A&P Test I
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
What region is the head?
Cephalic
Cheek
Buccal
Skull
Cranial
Face
Facial
Forehead
Frontal
Chin
Mental
Nose
Nasal
Base of skull
Occipital
Mouth
Oral
Eye
Orbital
Ear
Otic
Temple
Temporal
What region is the neck?
Cervical
Back of neck
Nuchal
What region is chest, abdomen, AND pelvic?
Trunk
Breast
Mammary
Chest
Pectoral
Shoulder blade
Scapular
Breastbone
Sternal
Spinal column
Vertebral
Shoulder
Acromial
Armpit
Axilla
Arm
Brachium/brachial
Forearm
antebrachium/antebrachial
Wrist
Carpal
Hand
Manual/manus
Palm
Palmar/volar
Fingers
Digital/phalangeal
Hip
Coxal
Lower back
Lumbar
Naval
Umbilical
Buttocks
Gluteal
Space between anus and genitals
Perineal
Pubic
Pubis
Between hips (back)
Sacral
Heel
Calcaneal
Shin
Crural
Toes
Digital/phalangeal
Thigh
Femoral
Kneecap
Patellar
Foot
Pedal
Sole
Plantar
Hollow behind knee
Popliteal
Calf
Sural
Ankle
Tarsal
Brain cavity
Cranial cavity
Chest cavity
Thoracic cavity
Abdomen & pelvic cavity
Abdominopelvic cavity
What is in the thoracic cavity?
Heart and lungs
Lung cavity
Pleural cavity
Heart cavity
Pericardial cavity
Sternum/heart cavity
Mediastinum
What is in the abdominopelvic cavity?
Abdomal: Stomach, liver, gall gladder, intenstines, spleen, kidneys, pancreas
Pelvic: Organs, uterus, urinary bladder, fallopian tube, part of large intestine
How many serous membranes?
Three
Serous lung
Pleura
Serous heart
Pericardium
