Biochemistry Section B
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
What is the equation for Gibbs Free Energy?
G=H-TS
Reactions are driven by changes in Gibbs Free Energy (G)
What value must G be for a reaction to be spontaneous?
Negative
What is H? What value must it be for a spontaneous reaction?
Enthalpy: the internal heat energy of the system. Must be less than zero for reaction to be spontaneous. Loses heat
What is S? What value must it be for a spontaneous reaction?
Entropy: randomness or disorder of the system. Must be more than zero for reaction to be spontaneous. More disorder
Examples of Enthalpy
1. Molecular interactions = weak bonds/interactions
2. Solvation
3. Electrochemical
Examples of Entropy
1. Caging of water molecules (decrease)
2. Folding of macromolecules (decrease)
3. Solvation (decrease)
All of these decrease disorder and in turn decrease entropy
What is the take away of Gibbs Free Energy?
Reactions are favored by a decrease in enthalpy that coincides with an increase in entropy
What are the four types of noncovalent bonds?
hydrogen bonding, ionic interactions, hydrophobic effect, and van der Waals interactions
What is a pro of noncovalent bonds?
Although individually all of these interactions are weak, they are cumulatively strong. They are not easily broken when used simultaneously.
How do noncovalent interactions affect macromolecules?
Affect macromolecular structure and function (bonding effects structure, structure effects function)
These bonds allow more complexity in an organism
What is hydrogen bonding?
Bonds that form between a hydrogen attached to an O, N, or F group and another O, N, or F group with lone pairs.
What is hydrogen bond strength sensitive to?
Direction. Straight alignment is favored because it gives a better structure.
How does charge polarity relate to hydrogen bonds?
There is an electrostatic attraction between an electronegative atom with the lone pairs (O, N, F) and the hydrogen atom.
How do hydrogen bonds affect water?
Gives water a higher freezing and boiling point.
van der Waals
When two uncharged atoms are brought very close together, their surrounding electron clouds influence each other. Random variations in the positions of the electrons around one nucleus may create a transient electric dipole, which induces a transient, opposite electric dipole in the nearby atom. The two dipoles weakly attract each other, bringing the two nuclei closer
Ionic Interactions
Interactions between charged molecules. Opposite charges attract and similar charges repel
Hydrophobic Effect
Nonpolar solutes interact poorly with surrounding water molecules, causing water to form a cage around the solute.
This allows nonpolar solutes to stick together and reduce the breaking of water:water interactions.
How does the hydrophobic effect influence entropy?
Decreases entropy and makes reaction less spontaneous.
What is solvation by water?
Requires interactions between the solute and water molecules in order for the solute to dissociate into the water.
What type of solutes does water prefer to interact with?
Water is polar. It only wants interactions that are relatively equal to water-water interactions and can cancel out the change (polar). They do not want interactions with solutes that disrupt these interactions (nonpolar).
What are the three types of solvation in water?
Hydrophilic, Hydrophobic, and Amphipathic
What are hydrophilic solutes? How do they dissolve in water?
Polar or ionic solutes such as charged atoms (COO- and NH3+), hydroxyl groups (OH), carbonyl groups (C=O), etc.
Easily dissolve in water (like dissolves like)
What are hydrophobic solutes? How do they dissolve in water?
Nonpolar solutes such as carbon-hydrogen chains and aromatic rings.
Do not easily dissolve in water
What are amphipathic solutes? How do they dissolve in water?
Solutes that are a combination of hydrophobic and hydrophilic groups. Often contain a hydrophilic group attached to a carbon-hydrogen chain or aromatic rings.
