Buoyancy and respiration
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Pelagic
liver makes up 20-30% of the body weight (Elasmobranchs)
Benthic
Liver makes up 5% of body weight (Elasmobranchs, sharks)
How do bony fishes regulate buoyancy?
1. Lipid accumulation
2. Water accumulation in tissues
3. Reduce ossification and muscular tissue
4. Gas bladder
How do sharks regulate buoyancy?
through lipid accumulation and reduction of ossification/ muscular tissue (cartilage)
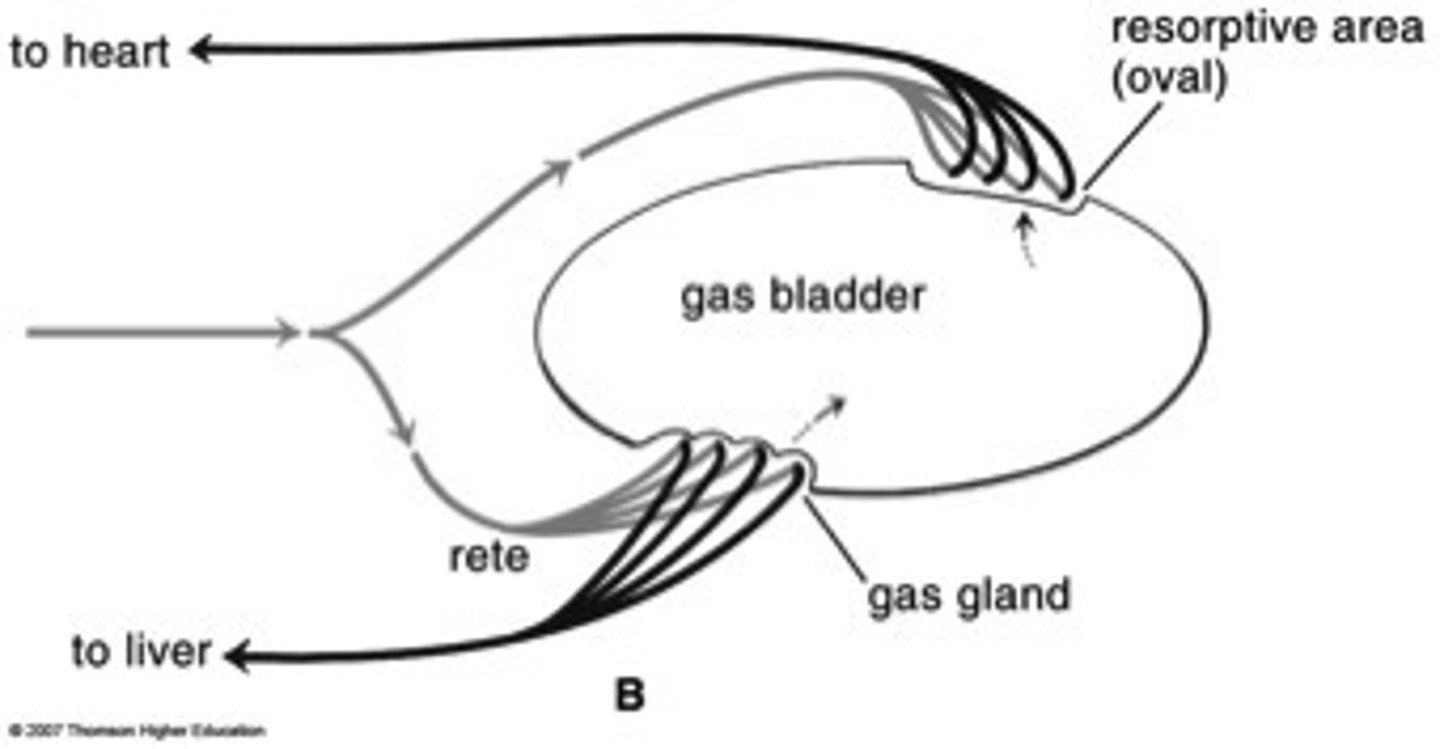
Gas bladder
