BE 359 Ch.14 Vesicular Traffic, Secretion, and Endocytosis
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
labels
various ____________ enable tracking protein movement through the secretory pathway to different destinations
sensitive secretory
components required for intracellular protein trafficking have been identified by analysis of yeast temperature-_______________ ________________ (sec) mutants
cell free
________-________ assays for intercompartmental protein transport have defined individual steps of the secretory pathway
transport vesicles
secretory and endocytic pathway protein trafficking, unifying principle: ____________ _____________ transport membrane and soluble proteins from one membrane-bounded compartment to another
secretory and endocytic
overview of the _______________ and ______________ pathways of protein sorting
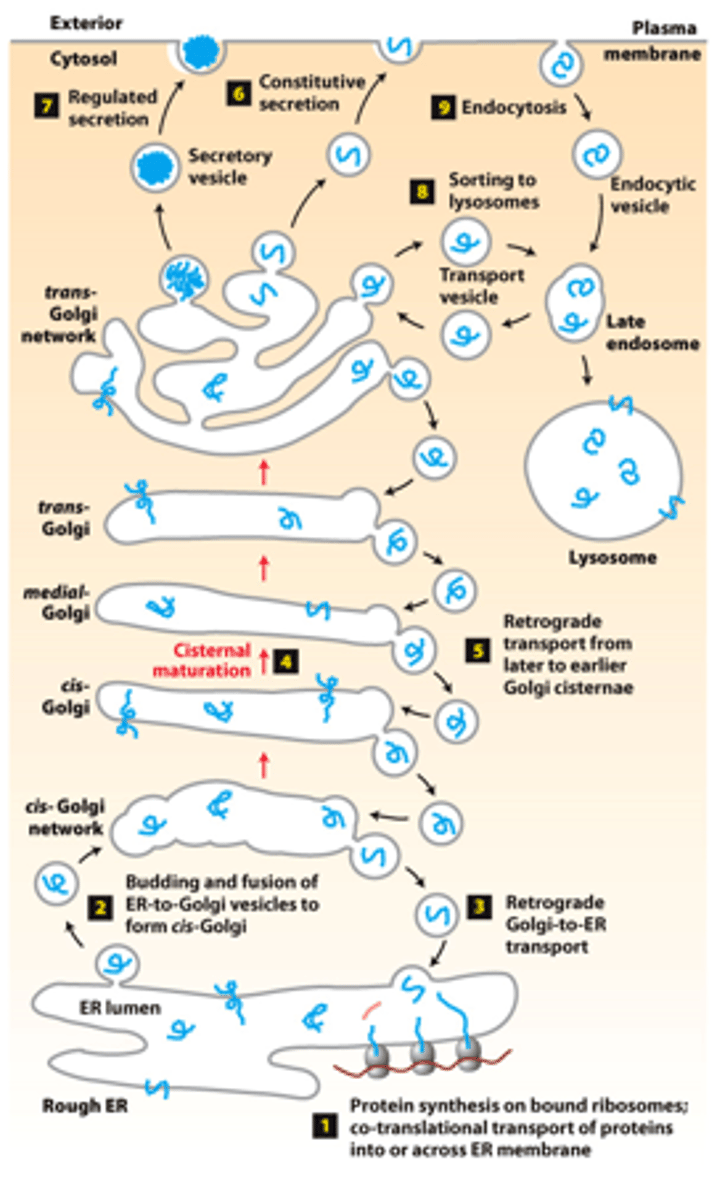
collect
protein sorting, transport vesicles: __________ cargo proteins in membrane budding from a donor compartment
deliver
protein sorting, transport vesicles: _________ deliver cargo proteins to the next compartment by fusing with the target membrane
