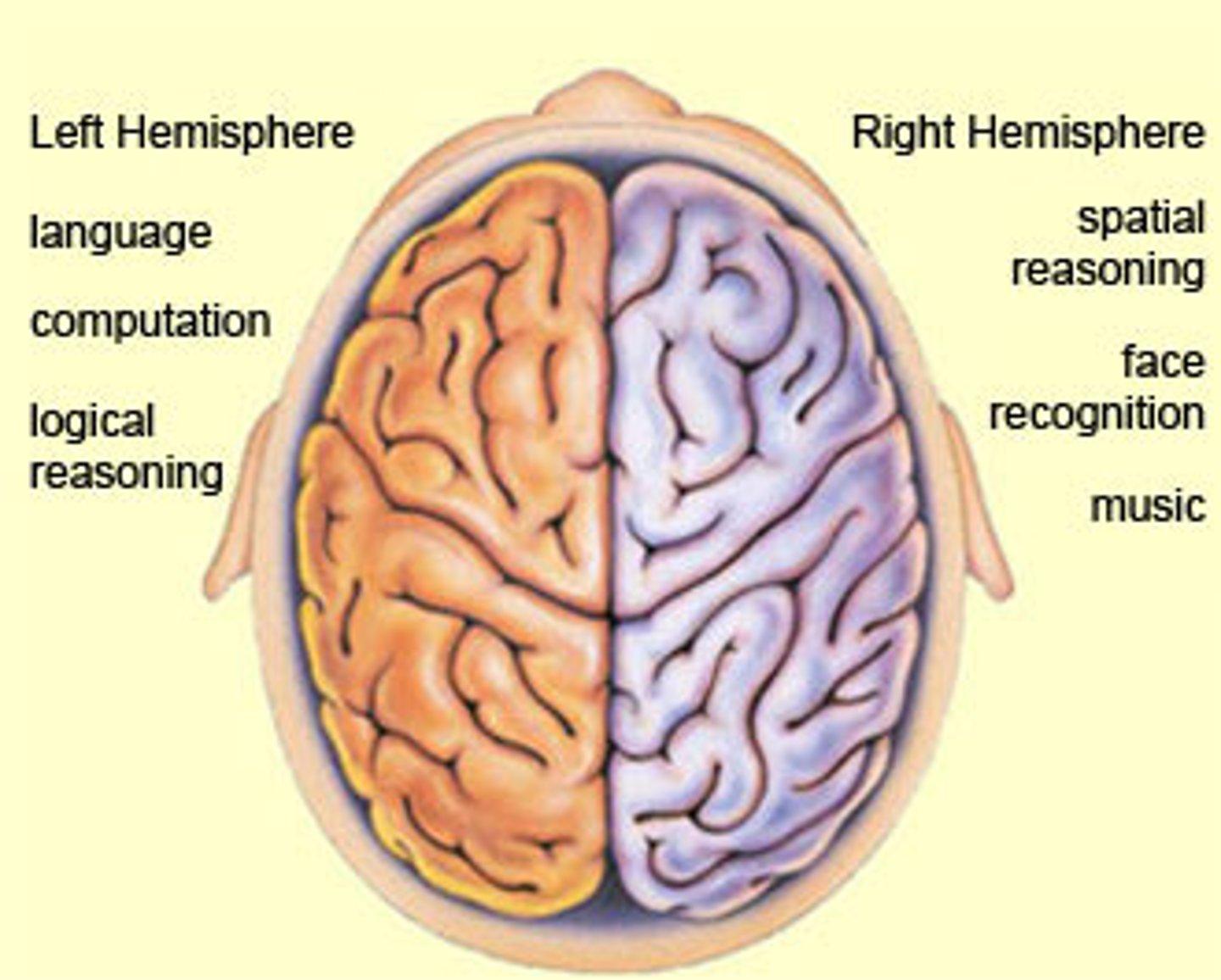
Corpus callosum
a thick band of nerve fibers that connects large areas of the cerebral cortex on each side of the brain and supports communication of information across the hemispheres
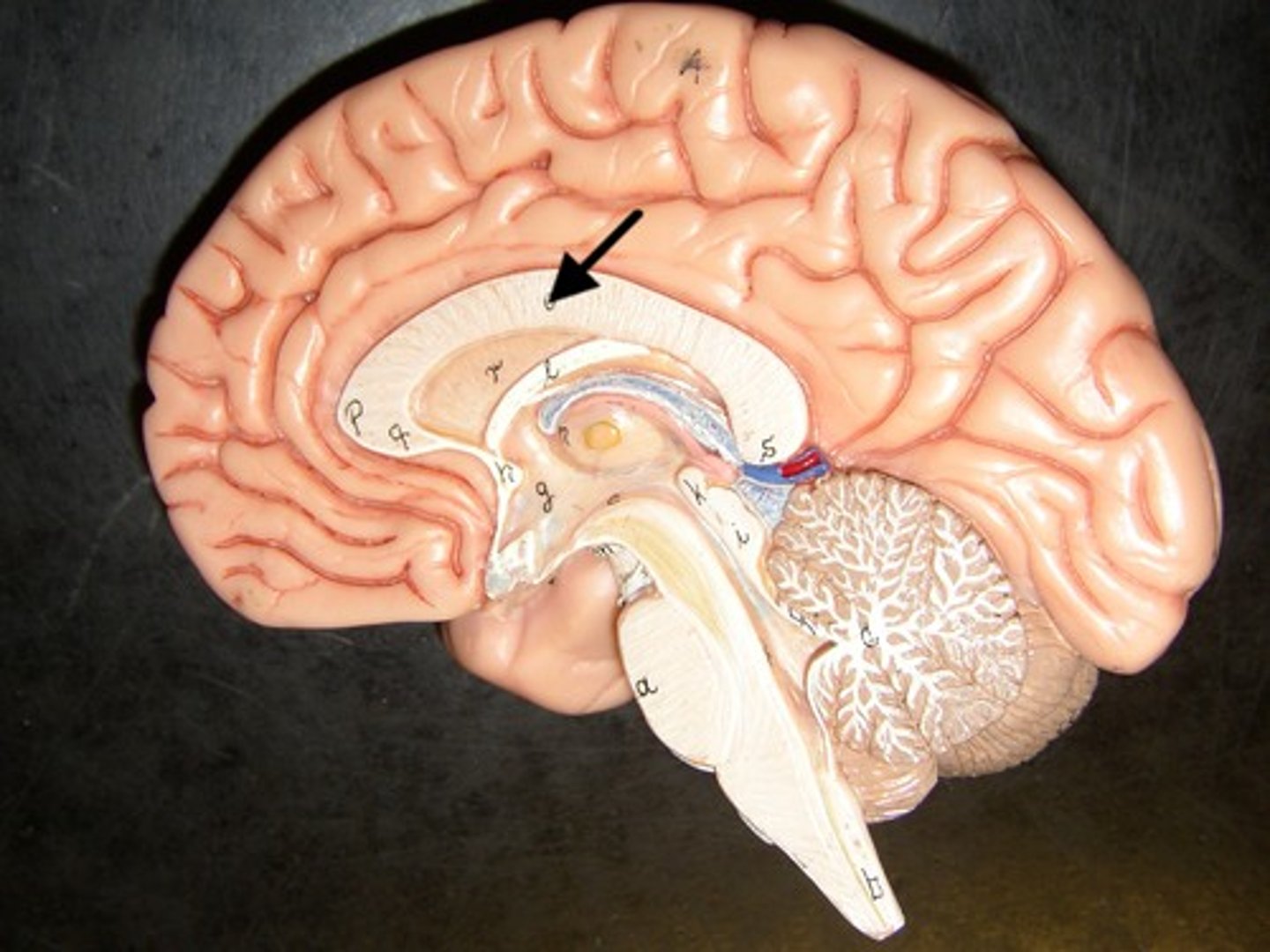
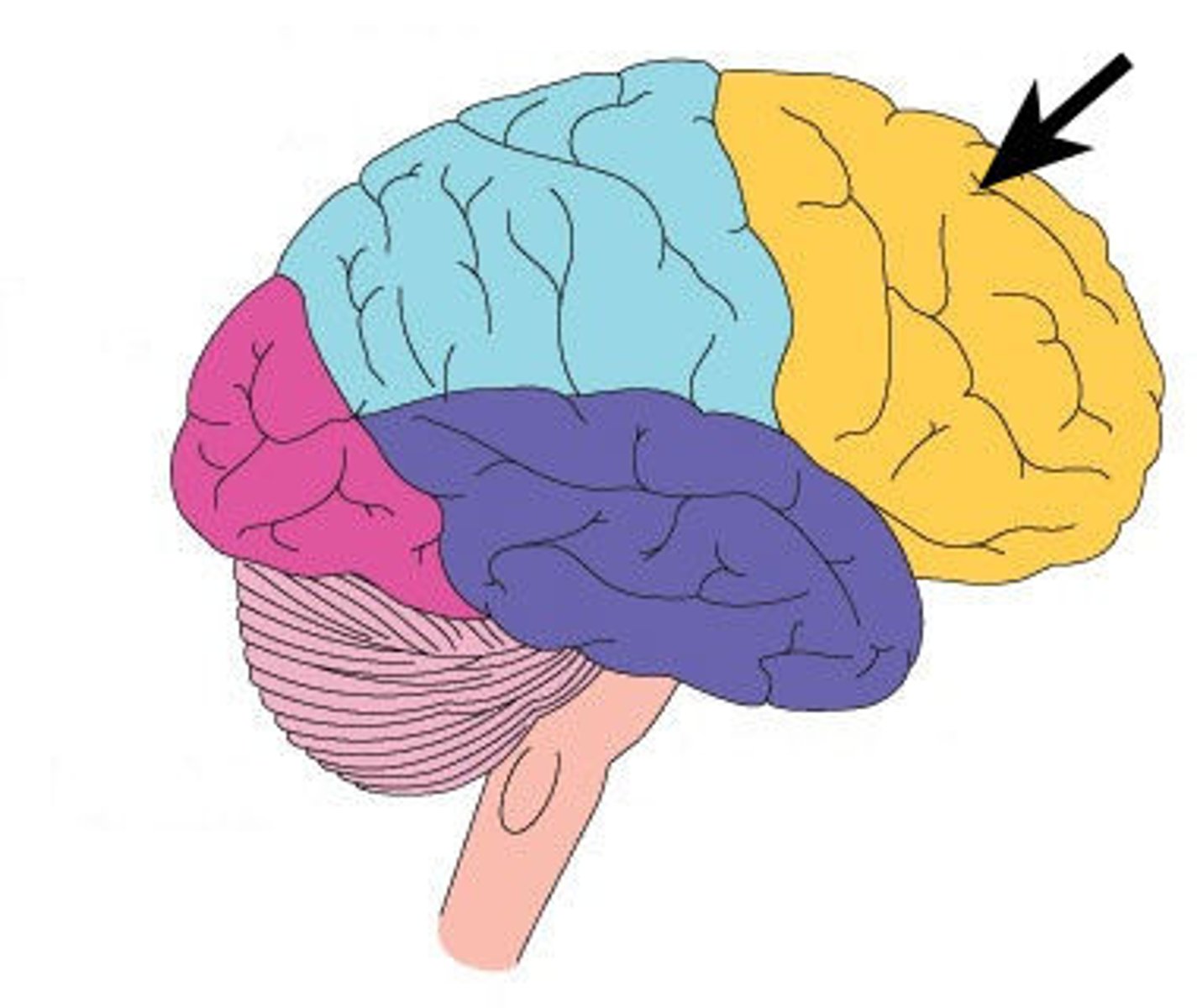
Frontal lobes
a region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
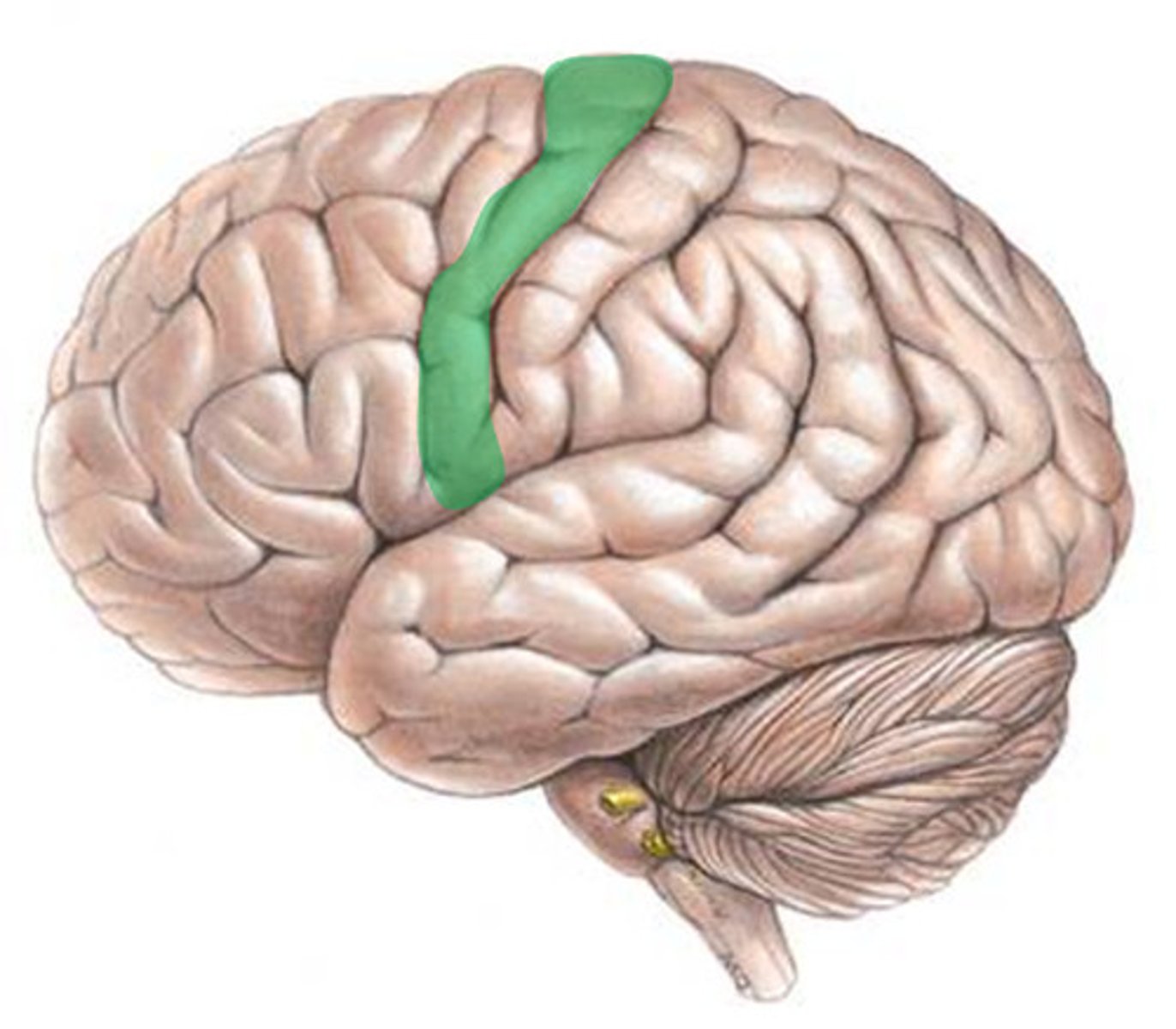
Motor cortex
an area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements
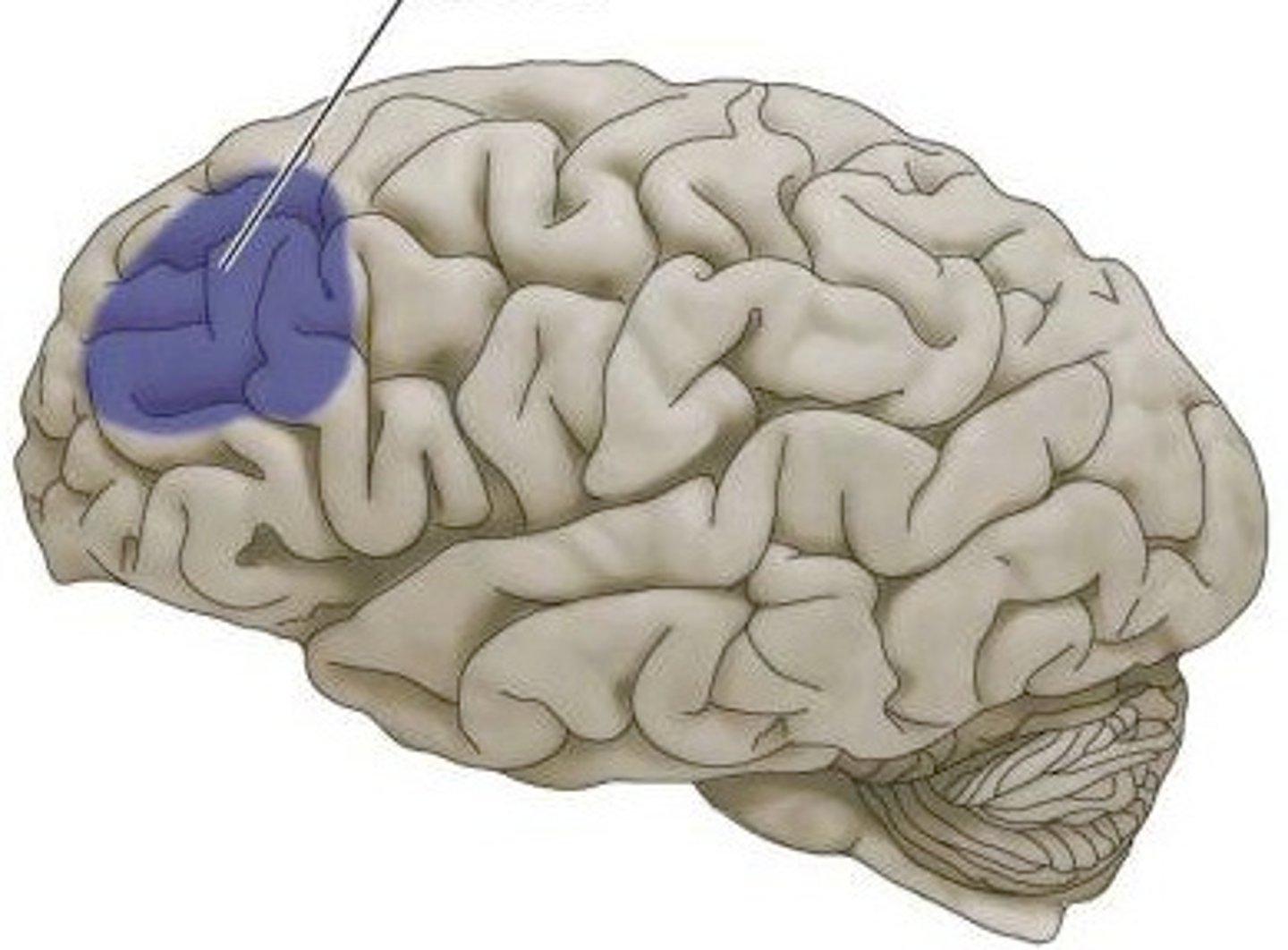
Prefrontal cortex