This is filled with CO2, oxygen, nitrogen
-saves energy by regulating buoyancy
-plays a role in respiration
-lost in some species
Why do freshwater fishes have a larger gas bladder?
Because freshwater is less dense (no salt) so a larger volume of gas is needed to achieve stable buoyancy
Barotrauma
Sudden change in pressure causes the gas bladder to expand and push against other organs
-bulging eyes
-bloated
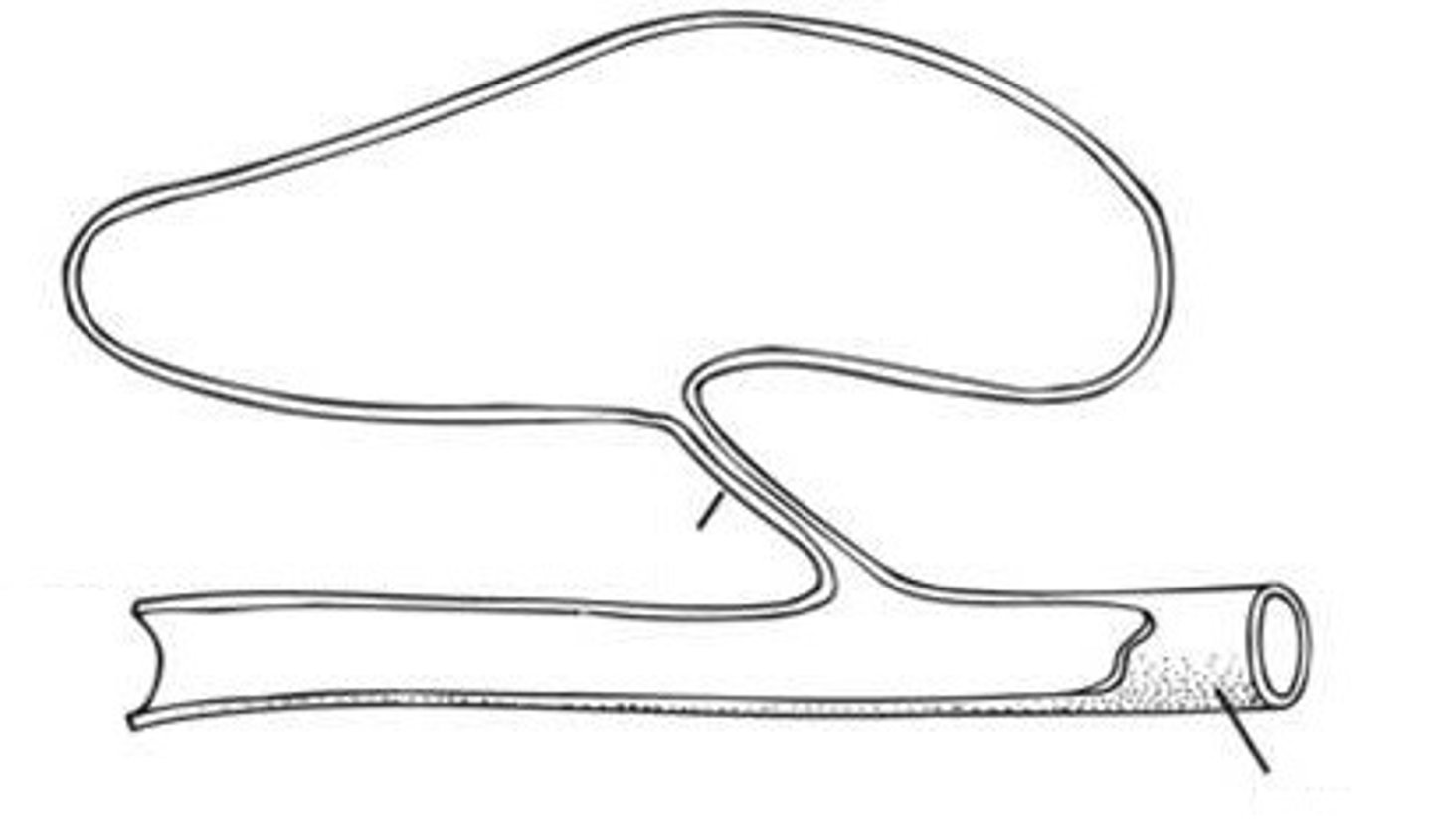
Physostomous
Gas bladder is attached to the gut by pneumatic duct
-Sturgeons and primitive fishes
