Leadership Midterm
1/203
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
204 Terms
why is OB important?
It can help you (1) think analytically and critically, (2) make better decisions, (3) communicate and collaborate more effectively with others, and (4) act with a sense of social responsibility in the workplace.
Managers’ work can be categorized into four different activities:
planning, organizing, leading, and controlling.
planning
The planning function encompasses defining an organization’s goals, establishing an overall strategy for achieving those goals, and developing a comprehensive set of plans to integrate and coordinate activities.
organizing
When managers design their work unit’s structure, they are organizing. The organizing function includes determining what tasks are to be done, who is to do them, how the tasks are to be grouped, who reports to whom, and where decisions are to be made.
leading
When managers motivate employees, direct their activities, select the most effective communication channels, or resolve conflicts, they are engaging in leading.
controlling
Management must monitor its organization’s performance and compare it with previously set goals to ensure that activities are going as they should. If there are any significant deviations, management’s job is to get the organization back on track.
Mintzberg concluded that managers perform ten different, highly interrelated roles or sets of behaviors - which are the most common?
(1) interpersonal, (2) informational, or (3) decisional.
Interpersonal Roles
Three types:
1.Leadership (This role includes hiring, training, motivating, and disciplining employees)
Figurehead (ceremonial and symbolic in nature.)
Liaison (contacting and fostering relationships with others who provide valuable information.)
informational role
Three types:
Monitor: collect information from outside organizations and institutions.
Disseminator: act as a conduit to transmit information to organizational members.
Spokesperson: act as a conduit to transmit information to organizational members.
Decisional Role
Four Types:
Entrepreneur: managers initiate and oversee new projects to improve their organization’s performance
Disturbance Handler: managers take corrective action in response to unforeseen problems
Resource Allocator: managers are responsible for allocating human, physical, and monetary resources.
Negotiator: they discuss issues and bargain with other units (internal or external) to gain advantages for their unit.
Organizational Behavior (OB)