cell surface, lysosomes
protein sorting, secretory pathway: distribution of soluble and membrane proteins synthesized by the rough ER to final destinations at the _________ __________ (including secretion) or in ______________
rough endoplasmic reticulum, protein trafficking
two stages of secretory pathway protein sorting
cotranslational insertion
secretory pathway, rough ER (stage 1): step 1--synthesis of proteins bearing an ER signal/targeting sequence-- __________________ _____________ of newly made polypeptide chains into the ER membrane or across it into the ER lumen
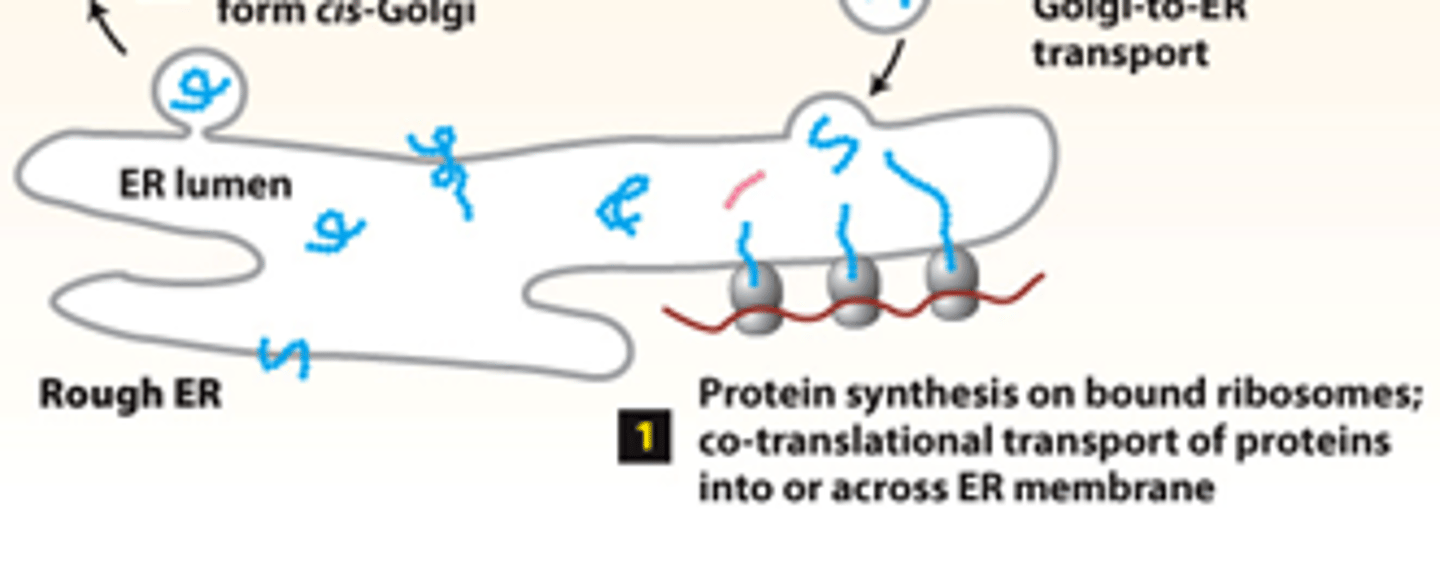
cis golgi cisternae
secretory pathway, protein trafficking (stage 2): step 2--proteins packaged into transport vesicles that bud from the ER and fuse together to form a new ______-_________ ___________
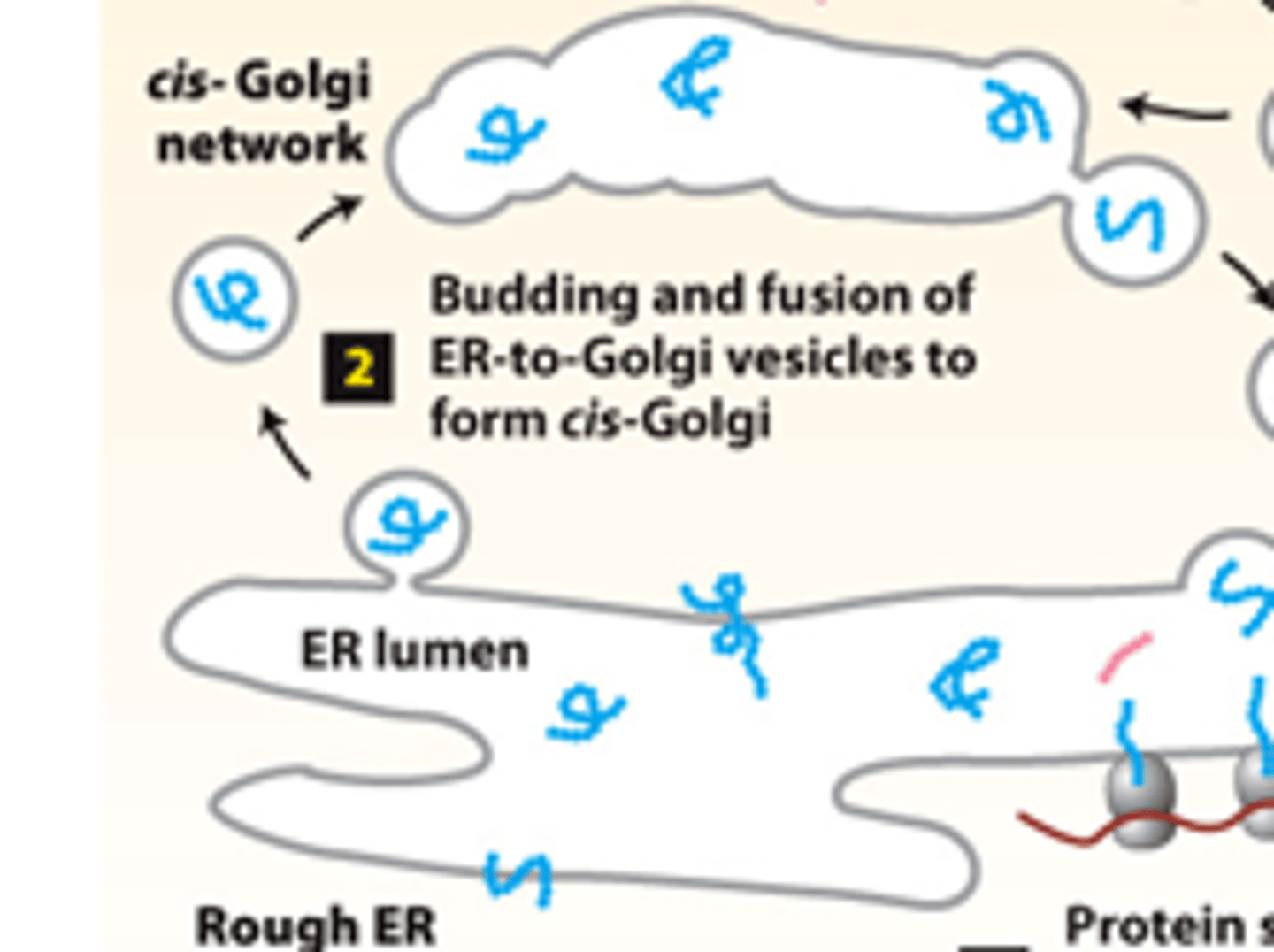
ER
secretory pathway, protein trafficking (stage 2): step 3--ER enzymes or structural proteins--retained in the _________
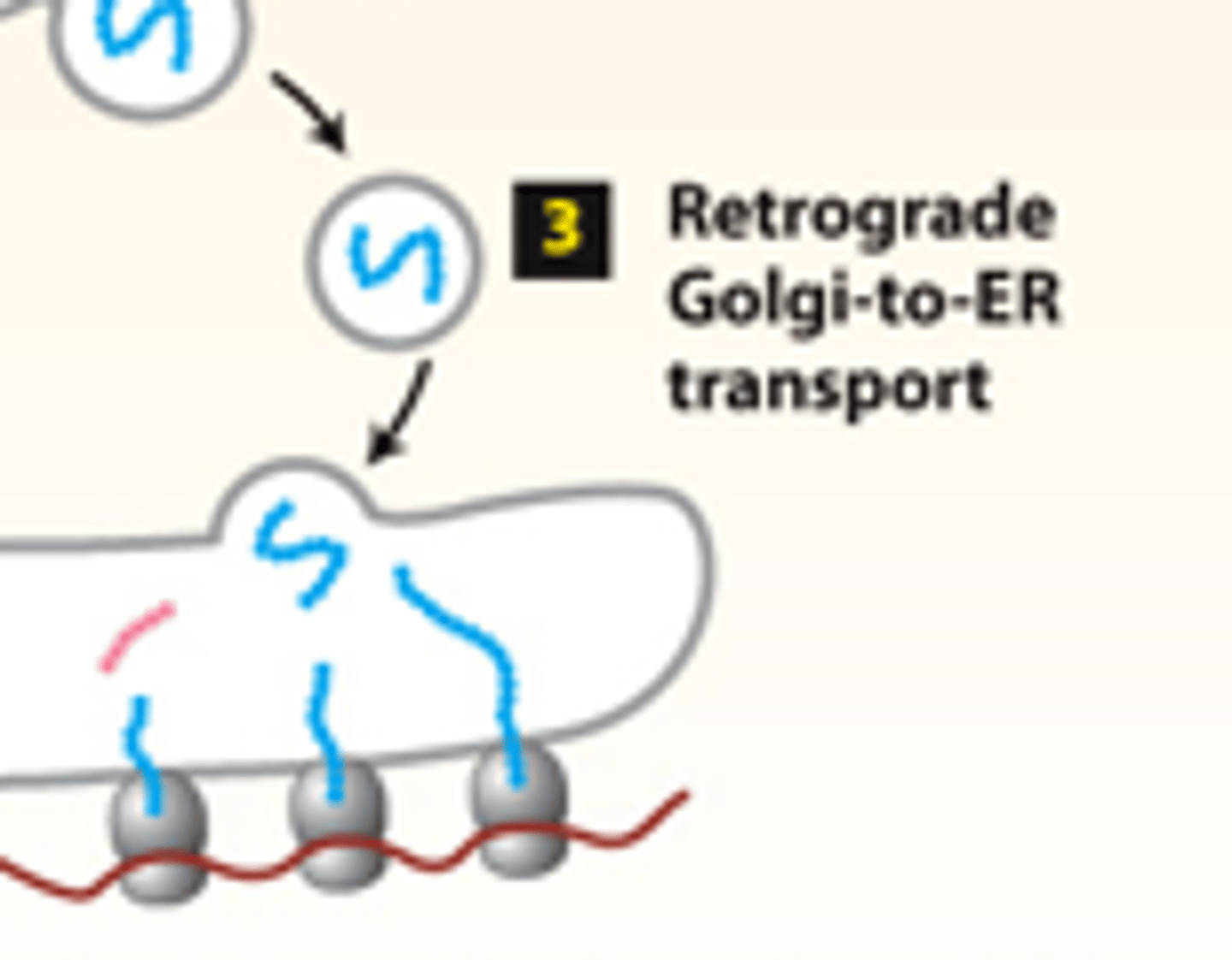
ER
