Architecture midterm review- second half
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Borromini tried hard to reconcile with _____ _____
sacred geometry
Borromini was more of a ____ than Bernini.
perfectionist
What style of architect were both Bernini and Borromini?
Italian baroque
What were Bernini and Borromini both moving away from?
Being so precise with geometry
Doric columns are less ____ than Ionic and can hold more ____.
decorative, weight
Soane was very much influenced by ____.
Piranesi
Piranesi’s pillar ordonnance was more concerned with ____ .
ornament and grandiosity
Alberti’s ordonnance was more concerned with ____.
scale
Architect of the ideal city of Chaux
Ledoux
Ledoux’s buildings clearly show their ____.
intention, use
The designs of ____ are much less obvious than those of ____ and ____.
Boullée, Ledoux, Lequeu
Boullée was supported by _____ ____ who wanted ____.
French revolutionaries, democracy
Boullée showed a movement away from the ___.
past
What idealistic place did Lequeu design?
The Island of Love and Fisherman’s Rest
What did the Island of Love and Fisherman’s Rest symbolize?
The peace people imagined for after the French unrest was over.
Boullée, Lequeu, and Ledoux were all ____.
French
This building shows Piranesi in all his glory
Santa Maria del Prioratto
Piranesi was very interested in ____ architecture and the ___.
impossible, past
What feelings does the Sublime evoke?
terror, overwhelm, intimidation, awe, respect, innumerability, darkness, largeness
What did Britain and its architects look back to?
The Roman empire
The Picturesque blends the ____ and the ____.
sublime, beautiful
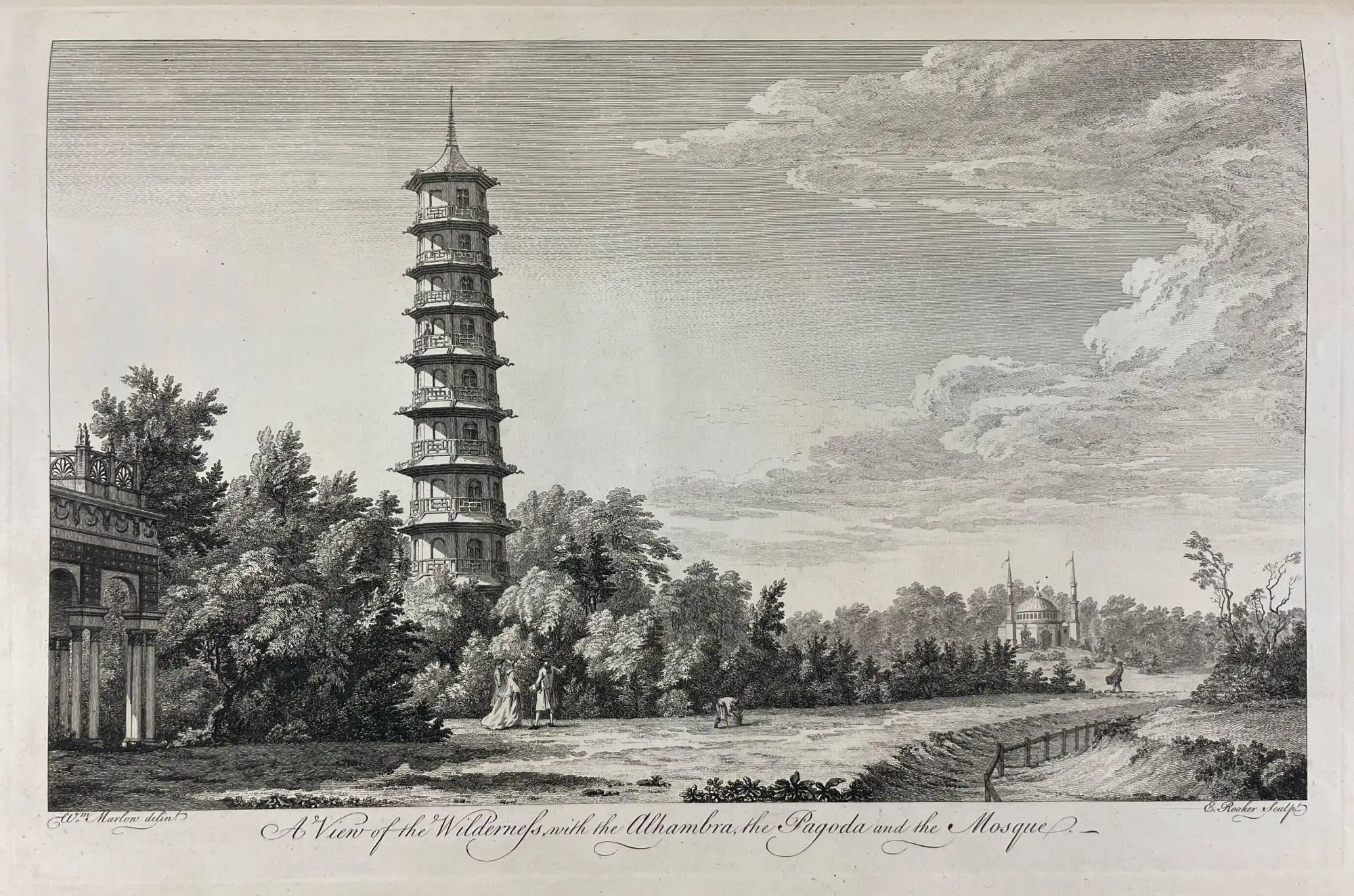

William Chambers known for his ___ at ___ _____.