the study of what people do in an organization and how their behavior affects the organization’s performance.
corporate social responsibility (CSR)
A businesses self-regulated actions to benefit society or the environment beyond what is required by law
positive organizational scholarship
It explores how organizations develop human strengths, foster vitality, build resilience, and unlock potential
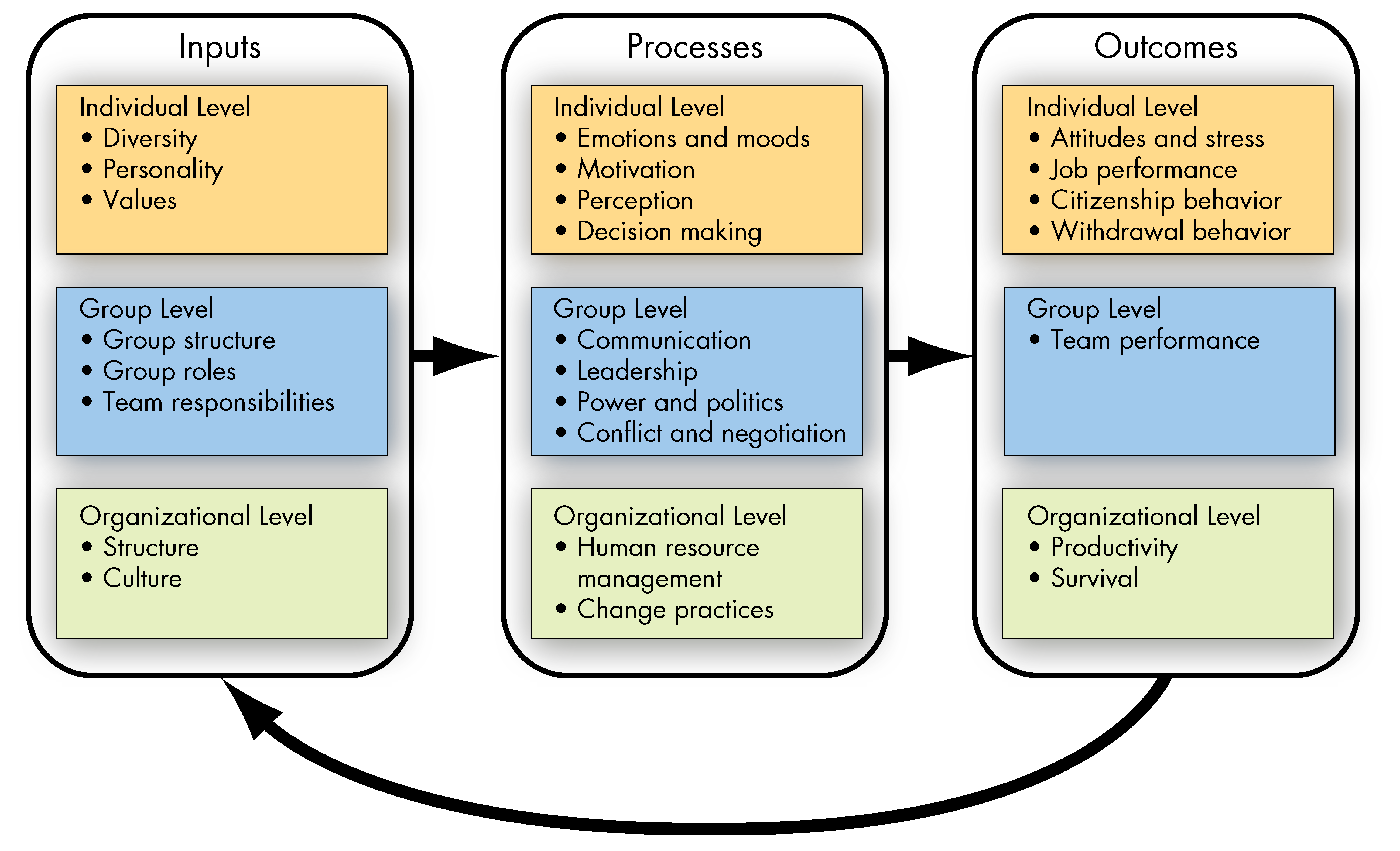
The OB Model - What is the three-level model of Organizational Behavior?
Inputs
Processes
Outcomes
I + P = O
Inputs
These are the foundational factors that shape behavior.
Individual level: diversity, personality, values.
Group level: structure, roles, team responsibilities.
Organizational level: structure, culture.
NOT EASILY CHANGED
Processes
These are the mechanisms through which inputs are transformed into outcomes.
Individual level: emotions, motivation, perception, decision-making.
Group level: communication, leadership, power/politics, conflict/negotiation.
Organizational level: HR management, change practices.
Outcomes
These are the results of inputs and processes.
Individual level: attitudes/stress, job performance, citizenship behavior, withdrawal behavior.
Group level: team performance.
Organizational level: productivity, survival.
MORE LIKELY TO CHANGE PROCESSES
Attitudes
are evaluative statements or judgements
they reflect how we feel about something
organizational citizenship behavior (OCB)
The discretionary behavior that is not part of an employee’s formal job requirements but contributes to the workplace’s psychological and social environment - Successful organizations have employees who do more than their usual job duties—who provide performance beyond expectations.
Productivity requires what 2 things
effectiveness
efficiency
person factors
are characteristics that give individuals their unique identities
situation factors
are elements outside us that influence what we do, the way we do it, and the ultimate results of our actions
When Problem solving we have to consider:
selection criteria
consequences
choice process
necessary resources
selection criteria
(such as its effects on bottom-line profits, its
impact on others, its impact on the reputation with customers or the
community, the organization’s values, and ethical implications)
consequences
(such as the trade-offs between who wins and
loses, ideal versus practical options, perfection versus excellence,
and superior versus satisfactory results)
choice process
may be an individual, team, or third-party
decision, and if more than one person is involved, the decision-
making method must be determined).