part of frontal lobe responsible for thinking, planning, and language
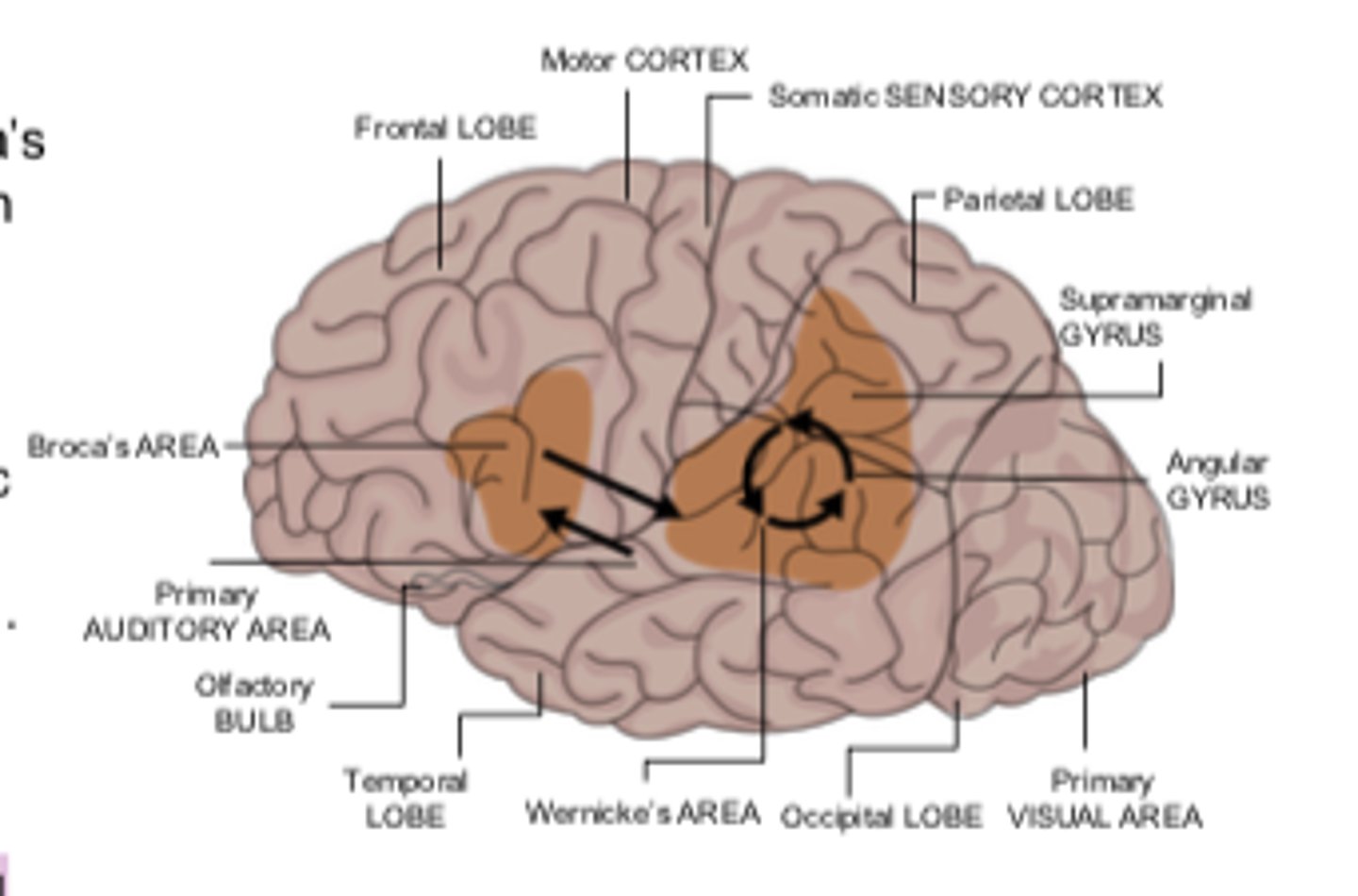
Broca's area
the language expression area in the frontal lobe (usually in the left hemisphere) that directs the muscle movements involved in speech
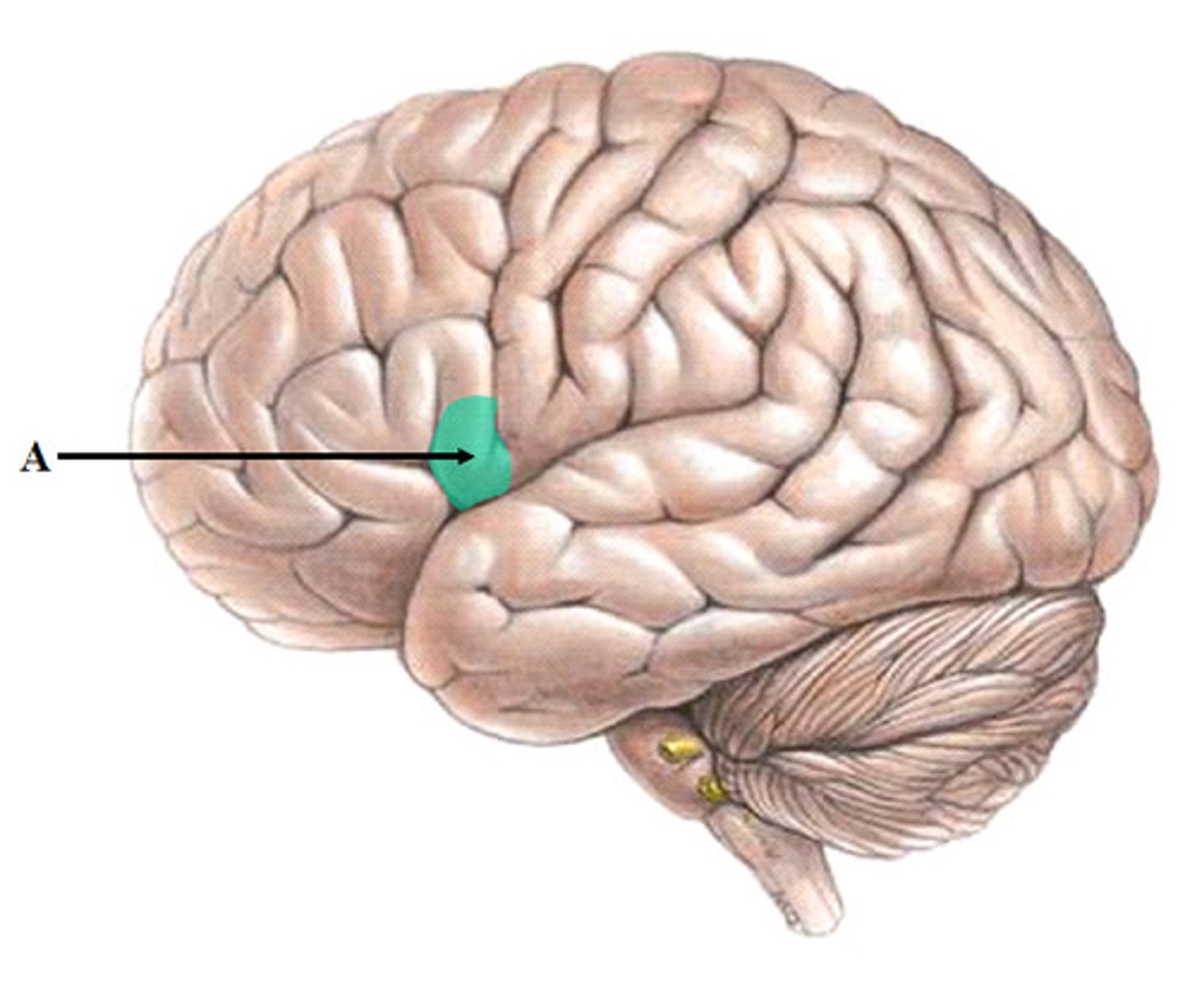
Parietal lobes
upper middle part of the cerebral cortex lying behind the frontal lobe that is specialized for touch and perception
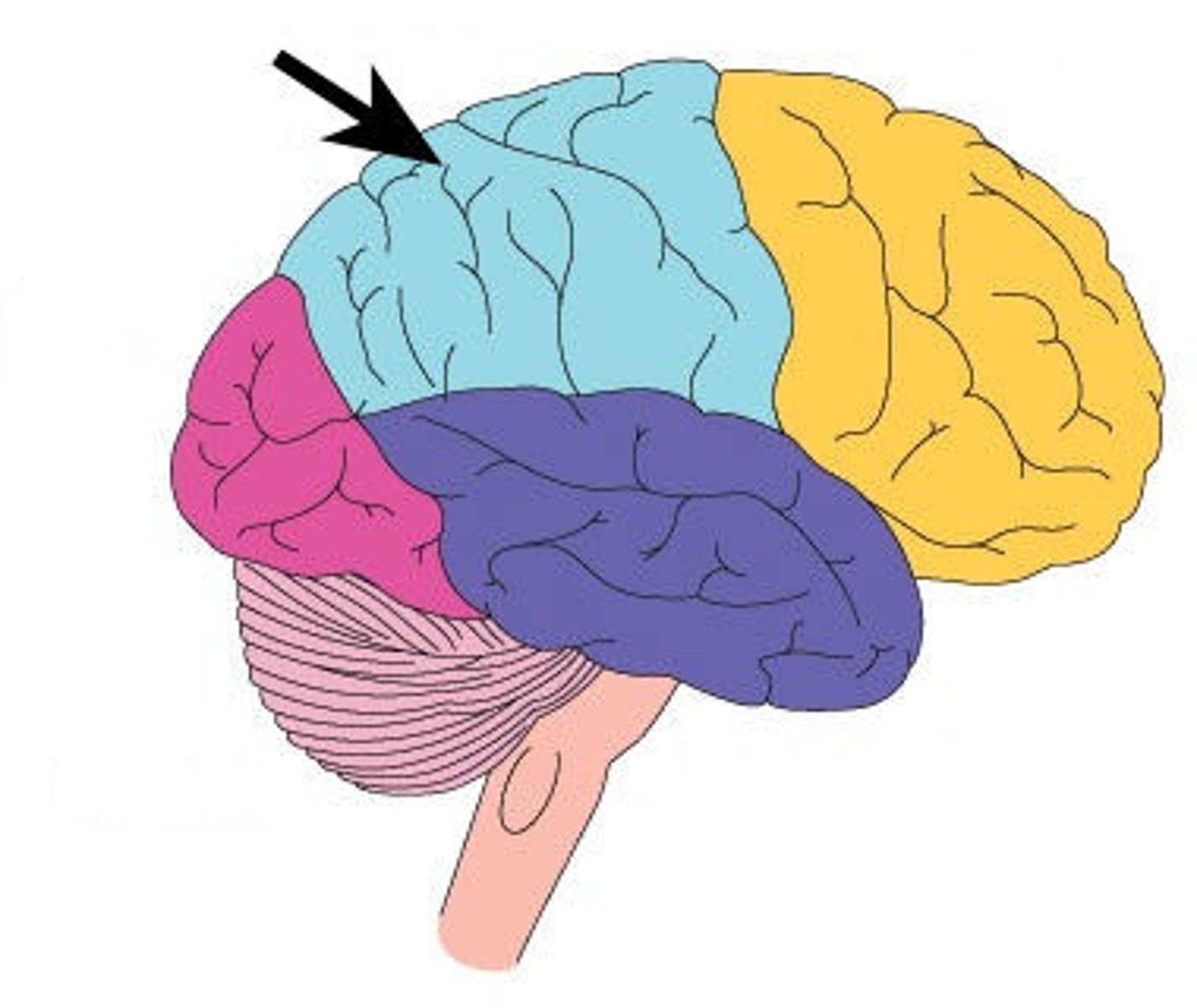
Temporal lobes
lower part of cerebral cortex involved in hearing, understanding language, and memory
