2.1 - 3.5 enviromental science
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
What type of molecule is water?
Polar
Why is water called the “Universal Solvent”?
Dissolves more substances than any other liquid
Which property of water allows it to move up plant stems against gravity?
Capillary Action
Which of the following is true about ice?
Ice floats because it is less dense than liquid water
True or False
Water has a neutral pH of 7.
True
True or False
The boiling point of water is 0°C (32°F).
False
What is the bioling point of Water?
water boils at 100°C / 212°F
True or False
Water covers more than 70% of Earth’s surface.
True
True or False
Salinity in seawater is mainly from sodium and chloride ions.
True
Explain why water has a high specific heat and why this is important for Earth’s climate.
High specific heat: Water requires a lot of energy to change temperature because of hydrogen bonding. absorbs a lot of heat before changing temperature.
This stabilizes Earth’s climate (oceans absorb/store heat, preventing extreme swings). → Climate Moderator
What are the three factors that increase the density of seawater?
Lower temperature (cold water is denser),
Higher salinity,
Greater depth/pressure.
Which process in the water cycle is directly caused by plants releasing water vapor?
Transpiration
Which process describes water entering soil and rock layers?
Infiltration
Which of the following is NOT a type of fog?
Precipitation fog
Which reservoir contains the largest percentage of Earth’s freshwater?
Glaciers and ice caps
True or False
The water cycle is driven primarily by solar energy.
True
True or False
Runoff is the movement of water from soil into underground aquifers.
False ❌ Runoff = water flowing across land into rivers/oceans. Infiltration is what moves water into aquifers.
True or False
Clouds play an important role in Earth’s energy balance by reflecting solar and terrestrial radiation.
True
What do Clouds do that is important for the earth’s Energy Balance?
clouds reflect incoming solar + outgoing terrestrial radiation.
they both reflect incoming solar energy, creating a cooling effect, and trap outgoing heat radiated from the Earth's surface, leading to a warming effect
True or False
About 2.5% of all water on Earth is freshwater.
True
Explain the difference between evaporation and transpiration.
Evaporation = water from oceans/lakes turns to vapor.
Transpiration = plants release water vapor through their leaves.
Of the world’s freshwater, roughly what percentages are in glaciers, groundwater, and surface water?
~70% glaciers/ice caps
~30% groundwater
~1% surface water
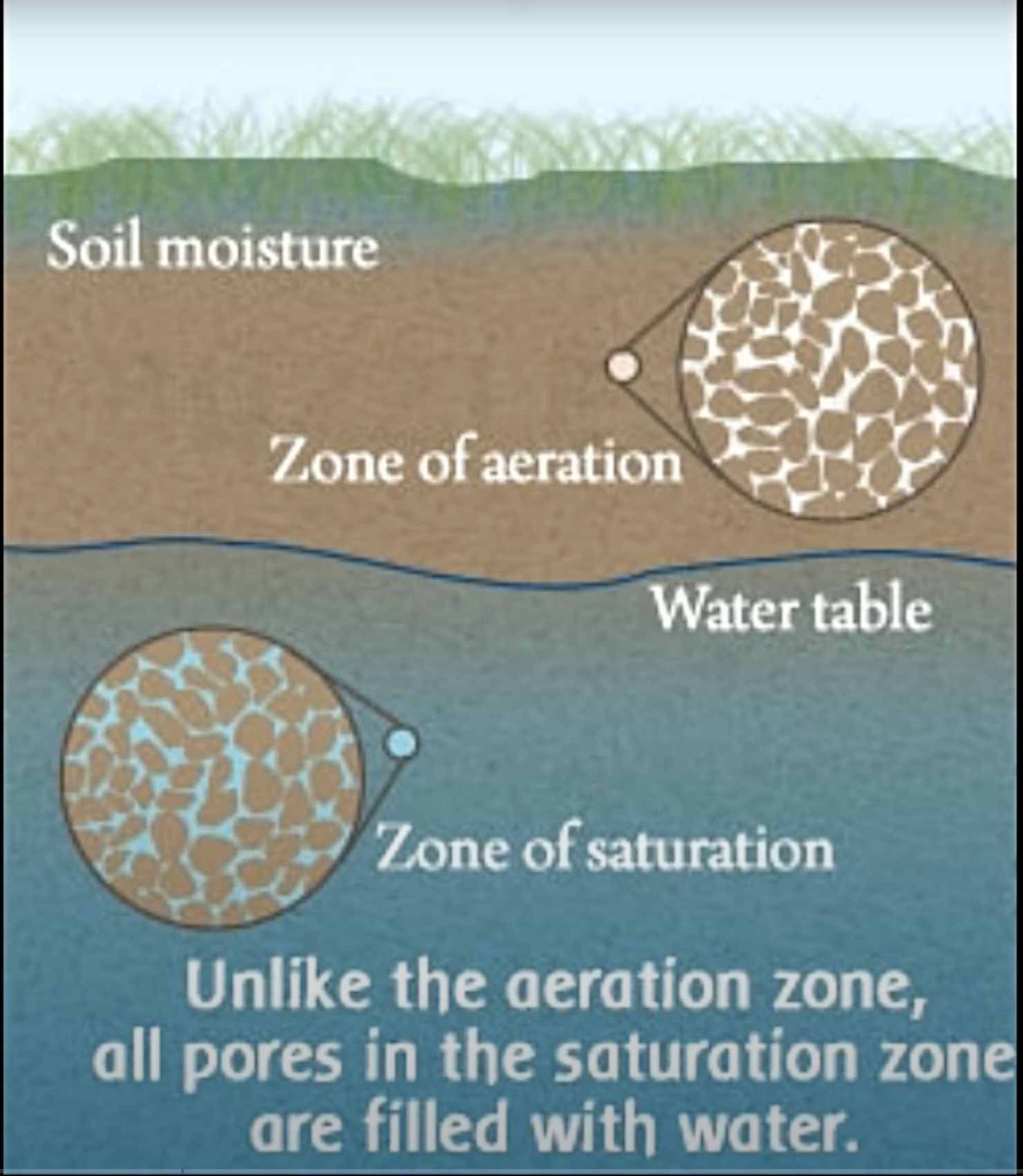
What is the term for the top of the saturated zone in an aquifer?
Water table