Attitudes have 3 components
Cognition
Affect
Behavior
Affective
the emotion or feeling of the attitude
Behavioral
the intention to behave in a certain way toward someone or something
Cognitive
Opinion or belief
What are the “ABC’s” of attitudes?
1.Affect
Behavior
Cognition
ABC Example
C: my boss gave a promotion to someone who didn’t deserve it
A: I HATE MY BOSS
B: I’m gonna start looking for a new job
cognitive dissonance
any incompatibility between two or more attitudes or between behavior and attitudes
EX: seeing a co worker you don’t like being treated unfairly at work - you might blame the co worker for as a means for maintaining consistency - rather than empathizing
organizational identification
is the degree to which an employee defines themselves by the same attributes they believe define their organization. In simple terms, it’s when people feel a sense of oneness or belonging with their workplace.
Mangers should….
be interested in their employees attitudes - this influences behavior ans indicates potential problems
organizational commitment
the extent to which an employee identifies with an ORG and it committed to its goals
perceived organizational support
the extent to which employees believe that ORG values their contributions and cares about their well-being
engagement
the extent that the EMP give their all (enthusiasm + urgency)
job satisfaction
affective + emotional response to job
what are the major job attitudes?
Job satisfaction
organizational commitment
POS (Perceived organizational support)
Employee engagement
psychological empowerment
employees’ beliefs in the degree to which they influence their work environment, competencies, meaningfulness of their job, and autonomy.
employees’ beliefs in the degree to which they influence their work environment, competencies, meaningfulness of their job, and autonomy.
what are the three aspects of commitment
continuance commitment
normative commitment
affective commitment
continuance commitment
Staying because you have to.
Based on the costs of leaving (e.g., losing pay, benefits, seniority).
Stronger if an employee has few job alternatives.
normative commitment
Staying because you feel you ought to.
Based on a sense of obligation or moral duty (e.g., loyalty, values, repayment to employer).
Stronger if the employee’s values are being tested or if they feel indebted to the company.
Affective commitment
Staying because you want to.
Based on emotional attachment and identification with the organization.
Research shows this type best predicts positive behaviors like:
Lower turnover
Higher attendance
Better performance
More organizational citizenship behaviors (helping beyond job description)
power distance
the degree to which people in a culture accept that power in institutions and organizations is distributed unequally
An employees job satisfaction level is…
the best single predictor of behavior
High pay alone is…
unlikely to create a satisfactory work environment
organizational commitment leads to…
greater employee retention
greater motivation in pursuit of organizational goals
employee engagement leads to…
increased customer loyalty and satisfaction
increased employee performance
financial performance
Responses to dissatisfaction
Voice
Exit
Loyalty
Neglect
Exit
is an active, destructive dimension that directs behavior toward leaving the job including looking for a new position or resigning.
Voice
is an active, constructive dimension that includes attempting to improve conditions, suggesting improvements, discussing problems with superiors, and undertaking union activity.
Loyalty
is a passive, constructive dimension that involves optimistically waiting for conditions to improve, speaking up for the organization in the face of external criticism, and trusting the organization and its management to “do the right thing.”
Neglect
is a passive, destructive dimension that allows conditions to worsen and includes chronic absenteeism or lateness, reduced effort, and an increased error rate.
Counterproductive Work Behaviors
Actions that actively damage the organization, including stealing,
behaving aggressively toward coworkers, or being late or absent
personality - job fit theory
a theory that identifies 6 personality types and proposes that the fit between personality type and occupational environment determines satisfaction and turnover
what are the 6 types in the personality - job fit theory?
