Topic 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/120
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:14 AM on 3/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
1
New cards
What is a saccharide?
A carbohydrate
2
New cards
What is the general formula for saccharides?
Cn(H20)n
3
New cards
Are monosaccharides soluble in water?
Yes
4
New cards
a) What is the formula of pentose?
b) Give two examples of a pentose sugar and their function
b) Give two examples of a pentose sugar and their function
a) C5H10O5
b) Deoxyribose (component of DNA)
Ribose (component of RNA)
b) Deoxyribose (component of DNA)
Ribose (component of RNA)
5
New cards
a) What is the formula for hexose?
b) Give three examples of a hexose sugar and their functions
b) Give three examples of a hexose sugar and their functions
a) C6H1206
b) Glucose (major respiratory substrate in animals and plants, monomer of disaccharides and polysaccharides)
Fructose (respiratory substrate, used for the synthesis of sucrose, and a constituent of nectar and fruit)
Galactose (respiratory substrate, and used for synthesis of lactose)
b) Glucose (major respiratory substrate in animals and plants, monomer of disaccharides and polysaccharides)
Fructose (respiratory substrate, used for the synthesis of sucrose, and a constituent of nectar and fruit)
Galactose (respiratory substrate, and used for synthesis of lactose)
6
New cards
What is an identifying feature of glucose?
An -OH on the 4th carbon down, on the right
7
New cards
What is an aldehyde group?
H-C=O
8
New cards
What is an identifying feature of fructose?
A ketone group on the second carbon
9
New cards
What is a ketone group?
C=O
10
New cards
What is an identifying feature of galactose?
Aldehyde group on the first carbon and an -OH on the 4th carbon, on the left
11
New cards
What is a stereoisomer?
Each of two or more compounds differing only in the spatial arrangement of their atoms. They have the same number of atoms, but different 3 dimensional arrangements
12
New cards
What is a structural isomer?
A type of isomer in which molecules with the same molecular formula have different bonding patterns and atomic organisation
13
New cards
What bond joins two monosaccharides together?
A glycosidic bond
14
New cards
Draw the ring formation of glucose.
\
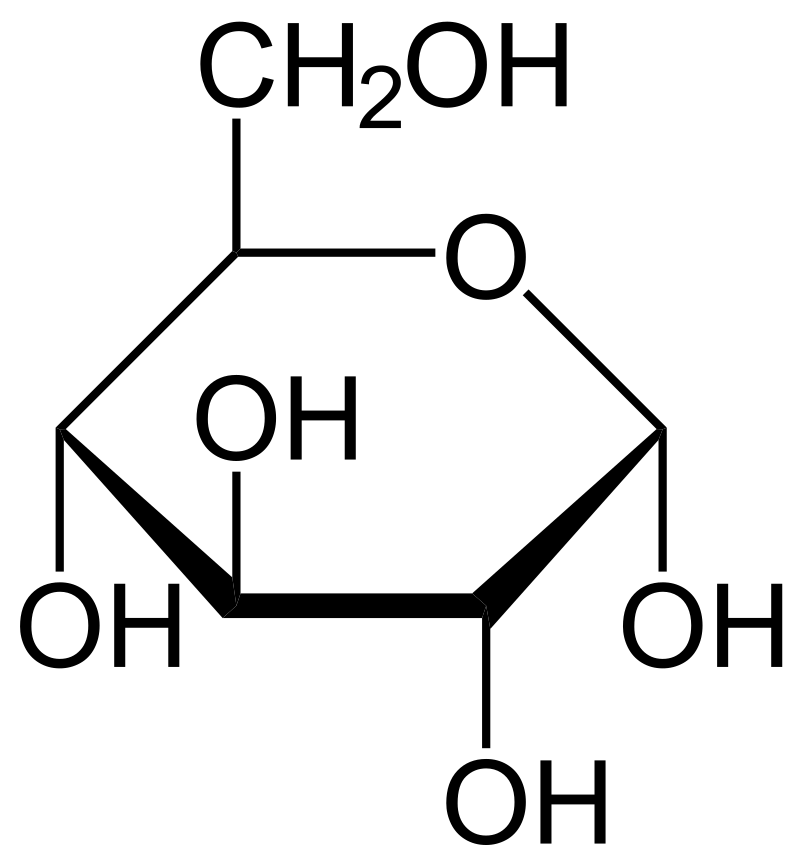
15
New cards
What is the difference between alpha and beta glucose?