Which type of aquifer is trapped between two impermeable layers of rock?
Confined aquifer
What is the zone of aeration?
above the water table, pores contain both air + water.
Which aquifer is Florida’s largest and stretches across multiple southeastern states?
Floridan aquifer
True or False
Overpumping groundwater in coastal areas can cause saltwater intrusion.
True
True or False
Recharge areas are regions where aquifers release water to the surface.
True
True or False
The Biscayne aquifer is shallow and provides water to southeast Florida.
True
Urbanization → pavement/canals reduce recharge by blocking infiltration.
Explain the difference between the zone of saturation and the zone of aeration.
Zone of saturation = pores completely filled with water (below water table).
Zone of aeration = pores partly filled with air + water (above water table).
How can canal construction in Florida threaten groundwater supplies?
Canals divert rainwater out to sea before it can infiltrate into aquifers.
This reduces groundwater recharge, threatening long-term water supplies.
Which of the following is not a type of freshwater ecosystem?
Estuaries
What makes estuaries highly productive ecosystems?
High nutrient input from mixing salt and freshwater.
Which coastal ecosystem helps buffer storm surges, reduce erosion, and store carbon?
Mangrove forests
Coral bleaching occurs mainly because of:
Warmer ocean temperatures stressing corals
True or False
Wetlands act as natural water filters and help control floods.
True
True or False
Coral reefs are sometimes called the “rainforests of the sea.”
True
True or False
Overfishing and pollution have little effect on saltwater ecosystems.
False
True or False
Mangroves are only found in cold, temperate climates.
False
List two ecosystem services that freshwater ecosystems provide.
Drinking water supply.
Irrigation for farming.
Habitat for biodiversity.
Nutrient cycling.
Flood control.
Give two human activities that threaten saltwater ecosystems.
Pollution (oil, plastics, agricultural runoff).
Overfishing.
Habitat destruction (draining wetlands, coral mining, coastal development).
Climate change (warming, sea-level rise, ocean acidification).
Which gas makes up about 78% of Earth’s atmosphere?
Nitrogen
Which layer of the atmosphere contains all weather events?
Trososphere
Which layer contains the ozone layer?
Stratosphere
In which layer do meteors usually burn up?
Mesosphere
The Montreal Protocol was created to address:
Ozon depletion
Which atmospheric circulation cell dominates the tropics?
Hadley Cell
In the Northern Hemisphere, the Coriolis Effect causes winds to:
Bend right, clockwise
Which type of front is formed when cold air forces warm air upward, often creating
Cold Front
Which scale is used to measure hurricane strength by wind speed?