Realistic
Investigative
Artistic
Social
Enterprising
Conventional
person - organization fit
a theory that people are attracted to and selected by organizations that match their values and leave when there is no compatibility.
personality
the total number of ways in which an individual reacts to and interacts with the world around them
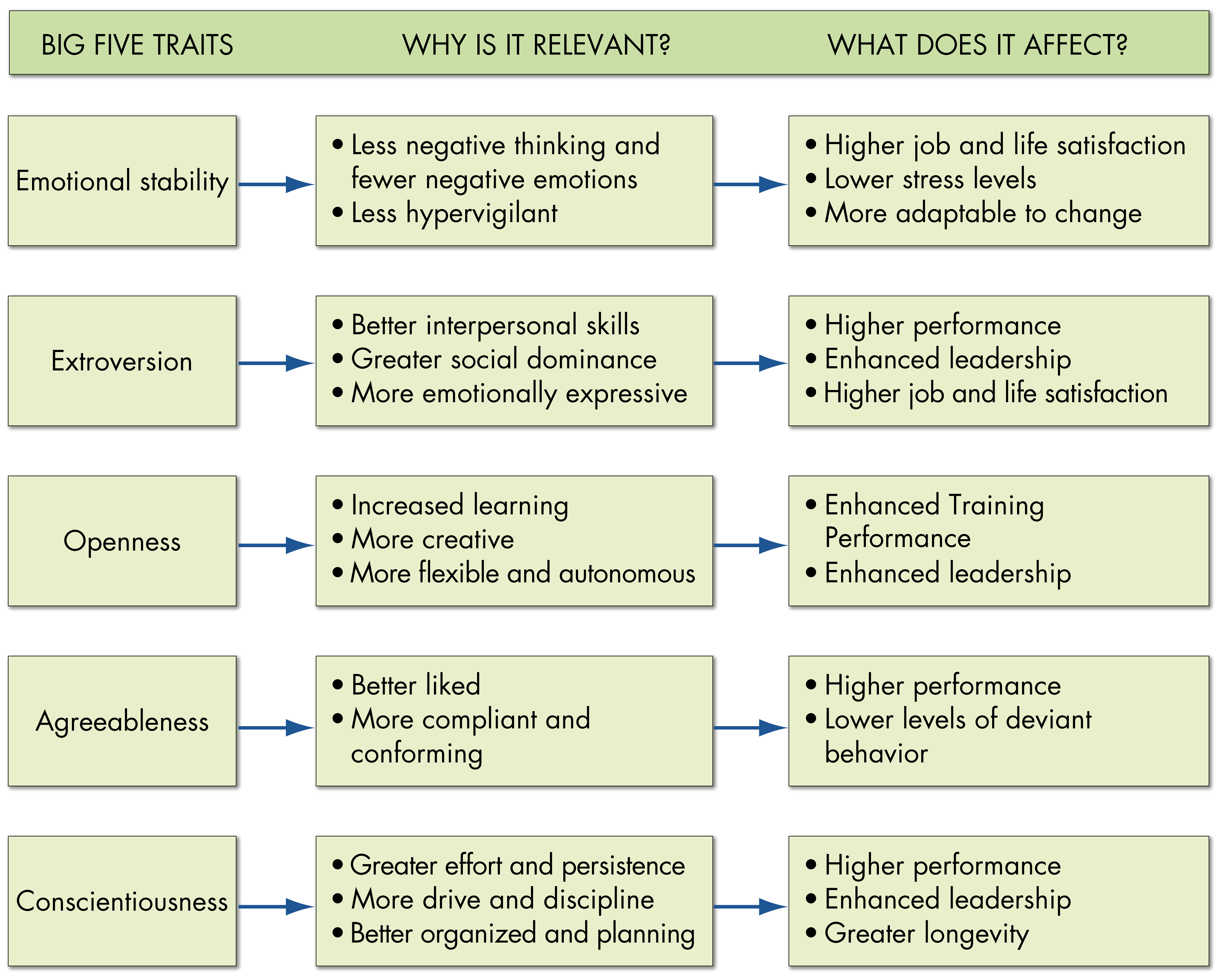
The Big Five Model
A personality model that proposes 5 basic dimensions encompass most if the differences in human personality
Conscientiousness
Emotional Stability
Extroversion
Openness to Experience
Agreeableness
Which of the Big Five can predict performance across all occupations?
conscientiousness
conscientiousness
a measure of personal consistency and reliability. A highly conscientious person is responsible, organized, dependable, and persistent. Those who score low on this dimension are easily distracted, disorganized, and unreliable.
emotional stability
this dimension taps a person’s ability to withstand stress. People with emotional stability tend to be calm, self-confident, and secure.