Identify Hydrophobic, Hydrophilic, and Amphipathic Groups
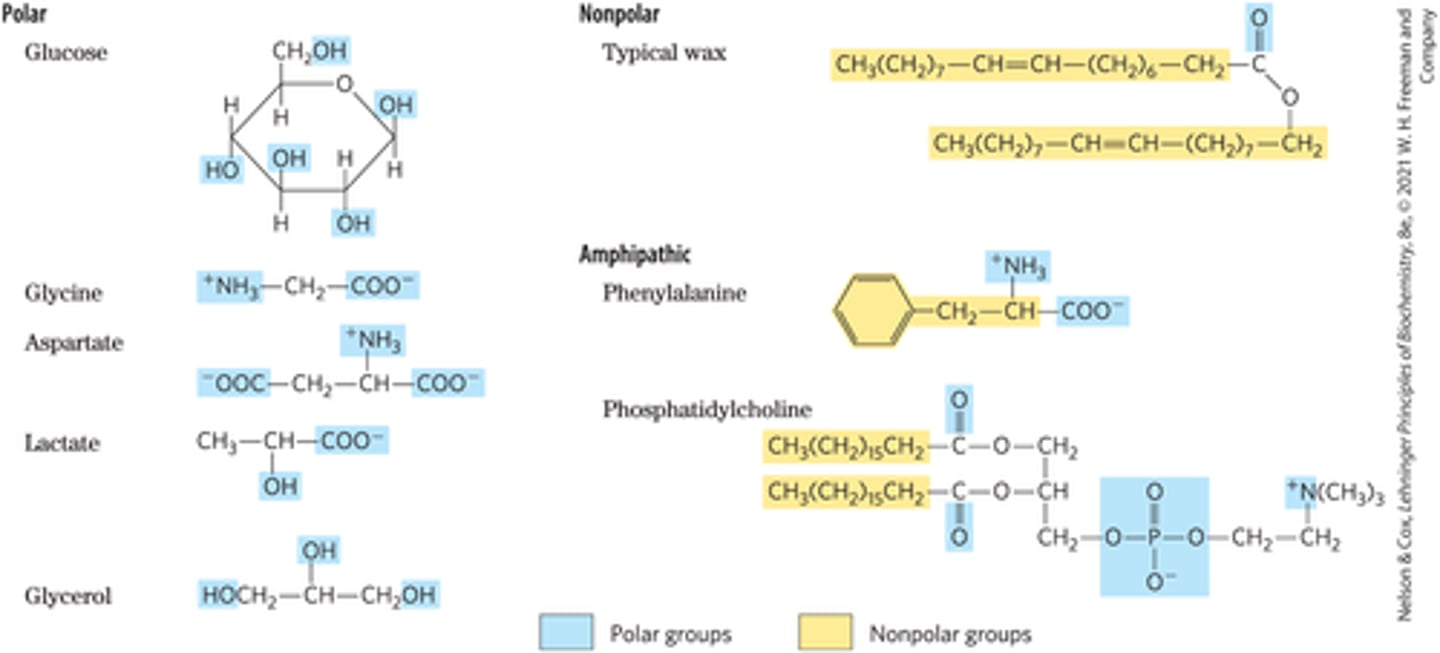
How do uncharged organics dissolve in water?
Uncharged solutes do not easily dissolve but interactions with water via hydrogen bonds all them to easily dissolve.
Electrostatics in Solvation
Occurs because of the high dielectric constant in the water. Water will dissolve salts or charged molecules by replacing solute:solute interactions with water:solute interactions.
How do nonpolar gases interact with water?
Do not easily dissolve. They are nonpolar and dissolving in water would decrease entropy in the system.
How do amphipathic molecules interact with water?
In water, amphipathic groups orient themselves so that the hydrophilic heads protect the hydrophobic tails from the water.
What are two types of complexes amphipathic molecules can form?
Micelles and Bilayers
Miscelle
look like a cell with wedge-shaped units.
Bilayer
look like a sheet with cylindrical units.
What is neutral pH?
[H+]=[OH-]= 10^-7 pH=7
How does neutral pH change in acidic conditions?
[H+] > [OH-] and pH<7
How does neutral pH change in basic conditions?
[H+] < [OH-] and pH>7
How do you calculate pH from H+ concentration?
pH= -log[H+] (measured in M)
How do you calculate pH from OH- concentration?
pOH= -log[OH-] then pH=14-pOH (measured in M)
How do you calculate pH if the concentration is in something other than M?
convert using metric units to get H concentration in M. Example: If given to you in mM, multiply concentration by 10^-3 to get M.
How do you calculate concentration of H+ from pH?
H+= 10^-pH
Example: pH=1... 10^-1... 0.1M
conjugate acid-base pair
consists of two substances related to each other by the donating and accepting of a single hydrogen ion
HA= [H+] + [A-]
What is Ka?