Saffir-Simpson Scale
Why don’t hurricanes form at the equator?
Coriolis Effect is absent
Which is NOT one of the five major pollutants measured by the Air Quality Index (AQI)?
Oxygen
Pre-industrial CO₂ levels were ~278 ppm. By 2016 they had risen to:
400+ ppm
Which property of water allows insects like water striders to walk on its surface?
Cohesion
Which process describes water vapor released from plants?
Transpiration
Which process moves water into aquifers and groundwater systems?
Infiltration
The largest percentage of Earth’s freshwater is found in:
Glaciers and ice caps
Which Florida aquifer is shallow and supplies water to SE Florida?
Biscayne aquifer
What causes saltwater intrusion into freshwater aquifers?
Overpumping groundwater in coastal areas
Which ecosystem is called the “rainforest of the sea”?
Coral reefs
Which coastal ecosystem protects shorelines from erosion and storm surges while storing carbon?
Mangroves
Which type of fog forms when warm, moist air moves over a cooler surface?
Advection fog
What is the average salinity of seawater?
35 ppt
Which process brings nutrient-rich deep water to the surface?
Upwellling
True or False
The troposphere contains about 75–80% of Earth’s atmospheric mass.
True
True or False
Air pressure increases with altitude.
False
True or False
High-pressure bands (around 30° latitude) are usually associated with deserts and dry weather.
True
True or False
Hurricanes often weaken when they move over land due to loss of warm water fuel.
True
True or False
The Saffir-Simpson Scale measures both wind speed and rainfall.
False
True or False
The greenhouse effect is entirely harmful to life on Earth.
False
True or False
The IPCC concluded with high certainty that human activity causes climate change.
True
True or False
Cohesion is when water molecules stick to other substances.
False
True or False
Capillary action results from both adhesion and cohesion.
True
True or False
Groundwater recharge areas are where water enters an aquifer.
True
True or False
The Biscayne aquifer is deeper and larger than the Floridan aquifer.
False
True or False
Wetlands help filter pollutants and control flooding
True
True or False
Coral bleaching is caused primarily by nutrient pollution from farms.
False
What are Estuaries?
nutrient-rich ecosystems where freshwater mixes with saltwater.
What is Radiation Fog?
ground cools overnight, air above cools.
Earth's surface rapidly cools by radiating heat into space, causing the air near the ground to cool to its dew point and condense into fog
What is Advection fog?
warm moist air moves over cold surface.
forms when warm, moist air moves horizontally across a cold surface, such as a cold body of water or land, cooling the air to its dew point and causing water vapor to condense into fog.
What is Upslope fog?
moist air pushed up mountains → cools → fog.
forms when moist air is forced up a hill or mountain slope by the wind, cooling as it rises and causing the water vapor to condense into fog.
Why does temperature decrease with altitude in the troposphere?
It’s farther from Earth’s surface heat source
Which process forms ozone (O₃) naturally in the stratosphere?
UV radiation splitting O₂ molecules and recombining
Which layer of the atmosphere has the highest temperatures due to absorption of solar radiation by nitrogen and oxygen?
Thermosphere
Around 30° latitude, descending air leads to deserts. Which global circulation cell is responsible?
Hadley Cell
Hurricanes weaken when they:
Move into colder water or over land
Which pollutant is a primary contributor to photochemical smog?
Nitrogen oxides
The main greenhouse gas responsible for long-term climate change is:
Carbon dioxide
The Coriolis Effect occurs because:
Earth rotates on its axis
Land subsidence due to overdrawing can cause:
Sinkholes, reduced recharge, and infrastructure damage.
Ecosystem with least vegetation:
Mud flats
The ocean Floor can be chracterized by which of the following conditions?
High pressure
How is salinity expressed?
in parts per thousand
Water is highly adhesive, which means that
water molecules stick to the molecules of other substances.
What would be an example of non-point source pollution?
a pollutant being carried by sediment laden river that flows through many farms
Which of the following species is invasive in the Florida Coral Reef Tract?
Lion fish
Life on Earth is dependent on all the properties of water as well as the abundance of water. Which property of water is probably most important for the functioning of organisms at the molecular level?
versatility as a solvent
Which of the following is NOT an example of agricultural pollution?
runoff of toxic chemicals from a mining operation
As a wave begins to feel bottom when it approaches shorelines, what happens to the wave?
Wavelength increases, and wave height decreases.
True or False
A riverbed with a shallow slope will yield high velocity streamflow.
False