In a scale: Neuroticism to Emotionally stable
most strongly related to life satisfaction and job satisfaction as well as reduced burnout and intentions to quit.
extroversion
this dimension captures our relational approach toward the social world. Extroverts tend to be gregarious, assertive, and sociable.
openness to experience
this dimension addresses the range of a person’s interests and their fascination with novelty. Open people are creative, curious, and artistically sensitive. Those at the low end of the category are conventional and find comfort in the familiar.
agreeableness
this dimension refers to an individual’s propensity to defer to others. Agreeable people are cooperative, warm, and trusting.
may lack ability to make tough calls
Big Five Model EX: Engineer
Low on extroversion ; high on conscientiousness
Big Five Model EX: Sales person
High on extraversion ; low on conscientiousness
The Dark Triad
A constellation of negative personality traits consisting of:
Machiavellianism
Narcissism
Psychopathy
Machiavellianism
is pragmatic, maintains emotional distance, and believes ends can justify means.
“I do whatever I have to do to get ahead,”
Narcissism
describes a person who has a grandiose sense of self-importance, requires excessive admiration, and is arrogant.
often have fantasies of grand success, a tendency to exploit situations and people, a sense of entitlement, and a lack of empathy. Can also be hypersensitive and fragile
Psychopathy
is defined as a lack of concern for others and a lack of guilt or remorse when actions cause harm,
Core Self-Evaluations (CSE)
are bottom-line conclusions individuals have about their capabilities, competence, and worth as a person.
Positive CSE
like themselves and see themselves as effective and in control of their environment.
perform better than others because they set more ambitious goals, are more committed to their goals, and persist longer in attempting to reach them
Negative CSE
tend to dislike themselves, question their capabilities, and view themselves as powerless over their environment.
self - monitoring
describes an individual’s ability to adjust behavior to external, situational factors.
High self-monitors show considerable adaptability in adjusting their behavior to external situational factors.
Low self-monitors tend to display their true dispositions and attitudes in every situation; hence, there is high consistency between who they are and what they do.
proactive personality
people that identify opportunities, show initiative, take action, and persevere until meaningful change occurs, compared to others who generally react to situations.
Situation Strength Theory
A theory indicating that the way personality translates into behavior depends on the strength of the situation
Strength of situation meaning degree to which norms, cues or standards dictate appropriate behavior
In simple terms: your personality shows more in weak situations and less in strong situations.