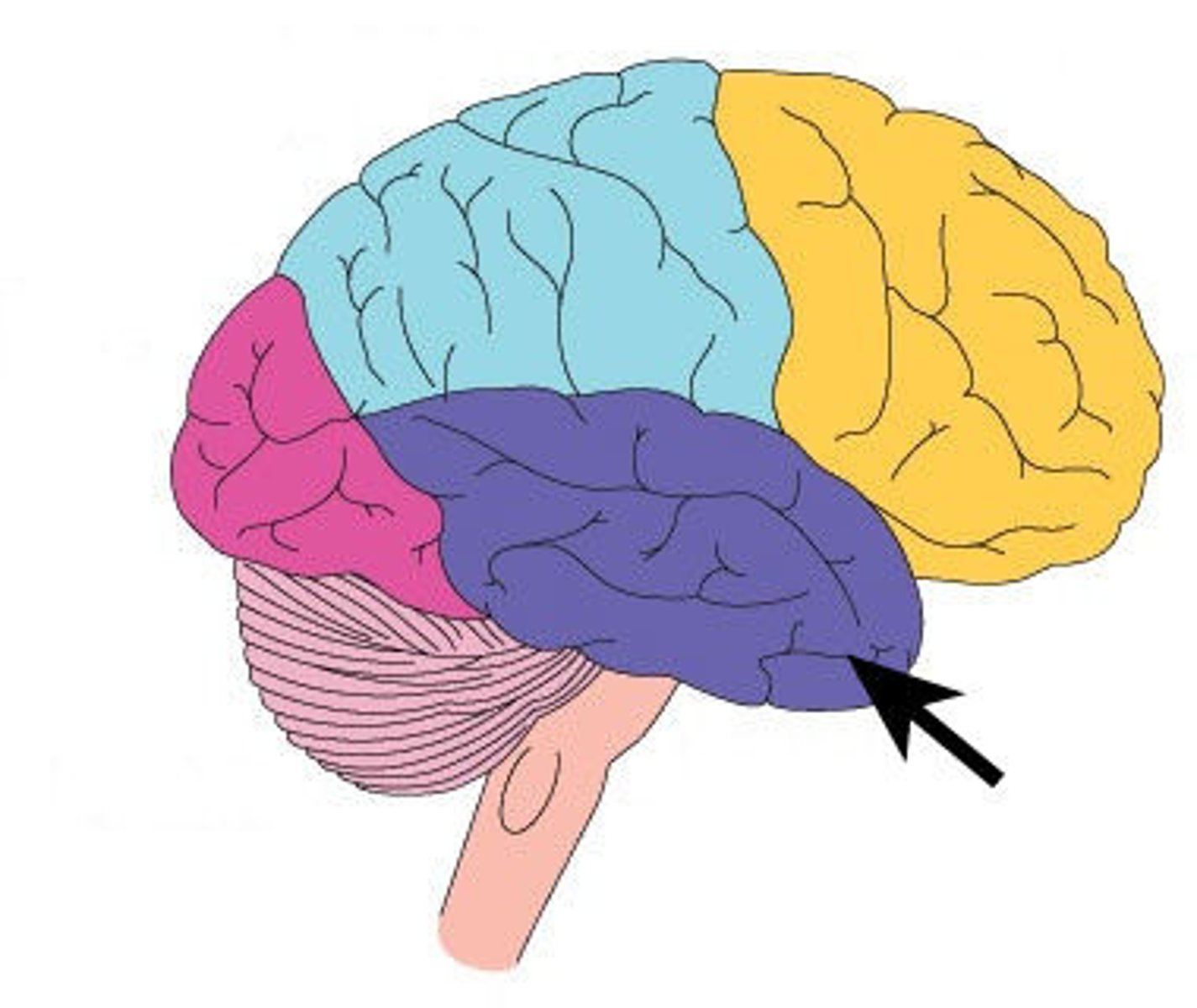
Wernicke's area
part of the temporal lobe involved in understanding speech
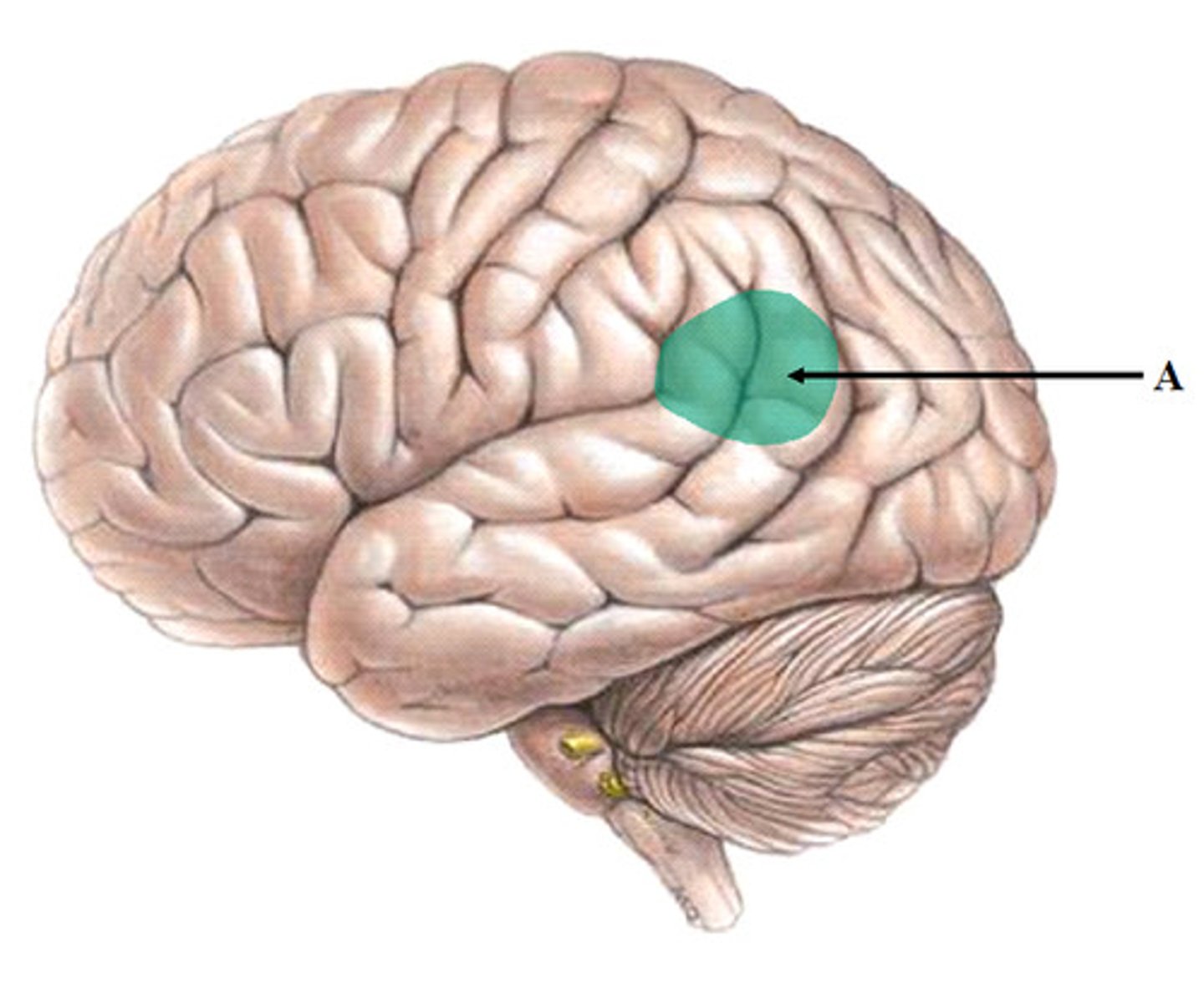
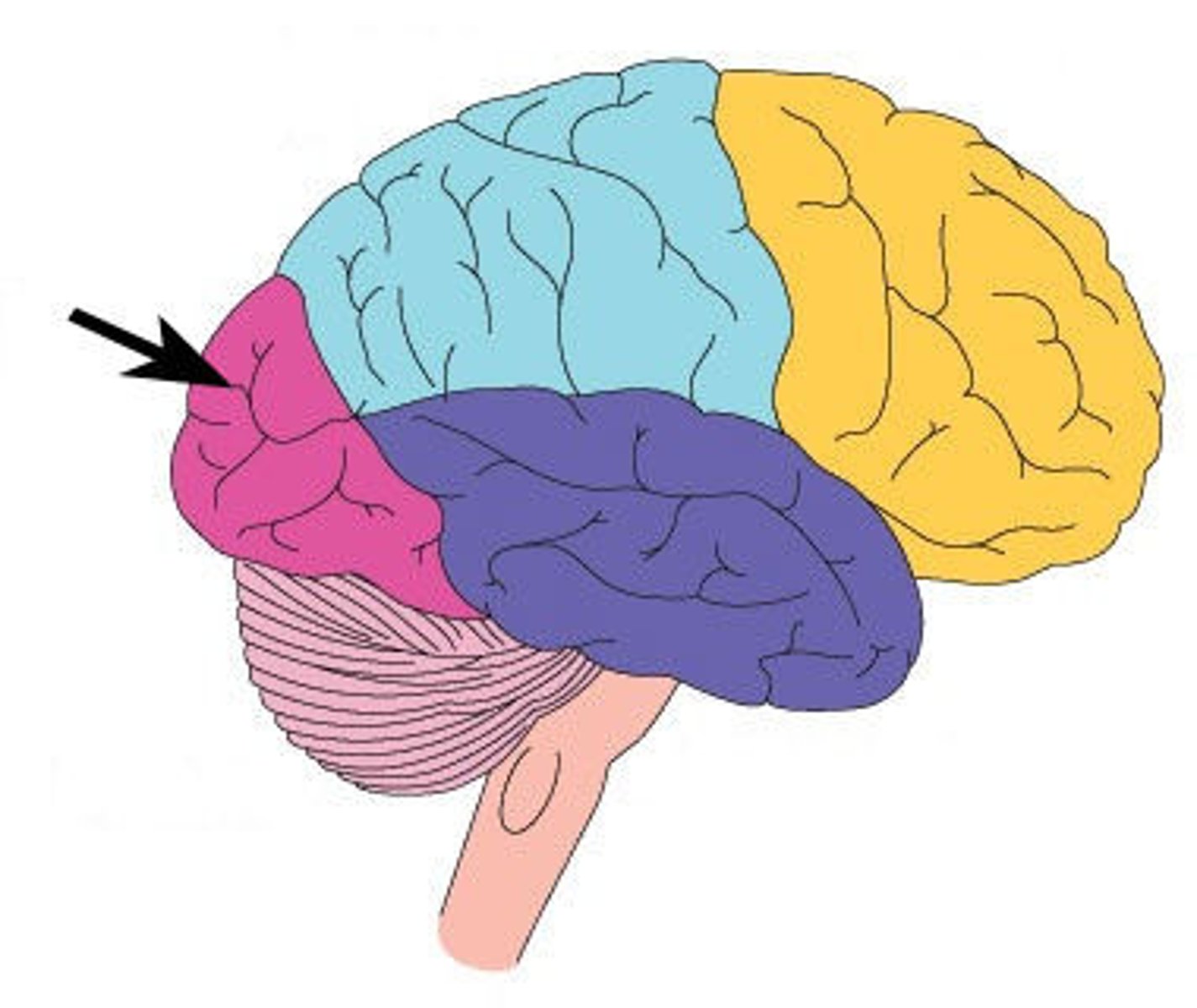
Occipital Lobes
back part of cerebral cortex specialized
for vision
Limbic system
emotional center of brain that also plays roles in smell, motivation, and memory
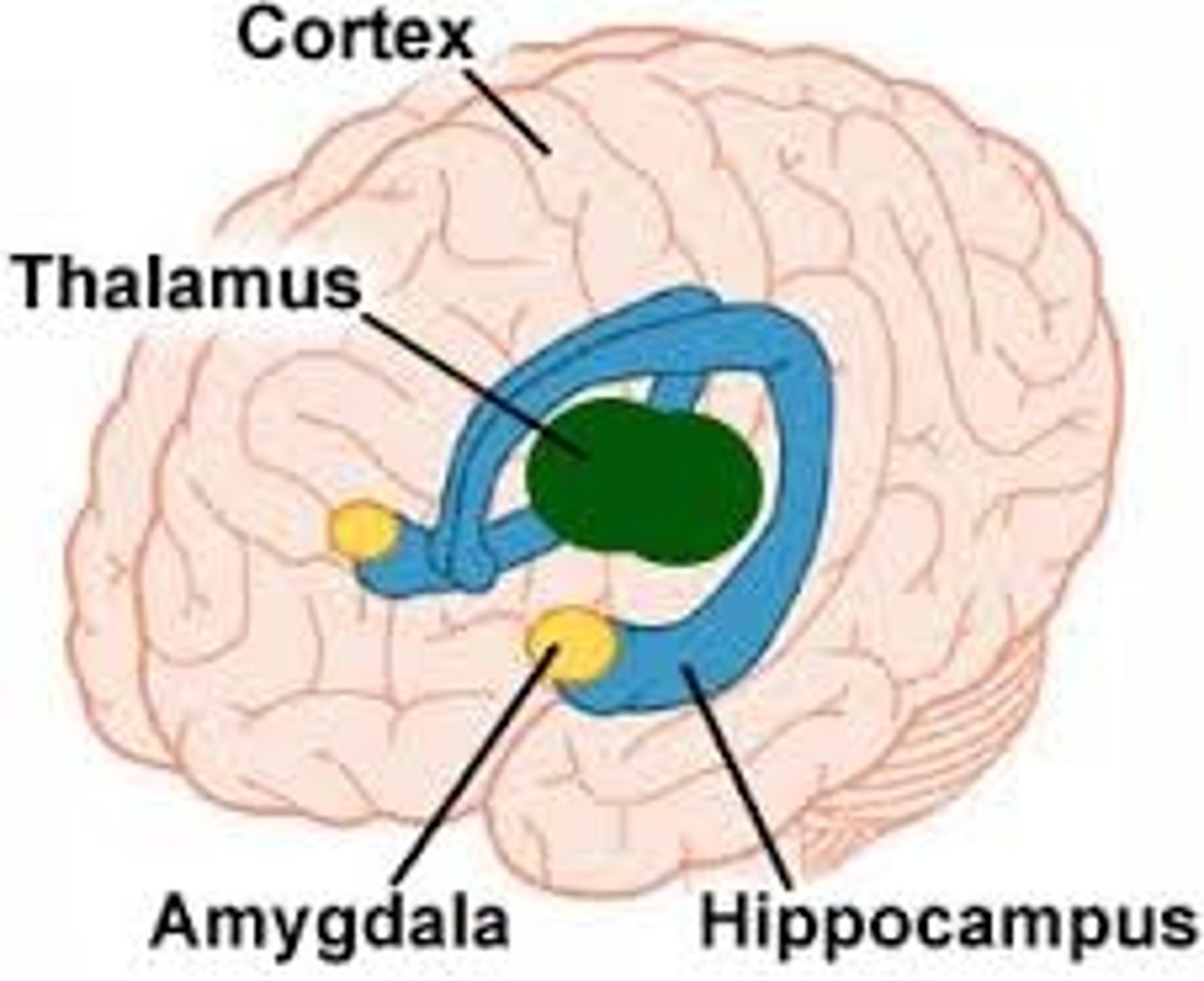
Thalamus
a forebrain structure that processes sensory information for all senses, except smell, and relays it to the cerebral cortex