follies, Kew Garden
What were Chambers’s three follies?
The Alhambra, Mosque, and Pagoda.
What does “walking through the world” symbolize as one walks through the follies, each in a different country’s style?
The idea that Britain was not just the land you were on but had a wider, global, empirical reach.
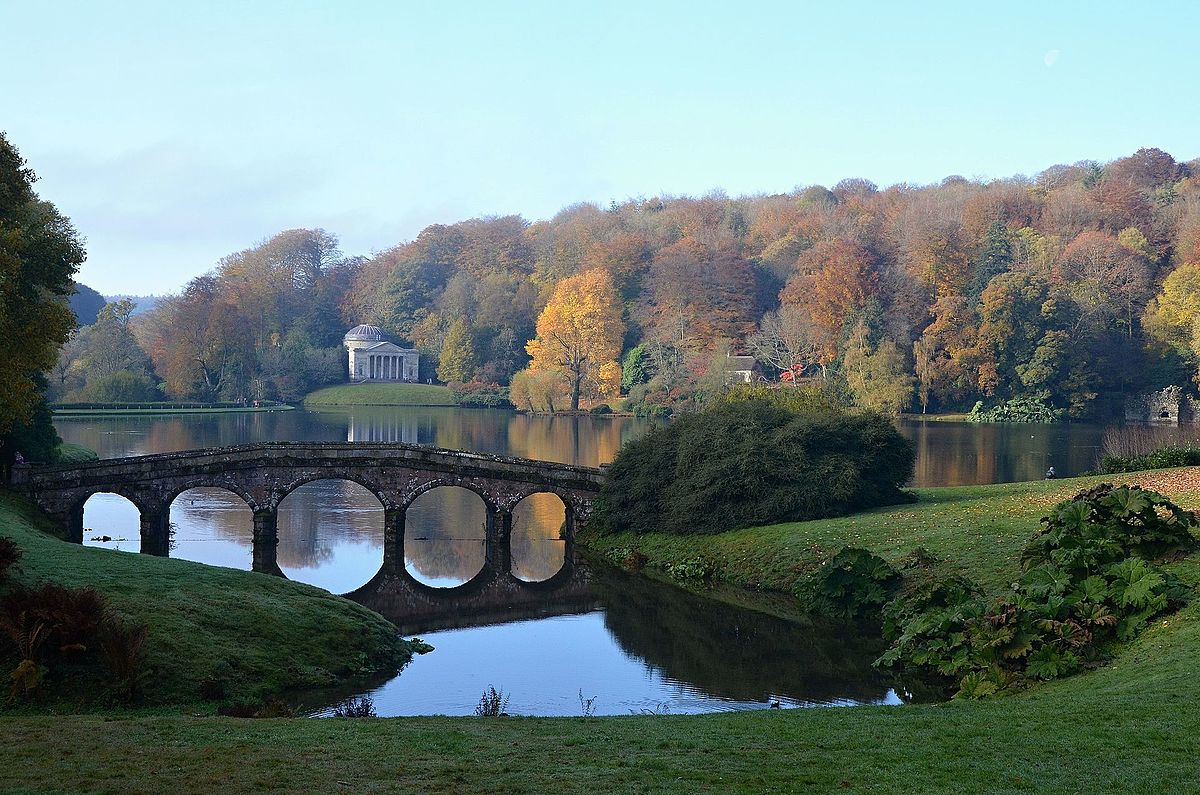

Who designed Stourhead and where was it?
Henry Hoare, England
Stourhead included mini ____.
pantheons

Who designed the Temple of Ancient Virtue and where was it?
William Kent, Stowe in England
Architecture became a _____ ____ during a time lacking unity with lots of feudal kingdoms.
unifying force
Which building of Schinkel’s alluded back to Rome and showed he knew his history?
The Altes Museum in Berlin
This building was revolutionary in Germany because of its lack of ornament
Bauakademie by Schinkel, his response to industrial factories he saw in England
Who designed the Crystal Palace?
