6.4 - Acid Deposition
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Acid Deposition
Can impact living systems and the built environment. The general term for acid coming down from the air
The pollution management of ______ often involves cross-border issues.
Acids
Chemicals that are able to give a hydrogen ion away.
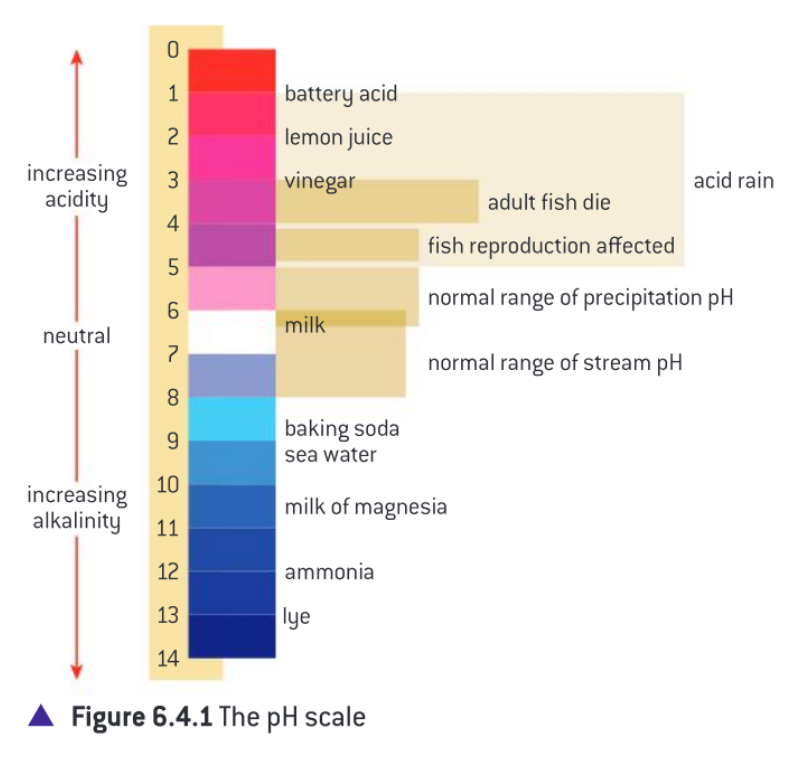
Normal unpolluted rain is slightly acidic and has a pH of about 5.6, cause by the presence of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
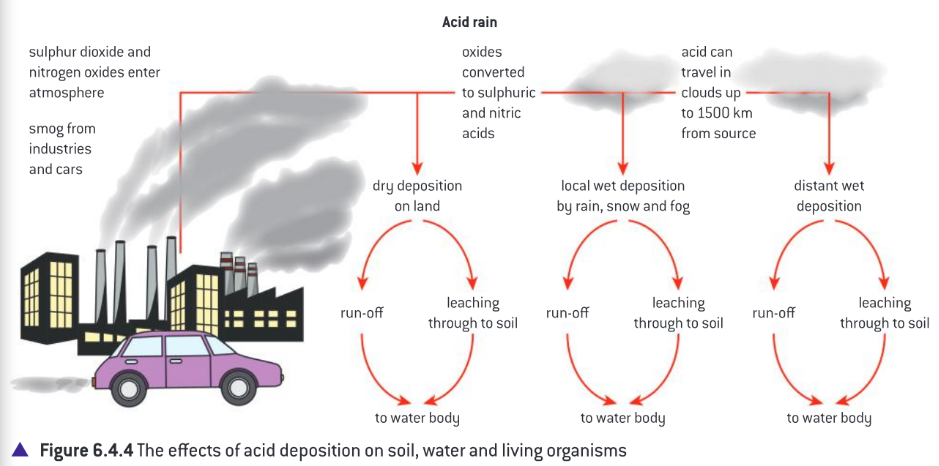
Wet deposition
When acid comes down in the form of rain or snow. Occurs at slightly longer distances from the sources of the primary pollutants.
It consists of sulphurous acid, sulphuric acid, and nitric acid
Dry deposition
When acid comes down as ash or dry particles. Usually occurs quite close to the source of the acidic substances.
It consists of sulphur dioxide, sulphur trioxide, and the nitrogen oxides
Primary Pollutants
Those that are directly emitted from the chimney of a factory or the exhaust pipe of a car, such as:
Sulfur Dioxide - SO2
Nitrogen Oxide - NOx
Secondary Pollutants
Primary pollutants react with other substances in the atmosphere and create different pollutants such as
Sulfuric acid - H₂SO₄
Nitric acid - HNO₃
Sulphur Dioxide
Naturally formed by volcanic eruptions and nitrogen oxides by lightning. _____ is formed when sulphur-containing fuels are combusted since sulphur is common in coal and oil

Direct effect
For example, acid on aquatic organisms and coniferous forests, such as:
chlorophyll loss & yellowing of tree leaves and buds leads to diminished growth
thinning cuticle (the waxy coating on needles)
symbiotic root microbes killed (ex. Rhizobium) limits nutrient uptake
Indirect toxic effects on fish
When the pH of rain drops below 5, aluminum ions which are normally insoluble, become soluble
This leads to the Al ions dissolving and leaching out of the soil and into streams
Aluminum disrupts salt, water, and oxygen-regulating systems in fish
It can also adhere to fish gills, causing suffocation
Lichens are sensitive to SO2 gases and may therefore be used as an indicator species

Effect of acid deposition on coniferous forests
Leaves and buds show yellowing (loss of chlorophyll) and damage in the form of thinning wax cuticles
These and other changes reduce growth, allowing nutrients to be leached out and washed away and pathogens and insects to gain entry
Symbiotic root microbes are killed and this greatly reduces the availability of nutrients, further reducing tree growth
It reduces the ability of soil particles to hold on to nutrients (Calcium, Magnesium, Potassium) ions which are then leached out
It releases toxic aluminum ions from soil particles which then damage root hairs
= trees are weakened and may die
Indirect nutrient effect
When soil can’t retain Calcium, Magnesium, Potassium ions, in an acidic environment. This leads to these nutrients leaching out of the soils and thus are unavailable to the trees.
Dissolved Aluminum ions damage root hairs (the smallest roots are the most effective at absorbing nutrients), so the trees are unable to absorb many nutrients
N-fixing bacteria don’t function as well, so less Nitrogen is added to the soil matrix

Pollution management strategies that include altering human activity
Switch to renewable energy sources to reduce fossil fuel use
Increase energy efficiency of household appliances
Use more public transportation to reduce the number of cars on the road
Use low-sulfur fuels

Pollution management strategies that include regulating and monitoring the release
Install scrubbers on smokestacks of coal-fired power plants to remove SO2
Catalytic converts installed on automobiles to remove SO2 and NOx (required by law in US, Canada, and Europe)


Pollution management strategies that include Cleanup and restoration
Add lime to acidified lakes and streams
Add lime to forestry plantations
UN Convention on Long-Range Transboundary Air Pollutants (LTRAP) - 1979; later ammended and modified by US, Canada, and Europe
The effects of acid deposition on soil, water, and living organisms