lec 11 - cellular models of transport
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
tight epithelia and Na+ homeostasis
the final checkpoint for Na+ balance and blood pressure regulation
tight epithelia of the distal nephron reabsorb a relatively small but critical fraction of filtered Na+
even a few % change here can shift ECF volume and therefore blood pressure
hormonal control (aldosterone or ANP) enables precise control
leaky absorptive epithelia
transport from the mucosal to serosal solution
epithelial ells in the small intestine and proximal tubule absorb large quantities of Na+, glucose, amino acids and several other solutes
these tissues prioritise speed and bulk transport over precise regulation
secondary active transporters drive the absorption of solutes from the luman across the apical membrane
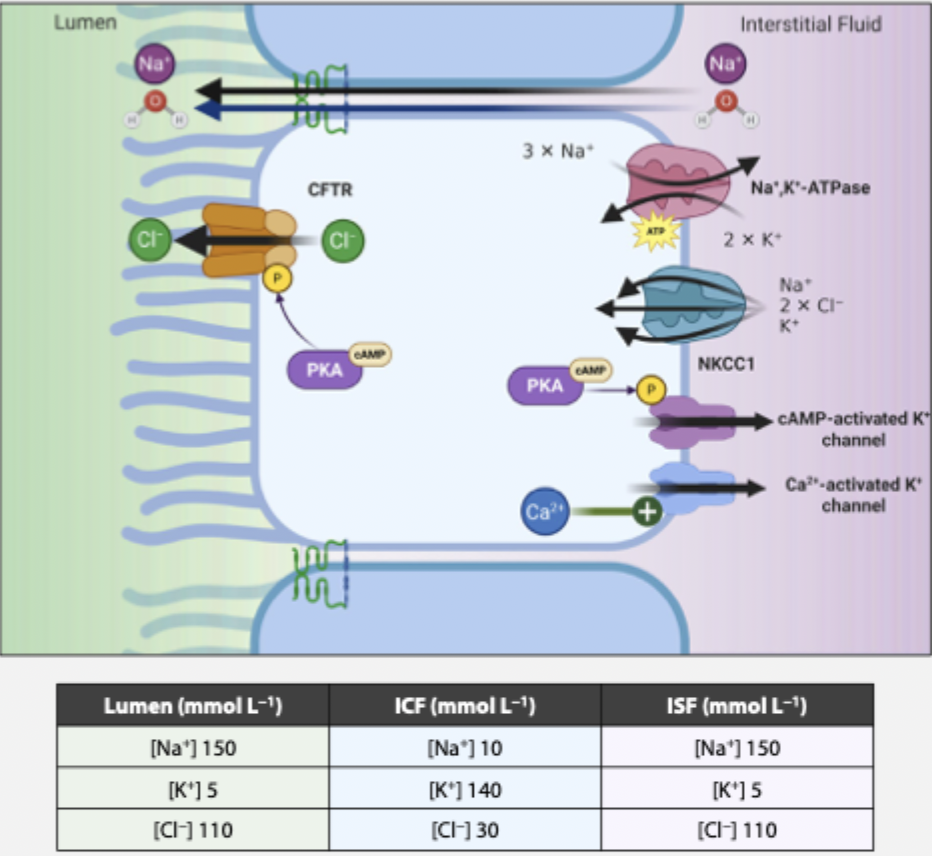
secretory epithelium
leaky allow paracellular water transport (isotonic secretion)