Hypothalamus
a structure below the thalamus responsible for maintaining a constant internal state
Amyglada
part of limbic system involved in
fear, excitement, and arousal
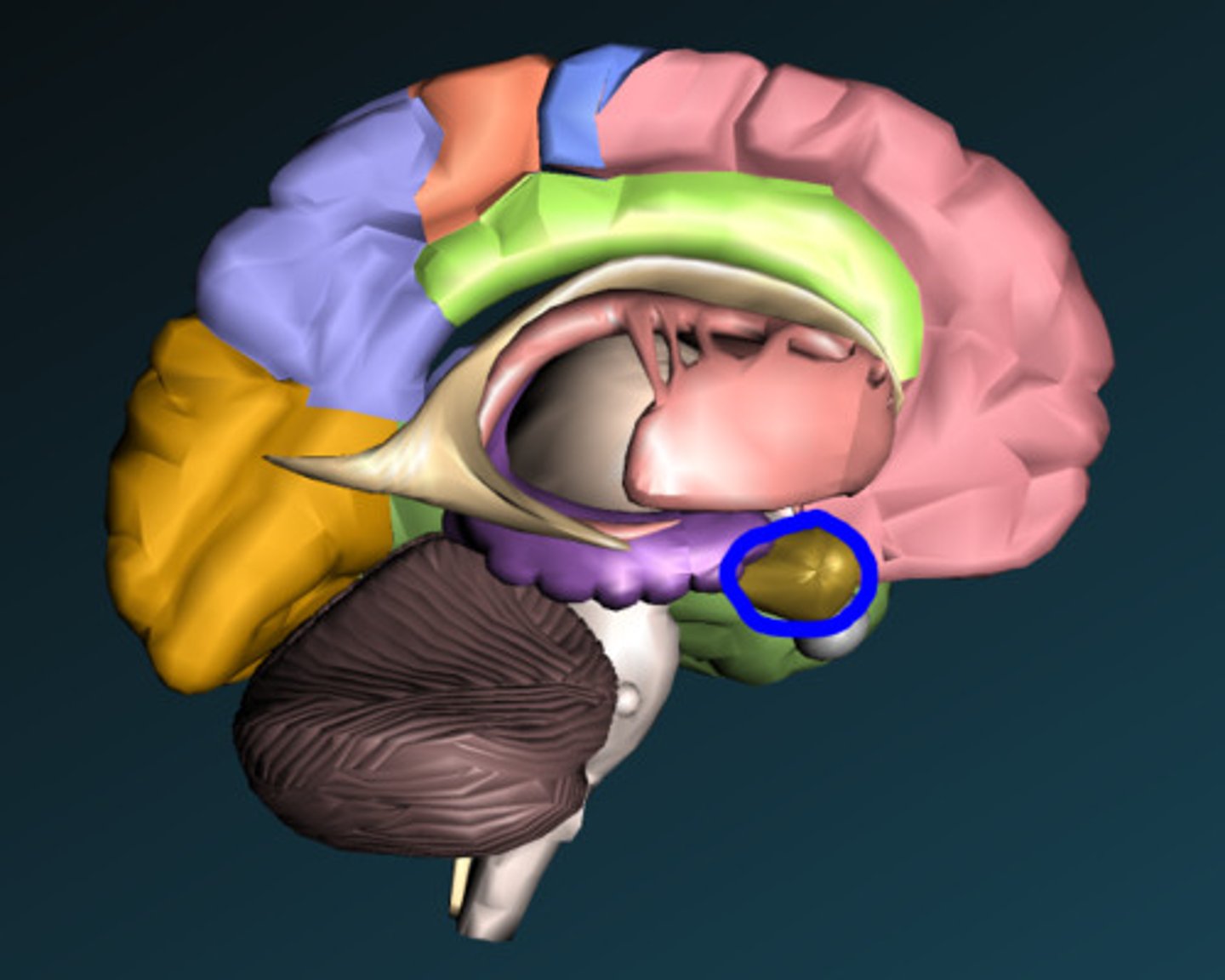
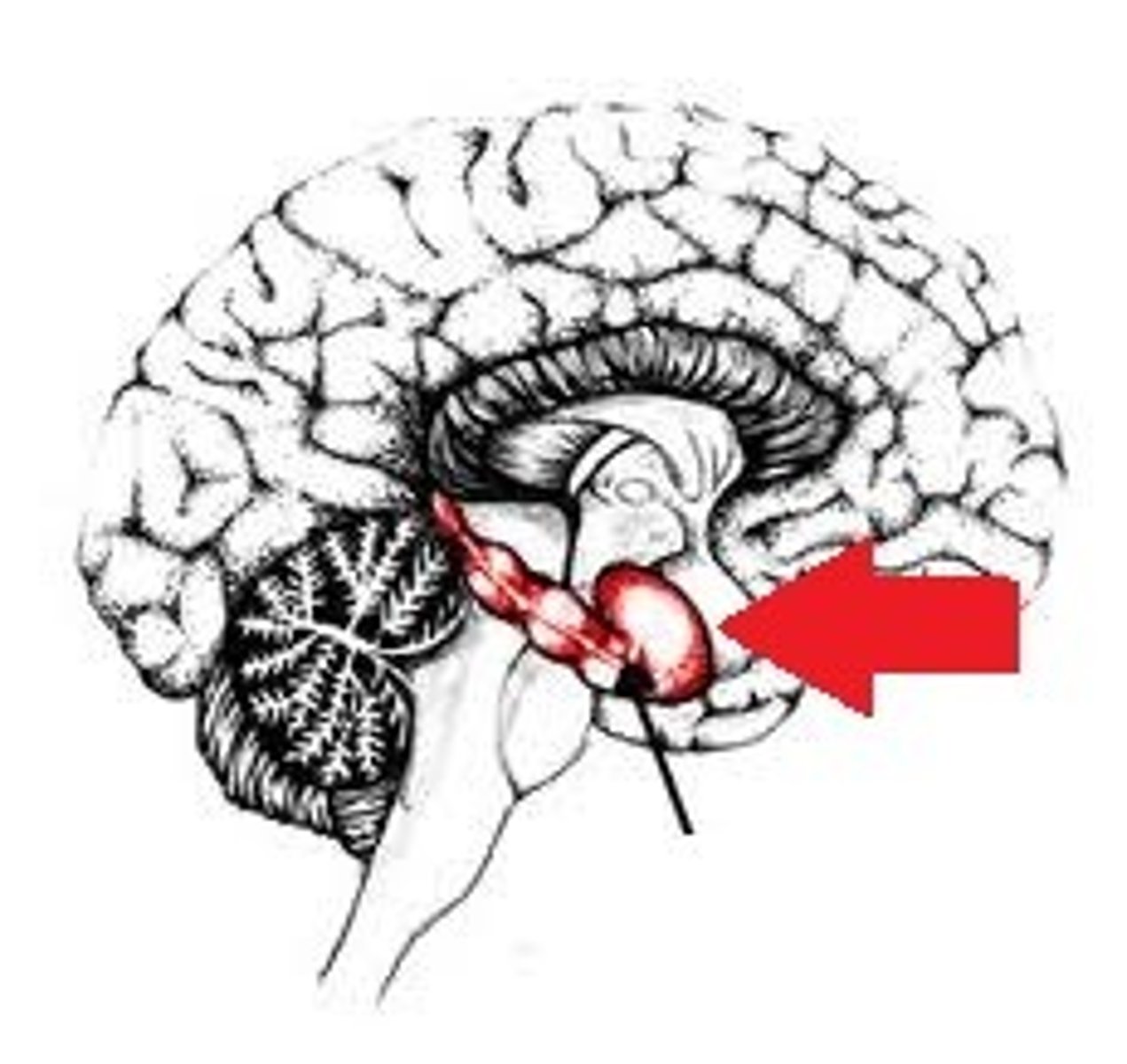
Hippocampus
part of the brain that plays a role in spatial
memory
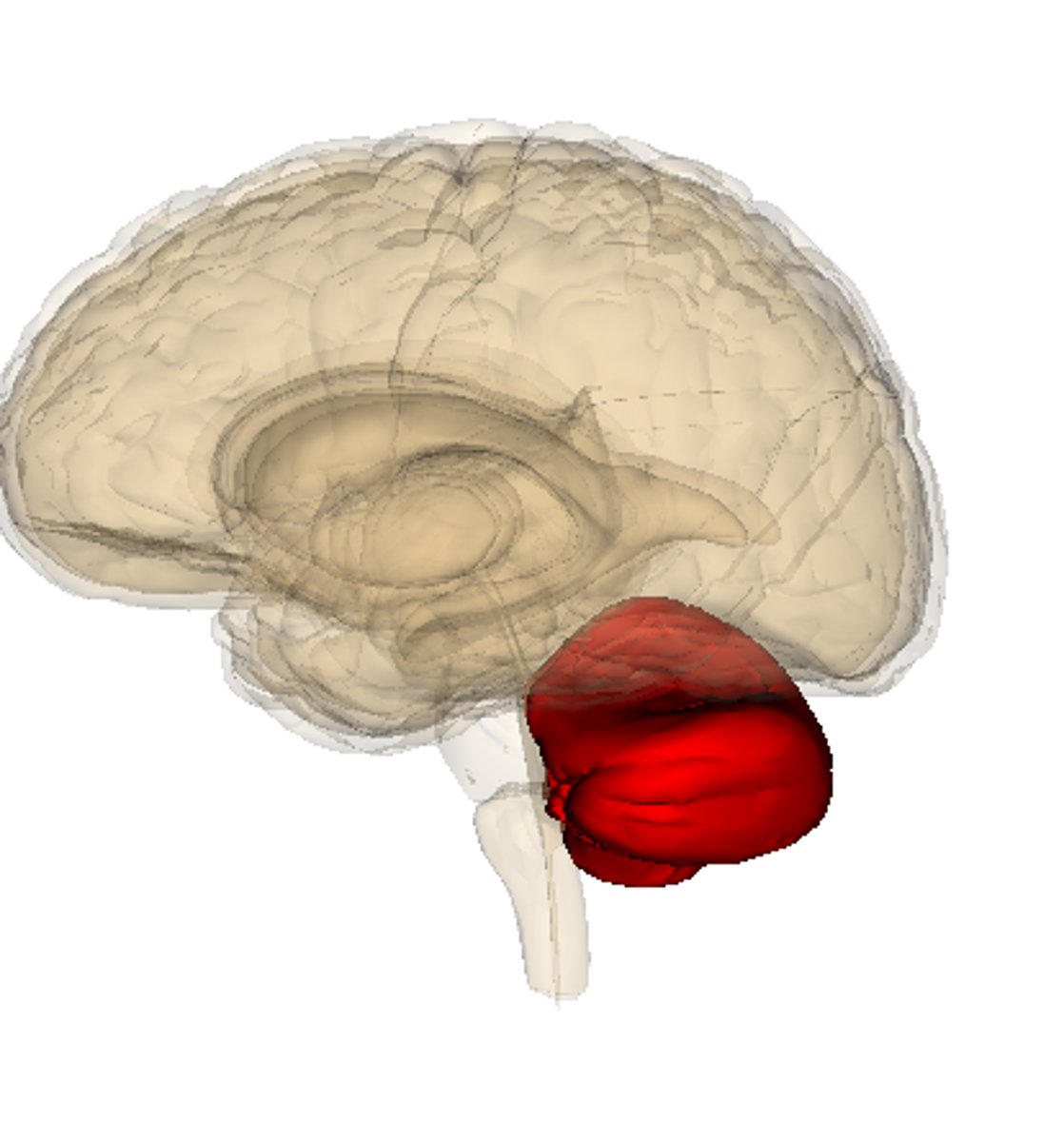
Cerebellum
part of the brain involved in balance for walking, standing, and other complex motor function
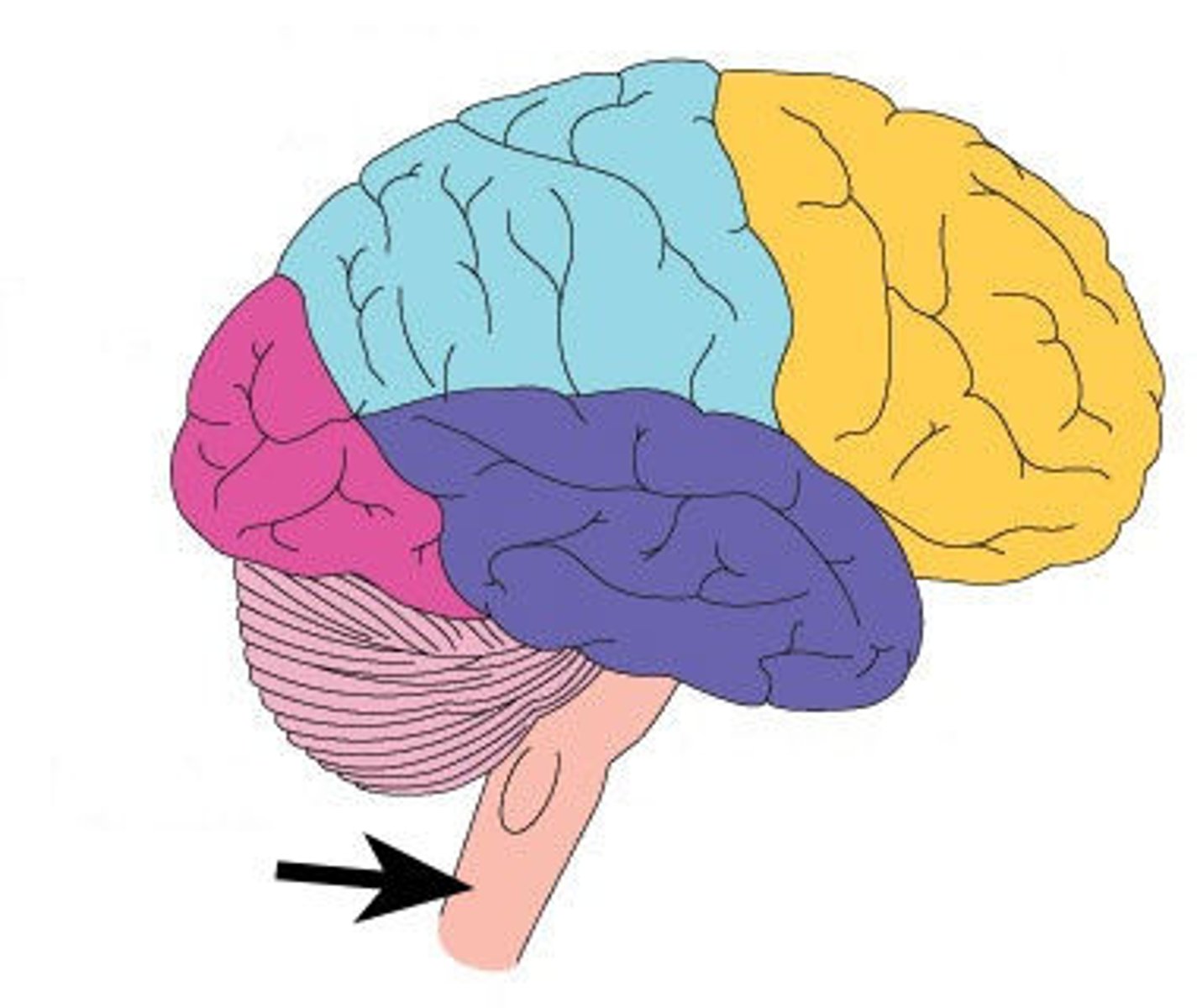
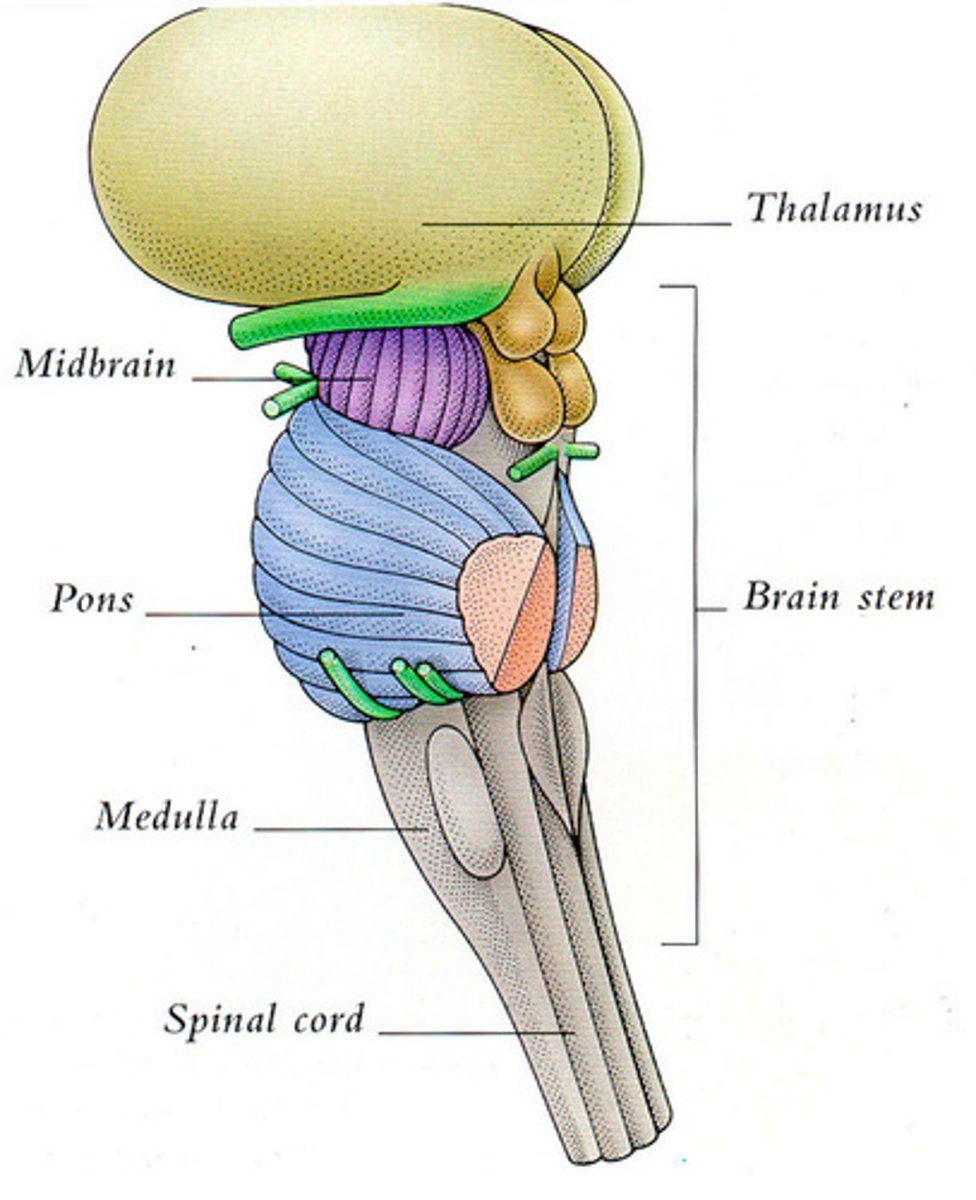
Brain stem