The tendency of an acid to lose a proton and form its conjugate acid.
The larger the Ka, the stronger the acid
What is Ka equation?
[H+][A-]/[HA]
What is pKa?
-logKa
How is dissociation related to acidity strength?
a stronger acid [HA] dissociates much easier to ionized state [H+][A-]
At what point can we measure proton concentration?
When the concentration of weak acid and its conjugate base are equal, this occurs at 50% dissociation.
What does Ka represent when concentration of conj. acid and base are equal?
When HA and A are equal, they cancel out in the Ka equation. This means that Ka is now equal solely to H concentration.
When are pH and pKa equal?
When solution is 50% dissociated, Ka=H+, the -log[Ka]=-log[H+]
This is the same equation as pH.
pH and pKa are equal
What determines point when conj. acid and base are equal?
This point is determined by how much strong base was added to get the acid to dissociate to 50%. The stronger the acid, the less base is needed to deprotonate it. If less base was needed to deprotonate it, we have a lower pKa/pH
What is the titration zone?
When pH and pKa are equal
When conj acid and conj base concentrations are equal
Known to be a buffer
What is a buffer?
Aqueous solutions that tend to resist changes in pH despite large additions of acid or base.
Where is the buffer zone the strongest?
Strongest at the midpoint of the titration curve. Decreases in strength the farther you go from it.
What is the range for the best buffering zone?
+/- 1 pH unit from the pKa
How do weak acids/bases react at low pH? High pH?
At low pH (high H+), bases participate in electrostatic bonds and gain an H, making them neutral (HA).
At high pH (low H+), acids participate in electrostatic bonds and lose an H making them basic (A-).
Electrostatic bonds occur more likely between molecules of differing charges
How does pH affect the charge of weak acids and bases?
a weak acid will become more negatively charged in a basic environment (high pH) (A-)
a weak base will become more positively charged in an acidic environment (low pH) (HA)
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation?
pH = pKa + log [A-]/[HA]
When pH=pKa, the buffering solution works best.
Henderson-Hasselbach Equation Example
7=4.8+log([A]/[HA])
2.2=log([A]/[HA])
10^2.2=[A]/[HA]
158 [A] per 1 [HA]
158/158+1=0.997x100= 99.7% deprotonated
When pH is not equal to pKa, what can we use the Henderson-Hasselbach equation for?
to calculate the molar ratio of proton donor and acceptor, given pH and pKa. This information tells you what fraction of the acid is deprotonated/protonated.
What do we measure using the HH equation when pH is increased/decreased?
When pH and pKa are equal, we know that conj acid and conj base are equal. It is 50% deprotonated. If we increase or decrease pH, we can determine the change in deprotonation/protonation of the acid.
How do we know if an acid is deprotonated or protonated when solutes are added?
We need to find the buffering zone and know the pKa of this zone. The pKa will indicate the pH. Knowing the pH of the titration zone will allow us to know if the acid was protonated or deprotonated at new pHs.
If we increase pH from the buffering zone, is the acid protonated or deprotonated?
Acid becomes deprotonated and loses H to become [A-]. When we run HH equation, the concentration represents the amount of acid deprotonated
If we decrease pH from the buffering zone, is the acid protonated or deprotonated?
Acid becomes protonated and gains H to become [HA]. When we run HH equation, the concentration represents the amount of acid protonated.
What is the magnitude of proton concentration change if we increase or decrease the pH by 1?
The concentration of protons increase or decrease by a magnitude of 10.
If we move 1 pH unit away from the buffering system, what is the effectiveness of that buffer? 2 pH? 3pH?
1/10 (10%) effective.
1/10 x 1/10 (1%) effective
1/10 x 1/10 x 1/10 (0.1%) effective
Same in both directions
What is an important buffer in the blood
Bicarbonate (HCO3-)
How is bicarbonate formed?
It is formed from carbonic acid produced from dissolved CO2 gase
Explain the equilibrium reaction between carbon dioxide and bicarbonate.
CO2 is blown off the lungs into the blood and reacts with H2O to create carbonic acid. Carbonic acid dissociates in the blood to create bicarbonate.