Serous abdominopelvic
Peritoneum
Right upper quadrant
liver, gall bladder
Right lower quadrant
appendix, right ovary
Left upper quadrant
stomach, spleen
Left lower Quadrant
Colon, left ovary
Epigastic
Stomach and left lobe of liver
Umbilical
Small intestine
Hypogastric
urinary bladder, uterus
Right hypochondriac
Right lobe of liver, gall bladder
Left hypochondriac
Spleen
Left lumbar
Left kidney, part of large intestine
Right lumbar
Left kidney, part of large intestine
Right iliac/inguinal
Appendix, right ovary
Left iliac/inguinal
Part of colon, left ovary
What is histology
Study of tissues by microscope
What is cytology
Studies of cells by microscope
What are the four basic tissues
Epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
Which germ layers does epithelial originate from?
Ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
What tissues are from mesoderm?
connective and muscle
What tissues are from ectoderm?
Nervous
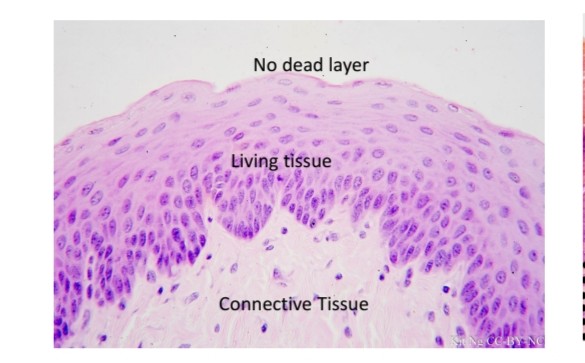
Stratified squamous epithelium
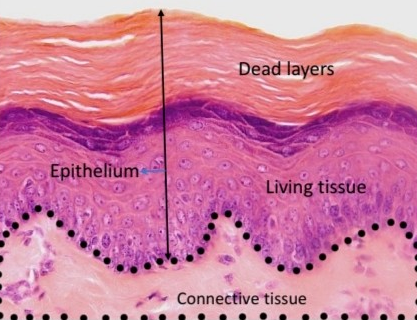
Name the tissue
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
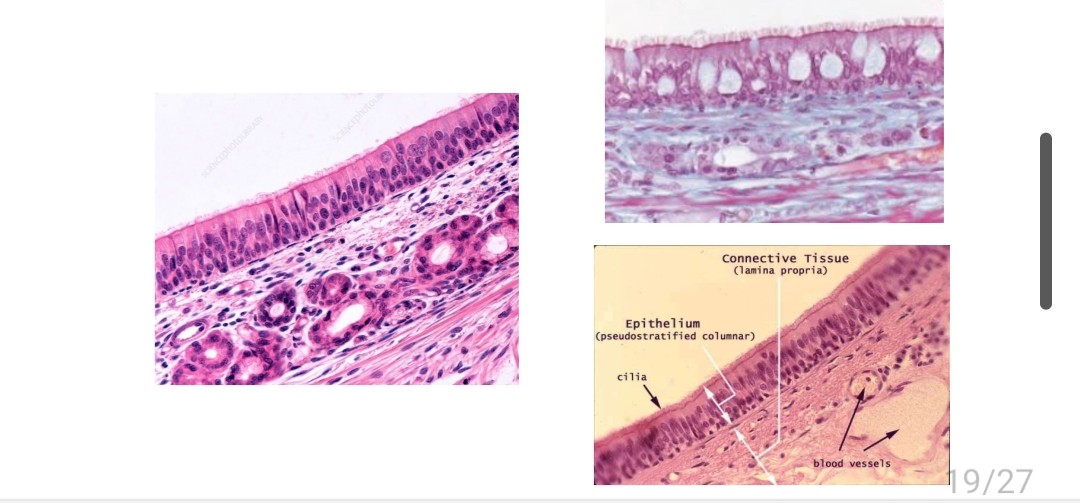
Name the tissue
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
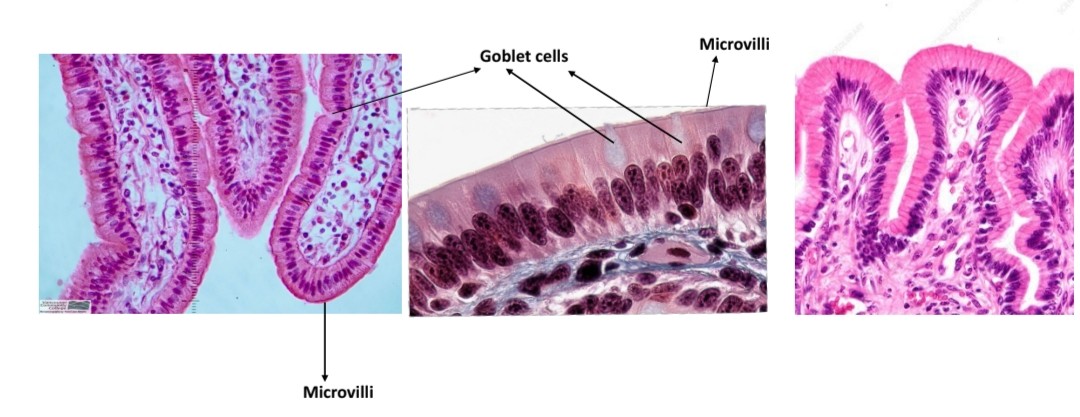
Name the tissue
Simple columnar epithelium
Name the tissue
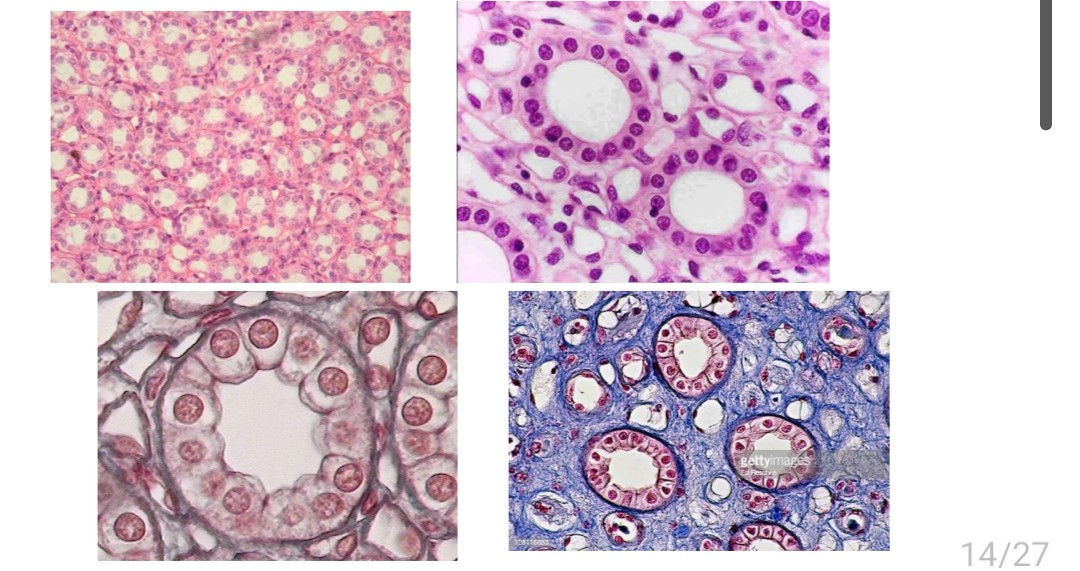
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Name the tissue