secretory pathway, protein trafficking (stage 2): step 3--ER enzymes or structural proteins--retrieved to the ER by vesicles that bud from the cis-golgi and fuse with the _________
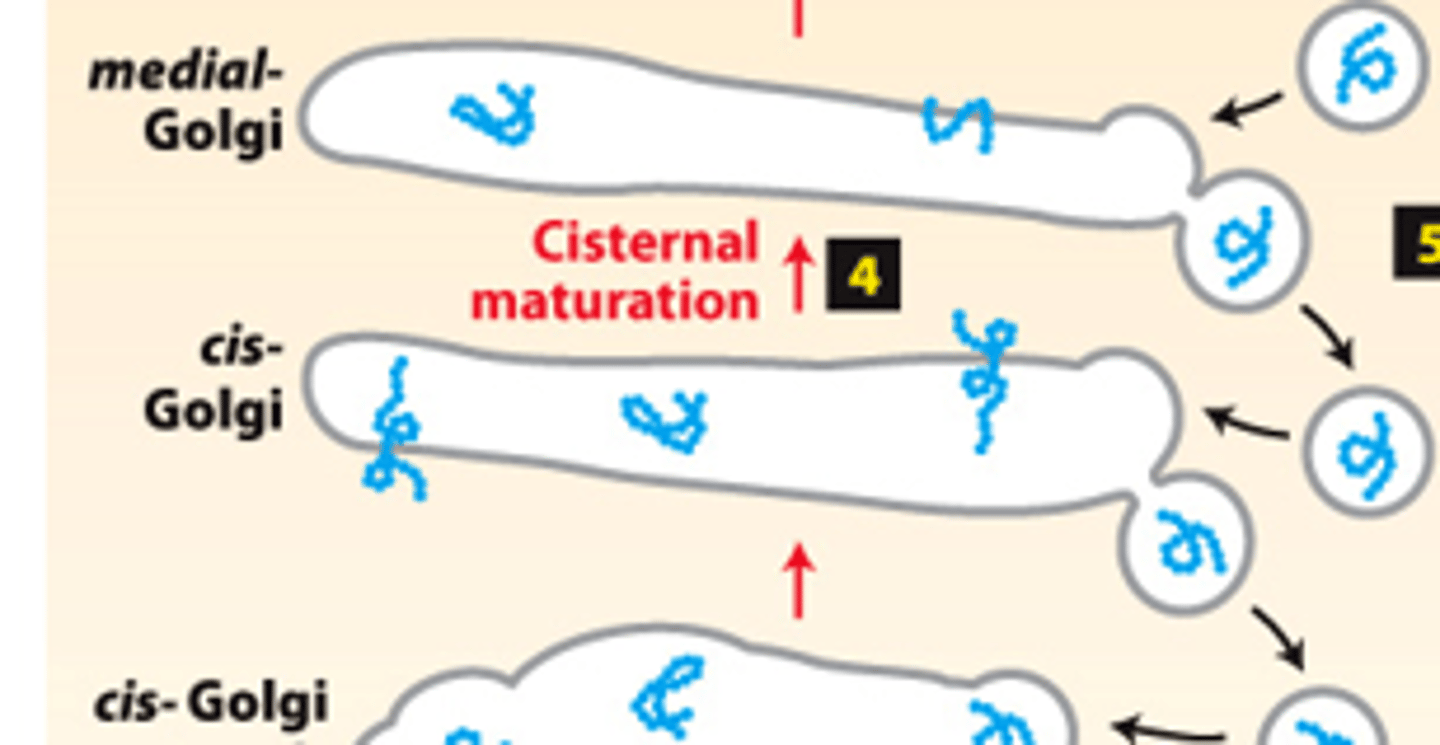
nonvesicular cisternal maturation
secretory pathway, protein trafficking (stage 2): step 4--each cis-Golgi cisterna and contents moves from the cis to the trans face of the Golgi complex by ________________ _____________ _______________
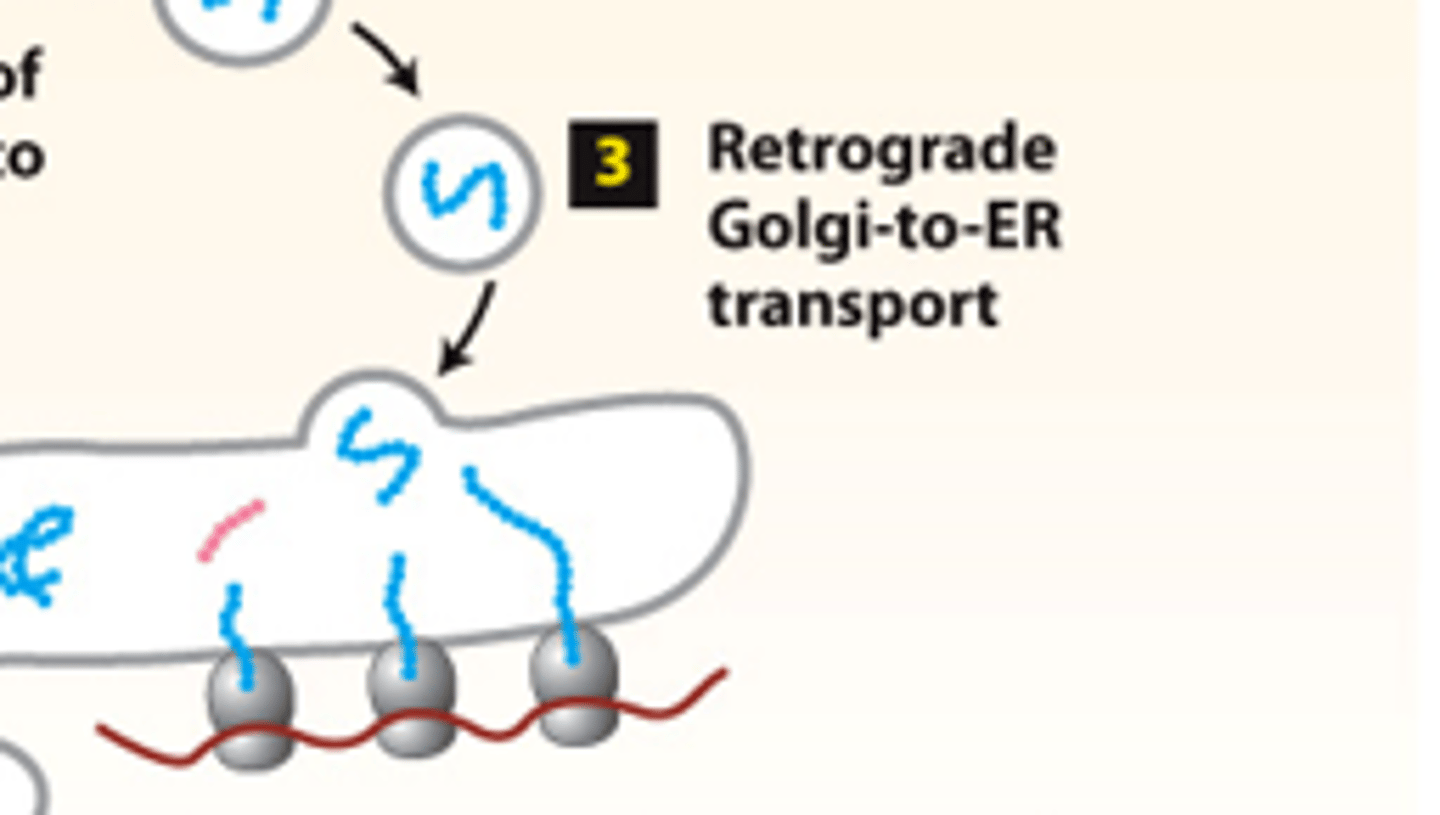
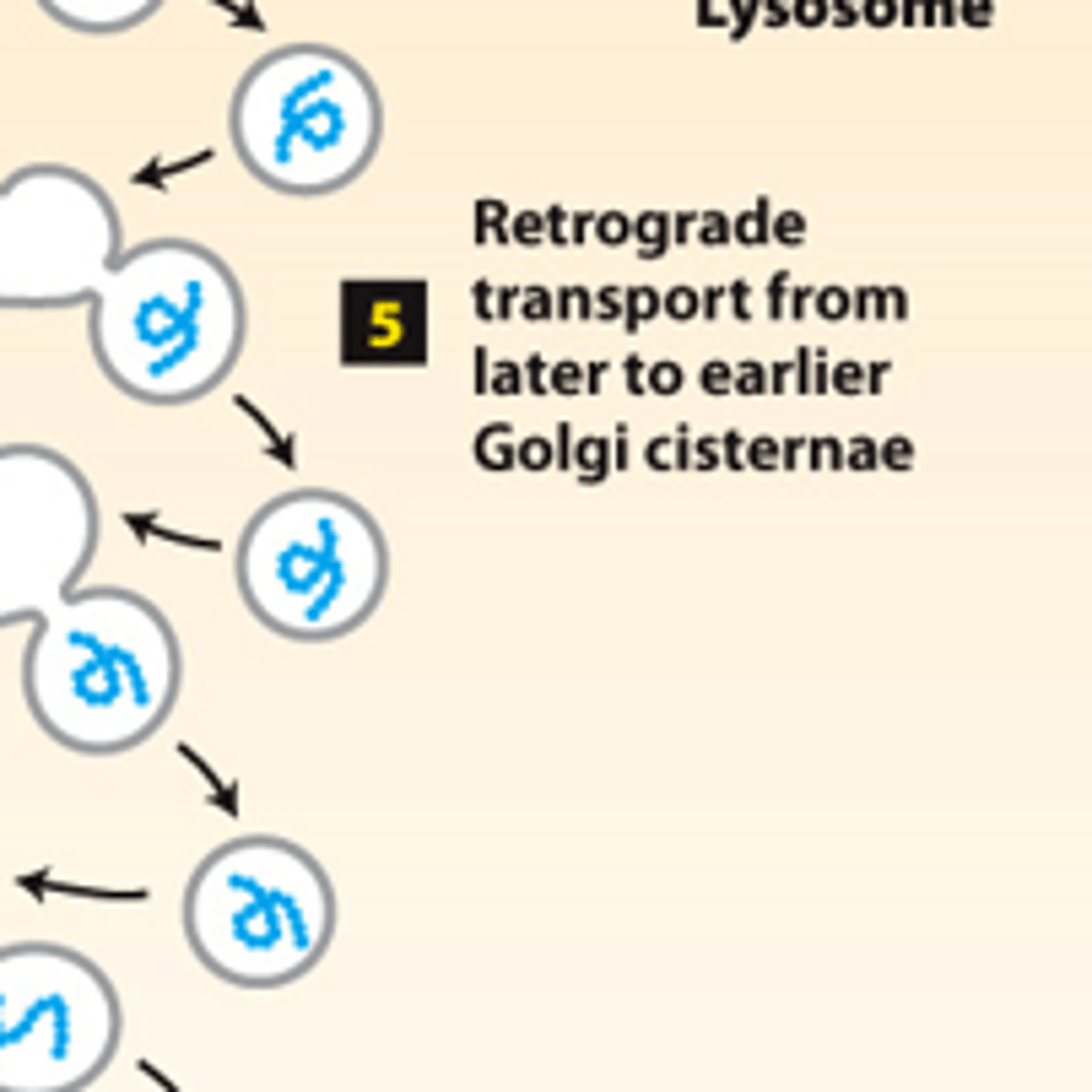
retrograde transport
secretory pathway, protein trafficking (stage 2): step 5--____________ ____________ vesicles move Golgi-resident proteins to the previous Golgi compartment
plasma membrane
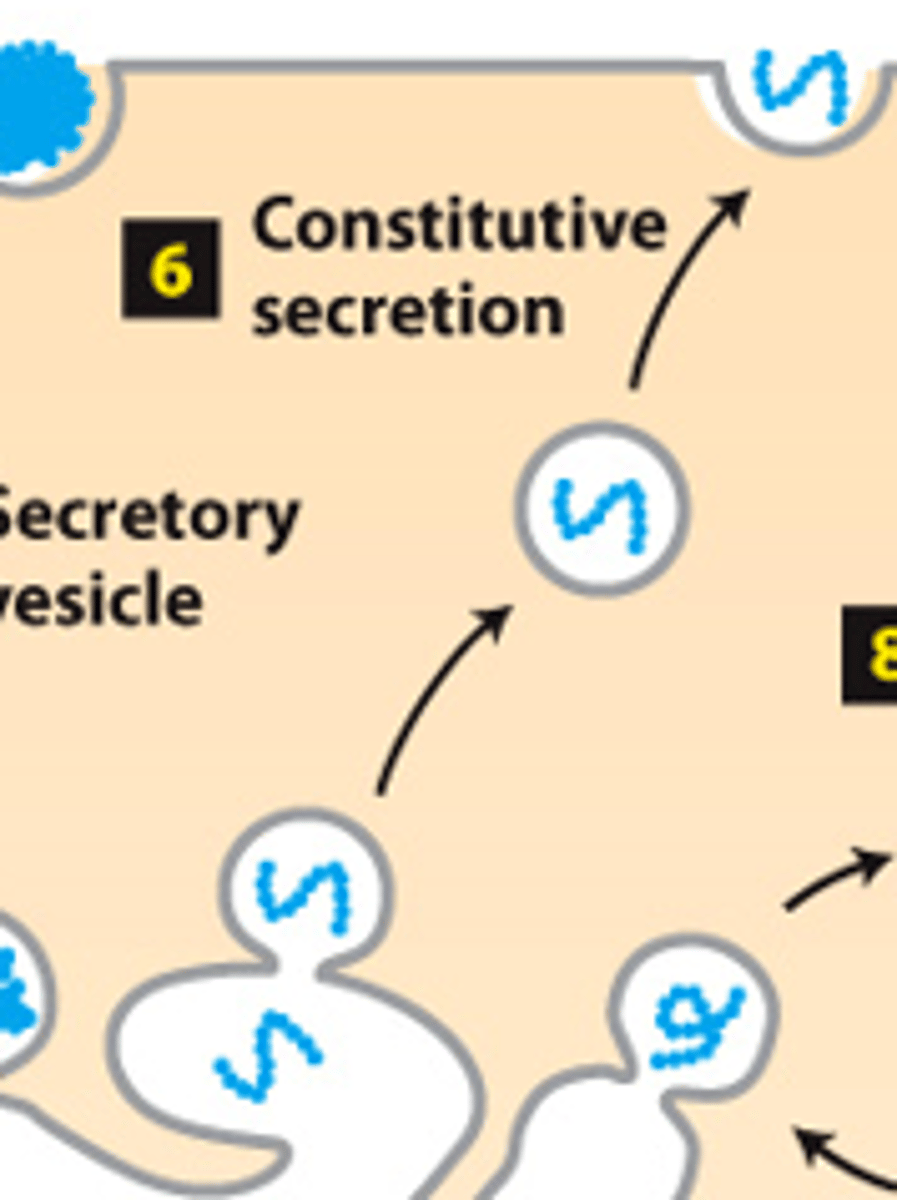
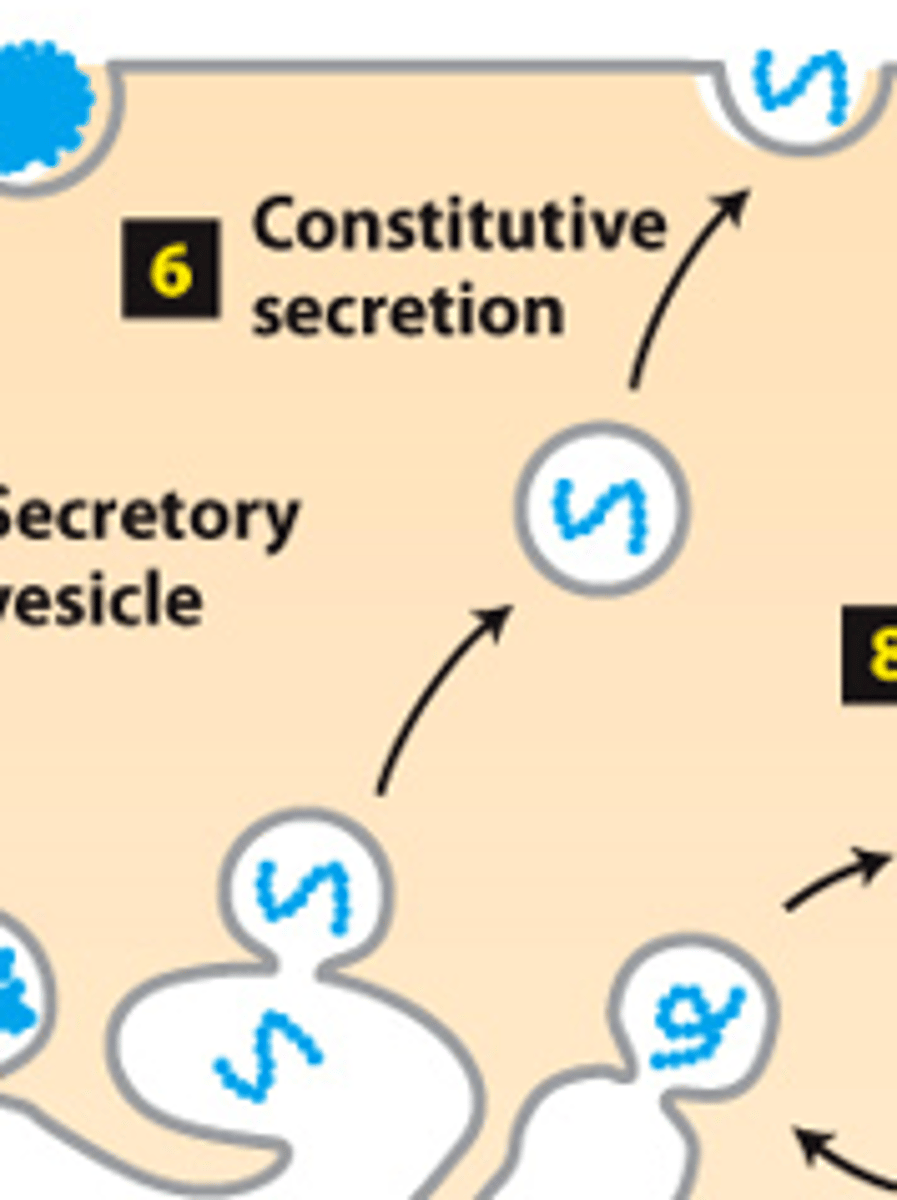
secretory pathway, protein trafficking (stage 2): step 6--constitutive secretion (all cells) - transport vesicles move continuously and fuse with the ___________ ______________
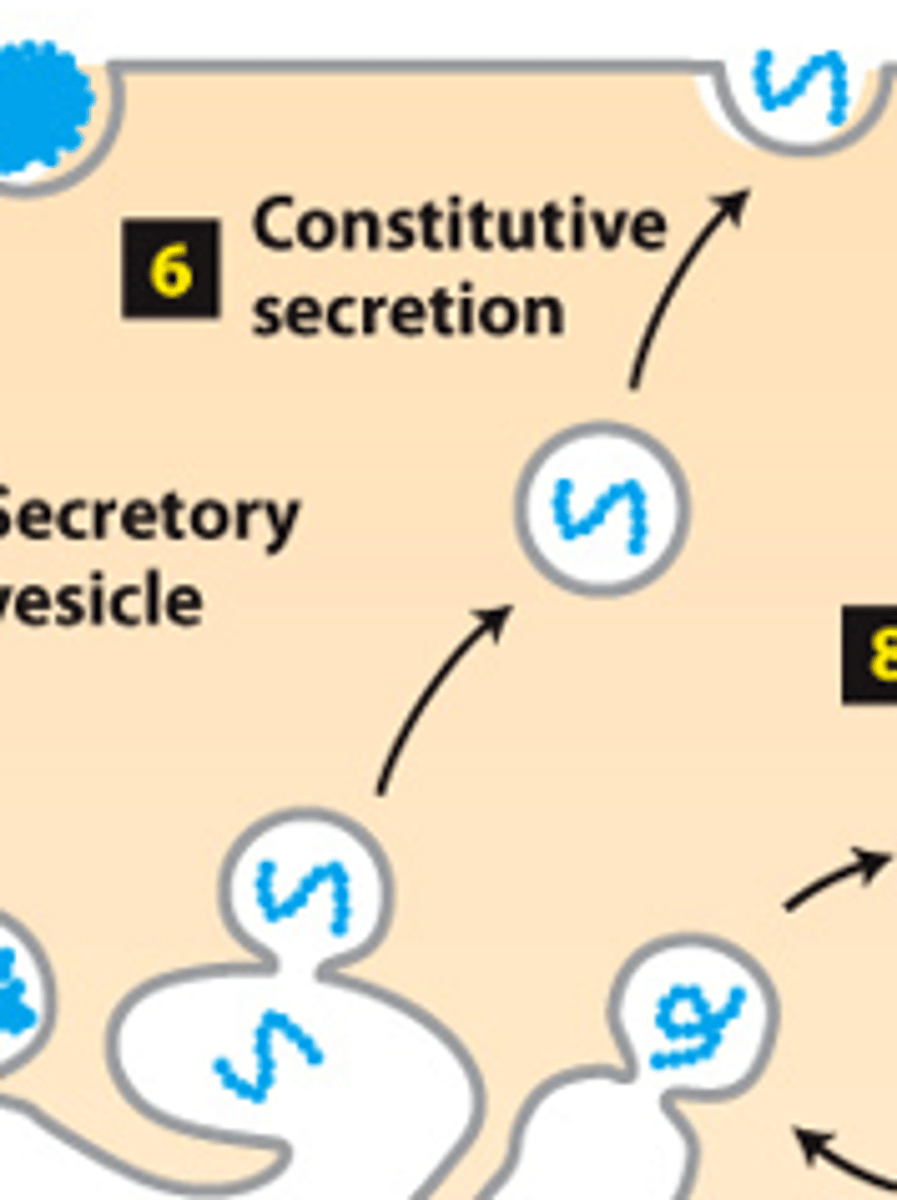
soluble