-inflate by gulping air or diffusion of gases from blood into bladder by gas gland
-Release gas through pneumatic duct
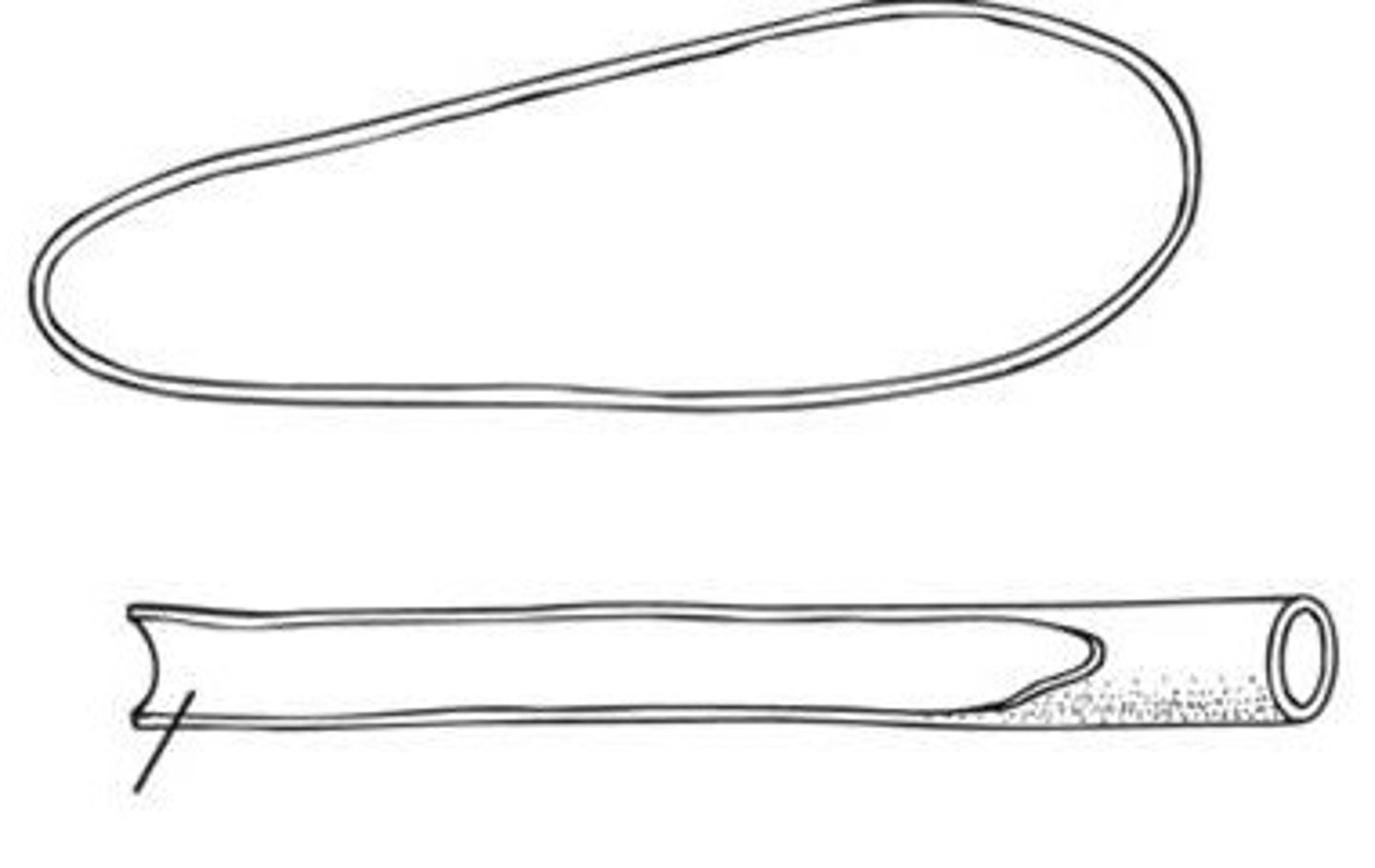
Physoclistous
Gas bladder does not have a connection to the gut
- Derived fishes, 2/3 of all fishes
- Increases or decreases by diffusion of gases in and out of blood
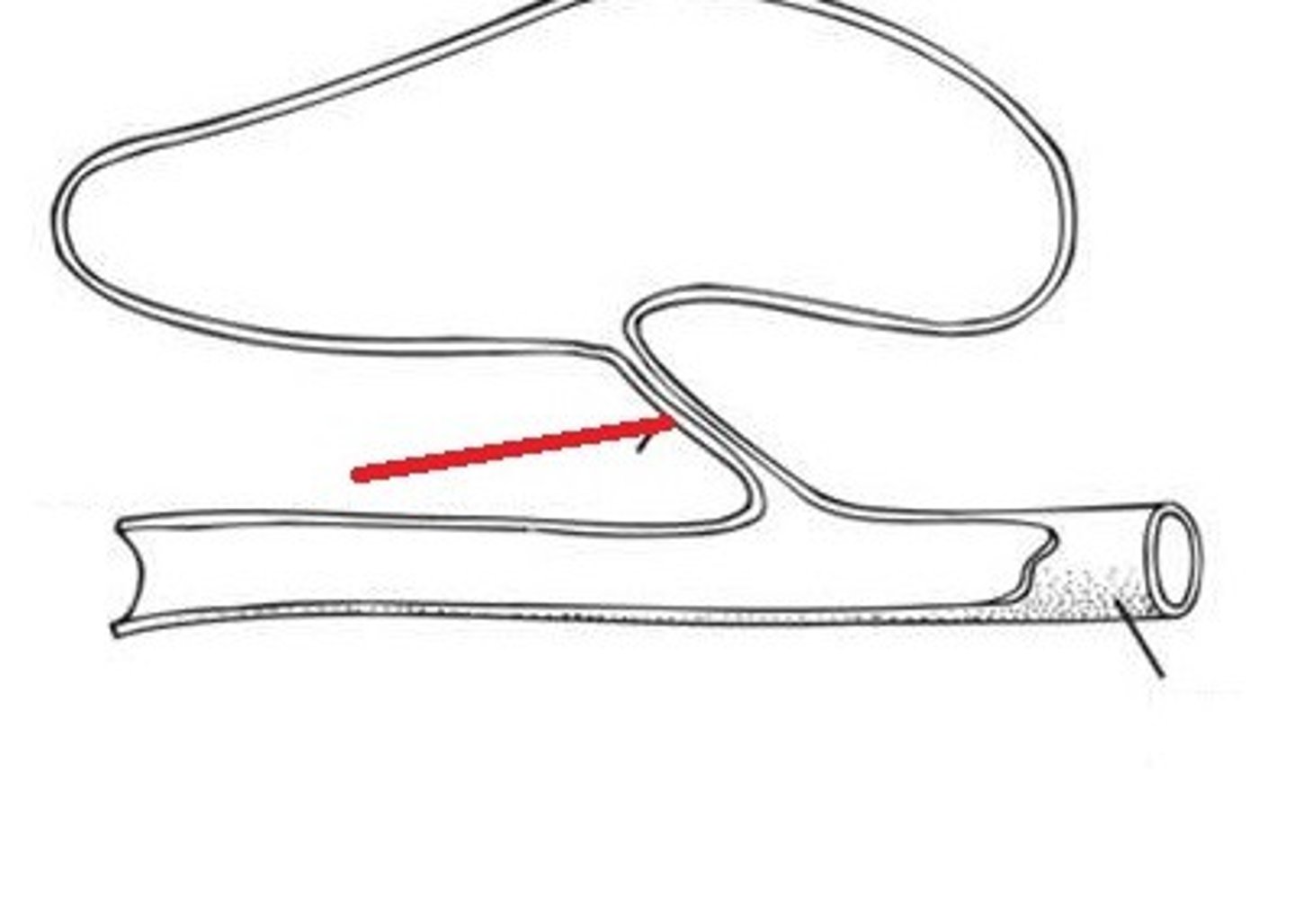
Pneumatic duct
a connective pathway between the gut and gas bladder, that allows air gulped in at the surface to enter it.
-ONLY in physostomous fishes.