This cycle repeats when carbonic acid loses water and is turned back into dissolved CO2 which converts back into gaseous CO2 and can start the cycle over again.
How can bicarbonate be an effective buffer if blood pH is 7.4 and bicarbonate is 3.4?
H2CO3 of blood plasma is in equilibrium with a large reserve capacity of CO2 (g) in the air space of the lungs. Creates an effective buffer
How are the lungs related to the blood buffer system?
They regulate the amount of CO2 blown off the lungs and in turn, how much HCO3- can be created.
How are the kidneys related to the blood buffer system?
Regulate the HCO3- that in turns control the pH levels in the blood
What is acidosis?
When aterial blood has a pH less than 7.35
How do the lungs relate to acidosis?
Lung diseases reduce the capacity to dispose of the CO2 produced by fuel oxidation in the tissues, with the resulting accumulation of H2CO3
How do the kidneys relate to acidosis?
Kidney failure results in a diminished capacity to regulate bicarbonate levels.
Can polar molecules cross the membrane? Nonpolar?
No, Yes
What is one way that polar solutes cross the membrane?
When a solute enters the blood, it can deprotonate (release its H+) and transfer over the membrane. It can then receive a new H+ that's inside the cell to complete its function
Example: Anesthetics
How do Amino Acids act like acids and bases?
Some free amino acid side chains can act as an acid or base
What amino acids have acidic side chains?
Histidine, Aspartate, Glutamate
What amino acids have basic side chains?
Tyrosine, Cysteine, Lysine, Arginine
Why are the activities of proteins sensitive to pH
Many amino acids may have to be in a specific charge state to be active. Their maximum activity will be where the pH is most compatible with their needed charge state.
What bonds are important for protein structure? Why?
Noncovalent bonds, they are more responsive to the environment
What are the components of an amino acid?
Amino, Carboxyl, R, and Hydrogen group attached to an alpha carbon
Which amino acid is not chiral?
Glycine. Its R group is another hydrogen
What is the configuration of amino acids?
L configuration. Configuration of group goes in a clockwise direction with amine being 1st priority, then carboxyl.
What are the 5 structural groups of amino acids?
Nonpolar/Aliphatic, Nonpolar Aromatic, Positively charged, Negatively charged, and Polar/uncharged
Characteristics of Nonpolar/Alipathic Amino Acids
primarily consist of hydrocarbon chains (including aromatics) and interact via van der Waals forces. They often cluster together in the hydrophobic area of a protein
Characteristics of Polar/Uncharged Amino Acids
Able to form hydrogen bonds with water and other polar molecules. Aids in solubility and interactions with water
Characteristics of Charged Amino Acids
positively charged and negatively charged amino acids can form ionic bonds with molecules of the opposite charge. This can aid in protein structure and in turn, function.
What is oligomerization?
coming together of smaller units to make a complex
What role does cysteine play in oligomerization?
Cysteine can be oxidized to form a disulfide group.
Two cysteine AAs next to each other will drop their hydrogen and form a hydrophobic bond.
How does Disulfide aid in protein structure?
They are covalent bonds and often stabilize proteins. Prevent unfolding
Free Amino Acids contain both _____ and _____?
Weak acids and bases
Weak acid is protonated/positively charged, Weak base is deprotonated/negatively charged, and zwitterion is neutral (both negative and positive charge)
What are some characteristics of Amino Acid Titration curves?
It has multiple buffering regions and an isoelectric point where zwitteron can be found.
Amino Acids with an ionizable R group have how many buffering regions?
3 curves. One for amino, carboxyl and R group
Amino Acids with a non ionizable R group have how many buffering regions?
2 curves. One for amino and carboxyl.