secretory pathway, protein trafficking (stage 2): step 6--constitutive secretion (all cells) - transport vesicles move continuously and fuse with the plasma membrane--___________ proteins are continuously secreted
membrane proteins
secretory pathway, protein trafficking (stage 2): step 6--constitutive secretion (all cells) - transport vesicles move continuously and fuse with the plasma membrane--____________ _____________ become plasma membrane proteins
regulated secretion
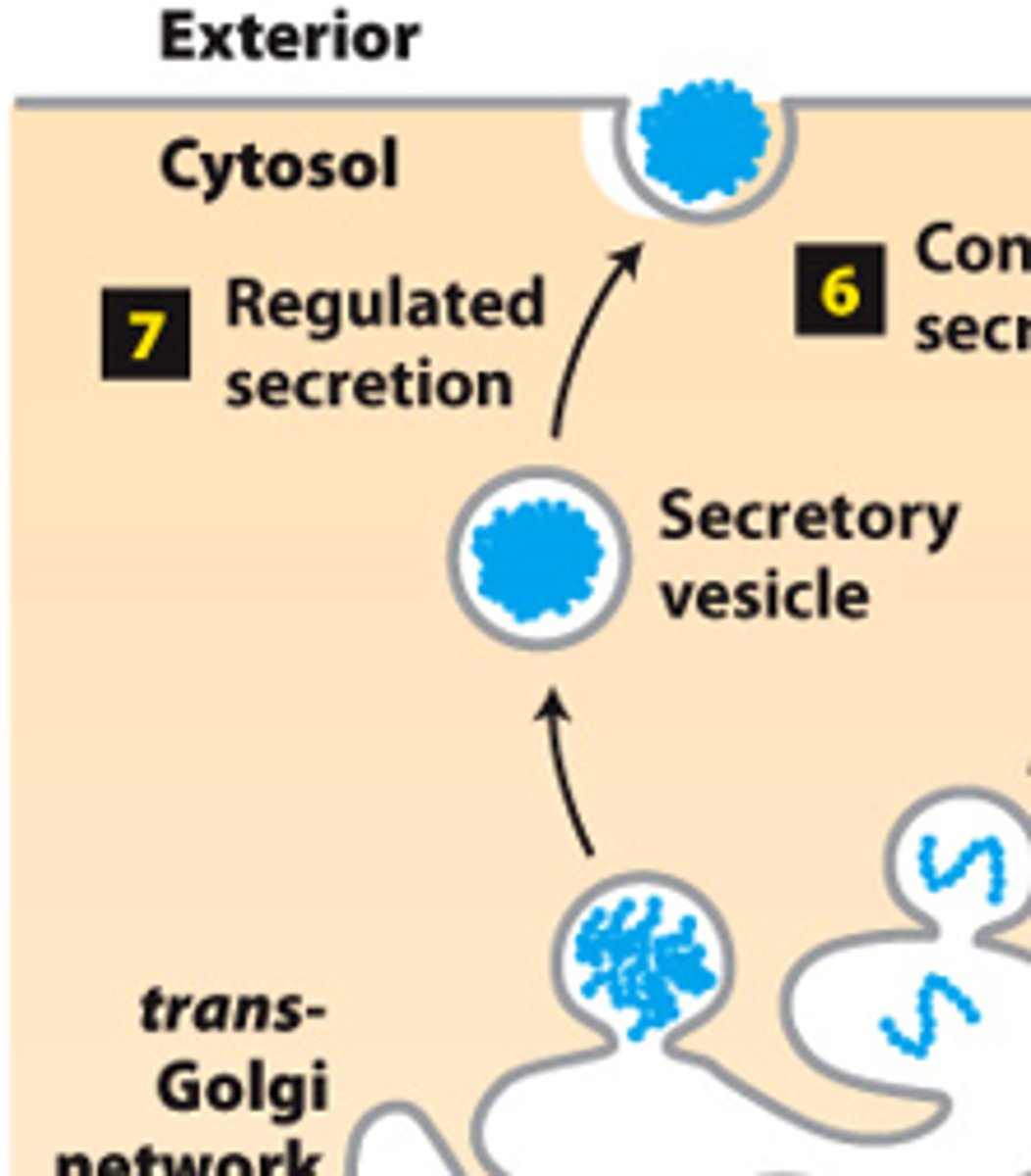
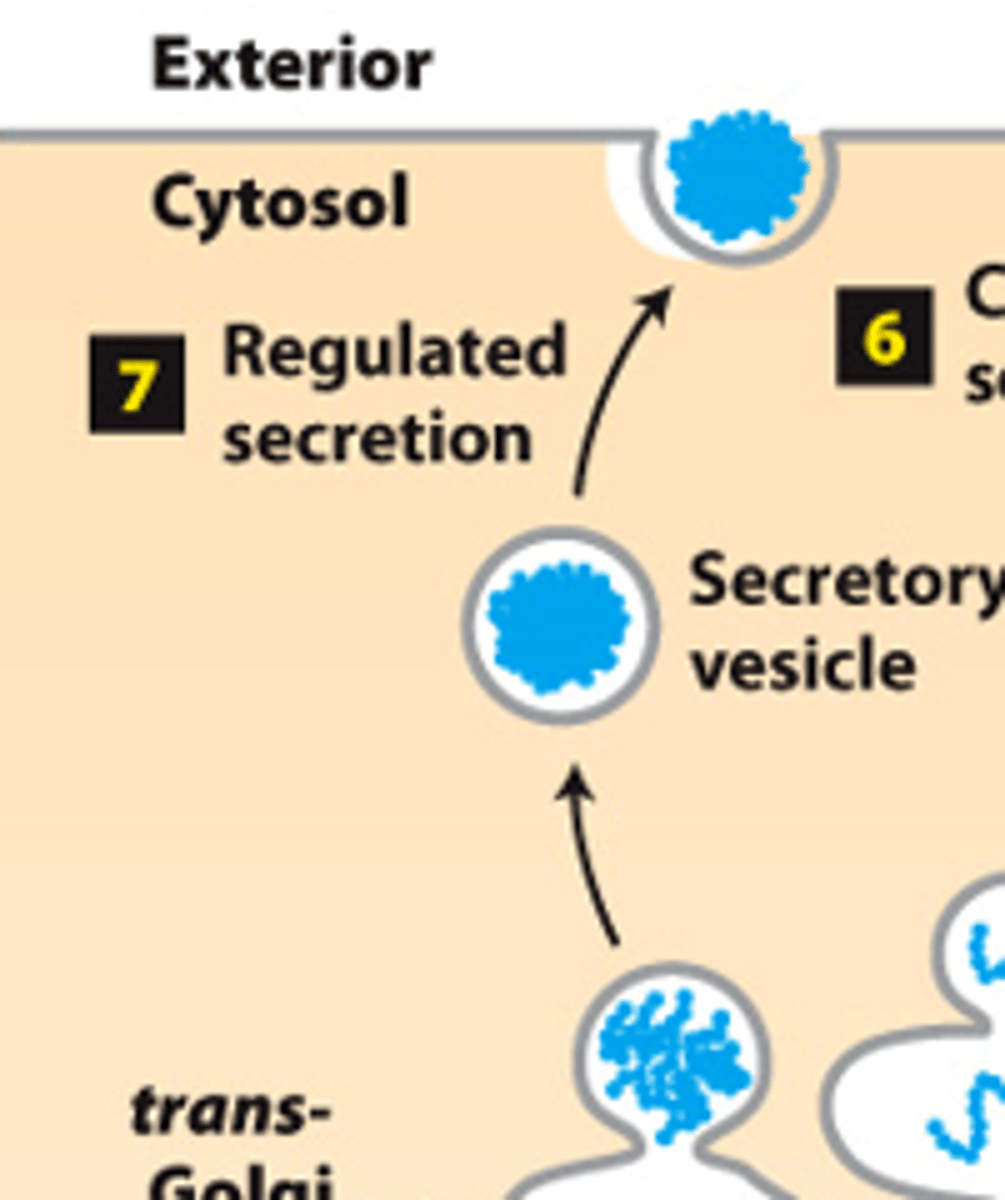
secretory pathway, protein trafficking (stage 2): step 7--___________ _______________--certain cell types
secretory vesicles
secretory pathway, protein trafficking (stage 2): step 7--regulated secretion (certain cell types)--proteins accumulated and stored in regulated _____________ ______________
neuronal, hormonal
secretory pathway, protein trafficking (stage 2): step 7--regulated secretion (certain cell types)--vesicles fuse with plasma membrane and secrete proteins only when cell receives a _______________ or _________________ signal secretion signal
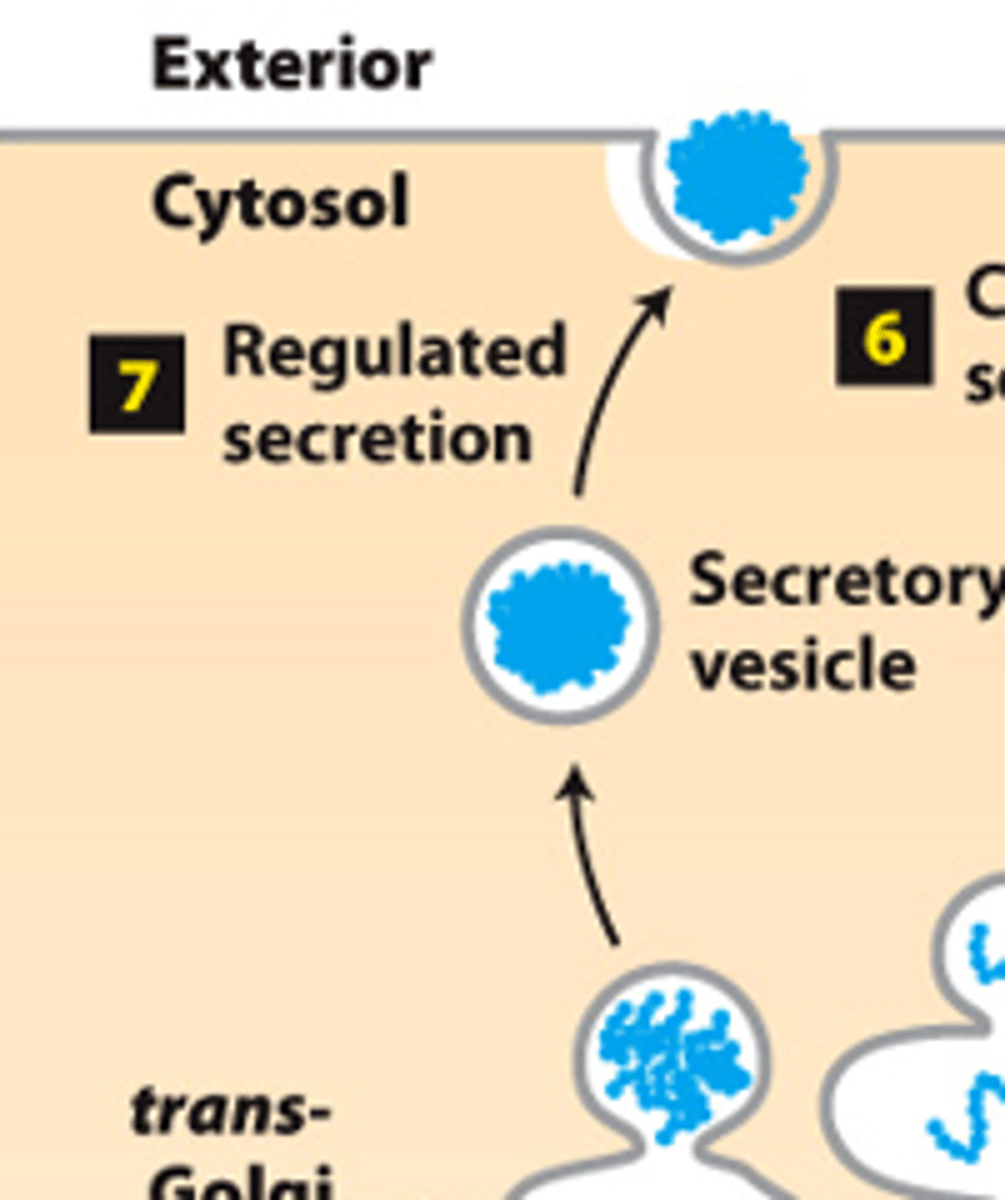