contains the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata; connects the cerebrum to the spinal cord and cerebellum
Reticular activating system (RAS)
network of neurons in the brain stem involved in mediation of behavior and arousal
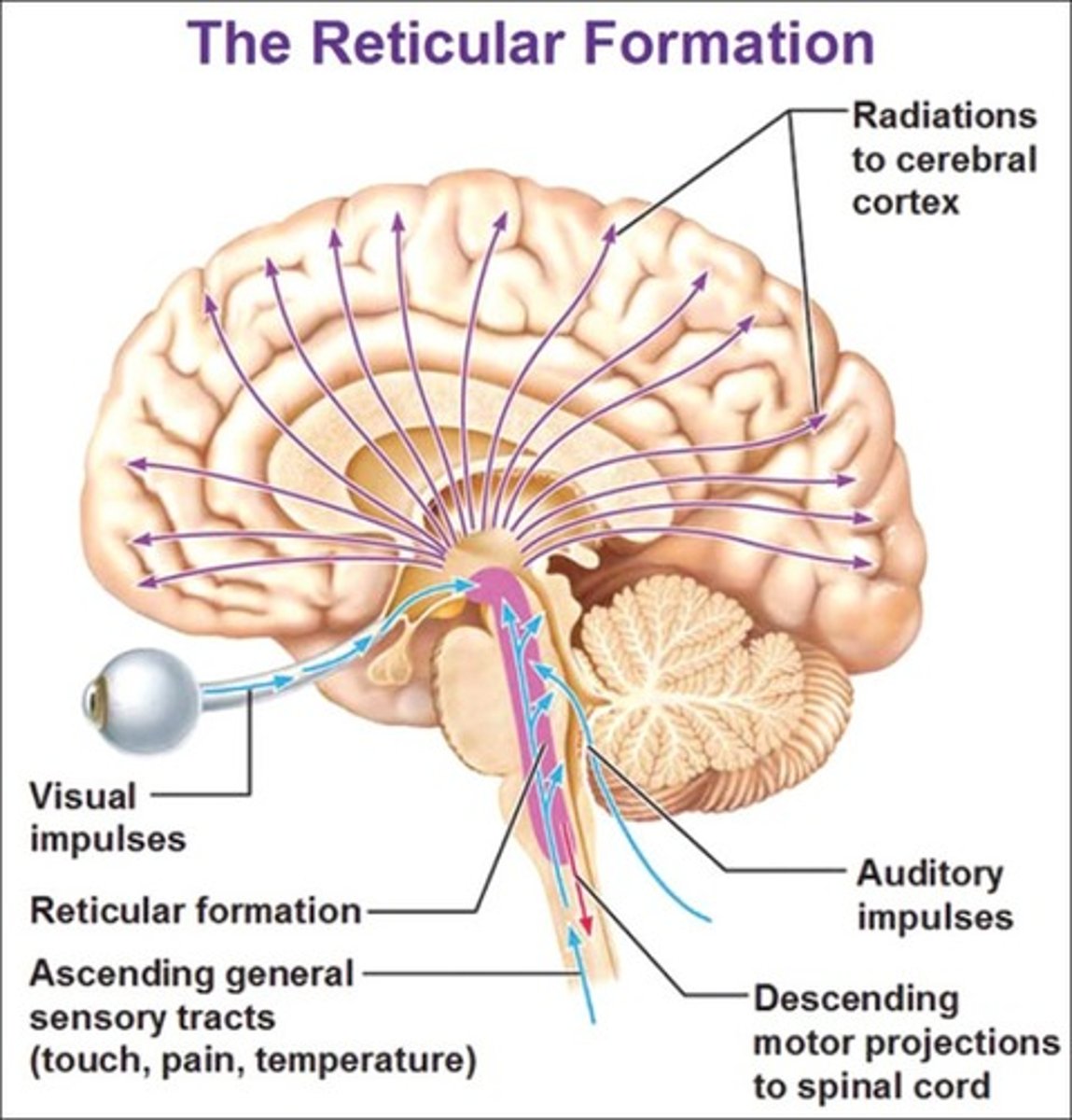
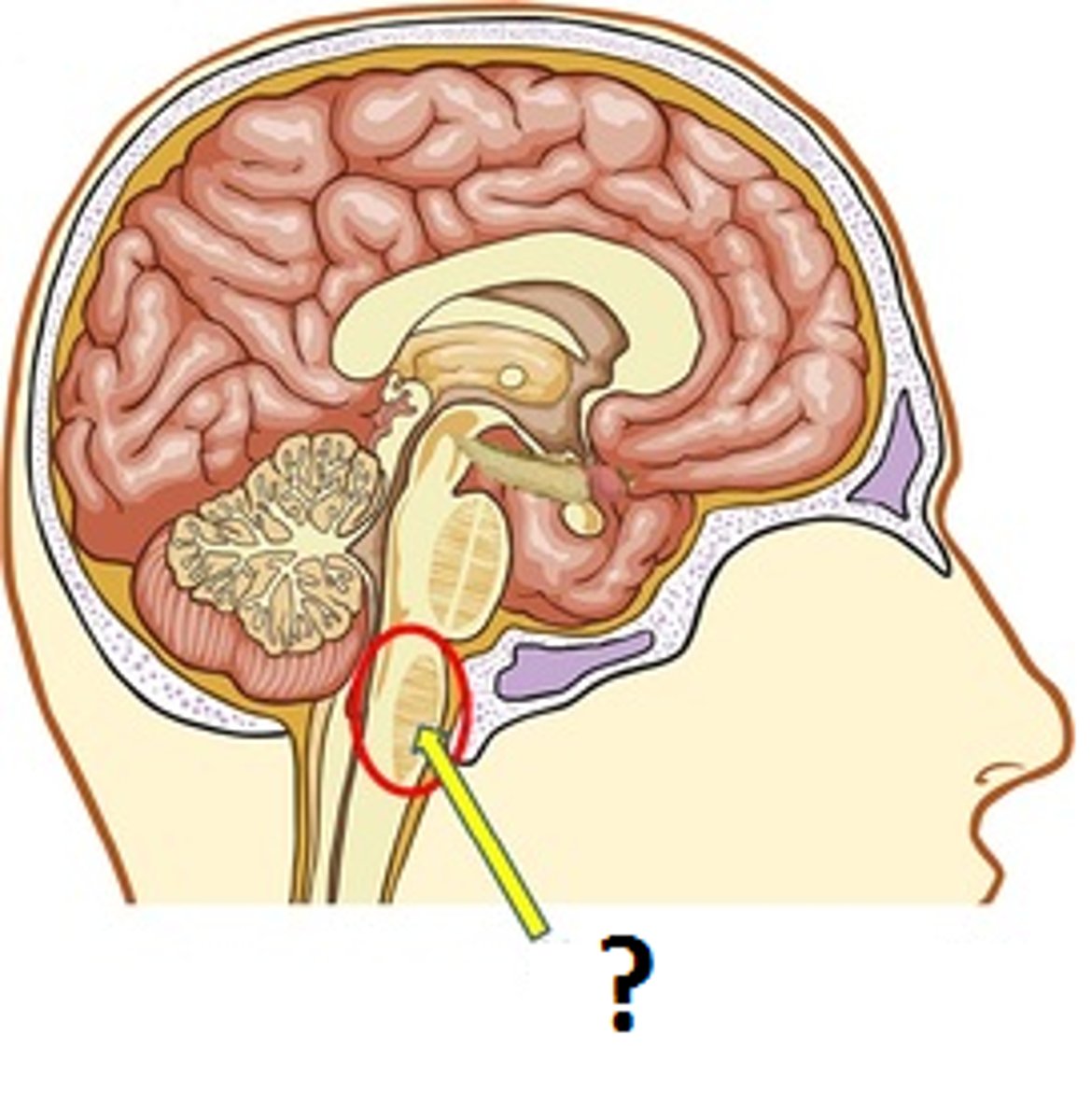
Medulla
part of brain stem involved in basic functions, such as heartbeat, breathing, and blood pressure
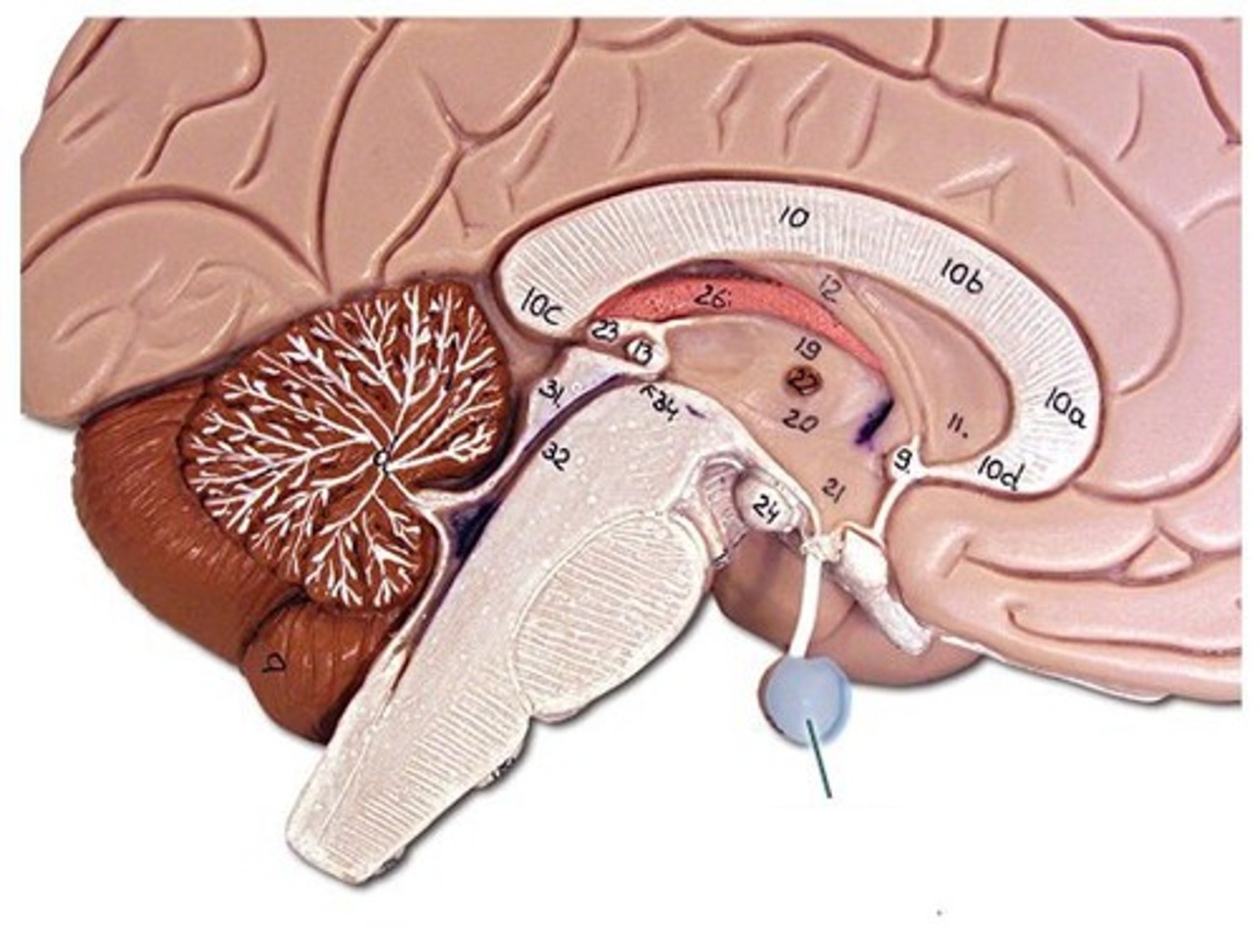
Pituitary gland
makes, stores, and releases several important hormones including those for growth and metabolism