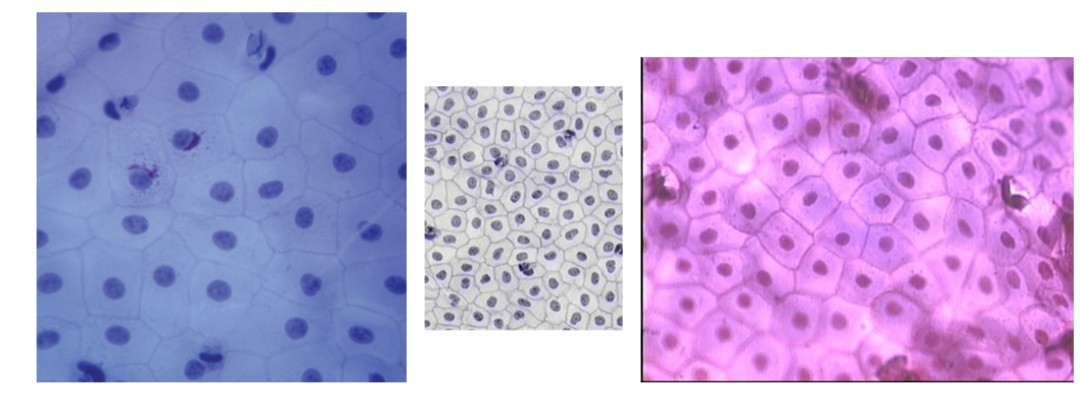
Simple squamous epithelium
Name the tissue
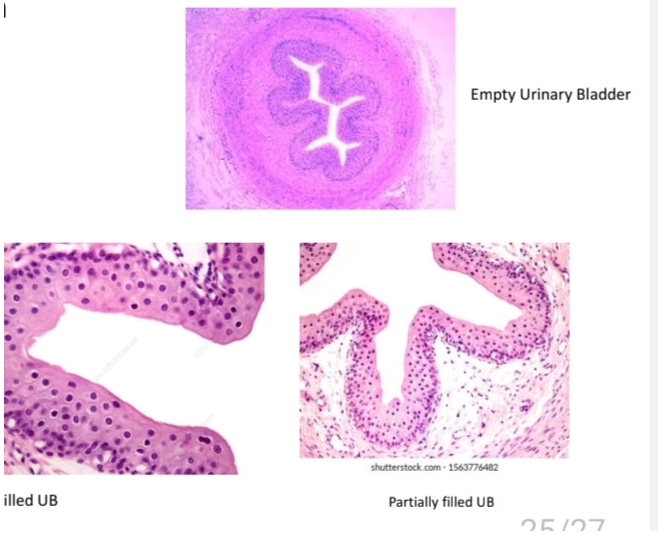
Transitional epithelium
Location and function of transitional epithelium
Bladder, allows distention of organs
Location and function of stratified squamous epithelium
Mouth, protect against friction
Location and function of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Skin, protection
Location and function of pseodustratified ciliated epithelium
Nasal cavity, secretes mucous to sweep debris
Location and function of simple columnar epithelium
Digestive canal, secretion & absorption
Location and function of simple cuboidal epithelium?
Kidney, secretion & absorption
Location and function of squamous epithelium
Heart, secretion
Function of goblet cells
Produce mucuous
Function of microvili
Increase surface area for absorption
Function of cili
To rid of debris
Define endothelium
Simple squamous lining cardiovascular system
Define mesothelium
Simple squamous lining serous membranes
Function of tight junction
Keep materials from leaking out of organs
Function of adhering junctions
Contain dense plaque protein connected by cadherin to join cells and form adhesion belts
Function of desmosomes
Also use cadherin to hook into cytoplasm and prevents epidermal cells from separating under tension
Function of hemidesmosomes
Join cells to basement membrane with glycoprotein integrals