gas gland
specialized tissue within the bladder responsible for secreting gases into it
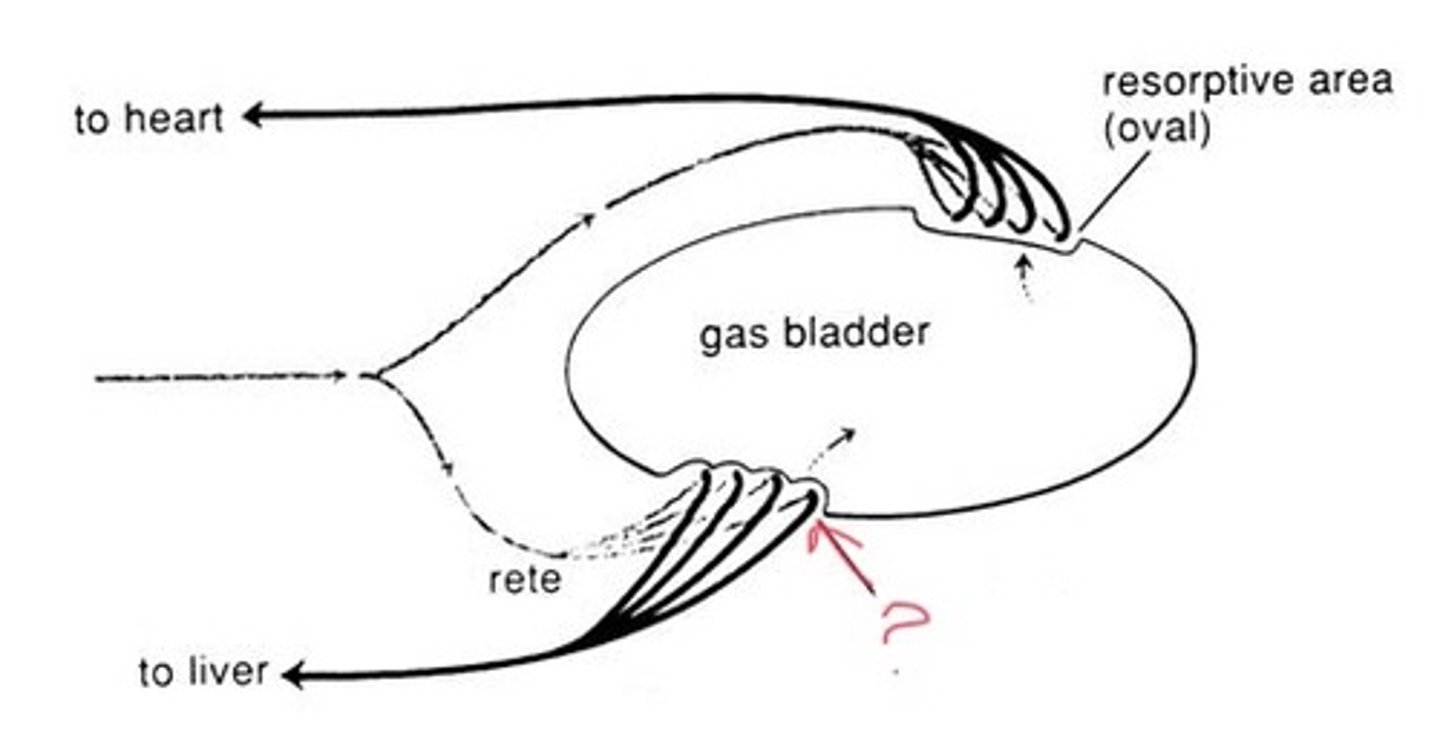
rete mirabile
a countercurrent exchange structure of capillaries that allows gas uptake in a fish swim bladder
Bohr effect
As blood pH decreases, oxygen affinity decreases
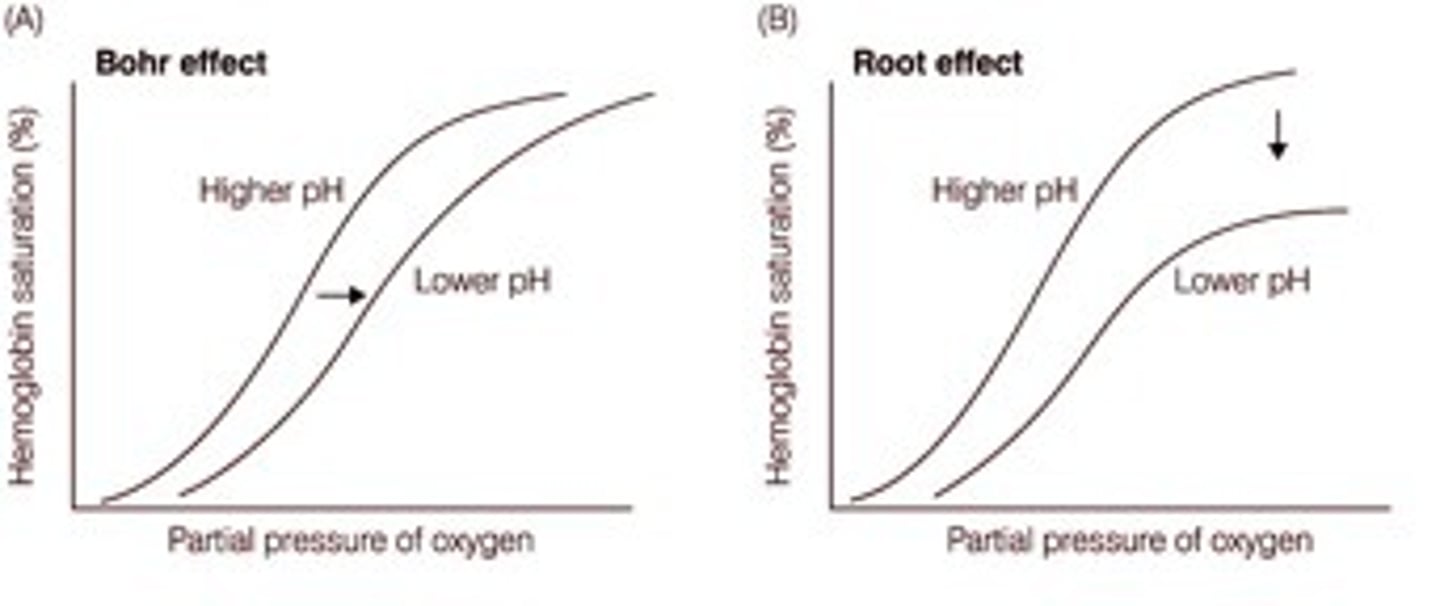
Root effect
Saturation (carrying capacity)
-low pH means low Saturation
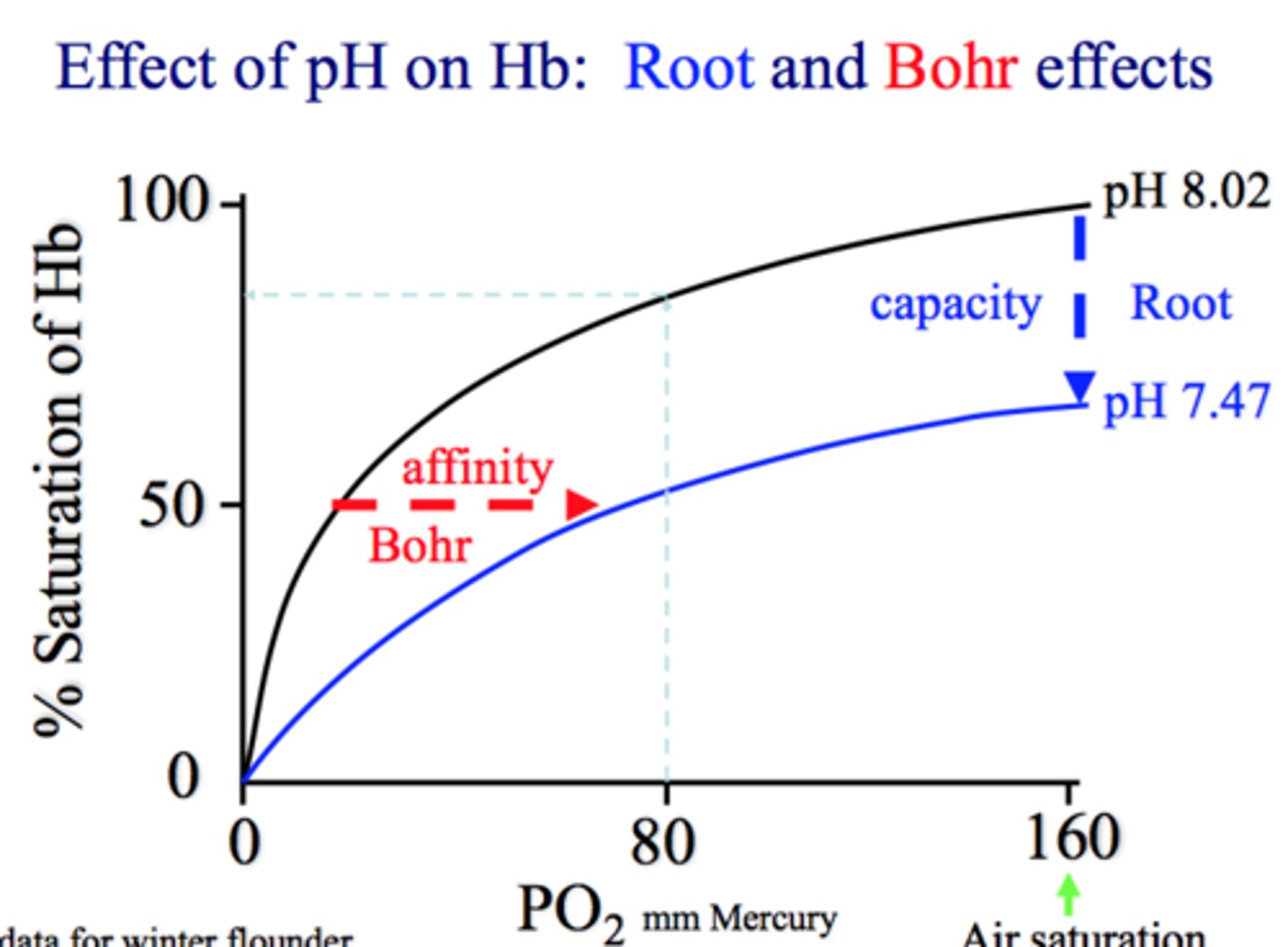
oxygen affinity of hemoglobin
ability of hemoglobin to bind with oxygen molecules.