Strong situation ex: military, courtroom, TSA
Weak situation ex: casual party, free time
Trait Activation Theory (TAT)
A theory that predicts that some situations, events, or interventions “activate” a trait more than others
TAT Example Commission:
a commissioned based compensation plan would likely activate extroversion b/c extroverted people are more reward-sensitive
ability
an individuals capacity to perform the various tasks in a job
Intellectual and physical
General Mental Ability (GMA)
An overall factor of intelligence, as suggested by the positive correlations among specific intellectual ability dimensions
Values
basic convictions that some actions and outcomes are more morally, socially or personally preferable than others
carry an individuals ideas about what is right, good or desirable
value system
a hierarchy based on a ranking of an individual’s values in terms of their intensity
Locus of control
describes how much personal responsibility someone takes for their behavior and its consequences
external locus of control
things happen to me
I blame others for failure
I cannot control my future
internal locus of control
higher motivation
higher expectations
more effort
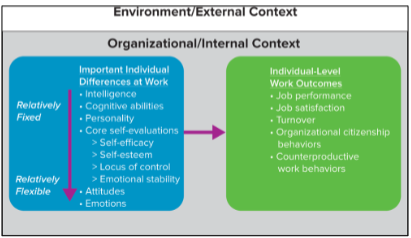
Relative Stability of Individual Differences
Traits like ones intelligence, personality are relatively fixed compared to attitudes and emotions that are relatively flexible. All of these, however, affect individual - level work outcomes
personality traits
summarize regularly in behavior
predict other, more specific behaviors
explain behavior
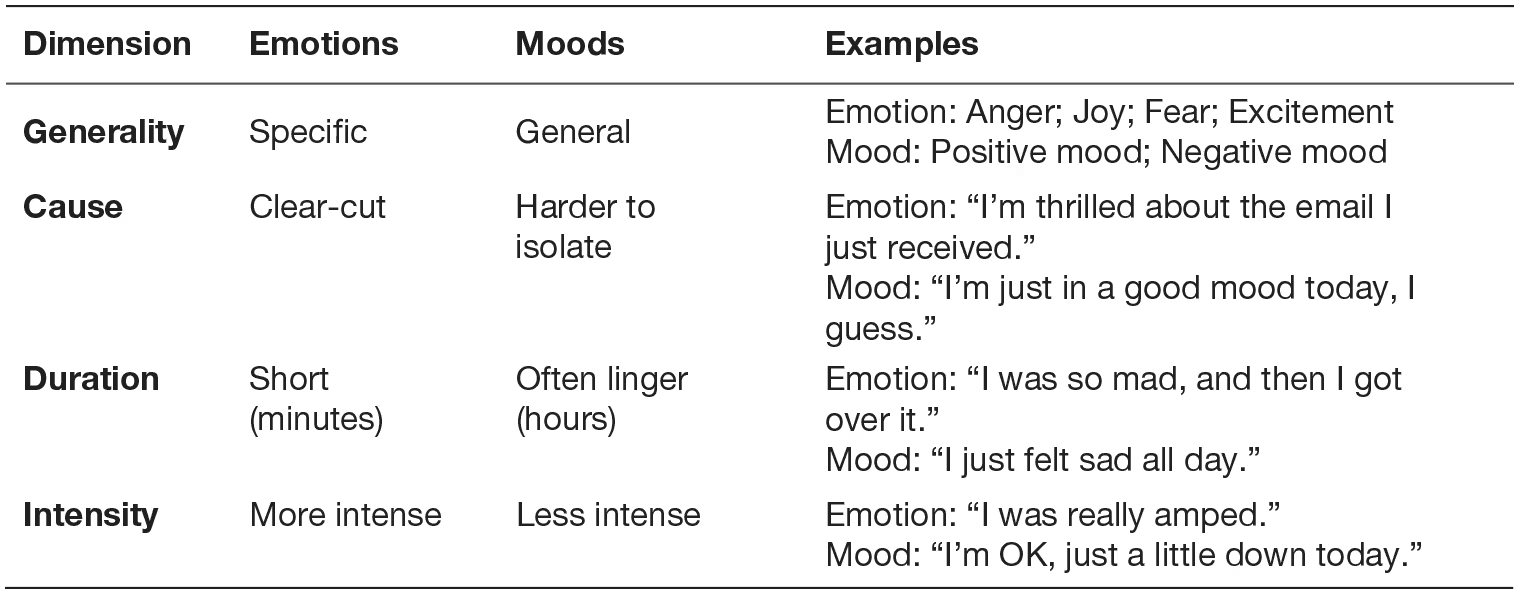