How are polypeptide sequences written?
from the amino acid term on the left to the c-terminal on the right. Weak acid is on the left and weak base is to the right
How do peptide bonds form?
by a condensation reaction between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another, loses water
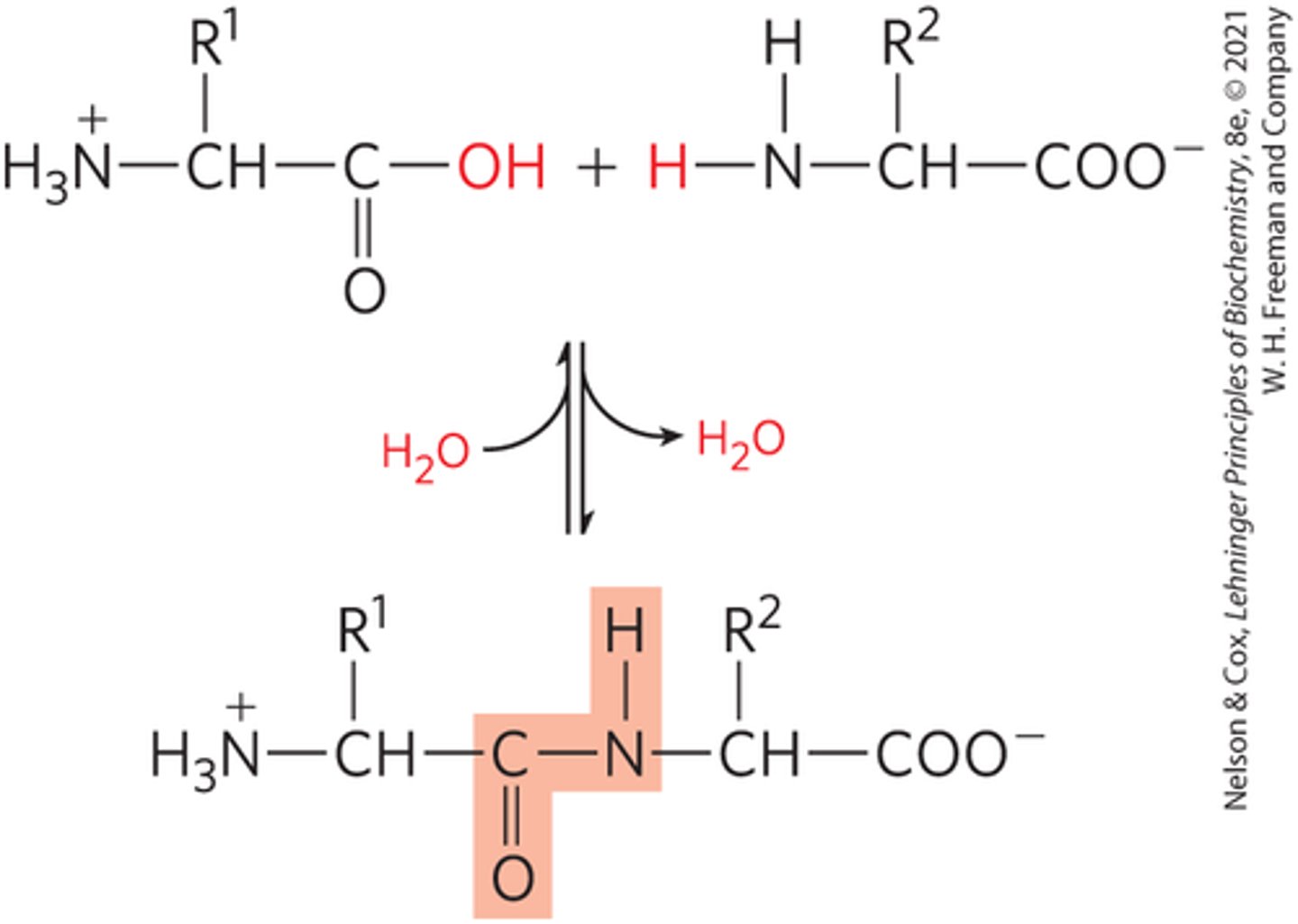
Peptide Nomenclature
3 AA= 2 peptide bonds, tripeptide
4 AA= 3 peptide bonds, tetrapeptide
Oligopeptide= a few amino acids
Polypeptide: many amino acids
What are some properties of peptide bonds?
Planar, dipole moment, and trans configuration.
What are peptide bonds planar?
Due to the double bond character in the resonance structure
Why do peptide bonds have a dipole moment?
Due to electrophilic nature of carbonyl carbon
Why do peptide bonds have a trans-configuration?
Due to steric restrictions of R groups