generally secretion of isotonic NaCl in the lumen is driven by Cl- secretion primarily through apical CFTR channes
required in many tissues: exocrine glands of the GI tract, respiratory epithelium, reproductive tract
electrogenic Cl- secretion
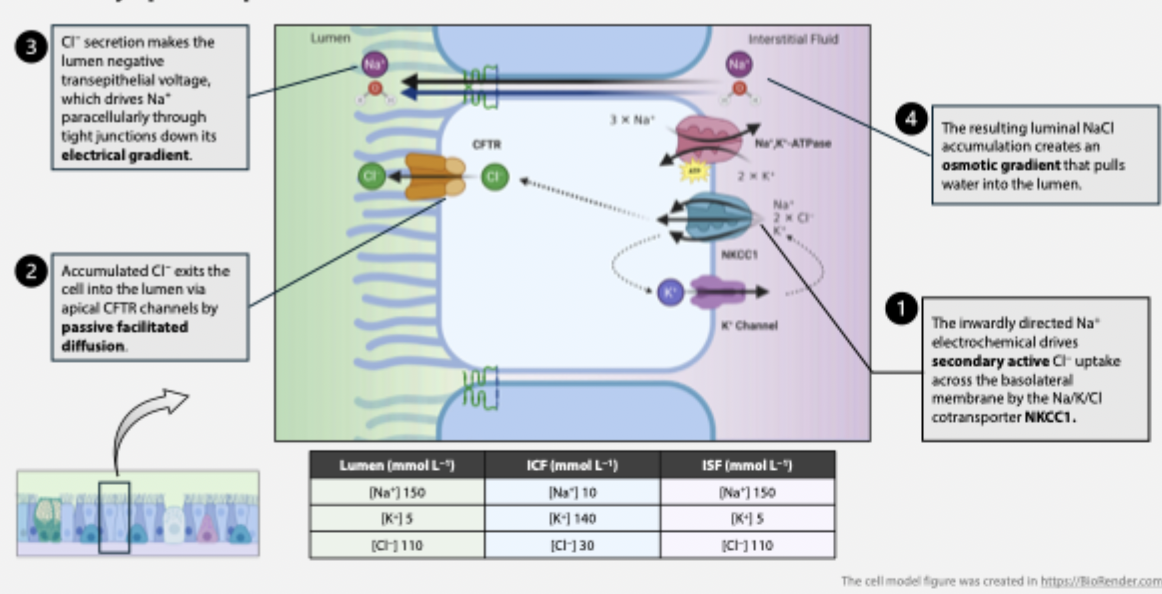
regulation of Cl- secretion why/how
to maintain the electrochemical driving force for Cl- movement
if Vm = ECl (-34.7mV) there is no net transport and secretion stops
Cl- secretion increases GCl during Cl- secretion which pulls Vm towards ECl
prevent this by increasing GK (open or insert more basolateral K+ channels)
K+ efflux keeps Vm below ECl
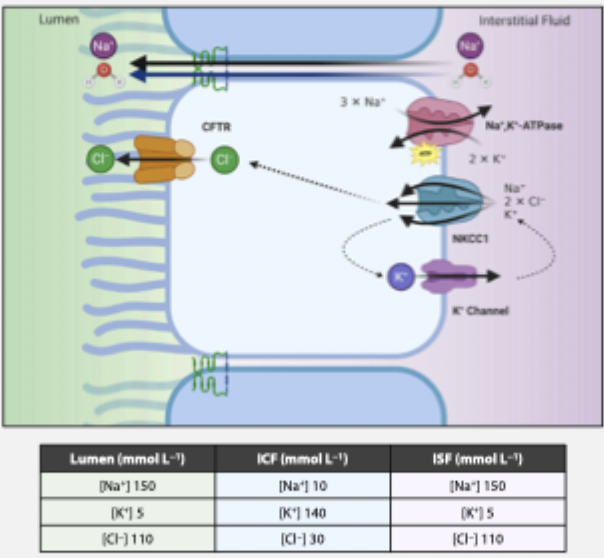
regulation of Cl- secretion - inputs
hormonal and neural inputs modulate intracellular cAMP or intracellular Ca2+ to control Cl- secretion
cAMP → activates PKA → phosphorylates CFTR → increases channel open probability
concurrently increases the actvity of PKA/cAMP activated basolateral K+ channels
Ca2+ increases open probability of Ca2+ sensitive basolateral K+ channels