Joseph Paxton
William Morris didn’t want his wallpaper designs to be for ____, but they did indeed become _____ ____.
aristocrats, luxury items
Who designed the Red House?
William Morris and Philip Webb in England
What was given to Queen Victoria and designed by Bhai Ram Singh in 1891?
The Durbar Room in the Osborne House on the Isle of Wight
What architect did American colonial style return to?
Palladio
What was Thomas Jefferson’s magnum opus?
The University of Virginia campus
Whose library ended up starting the Library of Congress?
Thomas Jefferson’s

What was Thomas Jefferson’s vacation home called?
Poplar Forest
Key concepts of American colonial architecture (5, RULLIC)
Return to Palladio, utopia, labor & liberty, involvement of slavery, construction of a nation
What building of Jefferson’s was inspired by a Greco Roman building he saw in Rome?
Richmond State Capitol Building
What was the name of Thomas Jefferson’s home estate/plantation?
Monticello
What did Jefferson do to hide slaves because he was embarrassed he owned them?
He planted trees to separate their quarters and crops from the main house and planned out ways to hide them when guests were over in his floor plans.
Westernization as _____
modernization
What did Frank Lloyd Wright (and others) consider himself?
a genius
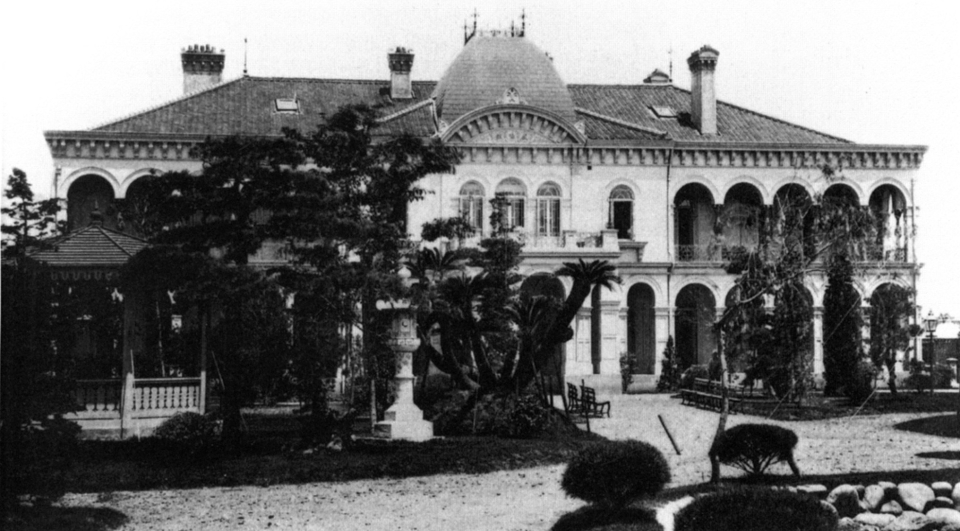

What is this building, who designed it, and where is it?
Rokumeikan, Josiah Conder, Tokyo, Japan
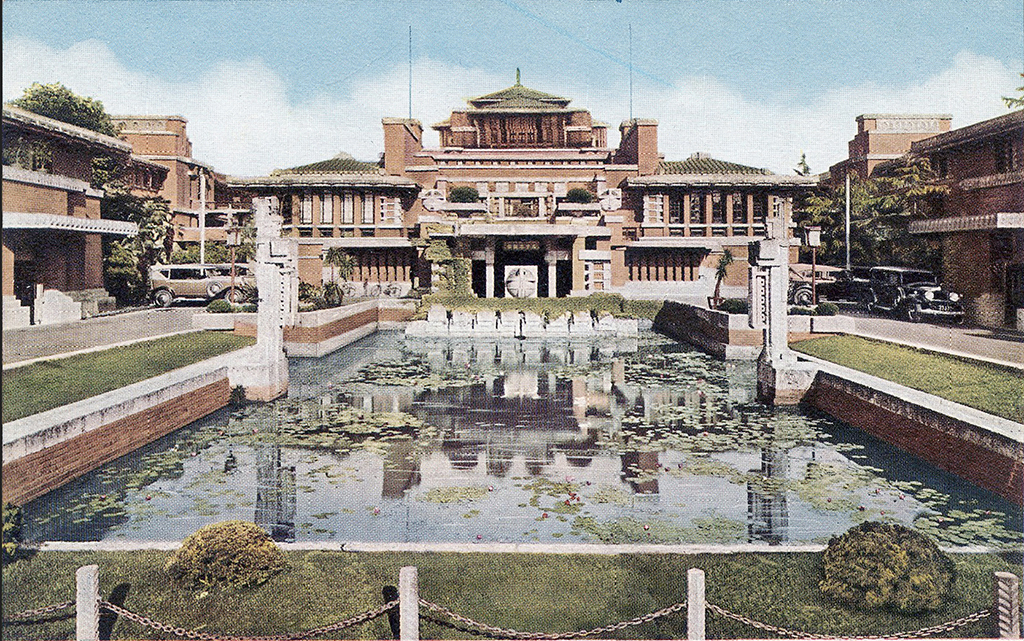

Wright’s Imperial Hotel failed to blend and was instead neither ___ nor ___.