endosome, lysosome
secretory pathway, protein trafficking (stage 2): step 8--lysosome-destined membrane and soluble proteins transported in vesicles that bud from the trans-golgi and fuse with the late ________________ for delivery to a ______________
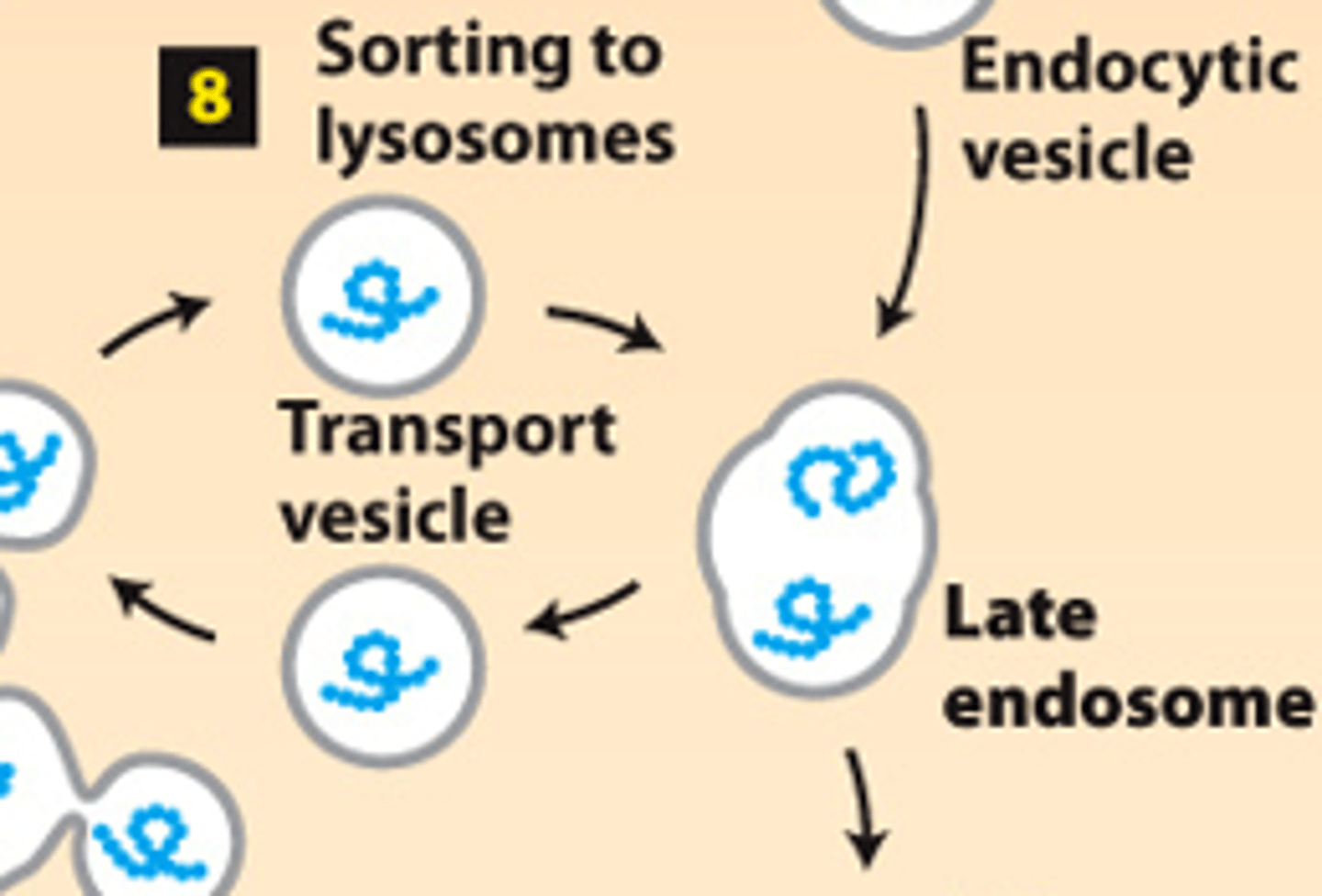
soluble extracellular
protein sorting, endocytic pathway: step 9--vesicles budding from the plasma membrane take up __________ _________________ proteins and deliver them to lysosomes via late endosomes
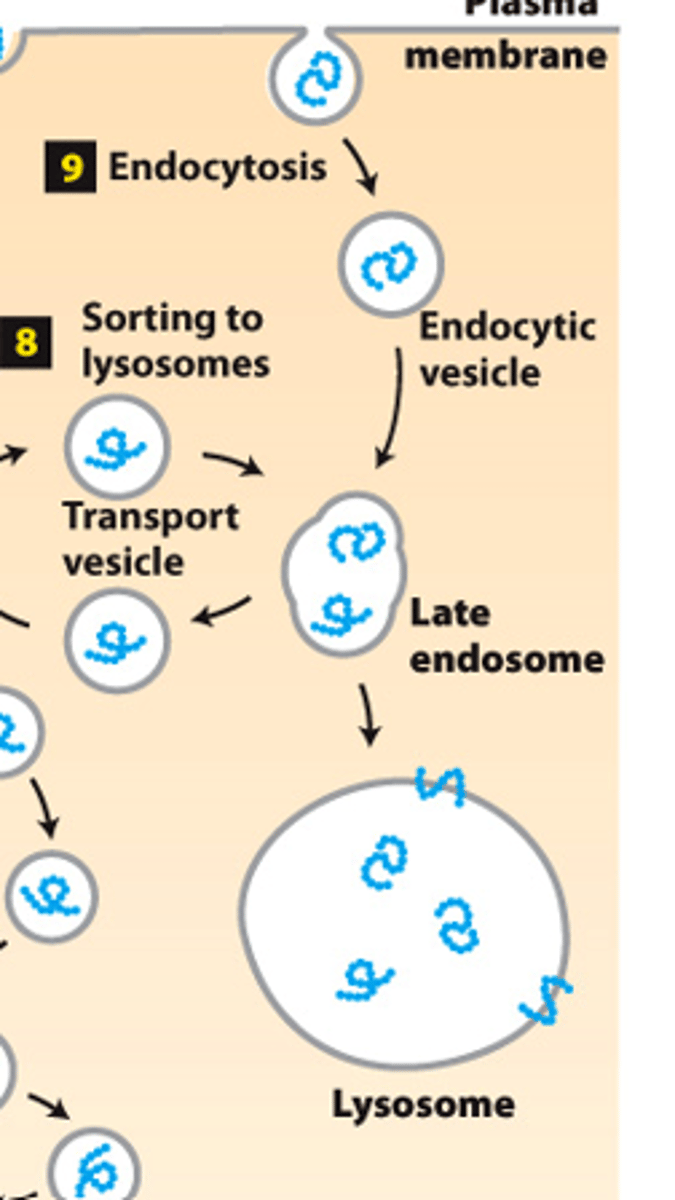
protein transport
three types of coated vesicles mediate ____________ _______________ through different pathways
small GTPase
________ ___________ proteins direct coat protein polymerization on donor membranes to pinch off vesicles carrying different cargoes
coat shedding
___________ ______________ exposes Rab and SNARE proteins that target vesicles for fusion with specific target membranes
budding, fusion
overview of vesicle ____________ and _____________ with a target membrane
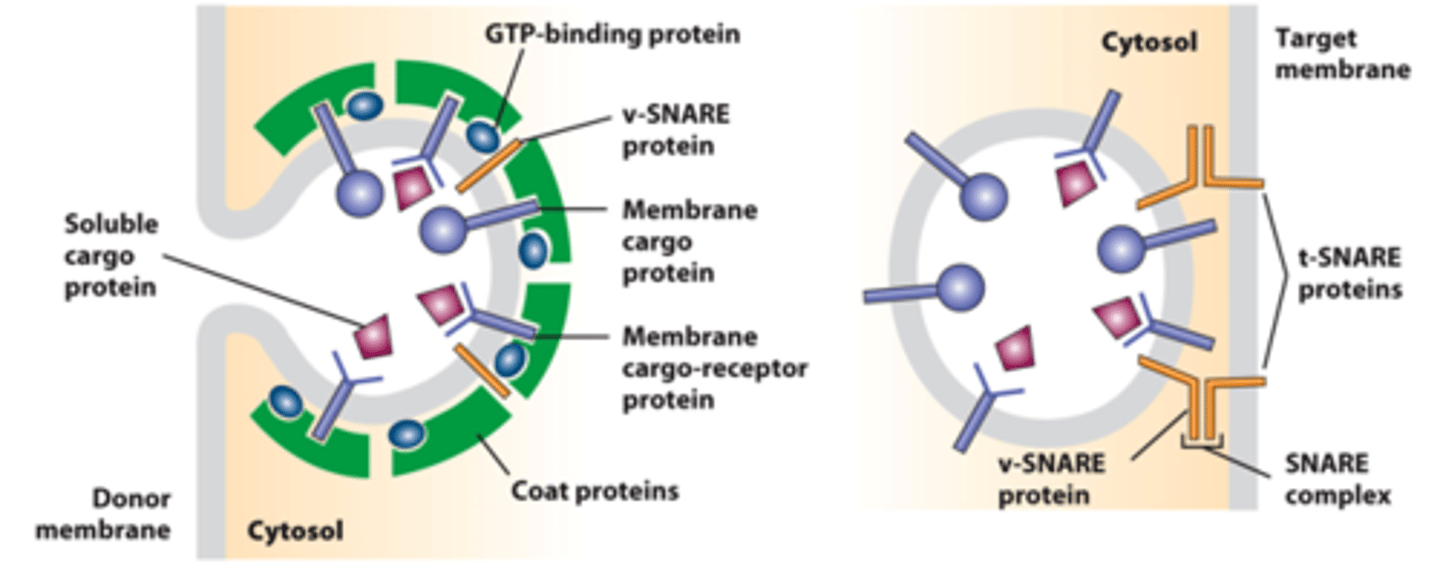
membrane
