chapter 3: labor productivity and comparative advantage - the ricardian model
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
the ricardian model
examines differences in the productivity of labor between countries
the specific factors model and the heckscher-ohlin model examines
the differences in
labor
labor skills
physical capital
land
other factors of production
between countries
trade may also arise due to
economies of scale (larger scale of production is more efficient)
the opportunity cost of producing something measures
the cost of not being able to produce something else with the resources used
comparative advantage will be determined by
comparing opportunity costs across countries
absolute advantage
when a producer can provide a good or service. in greater quantity for the same cost, or the same quantity at a lower cost, than its competitors
comparative advantage
is an economy’s ability to produce a particular good or service at a lower opportunity cost than its trading partners
what is the opportunity cost of producing computers vs roses
the opportunity cost of producing computers is the amount of roses not produced
what is the opportunity cost of producing roses vs. computers
the opportunity costs of producing roses is the amount of computers not producedsu
suppose that in the United States, 10 million roses could be produced with the same resources as 100,000 computers
suppose that in Colombia, 10 million roses could be produced with the same resources as 30,000 computers
Colombia has a lower opportunity cost of producing roses: has to stop producing fewer computers in order to free up resources to make a rose
a country has a comparative advantage in producing a good if the opportunity cost of producing that good is lower in the country than in other countries
the United States has a comparative advantage in computer production
Colombia has a comparative advantage in rose production
when countries specialize in production in which they have a comparative advantage
more goods and services can be produced and consumed
we formalize these ideas by constructing a one-factor Ricardian model using the following assumptions
labor is the only factor of production
labor productivity varies across countries due to differences in technology, but labor productivity in each country is constant
the supply of labor in each country is constant
two goods
competition allows workers to be paid a wage equal to the value of what they produce, and allows them to work in the industry that pays the higher wage
two countries: home and foreign
a unit labor requirement
indicates the constant number of hours labor required to produce one unit of output
a high unit labor requirement means
low labor productivity
labor productivity is how much
output one hour of labor creates
labor supply L
indicates the total amount of labor resources - the number of hours worked (a constant parameter)
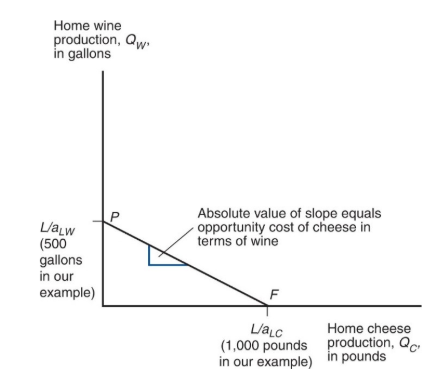
production possibility frontier PPF of an economy shows
the maximum amount of a good that can be produced for a fixed amount of resources
production possibility frontier PPF
is a curve on a graph that illustrates the possible quantities that can be produced of two products if both depend upon the same finite resource for their manufactureth
the PPF is also referred to as
production possibility curve
the line PF shows the maximum amount of cheese home can produce given any production of wine, and vice versa
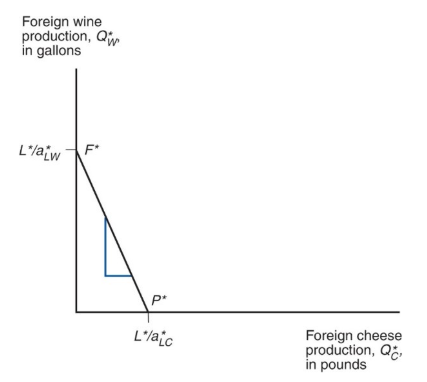
use * to indicate
foreign country variables
when one country can produce a unit of a good with less labor than another country, we saw that the first country has an ___________ in producing that good
absolute advantage
comparative advantage determines
the pattern of trade
because foreign relative unit labor requirement in cheese is higher than home’s (it needs to give up many more units of wine to produce one more unit of cheese), its production possibility frontier is steeper