The hydroxyl group on the 1st carbon is orientated downwards in alpha glucose, and upwards in beta glucose.
16
New cards
What is the difference between alpha glucose and galactose?
The orientation of the hydroxyl group on the 4th carbon. In galactose, it is positioned upwards (in the skeletal form), whereas in alpha glucose it is positioned downwards.
17
New cards
Name 2 monosaccharides which are stereoisomers of one another.
Galactose and alpha/beta glucose.
18
New cards
Name 2 monosaccharides which are structural isomers of one another.
Fructose and glucose/galactose.
19
New cards
How do disaccharides form?
A condensation reaction.
20
New cards
How are disaccharides split apart into two monosaccharides?
Through a hydrolysis reaction (where water is added).
21
New cards
How is sucrose formed?
The condensation of alpha glucose and fructose.
22
New cards
What is the glycosidic bond in sucrose?
a(1-2) glycosidic bond.
23
New cards
How is lactose formed?
The condensation of alpha glucose and galactose.
24
New cards
What is the glycosidic bond in lactose?
b(1-4) glycosidic bond.
25
New cards
How is maltose formed?
The condensation of alpha glucose and alpha glucose.
26
New cards
What is the glycosidic bond in maltose?
a(1-4) glycosidic bond.
27
New cards
Why is the soluble nature of glucose an advantage in terms of its function?
It allows the osmotic effect to take place for transport. If it was not able to be transported easily, then cells would not be able to respire efficiently and effectively.
28
New cards
What are the polysaccharides that make starch?
Amylose and amylopectin.
29
New cards
What percentage of starch is:
a) amylose
b) amylopectin
a) amylose
b) amylopectin
a) 30%
b)70%
b)70%
30
New cards
Why is it more beneficial that starch is made up of more amylopectin than amylose?
Amylopectin is branched but amylose is unbranched. The branches make it easier for enzymes to break the starch down and gives our bodies access to glucose much quicker. This is important as we are very metabolically active.
31
New cards
True or false? Starch does not contain alpha glucose.
False. Starch does contain alpha glucose. This creates the glycosidic bonds easily as the hydroxyl groups align to release water.
32
New cards
What is the structure of amylose?
* Amylose is an unbranched chain of (1-4) glucose
* It is between 200 and 5000 units long
* It forms an alpha helix shape (coiled) due to hydrogen bonding
* It is between 200 and 5000 units long
* It forms an alpha helix shape (coiled) due to hydrogen bonding
33
New cards
What is the structure of amylopectin?
* A branched chain of bonds on the (1-4) carbons and (1-6) carbons of glucose monomers
* It is between 5000 and 100 000 repeating units long
* It forms a network
* Not as good for storage as amylose is but is easier for enzymes to digest due to the branches
* It is between 5000 and 100 000 repeating units long
* It forms a network
* Not as good for storage as amylose is but is easier for enzymes to digest due to the branches
34
New cards
Give an enzyme which can break amylopectin down.
Amylase
35
New cards
What is the structure of glycogen?
A branched chain of (1-4) and (1-6) glucose.
36
New cards
What is the difference between amylopectin and glycogen?
Glycogen is similar to amylopectin however it is more branched and has less units.
37
New cards
Where do you find cellulose?
In the cell walls of plant cells.
38
New cards
What is the structure of cellulose?
* It is an unbranched straight chain of b(1-4) glucose
* The chains align parallel to each other forming tough fibres and a crystalline structure, all held together by hydrogen bonds
* Strong hydrogen bonding allows cellulose to give cells the structural support they require from the cell wall
* As cellulose is made from beta glucose, the hydroxyl groups wont align. This means there is an inversion on every other monomer unit
* The chains align parallel to each other forming tough fibres and a crystalline structure, all held together by hydrogen bonds
* Strong hydrogen bonding allows cellulose to give cells the structural support they require from the cell wall
* As cellulose is made from beta glucose, the hydroxyl groups wont align. This means there is an inversion on every other monomer unit
39
New cards
What is the equation for the Benedict’s test?
Sugar + CuSO4 → Oxidised sugar + Cu2O
40
New cards
What does Benedict’s solution test for?
Reducing sugars
41
New cards
Give 2 disaccharides that will react with Benedict’s.
Maltose and lactose.
42
New cards
Give the equations for testing for non-reducing sugars.