emotions
intense, discrete and short lived often caused by a specific event
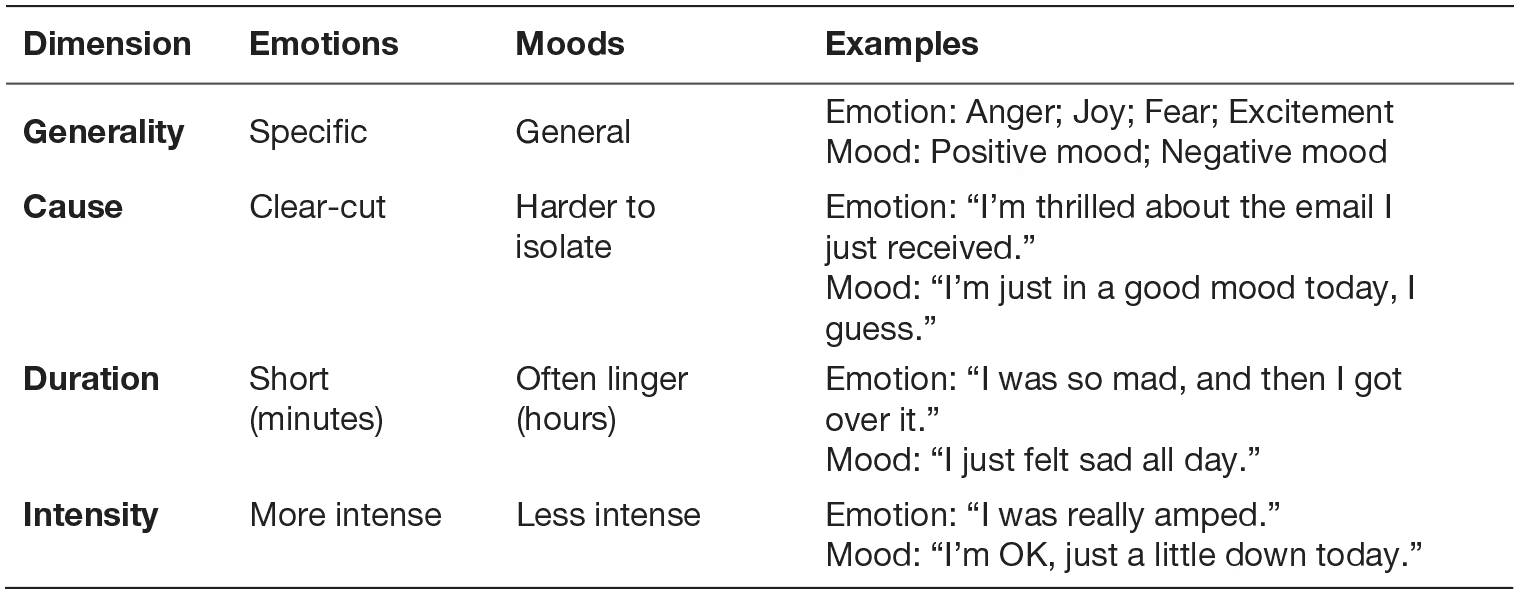
moods
feelings that tend to be longer lived and less intense than emotions and that lack a contextual stimulus
positive affect (PA)
an affective dimension that consists of specific positive emotions such as excitement, enthusiasm and elation at the high end
good mood
negative affect (NA)
an affective dimension that consists of emotions such as nervousness, stress and anxiety at the high end
bad mood
moral emotions
emotions that have moral implications b/c of our instant judgement of the situation that evokes them
ex: For instance, say you watch a video of a coworker making a sexist or racist slur. You might feel disgusted because it offends your sense of right and wrong and experience a variety of emotions based on your moral judgment of the situation.
positivity offset
the tendency of most individuals to experience a mildly positive mood at zero input (when nothing in particular is going on).
affect intensity
people experience the same emotions with different intensities; the degree to which they experience them is called their…
people with this feel emotions more deeply - when they are sad they are REALLY SAD
illusory correlation
the tendency of people to associate two events when in reality there is no connection
emotional labor
an employee’s expression of organizationally desired emotions during interpersonal transactions at work
flight attendants should be cheerful and funeral directors should be sad
felt emotions
an individuals actual emotions