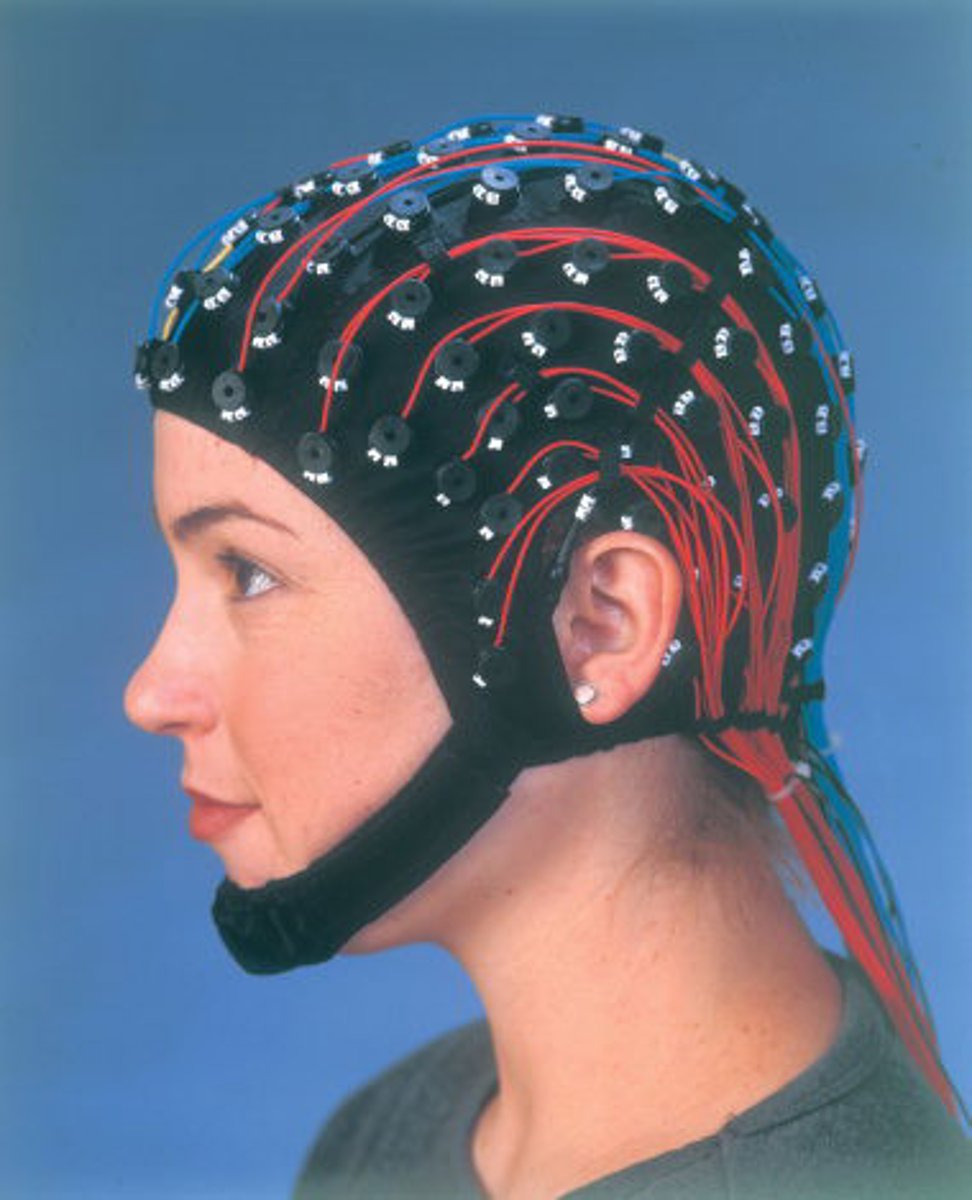
Electroencephalograph (EEG)
recording of the brain's electrical activity at the
surface of the skull
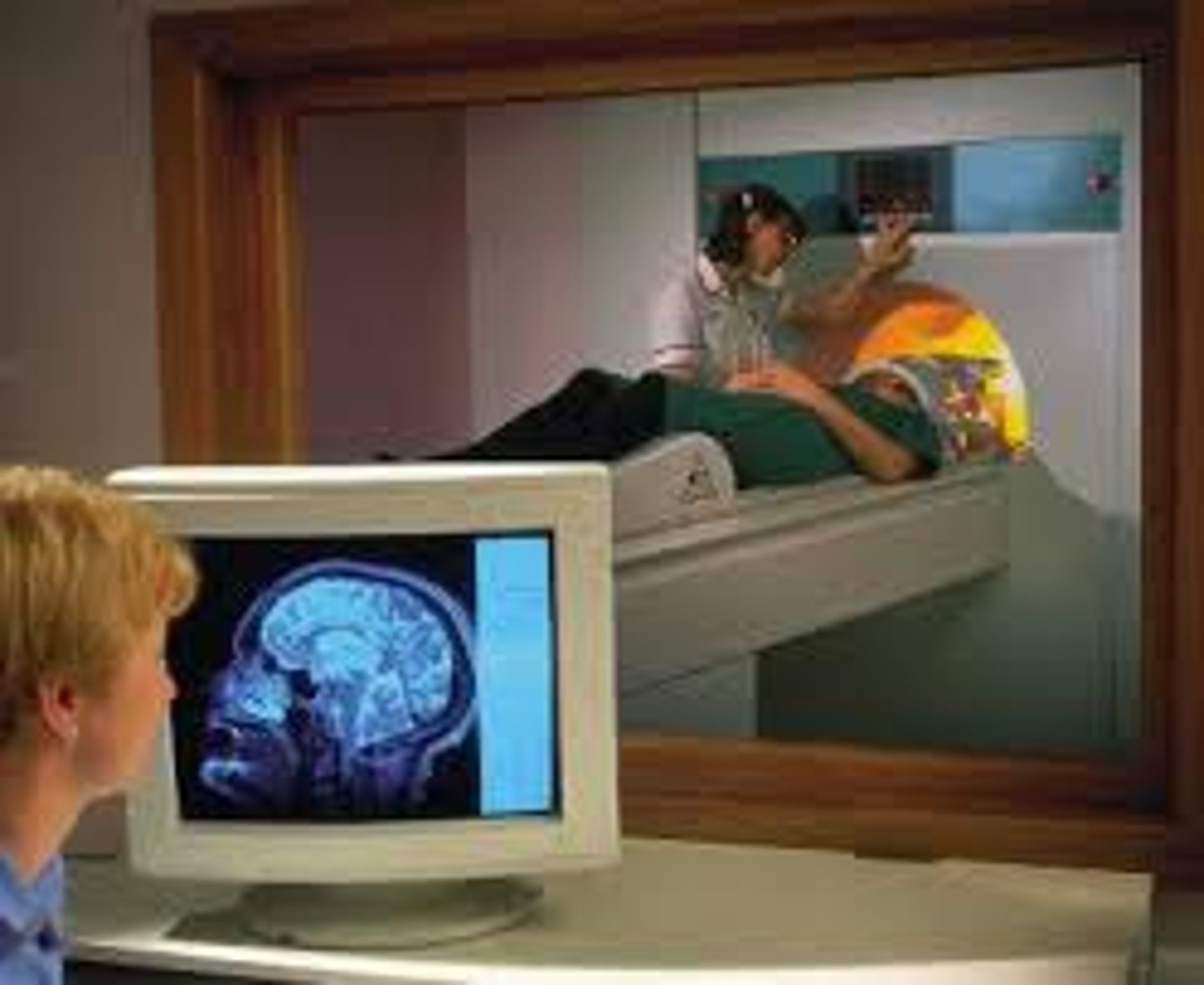
fMRI
a type of MRI scan that can show which areas of your brain are most active during specific functions
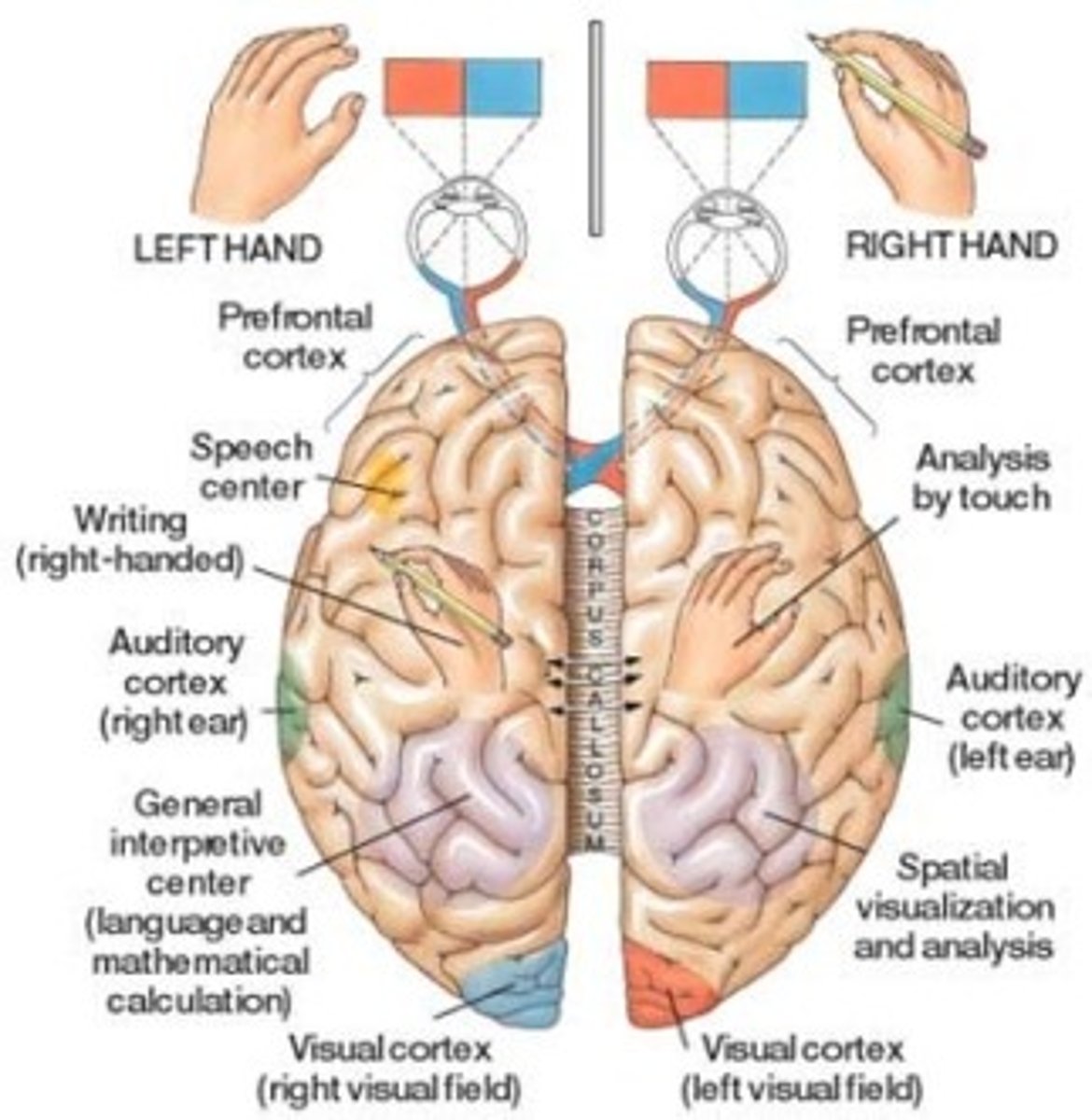
Split-brain research
study of patients with a severed corpus callosum; demonstrates right and left brain specialization; has been used to treat epilepsy
Brain stem