Step 1:
Sucrose + HCl → Glucose + Fructose
Step 2:
Glucose/Fructose + CuSO4 → Oxidised sugar + Cu2O
Sucrose + HCl → Glucose + Fructose
Step 2:
Glucose/Fructose + CuSO4 → Oxidised sugar + Cu2O
43
New cards
What is the equation for testing for starch?
Amylose + Iodine → Amylose-iodine complex
44
New cards
Are polysaccharides soluble in water?
No, they are not.
45
New cards
How does the dipole nature of water occur?
Oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen. The v-shaped structure leads to an uneven distribution of negative charge, resulting in a dipole.
46
New cards
The negative and positive elements of a water molecule facilitate…
hydrogen bonding.
47
New cards
How do water molecules form intermolecular forces?
The dipole on water molecules mutually attract each other, and connect through hydrogen bonding.
48
New cards
True or false? The electrons are evenly distributed in the energy levels of a water molecule.
False
49
New cards
How is water able to resist state change?
Water has a high specific heat capacity, high latent heat of vaporisation, and high latent heat of fusion to allow it to absorb a lot of energy.
50
New cards
True or false? Water can separate non-polar molecules.
False. These are hydrophobic.
51
New cards
What is the result of water’s cohesive nature?
The molecules stick together to create a high tensile strength and surface tension.
52
New cards
What will water molecules’ adhesion facilitate?
The adhesion will facilitate capillary action.
53
New cards
Explain how the dipolar nature of water is essential for living organisms. (2 marks)
* Water can form hydrogen bonds to hold it together as a liquid, allowing it to move in mass flow systems
* Water is a solvent and is a large component in the blood, allowing it to transports soluble molecules around the body
* Water is a solvent and is a large component in the blood, allowing it to transports soluble molecules around the body
54
New cards
Give three examples of a lipid.
* Fats
* Oils
* Waxes
* Oils
* Waxes
55
New cards
Are lipids soluble in water?
No, they are insoluble in water.
56
New cards
Give 5 types of lipids.
* Triglycerides
* Phospholipids
* Cholesterol
* Waxes
* Glycolipids
* Phospholipids
* Cholesterol
* Waxes
* Glycolipids
57
New cards
What are triglycerides composed of?
Glycerol and fatty acids.
58
New cards
What homologous series does glycerol belong to?
Alcohol
59
New cards
What defines something as an alcohol?
An alcohol is any organic compound whose molecules contain one or more hydroxyl groups attached to a carbon atom.
60
New cards
Draw glycerol.
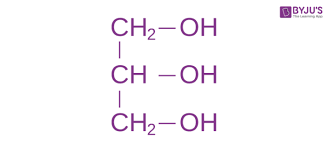
61
New cards
What homologous group do fatty acids belong to?
Carboxylic acids.
62
New cards
Describe the structure of a fatty acid.
* It is a long hydrocarbon chain, 14-22 carbons long
* It has a carboxyl group head which is hydrophilic
* It has an R group tail which is hydrophobic
* It has a carboxyl group head which is hydrophilic
* It has an R group tail which is hydrophobic
63
New cards
What is the general formula for a fatty/carboxylic acid?
CnH2n+1COOH
64
New cards
What is a saturated fat?
An organic molecule containing the greatest possible number of hydrogen atoms, without carbon-carbon double or triple bonds.
65
New cards
What is an unsaturated fat?
An organic molecule containing the greatest number of hydrogen atoms, with carbon-carbon double or triple bonds.
66
New cards
What state do saturated fats tend to be at room temperature?
Solid.
67
New cards
Where are saturated fats usually sourced from?
Animal sources.
68
New cards
What state do unsaturated fats tend to be at room temperature?
Liquid.
69
New cards
Where are unsaturated fats usually sourced from?
Plant sources.
70
New cards
How do the double bonds in unsaturated fats help enzyme activity?
The kink in the chain creates an instability and access point for enzymes.
71
New cards
What makes a triglyceride?
Glycerol and three fatty acids.
72
New cards
Draw the reaction for forming a triglyceride.