vesicles: bud from the donor ___________
fuse
vesicles: _______ with specific target membrane
protein coat
vesicles: assembly of a ___________ ________ drives vesicle formation and selection of specific cargo molecules
donor
vesicle budding from _________ membrane
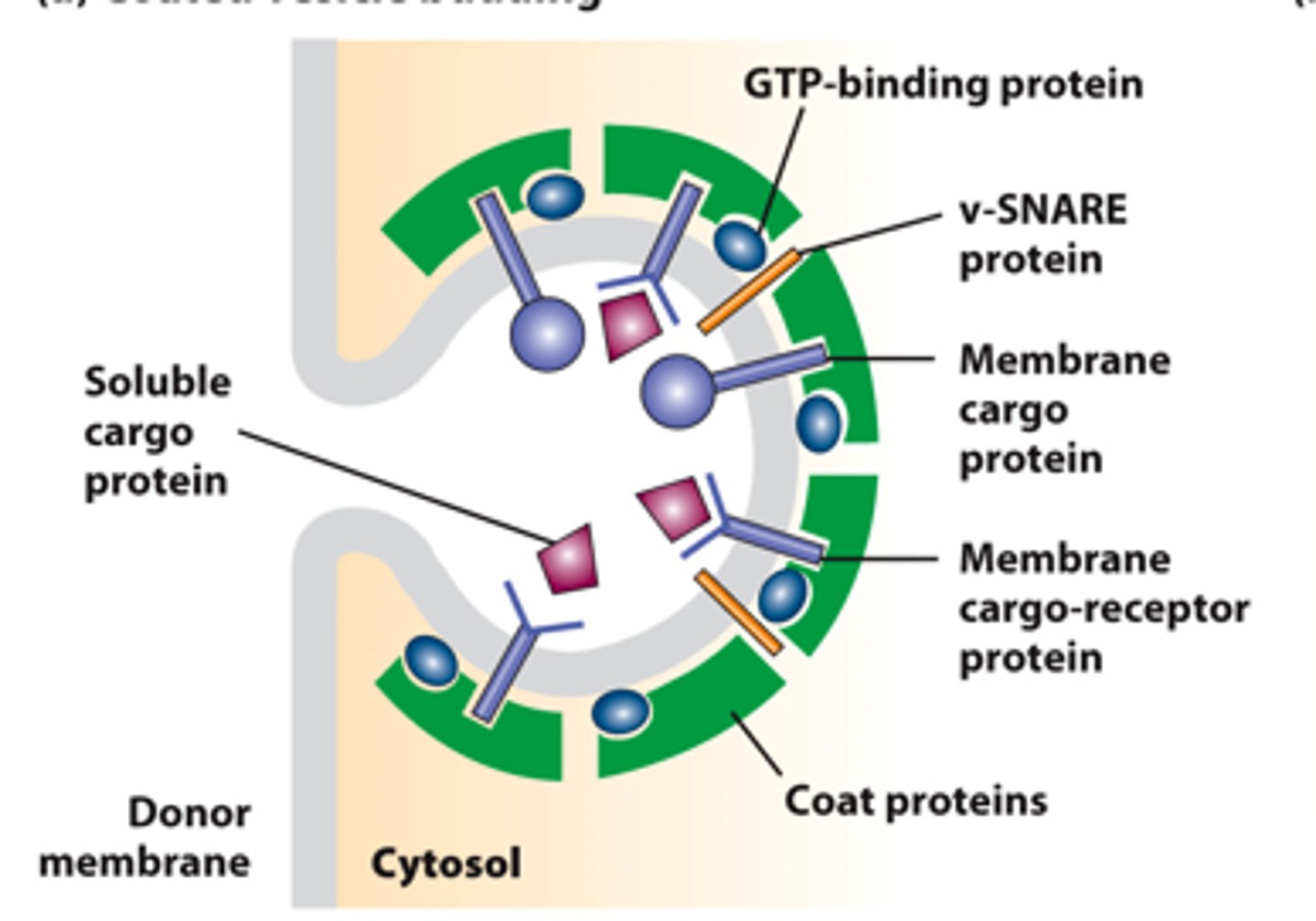
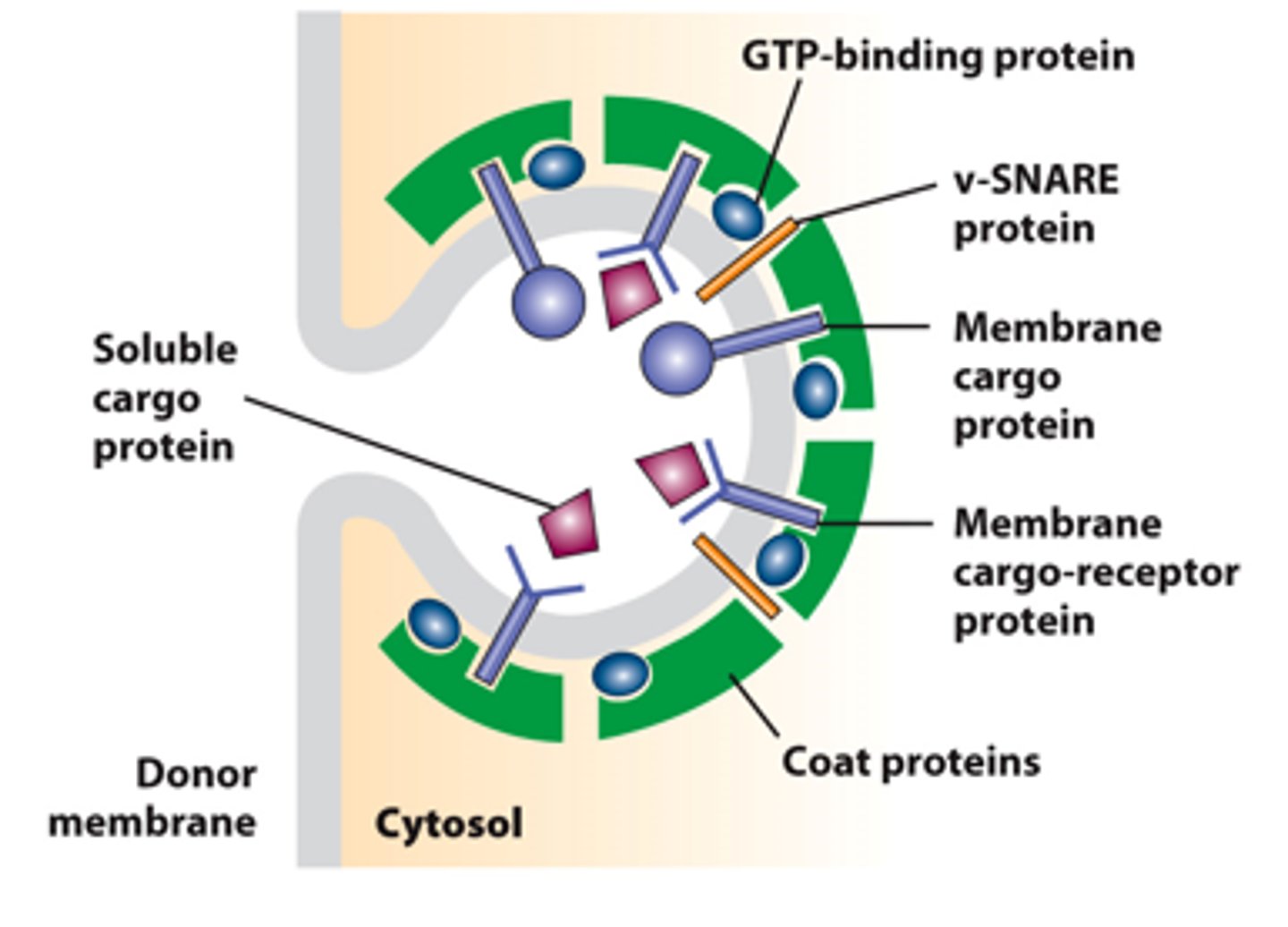
GTP binding
vesicle budding from donor membrane: recruitment of _______-__________ G proteins to a region of donor membrane
cytosolic coat
vesicle budding from donor membrane: ___________ ________ protein complexes bind to the cytosolic domain of membrane cargo proteins
coat binding
vesicle budding from donor membrane: _________ _____________ evaginates the membrane - typical transport vesicle; ~50 nm in diameter
cargo, receptors
vesicle budding from donor membrane: some _________ proteins act as _____________to bind soluble proteins in the lumen and capture them into the budding vesicle
SNARE
vesicle budding from donor membrane: donor membrane-specific ___________ proteins (vesicle-SNARES; v-SNARES) captured in budding vesicle membrane.