the RD and RD’ curves show that the demand for cheese relative to wine is a decreasing function of the price of cheese relative to that of wine, while the RS curve shows that the supply of cheese relative to wine is an increasing function of the same relative price
gains from trade comes from specializing
in the type of production that uses resources most efficiently and using the income generated from that production to buy the goods and services that countries desire
“using resources most efficiently” means
producing a good in which a country has a comparative advantage
domestic workers earn a higher income from cheese production because
the relative price of cheese increases with trade
foreign workers earn a higher income from wine production because
the relative price of cheese decreases with trade (making cheese cheaper), and the relative price of wine increases with trade
without trade
a country has to allocate resources to produce all of the goods that it wants to consumewi
with trade
a country can specialize its production and exchange for the mix of goods that it wants to consume
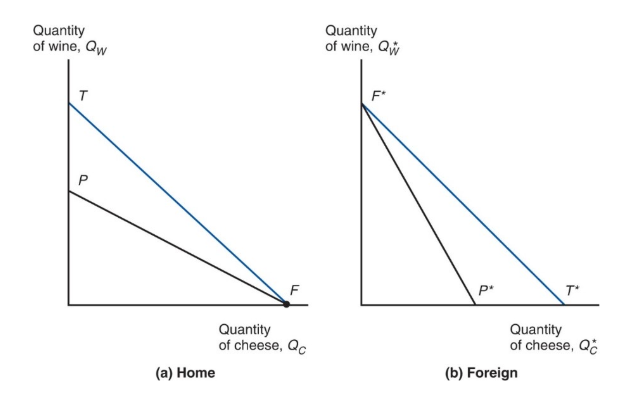
consumption possibilities expand beyond the production possibility frontier when
trade is allowed
with trade, consumption in each country is expanded because
world production is expanded when each country specializes in producing the good in which it has a comparative advantage
international trade allows home and foreign to consume anywhere within the outer lines, which lie outside the countries’ production frontiers
free trade is beneficial only if a country is
more productive than foreign countries
even an unproductive country benefits from free trade by
avoiding the high costs for goods that it would otherwise have to produce domestically
high costs derive from
inefficient uses of resources
the benefits of free trade do not depend on absolute advantage, rather
they depend on absolute advantage: specializing in industries that use resources most efficiently
free trade with countries that pay low wages hurts
high wage countries
while trade may reduce wages for some workers, thereby
affecting the distribution of income within a country, trade benefits consumers and other workers
consumers benefit from trade because
they can purchase goods more cheaply
producers/workers benefit from trade by
earning a higher income in the industries that use resources more efficiently, allowing them to earn higher prices and wages
free trade exploits less productive countries
whose workers make low-wages
the Ricardian model predicts
that countries completely specialize in production
the Ricardian model predicting countries completely specialize in production is a rare occurrence, because of what 3 reasons
more than one factor of production reduces the tendency of specialization
protectionism
transportation costs reduce or prevent trade, which may cause each country to produce the same good or service
non-traded goods and services (like haircuts and auto repairs) exist
due to high transport costs
countries tend to spend a large fraction of national income on
non-traded goods and services
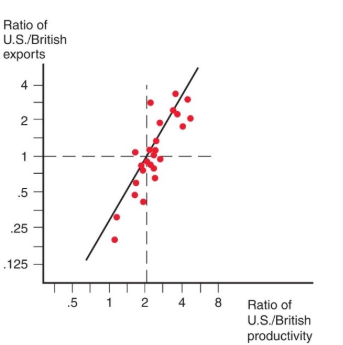
a comparative study showed that U.S. exports were high relative to British exports in industries in which the United States had high relative labor productivity.
each dot represents a different industry
a very poor country like Bangladesh can have a comparative advantage in clothing despite being less productive in clothing than other countries such as China because
it is even less productive compared to China in other sectors
the main implications of the Ricardian model are well supported by empirical evidence:
productivity differences play an important role in international trade
comparative advantage (not absolute advantage) matters for trade