connection to spinal cord that filters information flow between peripheral nervous system and the rest of the brain
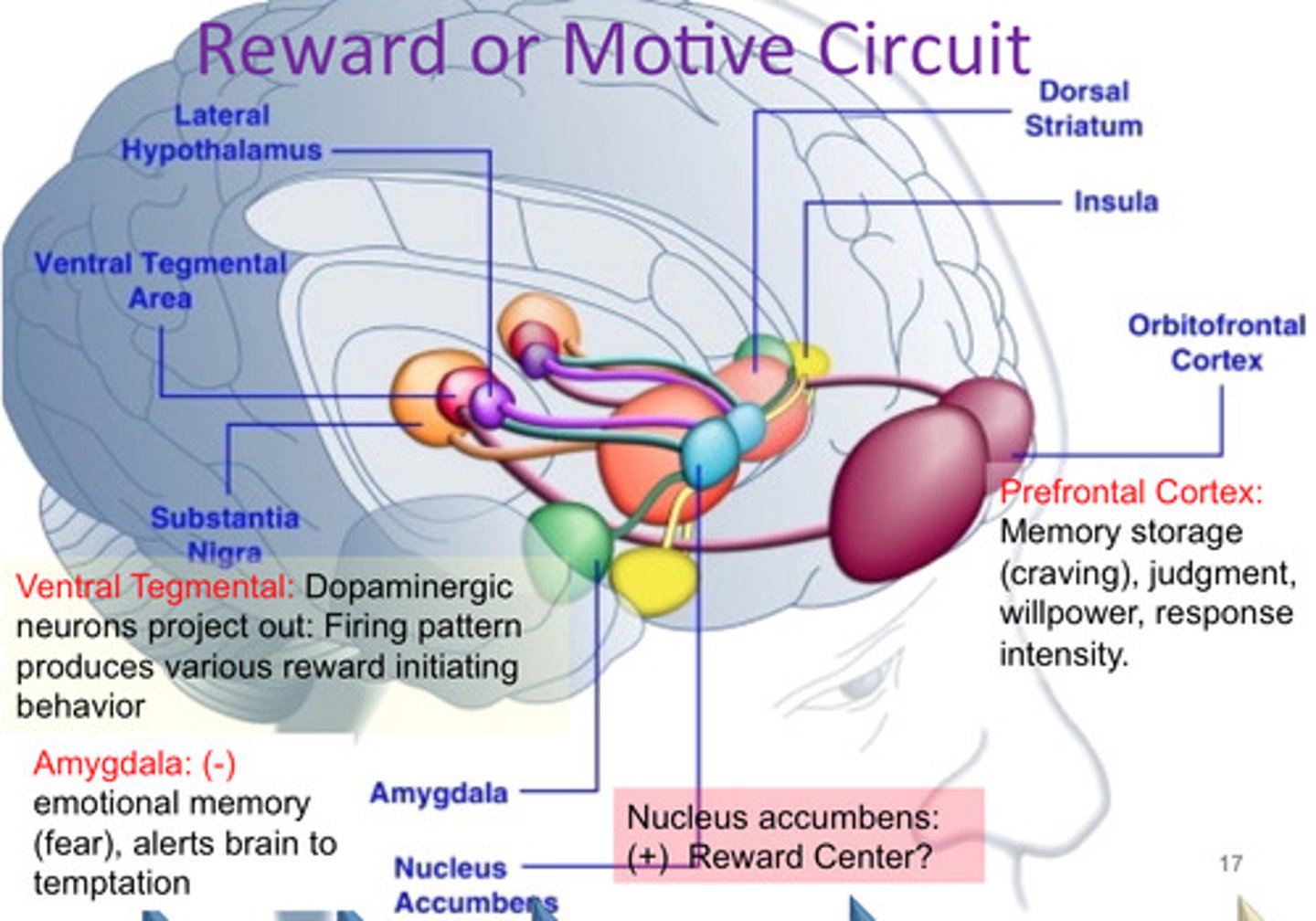
Reward center
a dopamine-rich pathway in the brain that produces feelings of pleasure when activated
Association areas
areas of the cerebral cortex responsible for the coordination and interpretation of information, as well as higher mental processing
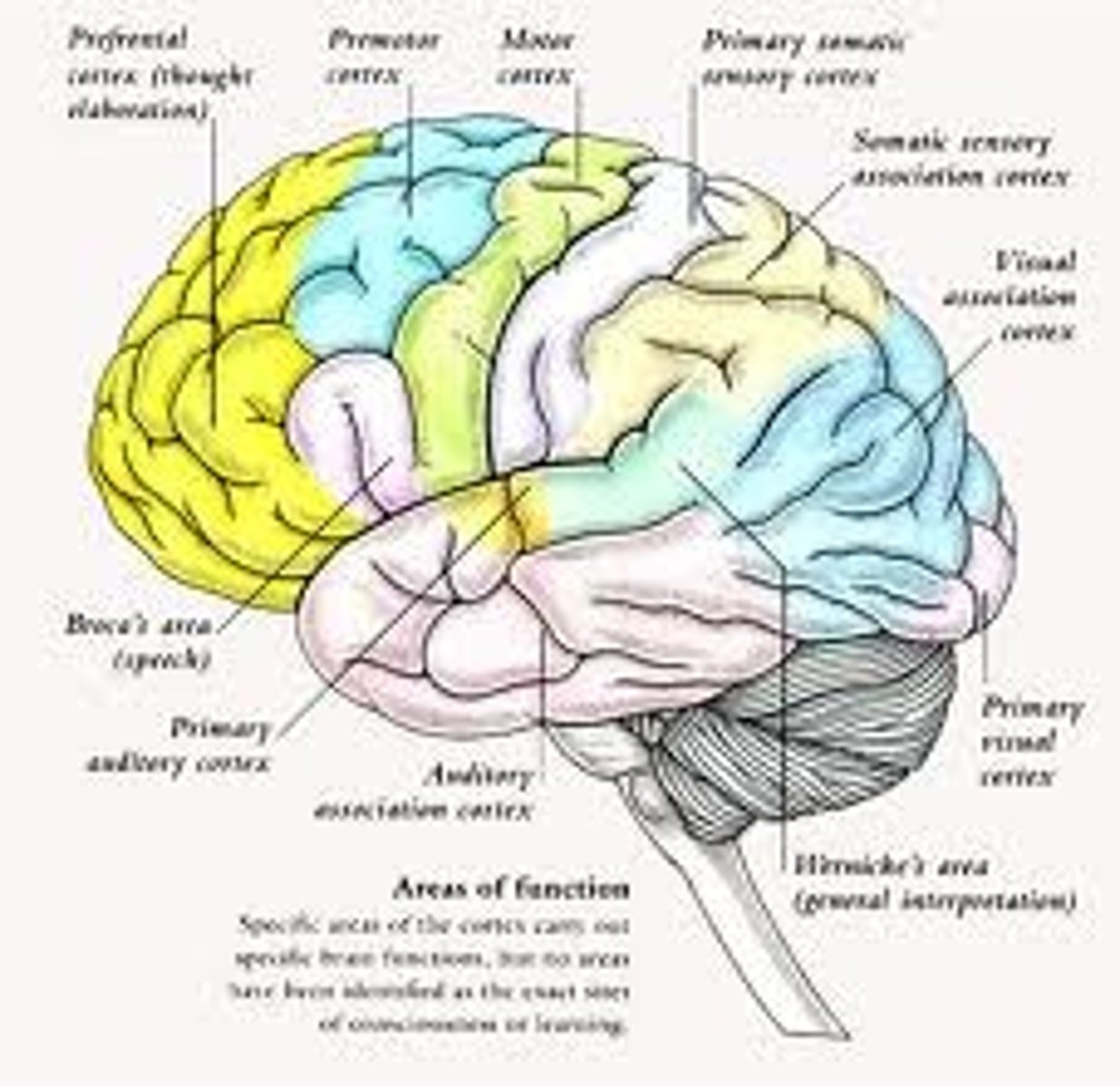
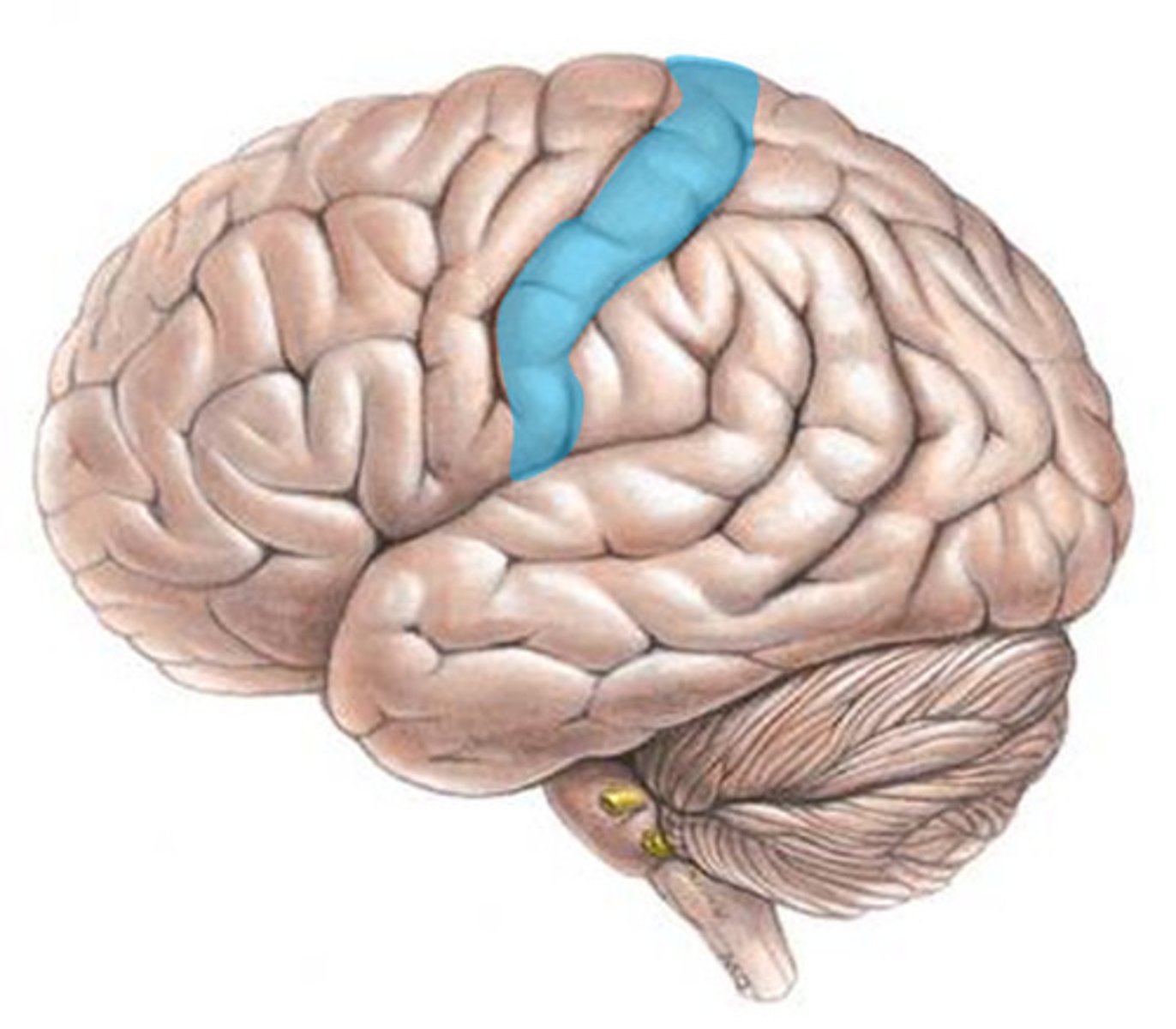
Somatosensory cortex
area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations
Linguistic processing