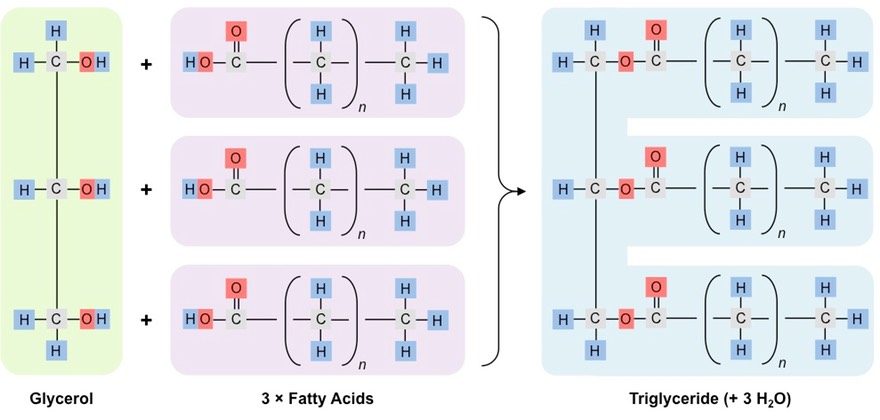
73
New cards
What kind of reaction forms triglycerides?
A condensation reaction.
74
New cards
What bond holds the molecules together?
An ester bond.
75
New cards
What is an ester?
Esters are a functional group commonly encountered in organic chemistry. They are characterized by a carbon bound to three other atoms: a single bond to a carbon, a double bond to an oxygen, and a single bond bound to another oxygen.
76
New cards
Draw an ester bond.
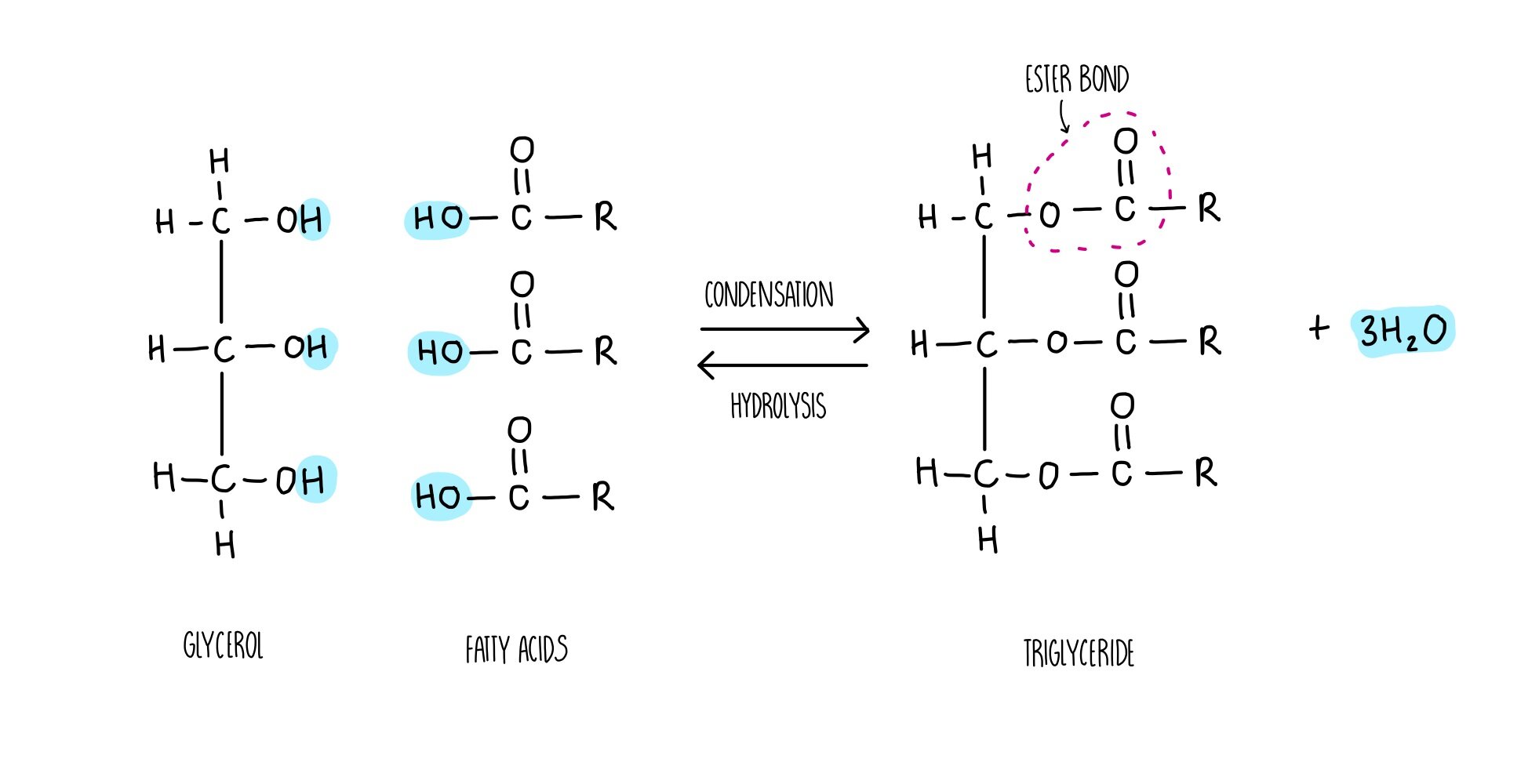
77
New cards
What is the difference between a saturated triglyceride, and an unsaturated triglyceride?