coated vesicle
vesicle budding from donor membrane: donor membrane fusion - pinches off ____________ ____________
uncoated
vesicle budding from donor membrane: coated vesicle ____________ in cytosol - uncovers projecting v-SNARES for fusion targeting
coated vesicle budding
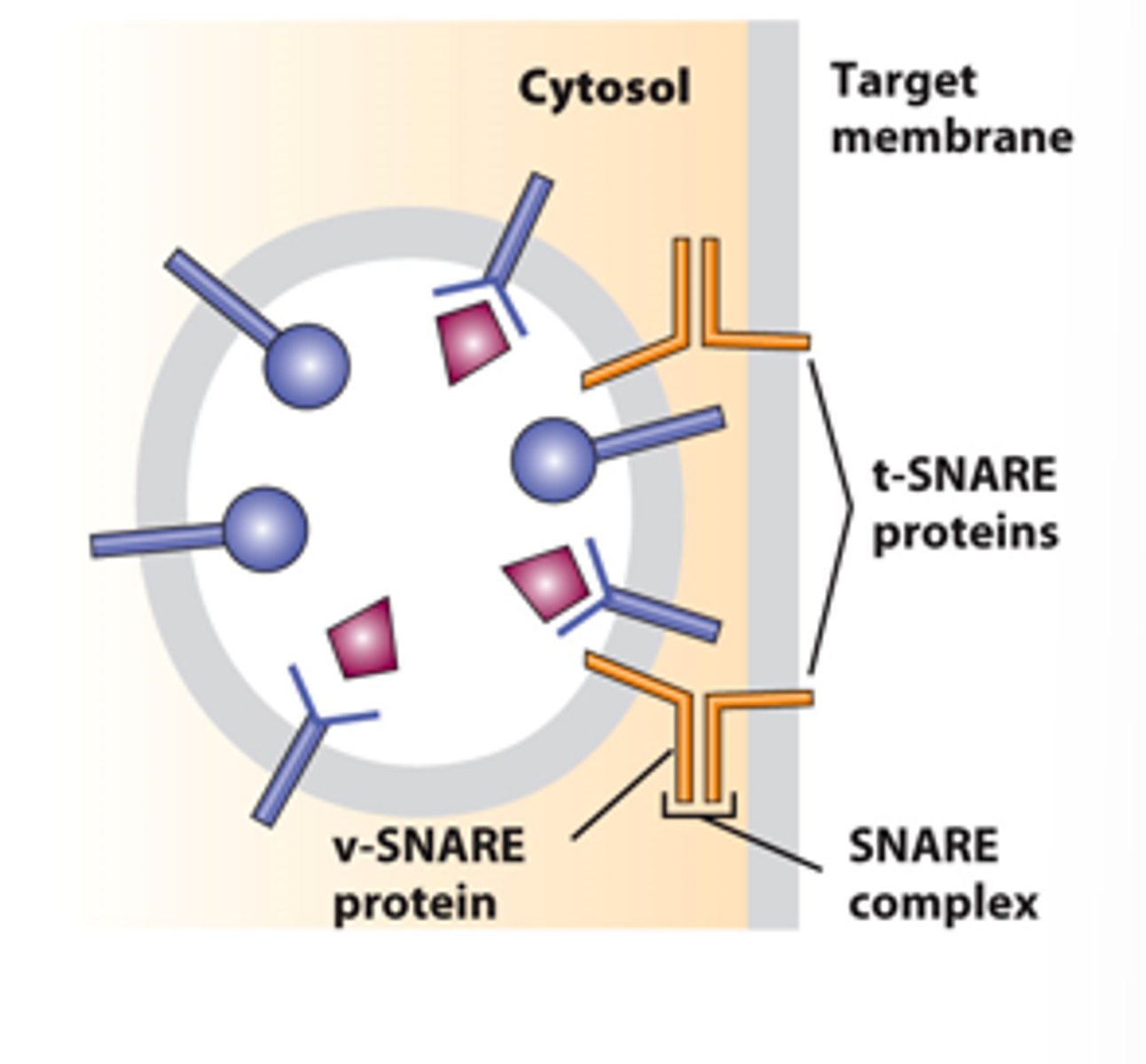
uncoated vesicle fusion
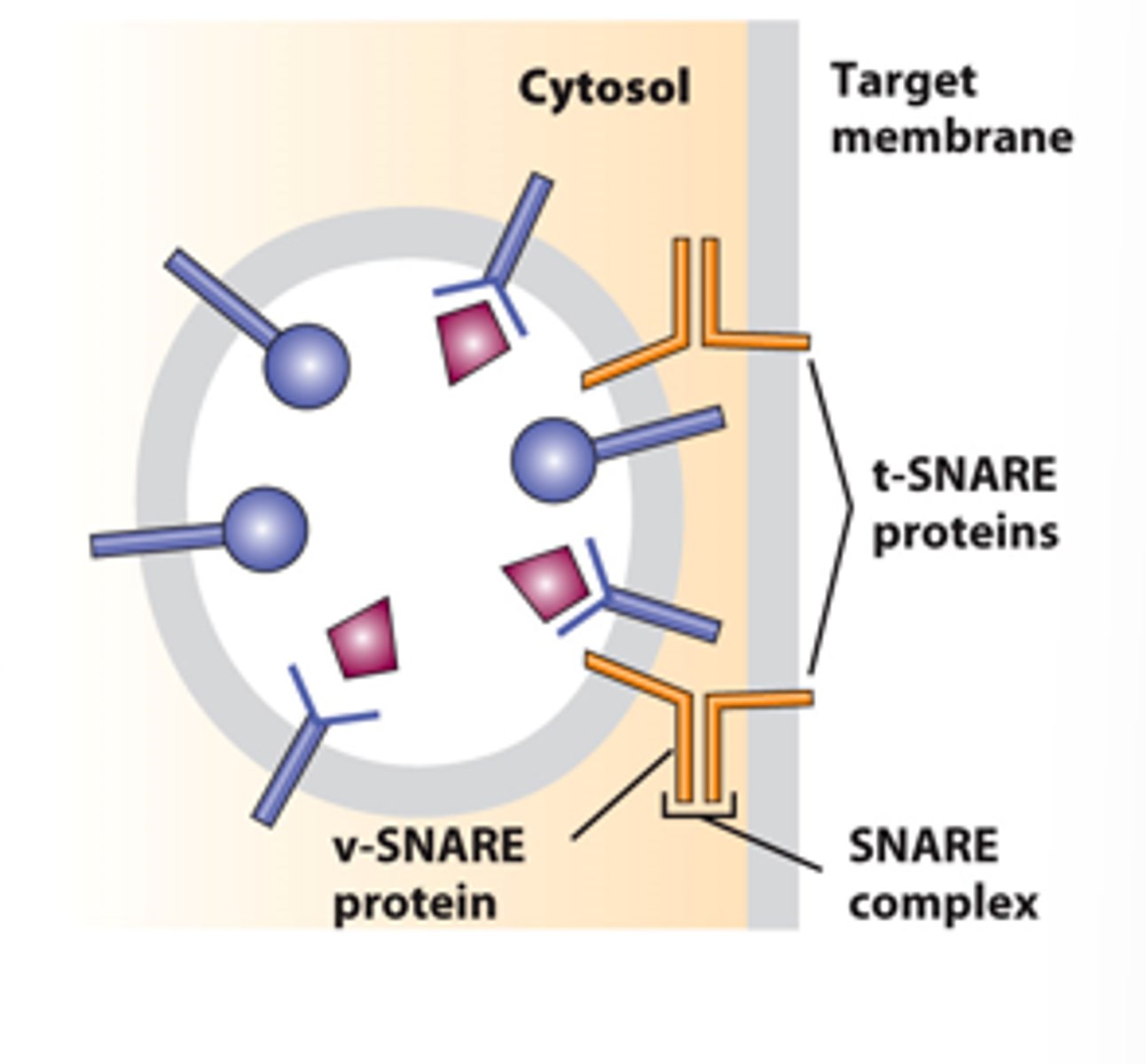
targeting
vesicle fusion with target membrane: ___________ -- interaction of specific v-SNARE with specific target membrane t-SNARES
fusion
vesicle fusion with target membrane: ___________ process
ER, cis golgi
transport step method, COPII: _______ to _______-____________
cis golgi, ER, golgi cisternae
transport step method, COPI: ______-__________ to ________ Later to earlier __________ ___________
COPII
coat proteins: Sec23/Sec24 and Sec13/Sec31 complexes, Sec16
Sar1
associated GTPase, OPII: __________
coatomers
coat proteins, OPI: ___________ containing seven different COP subunits
ARF
associated GTPase, OPI: __________
COPII, COPI
coated vesicles involved in protein trafficking
three, reversible polymerization
_________ major types of transport-specific coated vesicles--each with different type of protein coat formed by _____________ ___________ of a distinct set of coat and G protein subunits
GTPase
a conserved set of monomeric __________ switch proteins controls the assembly of different vesicle coats
trans golgi
vesicle-mediated protein trafficking from the _______-__________ network
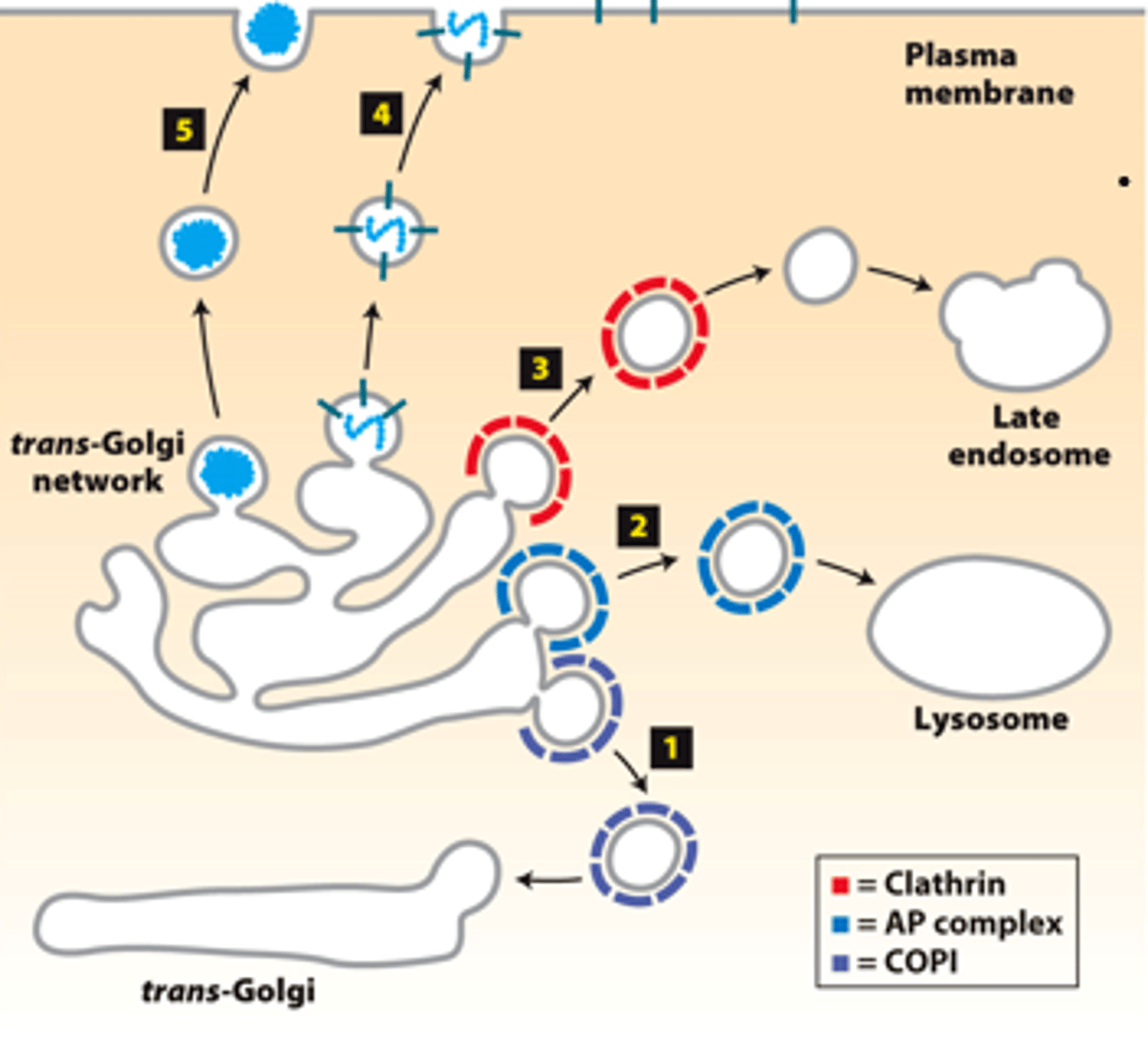
sorting
trans-golgi network: distal ____________ compartment
sorts
trans-golgi network: _________ proteins into five different types of vesicles for transport to the plasma membrane, endosomes, and lysosomes
five
how many different types of vesicles does the trans-golgi network sort into for transport?