-measure of how strongly hemoglobin attracts oxygen
salting out
Solutes/ gases cannot be dissolved in plasma so they are released into gas bladder
ram ventilation
Method of forcing water over gills by swimming with mouth open
-little energy usage
-tuna
-paddlefishes
-billfishes

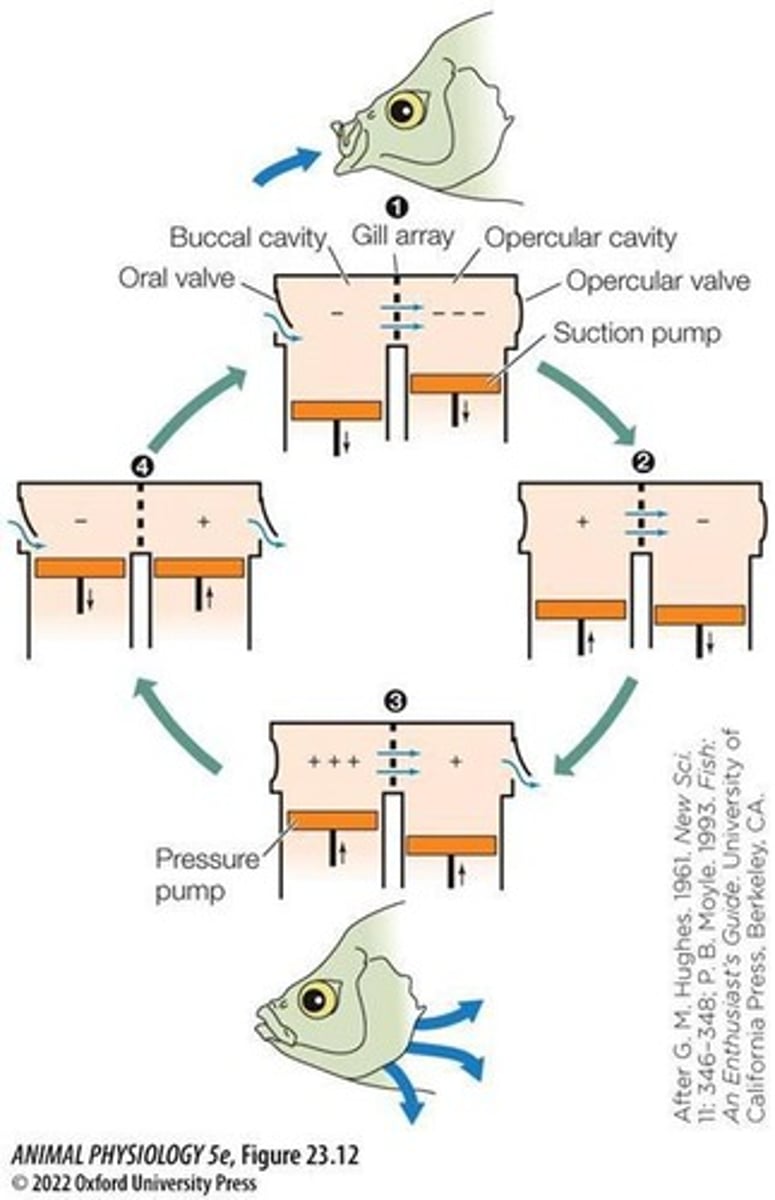
branchial pump
head of a fish contains two cavities separated by the gills: a buccal or mouth cavity and an opercular or gill cavity.