Saturated triglyceride:
* Difficult to digest
* Solid
* Very rigid structure
Unsaturated triglyceride:
* Branching in tertiary structure
* Easier to break down
* Liquid at room temperature
* Difficult to digest
* Solid
* Very rigid structure
Unsaturated triglyceride:
* Branching in tertiary structure
* Easier to break down
* Liquid at room temperature
78
New cards
What makes a phospholipid?
A phosphoglycerol and 2 fatty acids.
79
New cards
What is the difference between the third glycerol in a phospholipid, compared to in triglyceride?
The third glycerol has a phosphate group which replaces the third fatty acid chain.
80
New cards
What are the different types of circulatory systems?
* Open
* Closed
* Double
* Single
* Closed
* Double
* Single
81
New cards
What is a stroke?
* A very serious condition where the blood supply to the brain is cut off
* It can either be caused by a blood clot on the brain or a brain bleed
* It can either be caused by a blood clot on the brain or a brain bleed
82
New cards
What is a heart attack?
* A serious condition where the supply of blood to the heart is suddenly blocked
* The main cause is the blood vessels leading to the heart becoming blocked
* The main cause is the blood vessels leading to the heart becoming blocked
83
New cards
a) What is an arteriole?
b) What is a venule?
b) What is a venule?
a) The ‘bridge’ between the artery and capillaries
b) The ‘bridge’ between the veins and capillaries
b) The ‘bridge’ between the veins and capillaries
84
New cards
Why do bacteria not have a heart or circulatory system?
* They are very small so diffusion is effective enough
* High SA:V ratio
* Conc. gradient easily built in bacteria
* High SA:V ratio
* Conc. gradient easily built in bacteria
85
New cards
a) Describe the structure of the veins
b) Describe the structure of the arteries
c) Describe the structure of the capillaries
b) Describe the structure of the arteries
c) Describe the structure of the capillaries
a) Thin outer walls, thin layer of muscle and elastin, large lumen
b) Thick outer walls, endothelium reduces friction, thick inner layer of muscle and elastin, thick outer layer of collagen fibres
c) Incredibly small lumem, one cell thick
b) Thick outer walls, endothelium reduces friction, thick inner layer of muscle and elastin, thick outer layer of collagen fibres
c) Incredibly small lumem, one cell thick
86
New cards
a) Function of the left ventricle
b) Function of the atrioventricular valves
b) Function of the semilunar valves
b) Function of the atrioventricular valves
b) Function of the semilunar valves
a) Thicker muscle than RV for strong contraction to pump blood all around the body
b) Prevents the backflow of blood from ventricles into atria
c) Prevents the backflow of blood from the aorta or pulmonary artery into the ventricles
b) Prevents the backflow of blood from ventricles into atria
c) Prevents the backflow of blood from the aorta or pulmonary artery into the ventricles
87
New cards
What is atrial systole?
* Contraction of the atria forcing blood into the ventricles
* The atria fill
* Pressure then increases
* Valves open
* Blood fills the ventricles
* Excess blood is forced down into the ventricles as atria contract
* Ventricles relax
* The atria fill
* Pressure then increases
* Valves open
* Blood fills the ventricles
* Excess blood is forced down into the ventricles as atria contract
* Ventricles relax
88
New cards
What is ventricular systole?