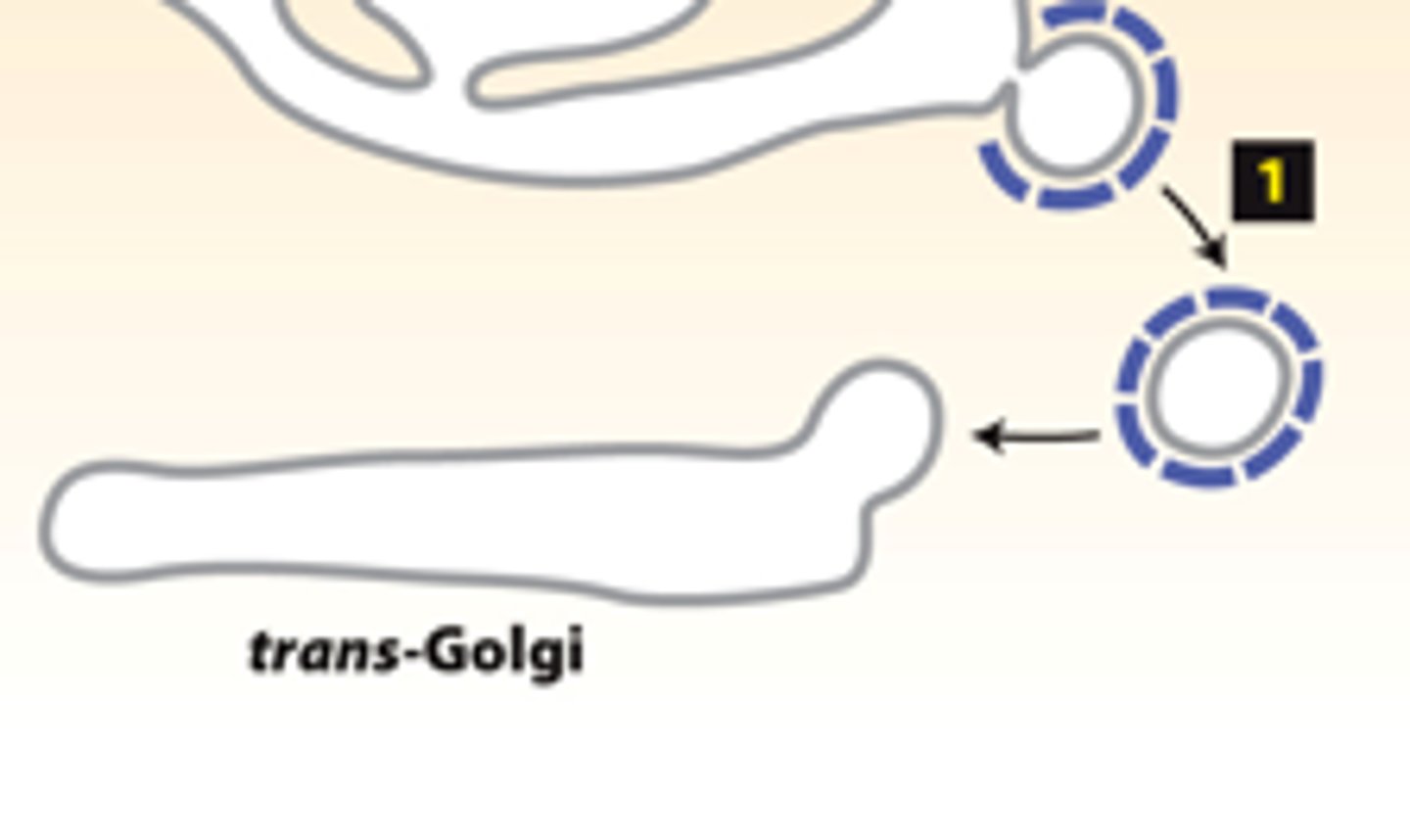
COPI vesices
five destinations trans-golgi complex sorts into for transport: retrograde transport of golgi enzymes to the trans-golgi (cisternal progression process)
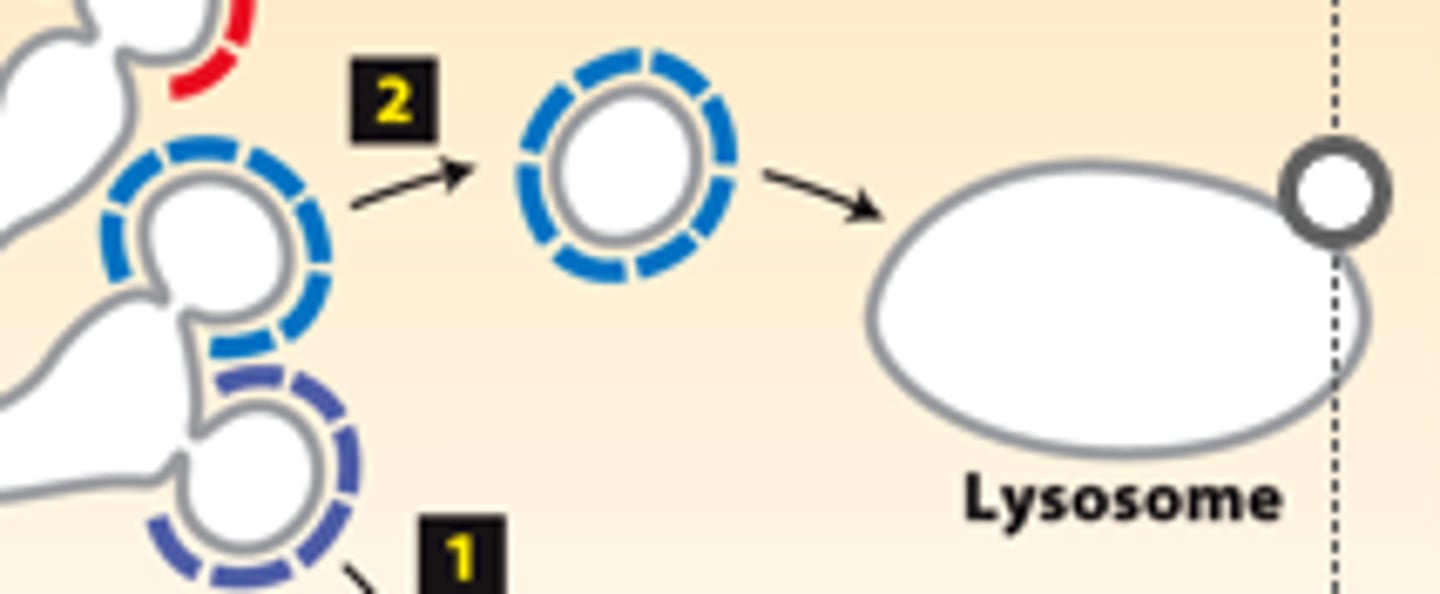
AP complex vesicles
five destinations trans-golgi complex sorts into for transport: may have clathrin coat, transport lysosomal enzymes directly to lysosomes
constitutive secretory vesicles
five destinations trans-golgi complex sorts into for transport: unknown coat, transport constitutively secreted proteins and plasma membrane proteins to the plasma membrane
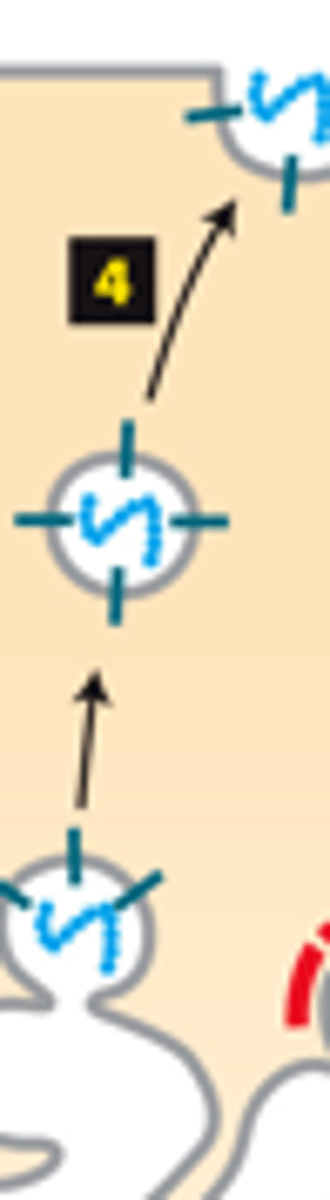
constitutive secretory vesicles
five destinations trans-golgi complex sorts into for transport: unknown coat, cargo proteins include ECM proteins, blood proteins, immunoglobulins
clathrin coated vesicles
five destinations trans-golgi complex sorts into for transport: (+AP2) transport lysosomal enzymes to late endosomes for eventual delivery to lysosomes
regulated secretory vesicles
five destinations trans-golgi complex sorts into for transport: unknown coat, store and process secreted proteins until signaled to fuse with the plasma membrane to secrete the proteins
ECM proteins, blood proteins, immunoglobulins
cargo proteins of constitutive secretory vesicles
regulated secretory vesicles
five destinations trans-golgi complex sorts into for transport: unknown coat, cargo proteins include digestive enzymes and peptide hormones
digestive enzymes, peptide hormones
what cargo proteins are included in the regulated secretory vesicles