-uses more energy
1. fish sucks in water into buccal cavity, buccal pump inactive
2. mouth closed, buccal pump active and pushes up to force water over gills into opercular cavity w/ inactive opercular pump
3. Opercular valve opens and opercular pump aactive to push water out of opercular cavity through the valve
Gill
-site of CO2 and O2 exchange
-Excretes nitrogenous wastes
-Essential for osmoregulation
Filament
contain lamellae
-can be hemi or holobranch
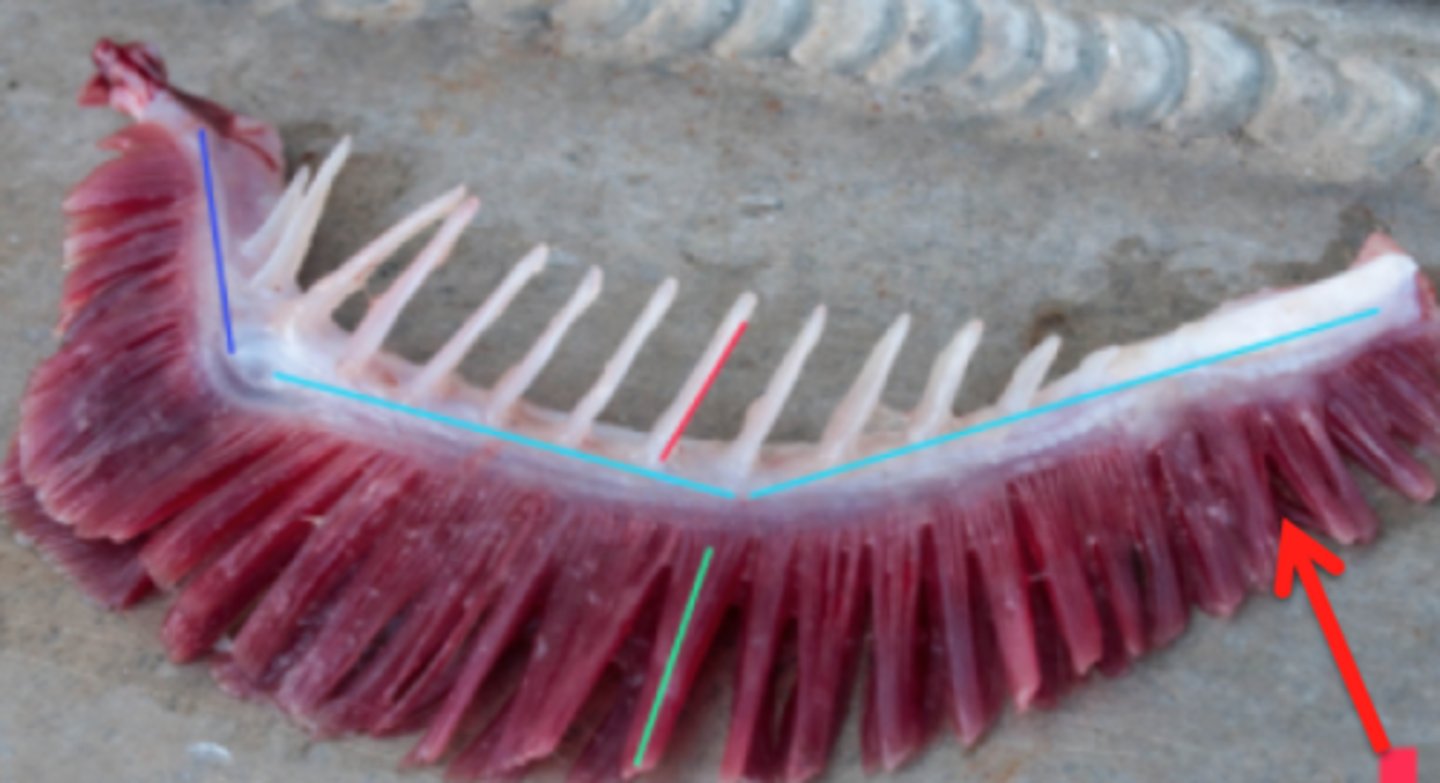

Lamellae
within filaments that are the side of gas exchange between blood and water