eastern, western
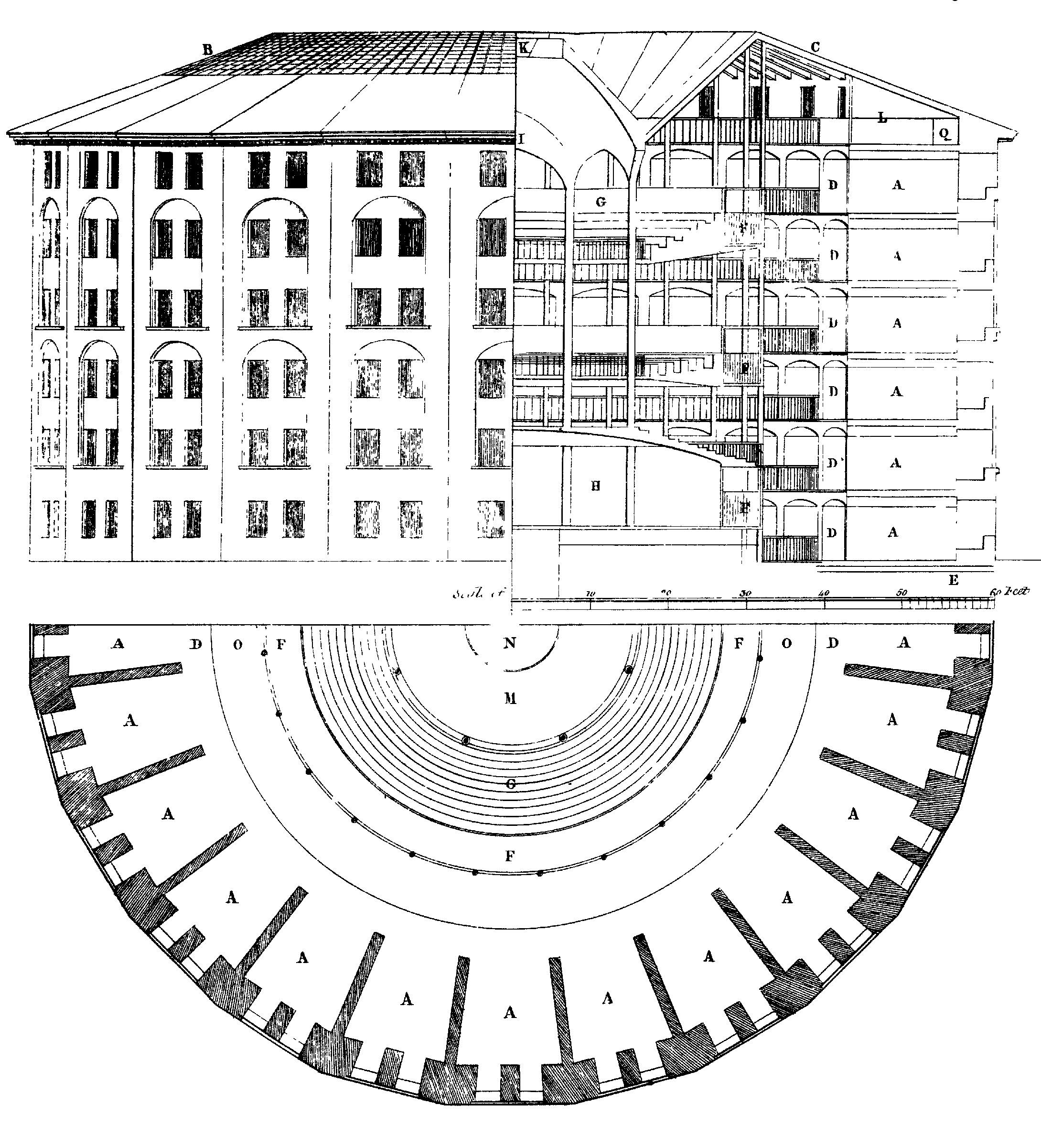
Name, architect, purpose?
Panopticon, Jeremy Bentham, prison
The brickwork for the Imperial Hotel was inspired by ____ ____
Mayan ruins
Key concepts of German architecture in early 1800s (6, ECLERI)
elevation, complex relationship with architectural styles, living within a variety of histories, establishing a collective German identity, romantical understanding of Germany, industrialization
Key concepts of British architecture in the 1800s (4, GIRD)
Gothic Revivalism, Industrial Revolution, relationship with India, decorative arts