when language areas of the brain connect meanings of words, grammar, and rules of language to put together an utterance
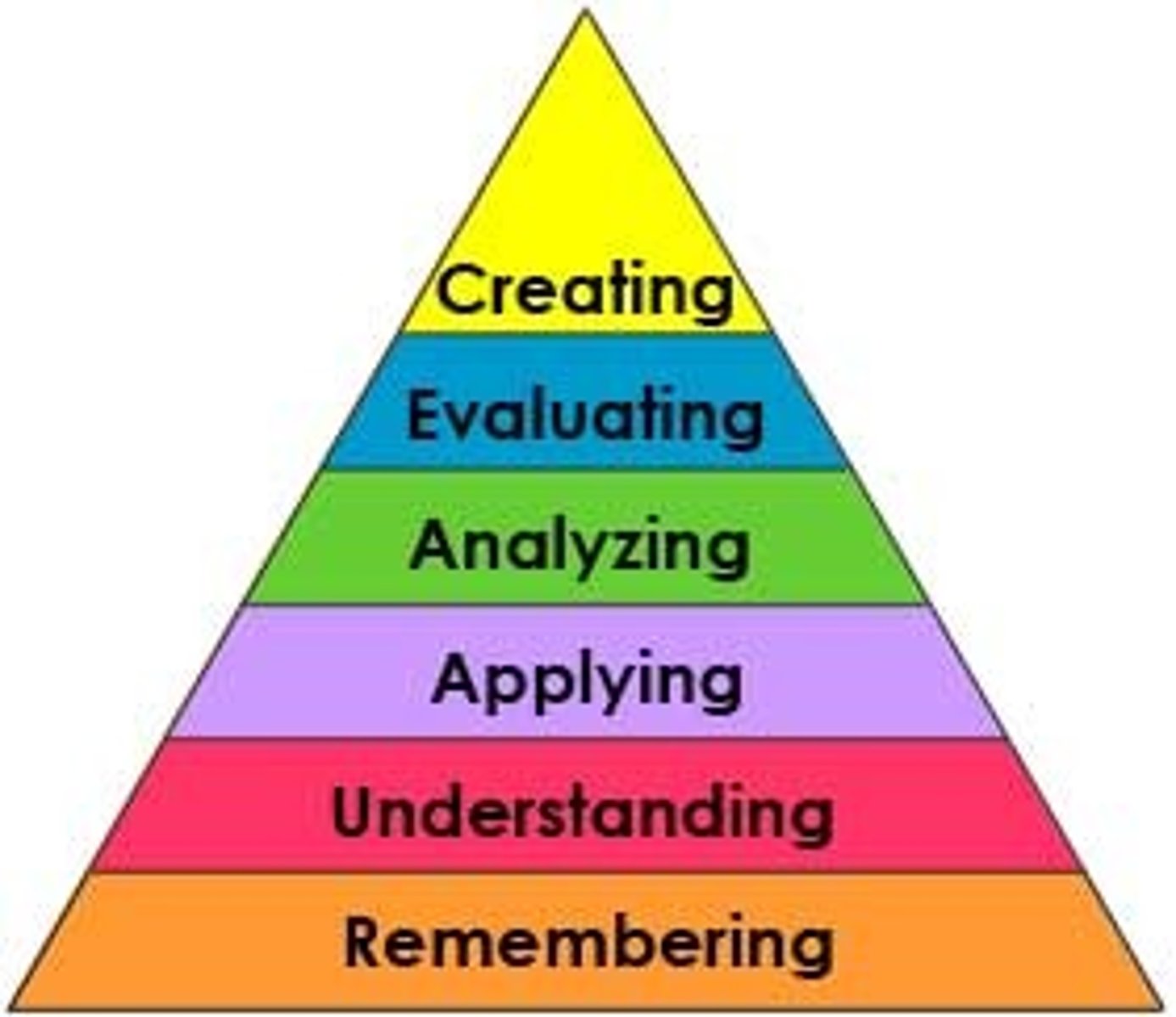
Higher order thinking
includes higher cognitive skills such as problem solving, thinking, reasoning, planning, and organizing
Executive functioning
a set of mental skills that include working memory, flexible thinking, and self-control
Hemispheric specialization
each hemisphere of the brain handles specific tasks (left - logic, language; right - creativity, spatial reasoning, art, emotion)