* Ventricles contract pushing blood into arteries
* Ventricles contract from heart base upwards
* Pressure in ventricles increase so the atrioventricular valves close
* The blood is pushed up and out of the arteries
* Atria relax
* Ventricles contract from heart base upwards
* Pressure in ventricles increase so the atrioventricular valves close
* The blood is pushed up and out of the arteries
* Atria relax
89
New cards
What is cardiac diastole?
* Vents. and atria are relaxed
* Pressure in vents. drop forcing the semilunar valves to close
* Atria fill with blood
* Blood returns to the heart
* Pressure in the atria rises above the vents. forcing the AV valves to open
* Blood flows passively into vents. without atrial systole
* The cycle begins again
* Pressure in vents. drop forcing the semilunar valves to close
* Atria fill with blood
* Blood returns to the heart
* Pressure in the atria rises above the vents. forcing the AV valves to open
* Blood flows passively into vents. without atrial systole
* The cycle begins again
90
New cards
What is the myogenic mechanism?
* How arteries and arterioles react to an increase or decrease of blood pressure to keep the blood flow constant within the blood vessel
* The response refers to the contraction initiated by the myocyte itself instead of an outside occurrence or stimulus such as nerve innervation
* The response refers to the contraction initiated by the myocyte itself instead of an outside occurrence or stimulus such as nerve innervation
91
New cards
How does the heart pump?
* Electrical impulses sent from pacemakers across nodes in the heart to cause contraction via electrostimulation
92
New cards
a) What is atherosclerosis?
b) What causes it?
b) What causes it?
a) A hardening of the arteries due to damage to the endothelium followed by an inflammatory response
b) 1) High bp damages the endo. layer
2) An inflam. response is triggered releasing wbc which releases cholesterol
3) Deposits build up forming an atheroma
4) Plaque forms from calcium salts and fibrous tissues building up forming swelling
5) The artery wall loses elasticity causing it to harden like furring
* The plaque increases bp by blocking the artery, causing further damage
b) 1) High bp damages the endo. layer
2) An inflam. response is triggered releasing wbc which releases cholesterol
3) Deposits build up forming an atheroma
4) Plaque forms from calcium salts and fibrous tissues building up forming swelling
5) The artery wall loses elasticity causing it to harden like furring
* The plaque increases bp by blocking the artery, causing further damage
93
New cards
How do blood clots form?
* Damaged blood vessels leave collagen fibres exposed, causing the release of activated platelets
* Thromboplastin arrives with calcium ions and vitamin K, where it converts prothrombin into thrombin
* Thrombin then converts fibrinogen into fibrin
* Fibrin is an insoluble, mesh-like substance which forms the blood clot
* Thromboplastin arrives with calcium ions and vitamin K, where it converts prothrombin into thrombin
* Thrombin then converts fibrinogen into fibrin
* Fibrin is an insoluble, mesh-like substance which forms the blood clot
94
New cards
What is an anticoagulant?
* Drugs which reduce blood clotting
95
New cards
How do anticoagulants work?
* They reduce levels of prothrombin in the bloodstream, thus reducing clotting
96
New cards
Give:
a) an example of an anticoagulant
b) the side effects of anticoagulants
a) an example of an anticoagulant
b) the side effects of anticoagulants
a) Warfarin
b) Fainting, osteoporosis, swelling of tissues, excess bleeding and can damage the foetus if taken when pregnant
b) Fainting, osteoporosis, swelling of tissues, excess bleeding and can damage the foetus if taken when pregnant
97
New cards
Give 2 issues with using daphnia to investigate heart rate.
* They move very quickly
* They cannot consent to the trial being conducted on them
* They cannot consent to the trial being conducted on them
98
New cards
Why do we use daphnia to investigate heart rate?
* They are transparent so we can see their heart
99
New cards
Why is a study alone not enough to prove a factor is a link?
* One study is not reliable
* If it is repeated and other scientists and studies come to the same conclusion, then it is more valid
* If it is repeated and other scientists and studies come to the same conclusion, then it is more valid
100
New cards
What is the purpose of an antihyperintensive?
* To reduce blood pressure
* Beta blockers reduce the heartbeats strength
* Vasodilators widen blood vessels
* Diuretics reduce the amount of Na reabsorbed in the kidneys meaning less water is reabsorbed reducing blood volume
* Beta blockers reduce the heartbeats strength
* Vasodilators widen blood vessels
* Diuretics reduce the amount of Na reabsorbed in the kidneys meaning less water is reabsorbed reducing blood volume