Afferent filament artery
this supplies blood to each lamella
-blood passes through lamellae countercurrent to direction of water flow
countercurrent exchange
the opposite flow of adjacent fluids that maximizes transfer rates
Gill arch
This supports the filaments and rakers
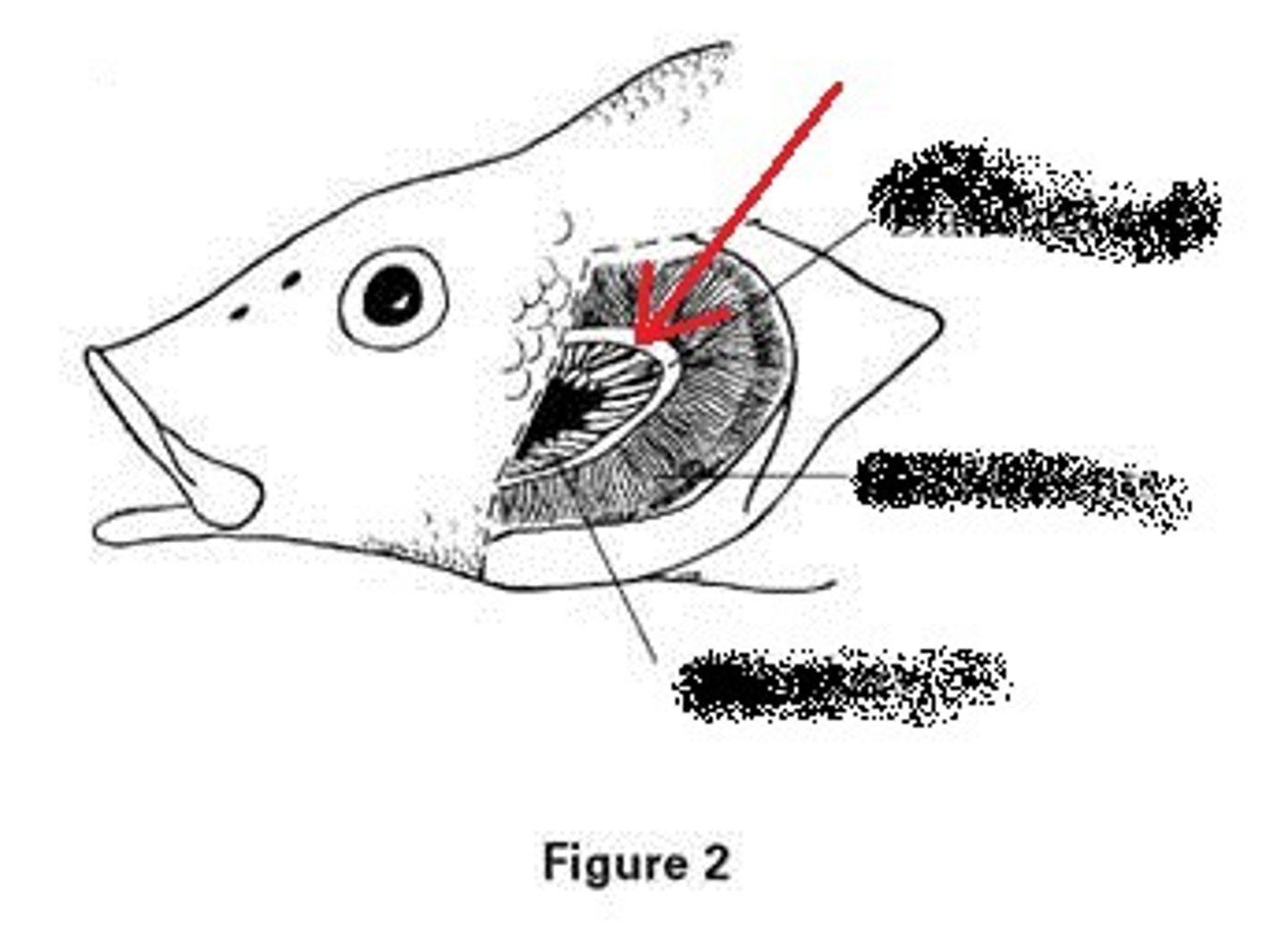
gill rakers
Projections on the gill arch that prevent large objects passing over filaments
-aids in capture of food
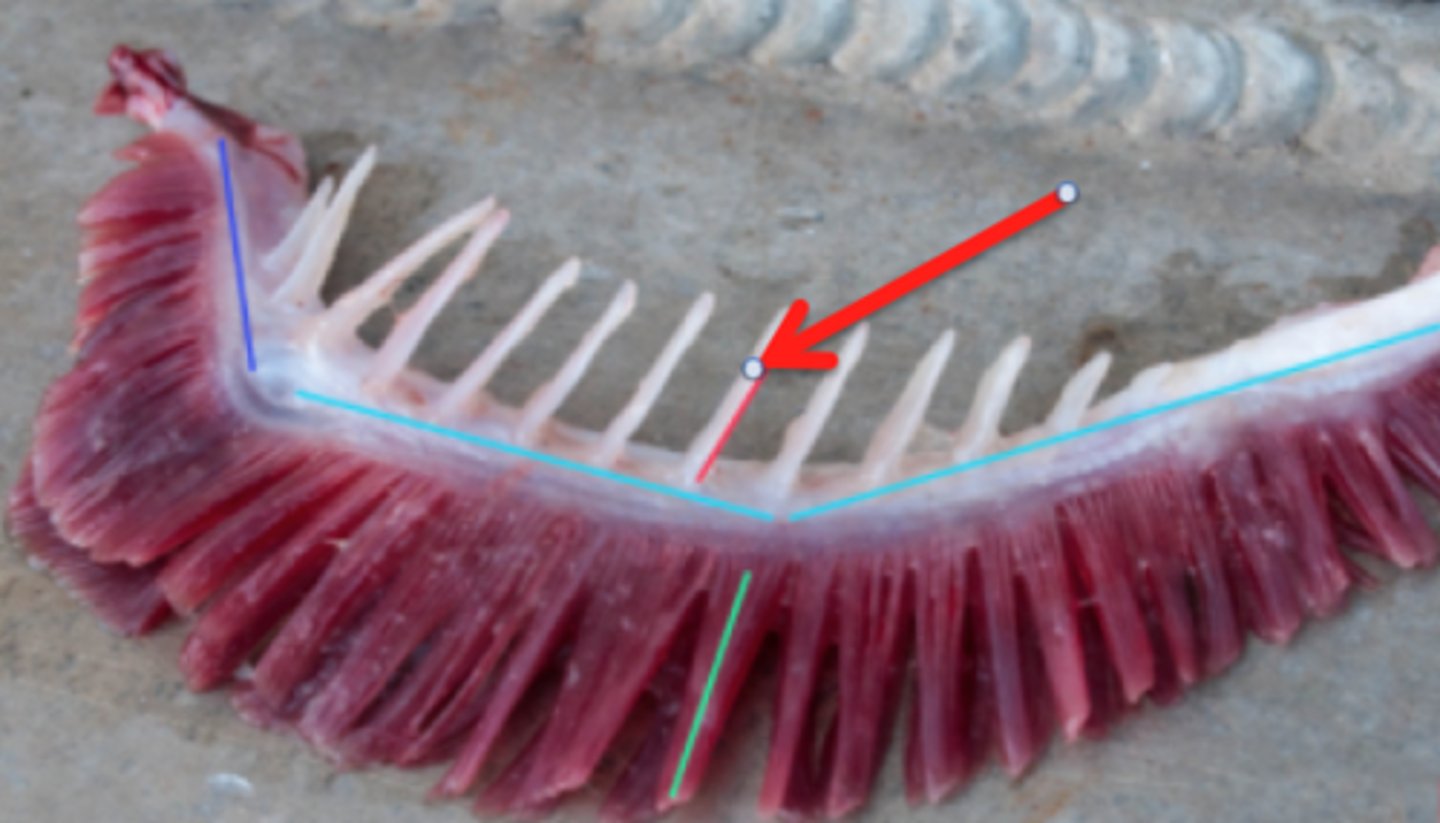

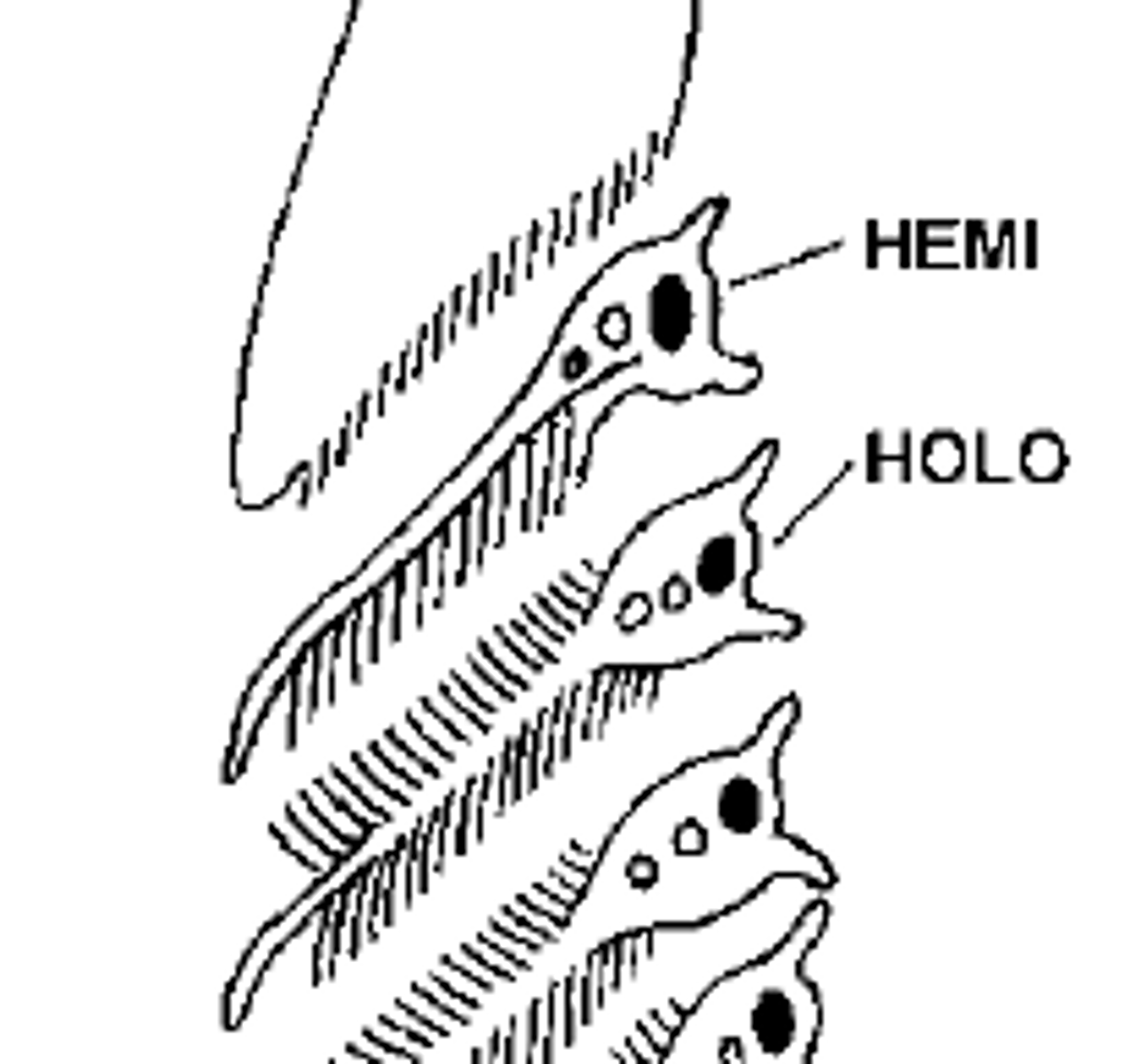
hemibranch
gill arch with filaments on only one side
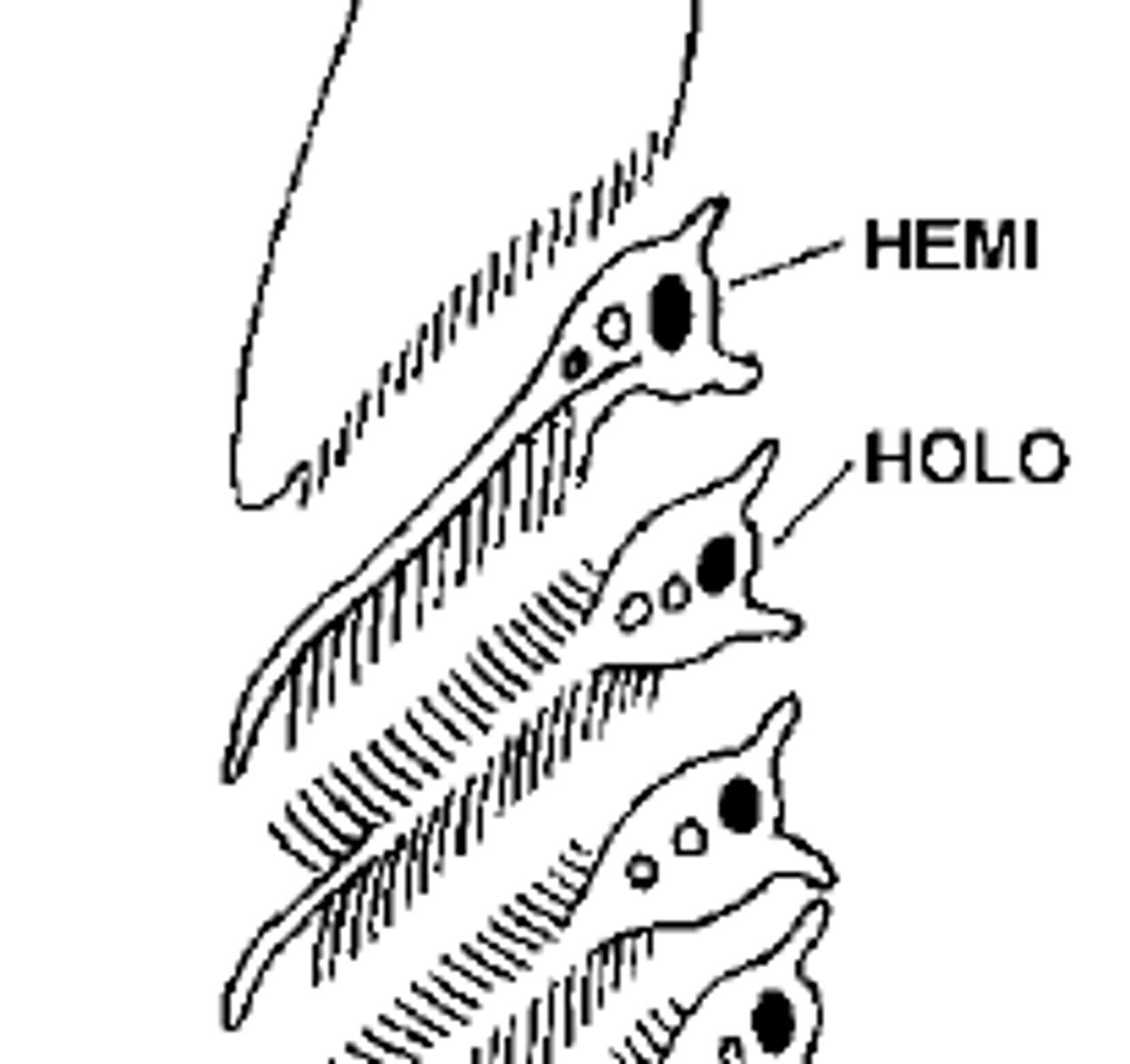
holobranch
Gill arch with filaments on both sides
Solubility of oxygen in water is affected by what?
1. temperature
2. elevation
3. salinity
monomeric
single heme polypeptide characteristic of lampreys and hagfish
Tetrameric
Hemoglobin has four subunits that can bind a single molecule of oxygen
Ways fish breathe (respire)
1. Skin- oxygen diffusion into capillaries (eels, larval fish)
2. Gas bladder- modified physostomous bladders (gars)
3. Lungs- modified gas bladder (lungfish)
4. Mouth- vascularized region roof of mouth (Electric eel, mudsucker)
5. Gut (Armoured catfish, loaches)